The Esterase Gs Derived from Geobacillus sp. JM6 Exhibits Hydrolytic Activity on the PET Model Substrates
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Protein Expression and Purification
2.4. Qualitative Detection of Protein BHET Hydrolysis Activity Using a Hydrolysis Ring Experiment
2.5. Colorimetric Experiment for the Quantitative Detection of Gs BHET Hydrolytic Activity
2.6. Kinetic Measurements
2.7. Colorimetric Experiments to Assess the Synergistic Hydrolytic Activity of Gs and MHETase on BHET
2.8. Colorimetric Experiment for the Quantitative Detection of the Thermal Stability of Gs Hydrolyzed BHET
2.9. Colorimetric Method for Detecting the Activity of Gs Hydrolyzed PET Nanoparticles
2.10. Colorimetric Method for Detecting the Hydrolytic Activity of Gs on 3PET
3. Results and Discussion
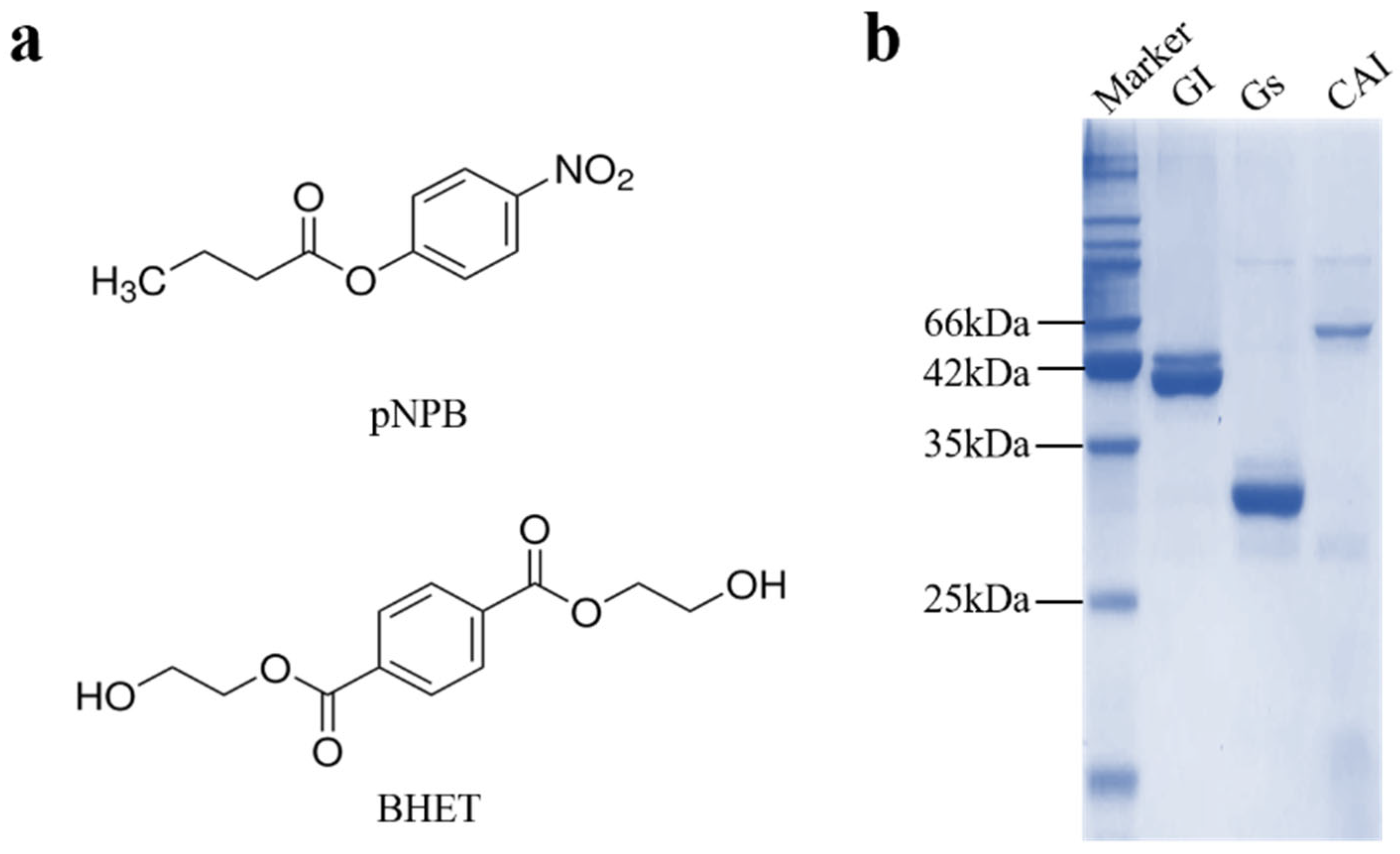
3.1. Comparison of Enzymatic Substrates and Protein Expression Purification
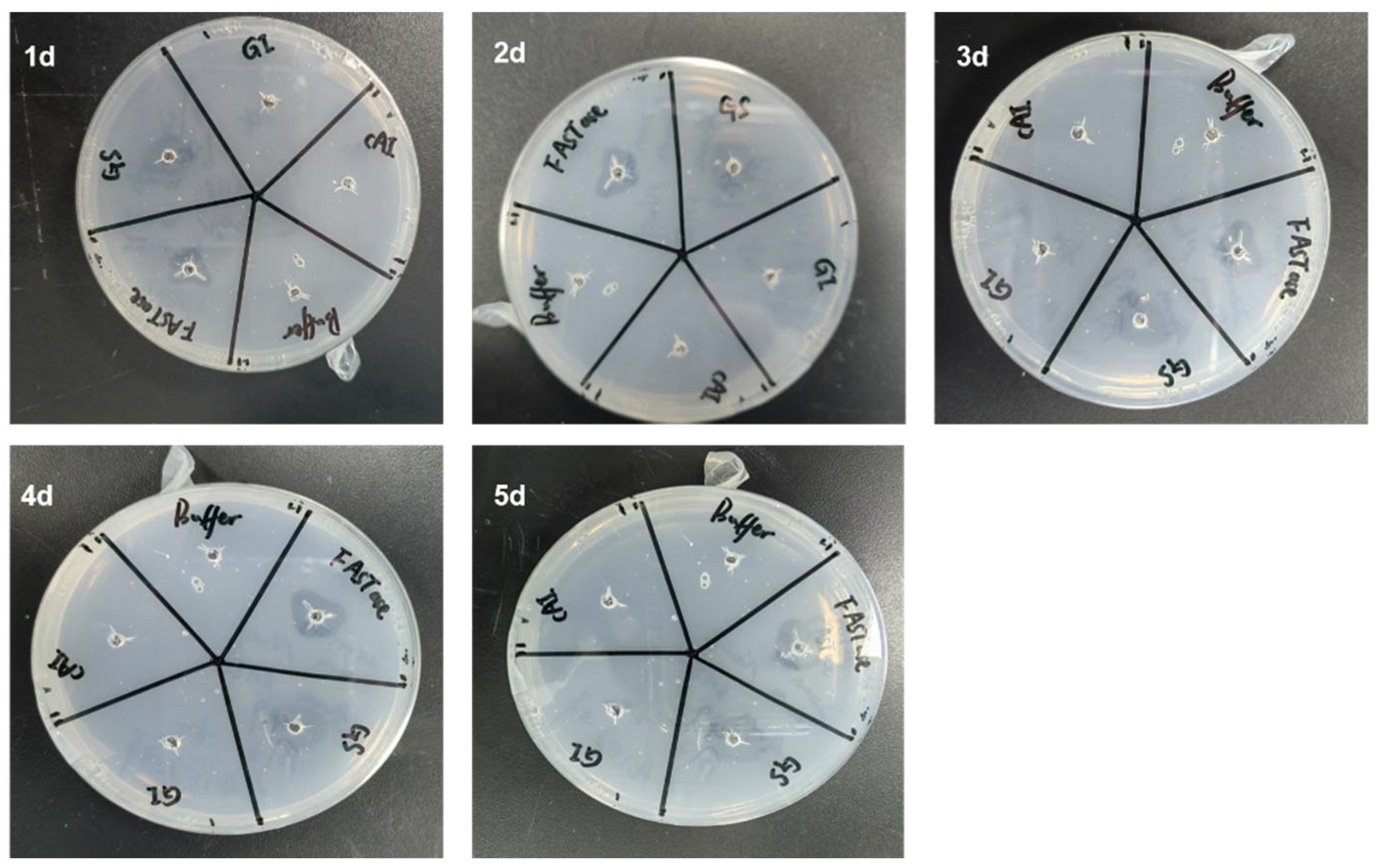
3.2. The Qualitative Detection Results from the Hydrolysis Zone Experiment Indicate That Gs Exhibits BHET Hydrolytic Activity
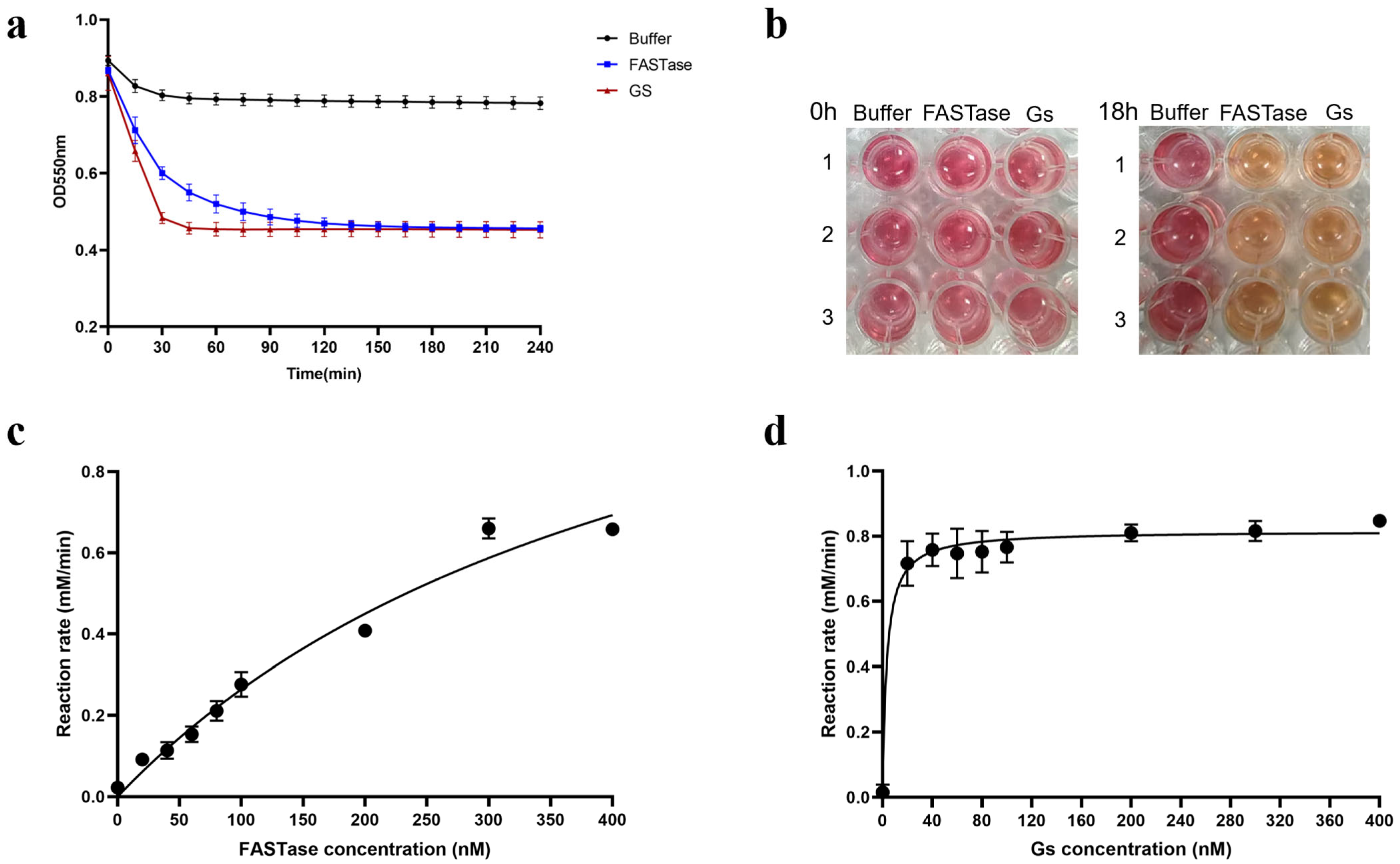
3.3. The Results of the Colorimetric Experiment Indicate That Gs Exhibits Hydrolytic Activity on BHET
3.4. The Results of the Colorimetric Experiment Indicate That Gs Does Not Possess the Hydrolytic Thermal Stability of BHET
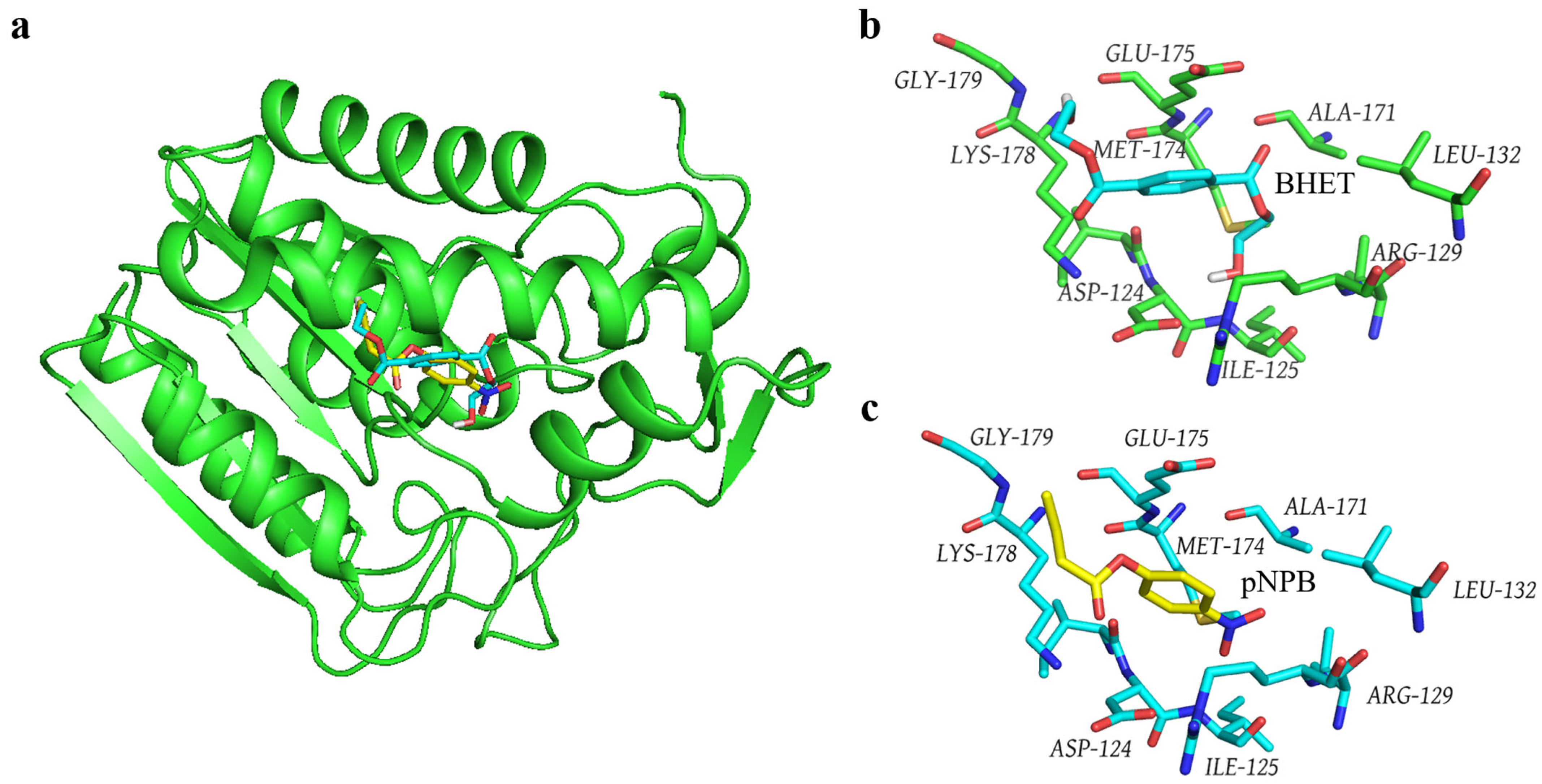
3.5. Molecular Docking of the Gs-BHET Complex
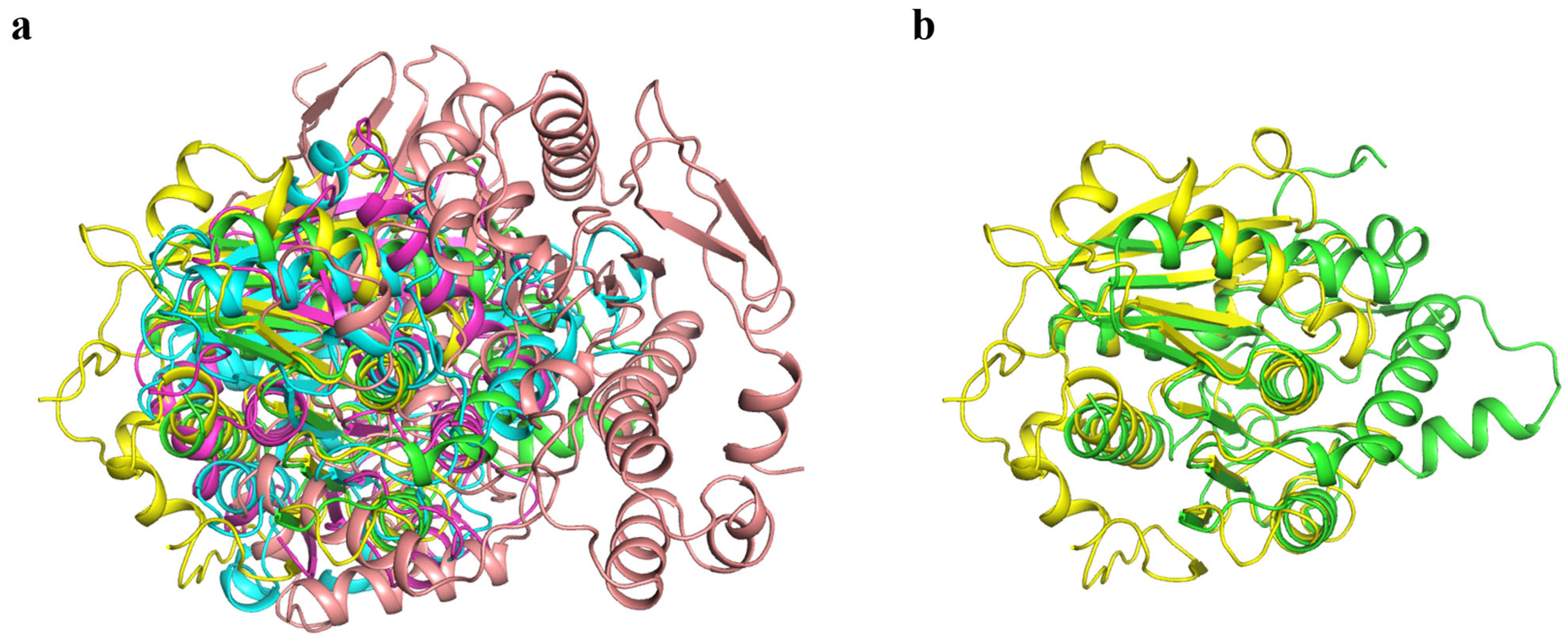
3.6. Comparison of the Structure of Gs and Other BHET Hydrolases
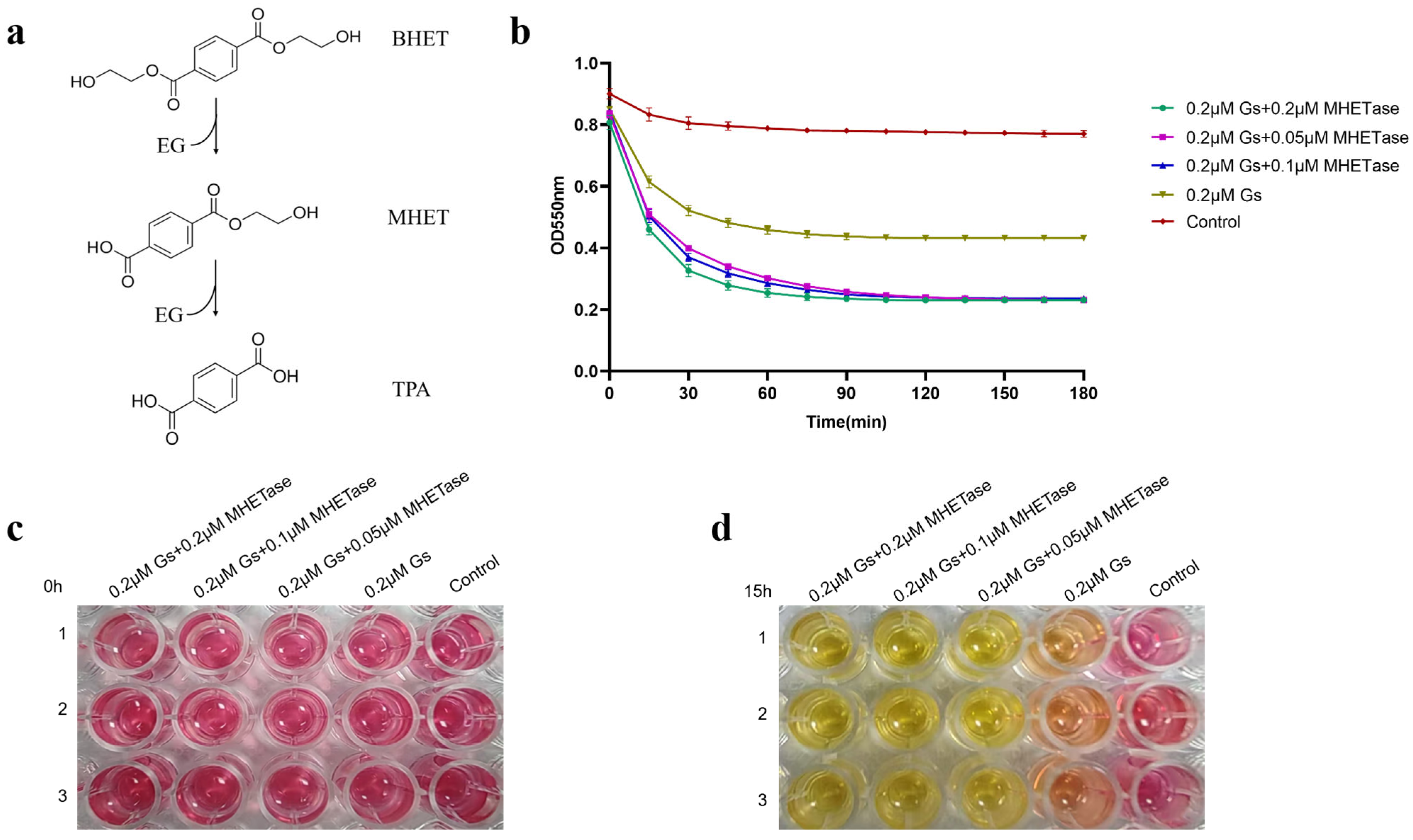
3.7. The Synergistic Action of Gs and MHETase Can Completely Hydrolyze BHET
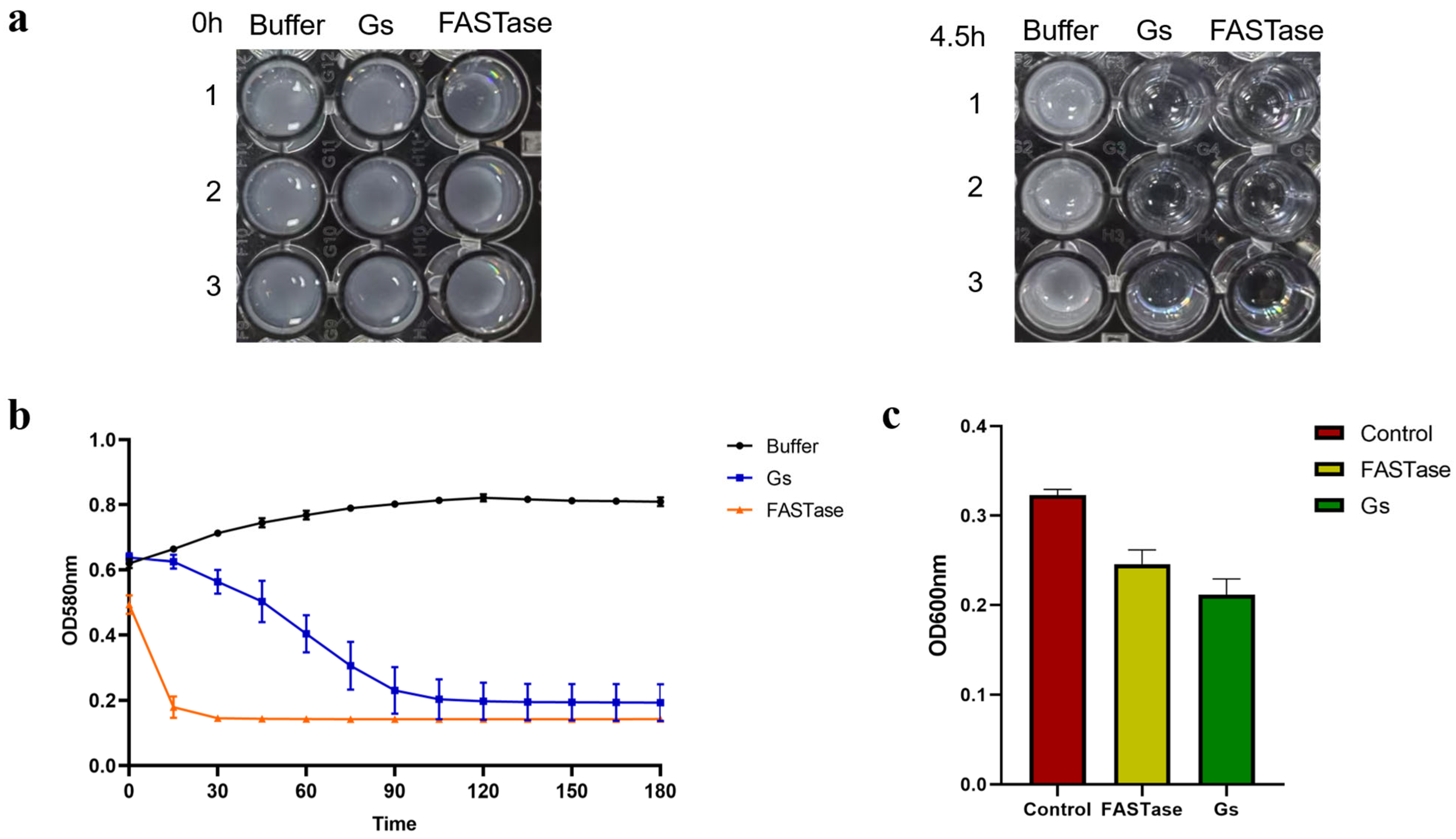
