Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance and Microbial Contamination in Commercial Veterinary Probiotic Products
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Sequencing and Sequence Analysis
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Bacillus spp.
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
2.4. Detection of ARGs
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
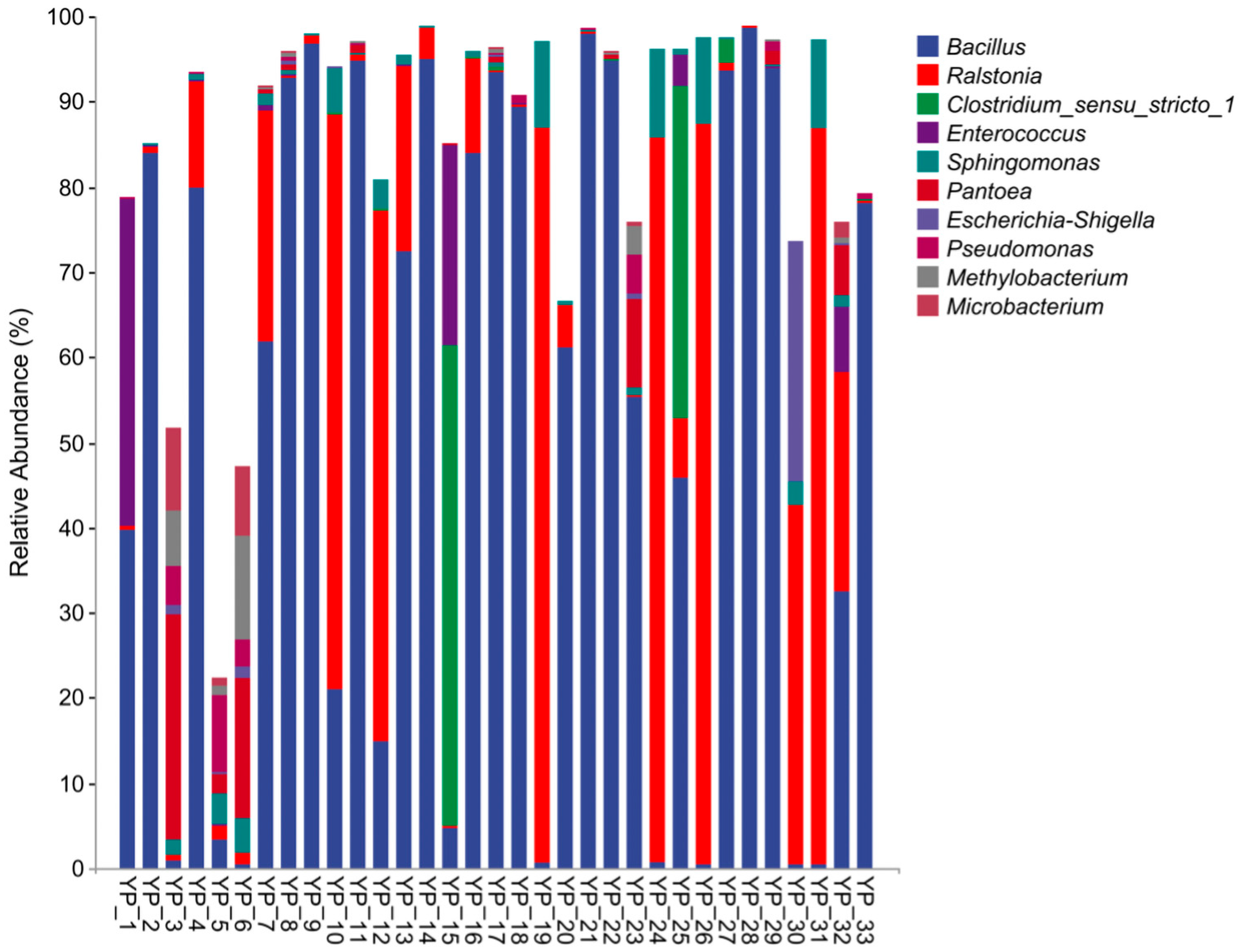
3.1. Microbial Composition, Isolation of Dominant Strains, and Accuracy Assessment of Labeling
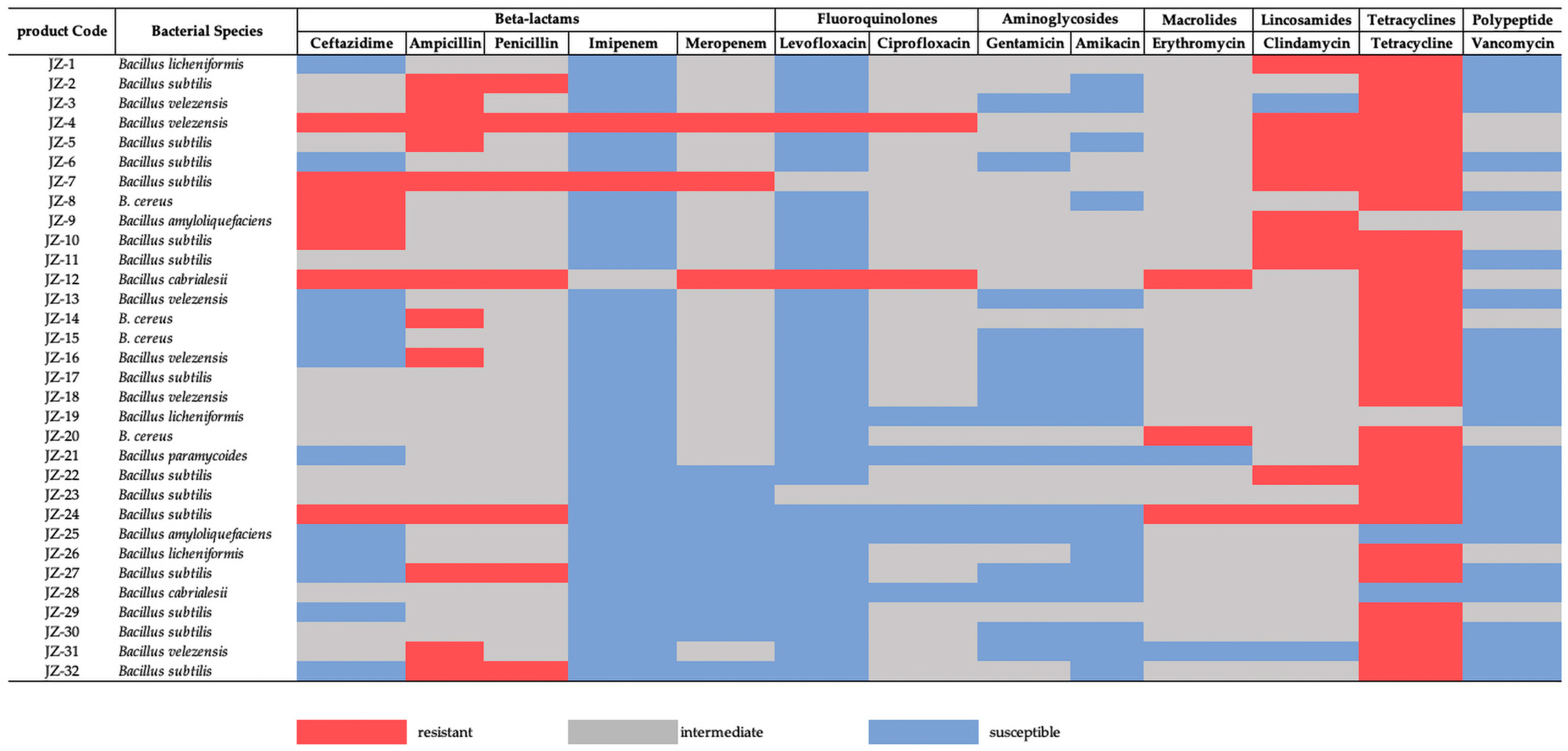
3.2. Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacillus spp.
