The Physiological Response of the Fiddler Crab Austruca lactea to Anthropogenic Low-Frequency Substrate-Borne Vibrations
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Target Species and Incubation
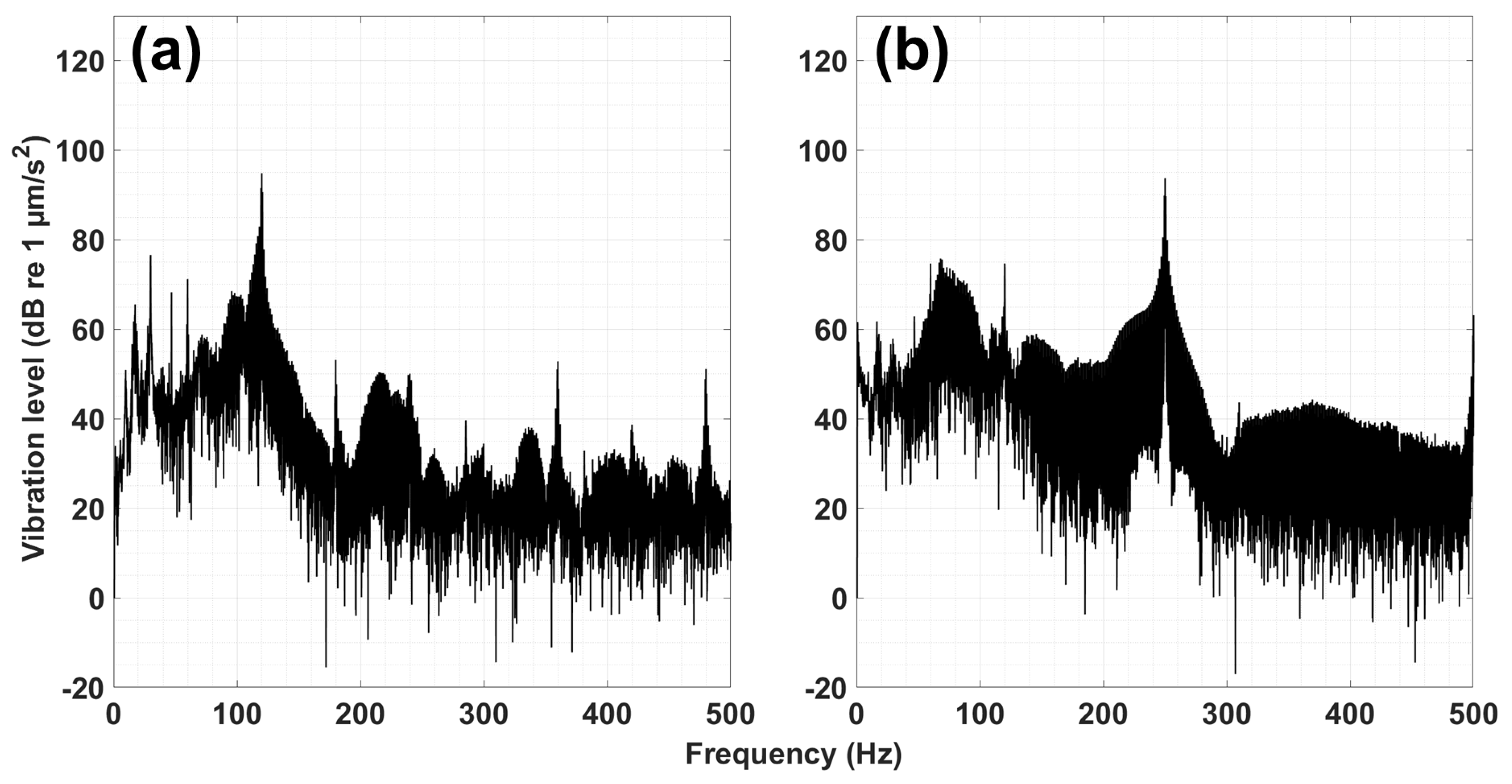
2.2. Experimental Setup and Procedures
2.3. Biochemical Measurements
2.4. Gene Expression of HSPs
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Lactate and ATP Concentration
3.2. Gene Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 kDa Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solé, M.; Kaifu, K.; Mooney, T.A.; Nedelec, S.L.; Olivier, F.; Radford, A.N.; Vazzana, M.; Wale, M.A.; Semmens, J.M.; Simpson, S.D. Marine Invertebrates and Noise. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M.; Hauton, C.; Godbold, J.A.; Wood, C.L.; Leighton, T.G.; White, P. Anthropogenic Sources of Underwater Sound Can Modify How Sediment-Dwelling Invertebrates Mediate Ecosystem Properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Chapuis, L.; Collin, S.P.; Costa, D.P.; Devassy, R.P.; Eguiluz, V.M.; Erbe, C.; Gordon, T.A.; Halpern, B.S.; Harding, H.R. The Soundscape of the Anthropocene Ocean. Science 2021, 371, eaba4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.; Howard, D.R. Substrate-Borne Vibrational Noise in the Anthropocene: From Land to Sea. In Biotremology: Physiology, Ecology, and Evolution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 123–155. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, L.; Elliott, M. Good or Bad Vibrations? Impacts of Anthropogenic Vibration on the Marine Epibenthos. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.A.; Popper, A.N.; Hice-Dunton, L.; Higgs, D.M.; Jenkins, E.; Krebs, J.M.; Mooney, T.A.; Rice, A.N.; Roberts, L.; Thomsen, F. Sound-Related Effects of Offshore Wind Energy on Fishes and Aquatic Invertebrates: Research Recommendations. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life: Principles and Practical Considerations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 1617–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Popper, A.N.; Haxel, J.; Staines, G.; Guan, S.; Nedelec, S.L.; Roberts, L.; Deng, Z.D. Marine Energy Converters: Potential Acoustic Effects on Fishes and Aquatic Invertebrates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popper, A.N.; Hice-Dunton, L.; Jenkins, E.; Higgs, D.M.; Krebs, J.; Mooney, A.; Rice, A.; Roberts, L.; Thomsen, F.; Vigness-Raposa, K. Offshore Wind Energy Development: Research Priorities for Sound and Vibration Effects on Fishes and Aquatic Invertebrates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 151, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potty, G.R.; Miller, J.H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Vigness-Raposa, K. Interface Wave Contribution to Acoustic Particle Motion during Offshore Wind Farm Construction. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life: Principles and Practical Considerations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rooz, A.F.H.; Hamidi, A. A Numerical Model for Continuous Impact Pile Driving Using Ale Adaptive Mesh Method. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 118, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.; Wessel, A. Shaking up Aquatic Substrates: Taking Lessons from Biotremology and Defining Terminology. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life: Principles and Practical Considerations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 85–99. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, P.S.; Wessel, A. Biotremology. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R187–R191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, S.R.; Giraldeau, L.-A.; Olsson, O.; McNamara, J.M.; Stephens, D.W. Information and Its Use by Animals in Evolutionary Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, A.N.; Salmon, M.; Horch, K.W. Acoustic Detection and Communication by Decapod Crustaceans. