Taurine-Dominated Feeding Attractant Mixture Induces Efficient Foraging in Neptunea cumingii
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
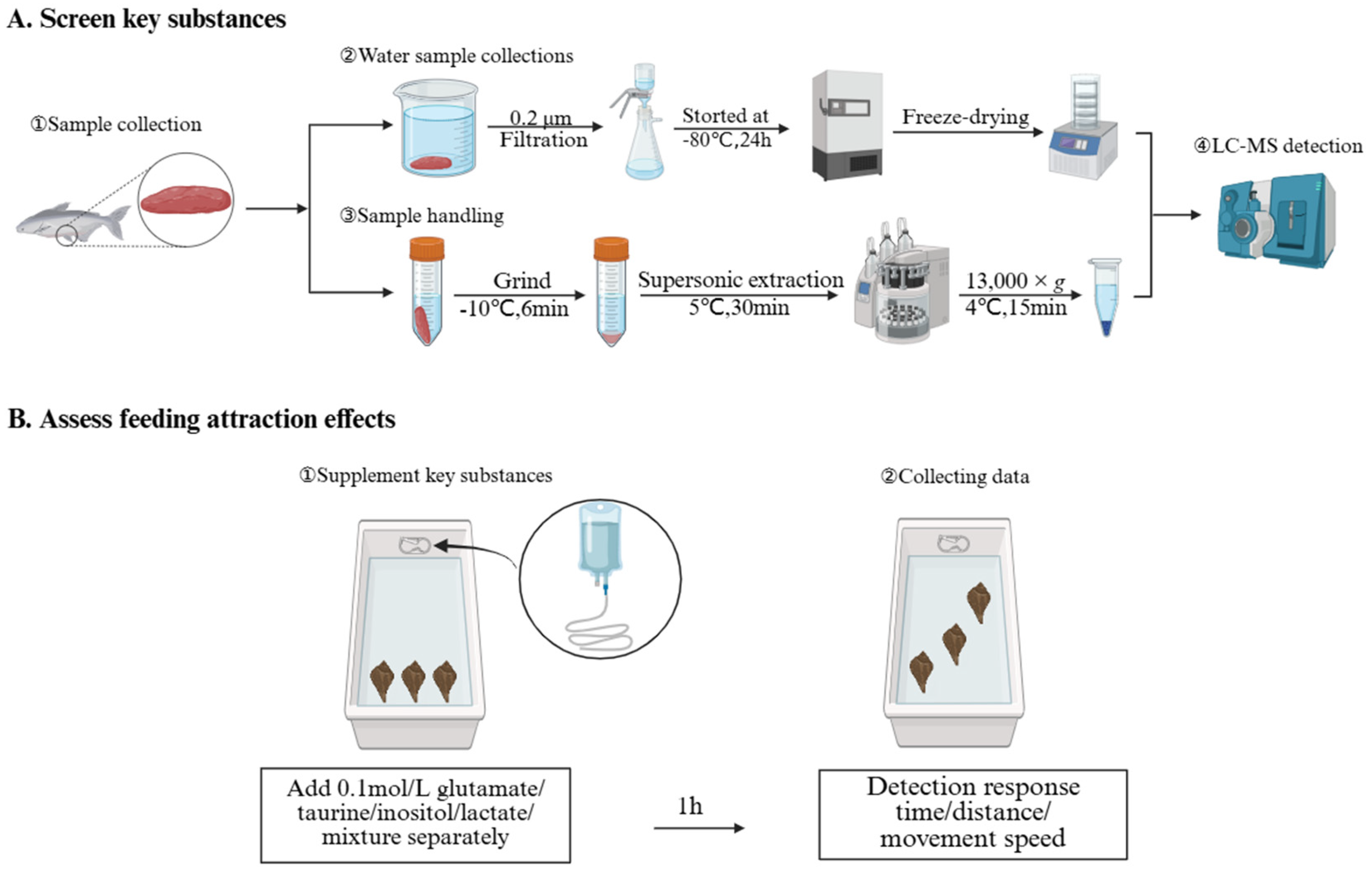
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Skate Meat Processing and Aqueous Extract Preparation
2.3. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. Foraging Behavior Assay
2.5. Collection and Analysis of Behavioral Data
2.6. Construction Standards for Attractant Efficacy Scoring System
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
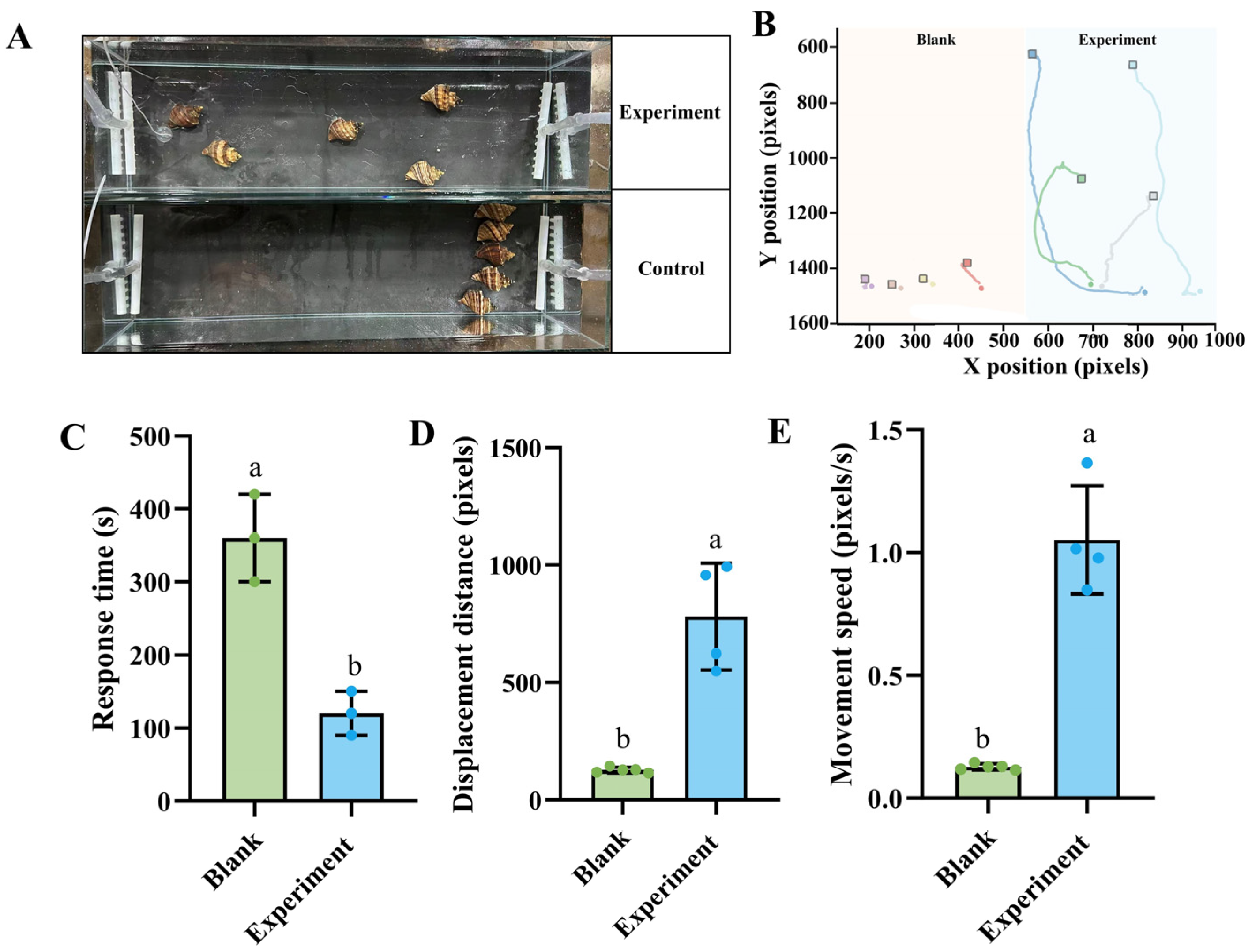
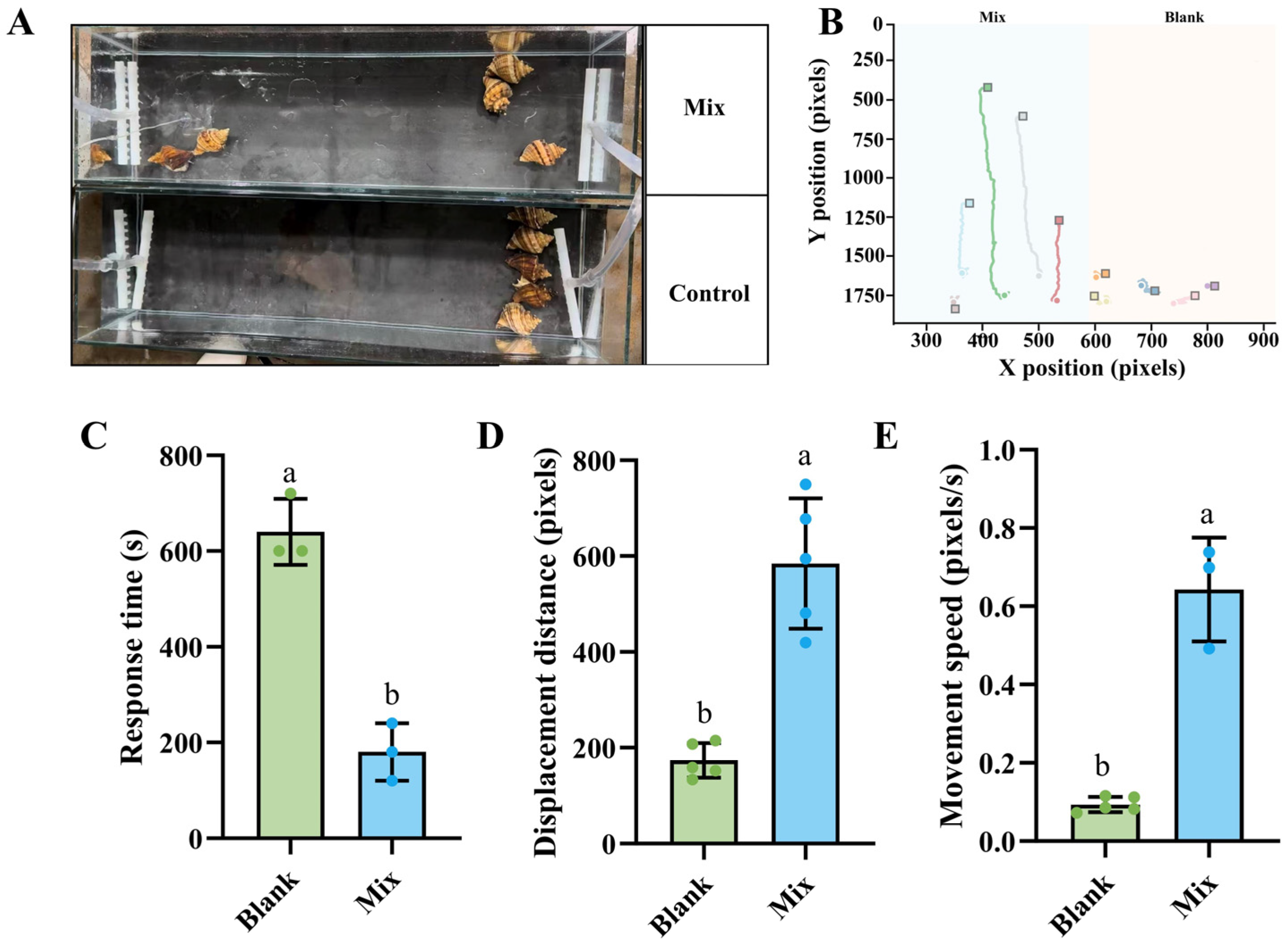
3.1. Effects of Skate Meat on Foraging Behavior of N. cumingii
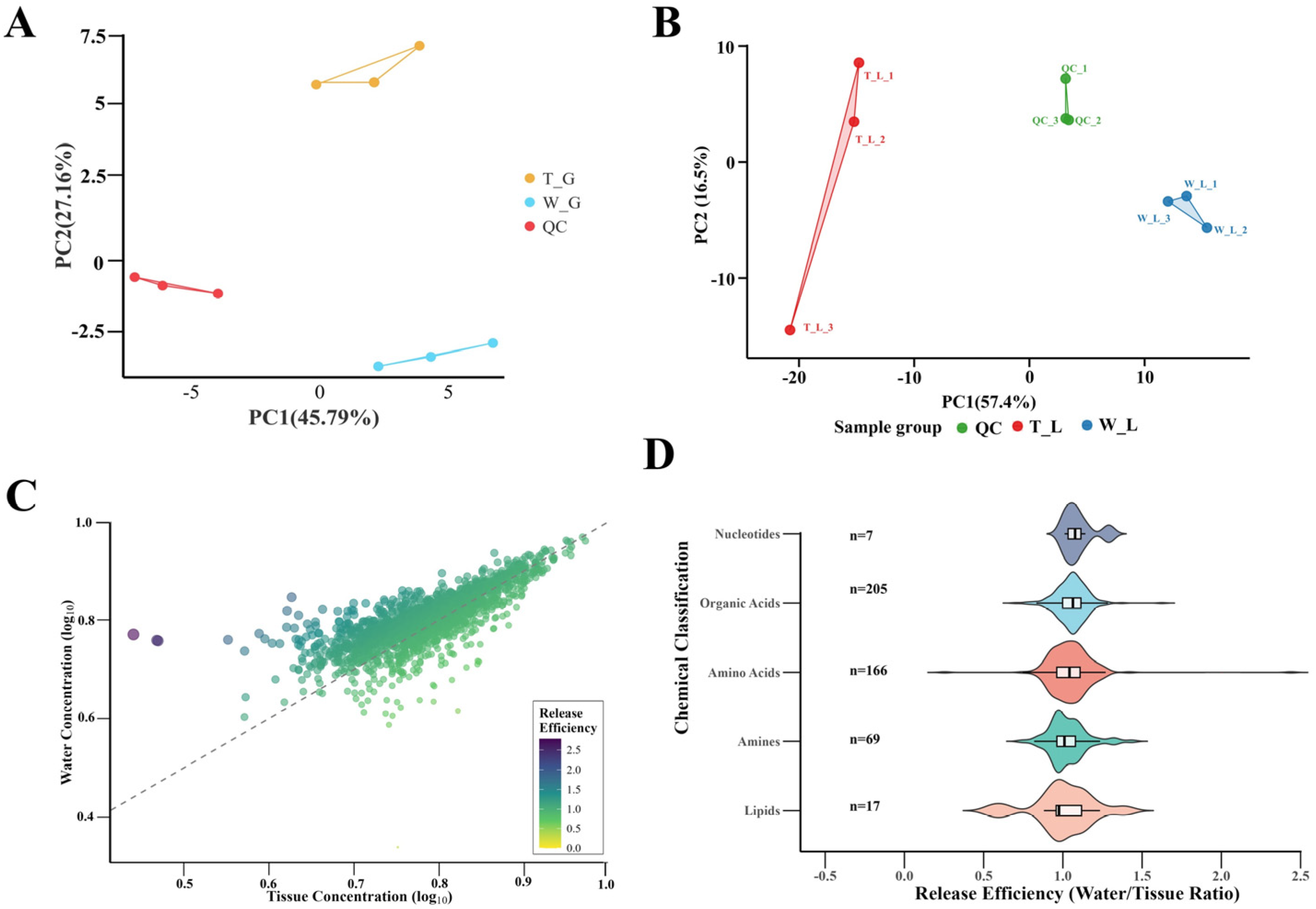
3.2. Screening of Key Metabolites Through Metabolomics
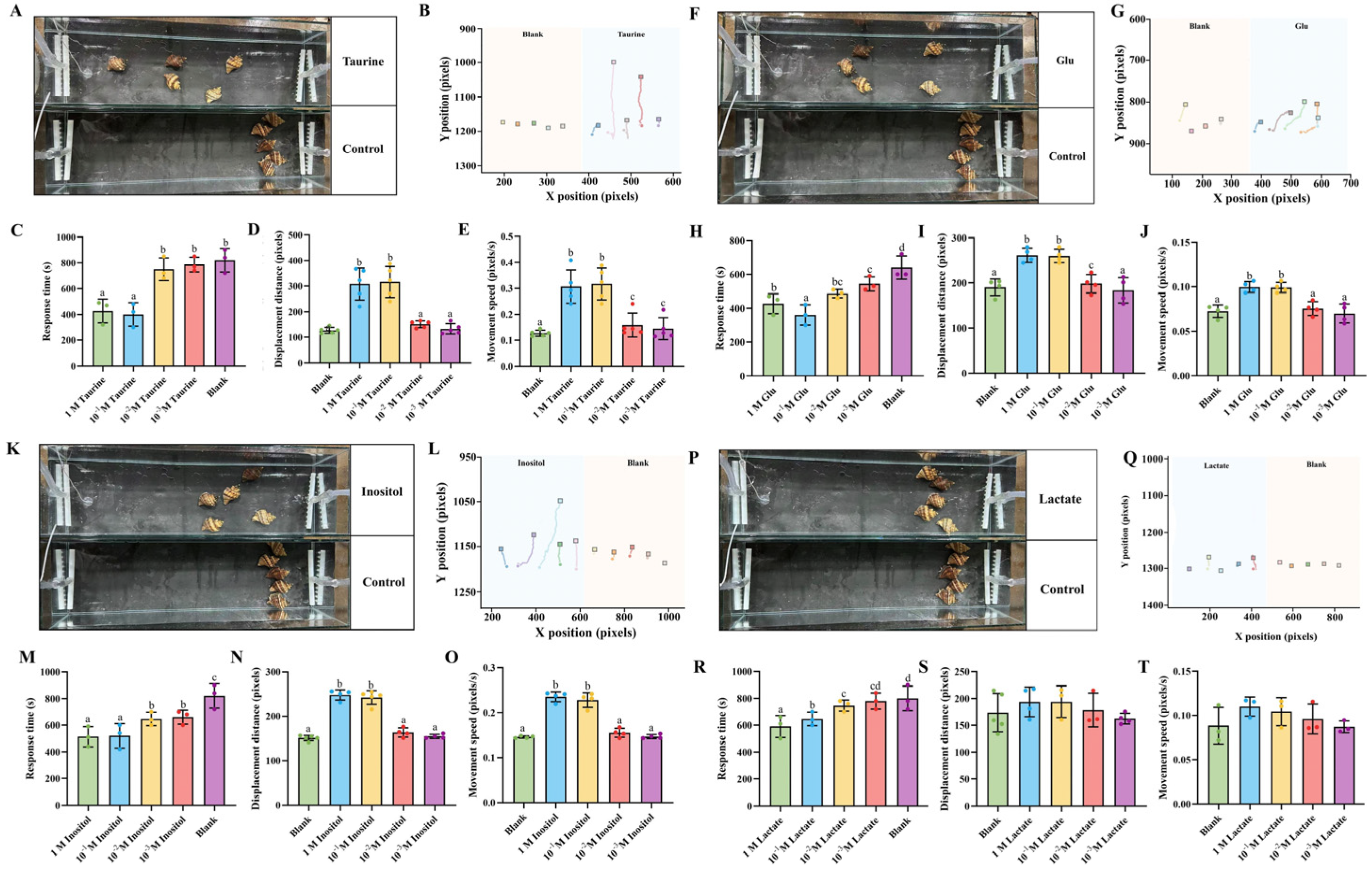
3.3. Effects of Individual Key Metabolites on Foraging Behavior of N. cumingii
3.4. Effects of Mixed Key Metabolites on Foraging Behavior of N. cumingii
3.5. Analysis of Attractant Efficacy Using Comprehensive Evaluation System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, X.; Zhao, J.; Liang, Z.; Chi, Q.; Mao, J.; Wang, X.; Chang, Y.; Hao, Z. Comparative analysis of Neptunea cumingii growth, related digestive and immune enzyme indicators, and liver transcriptome under different feeding conditions. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1013180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Construction and characterization of microsatellite markers for the Neptune whelk, Neptunea cumingii. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 9065–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Zhang, D.; Tian, Y.; Mao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Chang, Y.; Hao, Z. Genetic structure and local adaptation of Neptunea cumingii crosse populations in China based on GBS technology. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1154781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yang, M.; Song, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, T. Settlement and metamorphosis of Rapana venosa (Gastropoda: Muricidae) with implications for artificial culture. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.I.; Bruno, J.F.; Gaines, S.D.; Halpern, B.S.; Lester, S.E.; Kinlan, B.P.; Weiss, J.M. Temperature control of larval dispersal and the implications for marine ecology, evolution, and conservation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappalardo, P.; Fernández, M. Mode of larval development as a key factor to explain contrasting effects of temperature on species richness across oceans. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.J.; Krug, P.J.; Kupriyanova, E.K.; Byrne, M.; Emlet, R.B. The biogeography of marine invertebrate life histories. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munley, M.K.; Fairchild, E.A.; Jury, S.H.; Watson, W.H., III.; Edmundson, S.A. Laboratory investigations into alternative baits for the channeled whelk (Busycotypus canaliculatus) fishery. Fish. Res. 2024, 271, 106920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løkkeborg, S.; Siikavuopio, S.I.; Humborstad, O.-B.; Utne-Palm, A.C.; Ferter, K. Towards more efficient longline fisheries: Fish feeding behaviour, bait characteristics and development of alternative baits. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2014, 24, 985–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, S.; Deborde, C.; Richard, N.; Skiba-Cassy, S.; Moing, A.; Fauconneau, B. Metabolomics and fish nutrition: A review in the context of sustainable feed development. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFiore, B.P.; Cheng, B.S.; Dutka-Gianelli, J.; Kinchla, A.J.; Jordaan, A. An alternative bait for the American lobster fishery composed of fishery by-products to reduce reliance on forage fish. Fish. Res. 2025, 286, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryhn, A.C.; Königson, S.J.; Lunneryd, S.-G.; Bergenius, M.A. Green lamps as visual stimuli affect the catch efficiency of floating cod (Gadus morhua) pots in the Baltic Sea. Fish. Res. 2014, 157, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyeth, R.C. Olfactory navigation in aquatic gastropods. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222 (Suppl. S1), jeb185843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ache, B.W.; Carr, W.E. Chemoreception in aquatic invertebrates. In Neural Mechanisms in Taste; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.-L.; Yang, M.-J.; Song, H.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, X.-T. Gastropod chemoreception behaviors—Mechanisms underlying the perception and location of targets and implications for shellfish fishery development in aquatic environments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1042962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.S.; Liew, K.S.; Ebi, I.; Shapawi, R.; Mohamad Lal, M.T.; Liew, H.J.; Hamasaki, K.; Masuda, R.; Kawamura, G. Amino acids as chemoattractant and feeding stimulant for the commercially farmed decapod crustaceans: A brief review. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.W.; Stacey, N.E. Brief review of fish pheromones and discussion of their possible uses in the control of non-indigenous teleost fishes. