Identification of SNP Markers in the Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH) and Aspartate Aminotransferase 2 (AST2) Associated with Ammonia Nitrogen Tolerance in Penaeus monodon
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Ammonia Nitrogen Stress Test
2.3. Syntenic Analysis
2.4. Protein-Ligand Docking
2.5. Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.6. Screen of SNPs in the PmGDH and PmAST2
2.7. Genotyping of SNPs in the PmGDH and PmAST2
2.8. Association Analysis Between Candidate SNPs and Ammonia Nitrogen Tolerance
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
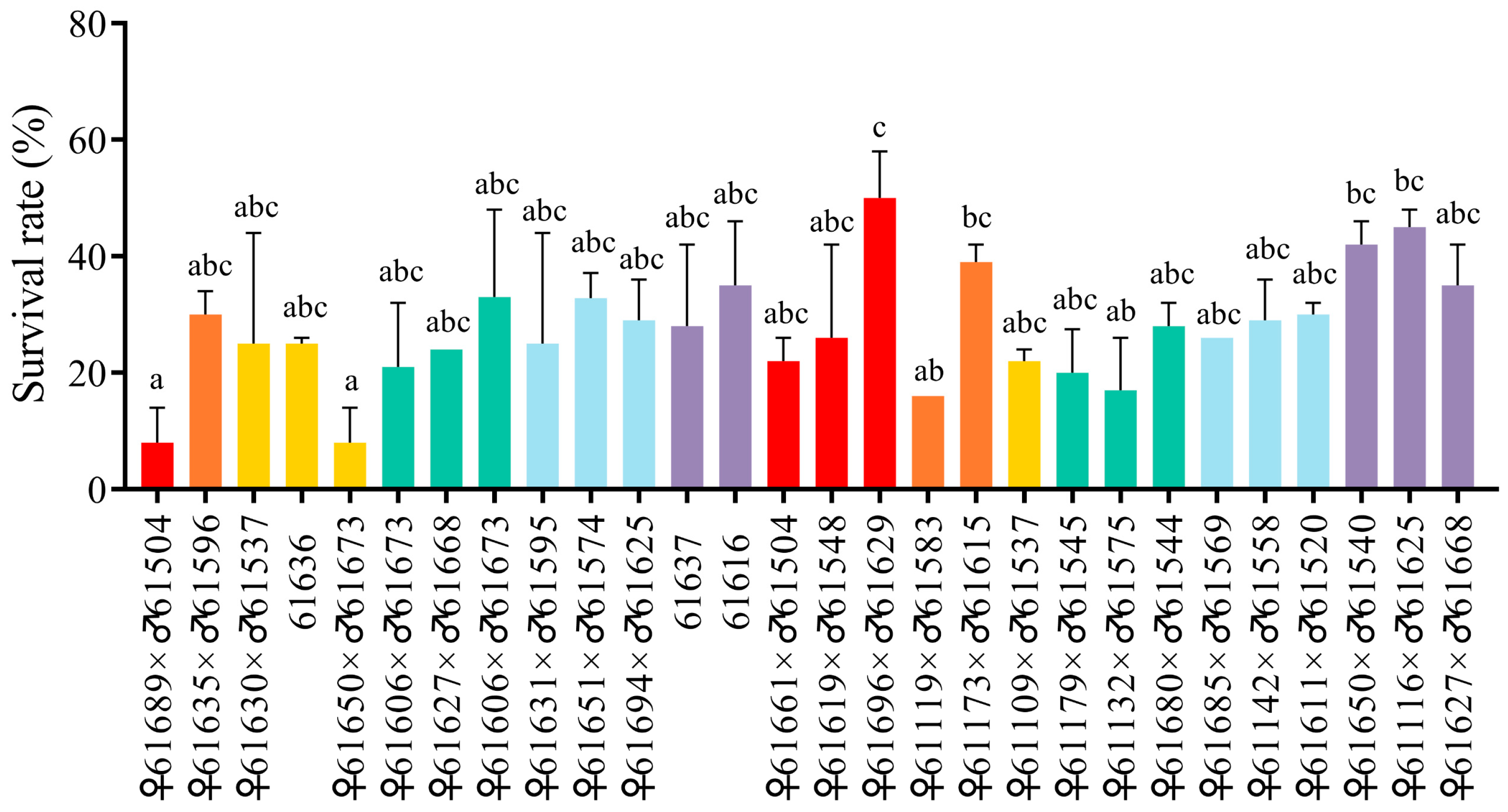
3.1. Susceptible and Resistant Families in the Ammonia-Nitrogen Stress Test
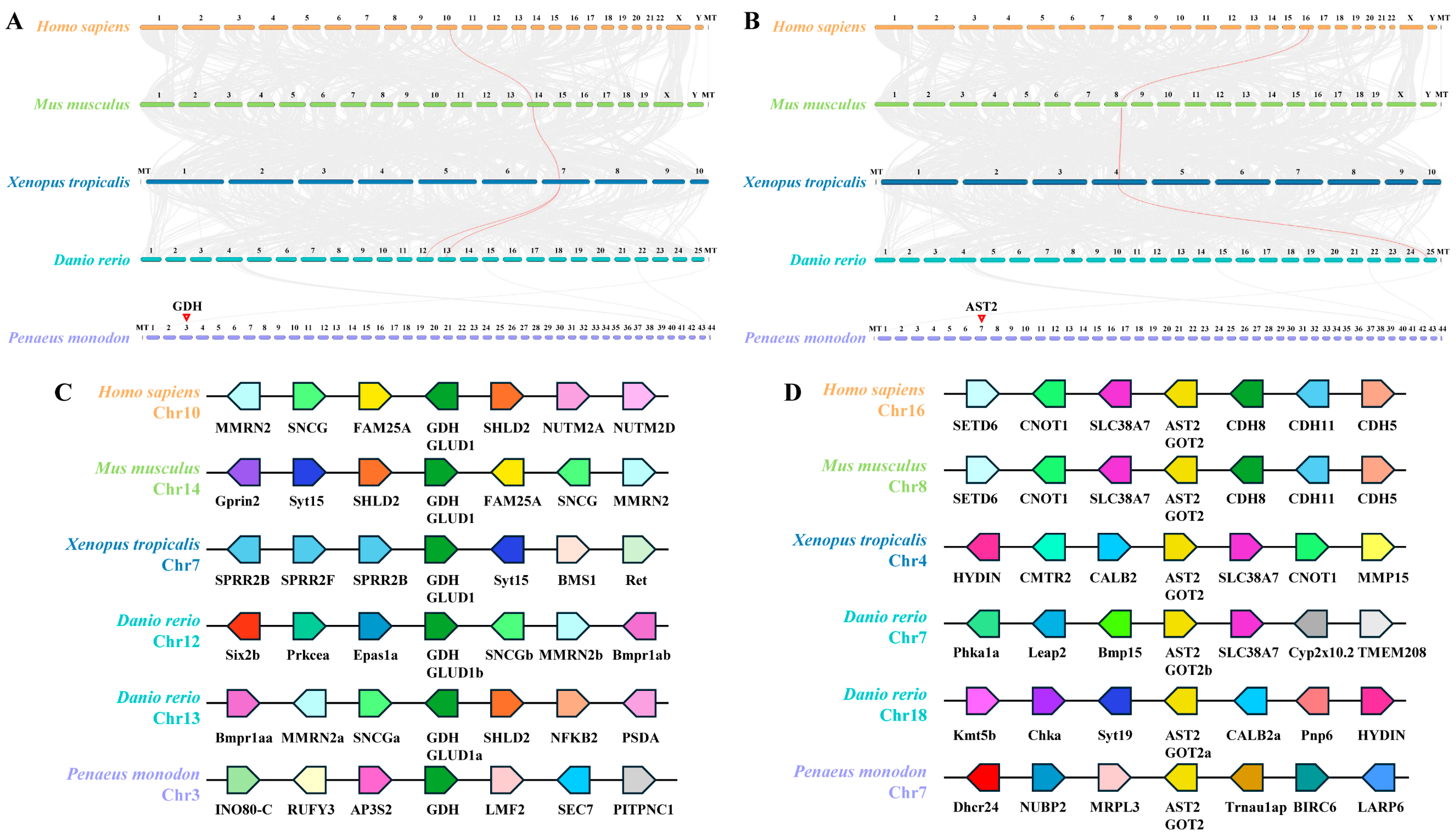
3.2. Synteny Analysis of PmGDH and PmAST2
3.3. The PmGDH-NH4+ Complex and the PmAST2-Asp Complex
3.4. Identification of SNPs in Exons of PmGDH and PmAST2
3.5. Genotyping of Potential SNPs
3.6. SNPs Are Associated with Ammonia Nitrogen Tolerance in P. monodon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, W.; Shen, H. A statistical analysis of China’s fisheries in the 12th five-year period. Aquac. Fish. 2016, 1, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.; Pan, L.; Xie, P.; Zheng, D.; Li, J. Immune responses and expression of immune-related genes in swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus exposed to elevated ambient ammonia-N stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 157, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, F.; Huang, J.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, L.; Qin, J.G. Ammonia and salinity tolerance of Penaeus monodon across eight breeding families. Springerplus 2016, 5, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, G.; Espinoza, V.; Vanegas, C.; Carrara, X.C. Acute Effect of Ammonia and Nitrite on Respiration of Penaeus setiferus Postlarvae under Different Oxygen Levels. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2010, 30, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrensky, A.; Wasielesky, W. Acute toxicity of ammonia to various life stages of the So Paulo shrimp, Penaeus paulensis Pérez-Farfante, 1967. Aquaculture 1995, 132, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, A.L. Effect of supplemental l-ascorbyl-2-polyphosphate (APP) in enriched live food on the immune response of Penaeus vannamei exposed to ammonia-N. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.C.M.; Hospital, F. The use of molecular genetics in the improvement of agricultural populations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xu, Z.; Ge, J. Application of DNA molecular markers in genetics and breeding of aquatic animals. J. Aquac. 2013, 34, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fuji, K.; Hasegawa, O.; Honda, K.; Kumasaka, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Okamoto, N. Marker-assisted breeding of a lymphocystis disease-resistant Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2007, 272, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, K.M.; Elmore, J.B.; Breyer, J.P.; Yaspan, B.L. A major zebrafish polymorphism resource for genetic mapping. