Evolutionary Dynamics of Chloroplast Genome and Codon Usage in the Genus Diospyros (Ebenaceae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Collection and Sequencing Procedure
2.2. Chloroplast Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Comparative Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes in the Genus Diospyros
2.3.1. Analysis of Simple Sequence Repeat in Chloroplast Genomes
2.3.2. Comparative Assessment of Chloroplast Genome Junction Regions
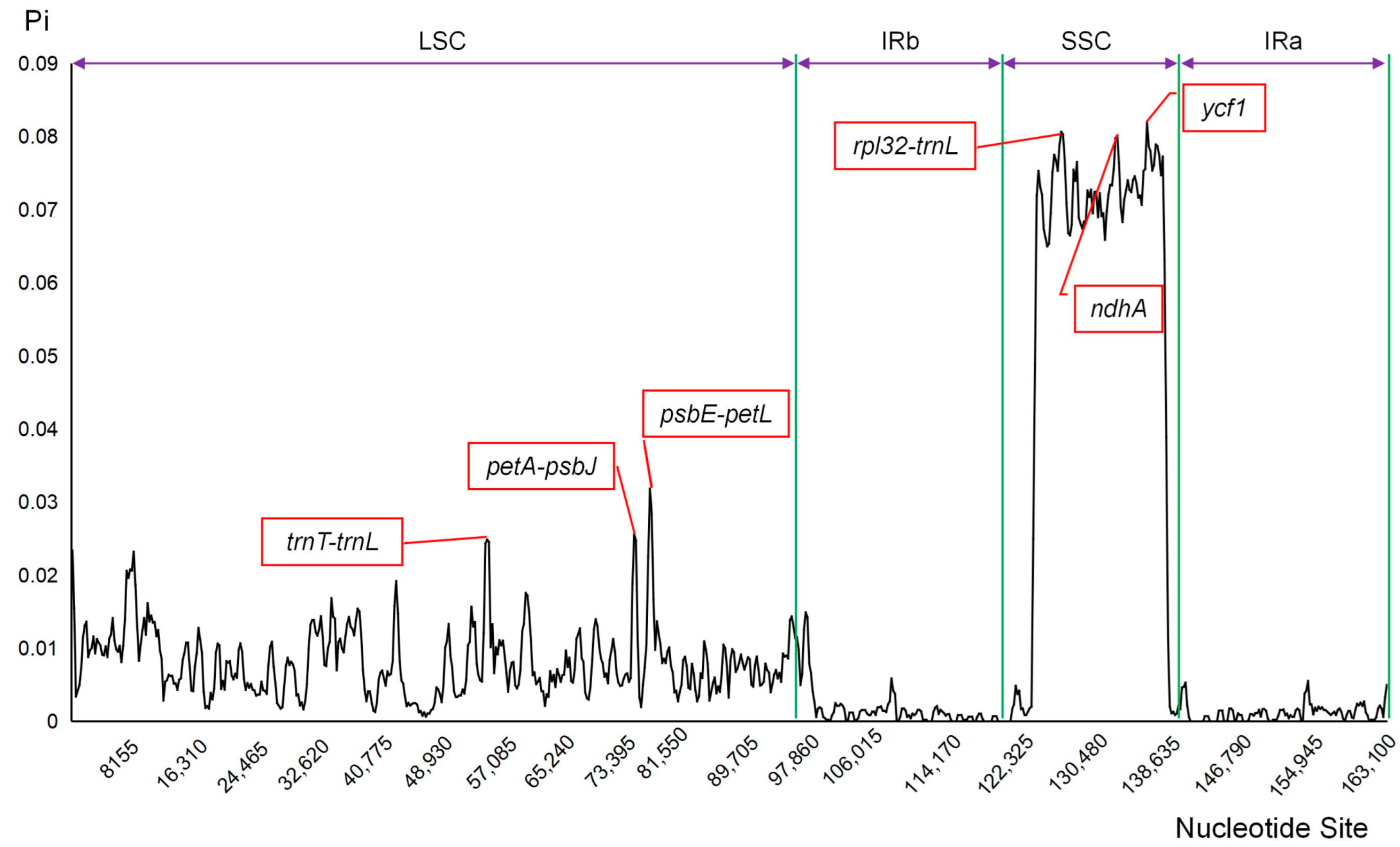
2.3.3. Evaluation of Nucleic Acid Polymorphism and Selective Pressure
2.3.4. Phylogenetic Tree Reconstruction and Time Estimation
2.4. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias Pattern in Chloroplast Genomes in Diospyros
2.4.1. Calculation of Parameters Related to Codon Usage Bias
2.4.2. Analysis of the Causes of Codon Usage Bias
2.4.3. Determination of Optimal Codons
3. Results
3.1. Chloroplast Genome Characters of Diospyros tsangii
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes in Diospyros
3.2.1. The Size and Structure of the Chloroplast Genome
3.2.2. Boundary Analysis of IR in the Genus Diospyros
3.2.3. Chloroplast Genome Sequence Variation and Selected Pressure Assessment
3.2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Codon Usage Bias in the Chloroplast Genomes of Diospyros
3.3.1. Codon Composition Characteristics and Preferences of Chloroplast Genomes
3.3.2. The Causes of Codon Usage Bias
3.3.3. Optimal Codons of Chloroplast Genome in Diospyros
4. Discussion
4.1. Chloroplast Genome Evolution Within Diospyros
4.2. Natural Selection and the Codon Preference of the Diospyros Chloroplast Genome
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.K.; Gilberg, M.G.; White, F. Diospyros Linnaeus. In Flora of China; Wu, Z.-Y., Raven, P.H., Hong, D.-Y., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996; Volume 15, pp. 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, L.; Guo, D.; Luo, Z. Number of Species and Geographical Distribution of Diospyros L. (Ebenaceae) in China. Hortic. Plant J. 2019, 5, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangjai, S.; Samuel, R.; Munzinger, J.; Forest, F.; Wallnöfer, B.; Barfuss, M.H.J.; Fischer, G.; Chase, M.W. A multi-locus plastid phylogenetic analysis of the pantropical genus Diospyros (Ebenaceae), with an emphasis on the radiation and biogeographic origins of the New Caledonian endemic species. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 52, 602–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-N.; Fan, J.-F.; Yue, X.; Wu, X.-R.; Li, L.-T. Radical scavenging activity and phenolic compounds in persimmon (Diospyros kaki L. cv. Mopan). J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, C24–C28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Leontowicz, H.; Leontowicz, M.; Namiesnik, J.; Jesion, I.; Gorinstein, S. Nutraceutical value of persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.) and its influence on some indices of atherosclerosis in an experiment on rats fed cholesterol-containing diet. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2008, 22, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, I.