Real-Time Functional Stratification of Tumor Cell Lines Using a Non-Cytotoxic Phospholipoproteomic Platform: A Label-Free Ex Vivo Model
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Limitations of Conventional Preclinical Models
1.2. Functional Justification for Real-Time Kinetic Monitoring
1.3. Emerging Role of Phospholipoproteomic Immunoformulation in Structural Immunoreprogramming
1.4. Basis of Platform–Tumor Functional Classification
1.5. Emerging Regulatory Logic: Early Validation and Documentation Platforms
1.6. Objective of the Study and Operational Experimental Framework
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Phenotypic Selection Criteria
2.2. Preparation and Structural Validation of Immunoactive Phospholipoproteomic Formulations
2.3. Experimental Design and Kinetic Monitoring (IncuCyte)
2.4. Functional Classification Criteria: Direction, Magnitude, Stability
2.5. Cell Death Assay and Secretome Profiling (Multiplex CBA)
2.6. Quality Control: Interbatch and Intra-Assay Validation
2.7. Calculation of the FSI (Functional Stratification Index)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
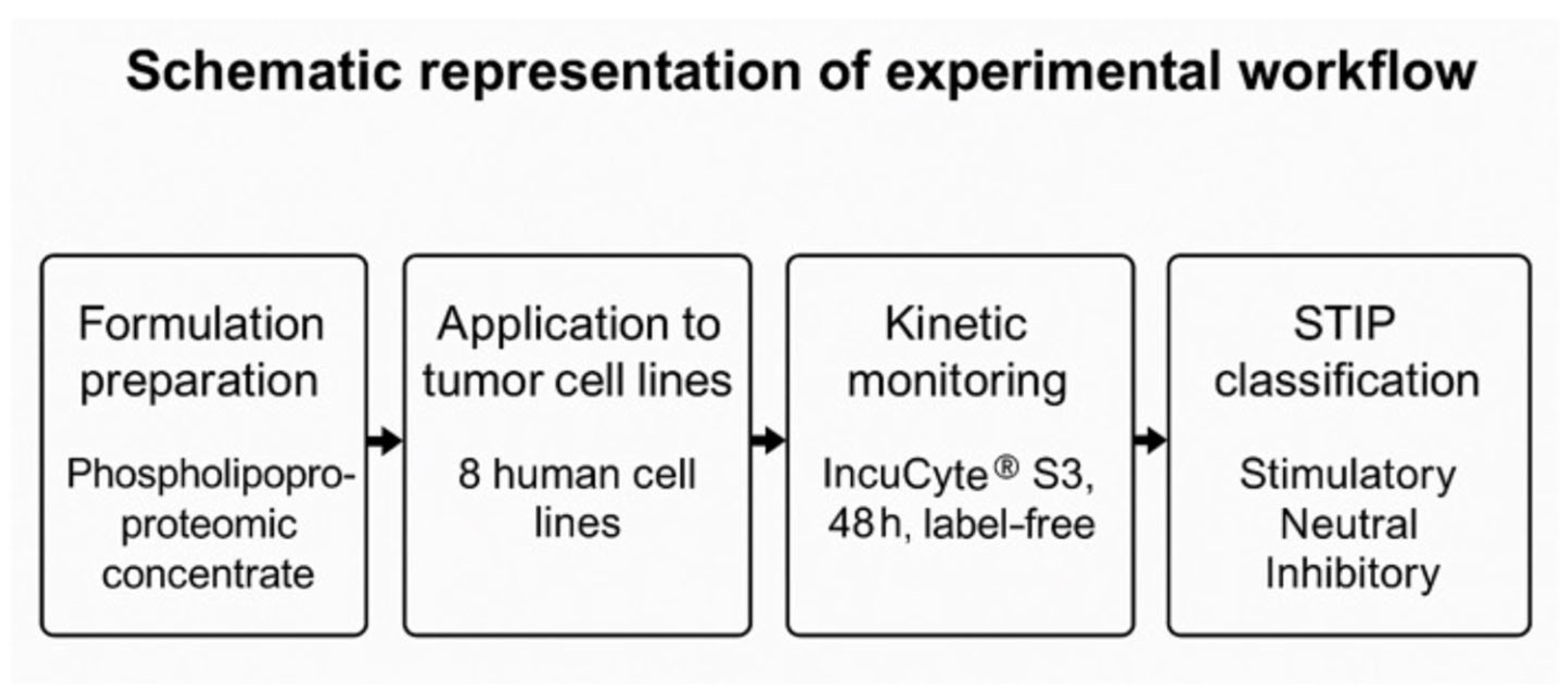
3. Results
3.1. Distinct Kinetic Trajectories: Structured Phenotypic Divergence

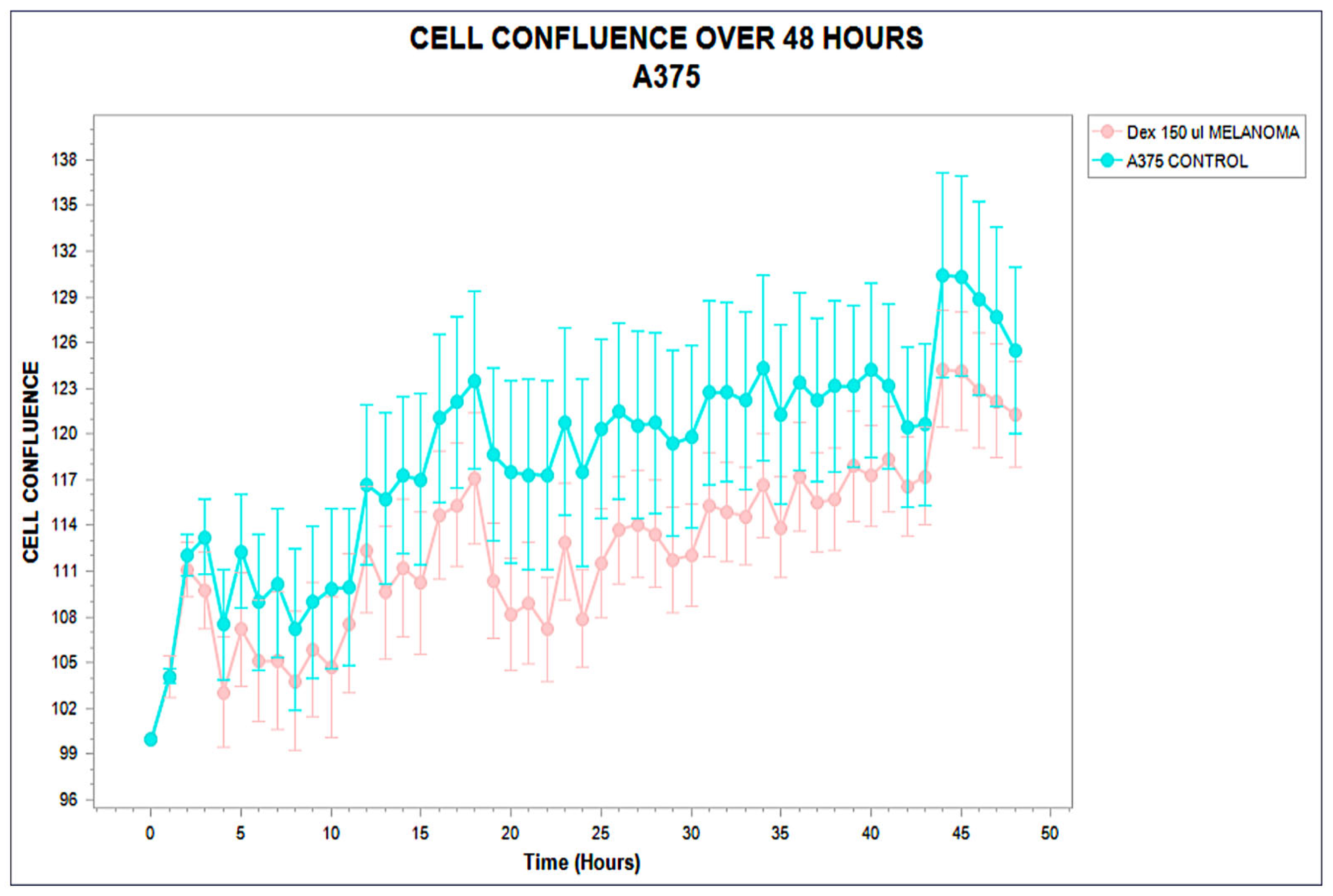
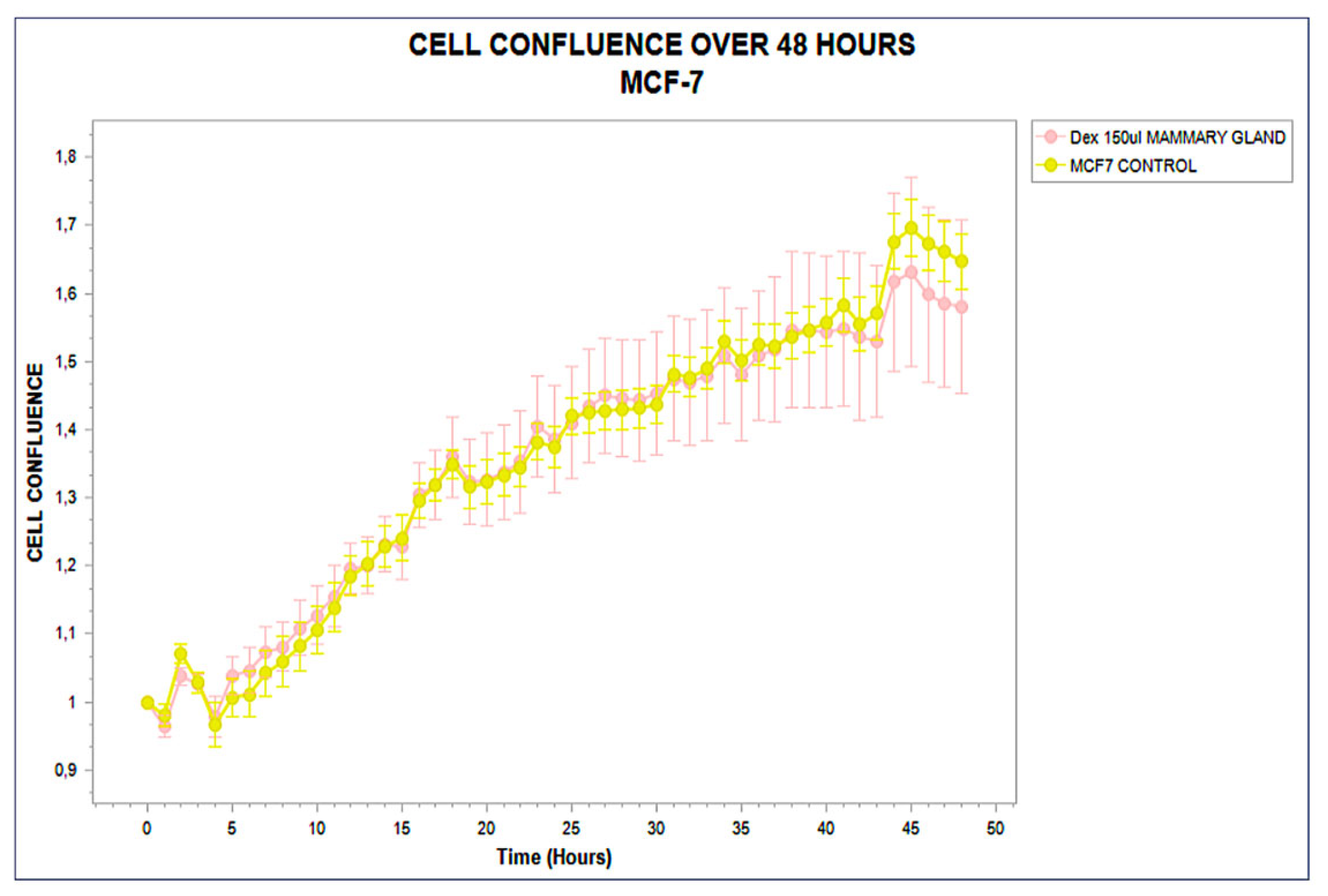
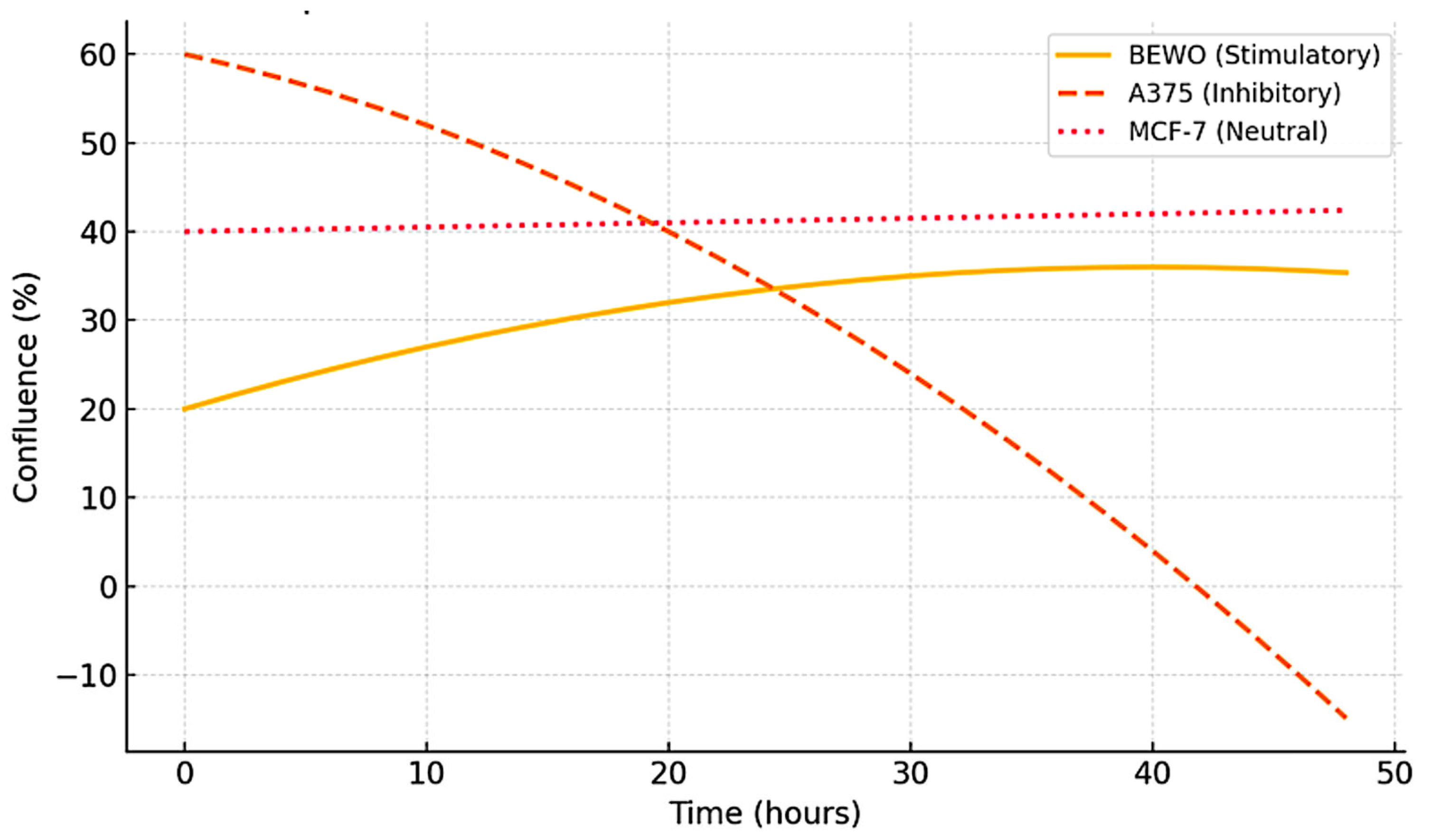
3.2. Functional Stratification (Stimulating, Inhibitory, and Neutral)


3.3. Interbatch Stability and Technical Traceability
3.4. Cell Death Analysis: Validation of Non-Cytotoxicity
3.5. Immunological Correlation: IL-6, IL-10, and IFN-γ

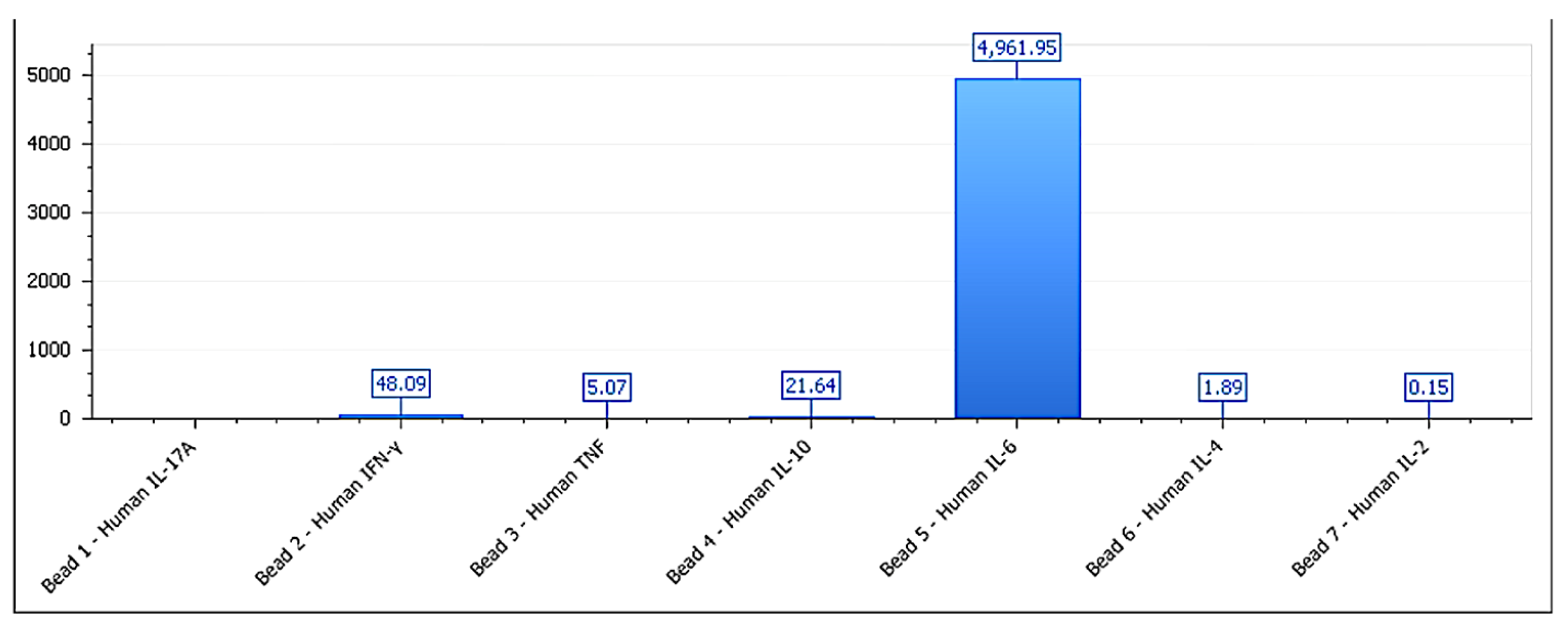

| Functional Group | IL-6 (pg/mL) | IFN-γ (pg/mL) | IL-10 (pg/mL) | IFN-γ/IL-10 Ratio | p-Value (vs. Control) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stimulatory | 168.5 ± 12.4 | 54.1 ± 9.3 | 39.2 ± 6.1 | 1.38 ± 0.17 | <0.001 |
| Inhibitory | 45.7 ± 7.9 | 83.6 ± 10.8 | 14.2 ± 3.4 | 5.89 ± 0.63 | <0.001 |
| Neutral | 62.3 ± 8.5 | 47.5 ± 6.2 | 45.2 ± 5.9 | 1.05 ± 0.14 | >0.05 |

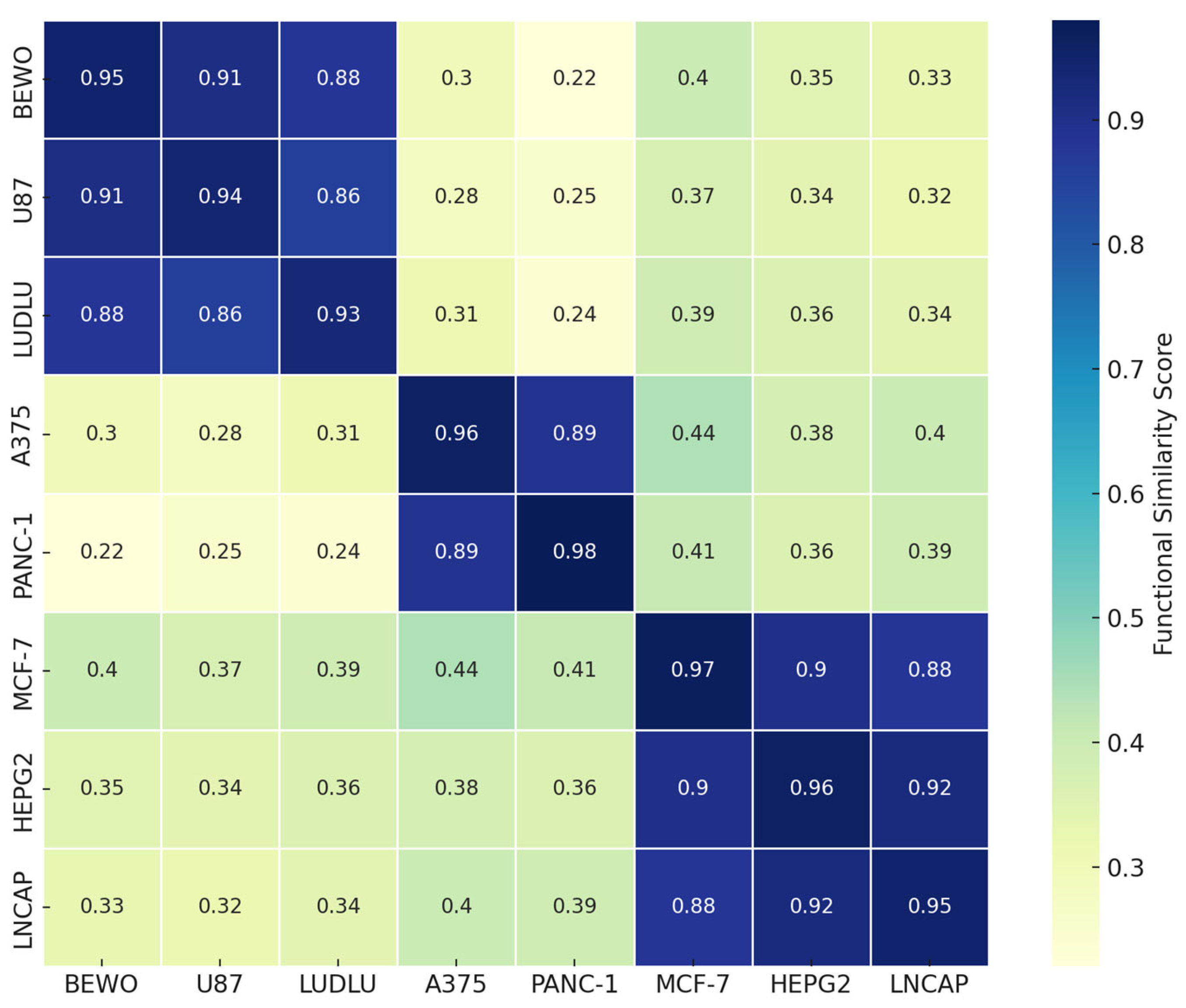
3.6. Cross-Functional Mapping Between Tumor Cell Lines and Phospholipoproteomic Formulations
| Cell Line | FV-001 | FV-002 | FV-003 | FV-004 | FV-005 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEWO | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| U87 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| LUDLU | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| A375 | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ |
| PANC-1 | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ |
| MCF-7 | — | — | — | — | — |
| HEPG2 | — | — | — | — | — |
| LNCAP-C42 | — | — | — | — | — |
3.7. FSI: Quantified Functional Ranking by Cell Line
| Cell Line | Log-Phase Slope (%/h) | AUC (Arbitrary Units) | Divergence Duration (h) | Plateau Stability (h) | FSI Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEWO | 2.9 | 428 | 28 | 38–48 | +42.3 |
| U87 | 2.4 | 385 | 22 | 32–48 | +33.7 |
| LUDLU | 1.8 | 362 | 18 | 30–48 | +29.4 |
| A375 | −2.5 | 219 | 24 | Suppressed | −26.1 |
| PANC-1 | −3.1 | 202 | 26 | Suppressed | −28.3 |
| MCF-7 | 0.3 | 321 | — | 0–48 (unchanged) | +3.2 |
| HEPG2 | −0.4 | 308 | — | 0–48 (unchanged) | −1.6 |
| LNCAP-C42 | −0.5 | 297 | — | 0–48 (unchanged) | −2.3 |

3.8. Phospholipoproteomic Compatibility Cluster (Heatmap or Topography)
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Classical Pharmacodynamic Models
4.2. Value as a Non-Invasive Functional Screening Platform
4.3. Immunophenotypic Logic and STIP Framework
4.4. Interbatch Traceability and Technical Consistency
4.5. Functional Validation Beyond Cytotoxicity