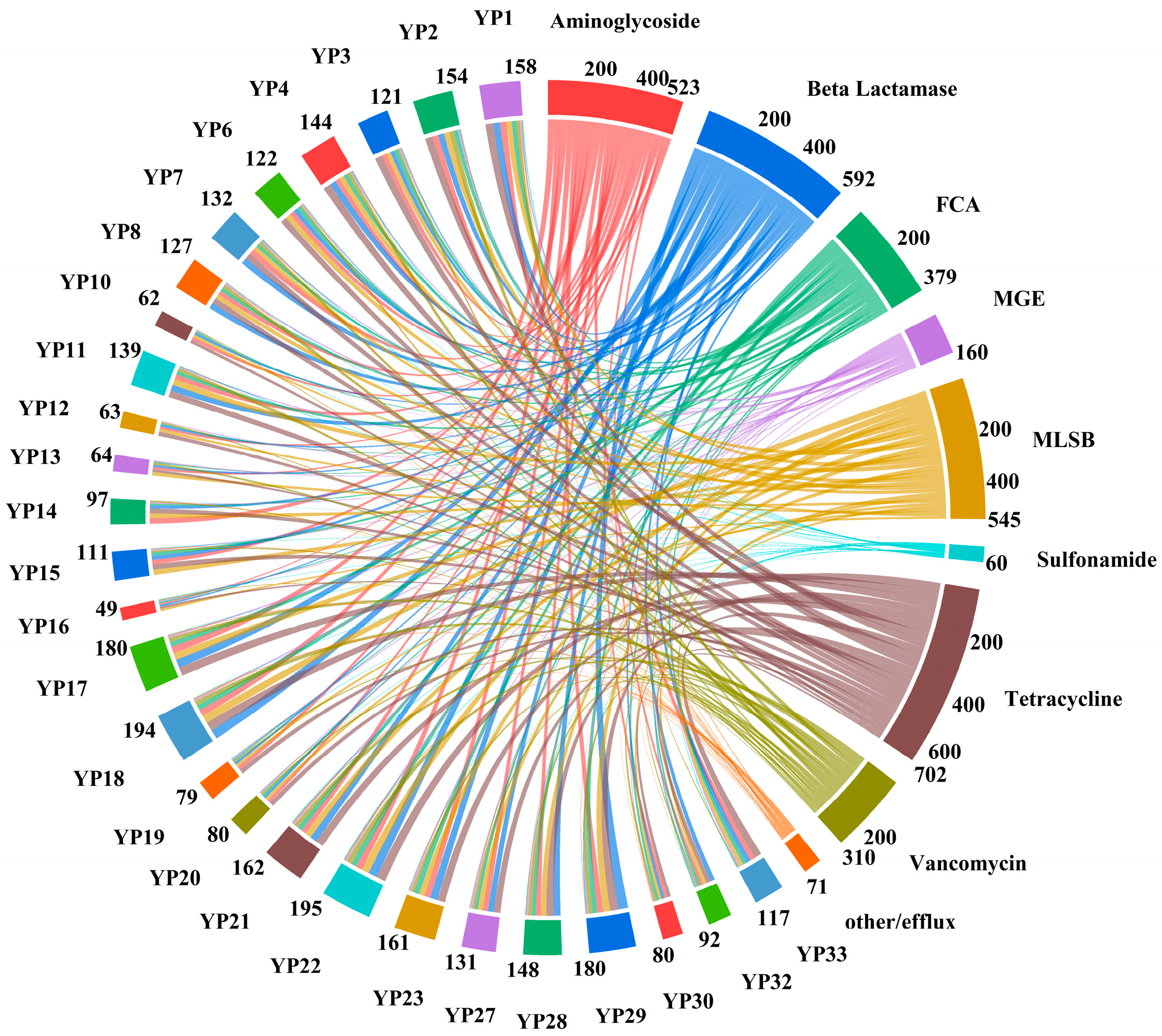
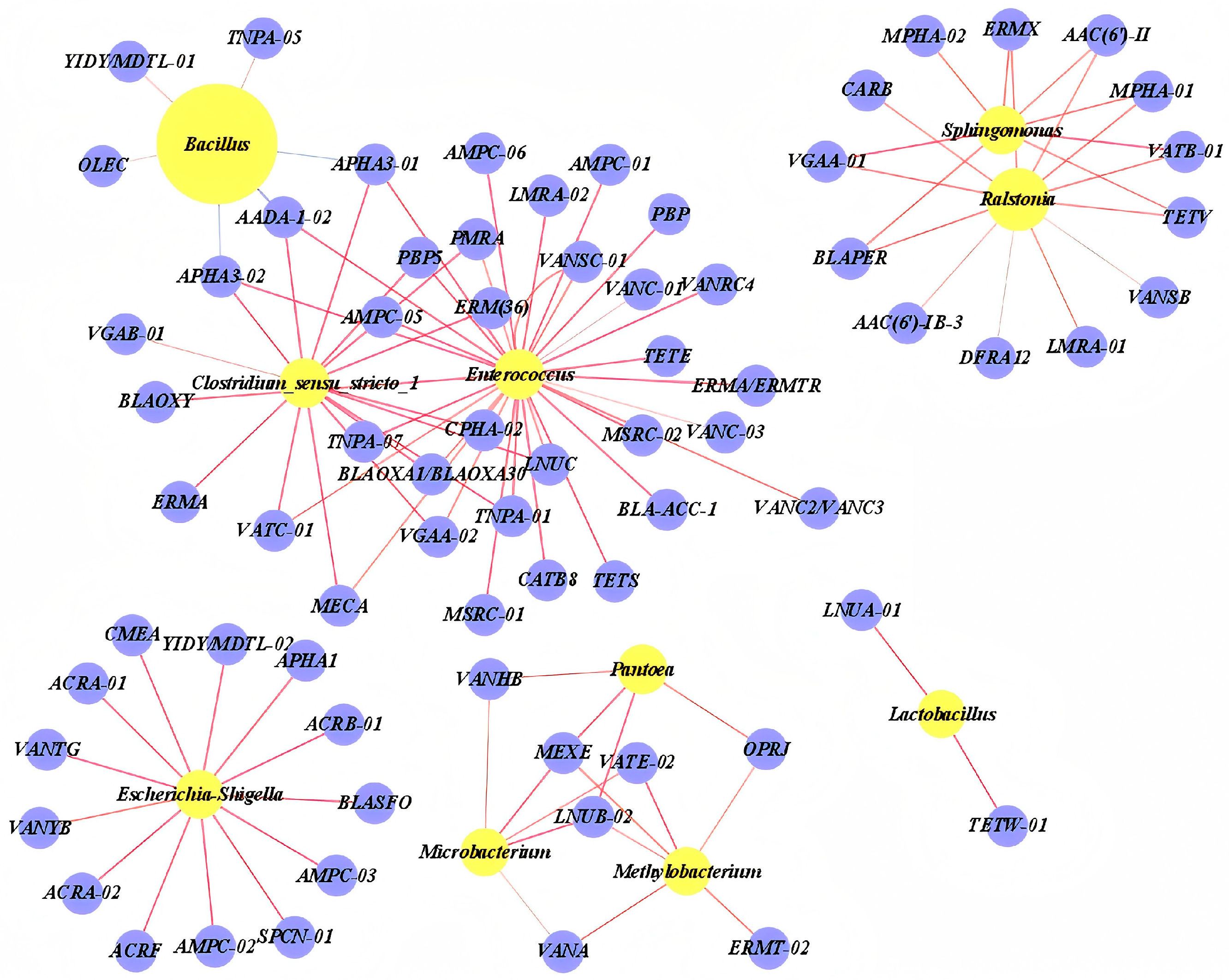
3.3. Abundance and Co-Occurrence of ARGs and MGEs