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Ren, H.; Xia, Z.; Yu, J. Genetic diversity and association analysis of two duplicated ODC genes polymorphisms with weight gain in Cyprinus carpio L. Aquaculture 2016, 459, 14–18. Aquaculture 2016, 459, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, N.; Fu, R.; Cao, D.; Si, Y. The polymorphism of chicken-type lysozyme gene in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) and its association with resistance/susceptibility to Listonella anguillarum. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 66, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, J. Gene set based association analyses for the WSSV resistance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, X.; Aweya, J.J.; Wang, F.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, Y. SNPs in the Toll1 receptor of Litopenaeus vannamei are associated with immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yue, X.; Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, B. Identification of an MITF gene and its polymorphisms associated with the Vibrio resistance trait in the clam Meretrix petechialis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Lin, Y.L.; Qin, H.; Xiong, Y.Y.; Jiang, D.L.; Lin, H.R.; Yu, Z.L.; Xia, J.H. Identifying a genome-wide QTL interval controlling for ammonia-nitrogen tolerance on chrLG1 of Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Fraslin, C.; Mukiibi, R.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Robledo, D.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. First genome-wide association and genomic prediction of ammonia-nitrogen tolerance in tiger pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes). Aquaculture 2025, 600, 742260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Ruan, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Jiang, S.; Bian, C.; Wu, B.; Shi, Q.; You, X. Genome resequencing of the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) for a genome-wide association study on ammonia tolerance. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janpoom, S.; Kaewduang, M.; Prasertlux, S.; Rongmung, P.; Ratdee, O.; Lirdwitayaprasit, T.; Klinbunga, S.; Khamnamtong, B. A SNP of the hemocyanin gene (LvHc) is a marker for high growth and ammonia-tolerance in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Hu, C.; Xu, H.; Ren, J.; Wu, B.; Dong, Y.; Lin, Z. Insight into the genetic basis of ammonia tolerance in razor clam Sinonovacula constricta by genome-wide association study. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, F.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Q.; He, J.; Jiang, S. Transcriptome reveals involvement of immune defense, oxidative imbalance, and apoptosis in ammonia-stress response of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, F.