Coal Gangue Ecological Matrix Coupled with Microalgae for Soil Improvement and Plant Growth in Reclaimed Mining Areas
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Chemicals
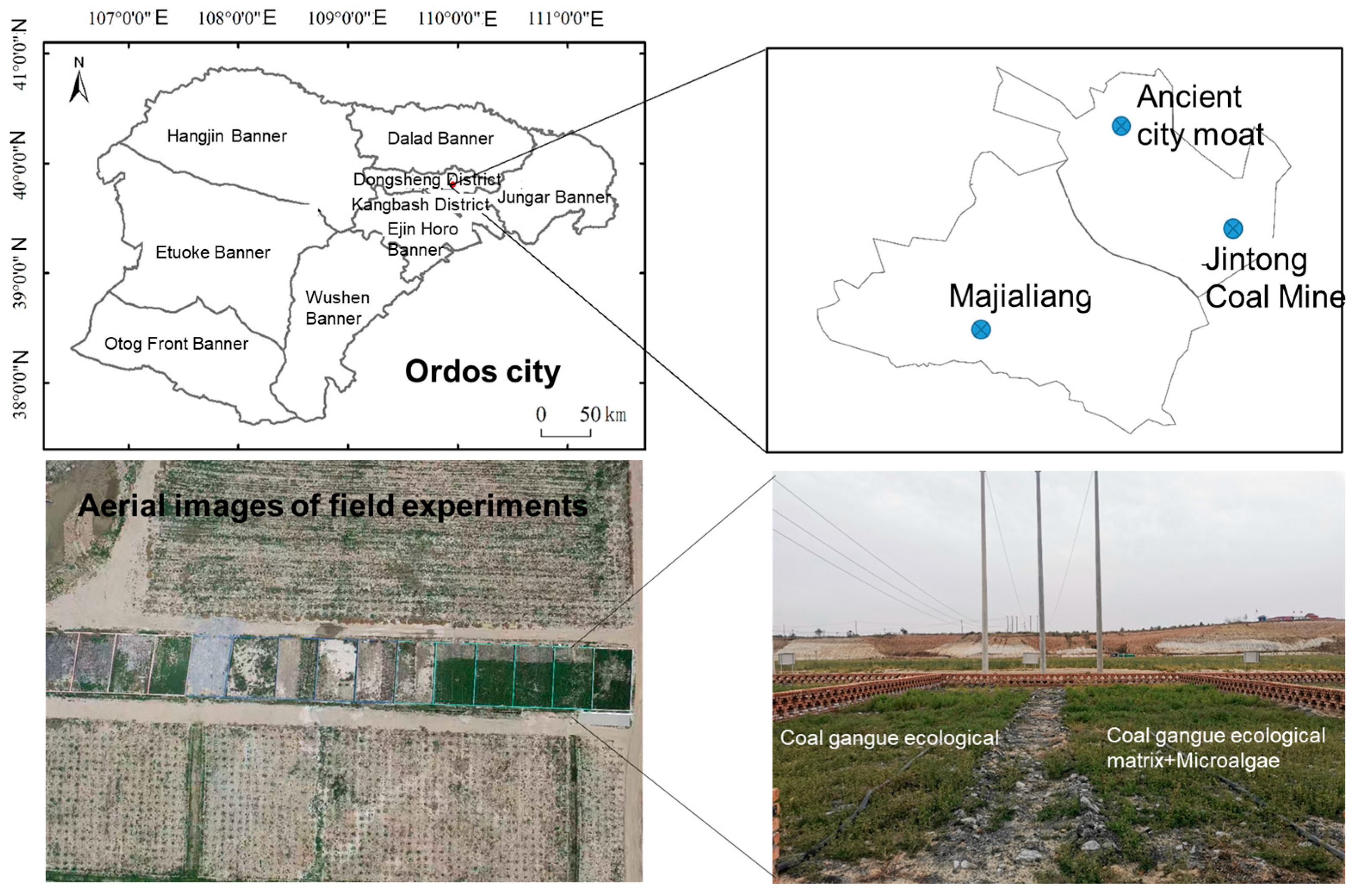
2.2. Field Experiment Design
2.3. Determination of Basic Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil
2.4. Enzyme Activity Assays
2.5. Soil Microbial Community Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
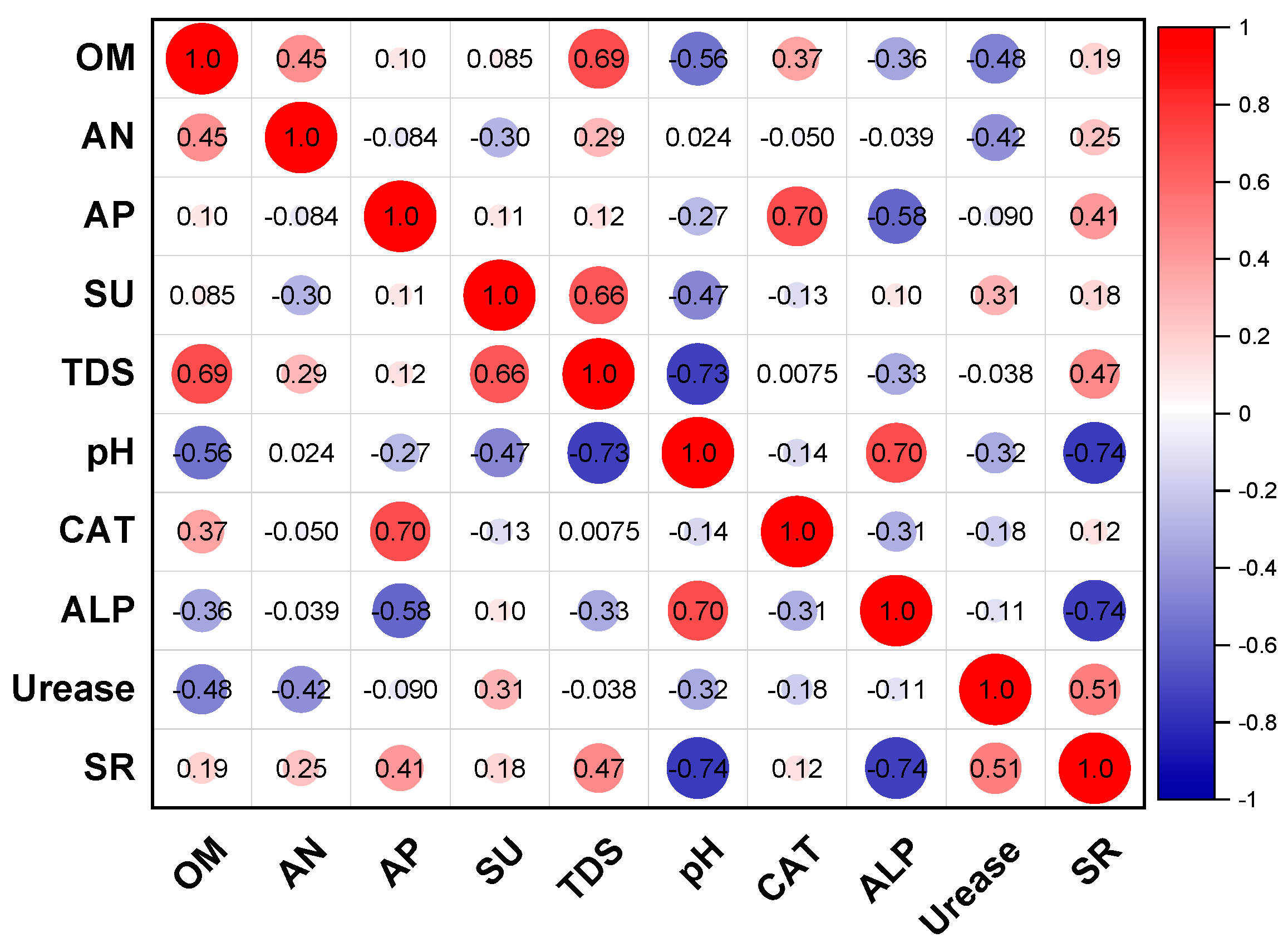
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Characteristics in Field Improvement Experiments
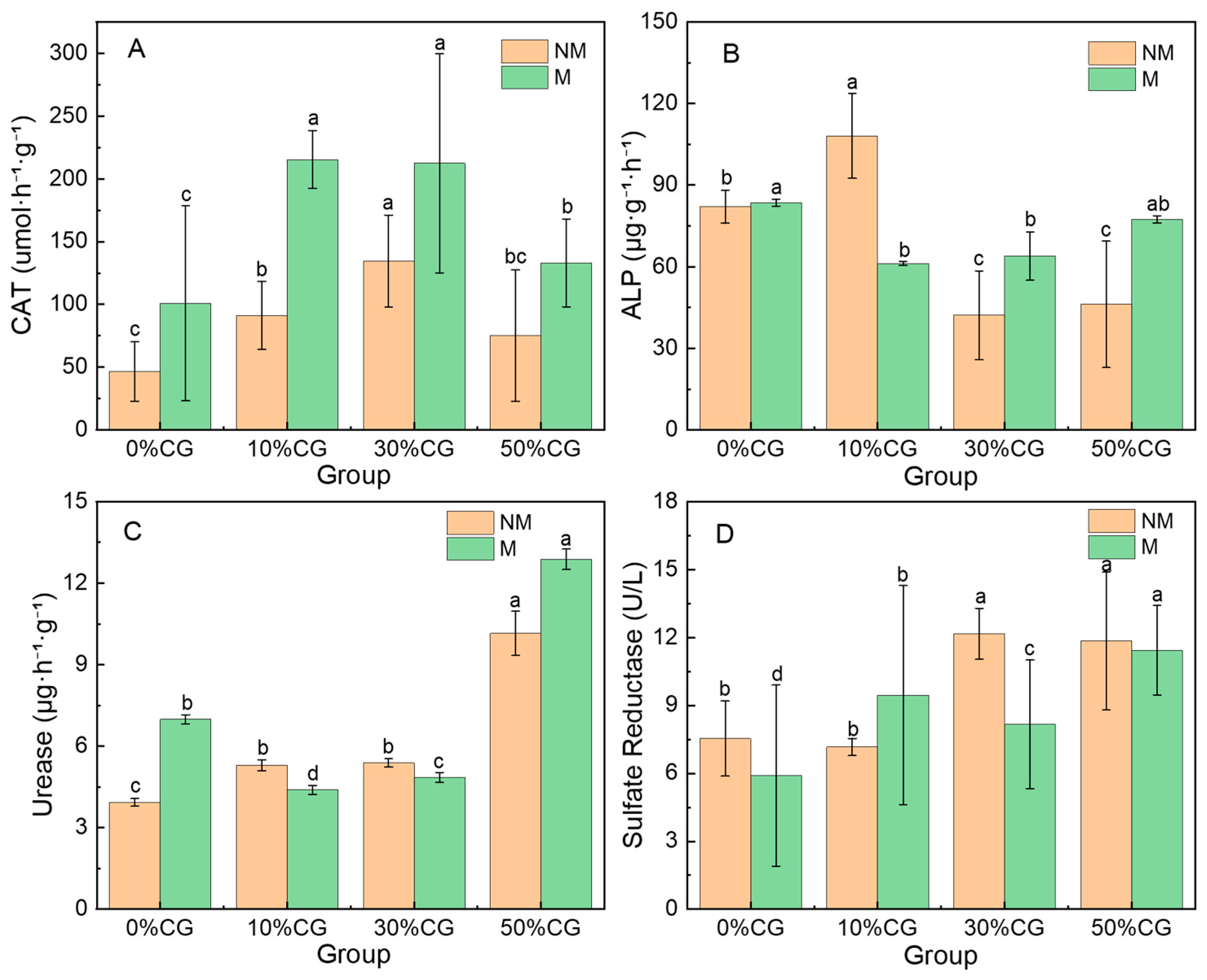
3.2. Effect on Soil Enzyme Activities by Improvement Strategy
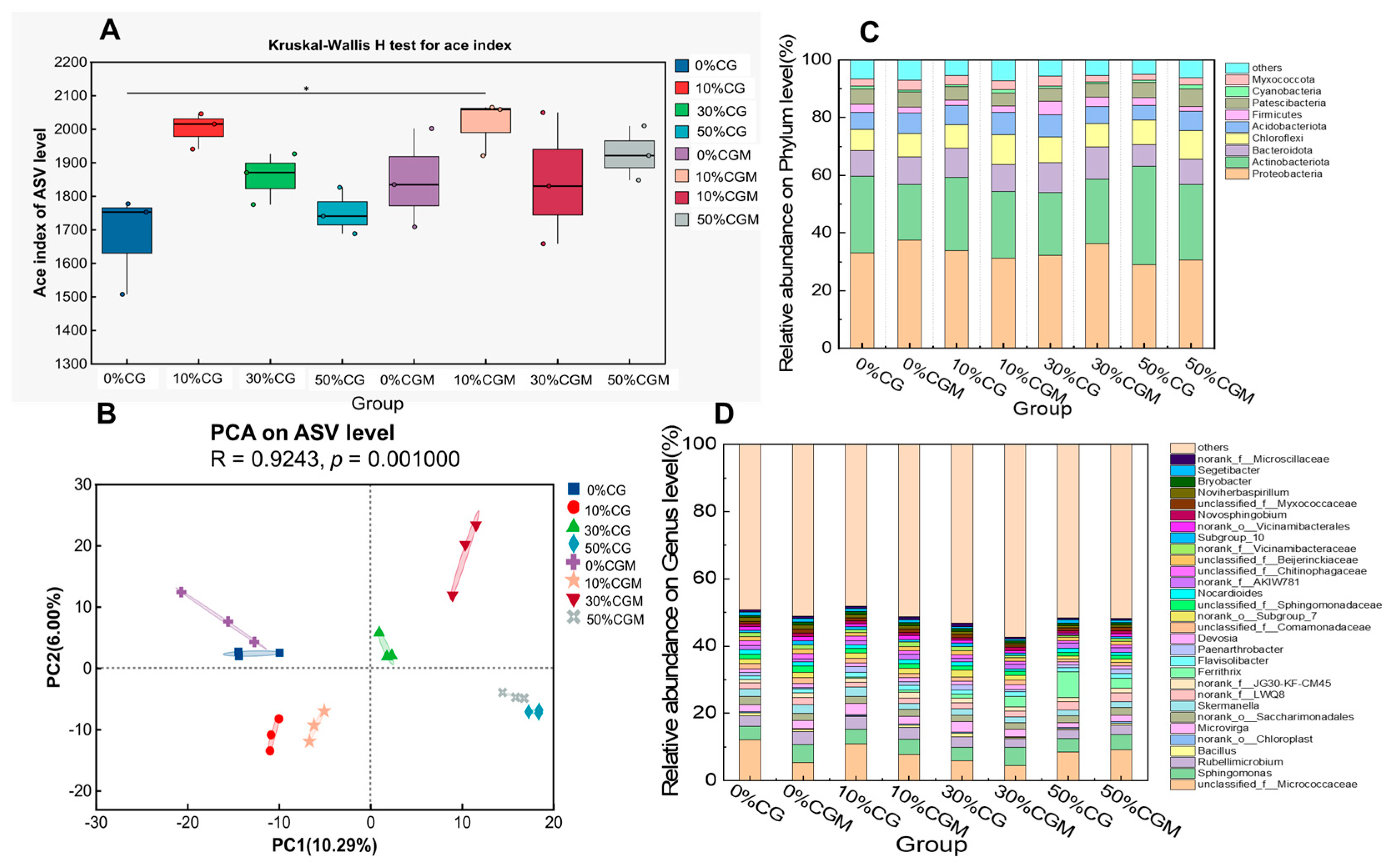
3.3. Effect of Improvement Strategy on Microbial Community Structure and Functions
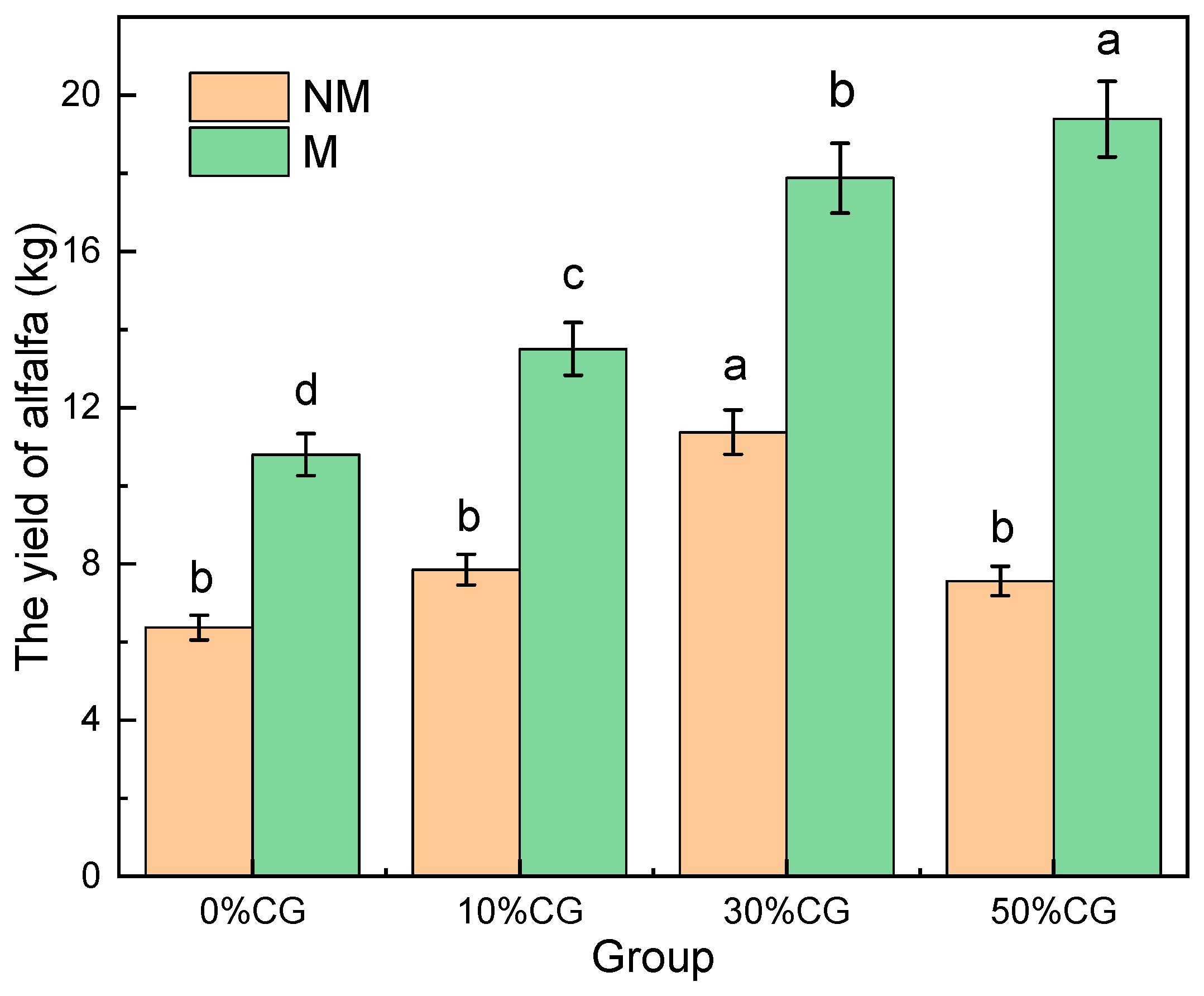
3.4. Growth Status of Plants in Different Groups
3.5. Mechanism of Soil Improvement by Coupling the Coal Gangue Ecological Matrix with Microalgae
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, X.X.; Li, J.; Shao, Y.; Ma, T.Y.; Zhang, R.; Su, Y.T. Assessing open-pit mining impacts on semi-arid grassland: A framework for boundary and intensity quantification. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 475, 143464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzehi, M.; Afrapoli, A.M. A novel framework for integrating environmental costs and carbon pricing in open-pit mine plans: Towards sustainable and green mining. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 468, 143059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Yu, X.Y.; Xu, D.M.; Peng, J. A spatial machine learning approach to exploring the impacts of coal mining and ecological restoration on regional ecosystem health. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.T.