Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies TNF and IL1B as Candidate Key Early-Response Genes in Macrophages Infected with Smooth Brucella Using a Comprehensive Bioinformatic Approach
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. DEGA of DEGs
2.4. GSEA of KEGG Pathways
2.5. PPI Network and Analysis
3. Results
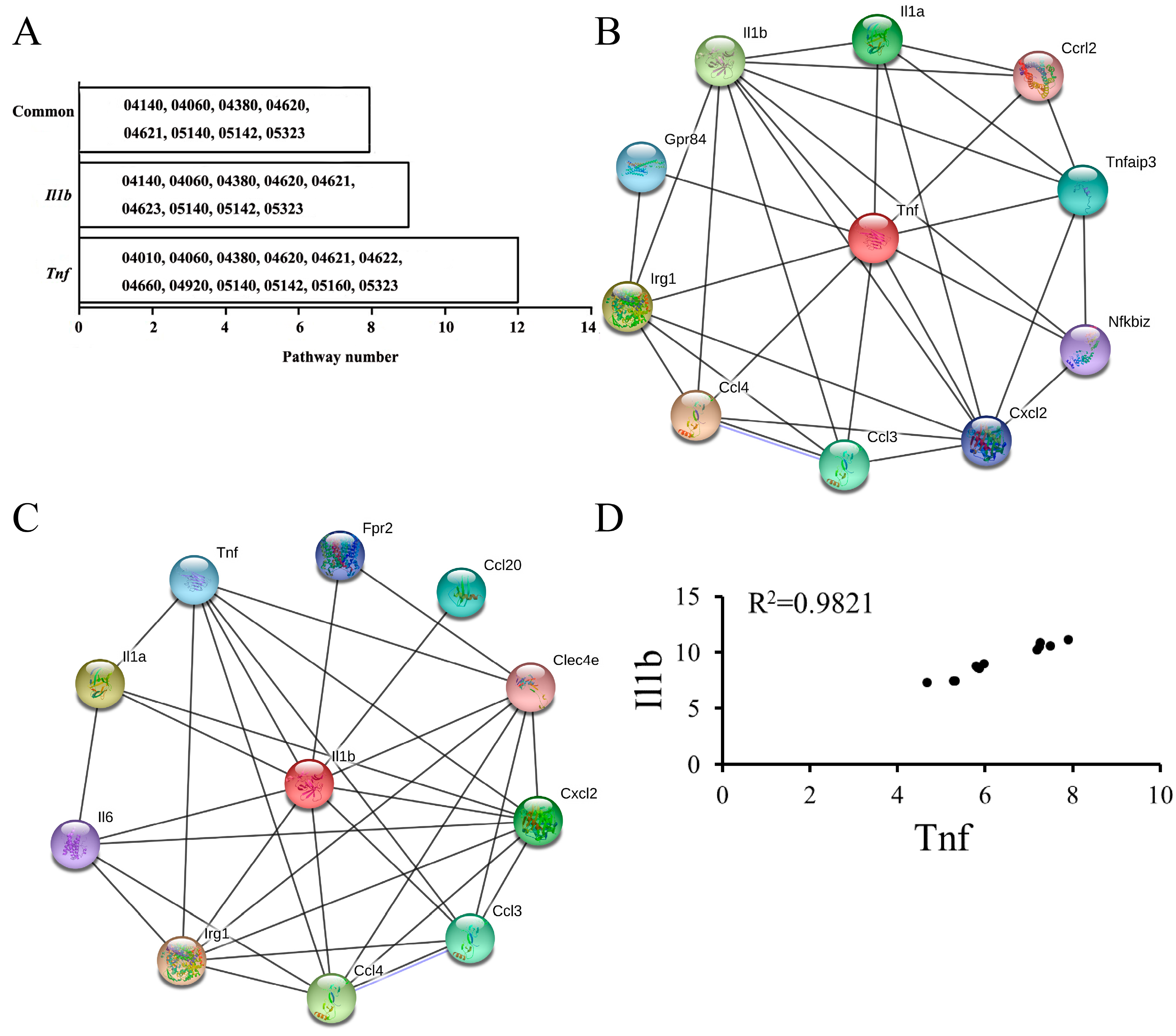
3.1. KEGG Pathways Identification
3.2. DEG Identification and Functional Analyses
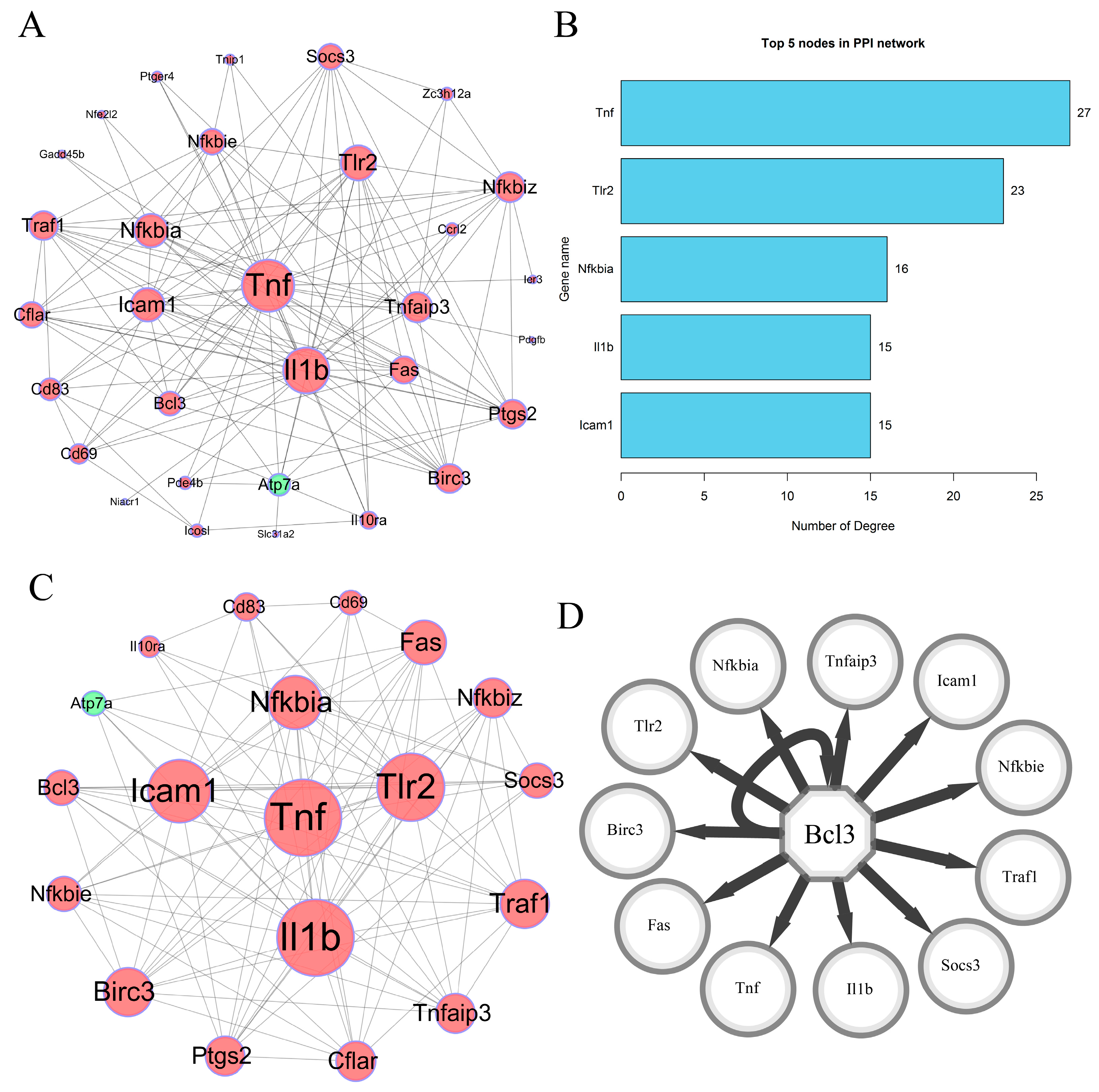
3.3. PPI Network Construction
3.4. Highly Correlated Module Analysis and Essential Gene Identification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.; Ding, X.; Ding, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Li, X.; Ghosh, D.; Schurig, G.G.; Sriranganathan, N.; Boyle, S.M.; He, Y. Proinflammatory Caspase-2-Mediated Macrophage Cell Death Induced by a Rough Attenuated Brucella Suis Strain. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, K.A.; Parvez, A.; Fahmy, N.A.; Hady, B.H.A.; Kumar, S.; Ganguly, A.; Atiya, A.; Elhassan, G.O.; Alfadly, S.O.; Parkkila, S.; et al. Brucellosis: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment—A Comprehensive Review. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2295398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Fan, Z.; Gao, R.; Li, X.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Research Progress on Complications of Brucellosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1136674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, C.G.; Scott, H.M.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Human Brucellosis: Widespread Information Deficiency Hinders an Understanding of Global Disease Frequency. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, C.G.; Johnson, V.E.; Scott, H.M.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Global Estimate of Human Brucellosis Incidence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.C.; Tatum, F.M. Swine Brucellosis: Current Perspectives. Vet. Med. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacka, P.; Zakowska, D.; Naylor, K.; Niemcewicz, M.; Bielawska-Drozd, A. Brucella—Virulence Factors, Pathogenesis and Treatment. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.B.; Kostoulas, P.; Gill, J.P.S.; Dhand, N.K. Cost-Benefit Analysis of Intervention Policies for Prevention and Control of Brucellosis in India. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.-B.; Lu, Q.-S.; Wang, L.-L.; Aishan, M.; Zhao, J.-S.; Tang, X.-Y.; Zhu, M.-T.; Reheman, M.; Chen, Q.-L.; Zhang, Y.-P. The Economic Burden of Brucellosis Care in China: Socioeconomic Status Inequality. J. Trop. Med. 2024, 2024, 7992287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, X.; Duan, K.; Peng, Q. Research Progress on Brucellosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 5598–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, E.E. Pediatric Brucellosis. An Update Review for the New Millennium. Saudi Med. J. 2018, 39, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, V.R.; Bowen, R.A.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M. Zoonotic Pathogens from Feral Swine That Pose a Significant Threat to Public Health. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, S.M.; Peterson-Burch, B.D.; Bricker, B.J.; Zuerner, R.L.; Qing, Z.; Li, L.