A Sec-Dependent Effector from “Candidatus Phytoplasma ziziphi” Suppresses Plant Immunity and Contributes to Pathogenicity
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Strains
2.2. Identification and Sequence Analysis of JWB790
2.3. Alkaline Phosphatase Assay
2.4. Agro-Infiltration Assays
2.5. Generation and Analysis of Transgenic A. thaliana Lines and Bacterial Inoculation Assay
2.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.7. RNA-Seq Analysis
3. Results
3.1. JWB790 Is a Sec-Dependent Effector and Expressed in JWB-Infected Tissues
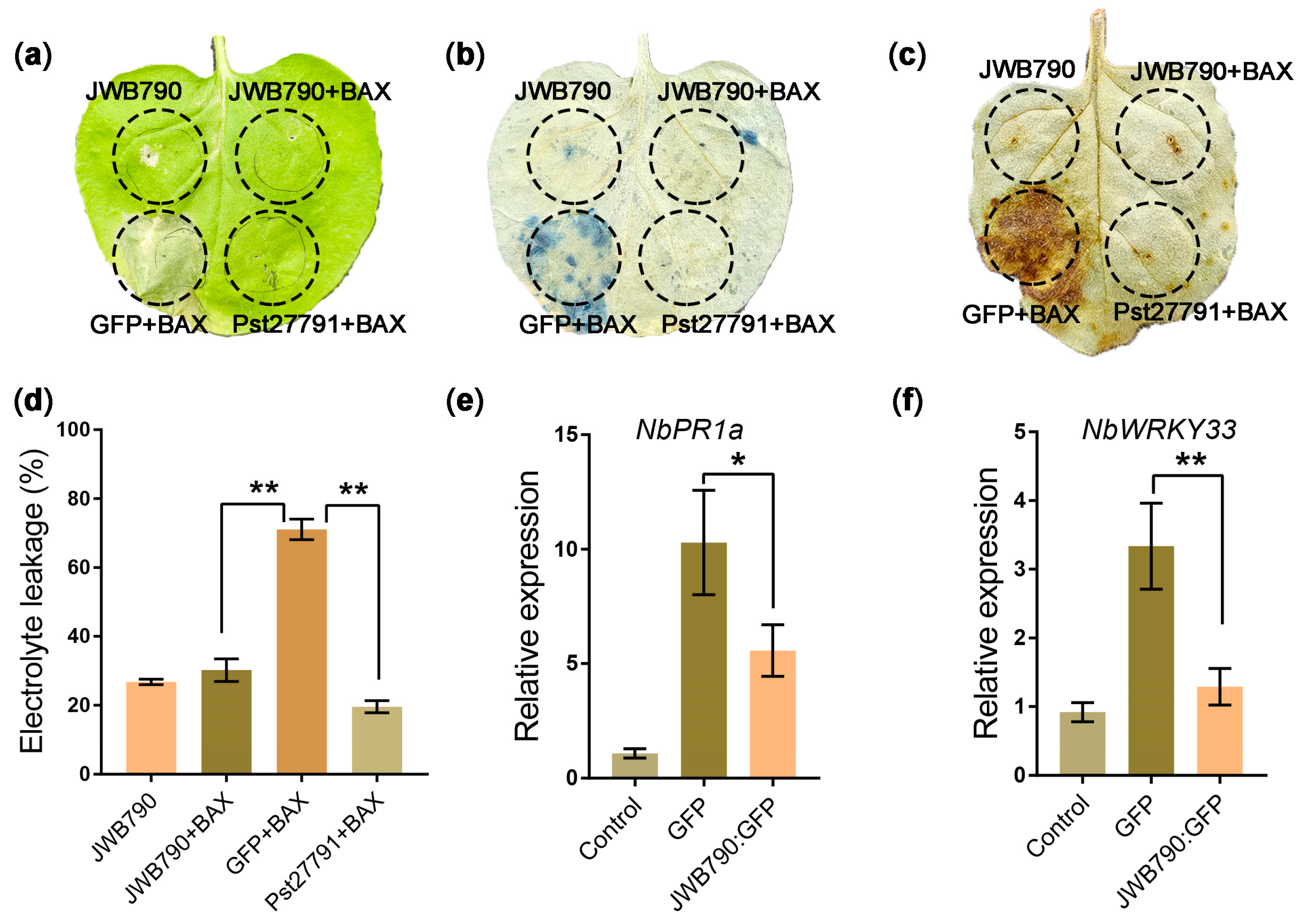
3.2. JWB790 Suppresses Cell Death and Basal Immune Response in Nicotiana benthamiana
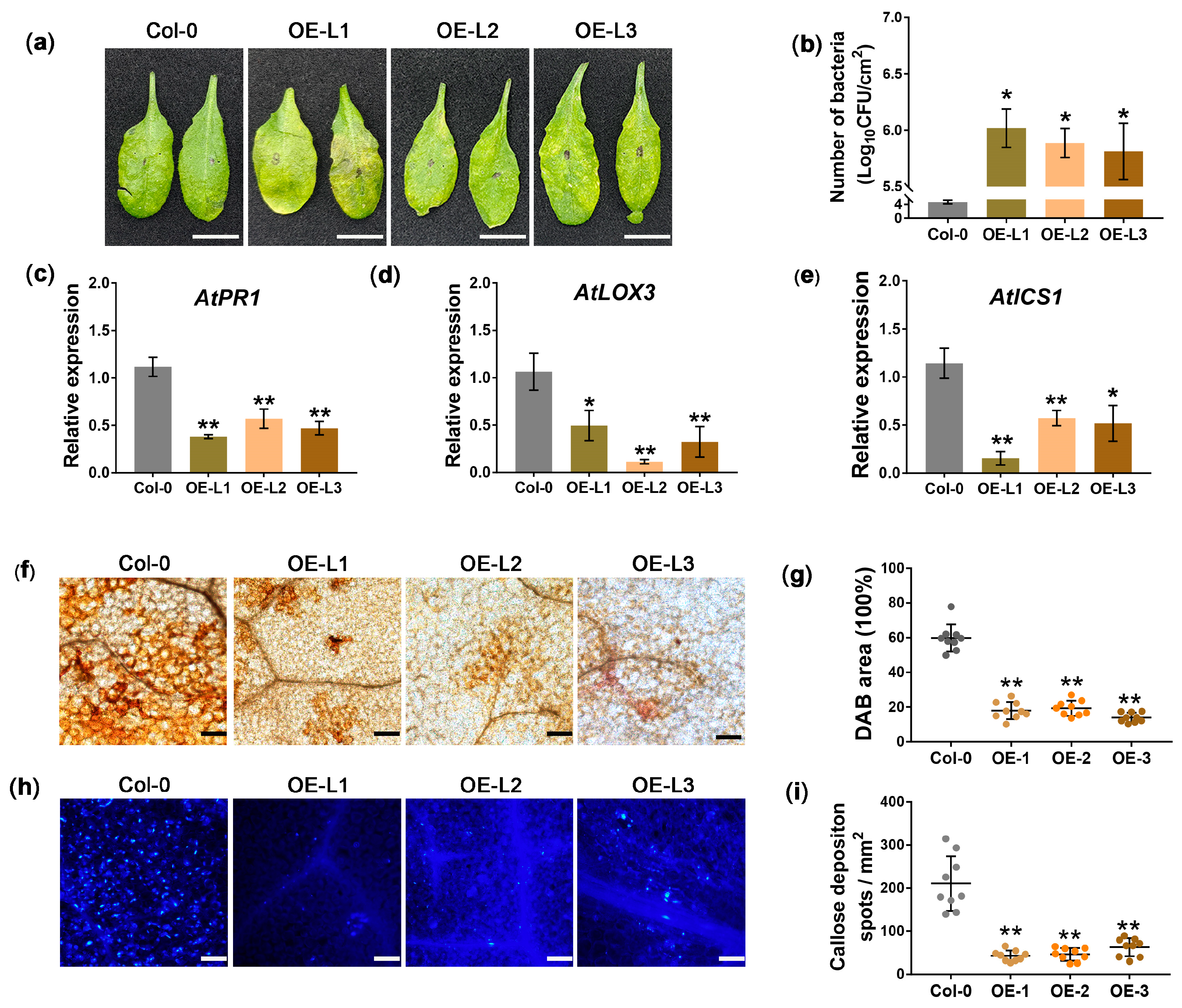
3.3. Overexpression of JWB790 in Arabidopsis thaliana Reduces Disease Resistance
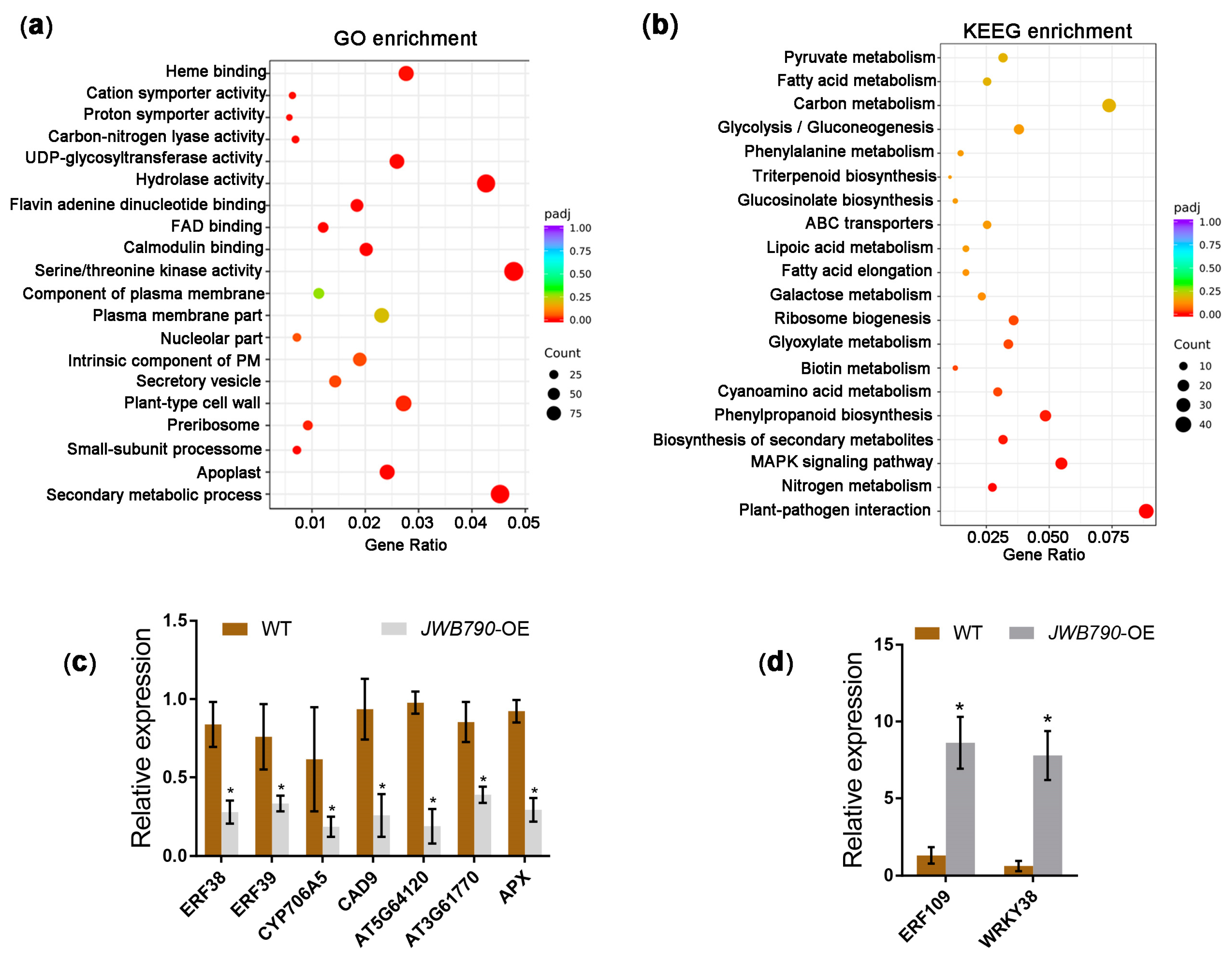
3.4. JWB790 Reprograms the Expression of Biotic Stimulus-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Pst | Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| JWB | Jujube Witches’ Broom |
| PTI | PAMP-Triggered Immunity |
| DAB | 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine Tetrahydrochloride Hydrate |
| PCD | Programmed Cell Death |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
References
- Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, S.; Stănică, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. The Historical and Current Research Progress on Jujube–a Superfruit for the Future. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Meinhardt, L.W.; Bailey, B.; Zhang, D. Genetic Improvement of Chinese Jujube for Disease Resistances: Status, Knowledge Gaps and Research Needs. Crop Breed. Genet. Genom. 2019, 1, e190015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, F.; Yao, Y.; Deng, M.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, N.; Huang, J.; et al. Jujube Witches’ Broom Phytoplasma Effectors SJP1 and SJP2 Induce Lateral Bud Outgrowth by Repressing the ZjBRC1-Controlled Auxin Efflux Channel. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 3257–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Song, L.; Jiao, Q.; Yang, S.; Gao, R.; Lu, X.; Zhou, G. Comparative Genome Analysis of Jujube Witches’-Broom Phytoplasma, an Obligate Pathogen That Causes Jujube Witches’-Broom Disease. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Zhao, J. The Genome of Candidatus phytoplasma Ziziphi Provides Insights into Their Biological Characteristics. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The Plant Immune System. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Apoplastic Proteases: Powerful Weapons against Pathogen Infection in Plants. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, C. Plant Pattern-Recognition Receptors. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toruño, T.Y.; Stergiopoulos, I.; Coaker, G. Plant-Pathogen Effectors: Cellular Probes Interfering with Plant Defenses in Spatial and Temporal Manners. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2016, 54, 419–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, L.; Choi, S.; He, S.Y.; Zipfel, C. The Conserved AvrE Family of Bacterial Effectors: Functions and Targets during Pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 33, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; McLellan, H.; Boevink, P.C.; Birch, P.R.J. All Roads Lead to Susceptibility: The Many Modes of Action of Fungal and Oomycete Intracellular Effectors. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugio, A.; MacLean, A.M.; Kingdom, H.N.; Grieve, V.M.; Manimekalai, R.; Hogenhout, S.A. Diverse Targets of Phytoplasma Effectors: From Plant Development to Defense against Insects. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chang, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, N.; Li, R. SDE19, a SEC-Dependent Effector from ‘Candidatus Liberibacter Asiaticus’ Suppresses Plant Immunity and Targets Citrus sinensis Sec12 to Interfere with Vesicle Trafficking. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Liu, Y.; Tian, S.; Guo, J.; Bai, X.; Zhu, H.; Kang, Z.; Guo, J. A Serine-Rich Effector from the Stripe Rust Pathogen Targets a Raf-like Kinase to Suppress Host Immunity. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Salicylic Acid: Biosynthesis, Perception, and Contributions to Plant Immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 50, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.Z.; Zhang, P.H.; Wu, Y.F. Identification of Wheat Blue Dwarf Phytoplasma Effectors Targeting Plant Proliferation and Defence Responses. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohmayer, A.; Moser, M.; Si-Ammour, A.; Krczal, G.; Boonrod, K. PM19_00185 of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma Mali’ Is a Protein That Functions as a E3 Ubiquitin Ligase. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 2019, 9, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sujata, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y. The ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma Tritici’ Effector SWP12 Degrades the Transcription Factor TaWRKY74 to Suppress Wheat Resistance. Plant J. 2022, 112, 1473–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, W.; Li, W. Candidatus Phytoplasma Ziziphi Encodes Non-Classically Secreted Proteins That Suppress Hypersensitive Cell Death Response in Nicotiana benthamiana. Phytopathol. Res. 2023, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.S.; Xu, Q.C.; Wan, C.P.; Kong, D.Z.; Lin, C.L.; Yu, S.S. Molecular Variation and Phylogeny of Thymidylate Kinase Genes of Candidatus Phytoplasma Ziziphi from Different Resistant and Susceptible Jujube Cultivars in China. Biology 2024, 13, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, C.S.; Wright, A. Fusions of Secreted Proteins to Alkaline Phosphatase: An Approach for Studying Protein Secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 5107–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, Q.; Ye, W.; Tao, K.; Duan, S.; Lu, C.; Yang, X.; Dong, S.; Zheng, X.; et al. The RxLR Effector Avh241 from Phytophthora Sojae Requires Plasma Membrane Localization to Induce Plant Cell Death. N. Phytol. 2012, 196, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Huang, G.; Meng, Y.; Shan, W. Phytophthora infestans RXLR Effector PITG20303 Targets a Potato MKK1 Protein to Suppress Plant Immunity. N. Phytol. 