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.M.; Bai, Z.K.; Feng, X.M.; Chen, B.H. Optimal allocation of technical reclamation and ecological restoration for a cost-effective solution in Pingshuo Opencast Coal Mine area of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Cao, Y.G.; Geng, B.J.; Yang, K.; Bai, Z.K. Succession law and model of reconstructed soil quality in an open-pit coal mine dump of the loess area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ai, Z.M.; Dang, X.H.; Zhu, S.M.; Xiao, L. Effects of different reclamation measures on soil quality restoration in open-pit mines: A meta-analysis based on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 203, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, T.D. Sustainable contributions of the use of phosphorus, potassium, coal and natural stone mine wastes in soil improvement and agriculture—A review. Resour. Policy 2025, 102, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.B.; Song, C.W.; Yan, C.; Jin, Z.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Lai, C.Y.; Wang, D.H. The use of coal gangue as a planting substrate in arid mining areas. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 56, e03328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Liao, L.B.; Lv, G.C. Environmental hazards and comprehensive utilization of solid waste coal gangue. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2024, 2, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.W.; Liu, X.R.; Shi, Z.W.; Liu, L.; Fatima, M.; Wang, Z.G.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.Y. Enhancement of the utilization of coal gangue as mineral fertilizers by the thermophilic bacterium Bacillus aerius. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, S.H.; Ren, P.Y.; Yan, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, B.; Zhao, Y.M.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Gao, P.C.; et al. Enhancing the carbon content of coal gangue for composting through sludge amendment: A feasibility study. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 348, 123439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Hu, Z.Q.; Ruan, M.Y. Characteristics of sulfate-reducing bacteria and organic bactericides and their potential to mitigate pollution caused by coal gangue acidification. Environ. Technol. 