Integrated miRNA–mRNA Profiling of C2C12 Myoblasts Indicates Regulatory Interactions Involved in Proliferation and Differentiation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Differentiation Induction
2.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.3. RNA Extraction and Library Preparation
2.4. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.5. Small RNA Sequencing Analysis
2.6. Time Series and WGCNA Analysis
2.7. Construction of mRNA-miRNA Regulatory Network
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
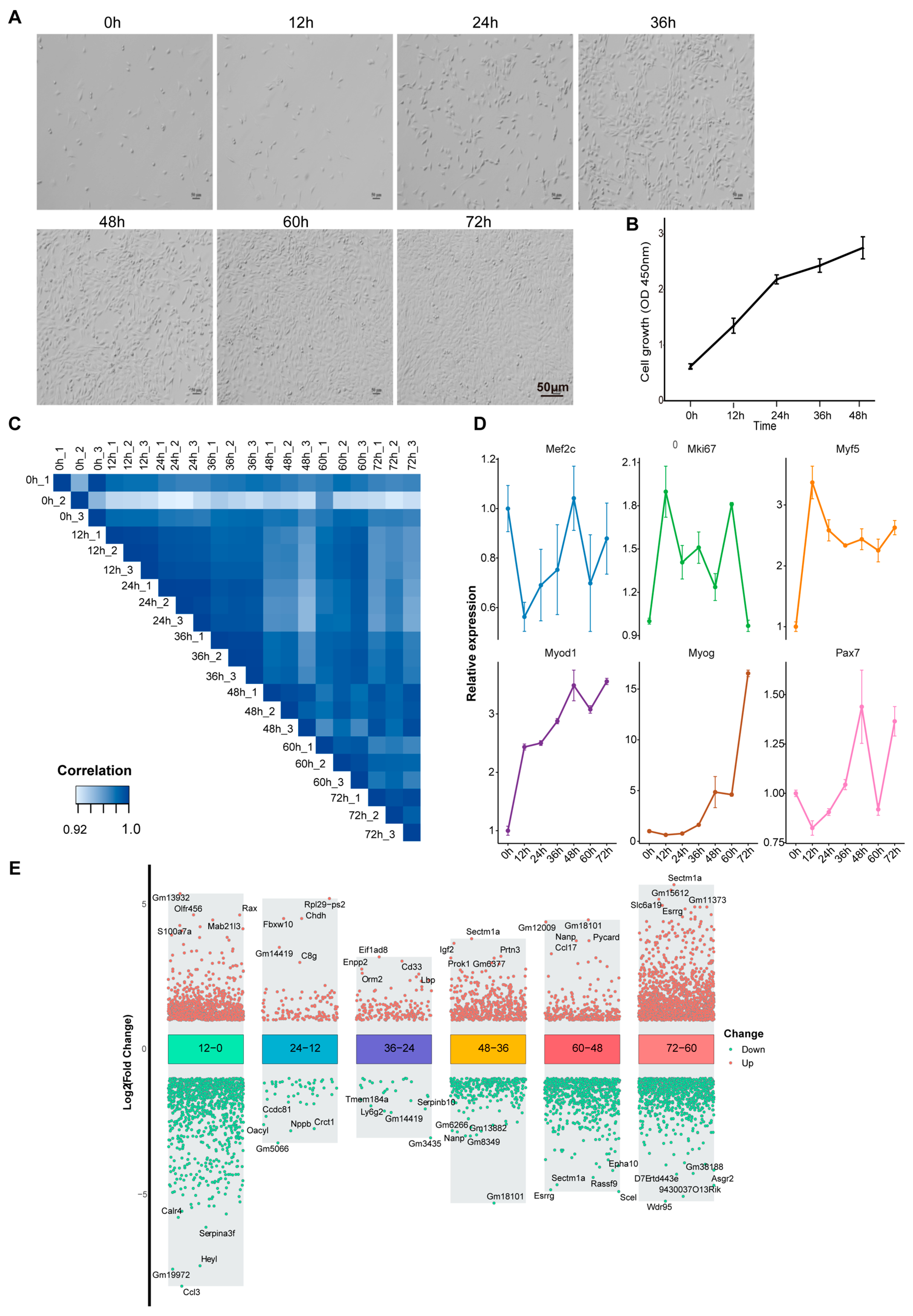
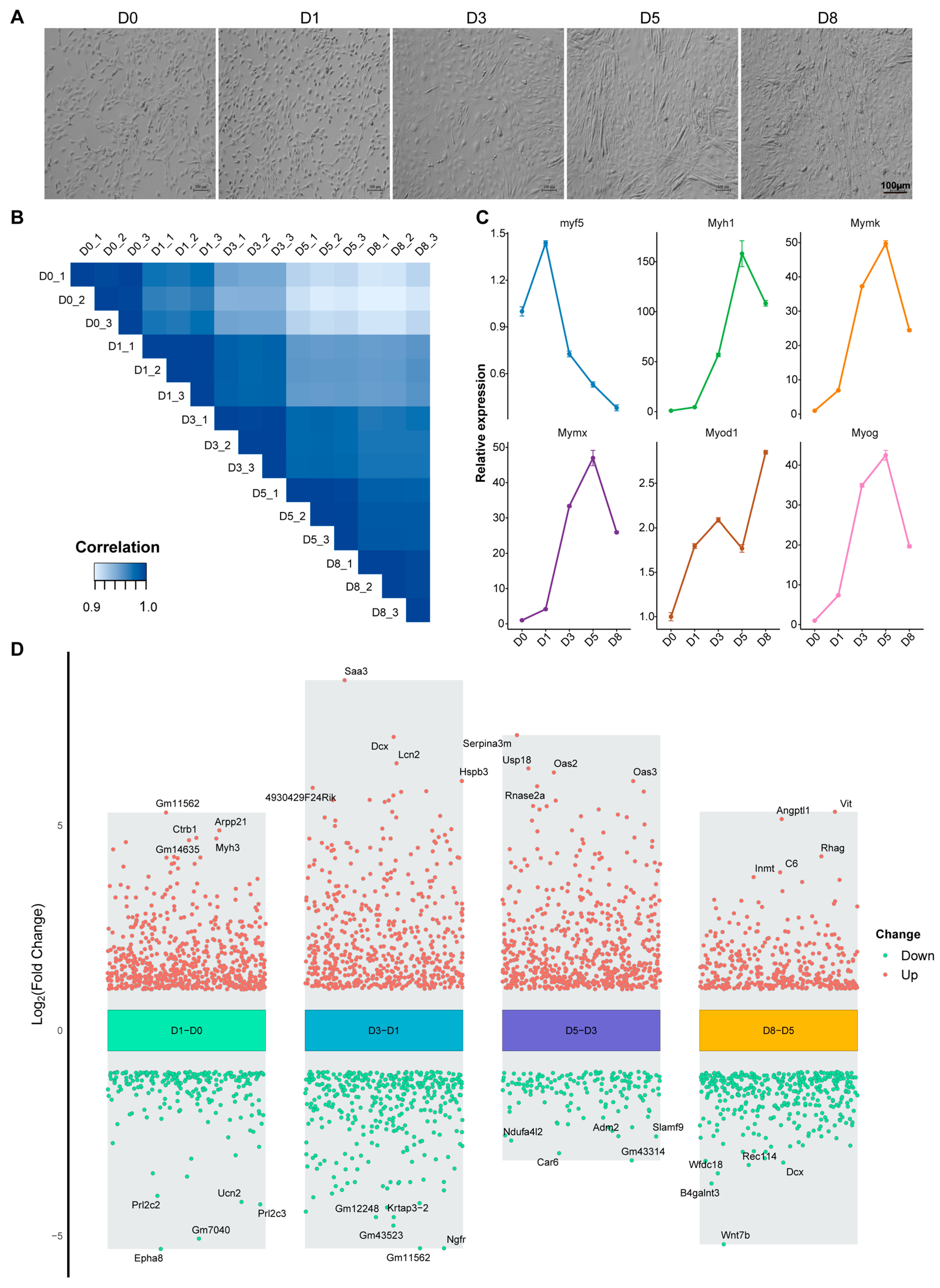
3.1. Transcriptome Dynamics During Proliferation and Differentiation of C2C12 Myoblasts
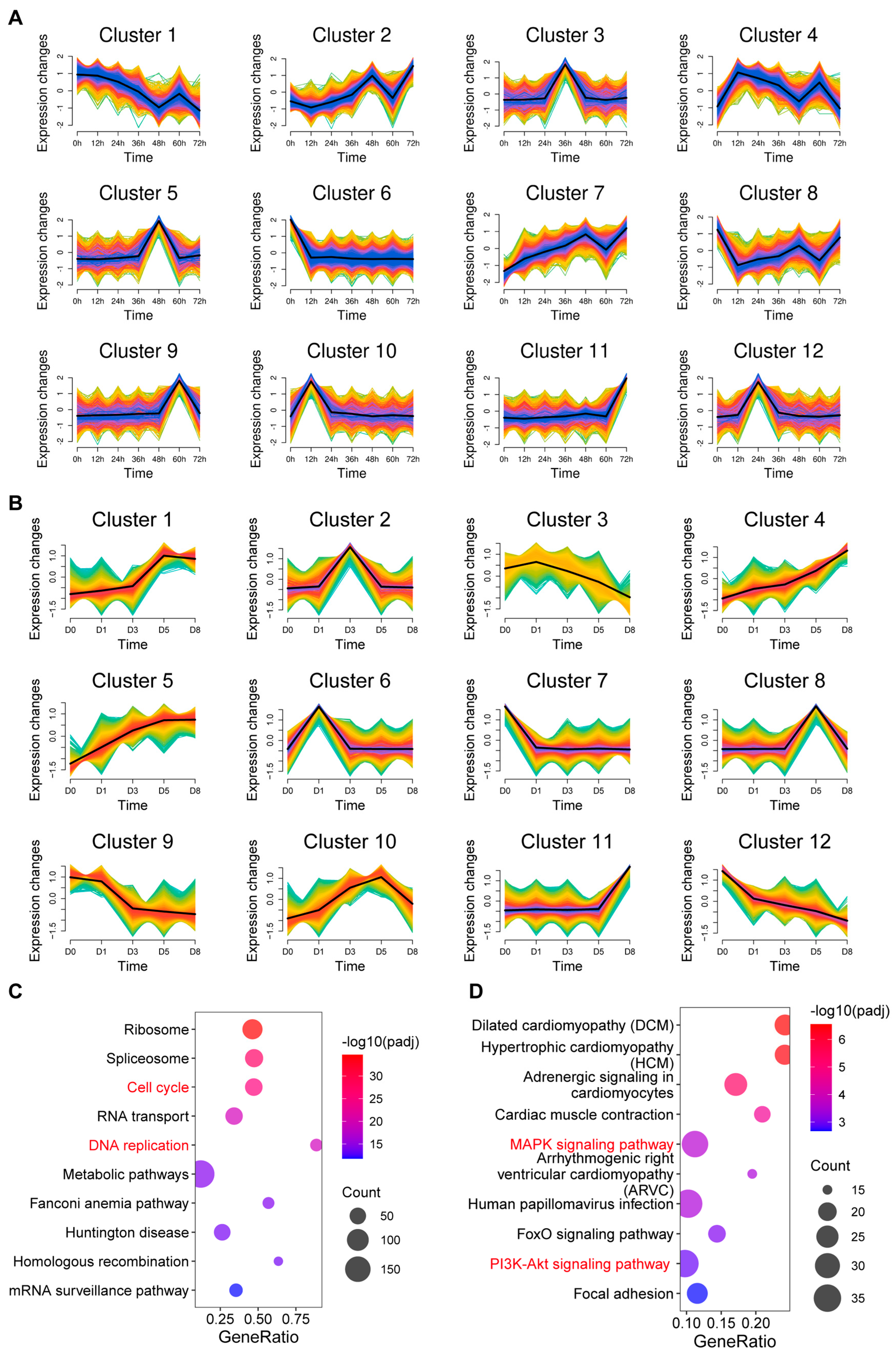
3.2. Co-Expression Analysis of mRNAs During Proliferation and Differentiation of C2C12 Myoblasts
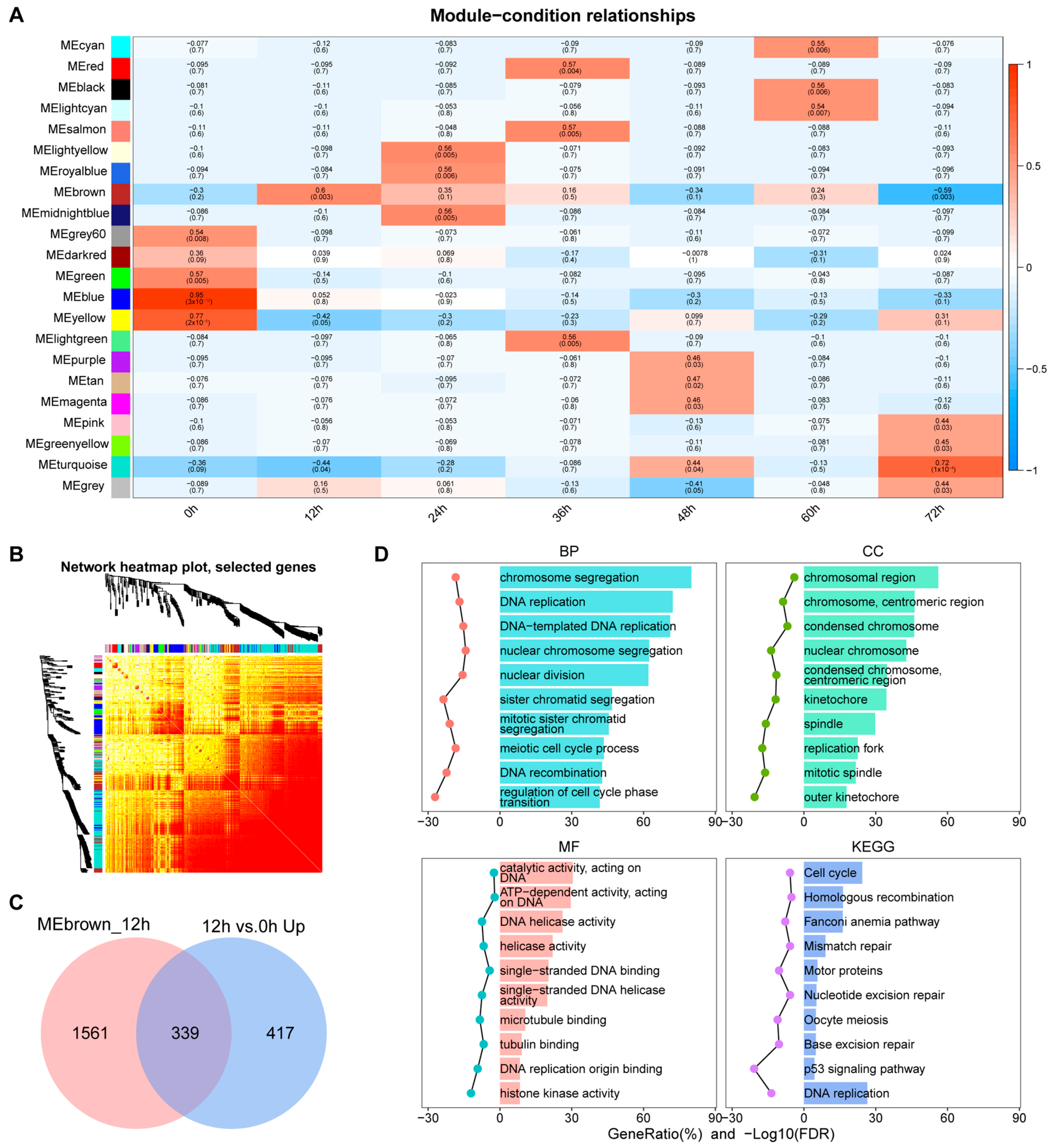
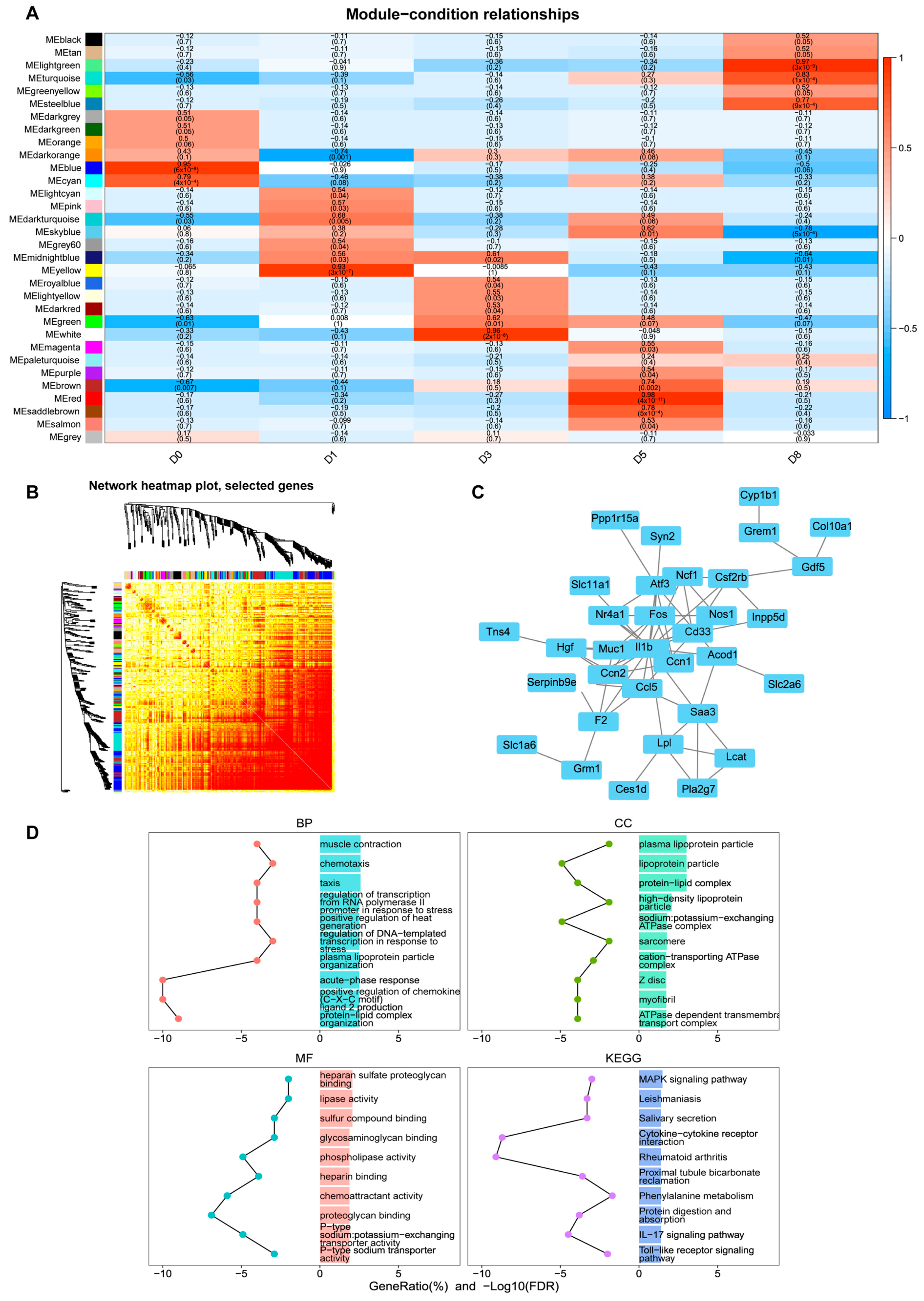
3.3. Identification of Key Co-Expression Modules Based on WGCNA
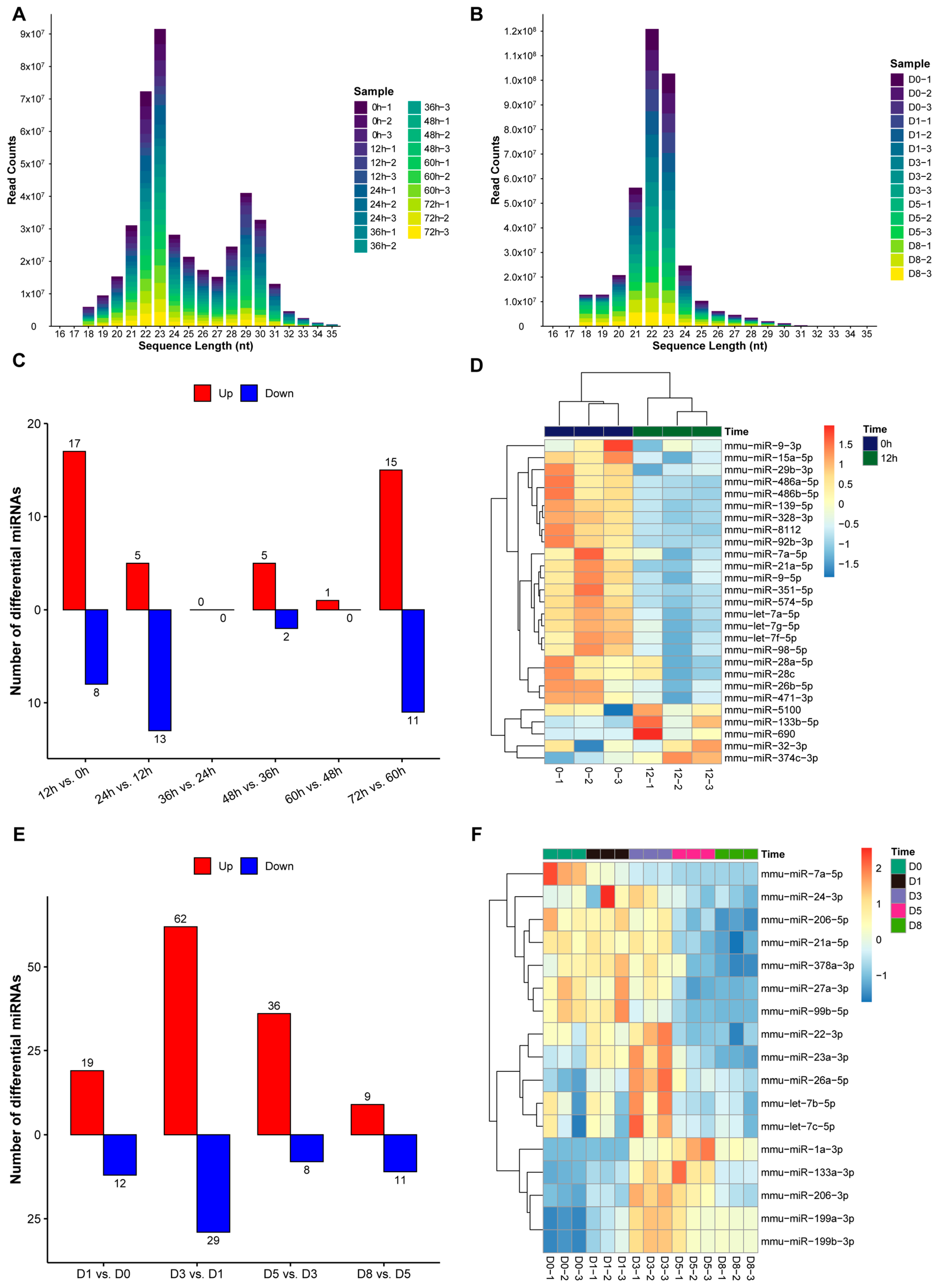
3.4. Expression Patterns of miRNAs During Proliferation and Differentiation of C2C12 Myoblasts
3.5. Target Gene Prediction and Functional Analysis of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
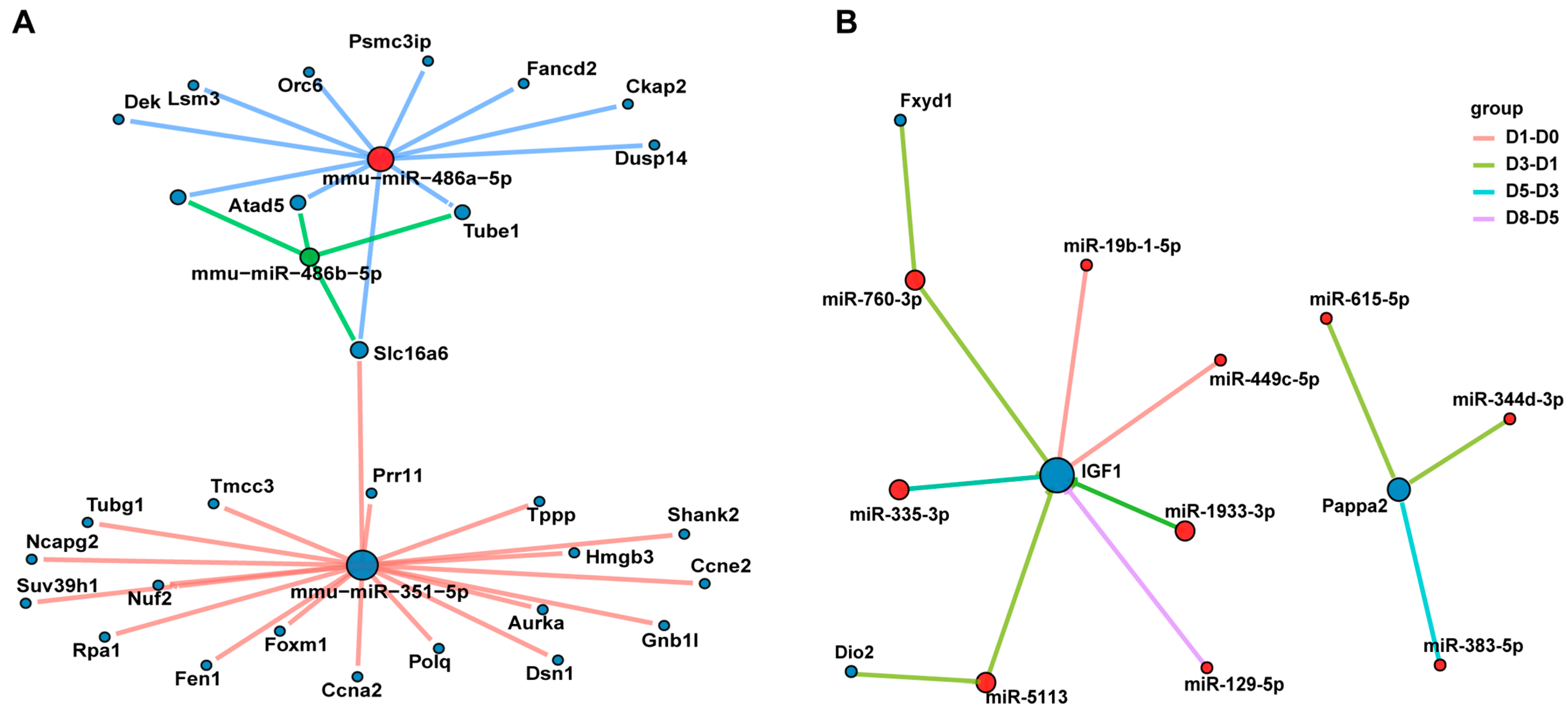
3.6. The miRNA–mRNA Interaction Network Reveals the Key Regulatory Axes of Muscle Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfe, R.R. The underappreciated role of muscle in health and disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, B.