Tensins in Cancer: Integration of Their Domain Functions, Context-Dependent Regulation and Biomarker Potential
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Domains of Tensins and Their Functional Implications
2.1. ABD
2.2. N-Terminal FAB
2.2.1. PTP Domain
2.2.2. C2 Domain
2.3. C-Terminal FAB
2.3.1. SH2 Domain
2.3.2. PTB Domain
2.4. Structural and Functional Divergence
3. Regulatory Roles of Tensins in Cellular and Physiological Processes
3.1. Cell Dhesion
3.2. Cell Migration and Invasion
3.3. Cell Proliferation
3.4. Mechanotransduction
4. Regulatory Roles of Tensins in Signaling Pathway Crosstalk
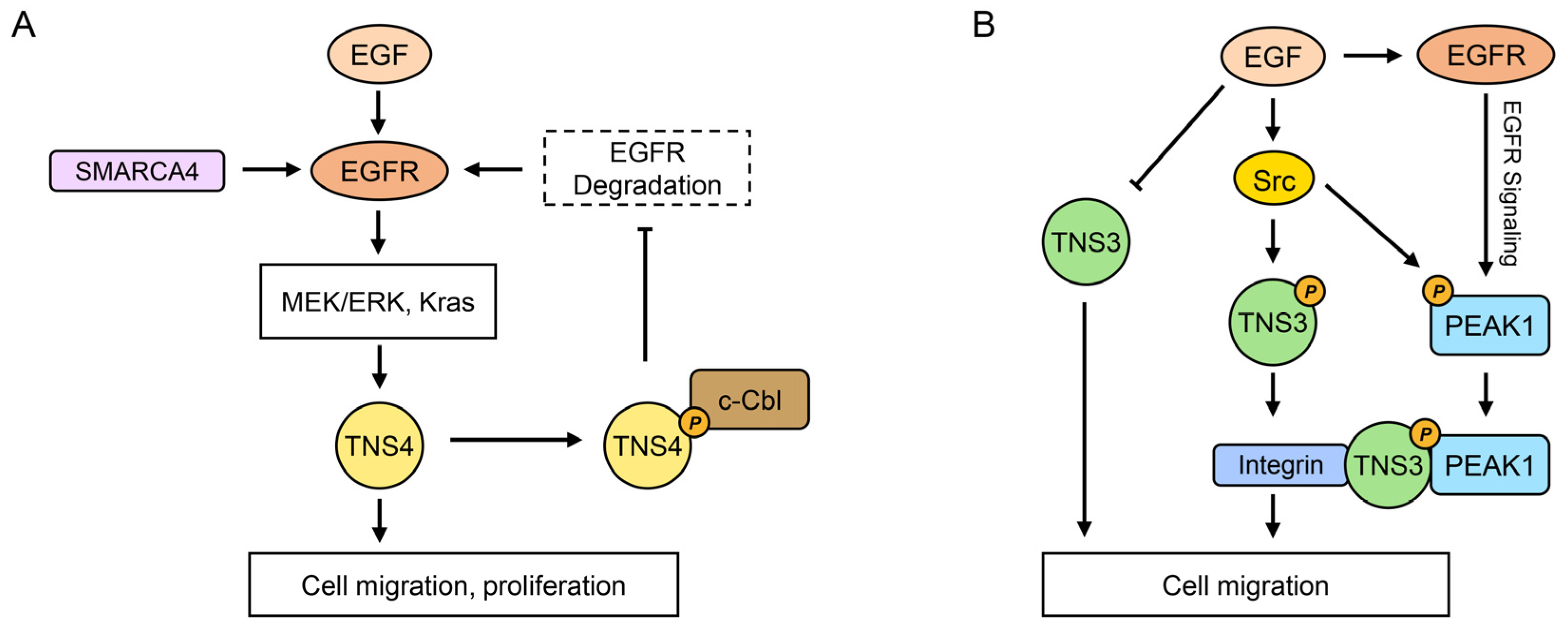
4.1. EGFR Signaling Pathways
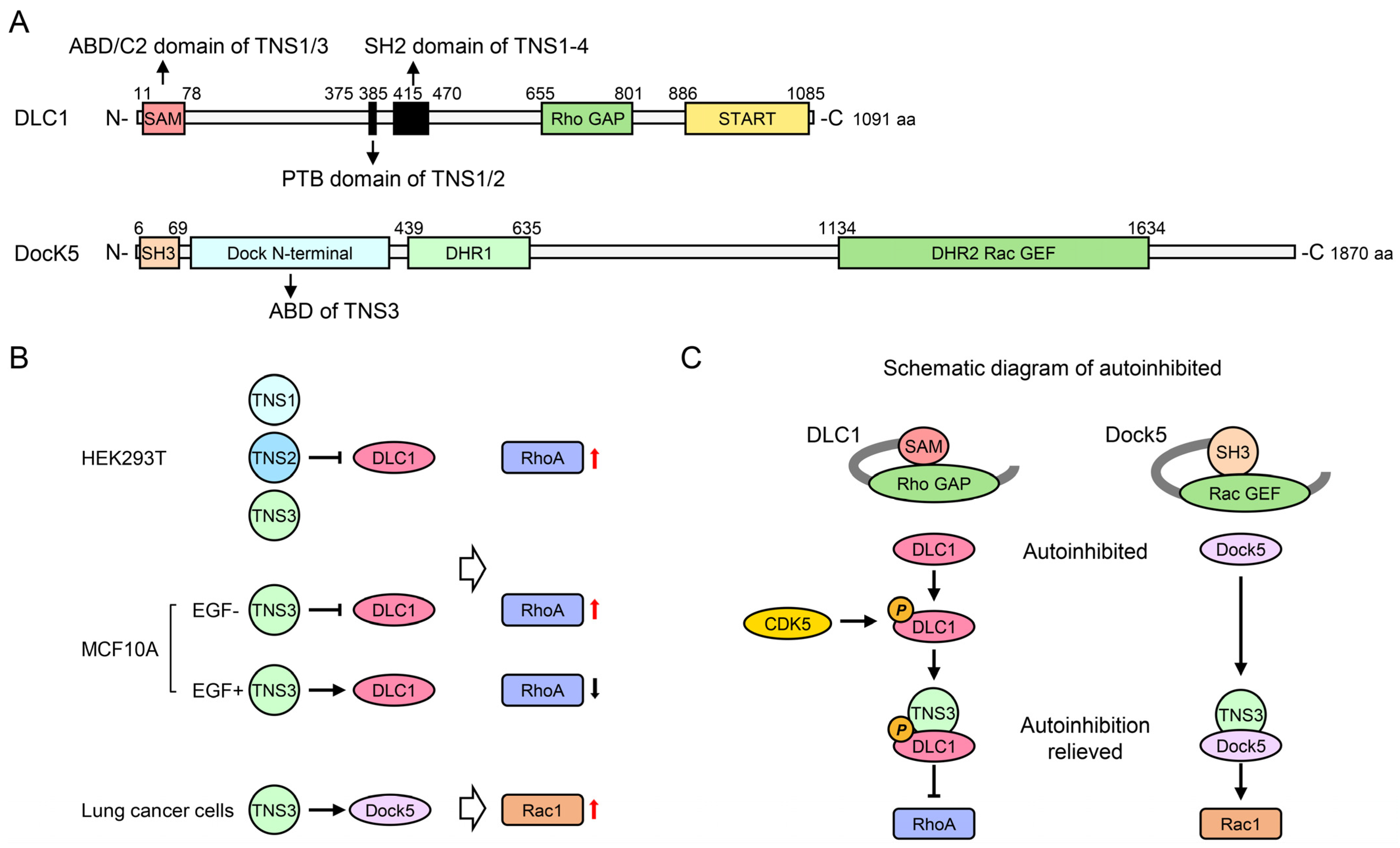
4.2. Rho GTPase Signaling Pathways
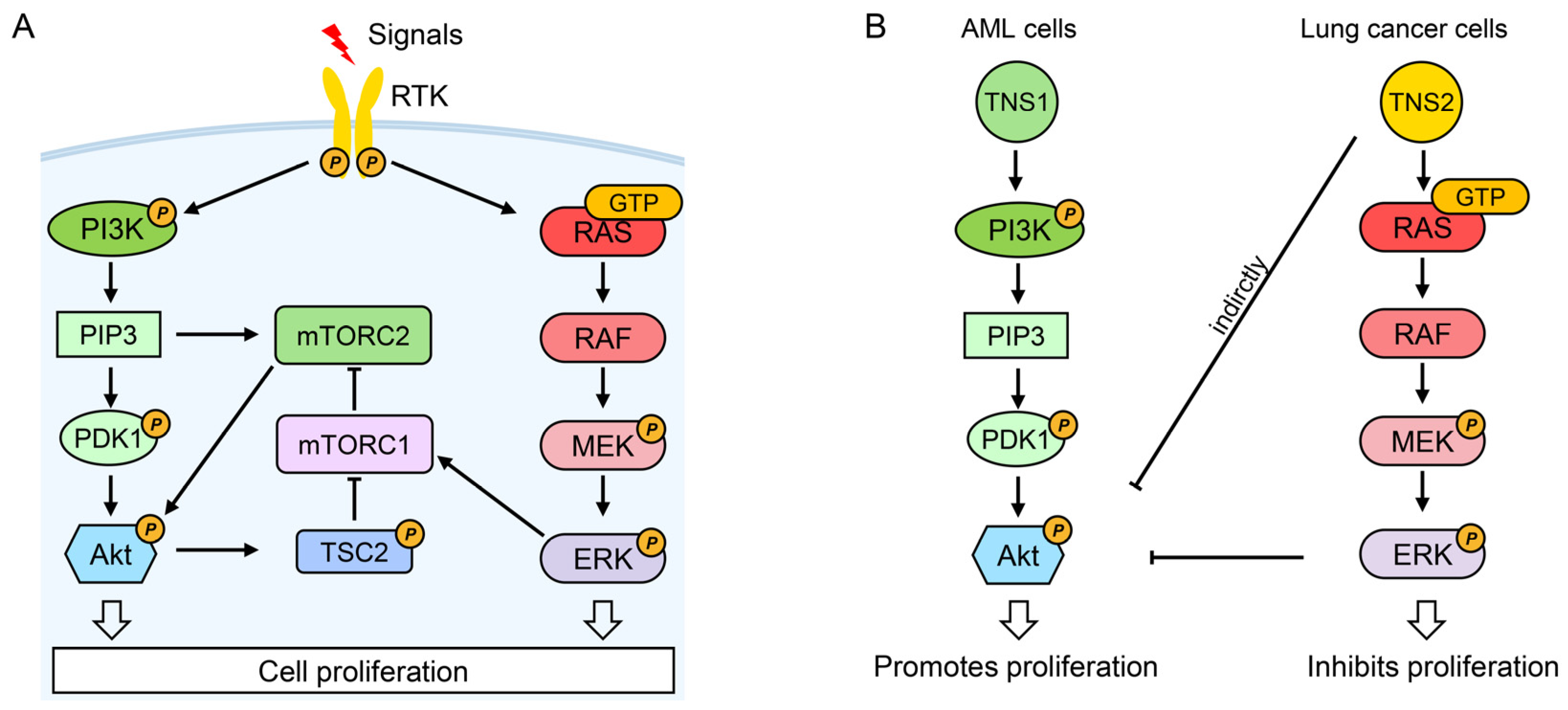
4.3. PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
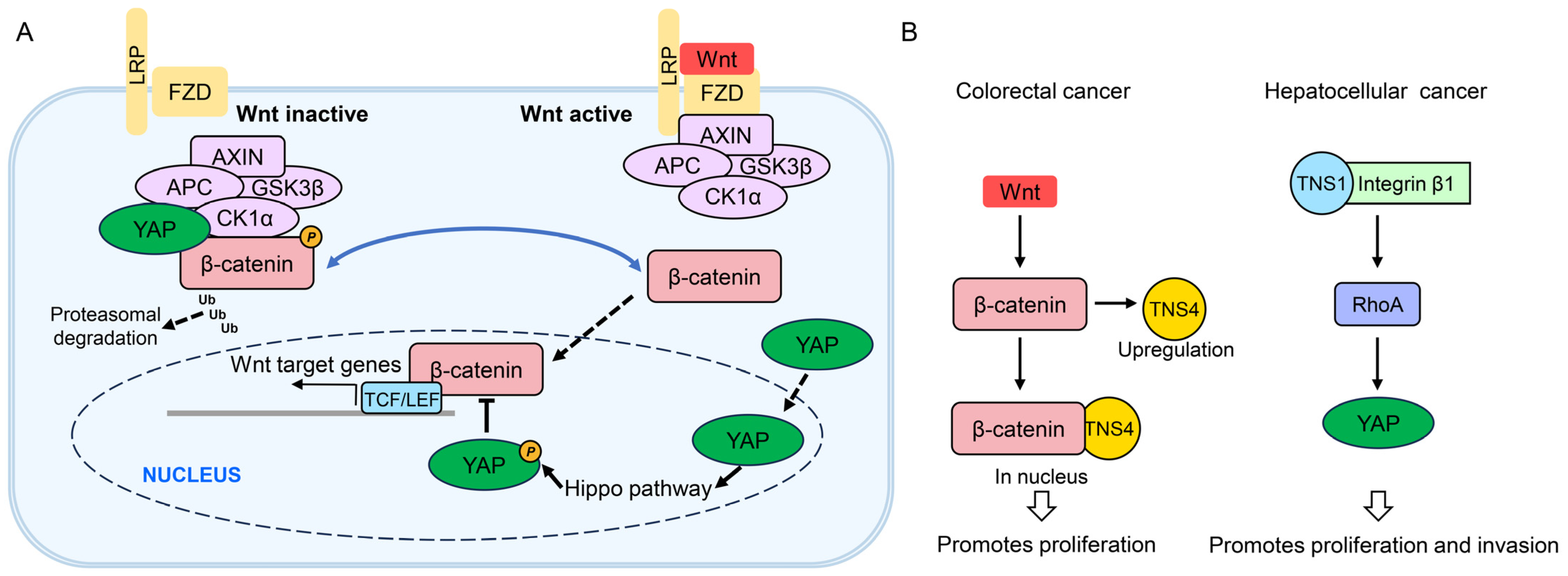
4.4. Wnt and YAP Signaling Pathways
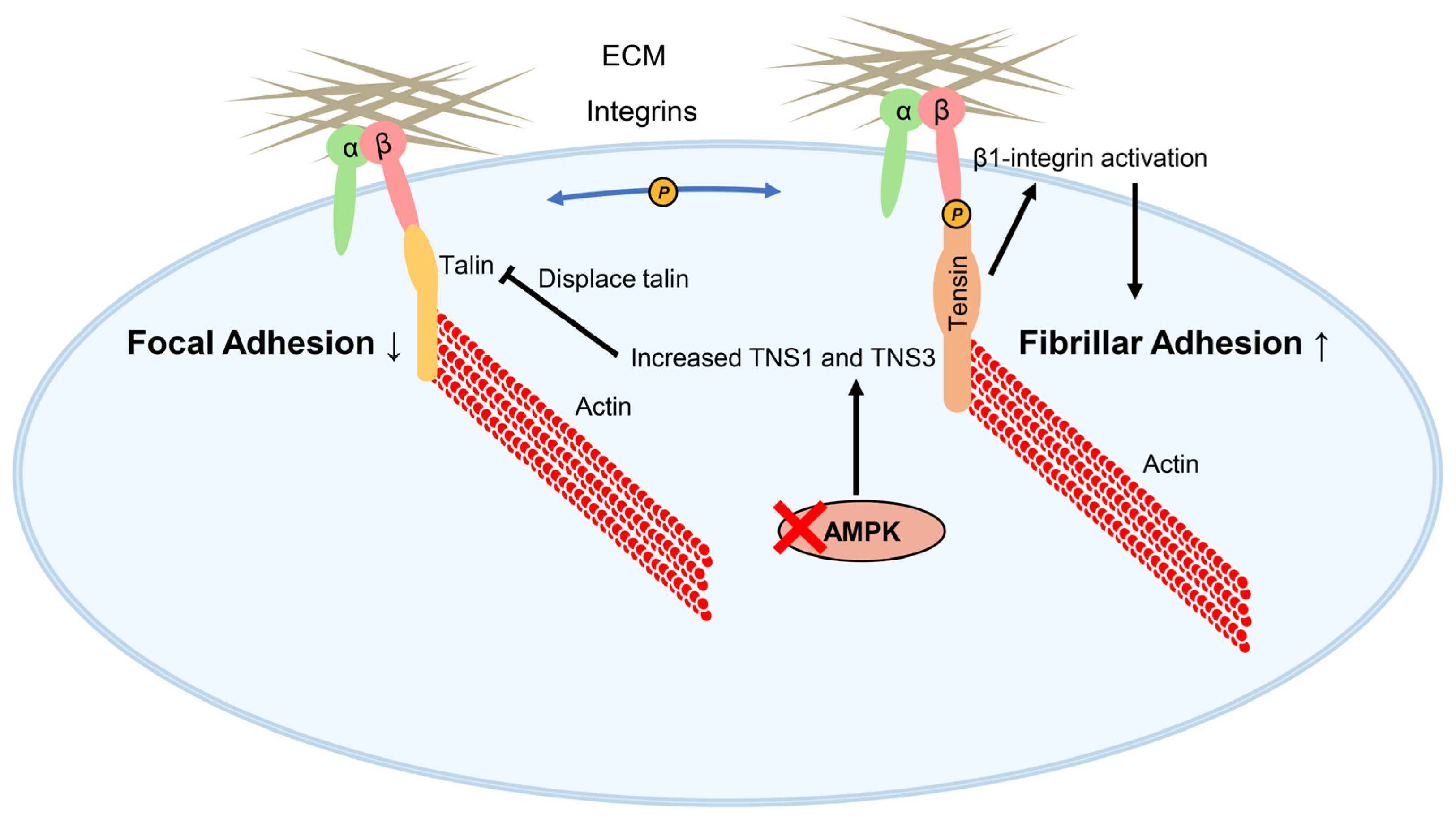
4.5. Tensins, Fibrillar Adhesion Formation, and AMPK
5. Regulatory Roles and Clinical Relevance of Tensins in Cancer
5.1. TNS1: Anti-Tumorigenic Roles in Prostate Cancer with Context-Dependent Oncogenicity
5.1.1. Anti-Tumorigenic Roles in Prostate Cancer
5.1.2. Oncogenic Roles in Colorectal, Liver, Gastric Cancers, and Leukemia
5.1.3. Dual Roles in Bladder, Lung, and Breast Cancers
5.2. TNS2: Tumor-Suppressive Dominance with Isoform-Specific Oncogenic Exceptions
5.3. TNS3: Context-Specific Tumor Suppression Versus ESCC Oncogenicity
5.3.1. Anti-Tumorigenic Roles in Lung, Glioblastoma, and Kidney Cancers
5.3.2. Oncogenic Role in Esophageal Cancer
5.3.3. Dual Roles in Thyroid, Gastric, and Breast Cancers
| Cancer | Effects | Clinical Correlation (Sample) | Molecular Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renal cell carcinoma | ↓ | ↓mRNA/protein = ↑tumor grade (223 tumors vs. 48 normal samples) [52] | Unclear |
| Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | ↑ | ↑protein = ↓OS (153 paired samples) [73]. | Unclear |
| Thyroid cancer | ↓ | ↓mRNA in most tumors (28 normal samples vs. 45 tumors) [54] | Unclear |
| ↓ | ↓mRNA in non-functioning thyroid follicular adenomas (18 normal samples vs. 50 tumors) [55] | ||
| Papillary thyroid carcinoma | ↑ | ↑mRNA = lymph node metastasis, ↓OS (GSE29265, GSE33630, GSE3467, GSE3678, GSE58545) [127] | |
| Breast cancer | ↓ | ↓protein in poorly differentiated tumors [128] | Activating DLC1 in MCF10A cells [16] |
| ↑ | Inhibiting DLC1 in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells [58,129] |
5.4. TNS4: Pan-Cancer Oncogenic Driver with Prostate-Specific Tumor Suppression
5.4.1. Predominant Oncogenic Roles Across Various Cancers
| Cancer | Effects | Clinical Correlation (Sample) | Molecular Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric cancer | ↑ | ↑mRNA/protein = ↑metastasis, ↓OS (114 paired samples) [131] | unclear |
| ↑ | ↑mRNA = ↓OS (134 patients) [132] | ||
| ↑ | ↑mRNA/protein = ↓survival (80 paired samples) [133] | ||
| ↑ | ↑mRNA/protein = ↑lymph node metastasis (7 paired samples) [135] | ||
| ↓ | ↓protein = ↓differentiation (89 tumors vs. 20 normal samples) [136] | ||
| Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | ↑ | ↑mRNA/protein = ↑metastasis, ↓OS (TCGA data and 134 paired samples) [89] | unclear |
| Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | ↑ | ↑mRNA/protein = ↓OS (patients from Stomatological Hospital at Nanjing Medical University, TCGA, GSE37991, GSE58911, GSE83519, GSE25099, GSE55550 and GSE30784) [137] | unclear |
| Colorectal cancer | ↑ | ↑mRNA/protein = later stage (UALCAN and GEPIA databases + 92 pairs of CRC tissues) [138] | TGF-β1 upregulating TNS4 [140] |
| TNS4 stabilizing Src post-transcriptionally [65] | |||
| promoting β-catenin/c-Myc-mediated aerobic glycolysis [138] | |||
| SMARCA4 enhancing EGFR signaling and TNS4 expression [84] | |||
| Non-small cell lung cancer | ↑ | ↑protein = ↑metastasis, ↓OS/DFS (20 LUAD tumors vs. 14 controls) [141] | EGF/STAT3 upregulating TNS4 [143] |
| ↑ | ↑mRNA = ↓OS/PFS (TCGA-LUAD data) [142] | TNS4 activating TGF-β1, inducing EMT [67] | |
| Gallbladder cancer | ↑ | Not available | GPRC5A/JAK2-STAT3/TNS4 axis [144] |
| Prostate cancer | ↓ | ↓mRNA in tumors (4 pairs + 3 tumors) [11] | TNS4 inhibiting EGFR [90] |
| Breast cancer | ↑ | ↑protein = ↑tumor size, grade, metastasis (1409 cases) [145] | STAT3 upregulating TNS4 [146] |
| ↓ | ↓mRNA on tumors (TCGA-BRCA data) [147] | TNS4 targeting VEGFA through c-Cbl-mediated β-catenin downregulation [147] |
5.4.2. Anti-Tumorigenic Role in Prostate Cancer
5.4.3. Dual Roles in Breast Cancer
5.5. Somatic Mutations in Tensins: Limited Prevalence and Uncertain Significance
6. Biomarker and Therapeutic Target Potential of Tensins in Cancer
6.1. Diagnostic Biomarker Potential
6.2. Prognostic Biomarker Potential
6.2.1. TNS1: Multi-Cancer Prognostic Utility via Modeling Strategies
6.2.2. TNS3: Metastasis-Specific Biomarker in PTC
6.2.3. TNS4: Core Component in Multi-Gene Signatures
6.3. Therapeutic Target Potential
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABD | Actin-binding domain |
| Akt | Protein kinase B |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| APC | Adenomatous polyposis coli |
| AXIN | Axis inhibition protein 1 |
| BCa | Bladder cancer |
| BRCA | Breast cancer |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblast |
| CK1α | Casein kinase 1 alpha |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| ERK | Extracellular regulated protein kinase |
| ESCC | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FAB | Focal adhesion binding |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| FZD | Frizzled |
| GAP | GTPase-activating protein |
| GC | Gastric cancer |
| GEF | Guanine nucleotide exchange factor |
| GIST | Gastrointestinal stromal tumor |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HEK | Human embryonic kidney |
| HFF | Human foreskin fibroblast |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LEF | Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor |
| LNM | Lymph node metastasis |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor |
| MIBC | Muscle-invasive bladder cancer |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| PFS | Progression free survival |
| PM | Peritoneal metastasis |
| PTB | Phosphotyrosine-binding |
| PTC | Papillary thyroid carcinoma |
| PTP | Protein tyrosine phosphatase |
| RCC | Renal cell carcinoma |
| RFS | Relapse-free survival |
| RhoA | Ras homolog family member A |
| RTK | Receptor tyrosine kinase |
| SAM | Sterile alpha motif |
| SH2 | Src homology 2 |
| TCF | T cell factor |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| UALCAN | The University of ALabama at Birmingham CANcer data analysis Portal |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
References