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2004, 38, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R. Applications of metabolomics to the environmental sciences. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, L.M.; Larsson, D.J. Contributions from metabolomics to fish research. Mol. Biosyst. 2008, 4, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Gatlin, D.M., III. Nucleotide nutrition in fish: Current knowledge and future applications. Aquaculture 2006, 251, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Koshio, S.; Kestemont, P. Recent advances of nucleotide nutrition research in aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1028–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Chen, X.; Zeng, Q.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Z.; Tan, B.; Xie, S. Effects of compound feed attractants on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal histology, protein synthesis, and immune response of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Animals 2022, 12, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Kong, F.; Song, X.; Tan, Q. The attractive effects of amino acids and some classical substances on grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 1489–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferner, M.C.; Smee, D.L.; Weissburg, M.J. Habitat complexity alters lethal and non-lethal olfactory interactions between predators and prey. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 374, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, Y.; Shi, M.; Jia, L.; Xu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Qi, C.; Ye, J. Effects of Dietary Glutamate on the Growth Performance and Antioxidant Capacity of Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fishes 2024, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, C.D.; Sorensen, P. Neural processing, perception, and behavioral responses to natural chemical stimuli by fish and crustaceans. J. Chem. Ecol. 2008, 34, 898–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Meyers, S.J.A.N. Chemoattraction and feeding stimulation in crustaceans. Aquac. Nutr. 1996, 2, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Tabrett, S.; Barclay, M.; Irvin, S.J.A.N. The efficacy of ingredients included in shrimp feeds to stimulate intake. Aquac. Nutr. 2005, 11, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.; Schousboe, A. Taurine interaction with neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS: An update. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Yue, M.; Chandra, D.; Keramidas, A.; Goldstein, P.A.; Homanics, G.E.; Harrison, N.L. Taurine is a potent activator of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the thalamus. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, E.; Song, M.; Yang, Y.; Qin, C.; Qin, J.; Chen, L. Comprehensive transcriptional and metabolomic analysis reveals the neuroprotective mechanism of dietary gamma-aminobutyric acid response to hypoxic stress in the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 135, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.; Crimaldi, J. Odor landscapes and animal behavior: Tracking odor plumes in different physical worlds. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 49, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, L.; MacKenzie, A.B.; Sluyter, R. Roles of ion Channels in immune Cells. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-de la Paz, L.; Zenteno, E.; Gulias-Cañizo, R.; Quiroz-Mercado, H. Taurine and GABA neurotransmitter receptors, a relationship with therapeutic potential? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.L.; Armstrong, N. Structure and function of glutamate receptor ion channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2009, 1793, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.T.; Wang, T.; Milsom, W.K.; Bayley, M. Lactate provides a strong pH-independent ventilatory signal in the facultative air-breathing teleost Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, T.; Rotgans, B.A.; McManus, D.P.; Cummins, S.F. Ionotropic receptors identified within the tentacle of the freshwater snail Biomphalaria glabrata, an intermediate host of Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.A.; Nardi, G.; Brown, E.R. AMPA/kainate and NMDA-like glutamate receptors at the chromatophore neuromuscular junction of the squid: Role in synaptic transmission and skin patterning. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittschof, D.; Cohen, J.H. Crustacean peptide and peptide-like pheromones and kairomones. Peptides 2004, 25, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. The inositol trisphosphate/calcium signaling pathway in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1261–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, R.K.; Butman, C.A. Chemical signaling processes in the marine environment. Biol. Bull. 2000, 198, 168–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, C.D.; Kozma, M.T.; Senatore, A.; Schmidt, M. Molecular mechanisms of reception and perireception in crustacean chemoreception: A comparative review. Chem. Senses 2016, 41, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentinčič, T. Taste and olfactory stimuli and behavior in fishes. In The Senses of Fish: Adaptations for the Reception of Natural Stimuli; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 90–108. [Google Scholar]