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, S. Single-Cell Sequencing Reveals Types of Hepatopancreatic Cells and Haemocytes in Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and Their Molecular Responses to Ammonia Stress. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 883043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Zhou, F.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, S. Characterization and expression analysis of a chitinase gene (PmChi-4) from black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) under pathogen infection and ambient ammonia nitrogen stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 62, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhou, K.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, L.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S. Characterization and expression analysis of a chitinase gene (PmChi-5) from black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) under pathogens infection and ambient ammonia-N stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, J.B.; Yoon, H.; Ringel, A.E.; Jeanfavre, S.; Clish, C.B.; Haigis, M.C. Metabolic recycling of ammonia via glutamate dehydrogenase supports breast cancer biomass. Science 2017, 358, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jian, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhou, F. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of aspartate aminotransferase(AST) in Penaeus monodon under ambient ammonia stress. South China Fish. Sci. 2017, 13, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Falin, Z.; Jinsong, C.; Jianhua, H.; Qibin, Y.; Lihua, Q.; Zhenhua, M.A.; Shigui, J. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) in Penaeus monodon under ammonia nitrogen stress. J. Fish. Sci. China 2016, 23, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, J.; Li, P.; Diao, H.; et al. Metabolic Response of Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon) to Acute Ammonia Nitrogen Stress. Biology 2025, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, D.; Alesi, G.N.; Fan, J.; Kang, H.B.; Lu, Z.; Boggon, T.J.; Jin, P.; Yi, H.; Wright, E.R.; et al. Glutamate Dehydrogenase 1 Signals through Antioxidant Glutathione Peroxidase 1 to Regulate Redox Homeostasis and Tumor Growth. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrego, J.; Sanford-Crane, H.; Oon, C.; Xiao, X.; Betts, C.B.; Sun, D.; Nagarajan, S.; Diaz, L.; Sandborg, H.; Bhattacharyya, S.; et al. A Cancer Cell-Intrinsic GOT2-PPARδ Axis Suppresses Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2414–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, B.D.; Som, R.; Rauckhorst, A.J.; Taylor, E.B.; Yu, L.; Sivitz, W.I. Hepatic glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase promotes mitochondrial respiration energized at complex II and alters whole body metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.J. The role of glutamine synthetase and glutamate dehydrogenase in cerebral ammonia homeostasis. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 2439–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerk, S.A.; Garcia-Bermudez, J.; Birsoy, K.; Sherman, M.H.; Shah, Y.M.; Lyssiotis, C.A. Spotlight on GOT2 in Cancer Metabolism. Onco Targets Ther. 2023, 16, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Dong, Y.; Sun, C.; Yao, H.; Lin, Z. Vital Role of Glutamate Dehydrogenase Gene in Ammonia Detoxification and the Association Between its SNPs and Ammonia Tolerance in Sinonovacula constricta. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 664804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertlux, S.; Yocawibun, P.; Janpoom, S.; Klinbunga, S.; Menasveta, P.; Khamnamtong, B. Differential expression of X-box binding protein 1 during ovarian development and association between its SNP and growth-related parameters of the giant tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.R.; Li, Y.D.; Jiang, S.G.; Yang, Q.B.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L.S.; Huang, J.H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.L. A CSDE1/Unr gene from Penaeus monodon: Molecular characterization, expression and association with tolerance to low salt stress. Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, N.T.T.; Jerry, D.R.; Edmunds, R.C.; Jones, D.B.; Zenger, K.R. Development of a global SNP resource for diversity, provenance, and parentage analyses on the Indo-Pacific giant black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Q.B.; Su, T.F. The toxicity of ammonia-N on Penaeus monodon and immune parameters. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2012, 21, 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Vignal, A.; Milan, D.; SanCristobal, M.; Eggen, A. A review on SNP and other types of molecular markers and their use in animal genetics. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2002, 34, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, C.F.H. Oxygen Consumption and Ammonia-N Excretion of Penaeus chinensis (Osbeck, 1765) Juveniles at Different Salinity Levels (Decapoda, Penaeidae). Crustaceana 1995, 68, 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, J.C. Hemocyanin oxygen affinity, and the fractionation of oxyhemocyanin and deoxyhemocyanin for Penaeus monodon exposed to elevated nitrite. Aquat. Toxicol. 1999, 45, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Arena, L.; Chen, L.; Wormhoudt, Q.A.V. Characterization and Tissue-Specific Expression of the Two Glutamate Dehydrogenase cDNAs in Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Crustac. Biol. 2009, 29, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shaofei, L.I.; Yuying, H.E.; Jitao, L.I.; Jian, L.I.; Ping, L.; Qianqian, G.E. Cloning and expression analysis of aspartate aminotransferase c DNA in Fenneropenaeus chinensis following ambient ammonia stresses. J. Fish. Sci. China 2014, 21, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Broeks, M.H.; van Karnebeek, C.D.M.