-C.; Jo, E.-K.; Bae, M.-S.; Lee, H.-J. Antioxidant and antigenotoxic activities of different parts of persimmon (Diospyros kaki cv. Fuyu) fruit. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.; Qiao, J.-J.; Lu, G.-Y.; Wu, G.; Xie, G.-Y.; Qin, M.-J. Identification of six species of medicinal Diospyros plants based on leaf macro-and micro-morphology. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 3942–3949, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Pu, T.-T.; Wang, Y.-R.; Li, H.-W.; Luo, Y.; Li, T.-S.; Fu, J.-M. Diversity of fruit quality in astringent and non-astringent persimmon fruit germplasm. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, C.; Abdin, M.Z.; Kumar, S. Chloroplast genome transformation of medicinal plant Artemisia annua. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2155–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-T.; Luo, Y.; Gan, L.; Ma, P.-F.; Gao, L.-M.; Yang, J.-B.; Cai, J.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Fritsch, P.W.; Zhang, T.; et al. Plastid phylogenomic insights into relationships of all flowering plant families. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Yin, X.-M.; Han, J.-P.; Sun, W.; Yao, H.; Song, J.-Y.; Li, X.-W. DNA barcoding in herbal medicine: Retrospective and prospective. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-M.; Wang, J.-R.; Feng, L.; Liu, S.; Pang, H.-B.; Qi, L.; Li, J.; Qiao, W.-H.; Zhang, L.-F.; Cheng, Y.-L.; et al. Inferring the evolutionary mechanism of the chloroplast genome size by comparing whole-chloroplast genome sequences in seed plants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrogojski, J.; Adamiec, M.; Luciński, R. The chloroplast genome: A review. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, E.B.; Downie, S.R.; Palmer, J.D. Chloroplast genome rearrangements and the evolution of giant lobelias from herbaceous ancestors. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosner, M.E.; Raubeson, L.A.; Jansen, R.K. Chloroplast DNA rearrangements in Campanulaceae: Phylogenetic utility of highly rearranged genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2004, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.-S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.-J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Lei, W.-S.; Shi, Y.-K.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.-H.; Xiang, X.-G. Plastome evolution, phylogenomics, and DNA barcoding investigation of Gastrochilus (Aeridinae, Orchidaceae), with a focus on the systematic position of Haraella retrocalla. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.-Z.; Liu, K.-J.; Deng, R.-Y.; Gao, Y.-W.; Liu, X.-Y.; Dong, W.-P.; Zhang, Z.-X. Insights into the phylogeny and chloroplast genome evolution of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, W.-C.; Liao, X.-Z.; Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, H.-Q.; Wu, D.-L.; Tembrock, R.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Gu, C.-H. Phylogeny, molecular evolution, and dating of divergences in Lagerstroemia using plastome sequences. Hortic. Plant J. 2023, 9, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.