2021, 229, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral Dip: A Simplified Method for Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Xin, X.F. Bacterial Infection and Hypersensitive Response Assays in Arabidopsis-Pseudomonas syringae Pathosystem. Bio-Protoc. 2021, 11, e4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Yang, H.; Yin, Z.; Liu, W.; Sun, L.; Wu, Y. Phytoplasma Effector SWP1 Induces Witches’ Broom Symptom by Destabilizing the TCP Transcription Factor BRANCHED1. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 2623–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamir, Y.; Guo, M.; Oh, H.S.; Petnicki-Ocwieja, T.; Chen, S.; Tang, X.; Dickman, M.B.; Collmer, A.; Alfano, J.R. Identification of Pseudomonas syringae Type III Effectors That Can Suppress Programmed Cell Death in Plants and Yeast. Plant J. 2004, 37, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur, L.A.J.; Kenton, P.; Lloyd, A.J.; Ougham, H.; Prats, E. The Hypersensitive Response; The Centenary Is upon Us but How Much Do We Know? J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.T.; Xu, P.; Zhao, P.X.; Liu, R.; Yu, L.H.; Xiang, C.B. Arabidopsis ERF109 Mediates Cross-Talk between Jasmonic Acid and Auxin Biosynthesis during Lateral Root Formation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C.; Lai, Z.; Fan, B.; Chen, Z. Arabidopsis WRKY38 and WRKY62 Transcription Factors Interact with Histone Deacetylase 19 in Basal Defense. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomkins, M.; Kliot, A.; Marée, A.F.; Hogenhout, S.A. A Multi-Layered Mechanistic Modelling Approach to Understand How Effector Genes Extend beyond Phytoplasma to Modulate Plant Hosts, Insect Vectors and the Environment. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 44, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Teixeira, P.J.P.L.; Biswas, S.; Finkel, O.M.; He, Y.; Salas-Gonzalez, I.; English, M.E.; Epple, P.; Mieczkowski, P.; Dangl, J.L. Pseudomonas syringae Type III Effector HopBB1 Promotes Host Transcriptional Repressor Degradation to Regulate Phytohormone Responses and Virulence. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceulemans, E.; Ibrahim, H.M.M.; De Coninck, B.; Goossens, A. Pathogen Effectors: Exploiting the Promiscuity of Plant Signaling Hubs. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musetti, R.; Paolacci, A.; Ciaffi, M.; Tanzarella, O.A.; Polizzotto, R.; Tubaro, F.; Mizzau, M.; Ermacora, P.; Badiani, M.; Osler, R. Phloem Cytochemical Modification and Gene Expression Following the Recovery of Apple Plants from Apple Proliferation Disease. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Gao, W.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xue, C. The Antioxidant Defense System in Chinese Jujube Is Triggered to Cope with Phytoplasma Invasion. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Feng, B.; He, P.; Shan, L. From Chaos to Harmony: Responses and Signaling upon Microbial Pattern Recognition. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 109–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, C.-P.; He, F.-X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Song, C.-S. A Sec-Dependent Effector from “Candidatus Phytoplasma ziziphi” Suppresses Plant Immunity and Contributes to Pathogenicity. Biology 2025, 14, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050528
Wan C-P, He F-X, Zhang W, Xu Q, Zhu Q-L, Song C-S. A Sec-Dependent Effector from “Candidatus Phytoplasma ziziphi” Suppresses Plant Immunity and Contributes to Pathogenicity. Biology. 2025; 14(5):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050528
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Cui-Ping, Fu-Xin He, Wei Zhang, Qian Xu, Qi-Liang Zhu, and Chuan-Sheng Song. 2025. "A Sec-Dependent Effector from “Candidatus Phytoplasma ziziphi” Suppresses Plant Immunity and Contributes to Pathogenicity" Biology 14, no. 5: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050528
APA StyleWan, C.-P., He, F.-X., Zhang, W., Xu, Q., Zhu, Q.-L., & Song, C.-S. (2025). A Sec-Dependent Effector from “Candidatus Phytoplasma ziziphi” Suppresses Plant Immunity and Contributes to Pathogenicity. Biology, 14(5), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050528