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Jans, J.J.M.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M. Inborn disorders of the malate aspartate shuttle. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cargill, M.; Altshuler, D.; Ireland, J.; Sklar, P.; Lander, E.S. Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, R. Molecular Signatures of Natural Selection. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, S.; Blanco, A.; Fernández-Marmiesse, A.; Alvarez-Iglesias, V.; Ruíz-Ponte, C.; Carracedo, A.; Vega, A. Multiplex SNaPshot for detection of BRCA1/2 common mutations in Spanish and Spanish related breast/ovarian cancer families. BMC Med. Genet. 2007, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Pabón, J.; Chasqui, L.; Muñoz, E.; Narváez-Barandica, J. Multiple origins define the genetic structure of tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon in the colombian Caribbean Sea. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araneda, C.; Lam, N.; Díaz, N.F.; Cortez, S.; Pérez, C.; Neira, R.; Iturra, P. Identification, development, and characterization of three molecular markers associated to spawning date in Coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquaculture 2009, 296, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, K.; Lhorente, J.P.; Bassini, L.; López, M.E.; Di Genova, A.; Maass, A.; Davidson, W.S.; Yánez, J.M. Genome wide association study for resistance to Caligus rogercresseyi in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) using a 50K SNP genotyping array. Aquaculture 2016, 472 (Suppl. 1), 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Li, J. Association between SNPs in interferon regulatory factor 2 (IRF-2) gene and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in freshwater mussel Hyriopsis cumingii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Kong, J.; Meng, X.; Cao, B.; Luo, K.; Dai, P.; Luan, S. Identification of SNP markers associated with tolerance to ammonia toxicity by selective genotyping from de novo assembled transcriptome in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 73, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, J. Genome-wide association study identified genes associated with ammonia nitrogen tolerance in Litopenaeus vannamei. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 961009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| SNP ID | Location | Position from Start Codon (bp) | Mutation Type | Variation | Amino Acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PmGDH-1083 | Exon 5 of PmGDH | 1083 | Absence | GGA | Glycine |
| PmGDH-1086 | Exon 5 of PmGDH | 1086 | Transition, synonymous | GGA/GGG | Glycine |
| PmGDH-1091 | Exon 5 of PmGDH | 1091 | Absence | AAC | Asparagine |
| PmGDH-1101 | Exon 5 of PmGDH | 1101 | Transition, synonymous | TAC/TAT | Tyrosine |