-Z.; Cai, X.-D.; Gong, M.; Xia, M.-Q.; Xing, H.-H.; Dong, S.-S.; Tian, S.-M.; Li, J.-L.; Lin, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; et al. Complete chloroplast genomes provide insights into evolution and phylogeny of Zingiber (Zingiberaceae). BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, X.-J.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Li, P.; Meng, H.-H.; Zhang, Y.-H. Plastome evolution of Engelhardia facilitates phylogeny of Juglandaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.-R.; Fu, H.-T.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, X.-H.; Lu, L.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Mo, G.-H.; Wen, F.; Li, J.; Bhanot, D.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of 385 chloroplast genomes unveils phylogenetic relationships and evolutionary history in cassava. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriarte, A.; Lamolle, G.; Musto, H. Codon usage bias: An endless tale. J. Mol. Evol. 2021, 89, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cai, X.-N.; Chen, Q.-Z.; Zhou, H.-X.; Cai, Y.; Ben, A.-L. Factors affecting synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genome of Oncidium Gower Ramsey. Evol. Bioinform. 2011, 7, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zheng, C.-C.; Huang, J.-G.; Zhang, S.-Z. Genome-wide comparative analysis of the codon usage patterns in plants. Genes Genom. 2016, 38, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duret, L. tRNA gene number and codon usage in the C. elegans genome are co-adapted for optimal translation of highly expressed genes. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, H.; Zavala, A.; Musto, H. Codon usage in Chlamydia trachomatis is the result of strand-specific mutational biases and a complex pattern of selective forces. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2000, 28, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fages-Lartaud, M.; Hundvin, K.; Hohmann-Marriott, M.F. Mechanisms governing codon usage bias and the implications for protein expression in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J. 2022, 112, 919–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-J.; Liu, L.-E.; Ren, Q.-D.; Zhang, T.; Hu, N.; Sun, J.; Zhou, W. Analysis of synonymous codon usage bias in the chloroplast genome of five Caragana. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Shi, Z.-J. Comparative study on codon usage patterns across chloroplast genomes of eighteen Taraxacum species. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-P.; Shi, M.-W.; Ma, H.; Ma, Y.-J.; Yao, B.-Q. Analysis of codon bias in chloroplast genomes of ten plants in Androsace. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2025, 56, 1355–1365, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small amounts of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq-versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2017, 45, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 26, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and Other Methods), version 4.0b10; Sinauer: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2003.