3.8. Gs Exhibits Hydrolytic Activity Towards 3PET and PET Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borrelle, S.B.; Ringma, J.; Law, K.L.; Monnahan, C.C.; Lebreton, L.; McGivern, A.; Murphy, E.; Jambeck, J.; Leonard, G.H.; Hilleary, M.A.; et al. Predicted Growth in Plastic Waste Exceeds Efforts to Mitigate Plastic Pollution. Science 2020, 369, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Hu, T.; Huang, W.; Song, B.; Qin, M.; Yi, H.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y. Can Incineration Completely Eliminate Plastic Wastes? An Investigation of Microplastics and Heavy Metals in the Bottom Ash and Fly Ash from an Incineration Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, K.S.; Ho, L.Y.; Lim, H.R.; Leong, H.Y.; Chew, K.W. Plastic Waste Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic: Crisis or Opportunity? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.Q.Y.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Tang, B.L. Toxicity of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Mammalian Systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human Health and Ocean Pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, J.; Brown, R.J.C.; Kim, K.-H. Environmental Fate, Ecotoxicity Biomarkers, and Potential Health Effects of Micro- and Nano-Scale Plastic Contamination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and Quantification of Plastic Particle Pollution in Human Blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Chao, T.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Cao, S. Improvement in the Thermal Stability of Is MHETase by Sequence and Structure-Guided Calculation. Molecules 2025, 30, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.D.; Rorrer, N.A.; Sullivan, K.P.; Otto, M.; McGeehan, J.E.; Román-Leshkov, Y.; Wierckx, N.; Beckham, G.T. Chemical and Biological Catalysis for Plastics Recycling and Upcycling. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Sherrell, P.C.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.-X.; Yang, J. How to Build a Microplastics-Free Environment: Strategies for Microplastics Degradation and Plastics Recycling. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, T.P.; Völker, C.; Kramm, J.; Landfester, K.; Wurm, F.R. Plastics of the Future? The Impact of Biodegradable Polymers on the Environment and on Society. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberl, A.; Heumann, S.; Brückner, T.; Araujo, R.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Kaufmann, F.; Kroutil, W.; Guebitz, G.M. Enzymatic Surface Hydrolysis of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) and Bis(Benzoyloxyethyl) Terephthalate by Lipase and Cutinase in the Presence of Surface Active Molecules. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 143, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Henehan, G.T.; Kinsella, G.K.; Ryan, B.J. An Extracellular Lipase from Amycolatopsis Mediterannei Is a Cutinase with Plastic Degrading Activity. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribitsch, D.; Acero, E.H.; Greimel, K.; Dellacher, A.; Zitzenbacher, S.; Marold, A.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Steinkellner, G.; Gruber, K.; Schwab, H.; et al. A New Esterase from Thermobifida Halotolerans Hydrolyses Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polylactic Acid (PLA). Polymers 2012, 4, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribitsch, D.; Heumann, S.; Trotscha, E.; Herrero Acero, E.; Greimel, K.; Leber, R.