4.6. Regulatory Integration and Anticipatory Documentation

4.7. Strategic Positioning for Regulatory Use
4.8. Projected Integration with 3D and Advanced Systems
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CBA | Cytometric Bead Array |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| CTD | Common Technical Document |
| CV% | Coefficient of Variation (Percentage) |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FSI | Functional Stratification Index |
| FV | Formulation Variant |
| HLA-A | Human Leukocyte Antigen A |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IncuCyte® | Real-time live-cell imaging system |
| LAL | Limulus Amebocyte Lysate |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| SAP | Structured Anticipatory Protocol |
| STIP | Structured Traceability and Immunophenotypic Platform |
| Th1 | Type 1 Helper T Cell |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
References
- Hato, L.; Vizcay, A.; Eguren, I.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Rodríguez, J.; Gállego Pérez-Larraya, J.; Sarobe, P.; Inogés, S.; Díaz de Cerio, A.L.; Santisteban, M. Dendritic cells in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Sandoval, R.; Gutierrez-Castro, F.; Rivadeneira, I.; Krakowiak, F.; Iturra, J. Advances in the translational application of immunotherapy with pulsed dendritic cell-derived exosomes. J. Clin. Biomed. Res. 2024, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurster, S.; Kumaresan, P.R.; Albert, N.D.; Hauser, P.J.; Lewis, R.E.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Live monitoring and analysis of fungal growth, viability, and mycelial morphology using the IncuCyte NeuroTrack processing module. mBio 2019, 10, e00673-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Sandoval, R.; Gutiérrez-Castro, F.; Muñoz-Godoy, N.; Rivadeneira, I.; Sobarzo, A.; Iturra, J.; Krakowiak, F.; Alarcón, L.; Dorado, W.; Lagos, A.; et al. Beyond exosomes: An ultrapurified phospholipoproteic complex (PLPC) as a scalable immunomodulatory platform for re-programming immune suppression in metastatic cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberger, S.; Karuthedom George, S.; Lauková, L.; Weiss, R.; Tripisciano, C.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Weber, V.; Allmaier, G.; Weiss, V.U. Targeting the structural integrity of extracellular platforms via nano electrospray gas-phase electrophoretic mobility molecular analysis (nES GEMMA). Membranes 2022, 12, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecca, A.; Barili, V.; Rizzo, D.; Olivani, A.; Biasini, E.; Laccabue, D.; Dalla Valle, R.; Ferrari, C.; Cariani, E.; Missale, G. Intratumor regulatory noncytotoxic NK cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells 2021, 10, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Ouyang, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, W. Non-cytotoxic nanoparticles re-educating macrophages achieving both innate and adaptive immune responses for tumor therapy. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, C.L.; Teixeira, M.M.; Adelson, D.L.; Buenz, E.J.; David, B.; Glaser, K.B.; Harata-Lee, Y.; Howes, M.R.; Izzo, A.A.; Maffia, P.; et al. Future directions for the discovery of natural product-derived immunomodulating drugs: An IUPHAR positional review. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausgruber, T.; Fortelny, N.; Fife-Gernedl, V.; Senekowitsch, M.; Schuster, L.C.; Lercher, A.; Nemc, A.; Schmidl, C.; Rendeiro, A.F.; Bergthaler, A.; et al. Structural cells are key regulators of organ-specific immune response. Nature 2020, 583, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siefen, T.; Lokhnauth, J.; Liang, A.; Larsen, C.C.; Lamprecht, A. An ex-vivo model for transsynovial drug permeation of intraarticular injectables in naive and arthritic synovium. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, M.; Przedborski, M.; Thiyagarajan, S.; Pellowe, M.; Verma, A.; Brijwani, N.; Datta, D.; Jain, M.; Shanthappa, B.U.; Kapoor, V.; et al. Integrating systems biology and an ex vivo human tumor model elucidates PD-1 blockade response dynamics. iScience 2020, 23, 101229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisci, G.; Rajsiglova, L.; Bibbo, S.; Ziccheddu, G.; Ricciardi, E.; Falvo, E.; De Laurenzi, V.; Sala, G.; Capone, E.; Colotti, G.; et al. A first-in-class non-cytotoxic nanocarrier based on a recombinant human ferritin boosts targeted therapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 309, 142843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Hernandez, M.O.; Zhao, Y.; Mehta, M.; Tran, B.; Kelly, M.; Rae, Z.; Hernandez, J.M.; Davis, J.L.; Martin, S.P.; et al. Tumor cell biodiversity drives microenvironmental reprogramming in liver cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 418–430.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, C.; Manley, E., Jr.; Neely, A.M.; Castillo, J.; Ramos Correa, M.; Velarde, D.A.; Yang, M.; Puente, P.E.; Romero, D.I.; Ren, B.; et al. Lack of racial and ethnic diversity in lung cancer cell lines contributes to lung cancer health disparities. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1187585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lou, P.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Lu, Y.; Wan, M.; Cheng, J.; et al. Unveiling the functional heterogeneity of endogenous tissue extracellular platforms in skeletal muscle through multi-omics. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 512, 162679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaletto, J.; Bernier, A.; McDougall, R.; Cline, M.S. Federated Analysis for Privacy-Preserving Data Sharing: A Technical and Legal Primer. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2023, 24, 347–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.T.; Nishimura, T.; Suetsugu, S. Ultracentrifugal separation, characterization, and functional study of extracellular platforms derived from serum-free cell culture. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, K.; Martin, K.; FitzGerald, S.; O’Sullivan, J.; Wu, Y.; Blanco, A.; Richardson, C.; Gee, M. A comparison of methods for the isolation and separation of extracellular platforms from protein and lipid particles in human serum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Dai, M.; Zhou, X.; Long, J.; Tian, W.; Yu, M. Comparison of two cell-free therapeutics derived from adipose tissue: Small extracellular platforms versus conditioned medium. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Valdés, A.I.; de la Fuente, C.; Hidalgo, Y.; Vega-Letter, A.M.; Tapia-Limonchi, R.; Khoury, M.; Alcayaga-Miranda, F. A chemically defined, xeno- and blood-free culture medium sustains increased production of small extracellular platforms from mesenchymal stem cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 619930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holme, B.; Bjørnerud, B.; Pedersen, N.M.; Rodriguez de la Ballina, L.; Wesche, J.; Haugsten, E.M. Automated tracking of cell migration in phase contrast images with CellTraxx. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Shi, B.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Long-term, real-time and label-free live cell image processing and analysis based on a combined algorithm of CellPose and watershed segmentation. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavikhamene, Z.; Sykora, D.J.; Mrksich, M.; Bagheri, N. Morphological features of single cells enable accurate automated classification of cancer from non-cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidda, A.K.; Chittaranjan, S.; Gorski, S.M. Real-time IncuCyte® Assay for the Dynamic Assessment of Live and Dead Cells in 2D Cultures. Bio Protoc. 2025, 15, e5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, F.; Habib, S.; Badruddza, K.; Rahman, M.; Islam, M.R.; Sultana, S.; Nessa, A. The association of cytokines IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-10 with the disease severity of COVID-19: A study from Bangladesh. Cureus 2024, 16, e57610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, R.; Kolte, A.; Ahlers, O.; Oswald, M.; Krauss, V.; Roell, D.; Sommerfeld, O.; Dimopoulos, G.; Tsangaris, I.; Antoniadou, E.; et al. Use of IFNγ/IL10 ratio for stratification of hydrocortisone therapy in patients with septic shock. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 607217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsergent, E.; Grisard, E.; Buchrieser, J.; Schwartz, O.; Théry, C.; Lavieu, G. Quantitative characterization of extracellular platform uptake and content delivery within mammalian cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Sandoval, R.; Gutiérrez-Castro, F.; Muñoz-Godoy, N.; Rivadeneira, I.; Sobarzo, A.; Alarcón, L.; Dorado, W.; Lagos, A.; Montenegro, D.; Muñoz, I.; et al. The Design of a Multistage Monitoring Protocol for Dendritic Cell-Derived Exosome (DEX) Immunotherapy: A Conceptual Framework for Molecular Quality Control and Immune Profiling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Li, A.; Cong, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Que, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, L. The phenotypic and the genetic response to the extreme high temperature provides new insight into thermal tolerance for the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deben, C.; Cardenas De La Hoz, E.; Rodrigues Fortes, F.; Le Compte, M.; Seghers, S.; Vanlanduit, S.; Vercammen, H.; Van Den Bogert, B.; Dusetti, N.; Lin, A.; et al. Development and validation of the Normalized Organoid Growth Rate (NOGR) metric in brightfield imaging-based assays. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Thrash, J.C. sparse-growth-curve: A computational pipeline for parsing cellular growth curves with low temporal resolution. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00296-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maculins, T.; Verschueren, E.; Hinkle, T.; Choi, M.; Chang, P.; Chalouni, C.; Rao, S.; Kwon, Y.; Lim, J.; Katakam, A.K.; et al. Multiplexed proteomics of autophagy-deficient murine macrophages reveals enhanced antimicrobial immunity via the oxidative stress response. eLife 2021, 10, e62320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.P.; Luo, L.J.; Chen, H.Z.; Chen, Q.T.; Bian, X.L.; Wu, S.F.; Zhou, J.X.; Zhao, W.X.; Liu, J.M.; Wang, X.M.; et al. Ectosomal PKM2 promotes HCC by inducing macrophage differentiation and remodeling the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 1192–1206.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.A.; Baba, S.K.; Sadida, H.Q.; Al Marzooqi, S.; Jerobin, J.; Altemani, F.H.; Santos, D.; Reddy, T.; Hamdan, L.; Youssef, N. Extracellular platforms as tools and targets in therapy for diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2024, 9, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Sandoval, R.; Gutierrez-Castro, F.; Muñoz-Godoy, N.; Rivadeneira, I.; Sobarzo, A.; Alarcón, L.; Dorado, W.; Lagos, A.; Montenegro, D.; Muñoz, I.; et al. Phospholipid-Rich DC-Vesicles with Preserved Immune Fingerprints: A Stable and Scalable Platform for Precision Immunotherapy. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Douglas, D.; Zhang, J.; Kumari, S.; Enuameh, M.S.; Dai, Y.; Wallace, C.T.; Watkins, S.C.; Shu, W.; Xing, J. Live-cell imaging and analysis reveal cell phenotypic transition dynamics inherently missing in snapshot data. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelles, J.D.; Mohammed, J.N.; Santos, L.C.; Legarda, D.; Ting, A.T.; Chipuk, J.E. Single-cell and population-level analyses using real-time kinetic labeling couples proliferation and cell death mechanisms. Dev. Cell 2019, 51, 277–291.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgaenko, K.; Arneja, A.; Ball, A.G.; Putelo, A.M.; Munson, J.M.; Rutkowski, M.R.; Pompano, R.R. Ex Vivo Model of Breast Cancer Cell Invasion in Live Lymph Node Tissue. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2025, 8, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maumus, M.; Rozier, P.; Boulestreau, J.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular platforms: Opportunities and challenges for clinical translation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, D.; Mussack, V.; Byrd, J.B. Separation, characterization, and standardization of extracellular platforms for drug delivery applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 348–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Wood, K.C.; Scott, J.E. A high throughput proliferation and cytotoxicity assay for co-cultured isogenic cell lines. MethodsX 2022, 9, 101927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazonova, E.V.; Chesnokov, M.S.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Kopeina, G.S. Drug toxicity assessment: Cell proliferation versus cell death. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Sandoval, R.; Gutierrez-Castro, F.; Rivadeneira, I.; Sobarzo, A.; Muñoz, N.; Krakowiak, F.; Iturra, J.; Montenegro, D.; Dorado, W.; Peña-Vargas, C.A. PlP-driven exosomal breakthroughs: Advancing immune solutions for complex tumor microenvironments. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43 (Suppl. 16), e14511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, I.S.; Hammond, P.T.; Irvine, D.J. Engineering strategies for immunomodulatory cytokine therapies: Challenges and clinical progress. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. Technol. Pharm. 2021, 1, e202100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatina, T.; Favaro, E.; Danilova, L.; Fertig, E.J.; Favorov, A.V.; Kagohara, L.T.; Martone, T.; Bussolati, B.; Romagnoli, R.; Albera, R.; et al. Extracellular platforms released by tumor endothelial cells spread immunosuppressive and transforming signals through various recipient cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiao, C.; Kong, X.; Yang, J.; Guo, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Xiu, H.; He, Y.; et al. Adhesion between EVs and tumor cells facilitated EV-encapsulated doxorubicin delivery via ICAM1. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 205, 107244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowiak, F.; Gutierrez-Sandoval, R.; Gutierrez-Castro, F.; Rivadeneira, I.; Sobarzo, A.; Muñoz, I.; Lagos, A.; Iturra, J.; Aguilera, R.; Toledo, A. PlP-powered exosomal therapeutics: Redefining immune activation in therapy-resistant tumor microenvironment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, e14512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichas, A.; Riley, A.K.; Nkinsi, N.T.; Kamlapurkar, S.; Parrish, P.C.R.; Lo, A.; Duke, F.; Chen, J.; Fung, I.; Watson, J.; et al. Integrative oncogene-dependency mapping identifies RIT1 vulnerabilities and synergies in lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, N.; Boeck, N.; Lamberti, G.; Lisandrelli, R.; Trajanoski, Z. Protocol for functional profiling of patient-derived organoids for precision oncology. STAR Protoc. 