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.-H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linan, A.G.; Schatz, G.E.; Lowry, P.P.; Miller, A.; Edwards, C.E. Ebony and the Mascarenes: The evolutionary relationships and biogeography of Diospyros (Ebenaceae) in the western Indian Ocean. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2019, 190, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, E.N.; Powell, J.R. Gene length and codon usage bias in Drosophila melanogaster, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 3188–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglsang, A. Impact of bias discrepancy and amino acid usage on estimates of the effective number of codons used in a gene. Gene 2008, 410, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Weon, S.; Lee, S.; Kang, C. Relative codon adaptation index, a sensitive measure of codon usage bias. Evol. Bioinform. 2010, 6, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, F. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicario, S.; Moriyama, E.N.; Powell, J.R. Codon usage in twelve species of Drosophila. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Dai, L.; Luo, M.-C.; Tang, F.-Q.; Tien, P.; Pan, Z.-S. Analysis of synonymous codon usage in classical swine fever virus. Virus Genes 2009, 38, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.-Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.-X.; Li, A.-S. plotnineSeqSuite: A Python package for visualizing sequence data using ggplot2 style. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Intrastrand parity rules of DNA base composition and usage biases of synonymous codons. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 40, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Translation-coupled violation of Parity Rule 2 in human genes is not the cause of heterogeneity of the DNA G+C content of third codon position. Gene 1999, 238, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Near homogeneity of PR2-bias fingerprints in the human genome and their implications in phylogenetic analyses. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 53, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.-X.; Bai, M.-Z.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Liu, Z.-J. The chloroplast genome evolution of Venus slipper (Paphiopedilum): IR expansion, SSC contraction, and highly rearranged SSC regions. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.-M.; Liu, H.-M.; Hu, J.-J.; Liang, Y.-Q.; Liang, J.-J.; Wuyun, T.; Tan, X.-F. Five complete chloroplast genome sequences from Diospyros: Genome organization and comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e015956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-Q.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.-M.; Lu, Y.-Z.; Yang, Z.-R.; Jin, X.-B.; Dong, W.-P.; Suo, Z.