3-Hydroxyacyl CoA Dehydratase 2 Is Essential for Embryonic Development and Hepatic Metabolic Function Under a Low-Fat, High-Carbohydrate Diet
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Hacd2−/− and Hacd2LKO Mice and Housing Conditions
2.2. Experimental Mouse Design
2.3. Embryo Acquisition and Analysis
2.4. Low Fat and High Carbohydrate Diet and Feeding
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Fatty Acid Methyl Ester (FAME) Analysis
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Analysis
2.8. Metabolic Phenotyping by Indirect Calorimetry
2.9. Metabolic Measurements
2.10. Biochemical Analyses
2.11. Flow Cytometry
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Germline Deletion of Hacd2 Causes Embryonic Lethality
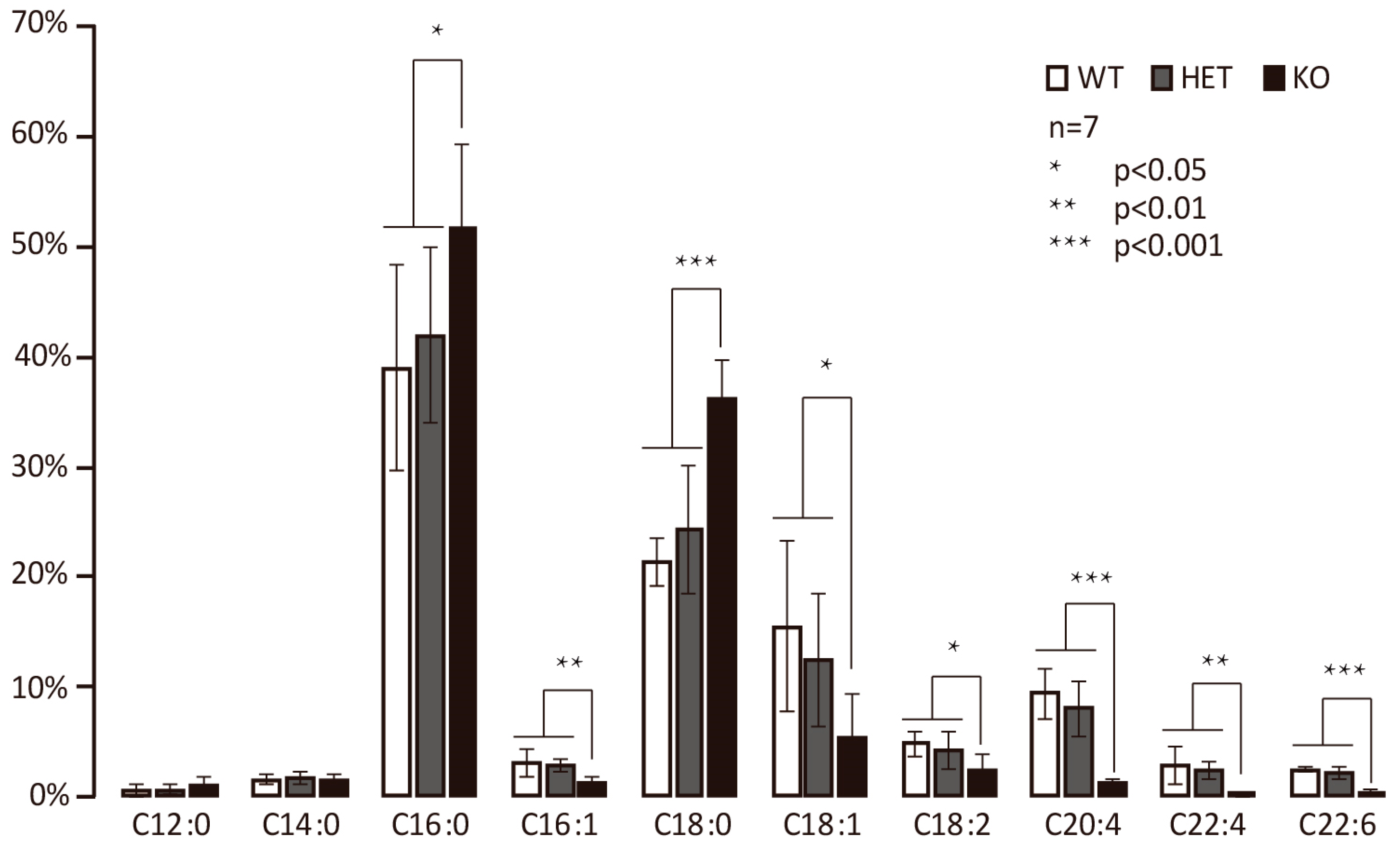
3.2. Hacd2 Knockout Impairs Elongation of C18 to C20 Fatty Acids in Mice
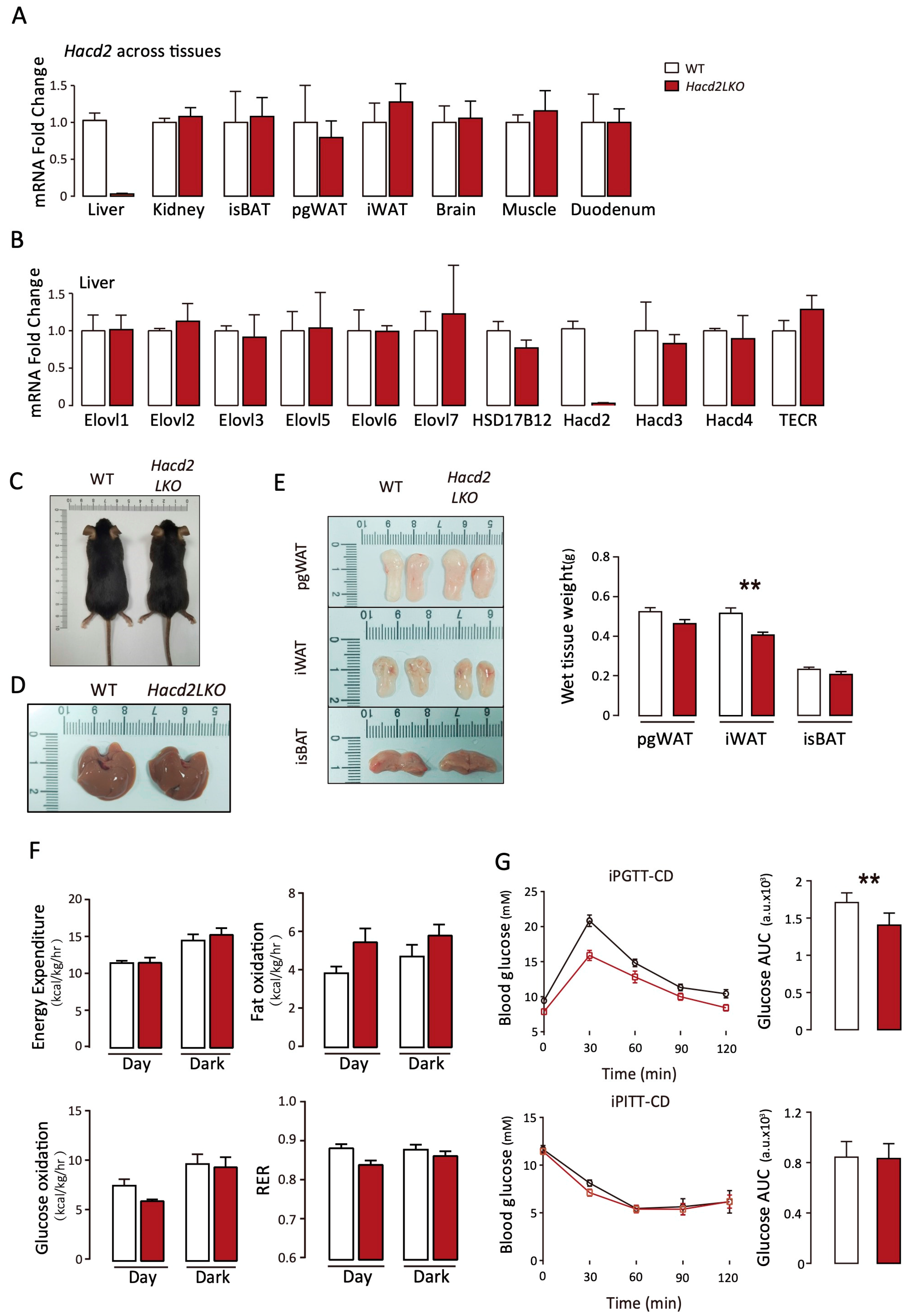
3.3. Liver-Specific Hacd2 Deficiency Affects iWAT Formation and Glucose Under Chow Diet
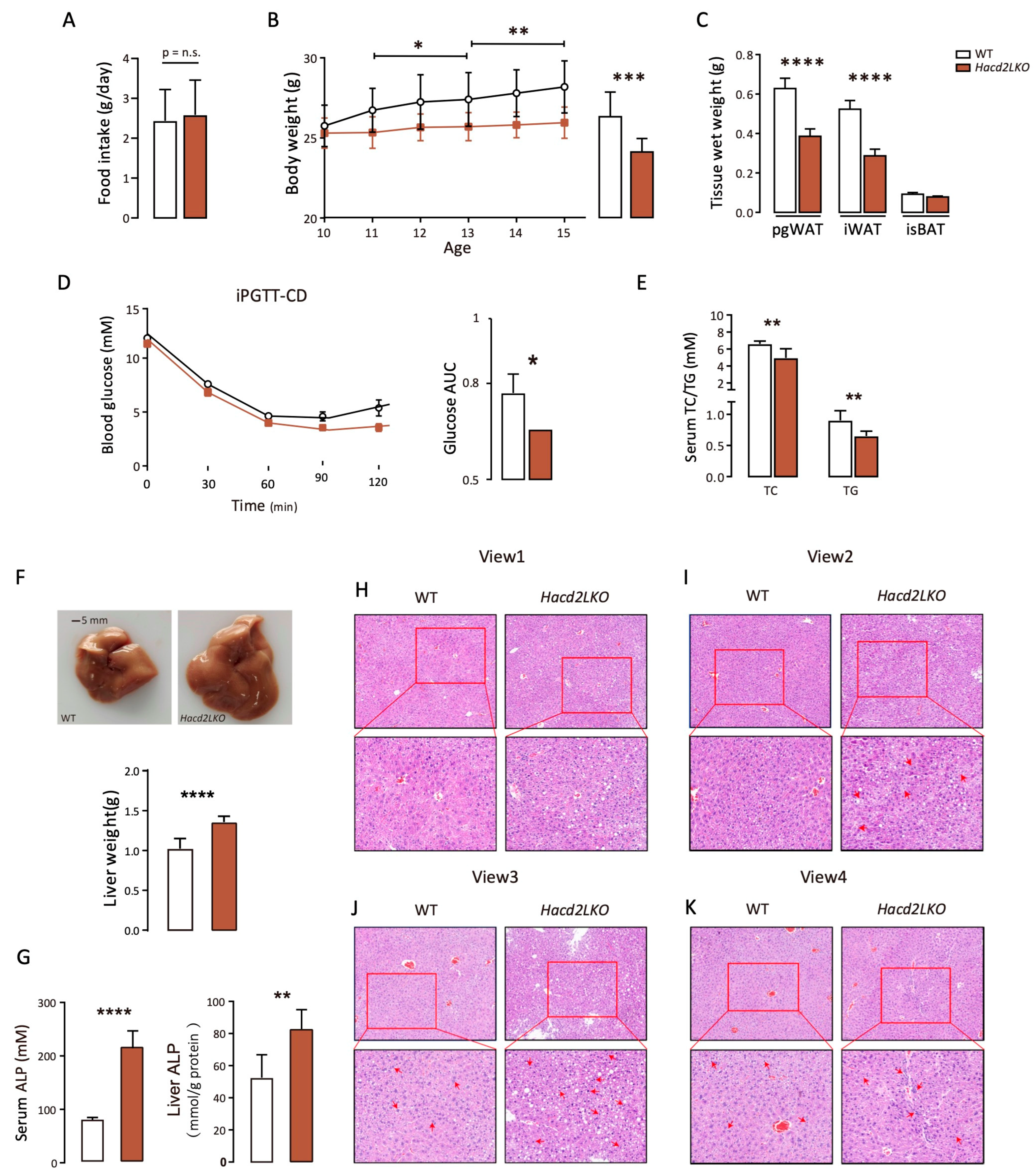
3.4. Liver-Specific Hacd2 Deficiency Impairs Hepatic Metabolic Homeostasis and Function Under an LFHCD
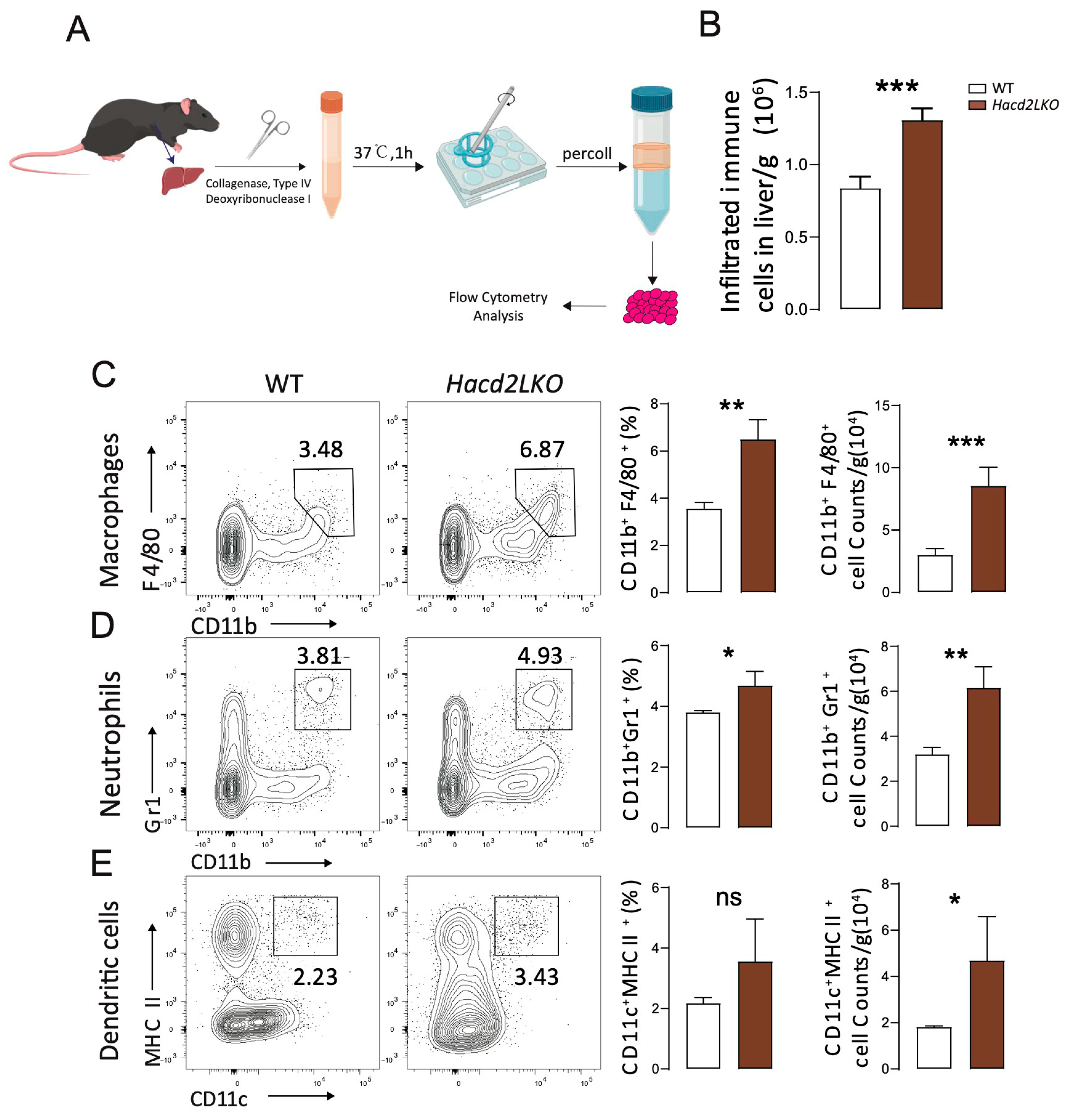
3.5. Hacd2 Deficiency Causes Liver Damage with Inflammation Under an LFHCD
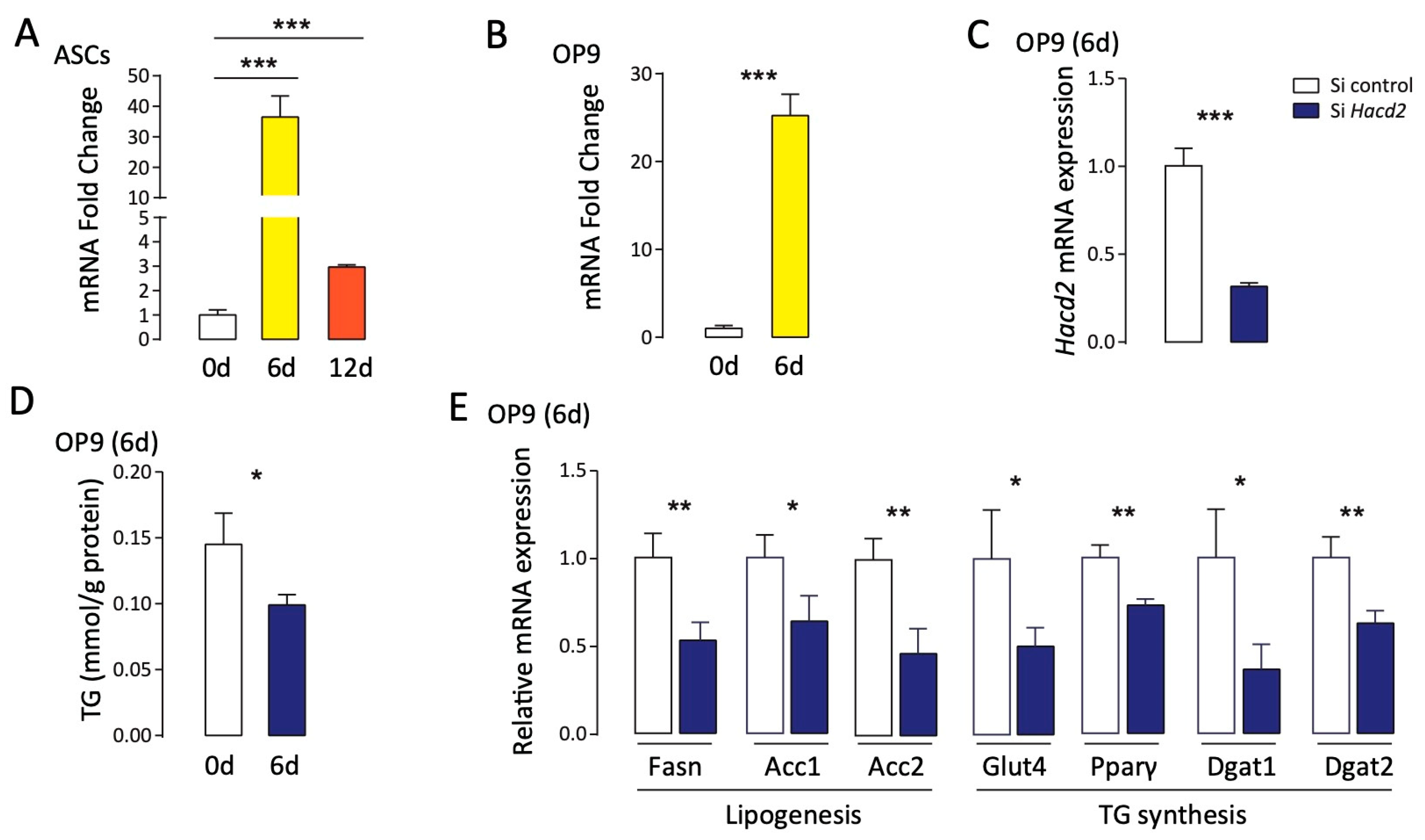
3.6. Hacd2 Is Essential for Triglyceride Synthesis During Adipocyte Differentiation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Dong, G. The Implications of FASN in Immune Cell Biology and Related Diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lv, R.; Ye, R.D.; Ren, R.; Yu, L. The 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydratase 1/2 Form Complex with Trans-2-Enoyl-CoA Reductase Involved in Substrates Transfer in Very Long Chain Fatty Acid Elongation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 704, 149588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Weng, S.; Lu, X.; Zhu, S.