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise metabolism and the molecular regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M.; Rigby, P.W. Gene regulatory networks and transcriptional mechanisms that control myogenesis. Dev. Cell 2014, 28, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiro, E.; Tajbakhsh, S. Epigenetic regulation of muscle development. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2017, 38, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archacka, K.; Ciemerych, M.A.; Florkowska, A.; Romanczuk, K. Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators of Myogenesis and Postexercise Muscle Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, F.; Hu, S.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Yan, X. MiR-20a and miR-106b negatively regulate autophagy induced by leucine deprivation via suppression of ULK1 expression in C2C12 myoblasts. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 2179–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.; Anderson, P.; Nassar, R.; Bunting, J.; Saba, Z.; Oakeley, A.; Malouf, N. C2C12 cells: Biophysical, biochemical, and immunocytochemical properties. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1994, 266, C1795–C1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaffe, D.; Saxel, O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature 1977, 270, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoez, A.M.; Sardón Puig, L.; Smith, J.A.; Gabriel, B.M.; Savikj, M.; Dollet, L.; Chibalin, A.V.; Krook, A.; Zierath, J.R.; Pillon, N.J. Comparative profiling of skeletal muscle models reveals heterogeneity of transcriptome and metabolism. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C615–C626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burattini, S.; Ferri, P.; Battistelli, M.; Curci, R.; Luchetti, F.; Falcieri, E. C2C12 murine myoblasts as a model of skeletal muscle development: Morpho-functional characterization. Eur. J. Histochem. 2004, 48, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Hernández, J.M.; García-González, E.G.; Brun, C.E.; Rudnicki, M.A. The myogenic regulatory factors, determinants of muscle development, cell identity and regeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsolak, F.; Milos, P.M. RNA sequencing: Advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheel, J.; Safrastyan, A.; Wollny, D. Advances in Non-Coding RNA Sequencing. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismuth, K.; Relaix, F. Genetic regulation of skeletal muscle development. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 3081–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Feng, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Shen, W. Transcriptomic regulatory analysis of skeletal muscle development in landrace pigs. Gene 2024, 915, 148407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, M.; Novak, J.; Bienertova-Vasku, J. Muscle-specific microRNAs in skeletal muscle development. Dev. Biol. 2016, 410, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, G.F.; Lozano-Velasco, E.; Munsterberg, A. microRNAs in skeletal muscle development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-F.; Mandel, E.M.; Thomson, J.M.; Wu, Q.; Callis, T.E.; Hammond, S.M.; Conlon, F.L.; Wang, D.