-L. Interspecific chloroplast genome sequence diversity and genomic resources in Diospyros. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-W.; Tan, X.-H.; Zhao, K.-K.; Zhu, Z.-X.; Wang, H.-F. Complete plastome sequences of Diospyros maclurei Merr. and Diospyros hainanensis Merr. (Ebenaceae): Two endemic species in Hainan Province, China. Mitochondrial DNA B 2018, 3, 1205–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.; Rouskin, S.; Ingolia, N.T.; Han, L.; Phizicky, E.M.; Weissman, J.S.; Koller, D. Causal signals between codon bias, mRNA structure, and the efficiency of translation and elongation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2014, 10, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathy, S.T.; Udayasuriyan, V.; Bhadana, V. Codon usage bias. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 539–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Dong, B.-R.; Fan, X.-J.; Wang, M.-X.; Wang, T.-Z.; Liu, Q.-P. Mutational bias and natural selection driving the synonymous codon usage of single-exon genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 2023, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, W.-Q.; Hu, X.-W.; Zhou, K.-B. Synonymous codon usage bias in the chloroplast genomes of 13 oil-tea Camellia samples from south China. Forests 2023, 14, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; He, S.-L.; He, J.; Zuo, Y.-J.; Guan, W.-L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.-J.; Meng, J. Plastid genomic features and phylogenetic placement in Rosa (Rosaceae) through comparative analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-J.; Shen, L.-W.; Chen, S.-Q.; Qu, S.; Hou, N. Codon usage profiling of chloroplast genome in Juglandaceae. Forests 2023, 14, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.H.; Gowri, G. Codon usage in higher plants, green algae, and cyanobacteria. Plant Physiol. 1990, 92, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Xu, B.-B.; Li, B.; Zhou, Q.-Q.; Wang, G.-Y.; Jiang, X.-Z.; Wang, C.-C.; Xu, Z.-D. Comparative analysis of codon usage patterns in chloroplast genomes of six Euphorbiaceae species. Peer J. 2020, 8, e8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Elizabeth, C.; Desmond, G.H.; Shields, D.C.; Kenneth, H.W.; Wright, F. Codon usage patterns in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable within species diversity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 8207–8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Emery, L.R.; Zeng, K. Forces that influence the evolution of codon bias. Philos. T. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-H.; Ding, Y.-Z.; He, Y.; Chu, Y.-F.; Zhao, P.; Ma, L.-Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Li, X.-R.; Liu, Y.