-L.; Kapur, V.; Alt, D.P.; Olsen, S.C. Completion of the Genome Sequence of Brucella Abortus and Comparison to the Highly Similar Genomes of Brucella Melitensis and Brucella Suis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2715–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, T.; Jin, Y.; Wang, A. Lipopolysaccharides of Brucella Suis S2 Impaired the Process of Decidualization in Early Pregnancy in Mice. Toxins 2023, 15, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifahmadian, M.; Arya, T.; Bessette, B.; Lecoq, L.; Ruediger, E.; Omichinski, J.G.; Baron, C. Monomer-to-Dimer Transition of Brucella Suis Type Iv Secretion System Component Virb8 Induces Conformational Changes. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1218–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.Y.; Abdullah, F.F.J.; Kadir, A.A.; Saharee, A.A. Immuno-Pathophysiological Responses of Mouse Model to Experimental Infection with Brucella Melitensis and Its Lipopolysaccharides Via Intraperitoneal Route. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 100, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Tian, M.; Zhang, G.; Ding, C.; Yu, S. A Novel Brucella T4ss Effector Rs15060 Acts on Bacterial Morphology, Lipopolysaccharide Core Synthesis and Host Proinflammatory Responses, Which Is Beneficial for Brucella Melitensis Virulence. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 292, 128015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Reichow, S.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Ding, X.; Lathigra, R.; Craig, J.C.; Sobral, B.W.S.; Schurig, G.G.; Sriranganathan, N.; Boyle, S.M. Brucella Melitensis Triggers Time-Dependent Modulation of Apoptosis and Down-Regulation of Mitochondrion-Associated Gene Expression in Mouse Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5035–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, J. Surviving inside a Macrophage: The Many Ways of Brucella. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roop, R.M., 2nd; Bellaire, B.H.; Valderas, M.W.; Cardelli, J.A. Adaptation of the Brucellae to Their Intracellular Niche. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorneles, E.M.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Araújo, M.S.; Sriranganathan, N.; Lage, A.P. Immune Response Triggered by Brucella Abortus Following Infection or Vaccination. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covert, J.; Mathison, A.J.; Eskra, L.; Banai, M.; Splitter, G. Brucella Melitensis, B. Neotomae and B. Ovis Elicit Common and Distinctive Macrophage Defense Transcriptional Responses. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 234, 1450–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Terraza, A.; Ouahrani-Bettache, S.; Liautard, J.-P.; Dornand, J. In Vitro Brucella Suis Infection Prevents the Programmed Cell Death of Human Monocytic Cells. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, J.; de Chastellier, C.; Franchini, D.-M.; Pizarro-Cerda, J.; Moreno, E.; Gorvel, J.-P. Brucella Evades Macrophage Killing Via Virb-Dependent Sustained Interactions with the Endoplasmic Reticulum. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zeng, H.; Li, M.; Xiao, Y.; Gu, G.; Song, Z.; Shuai, X.; Guo, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, B.; et al. The Mechanism of Chronic Intracellular Infection with Brucella Spp. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1129172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naroeni, A.; Jouy, N.; Ouahrani-Bettache, S.; Liautard, J.-P.; Porte, F. Brucella Suis-Impaired Specific Recognition of Phagosomes by Lysosomes Due to Phagosomal Membrane Modifications. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, G.N.; Staskevich, A.S.; Aballay, A.; Mayorga, L.S. Intracellular Trafficking of Brucella Abortus in J774 Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4255–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorvel, J.P.; Moreno, E. Brucella Intracellular Life: From Invasion to Intracellular Replication. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 90, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open Software Development for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizarry, R.A.; Hobbs, B.; Collin, F.; Beazer-Barclay, Y.D.; Antonellis, K.J.; Scherf, U.; Speed, T.P. Exploration, Normalization, and Summaries of High Density Oligonucleotide Array Probe Level Data. Biostatistics 2003, 4, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, L.; Cope, L.; Bolstad, B.M.; Irizarry, R.A. Affy–Analysis of Affymetrix Genechip Data at the Probe Level. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diboun, I.; Wernisch, L.; Orengo, C.A.; Koltzenburg, M. Microarray Analysis after Rna Amplification Can Detect Pronounced Differences in Gene Expression Using Limma. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mering, C.; Huynen, M.; Jaeggi, D.; Schmidt, S.; Bork, P.; Snel, B. String: A Database of Predicted Functional Associations between Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, M.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Pan, Y. Comparative Gene Expression Analysis in Mouse Models for Identifying Critical Pathways in Mammary Gland Development. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, G.D.; Hogue, C.W. An Automated Method for Finding Molecular Complexes in Large Protein Interaction Networks. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Wu, F.-X. Cytonca: A Cytoscape Plugin for Centrality Analysis and Evaluation of Protein Interaction Networks. Biosystems 2015, 127, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janky, R.; Verfaillie, A.; Imrichová, H.; Van de Sande, B.; Standaert, L.; Christiaens, V.; Hulselmans, G.; Herten, K.; Sanchez, M.N.; Potier, D.; et al. Iregulon: From a Gene List to a Gene Regulatory Network Using Large Motif and Track Collections. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, J. Modulation of Toll-Like Receptor Signaling in Innate Immunity by Natural Products. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 37, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, S.; Akira, S. Toll-Like Receptor and Innate Immunity. Seikagaku 2007, 79, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquero-Calvo, E.; Chaves-Olarte, E.; Weiss, D.S.; Guzmán-Verri, C.; Chacón-Díaz, C.; Rucavado, A.; Moriyón, I.; Moreno, E. Brucella Abortus Uses a Stealthy Strategy to Avoid Activation of the Innate Immune System During the Onset of Infection. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Xu, J. Important Biology Events and Pathways in Brucella Infection and Implications for Novel Antibiotic Drug Targets. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2013, 23, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, L.A.; Macedo, G.C.; Marinho, F.A.V.; Gomes, M.T.R.; Corsetti, P.P.; Silva, A.M.; Cassataro, J.; Giambartolomei, G.H.; Oliveira, S.C. Toll-Like Receptor 6 Plays an Important Role in Host Innate Resistance to Brucella Abortus Infection in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, A.M.; Gale, M., Jr. Rig-I in Rna Virus Recognition. Virology 2015, 479–480, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Li, K.; Kameyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Watashi, K.; et al. The RNA Sensor Rig-I Dually Functions as an Innate Sensor and Direct Antiviral Factor for Hepatitis B Virus. Immunity 2015, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Ding, S.-W.; Wang, M. Rig-I-Dependent Antiviral Immunity Is Effective against an Rna Virus Encoding a Potent Suppressor of Rnai. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Natsukawa, T.; Shinobu, N.; Imaizumi, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Taira, K.; Akira, S.; Fujita, T. The RNA Helicase Rig-I Has an Essential Function in Double-Stranded Rna-Induced Innate Antiviral Responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.T.; Gale, M., Jr.; Loo, Y.M. Rig-I and Other RNA Sensors in Antiviral Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 667–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Ismail, A.S.; Behrendt, C.L.; Wight-Carter, M.; Hooper, L.V.; Chen, Z.J. Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein (Mavs) Monitors Commensal Bacteria and Induces an Immune Response That Prevents Experimental Colitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17390–17395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.M.; Yang, H.; Tan, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, S.; et al. Transcriptomic Response to Yersinia Pestis: Rig-I Like Receptor Signaling Response Is Detrimental to the Host against Plague. J. Genet. Genom. 2014, 41, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, A.; Bowie, A.G. Innate Immune Recognition of DNA: A Recent History. Virology 2015, 479–480, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, S.E.; Baran, M.; Bowie, A.G. Cytosolic DNA Sensors Regulating Type I Interferon Induction. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzanillo, P.S.; Shiloh, M.U.; Portnoy, D.A.; Cox, J.S. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Activates the DNA-Dependent Cytosolic Surveillance Pathway within Macrophages. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Yu, J.-W.; Juliana, C.; Solorzano, L.; Kang, S.; Wu, J.; Datta, P.; McCormick, M.; Huang, L.; McDermott, E.; et al. The Aim2 Inflammasome Is Critical for Innate Immunity to Francisella Tularensis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, J. Intracellular Localization of Brucella Abortus and Francisella Tularensis in Primary Murine Macrophages. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 431, 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti, C.A.; Drake, K.L.; Lawhon, S.D.; Nunes, J.S.; Gull, T.; Khare, S.; Adams, L.G. Systems Biology Analysis of Temporal in Vivo Brucella Melitensis and Bovine Transcriptomes Predicts Host:Pathogen Protein-Protein Interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazza, L.; Mocellin, S. Tumor Necrosis Factor (Tnf) Biology and Cell Death. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 2736–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrad, B.; Strieter, R.M.; Standiford, T.J. Role of Tnf-Alpha in Pulmonary Host Defense in Murine Invasive Aspergillosis. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijneveld, A.W.; Florquin, S.; Branger, J.; Speelman, P.; Van Deventer, S.J.H.; van der Poll, T. Tnf-Alpha Compensates for the Impaired Host Defense of Il-1 Type I Receptor-Deficient Mice During Pneumococcal Pneumonia. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5240–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.A.; Parent, M.; Sathiyaseelan, J.; Jiang, X.; Baldwin, C.L. Immune Control of Brucella Abortus 2308 Infections in Balb/C Mice. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambartolomei, G.H.; Zwerdling, A.; Cassataro, J.; Bruno, L.; Fossati, C.A.; Philipp, M.T. Lipoproteins, Not Lipopolysaccharide, Are the Key Mediators of the Proinflammatory Response Elicited by Heat-Killed Brucella Abortus. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4635–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachal Pugh, C.; Fleshner, M.; Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F.; Rudy, J.W. The Immune System and Memory Consolidation: A Role for the Cytokine Il-1beta. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2001, 25, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.J.; Lanteri, M.C.; Blahnik, G.; Negash, A.; Suthar, M.S.; Brassil, M.M.; Sodhi, K.; Treuting, P.M.; Busch, M.P.; Norris, P.J.; et al. Il-1beta Signaling Promotes Cns-Intrinsic Immune Control of West Nile Virus Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The Complexity of Nf-Kappab Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, F.D.; Nibbs, R.J.B. Regulation of the Adaptive Immune Response by the Ikappab Family Protein Bcl-3. Cells 2016, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, G.; Deng, K.; Liu, Y. Bcl3 Exerts an Oncogenic Function by Regulating Stat3 in Human Cervical Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 6619–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, H.; Ha, H.L.; Tassi, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Claudio, E.; Siebenlist, U. The B-Cell Tumor Promoter Bcl-3 Suppresses Inflammation-Associated Colon Tumorigenesis in Epithelial Cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6203–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, H.; Nam, H.J.; Shin, H.-J.R.; Kim, D.; Ko, E.; Noh, D.-Y.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Bcl3-Dependent Stabilization of Ctbp1 Is Crucial for the Inhibition of Apoptosis and Tumor Progression in Breast Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 400, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Yang, R.; Chen, X.; Harhaj, E.W.; Wang, X.; Fan, Y. Regnase-1, a Rapid Response Ribonuclease Regulating Inflammation and Stress Responses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daams, R.; Tran, T.T.P.; Jemaà, M.; Sime, W.; Mickeviciute, R.; Ek, S.; Rönnstrand, L.; Kazi, J.U.; Massoumi, R. Enhancing Cell Death in B-Cell Malignancies through Targeted Inhibition of Bcl-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wörmann, S.; Ai, J.; Neuhöfer, P.; Lesina, M.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Ruess, D.; Treiber, M.; Witt, H.; Bassermann, F.; et al. Bcl3 Reduces the Sterile Inflammatory Response in Pancreatic and Biliary Tissues. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 499–512.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Uddin, M.M.; Padmanabhan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Bu, P.; Vancura, A.; Vancurova, I. The Proto-Oncogene Bcl3 Induces Immune Checkpoint Pd-L1 Expression, Mediating Proliferation of Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15483–15496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, N.; Liu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ye, D.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; et al. Bcl-3 Promotes Tnf-Induced Hepatocyte Apoptosis by Regulating the Deubiquitination of Rip1. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Mondragon, E.; Gomez-Chavez, F.; Murrieta-Coxca, M.; Vazquez-Sanchez, E.A.; Martinez-Torres, I.; Cancino-Diaz, M.E.; Rojas-Espinosa, O.; Cancino-Diaz, J.C.; Reyes-Sanchez, J.L.; Rodriguez-Munoz, R.; et al. Low Expression of Il-6 and Tnf-Alpha Correlates with the Presence of the Nuclear Regulators of Nf-Kappab, Ikappabns and Bcl-3, in the Uterus of Mice. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 68, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
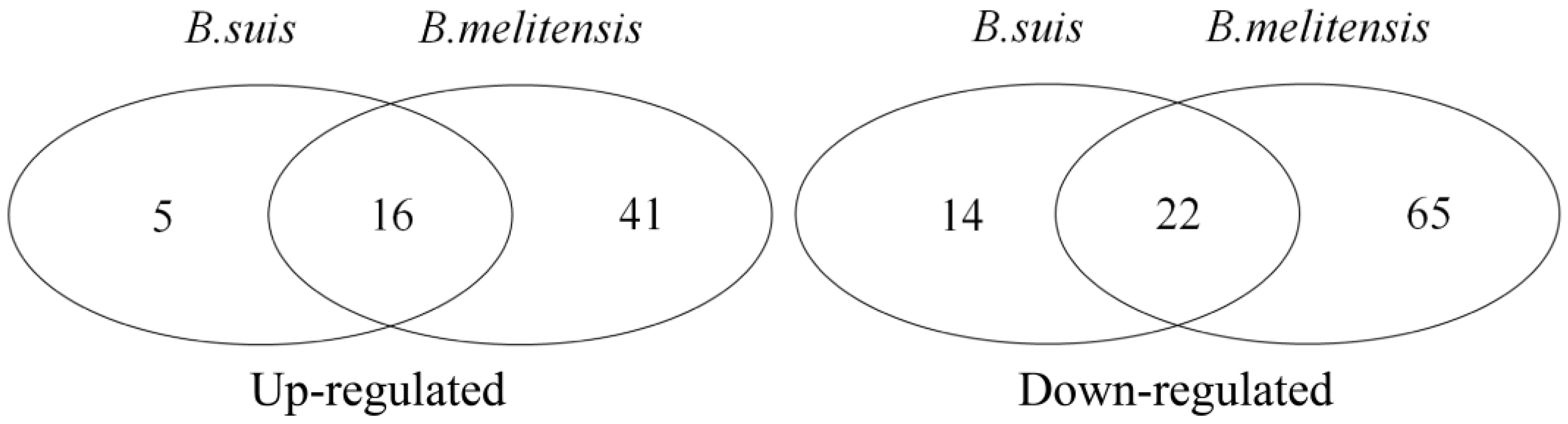
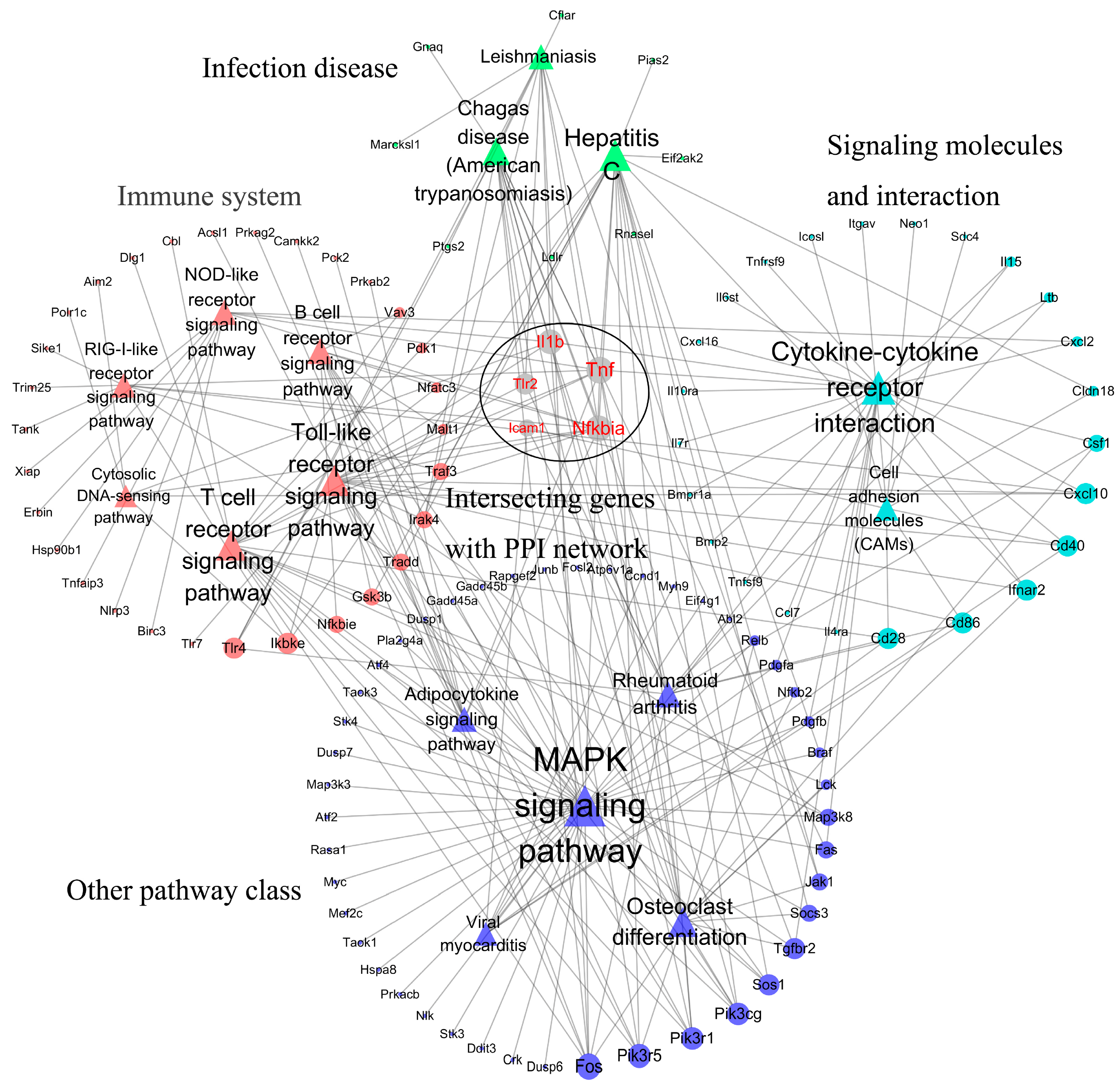
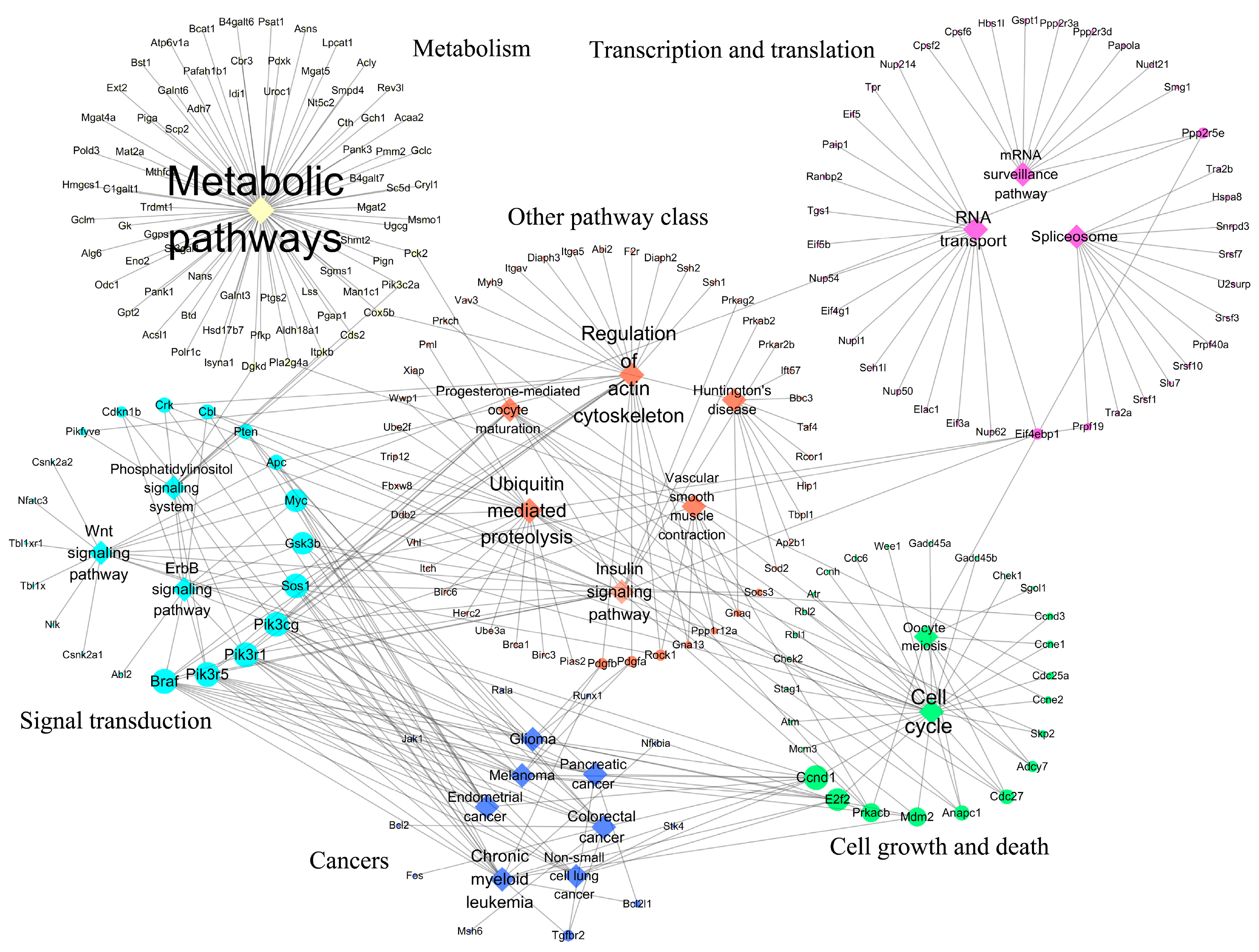
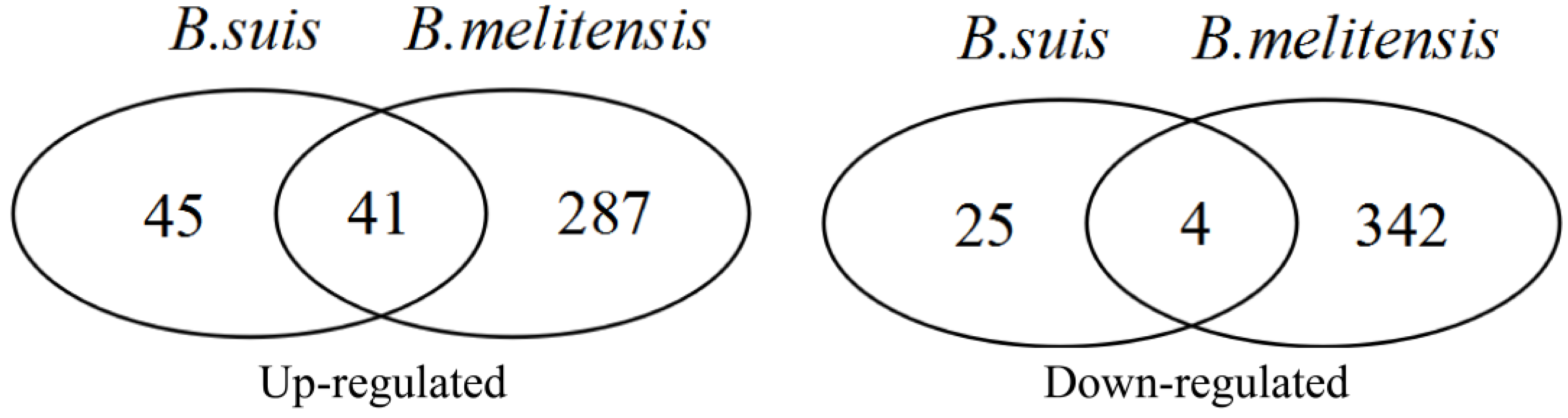