2020, 20, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.B.; Gong, W.H.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.X. Fixating lead in coal gangue with phosphate using phosphate-dissolving bacteria: Phosphorus dissolving characteristics of bacteria and adsorption mechanism of extracellular polymer. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 458, 131923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.N.; Pei, X.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Wei, Y.P.; Ge, Y.; Naveed, S.; Wang, S.; Chang, M.X. The roles of bacteria in resource recovery, wastewater treatment and carbon fixation by microalgae-bacteria consortia: A critical review. Algal Res. 2023, 69, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.T.; Bo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Tan, Y.H.; Zhou, C.X.; Yan, X.J.; Ruan, R.; Xu, Q.S.; Cheng, P.F. Potential applications for multifunctional microalgae in soil improvement. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1035332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.D.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Li, M.; Whelan, M.J. Microbial community composition and activity controls phosphorus transformation in rhizosphere soils of the Yeyahu Wetland in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.T.; Zhao, X.; Luo, W.Q.; Yuan, J.J.; Guo, Y.L.; Ji, X.N.; Hu, W.; Li, M.; Teng, Z.D. Noval porous phosphate-solubilizing bacteria beads loaded with BC/nZVI enhanced the transformation of lead fractions and its microecological regulation mechanism in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babos, D.V.; Costa, V.C.; Pereira-Filho, E.R. Wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WD-XRF) applied to speciation of sulphur in mineral supplement for cattle: Evaluation of the chemical and matrix effects. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.D.; Zhao, X.; Jia, B.J.; Ye, L.J.; Tian, S.J.; Guo, H.Y.; Guo, Y.L.; Ji, X.N.; Li, T.G.; Li, M. Bioremediation system consisted with Leclercia adecarboxylata and nZVI@Carbon/Phosphate for lead immobilization: The passivation mechanisms of chemical reaction and biological metabolism in soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 117888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Feng, Q.Y.; Southam, G.; Jin, T.; Li, Z. Changes in microbial community structure during the biooxidation of iron and inorganic/organic sulfur provide prediction of acid mine drainage from coal spoil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.Y.; Honda, K.; Derek, C.J.C. A review on microalgal-bacterial co-culture: The multifaceted role of beneficial bacteria towards enhancement of microalgal metabolite production. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xu, Z.; Yang, W.; Tang, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, D.L.; Prasanna, P.; Qu, Z.Y. Co-application of microalgae and biochar increases yield and mitigates greenhouse gas emissions in saline-alkali soil. Field Crops Res. 2025, 327, 109885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Jiang, H.; Yang, X.K.; Zhang, X.W.; Wu, Y.K.; Ye, N.H.; Liang, C.W. Application of microalgae in remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils and its stimulatory effect on wheat growth. Algal Res. 2025, 88, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.X.; Liu, W.; Duan, H.J.; Dong, H.W.; Li, J.C.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S.G.; Xu, T.T.; Guo, B.B. Improved effects of combined application of nitrogen-fixing bacteria Azotobacter beijerinckii and microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa on wheat growth and saline-alkali soil quality. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.K.; Wang, S.R.; Cai, J.J.; Li, H.; Jenkins, A.; Maberly, S.C.; May, L. The potential role of sediment organic phosphorus in algal growth in a low nutrient lake. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Mang, Q.; Li, Q.J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G.C. Microbial-algal symbiotic system drives reconstruction of nitrogen, phosphorus, and methane cycles for purification of pollutants in aquaculture water. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 430, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Huang, X.D.; Chen, W.T.; Fu, G.K.; Zhang, Z. Microalgae-assisted heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification process for cost-effective nitrogen and phosphorus removal from high-salinity wastewater: Performance, mechanism, and bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 390, 129901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Liang, W.D. Preparation of technosol based on coal gangue and its impact on plant growth in coal mining area. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 142998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.T. Recent advances in microalgae-driven carbon capture, utilization, and storage: Strain engineering through adaptive laboratory evolution and microbiome optimization. Green Carbon 2025, 3, 74–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.J.; Wang, H.S.; Wang, Z.X.; Liu, J.Z.; Li, Y.T.; Xia, L.; Song, S.X. Critical steps in the restoration of coal mine soils: Microbial-accelerated soil reconstruction. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.Y.; Han, L.; Li, P.F.; Li, Q.D.; Xie, L.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Kong, J.R.; Jia, R.; Li, D.Y.; Yang, G.P. The sulfate assimilation and reduction of marine microalgae and the regulation of illumination. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 191, 106156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.L.; Weyers, S.L.; Goemann, H.M.; Peyton, B.M. Microalgae, soil and plants: A critical review of microalgae as renewable resources for agriculture. Algal Res. 2021, 54, 102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhasheesh, Y.; Hasan, S.W.; Ghazal, A.; Show, P.L.; Tang, D.Y.Y.; Banat, F. Green strategies for enhanced microalgae processes: Leveraging bio-derived adsorbents, green solvents, and synthetic biology. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.Q.; Wang, J.; Duan, X.C.; Zou, M.Y.; Du, J.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Lu, G.N. Interactions between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)-degrading strain Sphingomonas sp. GY2B and nano bamboo charcoal. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 211, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.R.; Zhang, S.S.; Wang, R.; An, Z.J.; Sun, F.Q.; Shen, C.F.; Lin, H.J.; Su, X.M. A novel strategy for enhancing bioremediation of polychlorinated biphenyl-contaminated soil with resuscitation promoting factor and resuscitated strain. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 447, 13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.M.; Hu, J.M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhao, G.Y. Investigation on the action mechanisms of taurine on rumen microbial protein synthesis and nitrogen metabolism in beef steers using sodium sulfate as a contrast. Anim. Nutr. J. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.S.; Wang, Y.W.; Yang, X.; Lai, J.L.; Luo, X.G. Effects of long-term (10 years) remediation of Caragana on soil enzyme activities, heavy metals, microbial diversity and metabolic spectrum of coal gangue. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 181, 106679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, J.; Mal, J.; Singh, S.; Yadav, A.; Giri, B.S.; Pandey, A.; Sinha, R. Bioprospecting marine microalgae as sustainable bio-factories for value-added compounds. Algal Res. 2024, 79, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lu, M.T.; He, X.X.; Wan, Y.; Yu, X.J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Cai, M.M.; Yu, C. Eco-friendly utilization and microbiological characteristics of coal gangue substrate via functional microbial fermentation. Environ. Res. 2025, 271, 121035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, K.T.; Sun, Z.Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, G.Q.; Fan, C.X.; Lin, Z.B. Effects of microtopographic modification on soil labile organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities in urban restored wetlands. Effects of microtopographic modification on soil labile organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities in urban restored wetlands. Pedosphere 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ai, Z.P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Leng, P.F.; Qiao, Y.F.; Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Cheng, H.F.; Chen, G.; Li, F.D. Influence of long-term inorganic fertilization and straw incorporation on soil organic carbon: Roles of enzyme activity, labile organic carbon fractions, soil aggregates, and microbial traits. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 392, 109758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.T.; Tian, H.X.; Huang, Y.; Mu, X.L.; Tang, G.M.; Ma, H.G.; Megharaj, M.; Xu, W.L.; He, W.X. Recycled wheat straw biochar enhances nutrient-poor soil: Enzymatic kinetics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycling. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 124950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.K.; Jin, H.Y.; Zhang, C.; Lin, L.; Guo, X.Y.; Wang, A.B.; Shi, J.; Yao, X.H.; Gao, H.W. Alkaline phosphatase-mediated hydrolysis of dissolved organic phosphorus enhances phosphorus cycling in the Yellow Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 371, 125902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.L.; Dong, P.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, H.X.; Zhang, L.D.; Wang, H. Effects of filling substrates on remediation performance and sulfur transformation of sulfate reducing packed-bed bioreactors treating acid mine drainage. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 123026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Sun, J.; Han, L.F.; Liu, W.T.; Ding, Y.H. Microplastics regulate soil microbial activities: Evidence from catalase, dehydrogenase, and fluorescein diacetate hydrolase. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.F.; Yao, J.; Li, M.M.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, H.Q.; Jiang, S.; Tang, C.Y.; Sunahara, G.; Li, H.; Ma, B.; et al. Impact of steel slag, gypsum, and coal gangue on microbial immobilization of metal(loid)s in non-ferrous mine waste dumps. J. Hazard Mater. 2024, 480, 135750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Group | Primitive Soil | Soil Containing 10% Coal Gangue | Soil Containing 30% Coal Gangue | Soil Containing 50% Coal Gangue | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM | M | NM | M | NM | M | NM | M | |
| Group Name | 0% CG | 0% CGM | 10% CG | 10% CGM | 30% CG | 30% CGM | 50% CG | 50% CGM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Li, J.; Du, D.; Li, H.; Hao, J.; Teng, Z.; Ji, X. Coal Gangue Ecological Matrix Coupled with Microalgae for Soil Improvement and Plant Growth in Reclaimed Mining Areas. Biology 2025, 14, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070741
Yu S, Li J, Du D, Li H, Hao J, Teng Z, Ji X. Coal Gangue Ecological Matrix Coupled with Microalgae for Soil Improvement and Plant Growth in Reclaimed Mining Areas. Biology. 2025; 14(7):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070741
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shuyu, Jinning Li, Dandan Du, Hao Li, Jiayong Hao, Zedong Teng, and Xiang Ji. 2025. "Coal Gangue Ecological Matrix Coupled with Microalgae for Soil Improvement and Plant Growth in Reclaimed Mining Areas" Biology 14, no. 7: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070741
APA StyleYu, S., Li, J., Du, D., Li, H., Hao, J., Teng, Z., & Ji, X. (2025). Coal Gangue Ecological Matrix Coupled with Microalgae for Soil Improvement and Plant Growth in Reclaimed Mining Areas. Biology, 14(7), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070741