-S. The effect of multiple evolutionary selections on synonymous codon usage of genes in the Mycoplasma bovis genome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, Z.; Sablok, G.; Daskalova, E.; Zahmanova, G.; Apostolova, E.; Yahubyan, G.; Baev, V. Chloroplast genome analysis of resurrection tertiary relict Haberlea rhodopensis highlights genes important for desiccation stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.-M.; Deng, Y.-F.; Wang, J. The complete chloroplast genomes of Echinacanthus species (Acanthaceae): Phylogenetic relationships, adaptive evolution, and screening of molecular markers. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Cai, Q.-W.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, Z.-X.; Jiao, C.-Y.; Xu, C.-C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-L. Comparative analysis of codon bias in the chloroplast genomes of Theaceae species. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 824610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
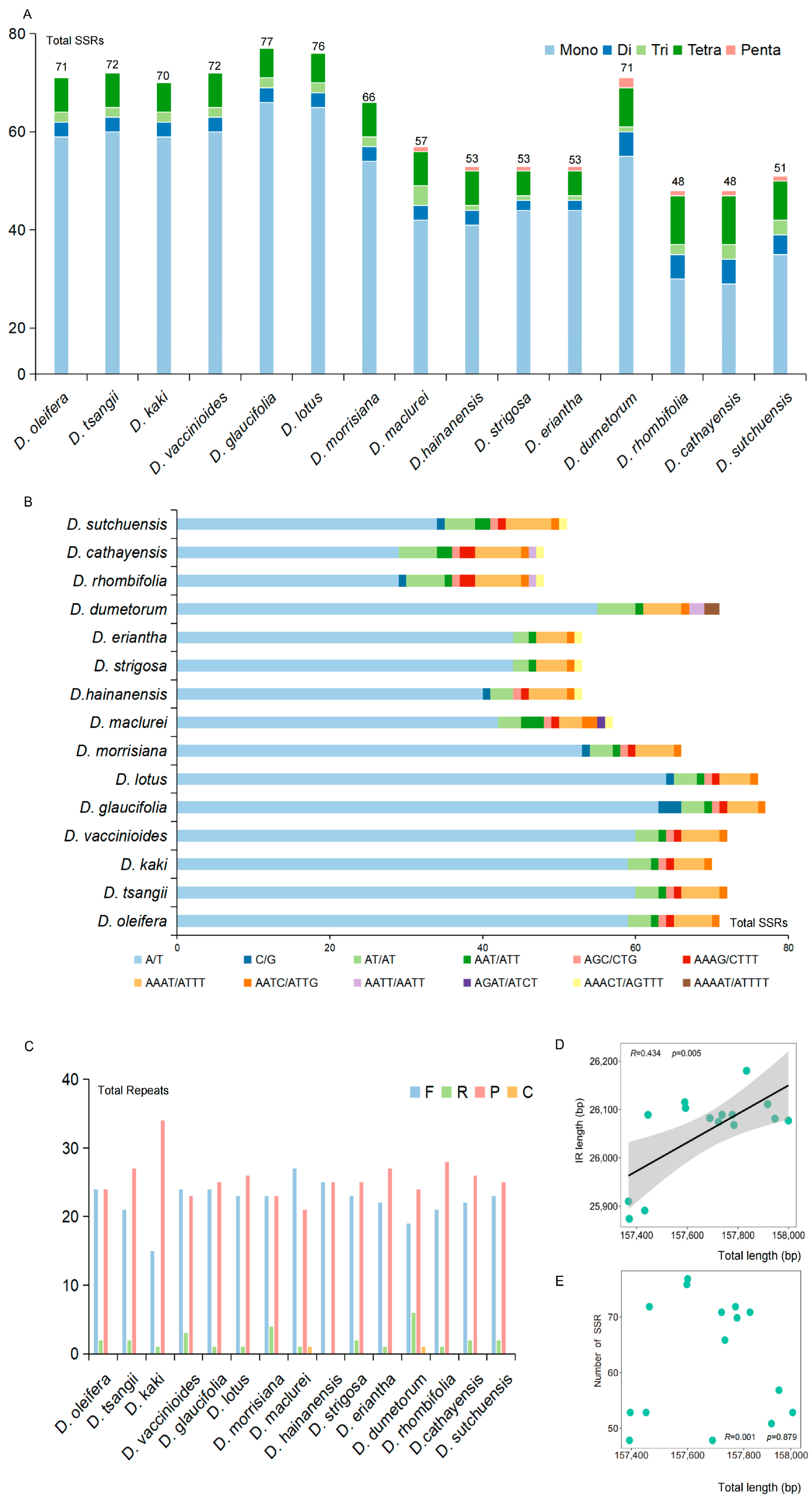




| Species | ID No. | Genome Size (bp) | LSC Length (bp) | SSC Length (bp) | IR Length (bp) | Gene Content | PCGs | tRNA Genes | rRNA Genes | GC% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. oleifera | NC030787 | 157,724 | 87,054 | 18,522 | 26,074 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. tsangii | PX413321 | 157,445 | 86,744 | 18,523 | 26,089 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. kaki | NC030789 | 157,784 | 87,109 | 18,536 | 26,068 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. vaccinioides | NC060861 | 157,778 | 87,066 | 18,534 | 26,089 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. glaucifolia | NC030784 | 157,593 | 86,974 | 18,413 | 26,103 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. lotus | NC030786 | 157,590 | 86,944 | 18,416 | 26,115 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. morrisiana | NC081461 | 157,737 | 87,104 | 18,455 | 26,089 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. maclurei | NC042161 | 157,946 | 87,387 | 18,397 | 26,081 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. hainanensis | NC042160 | 157,999 | 87,523 | 18,322 | 26,077 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. strigosa | OP480009 | 157,371 | 87,156 | 18,467 | 25,874 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. eriantha | NC081462 | 157,432 | 87,181 | 18,471 | 25,890 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. dumetorum | MF179487 | 157,834 | 86,995 | 18,479 | 26,180 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. rhombifolia | NC039556 | 157,368 | 87,233 | 18,325 | 25,910 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. cathayensis | MF288576 | 157,689 | 87,176 | 18,349 | 26,082 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| D. sutchuensis | NC067511 | 157,917 | 87,303 | 18,392 | 26,111 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.4 |