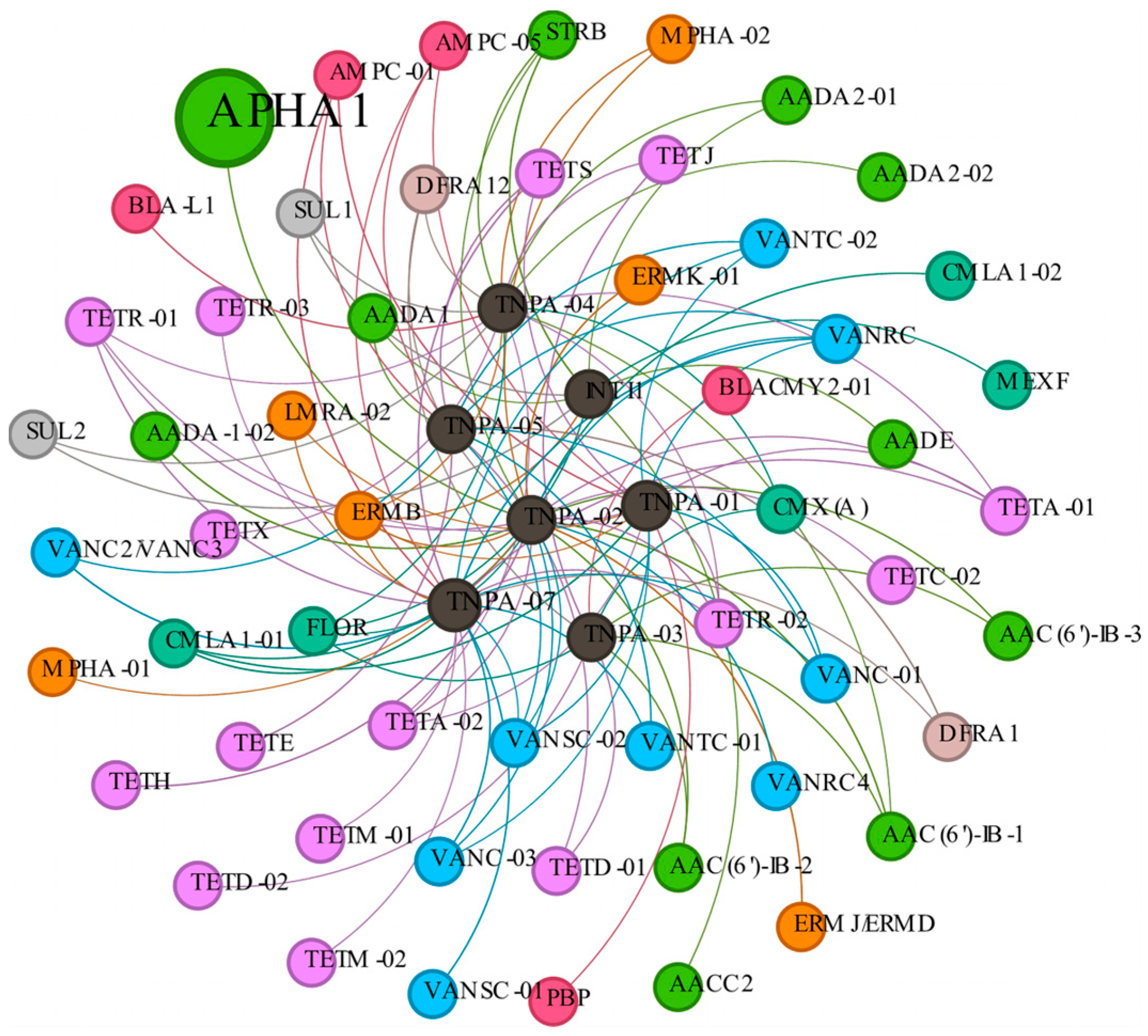
3.4. Co-Occurrence of ARGs and Bacterial Community
4. Discussion
4.1. Microbial Composition, Isolation of Dominant Strains, and Accuracy Assessment of Labeling
4.2. Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacillus spp.
