Dietary Astragalus Polysaccharides Can Improve the Immune Capacity and Reproductive Performance of the Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectus)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Seahorses and Astragalus Polysaccharides
2.2. Administration Route of APSs
2.3. Experiment 1: Effects of APSs on the Survival Rate, Growth, and Immunity of Seahorse Juveniles During Diet Conversion
2.3.1. Experiment 1 Protocol
2.3.2. Survival Rate and Growth Measurement
2.3.3. Plasma Immunocytokine Determination
2.3.4. Intestinal Microbiota Analysis
2.4. Experiment 2: Effects of APSs on the Reproductive Performance of Seahorse Broodstocks
2.4.1. Experiment 2 Protocol
2.4.2. Ovarian Metabolite Component Analysis
2.4.3. Mating Success Rate, Assessment Time Required Before Mating, Brood Size, and Newborn Body Height
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
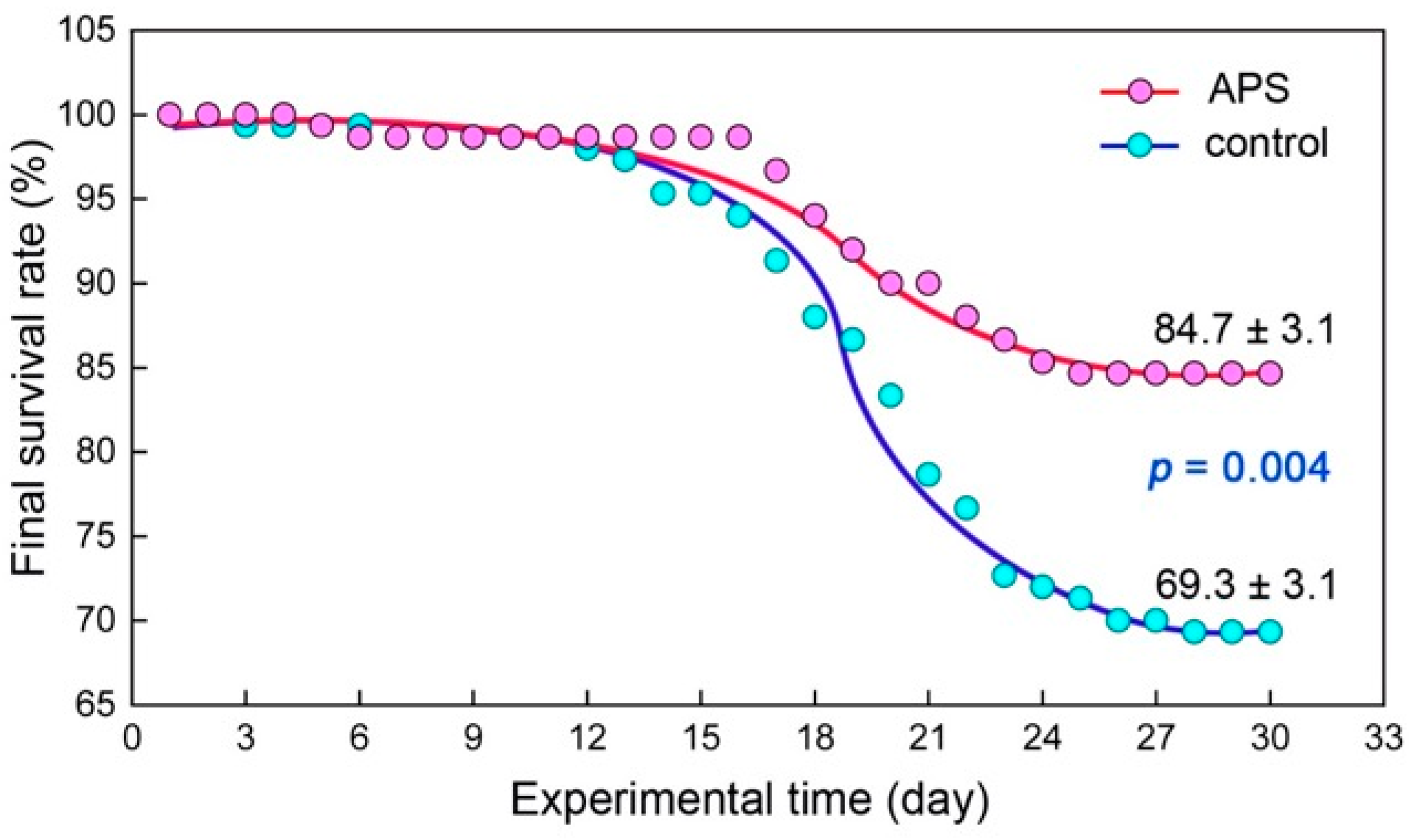
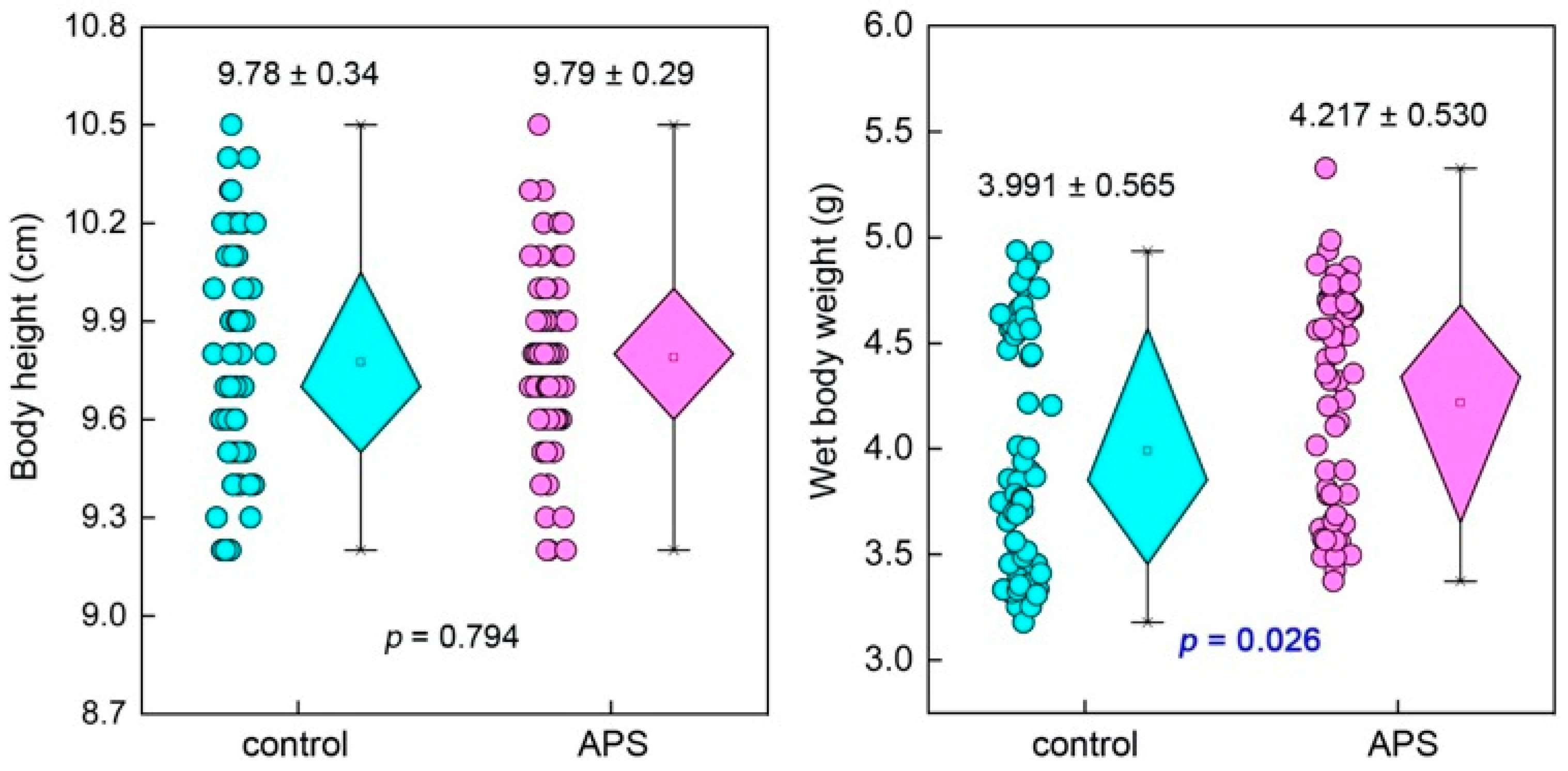
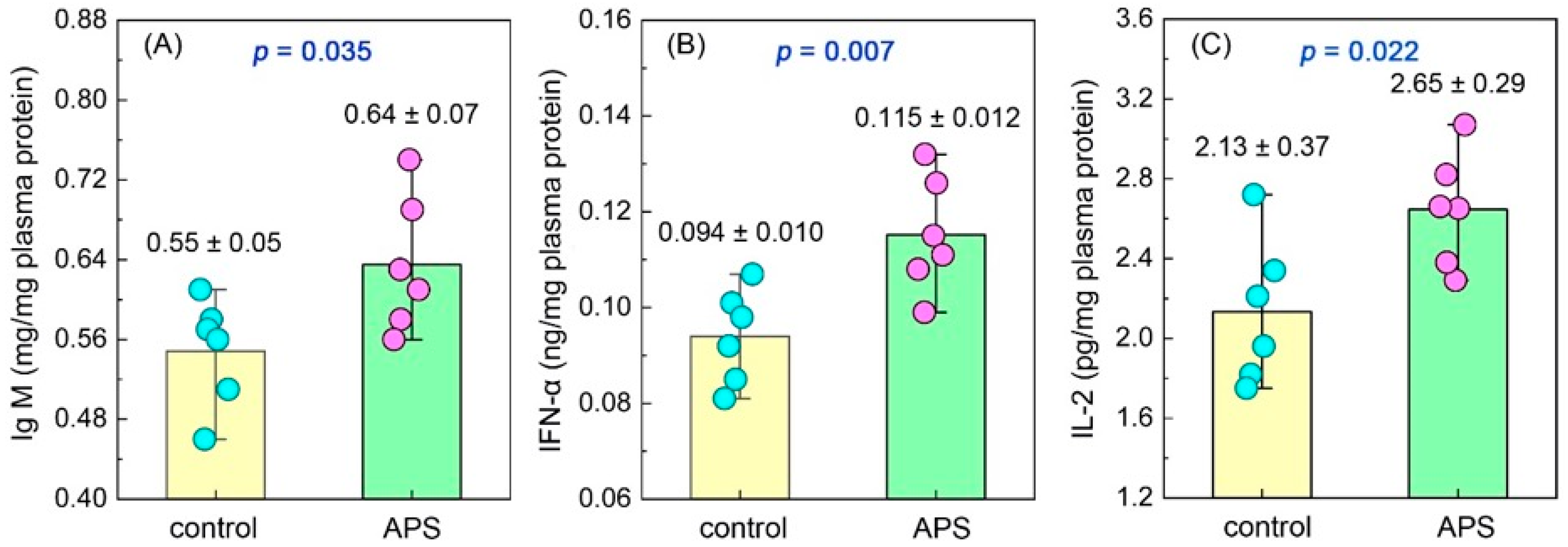
3.1. Effects of APSs on the Survival Rate, Growth, and Immunity of Seahorse Juveniles During Diet Conversion
3.1.1. Survival Rate and Growth
3.1.2. Plasma Immunocytokines
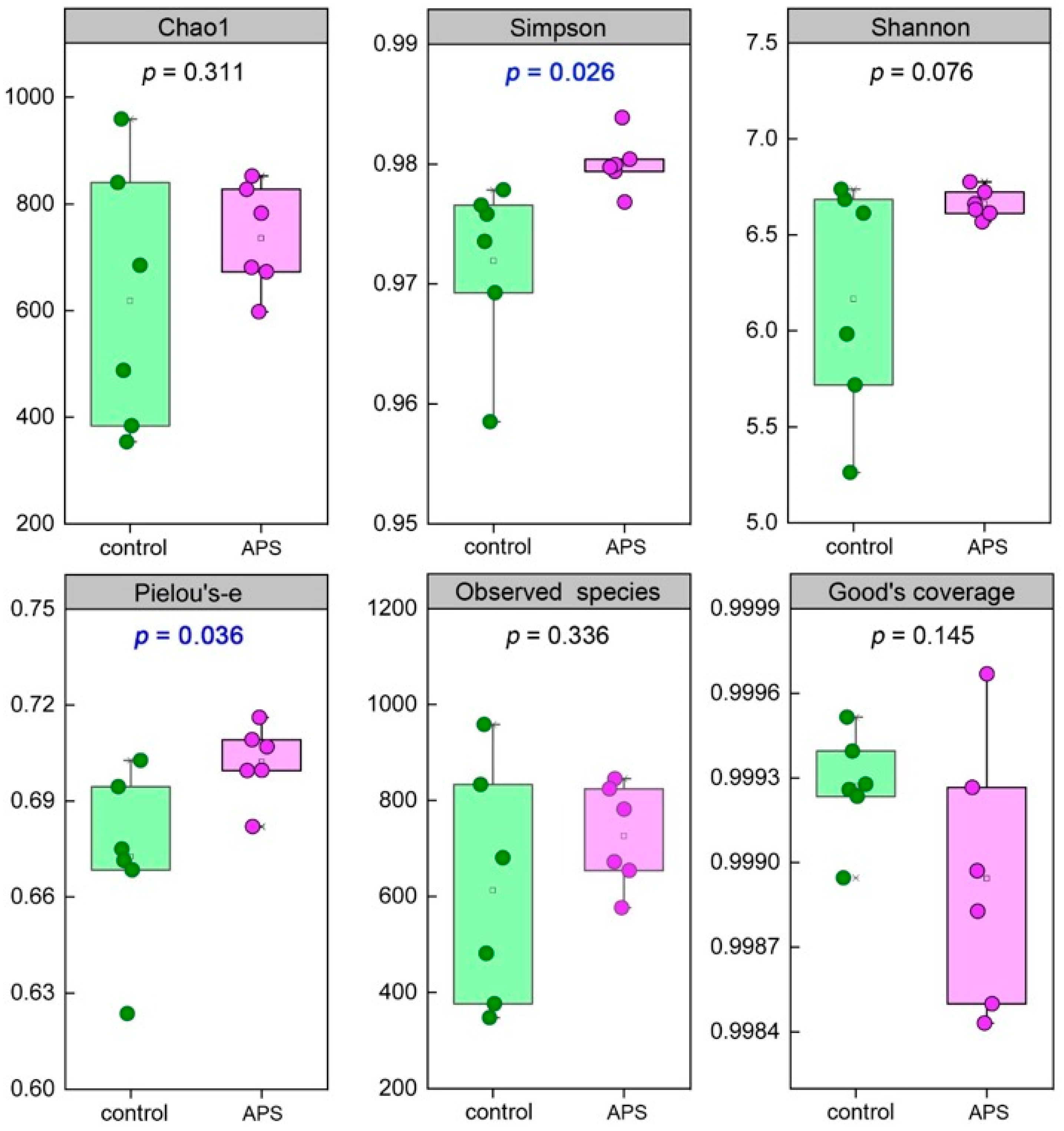
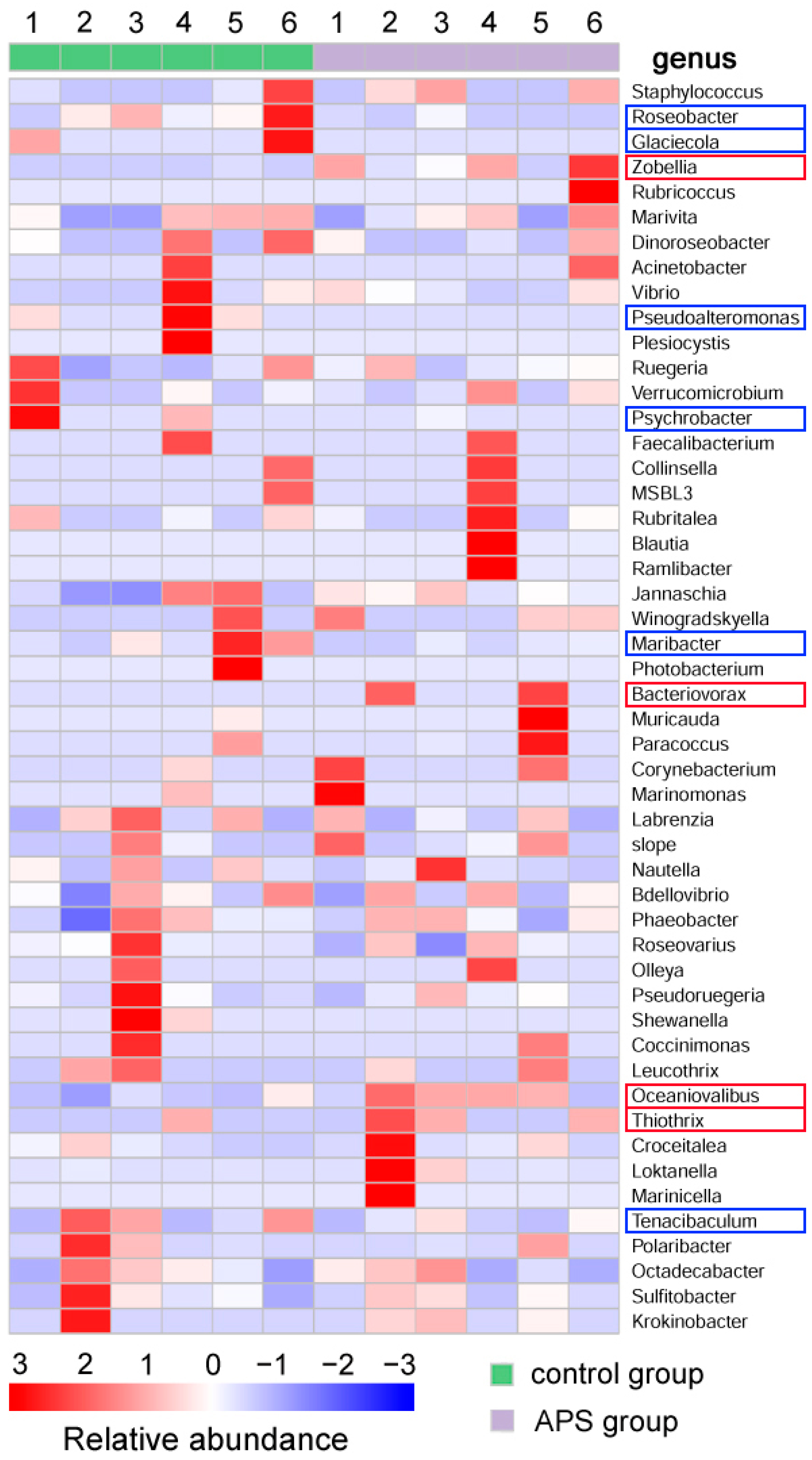
3.1.3. Intestinal Microbiota
3.2. Effects of APSs on the Reproductive Performance of Seahorse Broodstocks
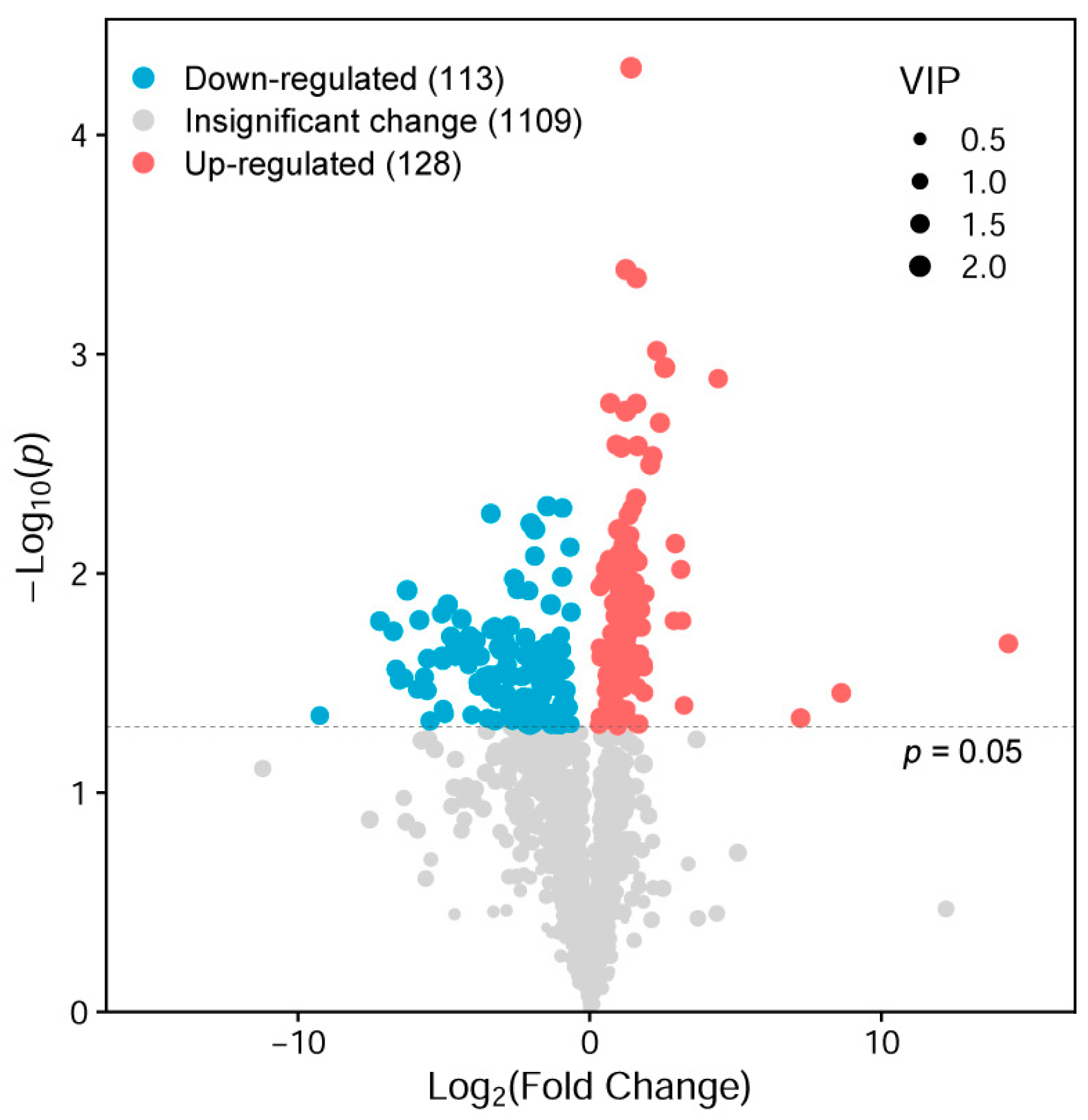
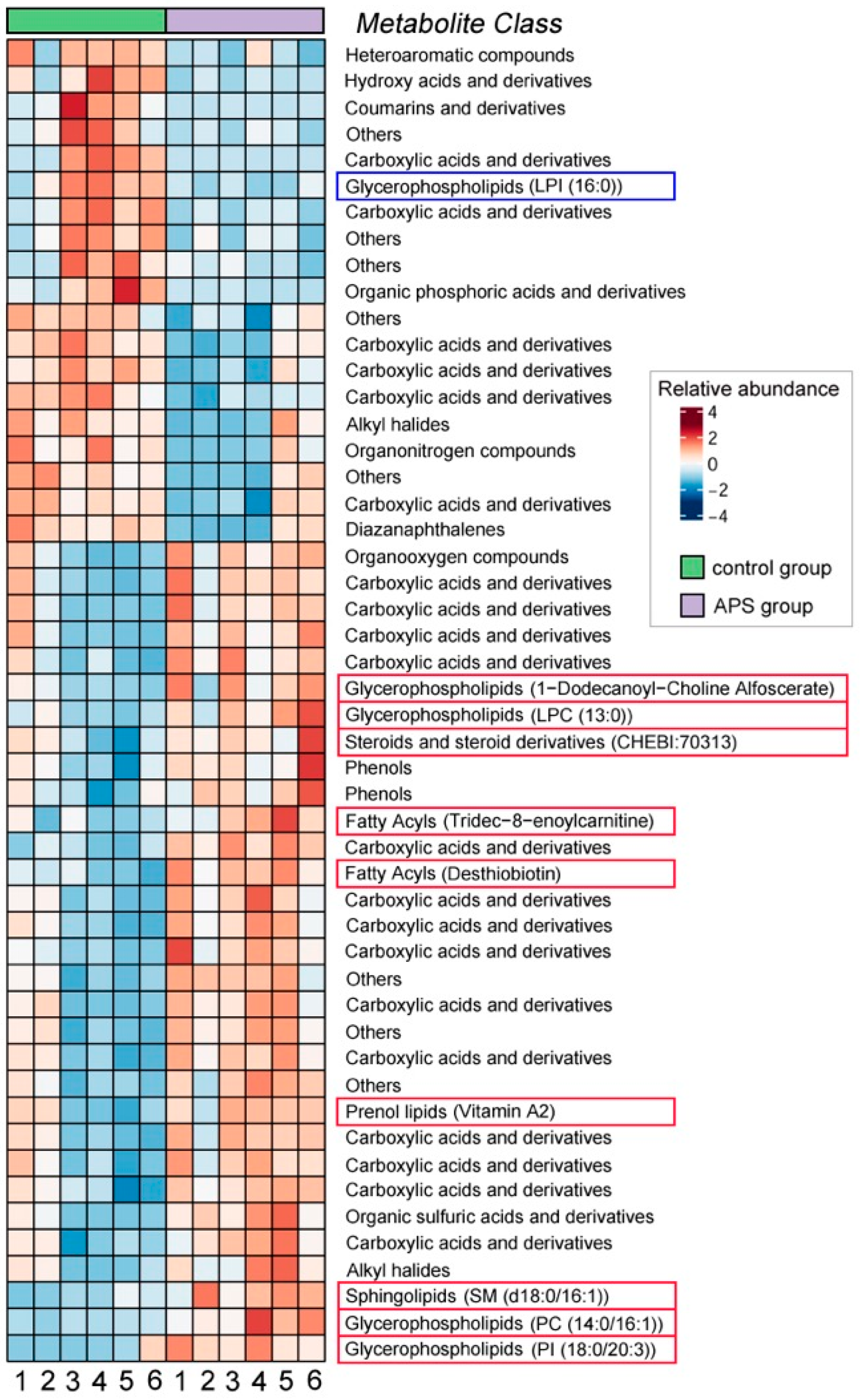
3.2.1. Ovarian Metabolite Components
3.2.2. Mating Success Rate and Assessment Time Required Before Mating
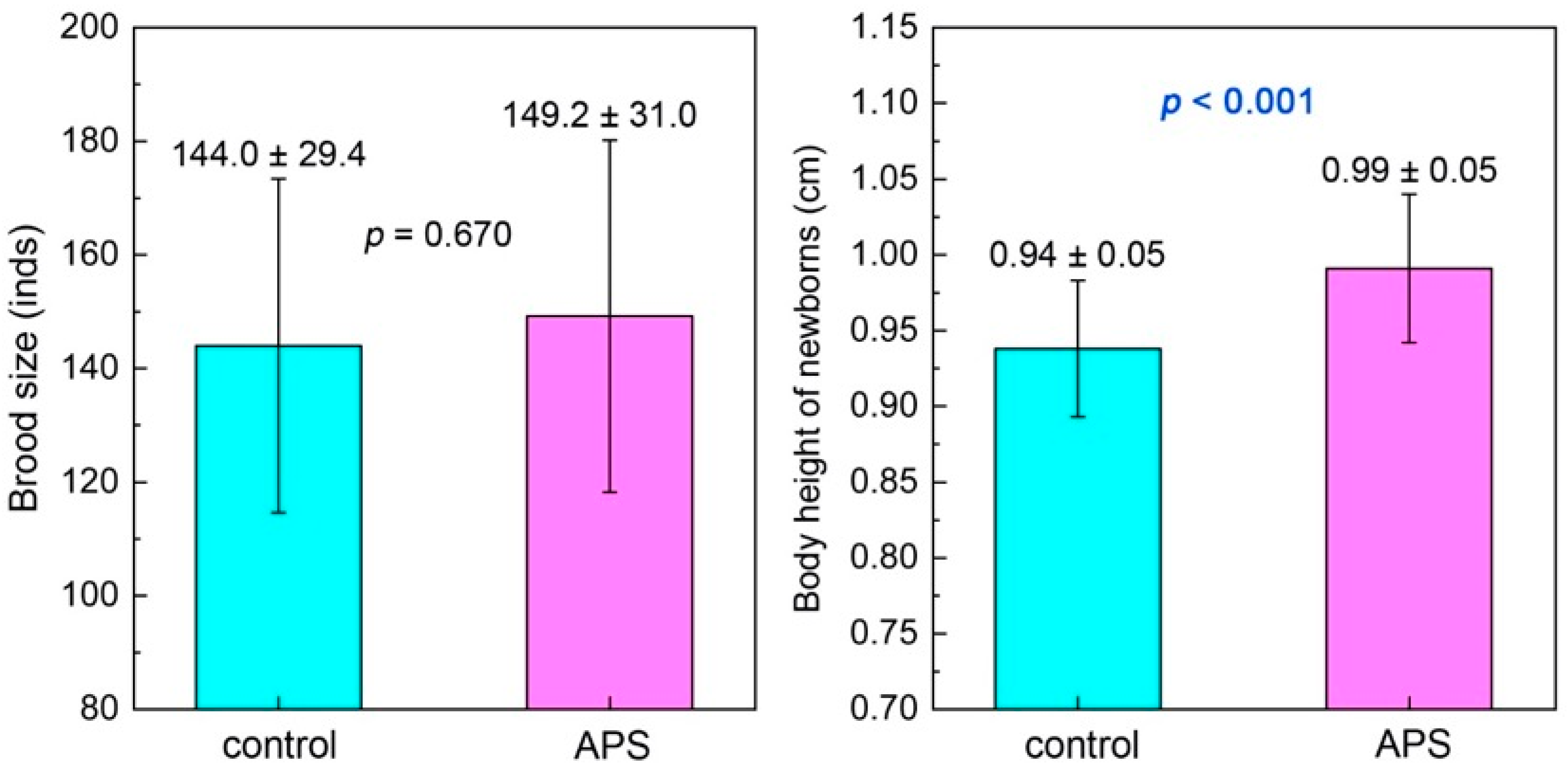
3.2.3. Brood Size and Newborn Body Height
4. Discussion
4.1. APSs Improve the Immune Capacity of Seahorse Juveniles
4.2. APSs Improve the Growth of Seahorse Juveniles
4.3. APSs Improve the Intestinal Microbiota of Seahorse Juveniles
4.4. APSs Improve the Reproductive Performance of Seahorse Broodstocks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koldewey, H.J.; Martin-Smith, K.M. A global review of seahorse aquaculture. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.C.; Vincent, A. Assessing the changes in international trade of marine fishes under CITES regulations—A case study of seahorses. Mar. Policy 2018, 88, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Armani, A.; Wen, J.; Lin, H.; Xu, Y.; Fan, S.; Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; et al. Molecular identification of seahorse and pipefish species sold as dried seafood in China: A market-based survey to highlight the actual needs for a proper trade. Food Control 2019, 103, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.Q.; Lin, Q.; Chen, Q.X.; Gao, Y.L.; Shen, L.; Lu, J.Y. Effects of food, temperature and light intensity on the feeding behavior of three-spot juveniles, Hippocampus trimaculatus Leach. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.L.; Sheng, J.Q.; Chen, Q.X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, J.Y. The effects of food and the sum of effective temperature on the embryonic development of the seahorse, Hippocampus kuda Bleeker. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhang, D. Breeding and juvenile culture of the lined seahorse, Hippocampus erectus. Aquaculture 2008, 277, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Qin, G.; Zhang, B.; Tan, S.; Sun, J.; Lin, Q. Effects of food, salinity, and ammonia-nitrogen on the physiology of juvenile seahorse (Hippocampus erectus) in two typical culture models in China. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y. Effects of stocking density on the survival, growth, and stress levels of the juvenile lined seahorse (Hippocampus erectus) in recirculating aquaculture systems. Biology 2024, 13, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.B.; Qi, J.F.; Lin, J.B.; Chen, X.X.; Luo, H.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, L.Y. Artificial propagation and seeding technique of Hippocampus abdominalis. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2022, 41, 701–707, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Q.; Teng, F. Research advances on the biological characteristics and breeding technology of seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis). Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 46, 190–198, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, F.; Su, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Z.; Gao, L.; Yan, H.; Xue, Y.; Lv, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Supplementation with Enterococcus faecium enhances growth performance, intestinal health and immunity of big-belly seahorses (Hippocampus abdominalis) during diet conversion. Aquacult. Rep. 2023, 28, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Weaning of juvenile seahorses Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810 from live to frozen food. Aquaculture 2009, 291, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liu, Y.L.; Qin, G.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.H. Effects of tributyltin on gonad and brood pouch development of male pregnant lined seahorse (Hippocampus erectus) at environmentally relevant concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, F.; Su, X.; Li, M.; Yan, H.; Zheng, S.; Ma, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Q.; et al. Reproductive toxicity and molecular mechanisms of benzo[a]pyrene exposure on ovary, testis, and brood pouch of sex-role-reversed seahorses (Hippocampus erectus). Environ. Pollut. 2025, 367, 125569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Xu, N.; Ding, T.; Cui, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fang, W.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. Effects of dietary Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) on survival, growth performance, activities of digestive enzyme, antioxidant responses and intestinal development of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ma, Z.; Lin, H. Effects of dietary Astragalus polysaccharides on growth, health and resistance to Vibrio harveyi of Lates calcarifer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Bian, C.; Zhou, N.; Shen, Z.; Yu, M. Dietary Astragalus polysaccharides improve the growth and innate immune response of giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii: Insights from the brain-gut axis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 243, 125158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.; Risha, E.; AbdelHamid, F.; Mahgoub, H.A.; Ibrahim, T. Effects of dietary Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) on growth performance, immunological