| PmGDH-1212 | Exon 6 of PmGDH | 1212 | Transversion, synonymous | ACC/ACA | Threonine |
| PmGDH-1227 | Exon 6 of PmGDH | 1227 | Transition, synonymous | CAA/CAG | Glutamine |
| PmGDH-1338 | Exon 6 of PmGDH | 1338 | Transversion, synonymous | GGT/GGA | Glycine |
| PmAST2-44 | Exon 1 of PmAST2 | 44 | Absence | AAC | Asparagine |
| PmAST2-78 | Exon 1 of PmAST2 | 78 | Transversion, synonymous | GCA/GCT | Alanine |
| PmAST2-132 | Exon 2 of PmAST2 | 132 | Transition, synonymous | GTT/GTC | Valine |
| PmAST2-180 | Exon 2 of PmAST2 | 180 | Transition, synonymous | GGC/GGT | Glycine |
| PmAST2-225 | Exon 2 of PmAST2 | 225 | Transition, synonymous | CCG/CCA | Proline |
| Family ID | Sample Size | SNP ID | Parents (♀ × ♂) | Genotype Frequency (%) | p-Value for Mendelian Ratio | Chi-Square Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. 9 | 50 | PmGDH-1101 | TT × CC | CT 96.0 | CC 4.0 | 0.043 * | 4.082 |
| 50 | PmGDH-1212 | CC × CC | CC 100 | \ | \ | \ | |
| 50 | PmGDH-1227 | GG × GG | GG 100 | \ | \ | \ | |
| 50 | PmAST2-132 | CC × TC | CT 96.0 | TT 4.0 | 0.000 ** | 64.438 | |
| 50 | PmAST2-225 | GG × GG | GG 100 | \ | \ | \ | |
| No. 3 | 49 | PmGDH-1101 | CT × CC | CC 44.9 | CT 55.1 | 0.479 | 0.501 |
| 49 | PmGDH-1212 | CA × CC | CA 49.0 | CC 51.0 | 0.888 | 0.020 | |
| 49 | PmGDH-1227 | GG × GG | GG 98.0 | GA 2.0 | 0.155 | 2.020 | |
| 49 | PmAST2-132 | TT × CT | TT 40.8 | CT 59.2 | 0.201 | 1.633 | |
| 49 | PmAST2-225 | GG × GG | GG 98.0 | GA 2.0 | 0.155 | 2.020 | |
| Geographic Groups | Sample Size | SNP ID | Genotype Frequency (%) | p-Value for Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium | Chi-Square Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| African group | 50 | PmGDH-1101 | TT 10.0 | CT 6.0 | CC 84.0 | <0.01 ** | 29.20 |
| 50 | PmGDH-1212 | AA 2.0 | AC 2.0 | CC 96.0 | <0.01 ** | 32.33 | |
| 50 | PmGDH-1227 | GA 8.0 | GG 92.0 | 0.79 | 0.06 | ||
| 50 | PmAST2-132 | TT 6.0 | CT76.0 | CC 18.0 | <0.01 ** | 22.17 | |
| 50 | PmAST2-225 | AA 4.0 | GA 8.0 | GG 88.0 | <0.01 ** | 14.95 | |
| Indonesian group | 56 | PmGDH-1101 | TT 33.9 | CT 41.1 | CC 25.0 | 0.18 | 1.83 |
| 56 | PmGDH-1212 | AC 10.7 | CC 89.3 | 0.70 | 0.15 | ||
| 56 | PmGDH-1227 | AA 1.8 | GA 35.7 | GG 62.5 | 0.35 | 0.86 | |
| 56 | PmAST2-132 | TT 44.6 | CT 51.8 | CC 3.6 | 0.08 | 3.17 | |
| 56 | PmAST2-225 | AA 1.8 | GA 28.6 | GG 69.6 | 0.70 | 0.15 | |
| Thai group | 50 | PmGDH-1101 | TT 38.0 | CT 42.0 | CC 20.0 | 0.31 | 1.01 |
| 50 | PmGDH-1212 | AA 2.0 | AC 20.0 | CC 78.0 | 0.65 | 0.21 | |
| 50 | PmGDH-1227 | GA 0.32 | GG 0.68 | 0.19 | 1.69 | ||
| 50 | PmAST2-132 | TT 42.0 | CT 56.0 | CC 2.0 | 0.02 * | 5.27 | |
| 50 | PmAST2-225 | GA 28.0 | GG 72.0 | 0.27 | 1.22 | ||
| SNP ID | Genotype | Genotype Frequency (%) | Chi-Square Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG | SG | ||||
| PmGDH1101 | CT | 12 (20.3) | 6 (8.6) | 4.88 | 0.027 * |
| CC | 47 (79.7) | 52 (91.4) | |||
| PmGDH1212 | AC | 2 (3.4) | 5 (8.6) | 3.191 | 0.074 |
| CC | 57 (96.6) | 53 (91.4) | |||