- Derby, C.D. Cephalopod ink: Production, chemistry, functions and applications. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2700–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Content | Standard Formula | Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improvement rate calculation | Response time improvement rate | (Control Value—Experimental Value)/Control Value × 100% | |
| Movement distance enhancement rate | (Experimental Value—Control Value)/Control Value × 100% | ||
| Movement speed enhancement rate | (Experimental Value—Control Value)/Control Value × 100% | ||
| Response time score | ≥70% | 100 points | Weight: 40 |
| 50–69% | 70–99 points (linear interpolation) | ||
| 30–49% | 40–69 points (linear interpolation) | ||
| <30% | <40 points | ||
| Movement distance/Speed score | ≥700% | 100 points | Weight: 35/25 |
| 200–699% | 60–99 points (linear interpolation) | ||
| 100–199% | 30–59 points (linear interpolation) | ||
| <100 | <30 | ||
| Effect level classification | Excellent | ≥90 points | |
| Good | 70–89 points | ||
| Fair | 50–69 points | ||
| Poor | <50 points |
| GC-MS | LC-MS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | POS | POS | NEG | Amino Acid |
| 1 | Lactic acid | Oleamide | Inosine | Taurine |
| 2 | Myo-Inositol | Trimethylamine N-oxide | Lactate | Glutamate |
| 3 | Arabitol | Linoleamide | Docosahexaenoic Acid | L-Isoleucine |
| 4 | Glucose | L-Phenylalanine | LysoPE | L-Phenylalanine |