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.Q. 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydratase 2 Deficiency Confers Resistance to Diet-Induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 605, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Y. HACD2 Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression by Enhancing PKM2 Dissociation from PRKN in a Dehydratase-Independent Manner. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 2025, 12, e2407942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipitone, R.M.; Ciccioli, C.; Infantino, G.; La Mantia, C.; Parisi, S.; Tulone, A.; Pennisi, G.; Grimaudo, S.; Petta, S. MAFLD: A Multisystem Disease. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 14, 20420188221145549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Yilmaz, Y. Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): A Multi-Systemic Disease Beyond the Liver. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, B.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.Q. Lactobacillus Plantarum ZS2058 Produces CLA to Ameliorate DSS-Induced Acute Colitis in Mice. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14457–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.Q. Multi-Dimensional, Comprehensive Sample Extraction Combined with LC-GC/MS Analysis for Complex Biological Samples: Application in the Metabolomics Study of Acute Pancreatitis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25837–25849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péronnet, F.; Massicotte, D. Table of Nonprotein Respiratory Quotient: An Update. Can. J. Sport Sci. 1991, 16, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeley, C.C.; Holland, J.F.; Towson, D.S.; Chamberlin, B.A. Interactive and Multi-Sensory Analysis of Complex Mixtures by an Automated Gas Chromatography System. J. Chromatogr. 1987, 399, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, X.; Wang, S.; Fulte, S.; Ma, X.; Ahamed, F.; Cui, W.; Liu, Z.; Rülicke, T.; Zatloukal, K.; Zong, W.-X.; et al. Hepatocytic P62 Suppresses Ductular Reaction and Tumorigenesis in Mouse Livers with mTORC1 Activation and Defective Autophagy. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Mu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Wu, J.; Tang, H.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Generic Diagramming Platform (GDP): A Comprehensive Database of High-Quality Biomedical Graphics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1670–D1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Lee, J.N.; Kim, Y.-I.; Nam, I.-K.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; Kwak, S.; Oh, G.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Yoo, H.J.; et al. The Fatty Acid Chain Elongase, Elovl1, Is Required for Kidney and Swim Bladder Development during Zebrafish Embryogenesis. Organogenesis 2016, 12, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantakari, P.; Lagerbohm, H.; Kaimainen, M.; Suomela, J.-P.; Strauss, L.; Sainio, K.; Pakarinen, P.; Poutanen, M. Hydroxysteroid (17{beta}) Dehydrogenase 12 Is Essential for Mouse Organogenesis and Embryonic Survival. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokela, H.; Rantakari, P.; Lamminen, T.; Strauss, L.; Ola, R.; Mutka, A.-L.; Gylling, H.; Miettinen, T.; Pakarinen, P.; Sainio, K.; et al. Hydroxysteroid (17beta) Dehydrogenase 7 Activity Is Essential for Fetal de Novo Cholesterol Synthesis and for Neuroectodermal Survival and Cardiovascular Differentiation in Early Mouse Embryos. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, Y.; Sheng, H.; Xu, G.; Jin, H.; Iqbal, T.; Elashry, M.; Zhang, K. Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Key Regulators of Bovine Oocyte Maturation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; He, M.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Qin, R.; Ye, D.; Zhai, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, P.; et al. Intestinal DHA-PA-PG Axis Promotes Digestive Organ Expansion by Mediating Usage of Maternally Deposited Yolk Lipids. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadhraoui, N.; Prola, A.; Vandestienne, A.; Blondelle, J.; Guillaud, L.; Courtin, G.; Bodak, M.; Prost, B.; Huet, H.; Wintrebert, M.; et al. Hacd2 Deficiency in Mice Leads to an Early and Lethal Mitochondrial Disease. Mol. Metab. 2023, 69, 101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, A.H.; Costa, A.B.; Engel, J.D.G.; Rezin, G.T. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Obesity. Life Sci. 2018, 192, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Li, H.; Liao, P.; Chen, L.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Zheng, M.; Gao, J. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Mechanisms and Advances in Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-H.