| Dataset | Chip Platform | Probes | Murine Cell Line | Brucella Strain | Infection Time Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE21117 | GPL1261 | 45k | J774.A1 | B. suis strain 1330 | 0 h |
| 4 h | |||||
| GSE5202 | GPL1261 | 45k | J774.A1 | B. melitensis strain 16M | 0 h |
| 4 h | |||||
| GSE8385 | GPL81 | 12,488 | RAW 264.7 | B. melitensis | 0 h |
| 4 h |
| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | Pathway Class | Enrichment Gene Number | Count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE21117 | GSE5202 | ||||
| Up-regulated | |||||
| mmu04010 | MAPK signaling pathway | Signal transduction | 46 | 104 | 34 |
| mmu04060 | Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | Signaling molecules and interaction | 27 | 51 | 23 |
| mmu04380 | Osteoclast differentiation | Development | 22 | 52 | 17 |
| mmu04514 | Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | Signaling molecules and interaction | 18 | 26 | 9 |
| mmu04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | 27 | 42 | 18 |
| mmu04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | 17 | 26 | 10 |
| mmu04622 | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | 12 | 24 | 9 |
| mmu04623 | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | Immune system | 11 | 23 | 6 |
| mmu04660 | T cell receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | 22 | 55 | 18 |
| mmu04662 | B cell receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | 16 | 38 | 11 |
| mmu04920 | Adipocytokine signaling pathway | Endocrine system | 14 | 30 | 10 |
| mmu05140 | Leishmaniasis | Infectious diseases | 18 | 24 | 10 |
| mmu05142 | Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | Infectious diseases | 20 | 40 | 14 |
| mmu05160 | Hepatitis C | Infectious diseases | 27 | 46 | 20 |
| mmu05323 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Immune diseases | 17 | 25 | 12 |
| mmu05416 | Viral myocarditis | Cardiovascular diseases | 13 | 25 | 8 |
| Down-regulated | |||||
| mmu01100 | Metabolic pathways | / | 97 | 378 | 73 |
| mmu03013 | RNA transport | Translation | 24 | 66 | 16 |
| mmu03015 | mRNA surveillance pathway | Translation | 15 | 33 | 10 |
| mmu03040 | Spliceosome | Transcription | 15 | 65 | 12 |
| mmu04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | Signal transduction | 15 | 42 | 12 |
| mmu04070 | Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | Signal transduction | 12 | 32 | 9 |
| mmu04110 | Cell cycle | Cell growth and death | 33 | 68 | 26 |
| mmu04114 | Oocyte meiosis | Cell growth and death | 13 | 42 | 8 |
| mmu04120 | Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis | Folding, sorting, and degradation | 27 | 66 | 22 |
| mmu04270 | Vascular smooth muscle contraction | Circulatory system | 11 | 29 | 9 |
| mmu04310 | Wnt signaling pathway | Signal transduction | 21 | 51 | 14 |
| mmu04810 | Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | Cell motility | 31 | 71 | 23 |
| mmu04910 | Insulin signaling pathway | Endocrine system | 19 | 63 | 15 |
| mmu04914 | Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | Endocrine system | 11 | 40 | 9 |
| mmu05016 | Huntington’s disease | Neurodegenerative diseases | 14 | 63 | 10 |
| mmu05210 | Colorectal cancer | Cancers | 15 | 34 | 12 |
| mmu05212 | Pancreatic cancer | Cancers | 14 | 40 | 10 |
| mmu05213 | Endometrial cancer | Cancers | 11 | 28 | 10 |
| mmu05214 | Glioma | Cancers | 14 | 32 | 11 |
| mmu05218 | Melanoma | Cancers | 14 | 29 | 10 |
| mmu05220 | Chronic myeloid leukemia | Cancers | 21 | 45 | 16 |
| mmu05223 | Non-small cell lung cancer | Cancers | 11 | 28 | 8 |
| Number | Probe ID | Gene Symbol | LogFC | Adjusted p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE21117 | GSE5202 | GSE21117 | GSE5202 | |||