2024, 5, 102887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturra, J.; Gutierrez-Sandoval, R.; Gutierrez-Castro, F.; Rivadeneira, I.; Sobarzo, A.; Alarcon, L.; Muñoz, I.; Montenegro, D.; Krakowiak, F.; Dorado, W. Disruptive advances in exosome lyophilization: Unlocking new frontiers in precision oncology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43 (Suppl. 16), e14522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gristina, V.; Bazan, V.; Barraco, N.; Taverna, S.; Manno, M.; Raccosta, S.; Carreca, A.P.; Bono, M.; Bazan Russo, T.D.; Pepe, F.; et al. On-treatment dynamics of circulating extracellular platforms in the first-line setting of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The LEXOVE prospective study. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 1422–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson Cullison, S.R.; Flemming, J.P.; Karagoz, K.; Wermuth, P.J.; Mahoney, M.G. Mechanisms of extracellular platform uptake and implications for the design of cancer therapeutics. J. Extracell. Biol. 2024, 3, e70017. [Google Scholar]
- Khatib, T.O.; Amanso, A.M.; Pedro, B.; Knippler, C.M.; Summerbell, E.R.; Zohbi, N.M.; Smith, R.; Foster, K.; Delgado, M.; Ali, T. A live-cell platform to isolate phenotypically defined subpopulations for spatial multi-omic profiling. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Sandoval, R.; Rivadeneira, I.; Gutierrez-Castro, F.; Sobarzo, A.; Muñoz, I.; Lagos, A.; Muñoz, N.; Krakowiak, F.; Aguilera, R.; Toledo, A. Decoding NAMPT and TIGAR: A molecular blueprint for reprogramming tumor metabolism and immunity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43 (Suppl. 16), e14537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Roberto, R.B.; Castellanos-Rueda, R.; Frey, S.; Egli, D.; Vazquez-Lombardi, R.; Kapetanovic, E.; Kucharczyk, J.; Reddy, S.T. A functional screening strategy for engineering chimeric antigen receptors with reduced on-target, off-tumor activation. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 2564–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Aicha, S.; Anwar, M.; Vilahur, G.; Martino, F.; Kyriazis, P.G.; de Winter, N.; Punjabi, P.P.; Angelini, G.D.; Sattler, S.; Emanueli, C.; et al. Small extracellular platforms in the pericardium modulate macrophage immunophenotype in coronary artery disease. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2024, 9, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixson, A.; Dawson, T.R.; Di Vizio, D.; Weaver, A.M. Context-specific regulation of extracellular platform biogenesis and cargo selection. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 454–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudte, S.; Klinghammer, K.; Jurmeister, P.S.; Jank, P.; Blohmer, J.U.; Liebs, S.; Rhein, P.; Hauser, A.E.; Tinhofer, I. Multiparametric phenotyping of circulating tumor cells for analysis of therapeutic targets, oncogenic signaling pathways and DNA repair markers. Cancers 2022, 14, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.E.; Gutierrez Castro, F.; Rivadeneira, I.; Krakowiak, F.; Iturra, J.; Dorado, W.; Aguilera, R. Innovative applications of neoantigens in dendritic cell-derived exosome (DEX) therapy and their impact on personalized cancer treatment. Immuno-Oncol. Technol. 