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y.-T.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Tan, J.; Guo, K.; Liu, Y.-T.; Zhao, S.-H.; Ning, Y.-Q.; et al. Interaction of PASTICCINO2 with Golgi Anti-Apoptotic Proteins Confers Resistance to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Is Dependent on Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acids. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 7267–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, W.D.; Green, P.G.; Lewis, A.J.M.; Arvidsson, P.; De Maria, G.L.; Arheden, H.; Heiberg, E.; Clarke, W.T.; Rodgers, C.T.; Valkovič, L.; et al. Retained Metabolic Flexibility of the Failing Human Heart. Circulation 2023, 148, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Gu, X.; Liu, X.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Huang, Z. Long-Chain Fatty Acids—The Turning Point between “mild” and “Severe” Acute Pancreatitis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talabieke, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Wan, Q.; Zhu, D.; Rao, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, P.; et al. Arachidonic Acid Synergizes with Aspirin Preventing Myocardial Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury and Mitigates Bleeding Risk. Cardiovasc. Res. 2025, 121, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, B.N.; Guhathakurta, S.; Tsang, T.H.; Schwabenland, M.; Renschler, G.; Herquel, B.; Bhardwaj, V.; Holz, H.; Stehle, T.; Bondareva, O.; et al. Neural Metabolic Imbalance Induced by MOF Dysfunction Triggers Pericyte Activation and Breakdown of Vasculature. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-Y.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Qiu, J.-G.; Lei, J.-X.; Li, M.-X.; Xu, N.; Liu, Y.-H.; Jin, Z.; Su, Z.-R.; Lee, S.M.-Y.; et al. Huangqin Decoction Ameliorates Ulcerative Colitis by Regulating Fatty Acid Metabolism to Mediate Macrophage Polarization via Activating FFAR4-AMPK-PPARα Pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 311, 116430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, S.; Vetuschi, A.; Gaudio, E.; Tessitore, A.; Capelli, R.; Alesse, E.; Latella, G.; Sferra, R.; Onori, P. Long-Term Abuse of a High-Carbohydrate Diet Is as Harmful as a High-Fat Diet for Development and Progression of Liver Injury in a Mouse Model of NAFLD/NASH. Nutrition 2020, 75–76, 110782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozawa, S.; Honda, A.; Kajiwara, N.; Takemoto, Y.; Nagase, T.; Nikami, H.; Okano, Y.; Nakashima, S.; Shimozawa, N. Induction of Peroxisomal Lipid Metabolism in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, G.; Tian, J.; Gong, W.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Xie, W.; et al. Dietary Betaine Attenuates High-Carbohydrate-Diet-Induced Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, Q.; Qu, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, L.; Wang, J. High-Carbohydrate Diet Consumption Poses a More Severe Liver Cholesterol Deposition than a High-Fat and High-Calorie Diet in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Q.; Li, L.-L.; Hu, A.; Deng, G.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.-F.; Liu, Y.-B.; Lu, X.-Y.; Qiu, Z.-P.; Shi, X.-J.; et al. Inhibition of ASGR1 Decreases Lipid Levels by Promoting Cholesterol Excretion. Nature 2022, 608, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Mating Genotype | Progeny Genotypes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hacd2+/+ | Hacd2+/− | Hacd2−/− | |
