The Role of MHC-II Diversity over Enclosure Design in Gut Microbiota Structuring of Captive Bengal Slow Lorises
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.3. DRB1 Exon 2 Gene Sequencing and Allele Calling
2.4. Polymorphism and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Microbial Diversity and Correlation Analysis
3. Results
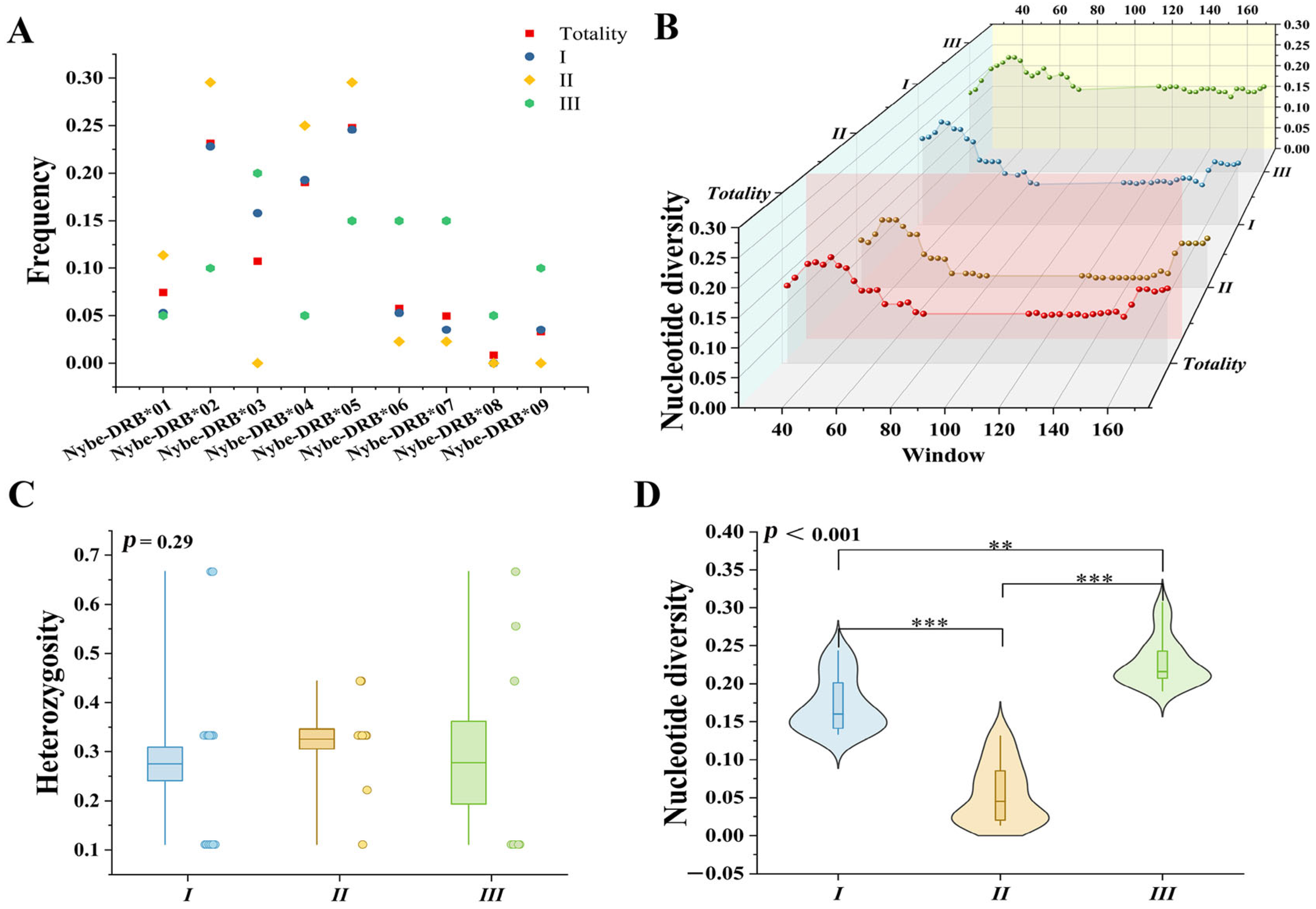
3.1. DRB1e2 Genetic Diversity
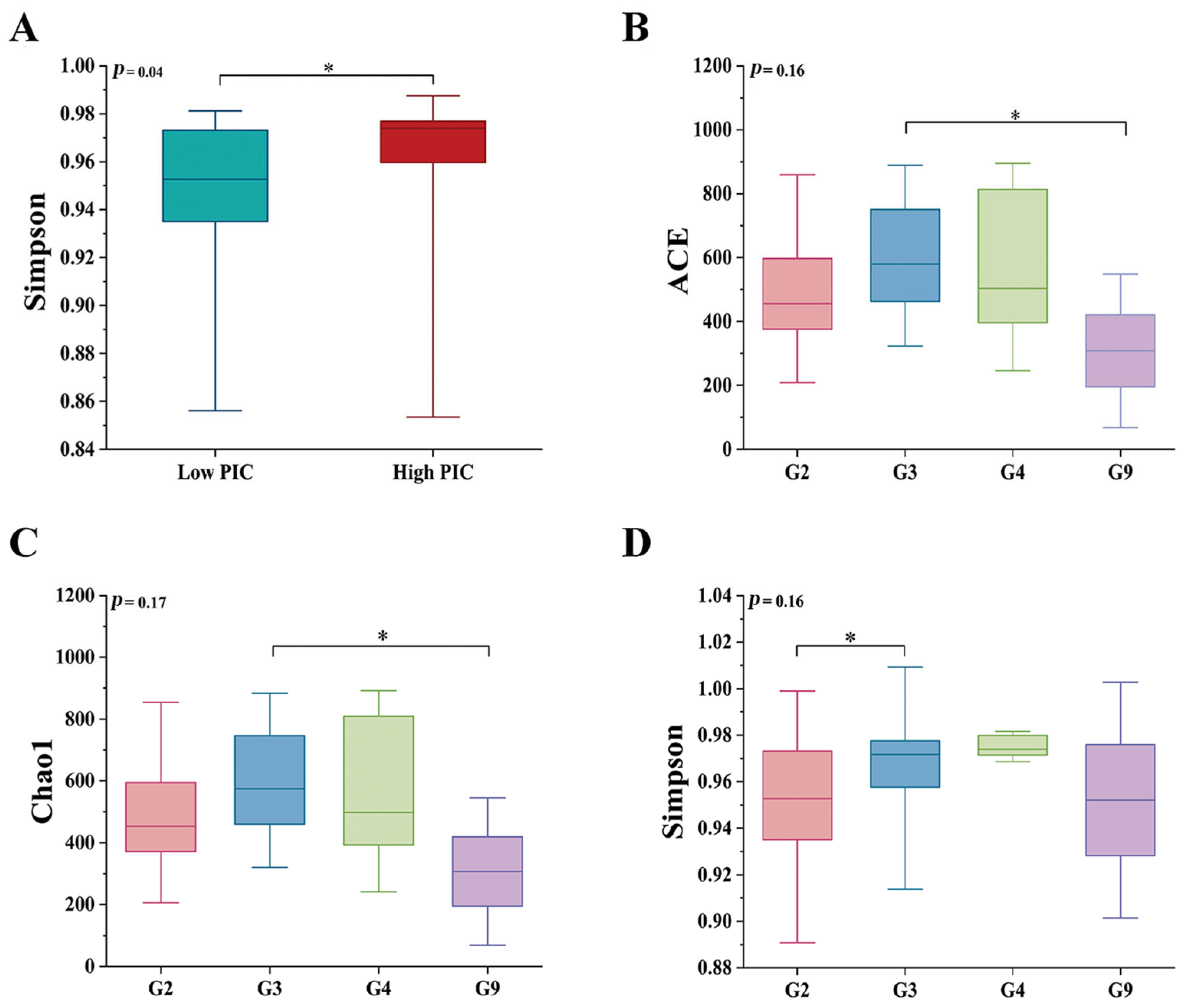
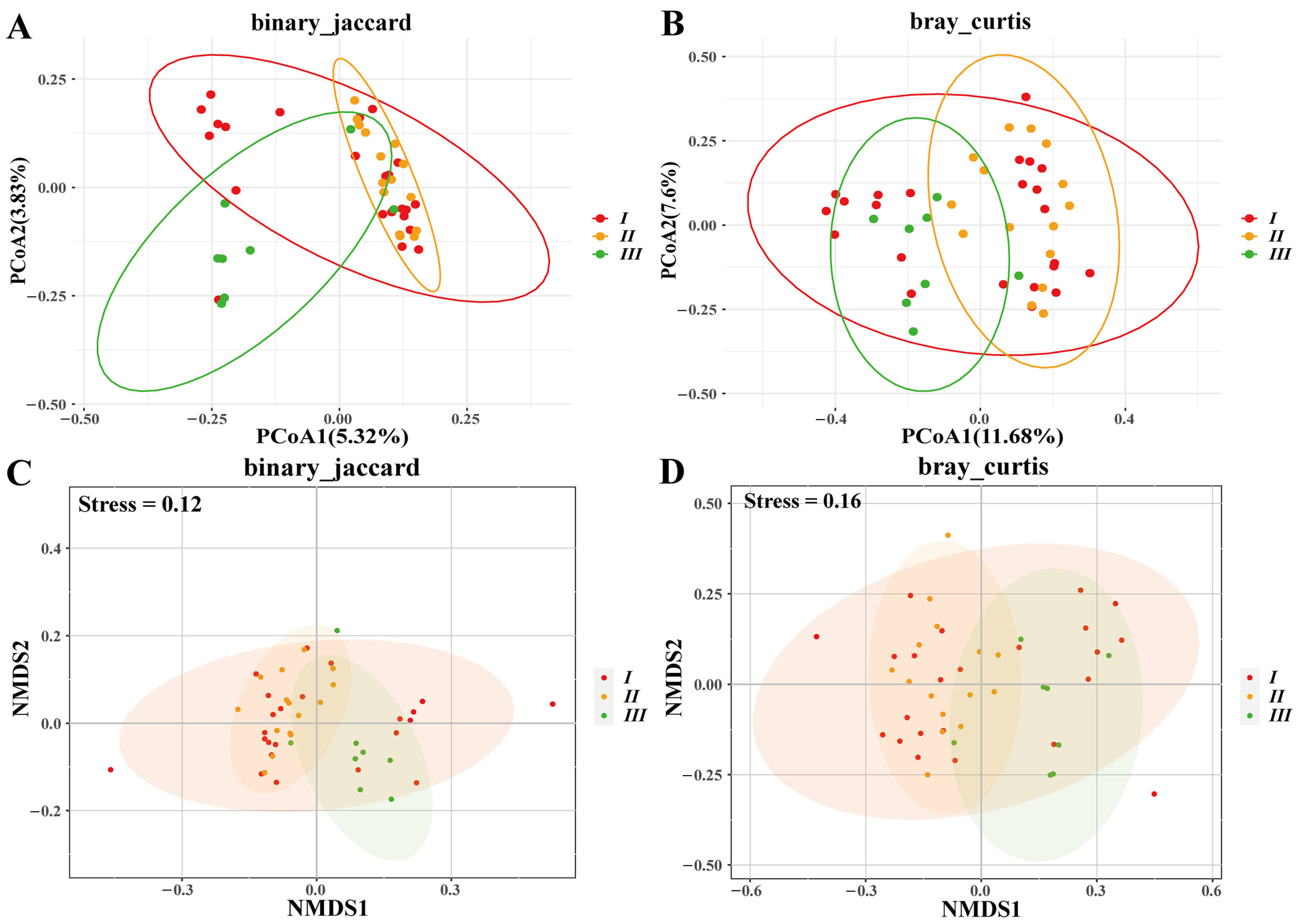
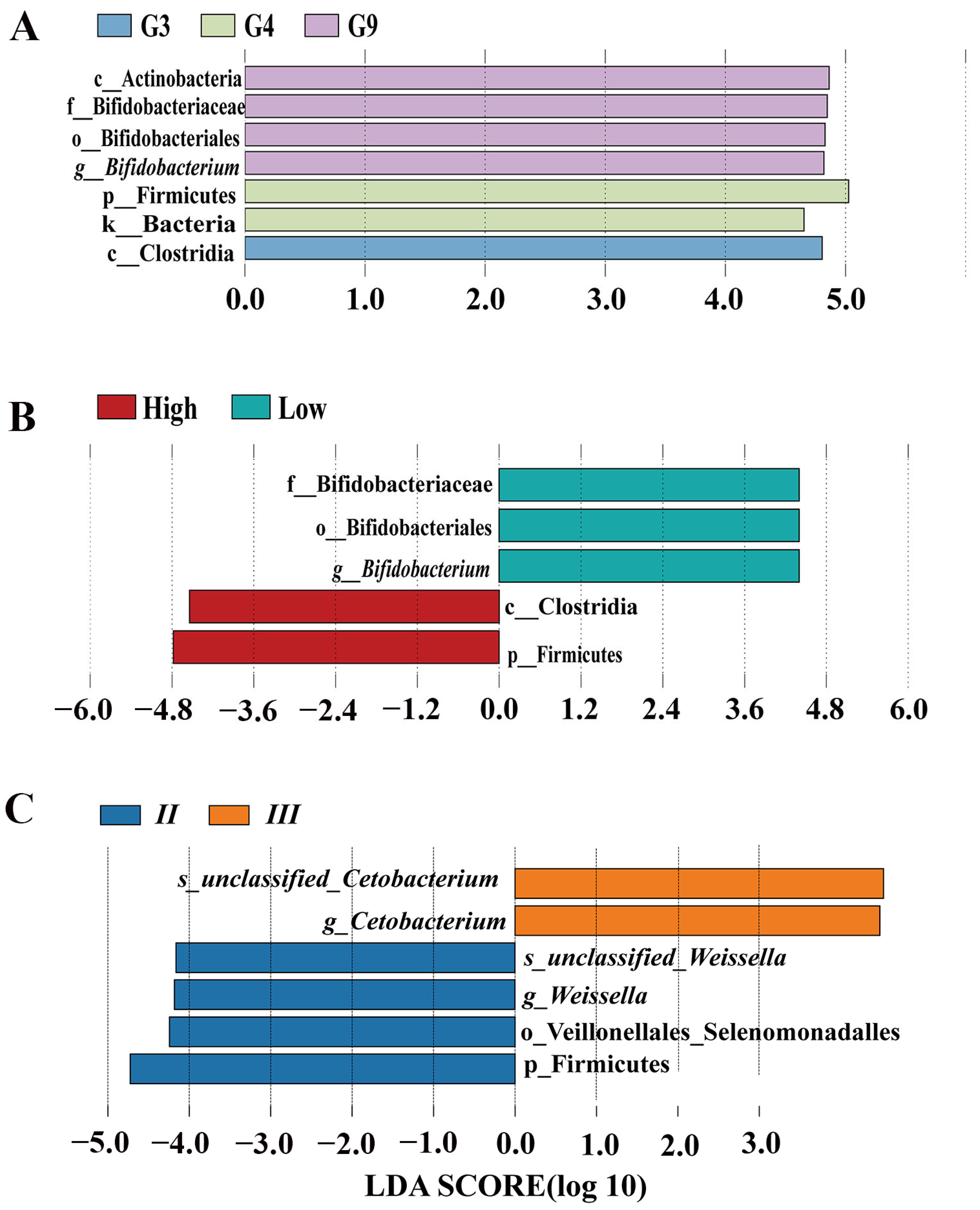
3.2. Group-Specific Variation
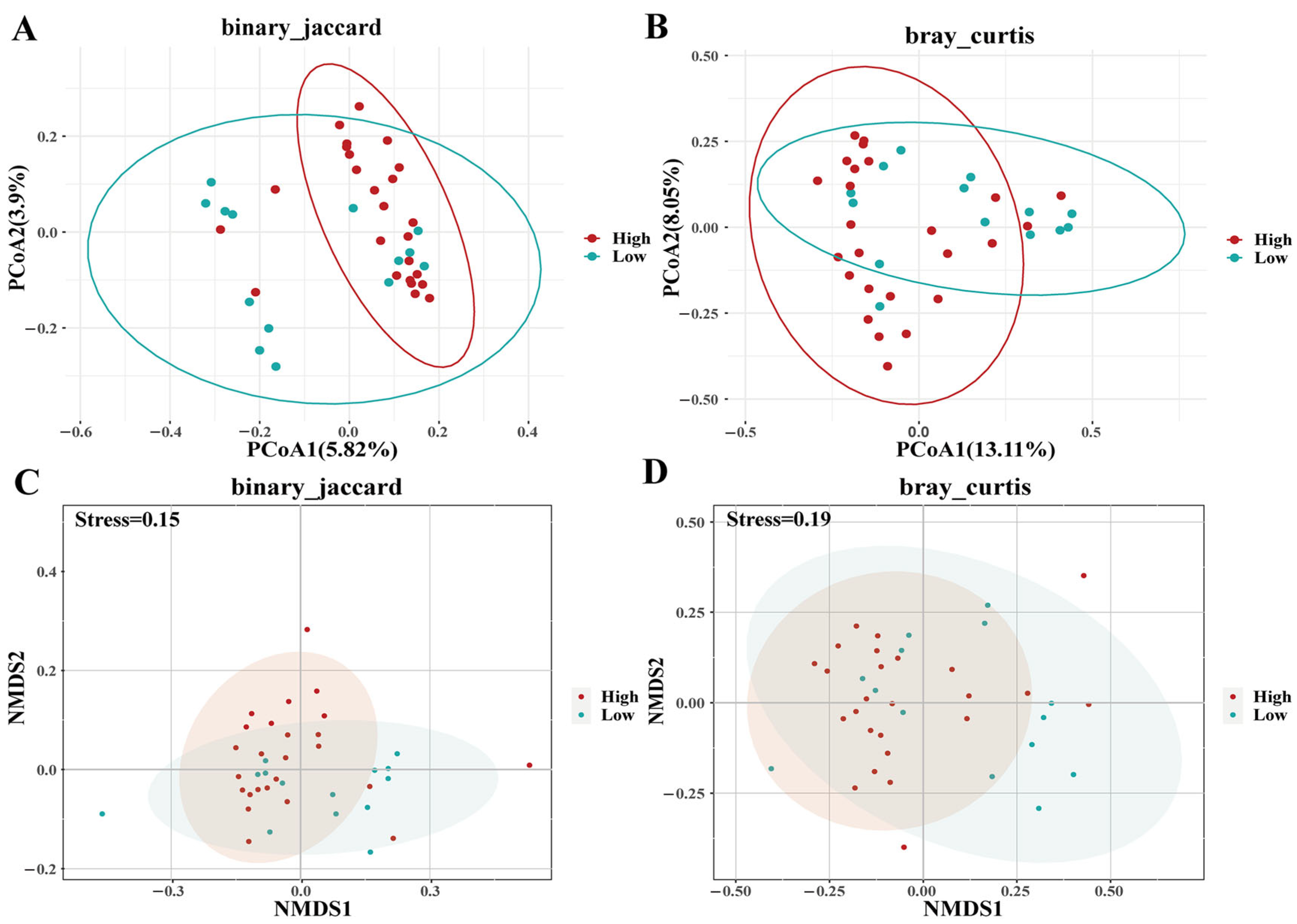
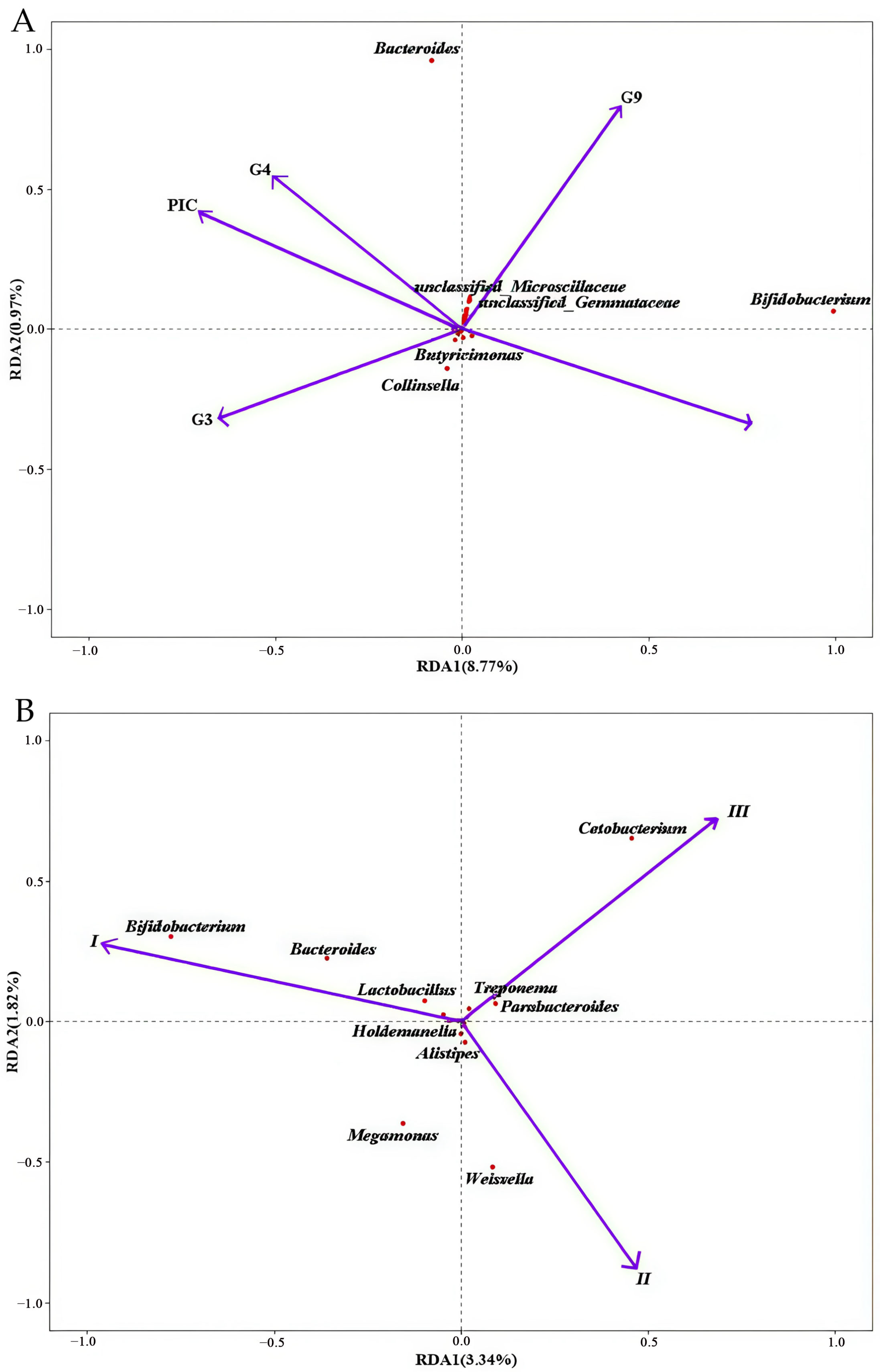
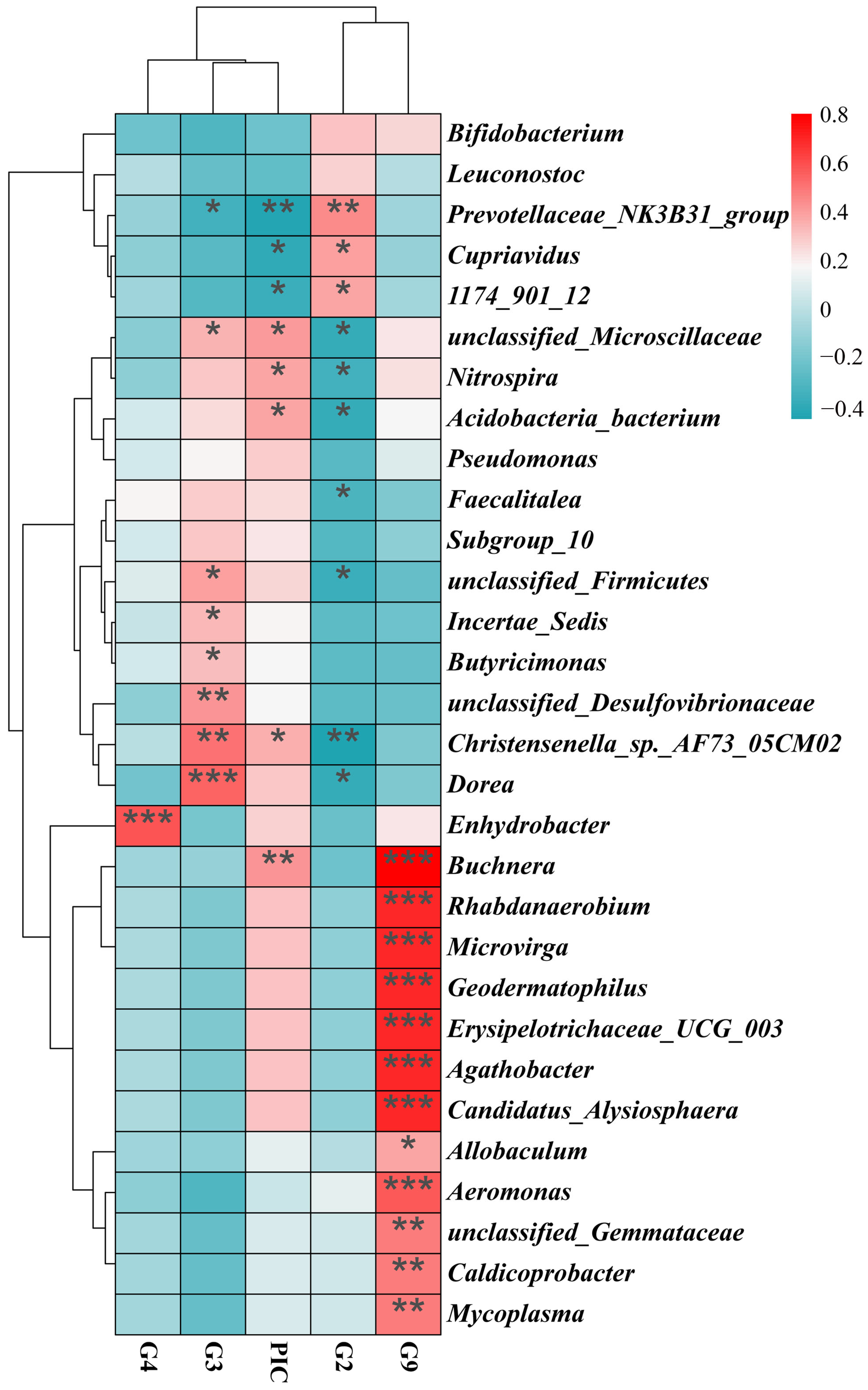
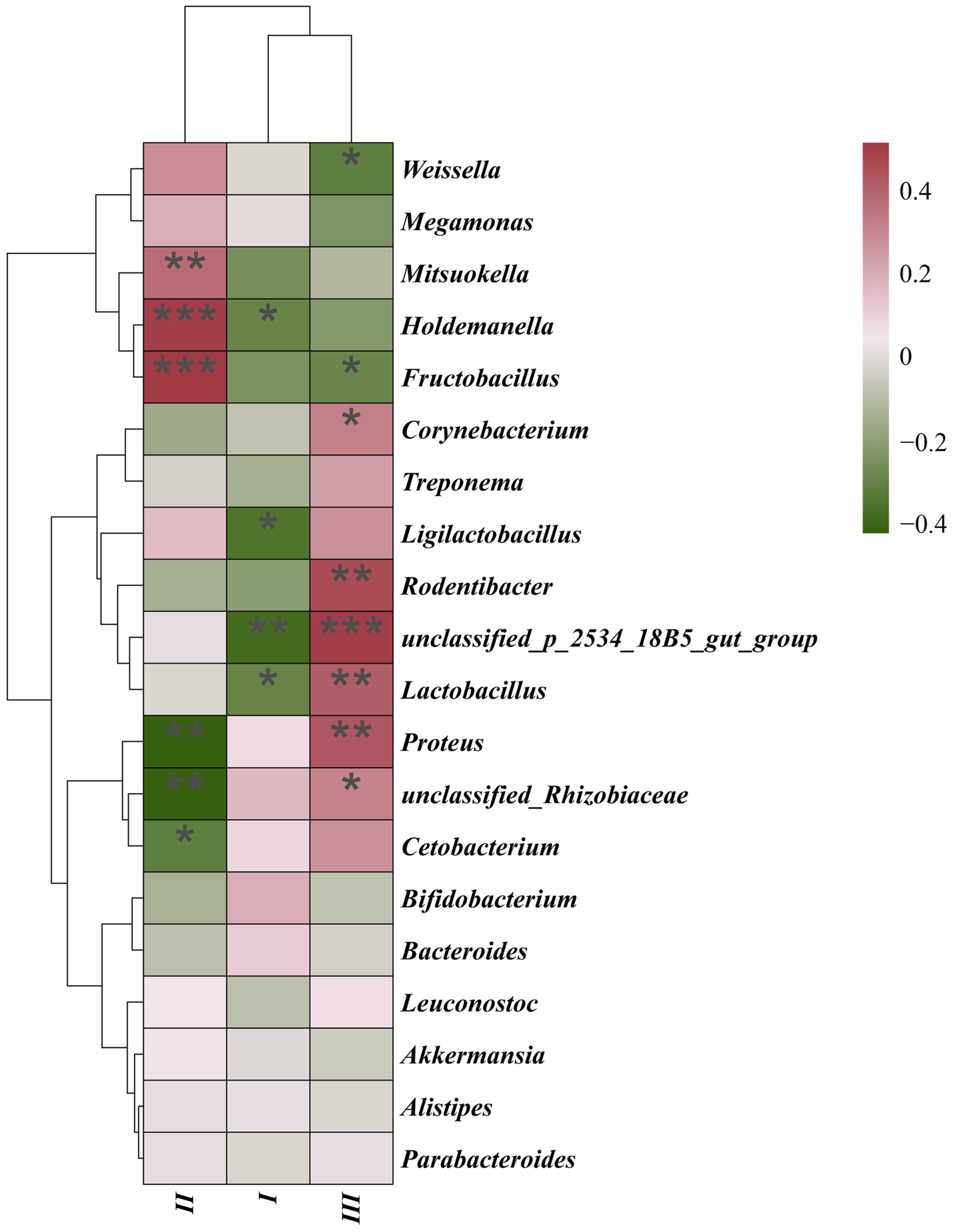
3.3. MHC–Microbiota Associations
3.4. Genotype-Specific Microbiota Associations
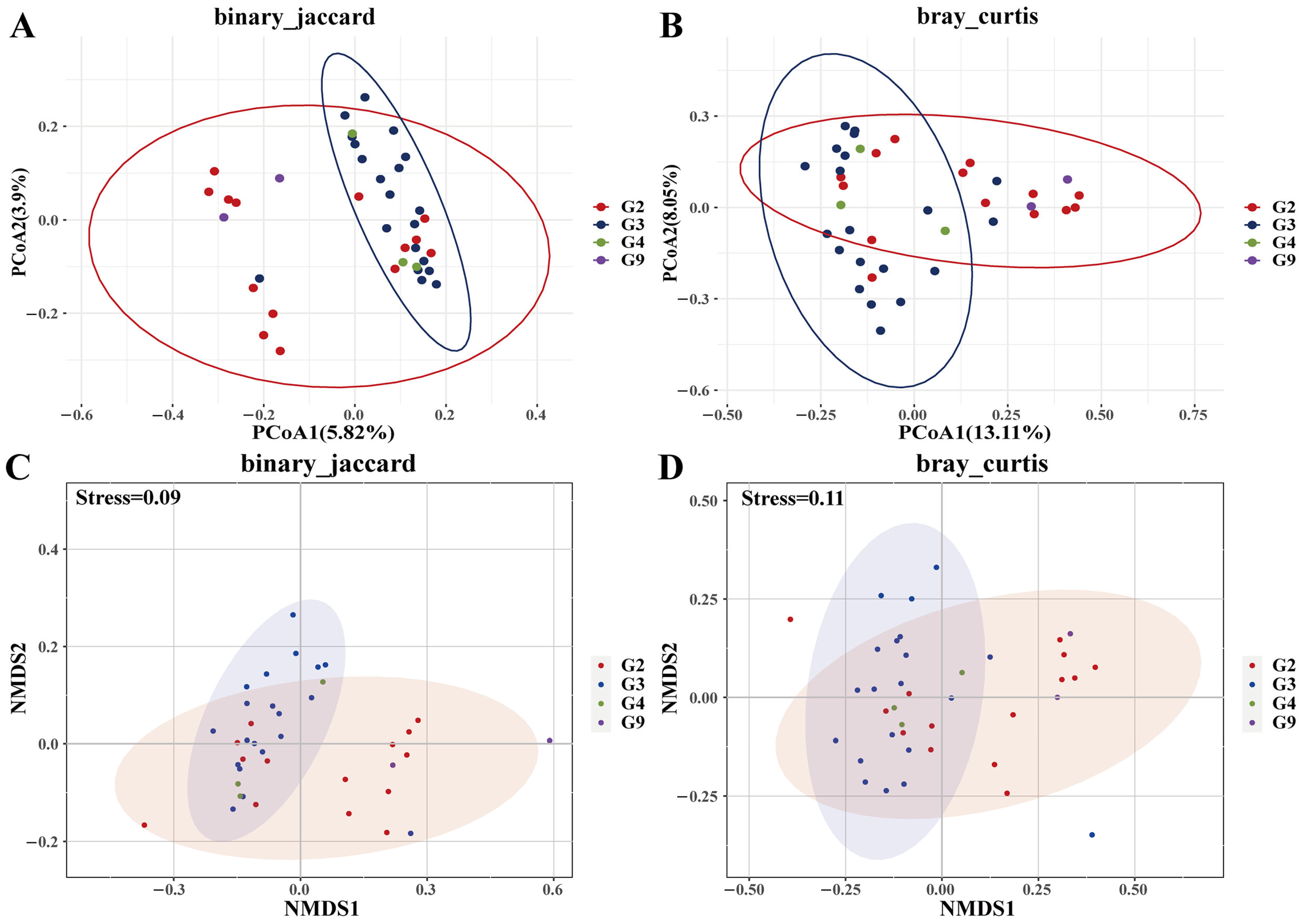
3.5. Enclosure Effects on Microbiota
4. Discussion
4.1. Association Between DRB1e2 and Microbial Community
4.2. Captive Environment as a Microbiota Modulator
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Saif, A.; Zhang, X.; Su, H. Analysis of winter survival strategies of sympatric black-necked cranes, and common cranes from the perspective of diet and gut microbiota. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholier, T.; Lavrinienko, A.; Kallio, E.R.; Watts, P.C.; Mappes, T. Effects of past and present habitat on the gut microbiota of a wild rodent. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2024, 291, 20232531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larzul, C.; Estellé, J.; Borey, M.; Blanc, F.; Lemonnier, G.; Billon, Y.; Thiam, M.G.; Quinquis, B.; Galleron, N.; Jardet, D.; et al. Driving gut microbiota enterotypes through host genetics. Microbiome 2024, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawden, E.G.; Wagner, T.; Schröder, J.; Effern, M.; Hinze, D.; Newland, L.; Attrill, G.H.; Lee, A.R.; Engel, S.; Freestone, D.; et al. CD4+ T cell immunity against cutaneous melanoma encompasses multifaceted MHC II–dependent responses. Sci. Immunol. 2024, 9, eadi9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, R.; Huang, L.-Y.; Germain, R.N. MHC class II interaction with CD4 mediated by a region analogous to the MHC class I binding site for CD8. Nature 1992, 356, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubinak, J.L.; Stephens, W.Z.; Soto, R.; Petersen, C.; Chiaro, T.; Gogokhia, L.; Bell, R.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Morrison, L.; et al. MHC variation sculpts individualized microbial communities that control susceptibility to enteric infection. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roland, M.M.; Mohammed, A.D.; Kubinak, J.L. How MHCII signaling promotes benign host-microbiota interactions. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, R.; Schmid, D.W.; Wasimuddin; Brändel, S.D.; Rasche, A.; Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C.; Tschapka, M.; Sommer, S. Interaction between MHC diversity and constitution, gut microbiota and Astrovirus infections in a neotropical bat. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 3342–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, B.K.; Wasimuddin; Schwensow, N.; Gillingham, M.A.F.; Ratovonamana, Y.R.; Rakotondranary, S.J.; Corman, V.; Drosten, C.; Ganzhorn, J.U.; Sommer, S. Evidence of MHC class I and II influencing viral and helminth infection via the microbiome in a non-human primate. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, A.T. The Gut Microbiome of Wild Lemurs: A Comparison of Sympatric Lemur catta and Propithecus verreauxi. Folia Primatol. 2015, 86, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Winter, I.I.; Qurkhuli, T.; de Groot, N.; de Vos-Rouweler, A.J.M.; van Hooft, P.; Heitkönig, I.M.A.; Prins, H.H.T.; Bontrop, R.E.; Doxiadis, G.G.M. Determining Mhc-DRB profiles in wild populations of three congeneric true lemur species by noninvasive methods. Immunogenetics 2019, 71, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.M.; Bergey, C.M.; Roos, C.; Higham, J.P. Relationship between genome-wide and MHC class I and II genetic diversity and complementarity in a nonhuman primate. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uren Webster, T.M.; Consuegra, S.; Hitchings, M.; Garcia de Leaniz, C. Interpopulation Variation in the Atlantic Salmon Microbiome Reflects Environmental and Genetic Diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00691-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.E.; Epps, C.W. Host, Microbiome, and Complex Space: Applying Population and Landscape Genetic Approaches to Gut Microbiome Research in Wild Populations. J. Hered. 2022, 113, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qingyong, N.; Xin, H.; Yu, W.; Xiangyun, M. Distribution and Conservation Status of Slow Lorises in Indo-China. In Evolution, Ecology and Conservation of Lorises and Pottos; Nekaris, K.A.I., Burrows, A.M., Eds.; Cambridge Studies in Biological and Evolutionary Anthropology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 326–338. [Google Scholar]
- Thạch, H.M.; Le, M.D.; Vũ, N.B.; Panariello, A.; Sethi, G.; Sterling, E.J.; Blair, M.E. Slow Loris Trade in Vietnam: Exploring Diverse Knowledge and Values. Folia Primatol. 2018, 89, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingyong, N.; Chen, Z.; Diyan, L.; Huailiang, X.; Yongfang, Y.; Mingwang, Z.; Xiaolan, F.; Bo, Z.; Deying, Y.; Meng, X. Effects of Dietary Alteration on the Gut Microbiome and Metabolome of the Rescued Bengal Slow Loris. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 650991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, V.J.; Song, S.J.; Delsuc, F.; Prest, T.L.; Oliverio, A.M.; Korpita, T.M.; Alexiev, A.; Amato, K.R.; Metcalf, J.L.; Kowalewski, M.; et al. The Effects of Captivity on the Mammalian Gut Microbiome. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxiadis, G.G.M.; Otting, N.; Groot, N.G.d.; Groot, N.d.; Rouweler, A.J.M.; Noort, R.; Verschoor, E.J.; Bontjer, I.; Bontrop, R.E. Evolutionary stability of MHC class II haplotypes in diverse rhesus macaque populations. Immunogenetics 2003, 55, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, P.; Huang, K.; Chen, D.; Guo, S.; Qi, X.; He, G.; Pan, R.; Li, B. The influence of positive selection and trans-species evolution on DPB diversity in the golden snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana). Primates 2016, 57, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierini, F.; Nutsua, M.; Böhme, L.; Özer, O.; Bonczarowska, J.; Susat, J.; Franke, A.; Nebel, A.; Krause-Kyora, B.; Lenz, T.L. Targeted analysis of polymorphic loci from low-coverage shotgun sequence data allows accurate genotyping of HLA genes in historical human populations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, L.J.; Ryvar, R.; Gaskell, R.M.; Addie, D.D.; Willoughby, K.; Carter, S.D.; Thomson, W.; Ollier, W.E.R.; Radford, A.D. Sequence