Taurine Supplementation Enhances the Resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei Postlarvae to Low-Salinity Stress
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Histological Sample Preparation
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.5. NKA Enzyme Activity Analysis
2.6. RNA Extraction and Transcriptomic Sequencing
2.7. Confirmation of the Illumina Sequencing Profiles by Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Taurine Enhances Survival and Growth of Litopenaeus vannamei Postlarvae Under Low-Salinity Stress
3.2. Taurine Protected the Histological Structure of L. vannamei Postlarvae Under Low-Salinity Stress
3.3. Taurine Alleviated the Overactivation of Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA) in Litopenaeus vannamei Postlarvae Under Low-Salinity Stress
3.4. Transcriptomic Sequencing Suggested the Protective Mechanism of Taurine in Shrimp Postlarvae Under Low-Salinity Stress
3.5. Validation of DGE by QPCR
4. Discussion
4.1. Taurine Significantly Improves Postlarval Survival and Repairs Tissue Damage Under Low-Salinity Stress
4.2. Taurine Maintains Ionic Homeostasis in Low-Salinity Environments Through NKA Regulation
4.3. Transcriptomics Reveals Taurine Enhances Osmoregulatory Adaptation via Wnt Signaling Pathway
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathan Muthu, C.M.; Vickram, A.S.; Bhavani Sowndharya, B.; Saravanan, A.; Kamalesh, R.; Dinakarkumar, Y. A comprehensive review on the utilization of probiotics in aquaculture towards sustainable shrimp farming. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 147, 109459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Sarker, A.; Choudhury, A.; Ahmed, N.; Shafi, A.A.; Niloy, N.T.; Hossain, M.S.; Ali, M.S.; Chowdhury, A.; Ferdaus, M.H. ShrimpDiseaseBD: An image dataset for detecting shrimp diseases in the aquaculture sector of Bangladesh. Data Brief. 2025, 60, 111553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Elias, N.; Hassan, M.; Mocktar, N.; Harun, N. Integrated overview on status, diagnosis and disease management of Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) in shrimp aquaculture through metallic nanoparticles (MNPs) application—A review. Aquaculture 2025, 595, 741649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, O.; Schwarz, M.; Senten, J.; Wasielesky, W.; Urick, S.; Carvalho, A.; McAlhaney, E.; Clarington, J.; Krummenauer, D. The super-intensive culture of Penaeus vannamei in low salinity water: A comparative study among recirculating aquaculture system, biofloc, and synbiotic systems. Aquaculture 2025, 596, 741774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havird, J.C.; Santos, S.R.; Henry, R.P. Osmoregulation in the Hawaiian anchialine shrimp Halocaridina rubra (Crustacea: Atyidae): Expression of ion transporters, mitochondria-rich cell proliferation and hemolymph osmolality during salinity transfers. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, R.P.; Lucu, C.; Onken, H.; Weihrauch, D. Multiple functions of the crustacean gill: Osmotic/ionic regulation, acid-base balance, ammonia excretion, and bioaccumulation of toxic metals. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffard-Mena, I.; Ponce-Rivas, E.; Sigala-Andrade, H.M.; Uranga-Solís, C.; Re, A.D.; Díaz, F.; Camacho-Jiménez, L. Evaluation of the osmoregulatory capacity and three stress biomarkers in white shrimp Penaeus vannamei exposed to different temperature and salinity conditions: Na+/K+ ATPase, Heat Shock Proteins (HSP), and Crustacean Hyperglycemic Hormones (CHHs). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 271, 110942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Xiong, S.; Wu, Z.; Ding, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhu, M.; Lee, W.T.; Nie, X.; Bian, J.S. Anti-Na+/K+-ATPase immunotherapy ameliorates α-synuclein pathology through activation of Na+/K+-ATPase α1-dependent autophagy. Sci Adv. 2021, 7, eabc5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucu, C.; Towle, D.W. Na(+)+K(+)-ATPase in gills of aquatic crustacea. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2003, 135, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, A.D.; Harke, S.N.; Panche, A. Biological mechanism of osmoregulatory stress in penaeid shrimp, Penaeus indicus. J. Proteom. Bioinform 2022, 15, 1000600. [Google Scholar]
- Venkitaraman, P.R.; Jayalakshmy, K.V.; Abhilash, K.R. Effect of eyestalk extirpation on haemolymph ionic concentration of Metapenaeus monoceros. J. Exp. Biol. Agric. Sci. 2013, 1, 318–326. [Google Scholar]