parameters, digestive enzymes, and intestinal morphology of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 38, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Mai, K.; He, G. Dietary Astragalus polysaccharides ameliorates the growth performance, antioxidant capacity and immune responses in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, B.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Evaluation of the effects of Astragalus polysaccharides as immunostimulants on the immune response of crucian carp and against SVCV in vitro and in vivo. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2022, 253, 109249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lu, J.; Quan, J.; Zhao, G.; Song, G.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z. Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus damage to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) spleen by promoting the efffcacy of inactivated vaccine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 159, 110180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourie, S.A.; Foster, S.J.; Cooper, E.W.T.; Vincent, A.C.J. A guide to the identification of seahorses. In Project Seahorse and TRAFFIC North America; University of British Columbia and World Wildlife Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, T.; Liu, X. A comparison of growth, survival, and fatty acid composition of the lined Seahorse, Hippocampus erectus, juveniles fed enriched Artemia and a calanoid copepod, Schmackeria dubia. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2015, 46, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tort, L.; Balasch, J.C.; Mackenzie, S. Fish immune system. A crossroads between innate and adaptive responses. Inmunología 2003, 22, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Pestka, S.; Krause, C.D.; Walter, M.R. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 202, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Huang, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, D.; Mo, T.; Liu, Q. The role of intestinal microbiota and metabolites in intestinal inflammation. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 288, 127838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.; Tyler, C.R.; Sumpter, J.P. Egg quality in fish: What makes a good egg? Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1997, 7, 387–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguila, A.A.; Mansir, A.T.; Manríquez, A.R. Using brine shrimp as a drug carrier for therapeutic applications in aquaculture. Aquacult. Eng. 1994, 13, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.P. Detection of Astragalus polysaccharide content by UV spectrophotometry. Mod. Livest. Technol. 2019, 8, 7–9, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Liu, X.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, X. Lactobacillus spp. as probiotics for prevention and treatment of enteritis in the lined seahorse (Hippocampus erectus) juveniles. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Sun, B.; Zhang, B.; Sun, L. Temperature induces metabolic reprogramming in fish during bacterial infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1010948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yin, F.; Lin, J. Criteria for assessing juvenile quality of the lined seahorse, Hippocampus erectus. Aquaculture 2011, 322, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardó, L.; Yin, G.; Xu, P.; Váradi, L.; Szigeti, G.; Jeney, Z.; Jeney, G. Chinese herbs (Astragalus membranaceus and Lonicera japonica) and boron enhance the non-speciffc immune response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 2008, 275, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Pan, X.; Gong, Y.; Xia, A.; Wu, G.; Tang, J.; Han, X. Effects of Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) on the expression of immune response genes in head kidney, gill and spleen of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Devi, G.; van Doan, H.; Tapingkae, W.; Balasundaram, C.; Arockiaraj, J.; Ringø, E. Changes in immune genes expression, immune response, digestive enzymes -antioxidant status, and growth of catla (Catla catla) fed with Astragalus polysaccharides against edwardsiellosis disease. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 121, 418–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.C.; Yusoff, F.M.; Shariff, M.; Kamarudin, M.S. Astaxanthin as feed supplement in aquatic animals. Rev. Aquacult. 