| Species | Codon No. | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GC_all | GC3s | ENCAVG | ENCMIN−ENCMAX | Genes with ENC ≤ 35 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. oleifera | 20,911 | 0.4697 | 0.3958 | 0.2788 | 0.3815 | 0.2801 | 45.25 | 33.81 (rps18)−54.25 (ycf3) | rps18, rpl16 |
| D. tsangii | 20,911 | 0.4698 | 0.3958 | 0.2791 | 0.3816 | 0.2805 | 45.27 | 33.81 (rps18)−54.70 (ycf3) | rps18, rpl16 |
| D. kaki | 20,913 | 0.4699 | 0.3958 | 0.2788 | 0.3815 | 0.2799 | 45.19 | 33.75 (rpl16)−54.25 (ycf3) | rpl16, rps18 |
| D. vaccinioides | 20,921 | 0.4697 | 0.3950 | 0.2778 | 0.3808 | 0.2789 | 45.17 | 33.75 (rpl16)−54.25 (ycf3) | rpl16, rps18 |
| D. glaucifolia | 20,921 | 0.4695 | 0.3946 | 0.2780 | 0.3807 | 0.2792 | 45.38 | 32.37 (rps18)−54.69 (ycf3) | rps18, rpl16 |
| D. lotus | 20,913 | 0.4697 | 0.3954 | 0.2790 | 0.3814 | 0.2803 | 45.43 | 32.37 (rps18)−54.69 (ycf3) | rps18, rpl16 |
| D. morrisiana | 20,921 | 0.4700 | 0.3944 | 0.2770 | 0.3805 | 0.2782 | 45.31 | 33.81 (rps18)−54.89 (ycf3) | rps18, rpl16 |
| D. maclurei | 20,219 | 0.4697 | 0.3958 | 0.2785 | 0.3813 | 0.2796 | 45.38 | 33.40 (rps18)−54.25 (ycf3) | rps18, rpl16 |
| D. hainanensis | 20,857 | 0.4709 | 0.3958 | 0.2787 | 0.3818 | 0.2800 | 45.31 | 34.24 (rpl16)−53.75 (ycf3) | rpl16, rps18, rps14 |
| D. strigosa | 20,957 | 0.4705 | 0.3949 | 0.2773 | 0.3809 | 0.2784 | 45.13 | 33.81 (rps18)−54.25 (ycf3) | rps18, rps14, rpl16 |
| D. eriantha | 20,958 | 0.4705 | 0.3948 | 0.2775 | 0.3809 | 0.2786 | 45.18 | 33.81 (rps18)−54.25 (ycf3) | rps18, rps14, rpl16 |
| D. dumetorum | 20,921 | 0.4703 | 0.3953 | 0.2788 | 0.3814 | 0.2802 | 45.36 | 34.47 (rps18)−54.25 (ycf3) | rps18, rps14, rpl16 |
| D. rhombifolia | 20,912 | 0.4706 | 0.3957 | 0.2784 | 0.3816 | 0.2796 | 45.21 | 33.81 (rps18)−53.66 (ycf3) | rps18 |
| D. cathayensis | 20,905 | 0.4706 | 0.3957 | 0.2790 | 0.3818 | 0.2802 | 45.31 | 33.81 (rps18)−53.66 (ycf3) | rps18 |
| D. sutchuensis | 20,886 | 0.4706 | 0.3954 | 0.2785 | 0.3815 | 0.2797 | 45.26 | 33.81 (rps18)−53.66 (ycf3) | rps18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Evolutionary Dynamics of Chloroplast Genome and Codon Usage in the Genus Diospyros (Ebenaceae). Biology 2025, 14, 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111568
Zhang J, Li Z. Evolutionary Dynamics of Chloroplast Genome and Codon Usage in the Genus Diospyros (Ebenaceae). Biology. 2025; 14(11):1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111568
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jisi, and Zhuo Li. 2025. "Evolutionary Dynamics of Chloroplast Genome and Codon Usage in the Genus Diospyros (Ebenaceae)" Biology 14, no. 11: 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111568
APA StyleZhang, J., & Li, Z. (2025). Evolutionary Dynamics of Chloroplast Genome and Codon Usage in the Genus Diospyros (Ebenaceae). Biology, 14(11), 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111568