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Deller, S.; Eiteljoerg, I.; Remler, P.; et al. Hydrolysis of Polyethyleneterephthalate by P-Nitrobenzylesterase from Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perz, V.; Hromic, A.; Baumschlager, A.; Steinkellner, G.; Pavkov-Keller, T.; Gruber, K.; Bleymaier, K.; Zitzenbacher, S.; Zankel, A.; Mayrhofer, C.; et al. An Esterase from Anaerobic Clostridium Hathewayi Can Hydrolyze Aliphatic-Aromatic Polyesters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zock, J.; Cantwell, C.; Swartling, J.; Hodges, R.; Pohl, T.; Sutton, K.; Rosteck, P.J.; McGilvray, D.; Queener, S. The Bacillus subtilis PnbA Gene Encoding P-Nitrobenzyl Esterase: Cloning, Sequence and High-Level Expression in Escherichia coli. Gene 1994, 151, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero Acero, E.; Ribitsch, D.; Steinkellner, G.; Gruber, K.; Greimel, K.; Eiteljoerg, I.; Trotscha, E.; Wei, R.; Zimmermann, W.; Zinn, M.; et al. Enzymatic Surface Hydrolysis of PET: Effect of Structural Diversity on Kinetic Properties of Cutinases from Thermobifida. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4632–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelle, S.B.; Ringma, J.; Law, K.L.; Monnahan, C.C.; Lebreton, L.; McGivern, A.; Murphy, E.; Jambeck, J.R.; Leonard, G.H.; Hilleary, M.A.; et al. Characterization of a New Cutinase from Thermobifida Alba for PET-Surface Hydrolysis. Science 2021, 4, 4632–4640. [Google Scholar]