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2001, 187, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, C.A.; Stanley, J.A. Sound Detection and Production Mechanisms in Aquatic Decapod and Stomatopod Crustaceans. J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226, jeb243537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, M.; Atsaides, S.P. Sensitivity to Substrate Vibration in the Fiddler Crab, Uca pugilator Bosc. Anim. Behav. 1969, 17, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, M.; Horch, K. Vibration Reception by the Fiddler Crab, Uca minax. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1973, 44, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, S.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, T. Where the Fiddlers Sing: Fiddler Crabs Change Their Tunes Depending on the Context. Anim. Behav. 2024, 207, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aicher, B.; Tautz, J. Vibrational Communication in the Fiddler Crab, Uca pugilator: I. Signal Transmission through the Substratum. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1990, 166, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Kim, T. The Effect of Anthropogenic Substrate-Borne Vibrations on Locomotion of the Fiddler Crab Austruca lactea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.; Laidre, M.E. Finding a Home in the Noise: Cross-Modal Impact of Anthropogenic Vibration on Animal Search Behaviour. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio041988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sal Moyano, M.P.; Ceraulo, M.; Luppi, T.; Gavio, M.A.; Buscaino, G. Anthropogenic and Biological Sound Effects on the Maternal Care Behavior of a Key Crab Species. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1050148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wale, M.A.; Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N. Noise Negatively Affects Foraging and Antipredator Behaviour in Shore Crabs. Anim. Behav. 2013, 86, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiciotto, F.; Moyano, M.P.S.; de Vincenzi, G.; Hidalgo, F.; Sciacca, V.; Bazterrica, M.C.; Corrias, V.; Lorusso, M.; Mazzola, S.; Buscaino, G. Are Semi-Terrestrial Crabs Threatened by Human Noise? Assessment of Behavioural and Biochemical Responses of Neohelice granulata (Brachyura, Varunidae) in Tank. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiciotto, F.; Vazzana, M.; Celi, M.; Maccarrone, V.; Ceraulo, M.; Buffa, G.; Arizza, V.; de Vincenzi, G.; Grammauta, R.; Mazzola, S. Underwater Noise from Boats: Measurement of Its Influence on the Behaviour and Biochemistry of the Common Prawn (Palaemon serratus, Pennant 1777). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 478, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wale, M.A.; Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N. Size-Dependent Physiological Responses of Shore Crabs to Single and Repeated Playback of Ship Noise. Biol. Lett. 2013, 9, 20121194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimon, C.; Simpson, S.D.; Hazelwood, R.A.; Bruintjes, R.; Urbina, M.A. Anthropogenic Underwater Vibrations Are Sensed and Stressful for the Shore Crab Carcinus Maenas. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celi, M.; Filiciotto, F.; Parrinello, D.; Buscaino, G.; Damiano, M.A.; Cuttitta, A.; D’Angelo, S.; Mazzola, S.; Vazzana, M. Physiological and Agonistic Behavioural Response of Procambarus clarkii to an Acoustic Stimulus. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwood, R.W.; Barr, S.; Patterson, L. Pain and Stress in Crustaceans? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 118, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Full, R.J.; Herrid, C.F. Fiddler Crab Exercise: The Energetic Cost of Running Sideways. J. Exp. Biol. 1984, 109, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dairi, R.; Outinen, O.; Kankaanpää, H. Anthropogenic Underwater Noise: A Review on Physiological and Molecular Responses of Marine Biota. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Kim, K.W.; Srygley, R.B.; Choe, J.C. Semilunar Courtship Rhythm of the Fiddler Crab Uca lactea in a Habitat with Great Tidal Variation. J. Ethol. 2004, 22, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.; Cheesman, S.; Breithaupt, T.; Elliott, M. Sensitivity of the Mussel Mytilus edulis to Substrate-Borne Vibration in Relation to Anthropogenically Generated Noise. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 538, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.; Cheesman, S.; Elliott, M.; Breithaupt, T. Sensitivity of Pagurus bernhardus (L.) to Substrate-Borne Vibration and Anthropogenic Noise. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 474, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttsche, K.M.; Steinhagen, U.; Juhl, P.M. Numerical Evaluation of Pile Vibration and Noise Emission during Offshore Pile Driving. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 99, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. An Experimental Study on the Charcteristics of Attenuation and Propagation of Construction Equipment Noise in Construction Field. Archit. Insitute Korea 1997, 13, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Whenham, V. Power Transfer and Vibrator-Pile-Soil Interactions Within the Framework of Vibratory Pile Driving. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Louvain, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, É.L.; Model, J.F.A.; Lima, M.V.; de Souza, S.K.; Rocha, D.S.; Fabres, R.B.; de Amaral, M.; Simões, L.A.R.; Vinagre, A.S. The Impact of Chasing Stress on the Metabolism of the Atlantic Ghost Crab Ocypode quadrata (Fabricius, 1787). J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2023, 339, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, E.-J.; Song, H.; Kim, B.-N.; Ha, H.K.; Choi, Y.; Kwon, J.-I.; Park, J.-H. Estimating Three-Dimensional Current Fields in the Yeosu Bay Using Coastal Acoustic Tomography System. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1362335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Romo, A.; Zenteno-Savín, T.; Racotta, I.S. Bioenergetic Status and Oxidative Stress during Escape Response until Exhaustion in Whiteleg Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 478, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.; Adamczewska, A.M. Utilisation of Glycogen, Atp and Arginine Phosphate in Exercise and Recovery in Terrestrial Red Crabs, Gecarcoidea natalis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2002, 133, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäde, G. Effects of Oxygen Deprivation during Anoxia and Muscular Work on the Energy Metabolism of the Crayfish, Orconectes limosus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1984, 77, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczewska, A.M.; Morris, S. Exercise in the Terrestrial Christmas Island Red Crab Gecarcoidea Natalis: Ii. Energetics of Locomotion. J. Exp. Biol. 1994, 188, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina, M.A.; Paschke, K.; Gebauer, P.; Cumillaf, J.P.; Rosas, C. Physiological Responses of the Southern King Crab, Lithodes Santolla (Decapoda: Lithodidae), to Aerial Exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 166, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumasa, M.; Murai, M. Changes in Blood Glucose and Lactate Levels of Male Fiddler Crabs: Effects of Aggression and Claw Waving. Anim. Behav. 2005, 69, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Sakamoto, K.; Henmi, Y.; Choe, J.C. To Court or Not to Court: Reproductive Decisions by Male Fiddler Crabs in Response to Fluctuating Food Availability. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2008, 62, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J. Fiddler Crabs of the Worlds Ocypodidae Genus Uca Princeton Unix; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumasa, M.; Murai, M.; Christy, J.H. A Low-Cost Sexual Ornament Reliably Signals Male Condition in the Fiddler Crab Uca beebei. Anim. Behav. 2013, 85, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.N.; Ye, H.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Zeng, X.; Gong, J. Expression of Hsp70 in the Mud Crab, Scylla paramamosain in Response to Bacterial, Osmotic, and Thermal Stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 2013, 18, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celi, M.; Filiciotto, F.; Maricchiolo, G.; Genovese, L.; Quinci, E.M.; Maccarrone, V.; Mazzola, S.; Vazzana, M.; Buscaino, G. Vessel Noise Pollution as a Human Threat to Fish: Assessment of the Stress Response in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata, Linnaeus 1758). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiciotto, F.; Vazzana, M.; Celi, M.; Maccarrone, V.; Ceraulo, M.; Buffa, G.; Di Stefano, V.; Mazzola, S.; Buscaino, G. Behavioural and Biochemical Stress Responses of Palinurus elephas after Exposure to Boat Noise Pollution in Tank. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Meng, X.; Gan, H.T.; Liu, T.H.; Yao, H.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Xu, G.C.; Xu, J.T. Immune Response, Mt and Hsp70 Gene Expression, and Bioaccumulation Induced by Lead Exposure of the Marine Crab, Charybdis japonica. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 210, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.F. Biomarker Studies in Stress Biology: From the Gene to Population, from the Organism to the Application. Biology 2021, 10, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.S.; Peck, L.S. Triggers of the Hsp70 Stress Response: Environmental Responses and Laboratory Manipulation in an Antarctic Marine Invertebrate (Nacella concinna). Cell Stress Chaperones 2009, 14, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primer Name | Sequence | GenBank Accession NO. |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH (F) | CTTCTTGCACCACCAACTGC | KJ133056.1 |
| GAPDH (R) | TCCACAACGGACACATCAGG | |
| HSP70 (F) | TGTACCGGCCTACTTCAACG | This study |
| HSP70(R) | AAGATGAGCACGTTGCGCT |
| Species | Shared Identity (%) | GenBank Accession NO. |
|---|---|---|
| Minuca mordax | 93.79 | KC355776.1 |
| Minuca burgersi | 93.79 | KF153223.1 |
| Minuca victoriana | 93.17 | KC355779.1 |
| Minuca rapax | 93.17 | KC355777.1 |
| Leptuca cumulanta | 93.17 | KF153224.1 |
| Leptuca thayeri | 91.93 | KC355778.1 |
| Leptuca uruguayensis | 91.93 | KF153227.1 |
| Leptuca leptodactyla | 91.93 | KF153225.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joo, S.; Cho, J.; Kim, T. The Physiological Response of the Fiddler Crab Austruca lactea to Anthropogenic Low-Frequency Substrate-Borne Vibrations. Biology 2025, 14, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080962
Joo S, Cho J, Kim T. The Physiological Response of the Fiddler Crab Austruca lactea to Anthropogenic Low-Frequency Substrate-Borne Vibrations. Biology. 2025; 14(8):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080962
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoo, Soobin, Jaemin Cho, and Taewon Kim. 2025. "The Physiological Response of the Fiddler Crab Austruca lactea to Anthropogenic Low-Frequency Substrate-Borne Vibrations" Biology 14, no. 8: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080962
APA StyleJoo, S., Cho, J., & Kim, T. (2025). The Physiological Response of the Fiddler Crab Austruca lactea to Anthropogenic Low-Frequency Substrate-Borne Vibrations. Biology, 14(8), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080962