4.3. Abundance and Co-Occurrence of ARGs and MGEs
4.4. Co-Occurrence of ARGs and Bacterial Community
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castanon, J.I. History of the use of antibiotic as growth promoters in European poultry feeds. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emes, E.; Belay, D.; Knight, G.M. The contribution of animal antibiotic use to antibiotic resistance in human infections: Panel evidence from Denmark. One Health 2024, 19, 100856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A. Broiler production without antibiotics: United States field perspectives. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 250, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Maravilla, E.; Parra, M.; Maisey, K.; Vargas, R.A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Tello, M.; Bermudez-Humaran, L.G. Importance of Probiotics in Fish Aquaculture: Towards the Identification and Design of Novel Probiotics. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Lu, Y.; Ding, W.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Jian, F.; Huang, S. The Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics in Livestock and Poultry Gut Health: A Review. Metabolites 2025, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Yang, Q.; He, F.; Lan, R.; Hao, J.; Ni, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, R. National Safety Survey of Animal-use Commercial Probiotics and Their Spillover Effects From Farm to Humans: An Emerging Threat to Public Health. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 2386–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutting, S.M. Bacillus probiotics. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Holzel, C.S.; Cui, Y.; Mayer, R.; Wang, Y.; Dietrich, R.; Didier, A.; Bassitta, R.; Martlbauer, E.; Ding, S. Probiotic Bacillus cereus Strains, a Potential Risk for Public Health in China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.S.; Martin, H. Assessment of commercial probiotic bacterial contents and label accuracy. Can. Vet. J. 2011, 52, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jezewska-Frackowiak, J.; Seroczynska, K.; Banaszczyk, J.; Jedrzejczak, G.; Zylicz-Stachula, A.; Skowron, P.M. The promises and risks of probiotic Bacillus species. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazerji, S.S.; Nardini, R.; Safdar, M.; Shehata, A.A.; Duarte, P.M. An Overview of Anthropogenic Actions as Drivers for Emerging and Re-Emerging Zoonotic Diseases. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Liao, X.; Hasan, M.; Elafify, M.; Kim, J.C.; Ding, T.; Ahn, J. The impact of probiotics on antibiotic resistance: Mechanisms, food safety risks, and regulatory considerations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, Q.L.; Shen, F.; Wu, Y.; Xu, S.; Fan, H.; Da, G.; Huang, R.J.; et al. Global Survey of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10975–10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Feng, T.; Yang, J.; Su, W.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Seasonal distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the Yellow River water and tap water, and their potential transmission from water to human. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Chen, T.; Cao, Z.; Zhong, S.; Wen, X.; Mi, J.; Ma, B.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liao, X.; et al. Antibiotic resistance genes in layer farms and their correlation with environmental samples. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, I.; Rahman, S.; Jan, A.T.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Mondal, A.H.; Haq, Q.M.R. Antibiotics, Resistome and Resistance Mechanisms: A Bacterial Perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing—EUCAST. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, Version 13.0. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 4 November 2025).