| ♂ WT♀Hacd2+/− | 68 | 72 | 0 |
| ♂ Hacd2+/−♀WT | 68 | 66 | 0 |
| ♂ Hacd2+/−♀Hacd2+/− | 169 | 272 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Wang, F.; Hua, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, K. 3-Hydroxyacyl CoA Dehydratase 2 Is Essential for Embryonic Development and Hepatic Metabolic Function Under a Low-Fat, High-Carbohydrate Diet. Biology 2025, 14, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060712
Wei L, Wang F, Hua L, Wang Q, Hu B, Yang Z, Li L, Liu C, Wang K. 3-Hydroxyacyl CoA Dehydratase 2 Is Essential for Embryonic Development and Hepatic Metabolic Function Under a Low-Fat, High-Carbohydrate Diet. Biology. 2025; 14(6):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060712
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Lengyun, Fengli Wang, Luoxue Hua, Qun Wang, Benfei Hu, Ziye Yang, Letao Li, Chenfeng Liu, and Kezhen Wang. 2025. "3-Hydroxyacyl CoA Dehydratase 2 Is Essential for Embryonic Development and Hepatic Metabolic Function Under a Low-Fat, High-Carbohydrate Diet" Biology 14, no. 6: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060712
APA StyleWei, L., Wang, F., Hua, L., Wang, Q., Hu, B., Yang, Z., Li, L., Liu, C., & Wang, K. (2025). 3-Hydroxyacyl CoA Dehydratase 2 Is Essential for Embryonic Development and Hepatic Metabolic Function Under a Low-Fat, High-Carbohydrate Diet. Biology, 14(6), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060712