2024, 24, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funck, F.; Pahl, J.; Kyjacova, L.; Freund, L.; Oehrl, S.; Gräbe, G.; Pezer, S.; Hassel, J.C.; Sleeman, J.; Cerwenka, A.; et al. Human innate immune cell crosstalk induces melanoma cell senescence. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1808424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyniak, P.; Hartman, M.L. Dual role of interferon-gamma in the response of melanoma patients to immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, R.E.; Gutierrez Castro, F.; Rivadeneira, I.; Krakowiak, F.; Iturra, J.; Dorado, W.; Aguilera, R. Optimized protocol for the accelerated production of dendritic cell-derived exosomes (DEXs): Achieving speed without compromising efficacy. Immuno-Oncol. Technol. 2024, 24, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, G.; Lei, J. Influencing immunity: Role of extracellular platforms in tumor immune checkpoint dynamics. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 2365–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, P.; Jain, R.; Rosenkrands-Lange, E.; Hey, C.; Koban, M.U. Regulatory pathways supporting expedited drug development and approval in ICH member countries. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2022, 57, 484–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claridge, B.; Lozano, J.; Poh, Q.H.; Greening, D.W. Development of extracellular platform therapeutics: Challenges, considerations, and opportunities. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 734720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezgin, S.; Danilik, O.; Yudaeva, A.; Kachanov, A.; Kostyusheva, A.; Karandashov, I.; Ponomareva, N.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr.; Parodi, A.; Chulanov, V.; et al. Basic guide for approaching drug delivery with extracellular platforms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caleb, J.; Yong, T. Is it time to start transitioning from 2D to 3D cell culture? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, R.; Sheng, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, F.; Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Su, J. Organoids and organoid extracellular platforms-based disease treatment strategies. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, J.; Hwang, B. Multiplexed multimodal single-cell technologies: From observation to perturbation analysis. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.Z.; Li, Z.H.; Bai, X.F.; Liu, C.J.; Zhang, X.Z. Hybrid platforms based on autologous tumor cell membrane and bacterial outer membrane to enhance innate immune response and personalized tumor immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 8609–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.; Martins, A.C.; Maceiras, A.R.; Liu, W.; Castro, I.; Castro, A.G.; Bandeira, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Cumano, A.; Li, Y.; et al. Interleukin-10 induces interferon-γ-dependent emergency myelopoiesis. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safont, G.; Villar-Hernández, R.; Smalchuk, D.; Stojanovic, Z.; Marín, A.; Lacoma, A.; Pérez-Cano, C.; López-Martínez, A.; Molina-Moya, B.; Solis, A.J.; et al. Measurement of IFN-γ and IL-2 for the assessment of the cellular immunity against SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Diaz, M.; Gonçalves, M.B.S.; Vieira, P.; Bell, V.; Viana, S.; Nunes, S.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Veiga, F. An overview of biosimilars—Development, quality, regulatory issues, and management in healthcare. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, T.; Kornauth, C.; Severin, Y.; Vladimer, G.I.; Pemovska, T.; Hadzijusufovic, E.; Agis, H.; Krauth, M.T.; Sperr, W.R.; Valent, P.; et al. Deep morphology learning enhances ex vivo drug profiling-based precision medicine. Blood Cancer Discov. 