- Kitadokoro, K.; Kakara, M.; Matsui, S.; Osokoshi, R.; Thumarat, U.; Kawai, F.; Kamitani, S. Structural Insights into the Unique Polylactate-Degrading Mechanism of Thermobifida alba Cutinase. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Yamato, S.; Kanaya, E.; Kim, J.-J.; Koga, Y.; Takano, K.; Kanaya, S. Isolation of a Novel Cutinase Homolog with Polyethylene Terephthalate-Degrading Activity from Leaf-Branch Compost by Using a Metagenomic Approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A Bacterium That Degrades and Assimilates Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Sheng, Y.; Cui, H.; Wang, M.; Wu, L.; Song, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, X.; Huang, H. Discovery and Mechanism-Guided Engineering of BHET Hydrolases for Improved PET Recycling and Upcycling. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, M.; Stubbe, J. PET Polymer Recycling. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 2316–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, N.; Robin, J.J.; Boutevin, B. Study of Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Virgin and Recycled Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Before and After Injection Molding. Eur. Polym. J. 2000, 36, 2075–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.B.; Verger, R.; Abousalham, A. Lipases or Esterases: Does It Really Matter? Toward a New Bio-Physico-Chemical Classification. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 861, 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chahinian, H.; Sarda, L. Distinction between Esterases and Lipases: Comparative Biochemical Properties of Sequence-Related Carboxylesterases. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.Y.; Zhang, X.S.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Jing, S.Y.; Qiao, M.H.; Ji, R. Improving the Thermostability and Catalytic Performance of the Bacillus subtilis Chitosanase BsCsn46A via Computational Design. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2024, 60, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, Z.; Cai, X.; Wu, Y. Expression, Purification, Crystallization, and PAN-Cancer Analysis of the Human RNA 3′-Terminal Phosphate Cyclase RTCA. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2025, 61, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusty Beech, J.; Clare, R.; Kincannon, W.M.; Erickson, E.; McGeehan, J.E.; Beckham, G.T.; DuBois, J.L. A Flexible Kinetic Assay Efficiently Sorts Prospective Biocatalysts for PET Plastic Subunit Hydrolysis†. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 8119–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.A.; Knoll, M.; Abdel-Fattah, Y.R.; Schmid, R.D.; Lange, S. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Thermostable Esterase and Lipase from Geobacillus Thermoleovorans YN Isolated from Desert Soil in Egypt. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Ni, H.; Liu, H.; Xiao, A.; Cai, H. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a New and Highly Thermostable Esterase from Geobacillus sp. JM6. J. Basic Microbiol. 2015, 55, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Jiao, L.; Xie, X.; Xu, L.; Yan, J.; Yang, M.; Yan, Y. Characterization of a New Thermostable and Organic Solution-Tolerant Lipase from Pseudomonas Fluorescens and Its Application in the Enrichment of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dierkes, R.F.; Perez-Garcia, P.; Costanzi, E.; Dittrich, J.; Cea, P.A.; Gurschke, M.; Applegate, V.; Partus, K.; Schmeisser, C.; et al. The Metagenome-Derived Esterase PET40 Is Highly Promiscuous and Hydrolyses Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). FEBS J. 2024, 291, 70–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Diaz, D.J.; Czarnecki, N.J.; Zhu, C.; Kim, W.; Shroff, R.; Acosta, D.J.; Alexander, B.R.; Cole, H.O.