| PmGDH1227 | GA | 8 (13.8) | 20 (34.5) | 28.151 | 0.000 ** |
| GG | 48 (82.8) | 28 (48.3) | |||
| AA | 2 (3.4) | 10 (17.2) | |||
| PmAST132 | TC | 11 (18.3) | 16 (28.1) | 12.908 | 0.002 ** |
| CC | 40 (66.7) | 24 (42.1) | |||
| TT | 9 (15.0) | 17 (29.8) | |||
| PmAST225 | GA | 2 (3.3) | 8 (14.0) | 9.517 | 0.009 ** |
| GG | 57 (95.0) | 46 (80.7) | |||
| AA | 1 (1.7) | 3 (5.3) | |||
| SNP ID | A1 | F_A | F_U | A2 | MAF | NCHROBS | Frequency | p-Value for Fisher | OR | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PmGDH-1101 | T | 0.1017 | 0.0431 | C | 0.0727 | 234 | 0.9274 | 0.1290 | 2.5130 | 0.3606 |
| PmGDH-1212 | A | 0.0170 | 0.0431 | C | 0.0299 | 234 | 0.9701 | 0.2785 | 0.3828 | 0.3606 |
| PmGDH-1227 | A | 0.1034 | 0.3448 | G | 0.2241 | 232 | 0.7759 | 0.0000 ** | 0.2192 | 0.0001 ** |
| PmAST2-132 | T | 0.2417 | 0.4386 | C | 0.3376 | 234 | 0.6624 | 0.0015 ** | 0.4079 | 0.0077 ** |
| PmAST2-225 | A | 0.0333 | 0.1228 | G | 0.0769 | 234 | 0.9231 | 0.0131 * | 0.2463 | 0.0522 |
| Locus | Haplotype | Susceptible Frequency (%) | Resistant Frequency (%) | Chi-Square Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PmGDH-1227/ PmAST2-132 | GC | 99 (45.0) | 163 (70.3) | 29.567 | 0.000 ** |
| GT | 43 (19.5) | 45 (19.4) | 0.002 | 0.968 | |
| AT | 49 (22.3) | 11 (4.7) | 26.511 | 0.000 ** | |
| AC | 29 (13.2) | 13 (5.6) | 7.694 | 0.006 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Shi, J.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, S.; et al. Identification of SNP Markers in the Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH) and Aspartate Aminotransferase 2 (AST2) Associated with Ammonia Nitrogen Tolerance in Penaeus monodon. Biology 2025, 14, 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111532
Ding Y, Chen J, Jiang S, Yang Q, Li Y, Huang J, Yang L, Shi J, Yu Y, Jiang S, et al. Identification of SNP Markers in the Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH) and Aspartate Aminotransferase 2 (AST2) Associated with Ammonia Nitrogen Tolerance in Penaeus monodon. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111532
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yangyang, Jinsong Chen, Song Jiang, Qibin Yang, Yundong Li, Jianhua Huang, Lishi Yang, Jianzhi Shi, Yebing Yu, Shigui Jiang, and et al. 2025. "Identification of SNP Markers in the Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH) and Aspartate Aminotransferase 2 (AST2) Associated with Ammonia Nitrogen Tolerance in Penaeus monodon" Biology 14, no. 11: 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111532
APA StyleDing, Y., Chen, J., Jiang, S., Yang, Q., Li, Y., Huang, J., Yang, L., Shi, J., Yu, Y., Jiang, S., & Zhou, F. (2025). Identification of SNP Markers in the Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH) and Aspartate Aminotransferase 2 (AST2) Associated with Ammonia Nitrogen Tolerance in Penaeus monodon. Biology, 14(11), 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111532