| Up-regulated | ||||||
| 1 | 1418133_at | Bcl3 | 1.6376 | 1.2896 | 2.10 × 10−5 | 6.27 × 10−7 |
| 2 | 1421392_a_at | Birc3 | 1.3919 | 1.2825 | 1.52 × 10−5 | 1.84 × 10−7 |
| 3 | 1427736_a_at | Ccrl2 | 1.6309 | 1.2135 | 6.79 × 10−5 | 7.38 × 10−7 |
| 4 | 1428735_at | Cd69 | 2.9727 | 1.6583 | 2.97 × 10−3 | 1.55 × 10−8 |
| 5 | 1416111_at | Cd83 | 1.5845 | 2.4933 | 3.59 × 10−5 | 1.48 × 10−9 |
| 6 | 1428750_at | Cdc42ep2 | 1.0463 | 1.6527 | 8.58 × 10−3 | 1.07 × 10−6 |
| 7 | 1424996_at | Cflar | 1.0649 | 1.5431 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 8.81 × 10−8 |
| 8 | 1449317_at | Cflar | 1.2286 | 1.1349 | 3.86 × 10−5 | 1.81 × 10−7 |
| 9 | 1416010_a_at | Ehd1 | 1.2293 | 1.5092 | 2.59 × 10−5 | 3.57 × 10−8 |
| 10 | 1416011_x_at | Ehd1 | 1.3414 | 1.5224 | 259 × 10−5 | 3.93 × 10−8 |
| 11 | 1416012_at | Ehd1 | 1.2436 | 1.6730 | 6.46 × 10−3 | 1.46 × 10−8 |
| 12 | 1448175_at | Ehd1 | 1.3386 | 1.6506 | 2.29 × 10−5 | 1.55 × 10−8 |
| 13 | 1450744_at | Ell2 | 1.0320 | 1.3000 | 2.11 × 10−3 | 2.27 × 10−7 |
| 14 | 1448021_at | Fam46c | 1.9514 | 1.7736 | 1.10 × 10−5 | 9.36 × 10−8 |
| 15 | 1460251_at | Fas | 1.0830 | 2.2110 | 6.62 × 10−5 | 7.27 × 10−9 |
| 16 | 1449773_s_at | Gadd45b | 1.6456 | 1.4205 | 2.04 × 10−2 | 1.81 × 10−7 |
| 17 | 1419721_at | Hcar2 | 1.1207 | 1.8983 | 1.77 × 10−2 | 2.77 × 10−8 |
| 18 | 1435626_a_at | Herpud1 | 1.9177 | 1.4910 | 1.22 × 10−6 | 3.85 × 10−7 |
| 19 | 1448185_at | Herpud1 | 2.1214 | 1.6464 | 1.22 × 10−6 | 1.66 × 10−8 |
| 20 | 1424067_at | Icam1 | 1.9478 | 1.5665 | 1.10 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−7 |
| 21 | 1419212_at | Icosl | 1.8808 | 1.4179 | 3.24 × 10−5 | 2.77 × 10−8 |
| 22 | 1419647_a_at | Ier3 | 1.4769 | 1.5453 | 5.77 × 10−6 | 1.42 × 10−8 |
| 23 | 1448731_at | Il10ra | 1.0320 | 1.3867 | 8.47 × 10−5 | 2.80 × 10−7 |
| 24 | 1449399_a_at | Il1b | 1.9577 | 1.4708 | 1.26 × 10−2 | 6.80 × 10−8 |
| 25 | 1448306_at | Nfkbia | 1.2173 | 1.9230 | 1.88 × 10−3 | 1.35 × 10−8 |
| 26 | 1449731_s_at | Nfkbia | 1.5581 | 1.7485 | 1.02 × 10−3 | 1.54 × 10−8 |
| 27 | 1431843_a_at | Nfkbie | 1.8611 | 1.3758 | 7.18 × 10−6 | 3.84 × 10−7 |
| 28 | 1458299_s_at | Nfkbie | 1.9203 | 1.9025 | 1.22 × 10−6 | 8.02 × 10−9 |
| 29 | 1417483_at | Nfkbiz | 3.8560 | 2.6059 | 1.71 × 10−5 | 8.00 × 10−10 |
| 30 | 1448728_a_at | Nfkbiz | 2.7324 | 2.4021 | 1.50 × 10−5 | 2.06 × 10−9 |
| 31 | 1422474_at | Pde4b | 1.3013 | 1.3126 | 4.47 × 10−5 | 2.04 × 10−7 |
| 32 | 1450413_at | Pdgfb | 1.6909 | 1.6032 | 1.54 × 10−3 | 1.92 × 10−8 |
| 33 | 1450414_at | Pdgfb | 1.5424 | 1.0075 | 7.70 × 10−5 | 1.01 × 10−6 |
| 34 | 1417801_a_at | Ppfibp2 | 1.2448 | 1.1562 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 9.74 × 10−7 |
| 35 | 1424208_at | Ptger4 | 1.0394 | 2.0903 | 1.37 × 10−2 | 4.41 × 10−9 |
| 36 | 1417263_at | Ptgs2 | 1.9088 | 1.7250 | 4.86 × 10−2 | 7.70 × 10−8 |
| 37 | 1423134_at | Rilpl2 | 1.0142 | 1.4033 | 9.48 × 10−5 | 4.12 × 10−8 |
| 38 | 1432478_a_at | Rnf19b | 1.4471 | 1.4949 | 9.28 × 10−5 | 4.42 × 10−8 |
| 39 | 1435226_at | Rnf19b | 1.3508 | 1.2286 | 8.32 × 10−5 | 1.70 × 10−7 |
| 40 | 1422054_a_at | Skil | 1.1581 | 1.2304 | 8.32 × 10−5 | 7.05 × 10−7 |
| 41 | 1452214_at | Skil | 1.1702 | 1.7727 | 1.50 × 10−5 | 7.27 × 10−9 |
| 42 | 1416654_at | Slc31a2 | 1.6967 | 2.0730 | 3.93 × 10−5 | 1.02 × 10−8 |
| 43 | 1453721_a_at | Slc31a2 | 1.1741 | 2.2449 | 3.68 × 10−3 | 1.06 × 10−9 |
| 44 | 1416576_at | Socs3 | 1.6717 | 1.1579 | 1.48 × 10−3 | 5.77 × 10−7 |
| 45 | 1455899_x_at | Socs3 | 4.0894 | 2.3810 | 8.01 × 10−5 | 8.00 × 10−10 |
| 46 | 1456212_x_at | Socs3 | 3.6576 | 1.9634 | 1.88 × 10−5 | 2.74 × 10−8 |
| 47 | 1419132_at | Tlr2 | 1.8123 | 2.1650 | 1.02 × 10−5 | 2.36 × 10−9 |