- Kiri, S.; Ryba, T. Cancer, metastasis, and the epigenome. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Y.G.; Manavathi, B. Focal adhesion dynamics in cellular function and disease. Cell. Signal. 2021, 85, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, E.; Mayor, R. Collective cell migration in development. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 212, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Riahi, R.; Torab, P.; Zhang, D.D.; Wong, P.K. Collective Cell Migration in 3D Epithelial Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worbs, T.; Hammerschmidt, S.I.; Förster, R. Dendritic cell migration in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillekås, H.; Rogers, M.S.; Straume, O. Are 90% of deaths from cancer caused by metastases? Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 5574–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Lu, M.L.; Lo, S.H.; Lin, S.; Butler, J.A.; Druker, B.J.; Roberts, T.M.; An, Q.; Chen, L.B. Presence of an SH2 domain in the actin-binding protein tensin. Science 1991, 252, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Duncan, I.C.; Bozorgchami, H.; Lo, S.H. Tensin1 and a previously undocumented family member, tensin2, positively regulate cell migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liao, Y.C.; Lo, S.H. Epidermal growth factor modulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a novel tensin family member, tensin3. Mol. Cancer Res. 2004, 2, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.H.; Lo, T.B. Cten, a COOH-terminal tensin-like protein with prostate restricted expression, is down-regulated in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4217–4221. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.C.; Lo, S.H. Tensins—Emerging insights into their domain functions, biological roles and disease relevance. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs254029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.Y.; Shih, Y.P.; Sun, P.; Hsieh, W.J.; Lin, W.C.; Lo, S.H. Down-regulation of tensin2 enhances tumorigenicity and is associated with a variety of cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38143–38153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.H.; Janmey, P.A.; Hartwig, J.H.; Chen, L.B. Interactions of tensin with actin and identification of its three distinct actin-binding domains. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 125, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.P.; Sun, P.; Wang, A.; Lo, S.H. Tensin1 positively regulates RhoA activity through its interaction with DLC1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015, 1853, 3258–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Voss, C.; Zhao, B.; Kaneko, T.; Li, S.S. Differential regulation of the activity of deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC1) by tensins controls cell migration and transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touaitahuata, H.; Morel, A.; Urbach, S.; Mateos-Langerak, J.; de Rossi, S.; Blangy, A. Tensin 3 is a new partner of Dock5 that controls osteoclast podosome organization and activity. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3449–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Pulido, R. The extended human PTPome: A growing tyrosine phosphatase family. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1404–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; Lee, M.N.; Yang, Y.R.; Jeong, H.; Ghim, J.; Noh, J.; Kim, J.; Ryu, D.; Park, S.; Song, P.; et al. C1-Ten is a protein tyrosine phosphatase of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1), regulating IRS-1 stability and muscle atrophy. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 1608–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Koh, A.; Lee, J.; Park, D.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, M.N.; Jo, K.J.; Tran, H.N.K.; Kim, E.; Min, B.S.; et al. Inhibition of C1-Ten PTPase activity reduces insulin resistance through IRS-1 and AMPK pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, M.; Kirkbride, J.; Elliott, E.; Lo, S.H.; Brautigan, D.L. Association of the tensin N-terminal protein-tyrosine phosphatase domain with the alpha isoform of protein phosphatase-1 in focal adhesions. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17806–17815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.H.; Daugherty, A.E.; Choi, C.K.; Horwitz, A.F.; Brautigan, D.L. Tensin1 requires protein phosphatase-1alpha in addition to RhoGAP DLC-1 to control cell polarization, migration, and invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 34713–34722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Qin, L.; Cao, X.; Zhong, S.; Voss, C.; Min, W.; Li, S.S.C. DLC1 SAM domain-binding peptides inhibit cancer cell growth and migration by inactivating RhoA. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Sheng, R.; Silkov, A.; Jung, D.J.; Wang, Z.G.; Xin, Y.; Kim, H.; Thiagarajan-Rosenkranz, P.; Song, S.; Yoon, Y.; et al. SH2 Domains Serve as Lipid-Binding Modules for pTyr-Signaling Proteins. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderwood, D.A.; Fujioka, Y.; de Pereda, J.M.; García-Alvarez, B.; Nakamoto, T.; Margolis, B.; McGlade, C.J.; Liddington, R.C.; Ginsberg, M.H. Integrin beta cytoplasmic domain interactions with phosphotyrosine-binding domains: A structural prototype for diversity in integrin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2272–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, M.; Amit, I.; Citri, A.; Shay, T.; Carvalho, S.; Lavi, S.; Milanezi, F.; Lyass, L.; Amariglio, N.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; et al. A reciprocal tensin-3-cten switch mediates EGF-driven mammary cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleverty, C.J.; Lin, D.C.; Liddington, R.C. Structure of the PTB domain of tensin1 and a model for its recruitment to fibrillar adhesions. Protein. Sci. 2007, 16, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizi, S.; Alindri, F.; Karlsson, R.; Dahlbäck, B. Interaction of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase with C1-TEN, a novel C1 domain-containing protein with homology to tensin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 299, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muharram, G.; Sahgal, P.; Korpela, T.; De Franceschi, N.; Kaukonen, R.; Clark, K.; Tulasne, D.; Carpén, O.; Ivaska, J. Tensin-4-dependent MET stabilization is essential for survival and proliferation in carcinoma cells. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Li, G.; Asmussen, H.K.; Asnaghi, L.; Vass, W.C.; Braverman, R.; Yamada, K.M.; Popescu, N.C.; Papageorge, A.G.; Lowy, D.R. Oncogenic inhibition by a deleted in liver cancer gene requires cooperation between tensin binding and Rho-specific GTPase-activating protein activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9012–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Liao, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tu, X. Solution structure of tensin2 SH2 domain and its phosphotyrosine-independent interaction with DLC-1. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Li, G.; Vass, W.C.; Papageorge, A.; Walker, R.C.; Asnaghi, L.; Steinbach, P.J.; Tosato, G.; Hunter, K.; Lowy, D.R. The Tensin-3 protein, including its SH2 domain, is phosphorylated by Src and contributes to tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.C.; Si, L.; deVere White, R.W.; Lo, S.H. The phosphotyrosine-independent interaction of DLC-1 and the SH2 domain of cten regulates focal adhesion localization and growth suppression activity of DLC-1. J. Cell Biol 2007, 176, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yam, J.W.; Ko, F.C.; Chan, C.Y.; Jin, D.Y.; Ng, I.O. Interaction of deleted in liver cancer 1 with tensin2 in caveolae and implications in tumor suppression. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8367–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.K.; Ko, F.C.; Ng, I.O.; Yam, J.W. Deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC1) utilizes a novel binding site for Tensin2 PTB domain interaction and is required for tumor-suppressive function. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, N.T.; Kuwabara, Y.; Conley, C.; Liao, Y.C.; Hong, S.Y.; Chen, M.; Shih, Y.P.; Chen, H.W.; Hsieh, F.; Lo, S.H. Phylogenetic analysis, expression patterns, and transcriptional regulation of human CTEN gene. Gene 2013, 520, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Chen, M.; Pandolfi, P.P. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: New modes and prospects. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynie, D.T. Molecular physiology of the tensin brotherhood of integrin adaptor proteins. Proteins 2014, 82, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Layseca, P.; Icha, J.; Hamidi, H.; Ivaska, J. Integrin trafficking in cells and tissues. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; He, T.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, D.; Shao, Z.; Xiao, G. Roles of focal adhesion proteins in skeleton and diseases. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B. 2023, 13, 998–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Cell adhesion: Integrating cytoskeletal dynamics and cellular tension. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadou, M.; Lilja, J.; Jacquemet, G.; Guzmán, C.; Rafaeva, M.; Alibert, C.; Yan, Y.; Sahgal, P.; Lerche, M.; Manneville, J.B.; et al. AMPK negatively regulates tensin-dependent integrin activity. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Howe, J.D.; Pullar, C.E.; Green, J.A.; Artym, V.V.; Yamada, K.M.; Critchley, D.R. Tensin 2 modulates cell contractility in 3D collagen gels through the RhoGAP DLC1. J. Cell Biochem. 2010, 109, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, W.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Lo, S.H.; Liao, Y.C. ΔNp63α Transcriptionally Regulates the Expression of CTEN That Is Associated with Prostate Cell Adhesion. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Tan, S.H.; Machiyama, H.; Kawauchi, K.; Araki, K.; Hirata, H.; Sawada, Y. Association between tensin 1 and p130Cas at focal adhesions links actin inward flux to cell migration. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Wang, L.; Shang, L.; Yang, S.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Miao, Y. miR-152/TNS1 axis inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression through Akt/mTOR/RhoA pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20201539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Ding, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhan, Q.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-548j functions as a metastasis promoter in human breast cancer by targeting Tensin1. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, B.; Li, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, G.; Sai, J. High miR-31-5p expression promotes colon adenocarcinoma progression by targeting TNS1. Aging 2020, 12, 7480–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Lv, Z.; Yang, C.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. LncRNA MAGI2-AS3 inhibits bladder cancer progression by targeting the miR-31-5p/TNS1 axis. Aging 2020, 12, 25547–25563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Yu, X.; Cao, X.; Jia, B.; Chen, R.; Li, J. lncRNA ZNRD1-AS1 promotes malignant lung cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis via the miR-942/TNS1 axis and is positively regulated by the m(6)A reader YTHDC2. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martuszewska, D.; Ljungberg, B.; Johansson, M.; Landberg, G.; Oslakovic, C.; Dahlbäck, B.; Hafizi, S. Tensin3 is a negative regulator of cell migration and all four Tensin family members are downregulated in human kidney cancer. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Lin, L.T.; Wang, M.L.; Laurent, B.; Hsu, C.H.; Pan, C.M.; Jiang, W.R.; Chen, P.Y.; Ma, H.I.; Chen, Y.W.; et al. Musashi-1 Enhances Glioblastoma Cell Migration and Cytoskeletal Dynamics through Translational Inhibition of Tensin3. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, I.; Takano, T.; Yoshida, H.; Matsuzuka, F.; Amino, N.; Miyauchi, A. Tensin3 is a novel thyroid-specific gene. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 36, R1–R8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, I.; Yamada, H.; Takano, T.; Nishihara, E.; Ito, Y.; Matsuzuka, F.; Miya, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshida, H.; Miyauchi, A.; et al. Increased expression levels of tensin3 mRNA in thyroid functional adenomas as compared to non-functioning adenomas. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2009, 117, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.A.; Górecki, D.C.; Mein, C.A.; Ljungberg, B.; Hafizi, S. CpG dinucleotide-specific hypermethylation of the TNS3 gene promoter in human renal cell carcinoma. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Gao, C.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, C.W.; Wu, M.; Li, L.Y. MLL3 suppresses tumorigenesis through regulating TNS3 enhancer activity. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinchi, Y.; Hieda, M.; Nishioka, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kimura, H.; Matsuura, S.; Matsuura, N. SUV420H2 suppresses breast cancer cell invasion through down regulation of the SH2 domain-containing focal adhesion protein tensin-3. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 334, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.C.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.C.; Cheon, Y.I.; Sung, E.S.