analysis of MHC DRB alleles in domestic cats from the United Kingdom. Immunogenetics 2002, 54, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pers, D.; Hansen, A.K. The boom and bust of the aphid’s essential amino acid metabolism across nymphal development. G3-Genes Genomes Genet. 2021, 11, jkab115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabana, F.; Clayton, J.B.; Nekaris, K.A.I.; Wirdateti, W.; Knights, D.; Seedorf, H. Nutrient-based diet modifications impact on the gut microbiome of the Javan slow loris (Nycticebus javanicus). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.W.; Stephens, W.Z.; Mohammed, A.D.; Round, J.L.; Kubinak, J.L. Does MHC heterozygosity influence microbiota form and function? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, J.B.; Vangay, P.; Huang, H.; Ward, T.; Hillmann, B.M.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Travis, D.A.; Long, H.T.; Tuan, B.V.; Minh, V.V.; et al. Captivity humanizes the primate microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10376–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G.; Burton, J. Use of Lactobacillus to prevent infection by pathogenic bacteria. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefer, A.; Seth-Smith, H.; Palma, F.; Schindler, S.; Freschi, L.; Dangel, A.; Berger, A.; D’Aeth, J.; Indra, A.; Fry, N.K.; et al. Phenotypic and genomic analysis of a large-scale Corynebacterium diphtheriae outbreak among migrant populations in Europe. medRxiv 2023. medRxiv:2023.11.10.23297228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
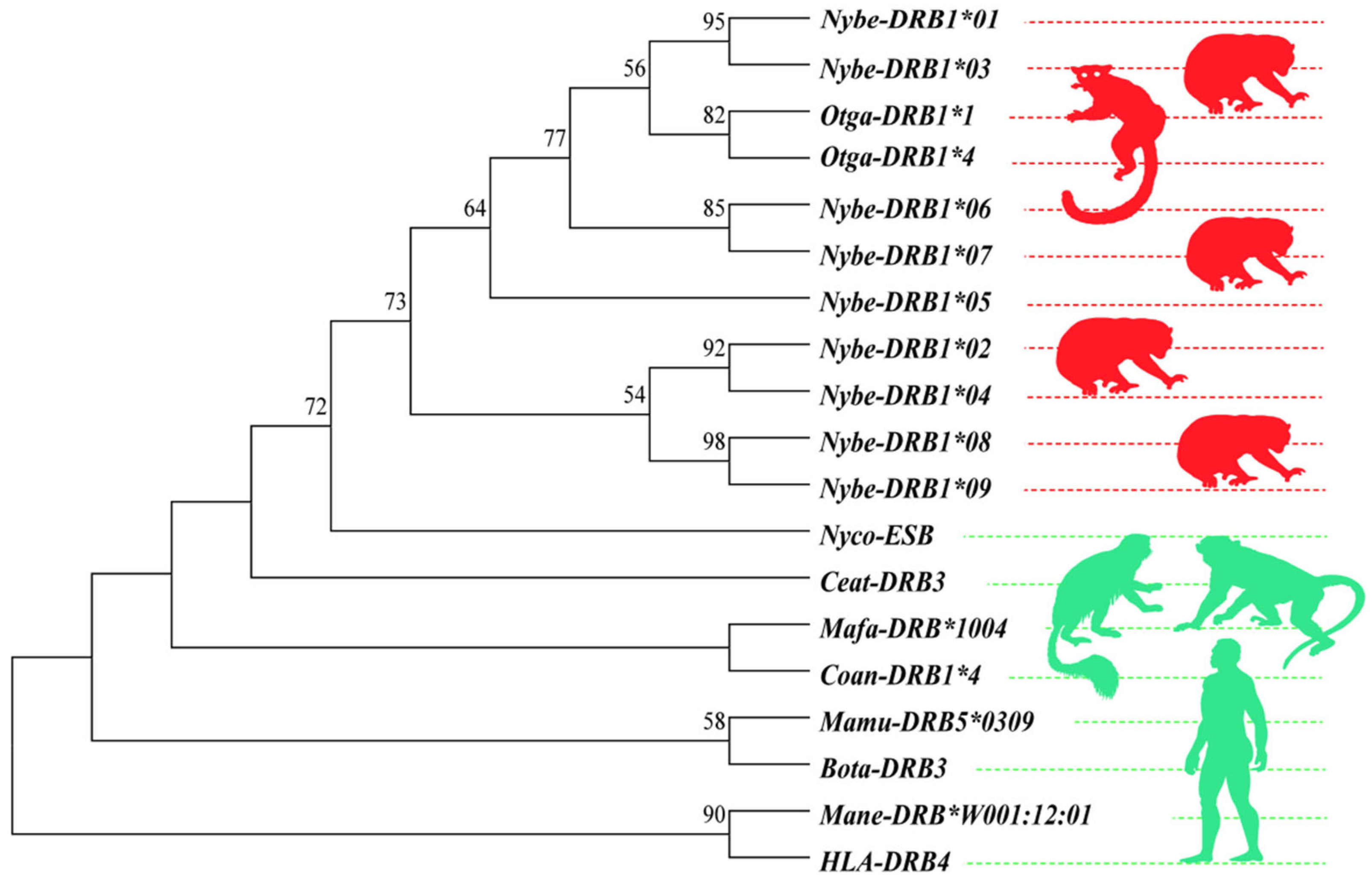
| Closely Related Species | Gene Symbol | Genebank Number |
|---|---|---|
| Nycticebus coucang | Nyco-ESB | XM053603395 |
| Otolemur garnettii | Otga-DRB1*1 | XM012804740 |
| Otolemur garnettii | Otga-DRB1*4 | XM003789065 |
| Macaca mulatta | Mamu-DRB5*0309 | EU934778 |
| Bos taurus | Bota-DRB3 | BT029914 |
| Macaca nemestrina | Mane-DRB*W001:12:01 | LN998245 |
| Macaca fascicularis | Mafa-DRB*1004 | KR632829 |
| Colobus angolensis | Coan-DRB1*4 | XR_001002085.1 |
| Cerocebus atys | Ceat-DRB3 | XM012070072 |
| Homo sapiens | HLA-DRB4 | MW60513 |
| Totality | I | II | III | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 46 | 23 | 15 | 8 |
| A | 9 | 8 | 6 | 9 |
| AE | 5.71 | 5.48 | 3.98 | 7.41 |
| AR | 9 | 8 | 6 | 9 |
| SNPs | 91 | 39 | 10 | 42 |
| PIS | 84 | 42 | 25 | 22 |
| PIC | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.87 |
| HE | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.3 | 0.31 |
| Tajima’s D | −0.21 | |||
| Pi | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.22 |
| Fst | −0.02 | |||