- Diwan, A.D.; Laxminarayana, A. Osmoregulatory ability of Penaeus indicus H Milne Edwards in relation to varying salinities. J. Anim. Sci. 1989, 98, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- van der Bosch de Aguilar, P. Neurosecretion and hydroelectrolytic regulation in Artemia salina (author’s transl). Experientia 1976, 32, 228–229. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, H.; Yoshikawa, N.; Sarower, M.G.; Okada, S. Physiological function and metabolism of free D-alanine in aquatic animals. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria, S.C.; Augusto, A.S.; McNamara, J.C. Intra- and extracellular osmotic regulation in the hololimnetic Caridea and Anomura: A phylogenetic perspective on the conquest of fresh water by the decapod Crustacea. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2011, 181, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ni, J.; Niu, D.; Zheng, G.; Li, Y. Physiological response of the razor clam Sinonovacula constricta exposed to hyposalinity stress. Aquac. Fish. 2024, 9, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salze, G.P.; Davis, D.A. Taurine: A critical nutrient for future fish feeds. Aquaculture 2015, 437, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kim, E.; Ho, W.K.; Earm, Y.E. Blockade of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel by taurine in rabbit ventricular myocytes. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1996, 28, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.R.; Liu, Y.J.; Tian, L.X.; Gan, L.; Yang, H.; Liang, G.; He, J. The effect of dietary taurine supplementation on growth performance, feed utilization and taurine contents in tissues of juvenile white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei, Boone, 1931) fed with low-fishmeal diets. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, M.; Zheng, X. Effect of dietary taurine supplementation on the growth, body composition, digestive enzyme activity and anti-stress ability of Litopenaeus vannamei in freshwater culture. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2017, 26, 706–715. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, H.; Li, Y.; Song, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, P.; Sun, Z.; Mai, K.; Tan, B.; Ye, C. Effect of taurine on growth and immune response of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) cultured at different temperatures. Aquaculture 2025, 594, 741393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, F.; Dong, S.; Lu, Y. De novo assembly and transcriptome analysis of osmoregulation in Litopenaeus vannamei under three cultivated conditions with different salinities. Gene 2016, 578, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, M.; Moshtaghi, A.; Mather, P.B.; Hurwood, D.A. Osmoregulation in decapod crustaceans: Physiological and genomic perspectives. Hydrobiologia 2018, 825, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, A.D.; Díaz, F.; Ponce-Rivas, E.; Giffard, I.; Munoz-Marquez, M.E.; Sigala-Andrade, H.M. Combined effect of temperature and salinity on the thermotolerance and osmotic pressure of juvenile white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone). J. Therm. Biol. 2012, 376, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.Q.; Luan, Z.H.; Jin, C.X. Effects of Na+/K+ and Mg2+/Ca2+ ratios in saline groundwaters on Na+–K+-ATPase activity, survival and growth of Marsupenaeus japonicus postlarvae. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.J.; Neill, W.H.; Lawrence, A.L.; Gatlin, D.M. Effect of salinity and body weight on ecophysiological performance of the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 380, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong-Robles, J.; Charmantier, G.; Boulo, V.; Lizárraga-Valdéz, J.; Enríquez-Paredes, L.M.; Giffard-Mena, I. Osmoregulation pattern and salinity tolerance of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) during post-embryonic development. Aquaculture 2014, 422–423, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Pan, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, Q. Transcriptomic response to low salinity stress in gills of the Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Genomics 2015, 24, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Chen, W.; Peng, K.; Huang, M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; et al. Rapid adaptive and acute stimulatory responses to low salinity stress in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei): Insights from integrative transcriptomic and proteomic analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 48, 101149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancey, P.H. Organic osmolytes as compatible, metabolic and counteracting cytoprotectants in high osmolarity and other stresses. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, K.; Toyohara, H.; Kinoshita, M.; Sakaguchi, M. Ubiquitous increase in taurine transporter mRNA in tissues of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus during high-salinity adaptation. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 23, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, T.; Feng, W.; He, J.; Han, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C. Evaluation of the dietary taurine requirement for early juvenile mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Aquaculture 2024, 586, 740754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velselvi, R.; Dasgupta, S.; Varghese, T.; Sahu, N.P.; Tripathi, G.; Panmei, H.; Singha, K.P.; Krishna, G. Taurine and/or inorganic potassium as dietary osmolyte counter the stress and enhance the growth of GIFT reared in ion imbalanced low saline water. Food Chem 2021, 4, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvasagam, T.; Felix, N.; Nazir, M.I.; Ranjan, A.; Prabu, E. Enhanced cholesterol utilization and impact on growth through taurine supplementation in high plant-based diets of Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei in biofloc system. Anim. Feed. Sci. Tech. 2024, 316, 116057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuller-Levis, G.B.; Park, E. Taurine and its chloramine: Modulators of immunity. Neurochem. Res. 2004, 29, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K.; Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Yan, X.; Huo, Z.; Qin, Y. Taurine promotes the rapid recovery of clams (Ruditapes philippinarum) after aerial exposure through the glutathione pathway and by inhibiting apoptosis. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 42, 102845. [Google Scholar]
- Apell, H.J.; Hitzler, T.; Schreiber, G. Modulation of the Na,K-ATPase by Magnesium Ions. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, D.L.; Verzi, M.P.; Burgents, J.E.; Tanner, C.A.; Glomski, K.; Lee, J.J.; Towle, D.W. Expression profiles of Na+,K+-ATPase during acute and chronic hypo-osmotic stress in the blue crab Callinectes sapidus. Biol. Bull. 2006, 211, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Ren, C.; Chen, C.; Fan, S.; Xia, J.J.; Lin, H.; Hu, C. The expression of Na, K-ATPase in Litopenaeus vannamei under salinity stress. Mar. Biol. Res. 2011, 7, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Dong, J.; Ren, C.; Zhang, L.; Dan, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C. Cloning and differential expression of Na, K-ATPase in Penaeus vannamei. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, M.A.; Racotta, I.S.; Civera, R.; Ibarra, L.; Hernández-Rodríguez, M.; Palacios, E. Effect of hypo—and hypersaline conditions on osmolality and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in juvenile shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) fed low—and high-HUFA diets. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leil, T.A.; Chen, Z.W.; Chang, C.S.; Olsen, R.W. GABAA receptor-associated protein traffics GABAA receptors to the plasma membrane in neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 11429–11438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geahchan, S.; Baharlouei, P.; Rahman, A. Marine Collagen: A Promising Biomaterial for Wound Healing, Skin Anti-Aging, and Bone Regeneration. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, G.; Yang, L.; Du, H.; Hou, L.; Ge, L.; Sylia, A.; Muhmood, A.; Chen, X.; Han, B.; Huang, K. Combination of zinc and selenium alleviates ochratoxin A-induced fibrosis via blocking ROS-dependent autophagy in HK-2 cells. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 69, 126881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahearn, G.A.; Duerr, J.M.; Zhuang, Z.; Brown, R.J.; Aslamkhan, A.; Killebrew, D.A. Ion transport processes of crustacean epithelial cells. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 1999, 72, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Lu, K.; Lai, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Li, N.; Peng, Y.; Gong, H. Effects of dietary 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 on growth, calcium-phosphorus metabolism, lipid metabolism and immunity of Litopenaeus vannamei at low salinity. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 35, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldenpfennig, C.; Teixeiro, E.; Daniels, M. NF-kB’s contribution to B cell fate decisions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1214095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, C.J.; Azuma, J.; Schaffer, S. Mechanism underlying the antioxidant activity of taurine: Prevention of mitochondrial oxidant production. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripps, H.; Shen, W. Review: Taurine: A “very essential” amino acid. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 2673–2686. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Shin, J.Y.; Kwon, O.S.; Jun, S.H.; Kang, N.G. Taurine and Polyphenol Complex Repaired Epidermal Keratinocyte Wounds by Regulating IL8 and TIMP2 Expression. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 8685–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Taurine represses age-associated gut hyperplasia in Drosophila via counteracting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, H.P.; Stapleton, P.P.; Neary, P.; Bouchier-Hayes, D. Immunonutrition: The role of taurine. Nutrition 1998, 14, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Bonfleur, M.L.; Batista, T.M.; Borck, P.C.; Carneiro, E.M. Regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism by the pancreatic and extra-pancreatic actions of taurine. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Piao, F. Taurine Ameliorates Apoptosis via AKT Pathway in the Kidney of Diabetic Rats. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1370, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, G.; Sun, L.; Wu, X.; Lin, Y.; Niu, X.; Kong, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, G. Brain transcriptome analysis of snakehead (Channa argus) under starvation and satiation conditions and identification of differentially expressed gene response to feeding regulation. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 40, 102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suehs, B.; Gatlin III, D.M. Evaluating the dietary taurine requirement of hybrid striped bass (Morone Chrysops × M. Saxatilis). Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, M.; Dong, Z.; Li, Y.; Niu, D. Function of taurine and its synthesis-related genes in hypertonic regulation of Sinonovacula constricta. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2024, 287, 111536. [Google Scholar]
- Mezzomo, N.J.; Fontana, B.D.; Müller, T.E.; Duarte, T.; Quadros, V.A.; Canzian, J.; Pompermaier, A.; Soares, S.M.; Koakoski, G.; Loro, V.L.; et al. Taurine modulates the stress response in zebrafish. Horm. Behav. 2019, 109, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Hu, Z.; Hu, C.; Bu, Q.; Yan, G.; Deng, P.; Lv, L.; Wu, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. Taurine protects methamphetamine-induced developmental angiogenesis defect through antioxidant mechanism. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 260, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

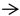 indicates intermuscular spaces;
indicates intermuscular spaces;  indicates the demarcation between visceral organs. Scale bar: 500 μm.
indicates the demarcation between visceral organs. Scale bar: 500 μm.
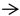 indicates intermuscular spaces;
indicates intermuscular spaces;  indicates the demarcation between visceral organs. Scale bar: 500 μm.
indicates the demarcation between visceral organs. Scale bar: 500 μm.





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Du, X.; Zou, J.; Wang, M.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q. Taurine Supplementation Enhances the Resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei Postlarvae to Low-Salinity Stress. Biology 2025, 14, 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081082
Wang H, Du X, Zou J, Wang M, Lei Y, Zhang B, Zhao Y, Jiang L, Chen X, Wang Q. Taurine Supplementation Enhances the Resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei Postlarvae to Low-Salinity Stress. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081082
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huaichi, Xinyue Du, Jiahong Zou, Mengya Wang, Yan Lei, Bin Zhang, Yongzhen Zhao, Linyuan Jiang, Xiaohan Chen, and Qingchao Wang. 2025. "Taurine Supplementation Enhances the Resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei Postlarvae to Low-Salinity Stress" Biology 14, no. 8: 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081082
APA StyleWang, H., Du, X., Zou, J., Wang, M., Lei, Y., Zhang, B., Zhao, Y., Jiang, L., Chen, X., & Wang, Q. (2025). Taurine Supplementation Enhances the Resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei Postlarvae to Low-Salinity Stress. Biology, 14(8), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081082