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Machine Learning-Aided Engineering of Hydrolases for PET Depolymerization. Nature 2022, 604, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, G.; Anglade, J.; Gavalda, S.; Tournier, V.; Chabot, N.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Weber, G.; Marty, A. Assessment of Four Engineered PET Degrading Enzymes Considering Large-Scale Industrial Applications. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 13156–13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, H.P.; Allen, M.D.; Donohoe, B.S.; Rorrer, N.A.; Kearns, F.L.; Silveira, R.L.; Pollard, B.C.; Dominick, G.; Duman, R.; El Omari, K.; et al. Characterization and Engineering of a Plastic-Degrading Aromatic Polyesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4350–E4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Cho, I.J.; Seo, H.; Son, H.F.; Sagong, H.-Y.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.-J. Structural Insight into Molecular Mechanism of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Degradation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong-Johnson, E.Z.L.; Voigt, C.A.; Sinskey, A.J. An Absorbance Method for Analysis of Enzymatic Degradation Kinetics of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Films. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satta, A.; Zampieri, G.; Loprete, G.; Campanaro, S.; Treu, L.; Bergantino, E. Metabolic and Enzymatic Engineering Strategies for Polyethylene Terephthalate Degradation and Valorization; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2024; Volume 23, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Świderek, K.; Velasco-Lozano, S.; Galmés, M.; Olazabal, I.; Sardon, H.; López-Gallego, F.; Moliner, V. Mechanistic Studies of a Lipase Unveil Effect of PH on Hydrolysis Products of Small PET Modules. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groseclose, T.M.; Kober, E.A.; Clark, M.; Moore, B.; Banerjee, S.; Bemmer, V.; Beckham, G.T.; Pickford, A.R.; Dale, T.T.; Nguyen, H.B. A High-Throughput Screening Platform for Engineering Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Hydrolases. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 14622–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, S.; Wei, Z.; Wei, Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, R. The Esterase Gs Derived from Geobacillus sp. JM6 Exhibits Hydrolytic Activity on the PET Model Substrates. Biology 2025, 14, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101387
Duan S, Wei Z, Wei Y, Cai X, Liu Y, Fan R. The Esterase Gs Derived from Geobacillus sp. JM6 Exhibits Hydrolytic Activity on the PET Model Substrates. Biology. 2025; 14(10):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101387
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Shuyan, Zhaoyi Wei, Yushan Wei, Xiaoyue Cai, Yixuan Liu, and Ruiran Fan. 2025. "The Esterase Gs Derived from Geobacillus sp. JM6 Exhibits Hydrolytic Activity on the PET Model Substrates" Biology 14, no. 10: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101387
APA StyleDuan, S., Wei, Z., Wei, Y., Cai, X., Liu, Y., & Fan, R. (2025). The Esterase Gs Derived from Geobacillus sp. JM6 Exhibits Hydrolytic Activity on the PET Model Substrates. Biology, 14(10), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101387