| Over mean distance | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.31 ± 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, R.; Zhang, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Yao, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Ni, Q.; et al. The Role of MHC-II Diversity over Enclosure Design in Gut Microbiota Structuring of Captive Bengal Slow Lorises. Biology 2025, 14, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081094
Jiang R, Zhang X, Xie L, Zhang Y, Zeng C, Yao Y, Xu H, Yang C, Wang X, Ni Q, et al. The Role of MHC-II Diversity over Enclosure Design in Gut Microbiota Structuring of Captive Bengal Slow Lorises. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081094
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Rong, Xiaojia Zhang, Lei Xie, Yan Zhang, Changjun Zeng, Yongfang Yao, Huailiang Xu, Caoyang Yang, Xiao Wang, Qingyong Ni, and et al. 2025. "The Role of MHC-II Diversity over Enclosure Design in Gut Microbiota Structuring of Captive Bengal Slow Lorises" Biology 14, no. 8: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081094
APA StyleJiang, R., Zhang, X., Xie, L., Zhang, Y., Zeng, C., Yao, Y., Xu, H., Yang, C., Wang, X., Ni, Q., Xie, M., & Li, C. (2025). The Role of MHC-II Diversity over Enclosure Design in Gut Microbiota Structuring of Captive Bengal Slow Lorises. Biology, 14(8), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081094