2018, 10, 738–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Lu, G.; Yin, H.; Wang, L.; Atuganile, M.; Dong, Z. Fish pigmentation and coloration: Molecular mechanisms and aquaculture perspectives. Rev. Aquacult. 2021, 13, 2395–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissio, P.G.; Darias, M.J.; Di Yorio, M.P.; Pérez Sirkin, D.I.; Delgadin, T.H. Fish skin pigmentation in aquaculture: The inffuence of rearing conditions and its neuroendocrine regulation. Gen. Comp. Endocr. 2021, 301, 113662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Shen, F.; Jiang, K. Females increase reproductive investment when mated to less sexually attractive males in a serially monogamous fish. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrajabian, M.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. A review of Astragalus species as foodstuffs, dietary supplements, a traditional Chinese medicine and a part of modern pharmaceutical science. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 13371–13382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xie, L.; Shen, M.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J. Recent advances in Astragalus polysaccharides: Structural characterization, bioactivities and gut microbiota modulation effects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 153, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y. Polysaccharides influence human health via microbiota-dependent and -independent pathways. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1030063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yu, S.; Long, T.; Zhou, X.; Bao, Y. Astragalus polysaccharides exerts immunomodulatory effects via TLR4-mediated MyD88-dependent signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 17, 44822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.; Peng, Z.; Hu, B.; Rao, X.; Li, J. HMGB1 participates in LPS-induced acute lung injury by activating the AIM2 inflammasome in macrophages and inducing polarization of M1 macrophages via TLR2, TLR4, and RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lai, J. Astragalus polysaccharide: A review of its immunomodulatory effect. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2022, 45, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Immunomodulatory activities of polysaccharides from Ganoderma on immune effector cells. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, H. Effect of three kinds of polysaccharide on protease activity, amylase activity in intestine and hepatopancreas of allogynogenetic silver crucian carp. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2005, 14, 468–471, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Apper, E.; Weissman, D.; Respondek, F.; Guyonvarch, A.; Baron, F.; Boisot, P.; Rodiles, A.; Merrifield, D.L. Hydrolysed wheat gluten as part of a diet based on animal and plant proteins supports good growth performance of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer), without impairing intestinal morphology or microbiota. Aquaculture 2016, 453, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spragge, F.; Bakkeren, E.; Jahn, M.T.; Araujo, E.B.N.; Pearson, C.F.; Wang, X.; Pankhurst, L.; Cunrath, O.; Foster, K.R. Microbiome diversity protects against pathogens by nutrient blocking. Science 2023, 382, 6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Liu, W.; Fan, X.; Wen, D.; Wu, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, B. Pharmaceutical potential for bioactive plant polysaccharides in treating disease and gut dysbiosis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1183130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, E.A.; Côté, I.M. Monogamy in marine fishes. Biol. Rev. 2004, 79, 351–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D. Does the female seahorse still prefer her mating partner after a period of separation? J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, M.P.; Shields, R.J.; Bell, M.V.; Bromage, N.R. Lipid class and fatty acid composition of eggs of Atlantic halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus (L.), in relation to egg quality in captive broodstock. Aquac. Res. 1993, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, N.; Sawaguchi, S.; Nomura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Matsubara, T. Utilization