- Adamski, P.; Byczkowska-Rostkowska, Z.; Gajewska, J.; Zakrzewski, A.J.; Klebukowska, L. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance of Bacillus sp. Isol. Raw Milk. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.K.; Kim, W.S.; Paik, H.D. Bacillus strains as human probiotics: Characterization, safety, microbiome, and probiotic carrier. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Shah, A.A.; Khan, R.U.; Khan, M.S.; Wanapat, M. Emerging trends and applications in health-boosting microorganisms-specific strains for enhancing animal health. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 183, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luise, D.; Bosi, P.; Raff, L.; Amatucci, L.; Virdis, S.; Trevisi, P. Bacillus spp. Probiotic Strains as a Potential Tool for Limiting the Use of Antibiotics, and Improving the Growth and Health of Pigs and Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 801827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO, F. Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. Prevention 2001, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Weese, J.S. Microbiologic evaluation of commercial probiotics. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 220, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimova, E.; Gorokhova, I.; Karimullina, G.; Yarullina, D. Alarming Antibiotic Resistance of Lactobacilli Isolated from Probiotic Preparations and Dietary Supplements. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Chen, Y.; Sun, T.; Wu, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Wen, J. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence characteristics and genotypes of Bacillus spp. from probiotic products of diverse origins. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredua-Agyeman, M.; Larbi, E.A. Inaccurate labelling practices in probiotic products: A regulatory shortfall in Accra, Ghana. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0322194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Q.; Lu, B.; Shen, H.; Liu, S.; Shi, Y.; Leptihn, S.; Li, H.; Wei, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Whole-genome analysis of probiotic product isolates reveals the presence of genes related to antimicrobial resistance, virulence factors, and toxic metabolites, posing potential health risks. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Han, J.K.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, J.I.; Kim, K.S. Various Enterotoxin and Other Virulence Factor Genes Widespread Among Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis Strains. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, T.H. Tetracycline Antibiotics and Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Yagihara, Y.; Tatsuno, K.; Okazaki, M.; Okugawa, S.; Moriya, K. Clinical characteristics and antimicrobial susceptibility of Bacillus cereus blood stream infections. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2015, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyirt, S.; Şanlıbaba, P.; Uymaz Tezel, B. Antibiotic Resistance in Probiotic Microorganisms. Turk. J. Agric.—Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 11, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Hossen, F.; Islam, M.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Siddique, N.; He, C.; Ahmed, F. Bacillus spp. Contamination: A Novel Risk Originated From Animal Feed to Human Food Chains in South-Eastern Bangladesh. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 783103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Islam, M.A.; Hossen, F.; Rahman, M.A.; Ahmed, F.; He, C. Emergence of multidrug-resistant Bacillus spp. derived from animal feed, food and human diarrhea in South-Eastern Bangladesh. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; He, L.Y.; Wu, D.L.; Gao, F.Z.; Zhang, M.; Zou, H.Y.; Yao, M.S.; Ying, G.G. Spread of airborne antibiotic resistance from animal farms to the environment: Dispersal pattern and exposure risk. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalewska, M.; Blazejewska, A.; Czapko, A.; Popowska, M. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Animal Manure—Consequences of Its Application in Agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 610656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, A.G.; Judge, M.F.; Nagy, S.A.; Papp, M.; Solymosi, N. A survey on antimicrobial resistance genes of frequently used probiotic bacteria, 1901 to 2022. Euro Surveill. 2023, 28, 2200272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R.; Gaze, W.H.; Pruden, A.; Smalla, K.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhu, Y.-G. Using the class 1 integron-integrase gene as a proxy for anthropogenic pollution. ISME J. 2014, 9, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, S.H.; Li, X.; Rashid, A.; Su, J.; Xu, J.; Brejnrod, A.D.; Su, J.Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhou, S.G.; et al. Co-selection of antibiotic resistance genes, and mobile genetic elements in the presence of heavy metals in poultry farm environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; An, X.L.; Huang, F.Y.; Su, J.Q. Antibiotic resistome in a landfill leachate treatment plant and effluent-receiving river. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, E.W.; Wang, P.; Smith, A.L.; Stadler, L.B. Determining Hosts of Antibiotic Resistance Genes: A Review of Methodological Advances. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Cui, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. Analysis of Resistance Gene Diversity in the Intestinal Microbiome of Broilers from Two Types of Broiler Farms in Hebei Province, China. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Liu, Y.; Shehata, E.; Feng, Y.; Lin, H.; Xue, J.; Li, Z. In-feed antibiotic use changed the behaviors of oxytetracycline, sulfamerazine, and ciprofloxacin and related antibiotic resistance genes during swine manure composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Product 1 | Source Area | Purpose of Application 2 | Ingredients on the Label | Isolates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xingtai, Hebei | A, D | Bacillus licheniformis | Bacillus licheniformis |