2022, 3, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouroupis, D.; Bowles, A.C.; Greif, D.N.; Leñero, C.; Best, T.M.; Kaplan, L.D.; Correa, D. Regulatory-compliant conditions during cell product manufacturing enhance in vitro immunomodulatory properties of infrapatellar fat pad-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, T.; Jain, N. Multicellular tumor spheroids: A convenient in vitro model for translational cancer research. Life Sci. 2024, 358, 123184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.Z.; Adine, C.; Mitriashkin, A.; Aw, B.J.; Iyer, N.G.; Fong, E.L.S. Making in vitro tumor models whole again. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Peng, S.I.; Jia, Y.Y.; Tong, E.; Atwood, S.X.; Sun, B.K. Comprehensive secretome profiling and CRISPR screen identifies SFRP1 as a key inhibitor of epidermal progenitor proliferation. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaldson-Bouchard, K.; Baldassarri, I.; Tavakol, D.N.; Graney, P.L.; Samaritano, M.; Cimetta, E.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Engineering complexity in human tissue models of cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 184, 114181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cell Line | Functional Category | Final Confluence (%) | Δ% vs. Control | p-Value | Intra-Assay CV% | Divergence Onset (ΔT, h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEWO | Stimulatory | 63.2 ± 2.1 | +34.1 | <0.001 | 6.4 | 10 |
| U87 | Stimulatory | 52.6 ± 1.8 | +16.7 | <0.01 | 5.9 | 18 |
| LUDLU | Stimulatory | 49.3 ± 2.5 | +12.4 | 0.04 | 7.1 | 20 |
| A375 | Inhibitory | 23.0 ± 1.5 | −21.1 | <0.001 | 6.2 | 12 |
| PANC-1 | Inhibitory | 20.5 ± 1.7 | −29.5 | <0.01 | 6.7 | 22 |
| MCF-7 | Neutral | 46.0 ± 1.6 | +1.6 | >0.1 | 4.3 | — |
| HEPG2 | Neutral | 43.2 ± 1.9 | −2.8 | >0.1 | 4.9 | — |
| LNCAP-C42 | Neutral | 41.5 ± 2.2 | −3.1 | >0.1 | 4.6 | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Sandoval, R.; Gutiérrez-Castro, F.; Muñoz-Godoy, N.; Rivadeneira, I.; Sobarzo, A.; Iturra, J.; Muñoz, I.; Peña-Vargas, C.; Vidal, M.; Krakowiak, F. Real-Time Functional Stratification of Tumor Cell Lines Using a Non-Cytotoxic Phospholipoproteomic Platform: A Label-Free Ex Vivo Model. Biology 2025, 14, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080953
Gutiérrez-Sandoval R, Gutiérrez-Castro F, Muñoz-Godoy N, Rivadeneira I, Sobarzo A, Iturra J, Muñoz I, Peña-Vargas C, Vidal M, Krakowiak F. Real-Time Functional Stratification of Tumor Cell Lines Using a Non-Cytotoxic Phospholipoproteomic Platform: A Label-Free Ex Vivo Model. Biology. 2025; 14(8):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080953
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Sandoval, Ramón, Francisco Gutiérrez-Castro, Natalia Muñoz-Godoy, Ider Rivadeneira, Adolay Sobarzo, Jordan Iturra, Ignacio Muñoz, Cristián Peña-Vargas, Matías Vidal, and Francisco Krakowiak. 2025. "Real-Time Functional Stratification of Tumor Cell Lines Using a Non-Cytotoxic Phospholipoproteomic Platform: A Label-Free Ex Vivo Model" Biology 14, no. 8: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080953
APA StyleGutiérrez-Sandoval, R., Gutiérrez-Castro, F., Muñoz-Godoy, N., Rivadeneira, I., Sobarzo, A., Iturra, J., Muñoz, I., Peña-Vargas, C., Vidal, M., & Krakowiak, F. (2025). Real-Time Functional Stratification of Tumor Cell Lines Using a Non-Cytotoxic Phospholipoproteomic Platform: A Label-Free Ex Vivo Model. Biology, 14(8), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080953