| 48 | 1419607_at | Tnf | 2.9434 | 1.7900 | 2.89 × 10−9 | 2.33 × 10−8 |
| 49 | 1433699_at | Tnfaip3 | 1.9794 | 2.3763 | 2.71 × 10−3 | 1.32 × 10−9 |
| 50 | 1450829_at | Tnfaip3 | 1.1995 | 1.1096 | 5.81 × 10−3 | 7.50 × 10−7 |
| 51 | 1427689_a_at | Tnip1 | 1.5081 | 1.5509 | 2.38 × 10−5 | 4.83 × 10−8 |
| 52 | 1423602_at | Traf1 | 1.6793 | 2.2973 | 2.21 × 10−5 | 1.95 × 10−7 |
| 53 | 1427348_at | Zc3h12a | 1.2715 | 1.7723 | 7.72 × 10−5 | 1.04 × 10−6 |
| 54 | 1444402_at | Zc3h12c | 2.9487 | 1.8413 | 1.52 × 10−5 | 4.68 × 10−9 |
| Down-regulated | ||||||
| 1 | 1418774_a_at | Atp7a | −1.3005 | −1.0209 | 1.48 × 10−5 | 1.95 × 10−6 |
| 2 | 1415834_at | Dusp6 | −1.1775 | −1.6091 | 3.70 × 10−3 | 8.99 × 10−8 |
| 3 | 1448890_at | Klf2 | −1.0636 | −1.9034 | 8.58 × 10−3 | 3.57 × 10−8 |
| 4 | 1427285_s_at | Malat1 | −1.1471 | −1.1179 | 7.27 × 10−5 | 5.10 × 10−5 |
| Rank | Gene | Subgraph | Degree | Eigenvector | Information | Betweenness | Closeness | Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tnf | 28,456.67 | 18 | 0.3470 | 4.8312 | 310.15 | 0.9091 | 25.49 |
| 2 | Il1b | 26,182.86 | 18 | 0.3470 | 4.7046 | 158.31 | 0.8108 | 20.84 |
| 3 | Tlr2 | 17,841.82 | 16 | 0.3470 | 4.3743 | 27.25 | 0.6818 | 12.61 |
| 4 | Icam1 | 16,906.33 | 15 | 0.3470 | 4.3095 | 19.51 | 0.6667 | 12.06 |
| 5 | Nfkbia | 16,117.95 | 13 | 0.3470 | 4.3095 | 34.27 | 0.6522 | 12.40 |
| 6 | Birc3 | 13,404.47 | 12 | 0.3470 | 4.0727 | 3.14 | 0.6122 | 10.26 |
| 7 | Traf1 | 12,295.37 | 12 | 0.3470 | 4.0727 | 6.24 | 0.6122 | 9.26 |
| 8 | Tnfaip3 | 11,955.47 | 10 | 0.3470 | 4.1597 | 22.63 | 0.6250 | 10.35 |
| 9 | Nfkbiz | 11,372.57 | 10 | 0.3470 | 4.1597 | 26.64 | 0.6250 | 9.89 |
| 10 | Fas | 10,675.32 | 11 | 0.3470 | 3.9756 | 7.70 | 0.6122 | 8.55 |
| 11 | Ptgs2 | 10,368.22 | 10 | 0.3470 | 4.0727 | 15.88 | 0.6250 | 9.42 |
| 12 | Nfkbie | 9154.65 | 9 | 0.3470 | 3.8666 | 6.54 | 0.5882 | 8.33 |
| 13 | Cflar | 9116.53 | 10 | 0.3470 | 3.8666 | 2.96 | 0.5882 | 7.61 |
| 14 | Bcl3 | 8139.34 | 9 | 0.3470 | 3.7435 | 2.08 | 0.5769 | 7.00 |
| 15 | Socs3 | 8047.73 | 9 | 0.3470 | 3.8666 | 9.93 | 0.5882 | 7.21 |
| 16 | Cd83 | 4734.80 | 7 | 0.3470 | 3.6033 | 5.47 | 0.5660 | 6.35 |
| 17 | Atp7a | 4670.12 | 6 | 0.3470 | 3.6033 | 59.50 | 0.5769 | 5.71 |
| 18 | Cd69 | 4128.84 | 6 | 0.3470 | 3.4422 | 3.75 | 0.5556 | 5.67 |
| 19 | Il10ra | 2774.70 | 5 | 0.3470 | 3.2550 | 3.40 | 0.5455 | 4.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Chen, Q. Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies TNF and IL1B as Candidate Key Early-Response Genes in Macrophages Infected with Smooth Brucella Using a Comprehensive Bioinformatic Approach. Biology 2025, 14, 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050579
Yang X, Chen Q. Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies TNF and IL1B as Candidate Key Early-Response Genes in Macrophages Infected with Smooth Brucella Using a Comprehensive Bioinformatic Approach. Biology. 2025; 14(5):579. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050579
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaoyu, and Qiang Chen. 2025. "Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies TNF and IL1B as Candidate Key Early-Response Genes in Macrophages Infected with Smooth Brucella Using a Comprehensive Bioinformatic Approach" Biology 14, no. 5: 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050579
APA StyleYang, X., & Chen, Q. (2025). Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies TNF and IL1B as Candidate Key Early-Response Genes in Macrophages Infected with Smooth Brucella Using a Comprehensive Bioinformatic Approach. Biology, 14(5), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050579