of free amino acids, yolk protein and lipids in developing eggs and yolk-sac larvae of Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Aquaculture 2008, 282, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tank No. | Control | APS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mating Status | 1 Time (Day) | Mating Status | Time (Day) | |
| 1# | √ | 6 | − | |
| 2# | √ | 7 | √ | 6 |
| 3# | − | √ | 5 | |
| 4# | − | √ | 3 | |
| 5# | √ | 8 | − | |
| 6# | √ | 6 | √ | 7 |
| 7# | − | − | ||
| 8# | √ | 10 | √ | 6 |
| 9# | √ | 7 | √ | 5 |
| 10# | √ | 9 | √ | 3 |
| 11# | − | − | ||
| 12# | − | √ | 3 | |
| 13# | √ | 7 | √ | 5 |
| 14# | √ | 8 | √ | 4 |
| 15# | √ | 8 | − | |
| 16# | − | √ | 8 | |
| 17# | √ | 9 | √ | 4 |
| 18# | − | − | ||
| 19# | √ | 10 | − | |
| 20# | − | √ | 5 | |
| Total | 12 | 13 | ||
| Mean | 7.92 ± 1.38 | (p < 0.001) | 4.92 ± 1.55 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, T.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, K. Dietary Astragalus Polysaccharides Can Improve the Immune Capacity and Reproductive Performance of the Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectus). Biology 2025, 14, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070767
Li S, Liu X, Lin T, Ren Y, Zhang D, Jiang K. Dietary Astragalus Polysaccharides Can Improve the Immune Capacity and Reproductive Performance of the Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectus). Biology. 2025; 14(7):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070767
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Siping, Xin Liu, Tingting Lin, Yuanhao Ren, Dong Zhang, and Keji Jiang. 2025. "Dietary Astragalus Polysaccharides Can Improve the Immune Capacity and Reproductive Performance of the Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectus)" Biology 14, no. 7: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070767
APA StyleLi, S., Liu, X., Lin, T., Ren, Y., Zhang, D., & Jiang, K. (2025). Dietary Astragalus Polysaccharides Can Improve the Immune Capacity and Reproductive Performance of the Lined Seahorse (Hippocampus erectus). Biology, 14(7), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070767