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, B.J. Tensin Regulates Fundamental Biological Processes by Interacting with Integrins of Tonsil-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizi, S.; Ibraimi, F.; Dahlbäck, B. C1-TEN is a negative regulator of the Akt/PKB signal transduction pathway and inhibits cell survival, proliferation, and migration. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainero, E.; Howe, J.D.; Caswell, P.T.; Jamieson, N.B.; Anderson, K.; Critchley, D.R.; Machesky, L.; Norman, J.C. Ligand-Occupied Integrin Internalization Links Nutrient Signaling to Invasive Migration. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albasri, A.; Seth, R.; Jackson, D.; Benhasouna, A.; Crook, S.; Nateri, A.S.; Chapman, R.; Ilyas, M. C-terminal Tensin-like (CTEN) is an oncogene which alters cell motility possibly through repression of E-cadherin in colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, S.; Albasri, A.; Cachat, J.; Ibrahem, S.; Muhammad, B.A.; Jackson, D.; Nateri, A.S.; Kindle, K.B.; Ilyas, M. Cten is targeted by Kras signalling to regulate cell motility in the colon and pancreas. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albasri, A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Fadhil, W.; Aleskandarany, M.; Liao, Y.C.; Jackson, D.; Lobo, D.N.; Lo, S.H.; Kumari, R.; Durrant, L.; et al. Cten signals through integrin-linked kinase (ILK) and may promote metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2997–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asiri, A.; Toss, M.S.; Raposo, T.P.; Akhlaq, M.; Thorpe, H.; Alfahed, A.; Asiri, A.; Ilyas, M. Cten promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in colorectal cancer through stabilisation of Src. Pathol. Int. 2019, 69, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, S.; Cachat, J.; Albasri, A.; Ahmed, M.; Jackson, D.; Zaitoun, A.; Guppy, N.; Otto, W.R.; Alison, M.R.; Kindle, K.B.; et al. C-terminal tensin-like gene functions as an oncogene and promotes cell motility in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2013, 42, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Cai, H.; Zhang, T. CTEN induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis in non small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.K.; Chiu, Y.T.; Sze, K.M.; Ng, I.O. Tensin4 is up-regulated by EGF-induced ERK1/2 activity and promotes cell proliferation and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20964–20976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoestroem, C.; Khosravi, S.; Zhang, G.; Martinka, M.; Li, G. C-terminal tensin-like protein is a novel prognostic marker for primary melanoma patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Xie, W.; Li, L.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; He, X. Elevated transgelin/TNS1 expression is a potential biomarker in human colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, S.; Song, W. Prazosin inhibits the proliferation and survival of acute myeloid leukaemia cells through down-regulating TNS1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.C.; Kim, H.S.; Park, H.Y.; Seo, Y.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.C.; Kwon, H.K.; Sung, E.S.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, B.J. Tensin-3 Regulates Integrin-Mediated Proliferation and Differentiation of Tonsil-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells 2019, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Yang, H.; Khan, S.; Li, R.; Zhou, S.; Ullah, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B. Pharmacological targeting of TNS3 with histone deacetylase inhibitor as a therapeutic strategy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 15336–15352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.M.; Liao, Y.C. Downregulation of C-Terminal Tensin-Like Protein (CTEN) Suppresses Prostate Cell Proliferation and Contributes to Acinar Morphogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Lu, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, D.; Ke, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, W. Development and functional validation of a disulfidoptosis-related gene prognostic model for lung adenocarcinoma based on bioinformatics and experimental validation. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1540578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber-Pérez, N.; Georgiadou, M.; Guzmán, C.; Isomursu, A.; Hamidi, H.; Ivaska, J. Mechano-responsiveness of fibrillar adhesions on stiffness-gradient gels. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs242909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goreczny, G.J.; Forsythe, I.J.; Turner, C.E. Hic-5 regulates fibrillar adhesion formation to control tumor extracellular matrix remodeling through interaction with tensin1. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, J.S.; Jacobs, K.A.; Heinrich, V.; Lo, S.H.; Yamada, S. Force-induced recruitment of cten along keratin network in epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19799–19801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, W.H.; Kotelawala, L.; Sweeney, C.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd. Mechanisms of ErbB receptor negative regulation and relevance in cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, H.; Akhlaq, M.; Jackson, D.; Al Ghamdi, S.; Storr, S.; Martin, S.; Ilyas, M. Multiple pathways regulate Cten in colorectal cancer without a Tensin switch. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 96, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, N.; Kang, K.; Kim, W.; Won, J.; Cho, J. Whole Transcriptome Analysis Identifies TNS4 as a Key Effector of Cetuximab and a Regulator of the Oncogenic Activity of KRAS Mutant Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Cells 2019, 8, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Liao, Y.C. Histone acetyltransferase p300 mediates the upregulation of CTEN induced by the activation of EGFR signaling in cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, B.; Gui, T.; Zeng, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Xu, P.; Hu, R.; et al. PRMT1-mediated H4R3me2a recruits SMARCA4 to promote colorectal cancer progression by enhancing EGFR signaling. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yao, B.; Liu, J.; Gong, G.W.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Pan, H.F.; Li, Q.; Yang, D.; Lu, P.; et al. The SMARCA4(R1157W) mutation facilitates chromatin remodeling and confers PRMT1/SMARCA4 inhibitors sensitivity in colorectal cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraway, K.L., 3rd. E3 ubiquitin ligases in ErbB receptor quantity control. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraham, R.; Yarden, Y. Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: Decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Shih, Y.P.; Li, T.