| 5 | Glycerol | Hexylamine | Citric acid | L-Tyrosine |
| Ranking | Test Substance | Behavioral Parameter Improvement Effects | Comprehensive Evaluation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response Time Improvement Rate (%) | Distance Enhancement Rate (%) | Speed Enhancement Rate (%) | Comprehensive Score | Effect Level | ||
| 1 | Skate meat | 70 | 515.4 | 746.2 | 94.8 | Excellent |
| 2 | Mix | 69 | 579.1 | 580.9 | 93.6 | Excellent |
| 3 | Taurine | 50 | 164.5 | 163 | 55.4 | Moderate |
| 4 | Glu | 44 | 33 | 33.3 | 38.5 | Poor |
| 5 | Inositol | 37 | 87.4 | 87.1 | 37.7 | Poor |
| 6 | Lactate | 3.3 | 20.6 | 20 | 21.7 | Poor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Ren, W.; Sun, P.; He, Z.; An, F.; Gao, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, M. Taurine-Dominated Feeding Attractant Mixture Induces Efficient Foraging in Neptunea cumingii. Biology 2025, 14, 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111627
Li D, Ren W, Sun P, He Z, An F, Gao L, Zhang X, Li M. Taurine-Dominated Feeding Attractant Mixture Induces Efficient Foraging in Neptunea cumingii. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111627
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Deliang, Wenjing Ren, Pengcheng Sun, Zhaoyu He, Fenghe An, Lei Gao, Xueshu Zhang, and Ming Li. 2025. "Taurine-Dominated Feeding Attractant Mixture Induces Efficient Foraging in Neptunea cumingii" Biology 14, no. 11: 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111627
APA StyleLi, D., Ren, W., Sun, P., He, Z., An, F., Gao, L., Zhang, X., & Li, M. (2025). Taurine-Dominated Feeding Attractant Mixture Induces Efficient Foraging in Neptunea cumingii. Biology, 14(11), 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111627