-Z. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Sivaprasad, U.; Malhotra, A.; Dutta, A. Muscle-specific microRNA miR-206 promotes muscle differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Wu, W.; Wei, J.; Li, P.; Huang, R. miR-22 regulates C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation by targeting TGFBR1. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 97, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedländer, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Futschik, M.E. Mfuzz: A software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation 2007, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, Y.; Kechris, K.J.; Tabakoff, B.; Hoffman, P.; Radcliffe, R.A.; Bowler, R.; Mahaffey, S.; Rossi, S.; Calin, G.A.; Bemis, L. The multiMiR R package and database: Integration of microRNA–target interactions along with their disease and drug associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsuksili, S.; Du, Y.; Hadlich, F.; Siengdee, P.; Murani, E.; Schwerin, M.; Wimmers, K. Correlated mRNAs and miRNAs from co-expression and regulatory networks affect porcine muscle and finally meat properties. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsuksili, S.; Siengdee, P.; Du, Y.; Trakooljul, N.; Murani, E.; Schwerin, M.; Wimmers, K. Identification of common regulators of genes in co-expression networks affecting muscle and meat properties. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, J.; Feng, S.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Long, K.; Liu, L. Guanidinoacetic acid regulates myogenic differentiation and muscle growth through miR-133a-3p and miR-1a-3p co-mediated Akt/mTOR/S6K signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salant, G.M.; Tat, K.L.; Goodrich, J.A.; Kugel, J.F. miR-206 knockout shows it is critical for myogenesis and directly regulates newly identified target mRNAs. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M.; Relaix, F. PAX3 and PAX7 as upstream regulators of myogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 44, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Orso, S.; Juan, A.H.; Ko, K.-D.; Naz, F.; Perovanovic, J.; Gutierrez-Cruz, G.; Feng, X.; Sartorelli, V. Single cell analysis of adult mouse skeletal muscle stem cells in homeostatic and regenerative conditions. Development 2019, 146, dev174177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Gu, T.; Lu, L.; Cao, Z.; Song, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, G.; Xu, Q.; Chen, G. Roles of miRNA-1 and miRNA-133 in the Proliferation and Differentiation of Myoblasts in Duck Skeletal Muscle. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3490–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.S.; Casar, J.C.; Motohashi, N.; Myers, J.A.; Eisenberg, I.; Gonzalez, R.T.; Estrella, E.A.; Kang, P.B.; Kawahara, G.; Kunkel, L.M. Regulation of DMD pathology by an ankyrin-encoded miRNA. Skelet. Muscle 2011, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.