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd; Lo, S.H. CTEN prolongs signaling by EGFR through reducing its ligand-induced degradation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5266–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Wang, W.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Fan, Z.W.; Xie, X.F.; Yang, L.Y.; Chang, C.; Cai, Y.; Hao, J.J.; Wang, M.R.; et al. The miR-1224-5p/TNS4/EGFR axis inhibits tumour progression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mizokami, A.; Izumi, K.; Narimoto, K.; Shima, T.; Zhang, J.; Dai, J.; Keller, E.T.; Namiki, M. CTEN/tensin 4 expression induces sensitivity to paclitaxel in prostate cancer. Prostate 2010, 70, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidema, A.; Atherton, P.; Kreft, M.; Hoekman, L.; Bleijerveld, O.B.; Nagaraj, N.; Chen, N.; Fässler, R.; Sonnenberg, A. PEAK1 Y635 phosphorylation regulates cell migration through association with Tensin3 and integrins. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 221, e202108027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Croucher, D.R.; Soliman, M.A.; St-Denis, N.; Pasculescu, A.; Taylor, L.; Tate, S.A.; Hardy, W.R.; Colwill, K.; et al. Temporal regulation of EGF signalling networks by the scaffold protein Shc1. Nature 2013, 499, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boureux, A.; Vignal, E.; Faure, S.; Fort, P. Evolution of the Rho family of ras-like GTPases in eukaryotes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, M.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Deciphering the molecular and functional basis of Dbl family proteins: A novel systematic approach toward classification of selective activation of the Rho family proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 4486–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tcherkezian, J.; Lamarche-Vane, N. Current knowledge of the large RhoGAP family of proteins. Biol. Cell 2007, 99, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, C.D.; Burridge, K. The on-off relationship of Rho and Rac during integrin-mediated adhesion and cell migration. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e27958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.C.; Lo, S.H. Deleted in liver cancer-1 (DLC-1): A tumor suppressor not just for liver. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumiya, S.; Tanji, M.; Ishizaki, T. Rho signaling, ROCK and mDia1, in transformation, metastasis and invasion. Cancer Metastasis. Rev. 2009, 28, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Healy, K.D.; Der, C.J.; Sciaky, N.; Bang, Y.J.; Juliano, R.L. Effects of structure of Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC-1 on cell morphology and migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 32762–32770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.K.; Qian, X.; Mertins, P.; Wang, D.; Papageorge, A.G.; Carr, S.A.; Lowy, D.R. CDK5 is a major regulator of the tumor suppressor DLC1. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 207, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Kaneko, T.; Li, J.S.; Liu, A.D.; Voss, C.; Li, S.S. A phosphorylation switch controls the spatiotemporal activation of Rho GTPases in directional cell migration. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wei, J.; Liu, P. Attacking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment in human cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Luo, T.; Shi, H. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MEK/ERK pathways for cancer therapy. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, R.; Manzoor, M.; Hussain, A. Wnt signaling pathway: A comprehensive review. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rim, E.Y.; Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. The Wnt Pathway: From Signaling Mechanisms to Synthetic Modulators. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2022, 91, 571–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.C.; Chen, N.T.; Shih, Y.P.; Dong, Y.; Lo, S.H. Up-regulation of C-terminal tensin-like molecule promotes the tumorigenicity of colon cancer through beta-catenin. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4563–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, T.P.; Alfahed, A.; Nateri, A.S.; Ilyas, M. Tensin4 (TNS4) is upregulated by Wnt signalling in adenomas in multiple intestinal neoplasia (Min) mice. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 101, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Shang, Y.; Lin, J. YAP-mediated crosstalk between the Wnt and Hippo signaling pathways (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4101–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Martin, J.F. Hippo Pathway: An Emerging Regulator of Craniofacial and Dental Development. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Adebowale, K.; Váncza, L.; Li, Y.; Rabbi, M.F.; Kunimoto, K.; Chen, D.; Mozes, G.; Chiu, D.K.; Li, Y.; et al. Matrix viscoelasticity promotes liver cancer progression in the pre-cirrhotic liver. Nature 2024, 626, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernau, K.; Torr, E.E.; Evans, M.D.; Aoki, J.K.; Ngam, C.R.; Sandbo, N. Tensin 1 Is Essential for Myofibroblast Differentiation and Extracellular Matrix Formation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 56, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Peng, D.; Cai, Z.; Lin, H.K. AMPK signaling and its targeting in cancer progression and treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, F. Tensin 1 regulated by hepatic leukemia factor represses the progression of prostate cancer. Mutagenesis 2023, 38, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.W.; Ming, X.L.; Rong, Y.; Huang, C.Q.; Weng, H.; Chen, H.; Bian, J.M.; Wang, F.B. Diagnostic Value Investigation and Bioinformatics Analysis of miR-31 in Patients with Lymph Node Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer. Anal. Cell Pathol. 2019, 2019, 9740475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Ren, X.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Yuan, J.; Yuan, J.; Tong, Q. RNA-Binding Protein COL14A1, TNS1, NUSAP1 and YWHAE Are Valid Biomarkers to Predict Peritoneal Metastasis in Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 830688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Huang, B.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ou, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. Identification of Lymph Node Metastasis-Related Key Genes and Prognostic Risk Model in Bladder Cancer by Co-Expression Analysis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 633299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Bao, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Sun, G.; Sun, X.; Fu, T.; Wang, Y.; Liang, P. MicroRNA-522-3p promotes brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting Tensin 1 and modulating blood-brain barrier permeability. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 442, 114199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, S.; Zheng, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Ma, J.; Zhang, B.; Huang, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, C. miR-31-5p modulates cell progression in lung adenocarcinoma through TNS1/p53 axis. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2022, 198, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Diermeier, S.D.; Yu, A.T.; Brine, L.D.; Russo, S.; Bhatia, S.; Alsudani, H.; Kostroff, K.; Bhuiya, T.; Brogi, E.; et al. MaTAR25 lncRNA regulates the Tensin1 gene to impact breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.B.; Huang, Z.L.; Xu, Y.H.; Huang, J.; Huang, X.Y.; Huang, X.Y. Systematic analysis of gene expression profiles reveals prognostic stratification and underlying mechanisms for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yam, J.W.; Ko, F.C.; Chan, C.Y.; Yau, T.O.; Tung, E.K.; Leung, T.H.; Jin, D.Y.; Ng, I.O. Tensin2 variant 3 is associated with aggressive tumor behavior in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2006, 44, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Cheng, A.N.; Lee, A.Y.; Cho, C.Y.; Huang, J.S.; Chuang, S.E. AXL phosphorylates and up-regulates TNS2 and its implications in IRS-1-associated metabolism in cancer cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Shu, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, D.; Bao, J.; Milne, R.L.; Giles, G.G.; Wu, C.; Du, M.; White, E.; et al. Associations between Genetically Predicted Blood Protein Biomarkers and Pancreatic Cancer Risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2020, 29, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Qi, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Jin, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhu, X.; Luo, J.; et al. Using a human bronchial epithelial cell-based malignant transformation model to explore the function of hsa-miR-200 family in the progress of PM(2.5)-induced lung cancer development. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 319, 120981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bian, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, C.; Gao, Y.; Tian, B.; Xia, W.; Wang, W.; Xin, L.; Lin, H.; et al. EIF4A3-mediated oncogenic circRNA hsa_circ_0001165 advances esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-381-3p/TNS3 pathway. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2024, 40, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Ye, R.; Ha, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, R.; Di, X.; Zou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z. Prediction Biomarkers Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis were Identified in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2021, 24, 1395–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizioł, M.; Zińczuk, J.; Zaręba, K.; Guzińska-Ustymowicz, K.; Pryczynicz, A. Immunohistochemical Analysis of the Expression of Adhesion Proteins: TNS1, TNS2 and TNS3 in Correlation with Clinicopathological Parameters in Gastric Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veß, A.; Blache, U.; Leitner, L.; Kurz, A.R.M.; Ehrenpfordt, A.; Sixt, M.; Posern, G. A dual phenotype of MDA-MB-468 cancer cells reveals mutual regulation of tensin3 and adhesion plasticity. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 2172–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.C.; Ebersberger, S.; Fink, A.F.; Lampe, S.; Weigert, A.; Schmid, T.; Ebersberger, I.; Syed, S.N.; Brüne, B. Apoptotic tumor cell-derived microRNA-375 uses CD36 to alter the tumor-associated macrophage phenotype. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakashita, K.; Mimori, K.; Tanaka, F.; Kamohara, Y.; Inoue, H.; Sawada, T.; Hirakawa, K.; Mori, M. Prognostic relevance of Tensin4 expression in human gastric cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawazaki, S.; Oshima, T.; Sakamaki, K.; Aoyama, T.; Sato, T.; Shiozawa, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Rino, Y.; Imada, T.; Masuda, M. Clinical Significance of Tensin 4 Gene Expression in Patients with Gastric Cancer. In Vivo 2017, 31, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Sun, L.; Wan, J.; Xu, R.; He, S.; Zhu, X. Tensin4 promotes invasion and migration of gastric cancer cells via regulating AKT/GSK-3β/snail signaling pathway. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, H.; Kim, H.J.; Haam, K.; Sohn, H.A.; Shin, Y.J.; Go, H.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.I.; Song, K.S.; et al. Epigenetic Activation of Tensin 4 Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression. Mol. Cells 2023, 46, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Su, G.H.; Bao, T.S.; He, W.P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Xie, J.X.; Wang, F.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S.; et al. TNS4 promotes lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer by interacting with integrin Β1 and inducing the activation of fibroblastic reticular cell. Cancer Cell Int. 2025, 25, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizioł, M.; Zińczuk, J.; Zaręba, K.; Guzińska-Ustymowicz, K.; Pryczynicz, A. Increased tensin 4 expression is related to the histological type of gastric cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Mai, Z.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Cui, L.; Yu, J. Hypoxia-driven TNS4 fosters HNSCC tumorigenesis by stabilizing integrin α5β1 complex and triggering FAK-mediated Akt and TGFβ signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xu, C. Tensin 4 facilitates aerobic glycolysis, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the β-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 28, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, T.P.; Susanti, S.; Ilyas, M. Investigating TNS4 in the Colorectal Tumor Microenvironment Using 3D Spheroid Models of Invasion. Adv. Biosyst. 2020, 4, e2000031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, A.; Raposo, T.P.; Alfahed, A.; Ilyas, M. TGFβ1-induced cell motility but not cell proliferation is mediated through Cten in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 99, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misono, S.