| 2 | Bayan Nur, Inner Mongolia | A, C, D | Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis | Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus velezensis, |
| 3 | Heilongjiang | B, D | Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus licheniformis | None |
| 4 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | B, D | Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus velezensis |
| 5 | Shijiazhuang, Hebei | A | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 6 | Heilongjiang | A, B, E | Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 7 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | B, D | Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 8 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | A, D | Lactobacillus plantarum, Bacillus subtilis Saccharomyces cerevisiae, | Bacillus cereus, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens |
| 9 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | A, D, E | Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis | None |
| 10 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | A, C | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 11 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | A, B, C, D, F | Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 12 | Shenzhen, Guangdong | A, B, C, D, E | Lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus licheniformis | Bacillus cabrialesii |
| 13 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | A, D | Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, | Bacillus velezensis |
| 14 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | A, C | Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus cereus |
| 15 | Pizhou, Jiangsu | A, B, C, D | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus cereus |
| 16 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | A, B, C | Bacillus subtilis, Yeast | Bacillus velezensis |
| 17 | Xianyang, Shaanxi | A, B, E | Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 18 | Nanning, Guangxi | A, B, E | Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus velezensis |
| 19 * | Shandong | A, D | Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus licheniformis |
| 20 | Shandong | A, B, C, E | Lactobacillus plantarum, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus cereus |
| 21 | Shangqiu, Henan | A, D | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus paramycoides |
| 22 | Fuyang, Anhui | A, B, C, E | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 23 | Xilingol League, Inner Mongolia | C | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 24 | Baoding, Hebei | A, C, D | Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Bacillus licheniformis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 25 | Dalian, Liaoning | A, B, C | Clostridium butyricum, Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens |
| 26 | Weifang, Shandong | A, B, C, D | Bifidobacterium, Bacillus licheniformis Streptococcus | Bacillus licheniformis |
| 27 | Chengdu, Sichuan | A, B, C, D, E | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 28 | Jinan, Shandong | A, B, E | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus cabrialesii |
| 29 | Nanchang, Jiangxi | A, B, E | Bacillus subtilis, Lactobacillus plantarum | Bacillus subtilis |
| 30 | Shangqiu, Henan | A, B, D | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| 31 | Shangqiu, Henan | A, B, E | Bacillus subtilis | None |
| 32 | Harbin, Heilongjiang | A, B, D | Bacillus subtilis | Bacillus velezensis |
| 33 * | Shijiazhuang, Hebei | A, B, D | Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Bacillus subtilis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, T. Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance and Microbial Contamination in Commercial Veterinary Probiotic Products. Biology 2025, 14, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111612
Guan S, Wang C, Zhang Z, Wang M, Zhao X, Zhang T. Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance and Microbial Contamination in Commercial Veterinary Probiotic Products. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111612
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Shuo, Chunguang Wang, Zongshu Zhang, Mengfan Wang, Xinghua Zhao, and Tie Zhang. 2025. "Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance and Microbial Contamination in Commercial Veterinary Probiotic Products" Biology 14, no. 11: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111612
APA StyleGuan, S., Wang, C., Zhang, Z., Wang, M., Zhao, X., & Zhang, T. (2025). Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance and Microbial Contamination in Commercial Veterinary Probiotic Products. Biology, 14(11), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111612