-N.; Yang, L.-W.; Deng, S.-Y. Effects of miR-486 on proliferation of sheep (Ovis aries) skeletal muscle satellite cells and expression of genes related to PI3K-Akt signal pathway. J. South. Agric. 2021, 52, 2276–2283. [Google Scholar]
- Ozorhan, U.; Tuna, B.G.; Cicekdal, M.B.; Kuskucu, A.; Bayrak, O.F.; Yilmaz, B.; Demirel, P.B.; Cleary, M.P.; Dogan, S. Long-term chronic caloric restriction alters miRNA profiles in the brain of ageing mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, C.; Berber, P.; Karlstetter, M.; Aslanidis, A.; Strunz, T.; Langmann, T.; Grassmann, F.; Weber, B.H. A circulating microRNA profile in a laser-induced mouse model of choroidal neovascularization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, H.; Geng, C.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Pang, J.; Shu, T.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Y. Elevated IgE promotes cardiac fibrosis by suppressing miR-486a-5p. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7600–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.; Lynch IV, T.; McGuinness, M.; Jones, W.K. MiR-486a-5p Exerts Cardioprotection Against Ischemia Repefusion via Suppression of PDCD4. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 676.5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkes, C.A.; Tapscott, S.J. MyoD and the transcriptional control of myogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 16, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, D.; Madhala, D.; Ardon, E.; Reshef, R.; Halevy, O. Sonic hedgehog promotes proliferation and differentiation of adult muscle cells: Involvement of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Cui, F.; Mao, Z.; Li, Z.; Yi, X.; Zhou, J.; Cao, J.; Li, X.; Qian, Z. miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization. Open Med. 2024, 19, 20240912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.U.; Sass, S.; Mueller, N.S.; Krebs, S.; Bauersachs, S.; Kaiser, S.; Blum, H.; Thirion, C.; Krause, S.; Theis, F.J. Integrative analysis of microRNA and mRNA data reveals an orchestrated function of microRNAs in skeletal myocyte differentiation in response to TNF-α or IGF1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Huang, K.; He, Y.; Cai, Z.; He, Y. circNup188/miR-760–3p/Map3k8 axis regulates inflammation in cerebral ischemia. Mol. Cell. Probes 2022, 64, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, H.; Li, L.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Chu, M.; Sha, X.; Zhao, J. Anti-CHAC1 exosomes for nose-to-brain delivery of miR-760-3p in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury mice inhibiting neuron ferroptosis. J. Nanobiotechnology 2023, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, S.; Dyar, K.A.; Ciciliot, S.; Blaauw, B.; Sandri, M. Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4294–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentice, M.; Marsili, A.; Ambrosio, R.; Guardiola, O.; Sibilio, A.; Paik, J.-H.; Minchiotti, G.; DePinho, R.A.; Fenzi, G.; Larsen, P.R. The FoxO3/type 2 deiodinase pathway is required for normal mouse myogenesis and muscle regeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4021–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamajski, S.; Oldberg, Å. The role of small leucine-rich proteoglycans in collagen fibrillogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2010, 29, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, X.; Ma, J. Integrated miRNA–mRNA Profiling of C2C12 Myoblasts Indicates Regulatory Interactions Involved in Proliferation and Differentiation. Biology 2025, 14, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050574
Chang X, Ma J. Integrated miRNA–mRNA Profiling of C2C12 Myoblasts Indicates Regulatory Interactions Involved in Proliferation and Differentiation. Biology. 2025; 14(5):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050574
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Xiaolong, and Junwu Ma. 2025. "Integrated miRNA–mRNA Profiling of C2C12 Myoblasts Indicates Regulatory Interactions Involved in Proliferation and Differentiation" Biology 14, no. 5: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050574
APA StyleChang, X., & Ma, J. (2025). Integrated miRNA–mRNA Profiling of C2C12 Myoblasts Indicates Regulatory Interactions Involved in Proliferation and Differentiation. Biology, 14(5), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050574