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Yamada, Y.; Uchida, A.; Sanada, H.; Moriya, S.; Kikkawa, N.; Kumamoto, T.; Suetsugu, T.; et al. Molecular Pathogenesis of Gene Regulation by the miR-150 Duplex: miR-150-3p Regulates TNS4 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Gao, X.; Liu, W.; Xue, W. Mining TCGA and GEO databases for the prediction of poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma based on up-regulated expression of TNS4. Medicine 2022, 101, e31120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.T.; Reece, T.B.; Foley, L.S.; Sjoberg, A.; Meng, X.; Fullerton, D.A.; Weyant, M.J. C-terminal tensin-like protein mediates invasion of human lung cancer cells and is regulated by signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Li, G.; Pu, P.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Geng, Y.; Liu, Y. GPRC5A promotes gallbladder cancer metastasis by upregulating TNS4 via the JAK2-STAT3 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2024, 598, 217067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albasri, A.; Aleskandarany, M.; Benhasouna, A.; Powe, D.G.; Ellis, I.O.; Ilyas, M.; Green, A.R. CTEN (C-terminal tensin-like), a novel oncogene overexpressed in invasive breast carcinoma of poor prognosis. Breast. Cancer Res. Treat 2011, 126, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, I.; Pensa, S.; Pannellini, T.; Quaglino, E.; Maritano, D.; Demaria, M.; Voster, A.; Turkson, J.; Cavallo, F.; Watson, C.J.; et al. Constitutively active Stat3 enhances neu-mediated migration and metastasis in mammary tumors via upregulation of Cten. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, B.; Cao, M.; Shao, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, T. CTEN Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis and Growth by Targeting VEGFA Through Down-Regulation of β-Catenin in Breast Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat 2021, 20, 15330338211045506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.S.; Lo, S.H.; Lo, S.H. Cleavage of cten by caspase-3 during apoptosis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4311–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghel, G.J.; Lin, W.Y.; Whitehouse, H.; Brock, I.; Hammond, D.; Bury, J.; Stephenson, Y.; George, R.; Cox, A. Identification of candidate driver genes in common focal chromosomal aberrations of microsatellite stable colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiò, C.; Natrajan, R.; Shiu, K.K.; Lambros, M.B.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Tan, D.S.; Lord, C.J.; Hungermann, D.; Fenwick, K.; Tamber, N.; et al. The genomic profile of HER2-amplified breast cancers: The influence of ER status. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.F.; Chen, J.Y.; Kuo, P.C.; Lai, H.F.; Lee, T.L.; Tai, S.K.; Kuo, C.S.; Chen, H.S.; Li, W.S.; Li, C.F. A Shift in Molecular Drivers of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Following the 2017 World Health Organization Classification: Characterization of 554 Consecutive Tumors with Emphasis on BRAF-Negative Cases. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Woo, S.; Kang, B.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, C.I.; Kyung, D.S.; Kim, H.P.; Kim, G.; et al. Concordance of ctDNA and tissue genomic profiling in advanced biliary tract cancer. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, K.; Kiyokawa, N.; Watanabe, S.; Iwafuchi, H.; Nakazawa, A.; Ishiwata, K.; Ogata-Kawata, H.; Nakabayashi, K.; Okamura, K.; Tanaka, F.; et al. Characteristics of genetic alterations of peripheral T-cell lymphoma in childhood including identification of novel fusion genes: The Japan Children’s Cancer Group (JCCG). Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuki, M.; Hirohashi, Y.; Nakatsugawa, M.; Murai, A.; Kubo, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Tokita, S.; Murata, K.; Kanaseki, T.; Tsukahara, T.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T cells recognize a heterogeneously expressed functional neoantigen in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Wen, L.; Jiang, H.; Wen, D.; Shu, B.; et al. Characterization of a germline variant TNS1 c.2999-1G > C in a hereditary cancer syndrome family. Gene 2024, 908, 148304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmikangas, S.; Böhling, T.; Merikoski, N.; Jagdeo, J.; Sampo, M.; Vesterinen, T.; Sihto, H. Tensin2 Is a Novel Diagnostic Marker in GIST, Associated with Gastric Location and Non-Metastatic Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.C.; Menias, C.O.; Gaballah, A.H.; Shroff, S.; Taggart, M.W.; Garg, N.; Elsayes, K.M. Beyond the GIST: Mesenchymal tumors of the stomach. Radiographics 2013, 33, 1673–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsmár, É.; Kocsmár, I.; Szalai, L.; Lendvai, G.; Szijártó, A.; Schaff, Z.; Kiss, A.; Kovalszky, I.; Papp, G.; Lotz, G. Cross-testing of major molecular markers indicates distinct pathways of tumorigenesis in gastric adenocarcinomas and synchronous gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swalchick, W.; Shamekh, R.; Bui, M.M. Is DOG1 Immunoreactivity Specific to Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor? Cancer Control 2015, 22, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeljic, K.; Pavlovic, D.; Stojkovic, G.; Dragicevic, S.; Ljubicic, J.; Todorovic, N.; Nikolic, A. Analysis of TNS3-203 and LRRFIP1-211 Transcripts as Oral Cancer Biomarkers. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2025, 54, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, J.; Zhou, J. Development and Validation of an Autophagy-Stroma-Based Microenvironment Gene Signature for Risk Stratification in Colorectal Cancer. Onco. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 3503–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Yu, F.; Tan, Y.F.; Huo, J.P.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.J.; Li, J.M. Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Components Identifies Five Stroma-Related Genes with Prognostic Implications in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2022, 37, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Deng, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, J.; Huang, Q. Predicting tumor repopulation through the gene panel derived from radiation resistant colorectal cancer cells. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, X.; Zhang, M.; Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Chen, W. Development and Validation of a Seven-Gene Signature for Predicting the Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1836542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ruan, Y.Q.; Qu, L.H.; Li, Z.H.; Xie, C.; Pan, Y.Q.; Li, H.F.; Li, D.B. Prognostic Modeling of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Hypoxia and Ferroptosis-Related Genes. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 1022580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, H.; Guo, H.; Du, K.; Chen, D. Integrative analysis illustrates the role of PCDH7 in lung cancer development, cisplatin resistance, and immunotherapy resistance: An underlying target. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1217213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.; Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Qiu, F.; Mo, G. A scoring model based on bacterial lipopolysaccharide-related genes to predict prognosis in NSCLC. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1408000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Huo, S. Establishment of a Lymph Node Metastasis-Associated Prognostic Signature for Lung Adenocarcinoma. Genet. Res. 2023, 2023, 6585109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yang, X.; Chen, W.; Wei, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; He, H.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, F. Developing and experimental validating a T cell senescence-related gene signature to predict prognosis and immunotherapeutic sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer. Gene 2025, 941, 149233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, N.; Chen, Q.; Yin, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, G.; Habib, J.R.; Chen, J.; Yu, J.; Lou, W.; Wu, W. Identification of an Immune-Related BAT Signature for Predicting Adjuvant Chemotherapy Response and Overall Survival in Patients with Resected Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 26, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xu, H. Integrins as attractive targets for cancer therapeutics. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B. 2021, 11, 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, Z. The clinical efficacy and safety of paclitaxel combined with avastin for NSCLC patients diagnosed with malignant pleural effusion. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2018, 64, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisato, R.E.; Tille, J.C.; Jonczyk, A.; Goodman, S.L.; Pepper, M.S. alphav beta 3 and alphav beta 5 integrin antagonists inhibit angiogenesis in vitro. Angiogenesis 2003, 6, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadybekov, A.V.; Katritch, V. Computational approaches streamlining drug discovery. Nature 2023, 616, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamathevan, J.; Clark, D.; Czodrowski, P.; Dunham, I.; Ferran, E.; Lee, G.; Li, B.; Madabhushi, A.; Shah, P.; Spitzer, M.; et al. Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cancer | Effects | Clinical Correlation (Sample) | Molecular Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prostate cancer | ↓ | Not available | Activating p53 signaling [114] |
| Colorectal cancer | ↑ | ↑mRNA/protein = ↓OS (TCGA and HPA databases) [70] | Unclear |
| ↑ | ↑mRNA = ↓OS and DFS (362 patients) [115] | ||
| ↑ | ↑mRNA = ↓survival (TCGA + UALCAN databases) [49] | ||
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | ↑ | Not available | TNS1–integrin β1–RhoA–YAP mechanotransduction axis |
| Gastric cancer | ↑ | ↑mRNA = ↑peritoneal metastasis (221 patients) [116] | Unclear |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | ↑ | Not available | Activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling [71] |
| Bladder cancer | ↓ | ↓mRNA = ↑metastasis (TCGA data + 45 paired samples) [50] | Unclear |
| ↑ | ↑mRNA = ↓OS (TCGA data + GSE13507) [117] | ||
| Non-small-cell lung cancer | ↑ | ↑mRNA = ↓OS (36 paired samples) [47] | Activating Akt/mTOR/RhoA axis |
| ↓ | Not available | microRNA-522-3p suppressing TNS1 [118] | |
| ↓ | miR-31-5p inhibiting TNS1/p53 axis [119] | ||
| Breast cancer | ↓ | Not available | MaTAR25 upregulating TNS1 [120] |
| ↑ | miR-548j inhibiting TNS1 [48] |
| Cancer Type | Gene Signature | Prognosis | Validation Datasets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle-invasive Bladder cancer | KLK6, TNS1, TRIM56 | High risk scores predict poor OS | TCGA database and E-MTAB-1803 cohort [121] |
| Colorectal cancer | TNS1, TAGLN, SFRP4 | High risk scores correlate with advanced tumors and poor OS | GSE39582 microarray, GSE17538, GSE38832, and TCGA datasets and clinical samples from the First Hospital of China Medical University [161] |
| ITGA7, PTPN14, SCG2, TNS1, and GRP | High stromal scores correlate with advanced tumor stages and poor OS and relapse-free survival | GSE39582, GSE17536, and TCGA [162] | |
| Gastric cancer | COL14A1, TNS1, NUSAP1, and YWHAE | High risk scores predict poor OS | 221 samples from GSE62254 cohort [116] |
| Cancer Type | Gene Signature | Prognosis | Validation Datasets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | LGR5, KCNN4, TNS4, CENPH | High risk scores predict more radiation resistance, tumor progression, and poor PFS | TCGA database and GSE97543 [163] |
| Non-small-cell lung cancer | NTSR1, RHOV, KLK8, TNS4, C1QTNF6, IVL and B4GALNT2 | High risk scores predict poor survival rate | TCGA-LUAD dataset and GSE26939 [164] |
| MAPK4, TNS4, WFDC2, FSTL3, ITGA2, KLK11, PHLDB2, VGLL3, SNX30, KCNQ3, SMAD9, ANGPTL4, LAMA3 and STK32A | High risk scores predict advanced tumor stage and poor survival rate | TCGA-LUAD and GSE31210 [165] | |
| GPX8, BCAR3, TNS4 | High risk scores predict poor survival rate | GSE21656, GSE108214, and TCGA data [166] | |
| VIPR1, NEK2, HMGA1, FERMT1, SLC7A and TNS4 | High risk scores predict poor survival rate | TCGA data and GSE37745 [167] | |
| ANGPTL4, BARX2, GPR98, KRT6A, PTPRH, RGS20, TCN1 and TNS4 | High risk scores predict poor OS | TCGA data, GSE68465, GSE42127, GSE50081 [168] | |
| SLC2A1, TNS4, GGTLC1 | High risk scores predict poor OS and PFS | TCGA-LUSC, TCGA-LUAD, GSE19188, GSE30219, GSE37745, GSE50081, GSE29013, GSE31210, GSE4573, GSE68465 [169] | |
| Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | COL14A1, TNS1, NUSAP1, YWHAE | High risk scores predict better response to adjuvant chemotherapy after surgical resection and poor OS | TCGA data and 26 patients from Zhongshan Hospital of Fudan University [170] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, J.; Zhao, H.; Wei, L.; Jiang, J.; Xia, W. Tensins in Cancer: Integration of Their Domain Functions, Context-Dependent Regulation and Biomarker Potential. Biology 2025, 14, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081053
Zheng J, Zhao H, Wei L, Jiang J, Xia W. Tensins in Cancer: Integration of Their Domain Functions, Context-Dependent Regulation and Biomarker Potential. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081053
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Junyi, Hualong Zhao, Lisha Wei, Jinjun Jiang, and Wenlong Xia. 2025. "Tensins in Cancer: Integration of Their Domain Functions, Context-Dependent Regulation and Biomarker Potential" Biology 14, no. 8: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081053
APA StyleZheng, J., Zhao, H., Wei, L., Jiang, J., & Xia, W. (2025). Tensins in Cancer: Integration of Their Domain Functions, Context-Dependent Regulation and Biomarker Potential. Biology, 14(8), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081053







