Insect Community Diversity in Photovoltaic Power Station and Its Response to Environmental Factors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
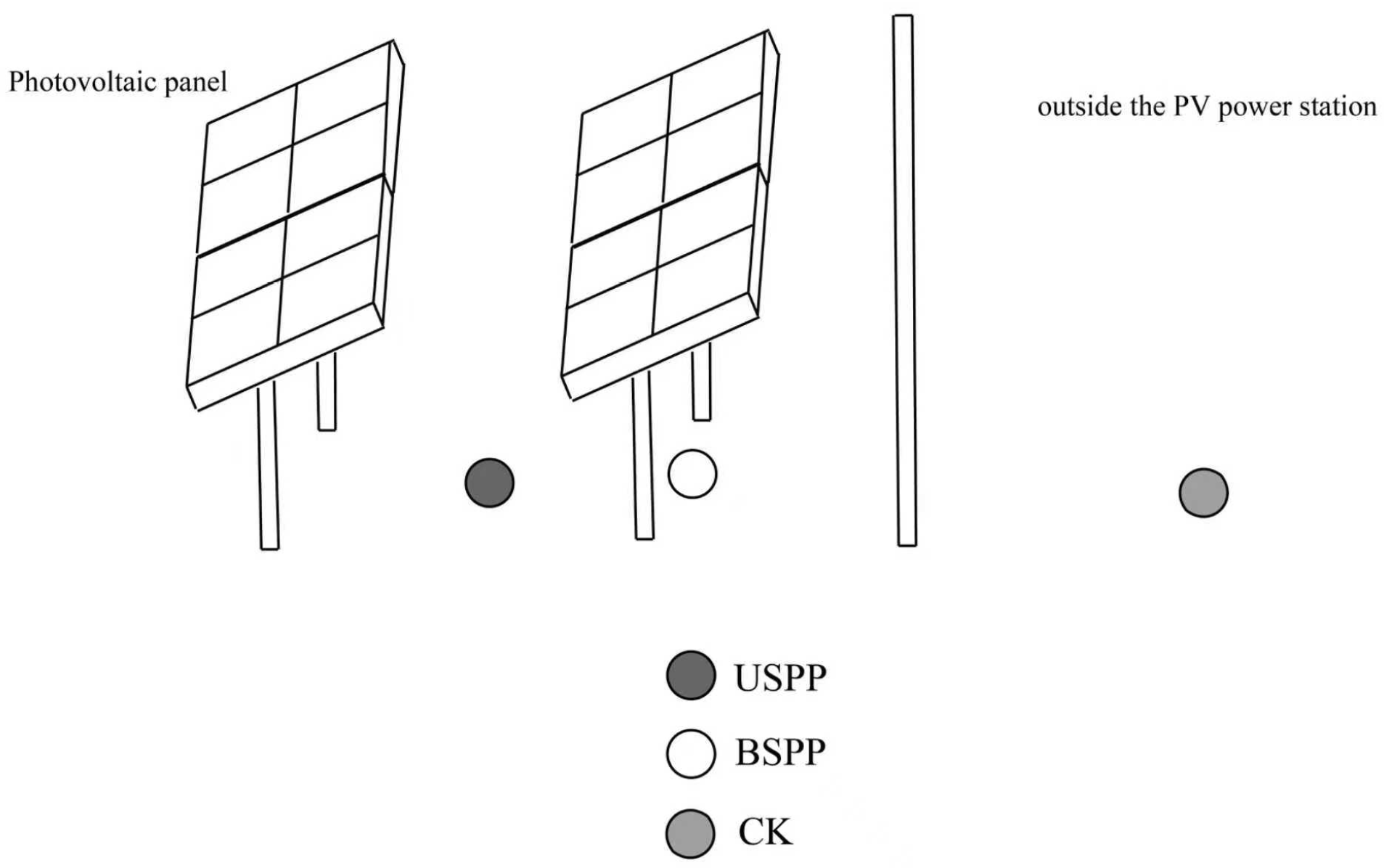
2.1. Monitoring Area
2.2. Survey Methodology
2.2.1. Insect Species Survey Methods
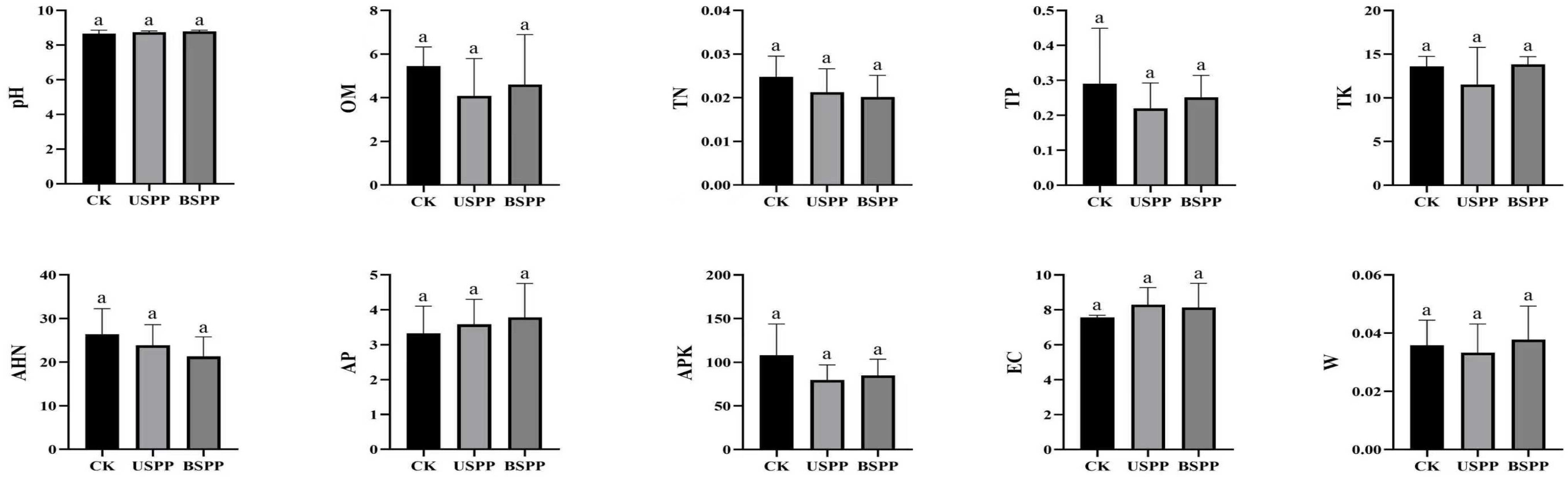
2.2.2. Soil Factor Investigation Methodology
2.2.3. Electromagnetic Radiation and Noise Measurement Methods
2.2.4. Vegetation Factor Survey Methods
2.3. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
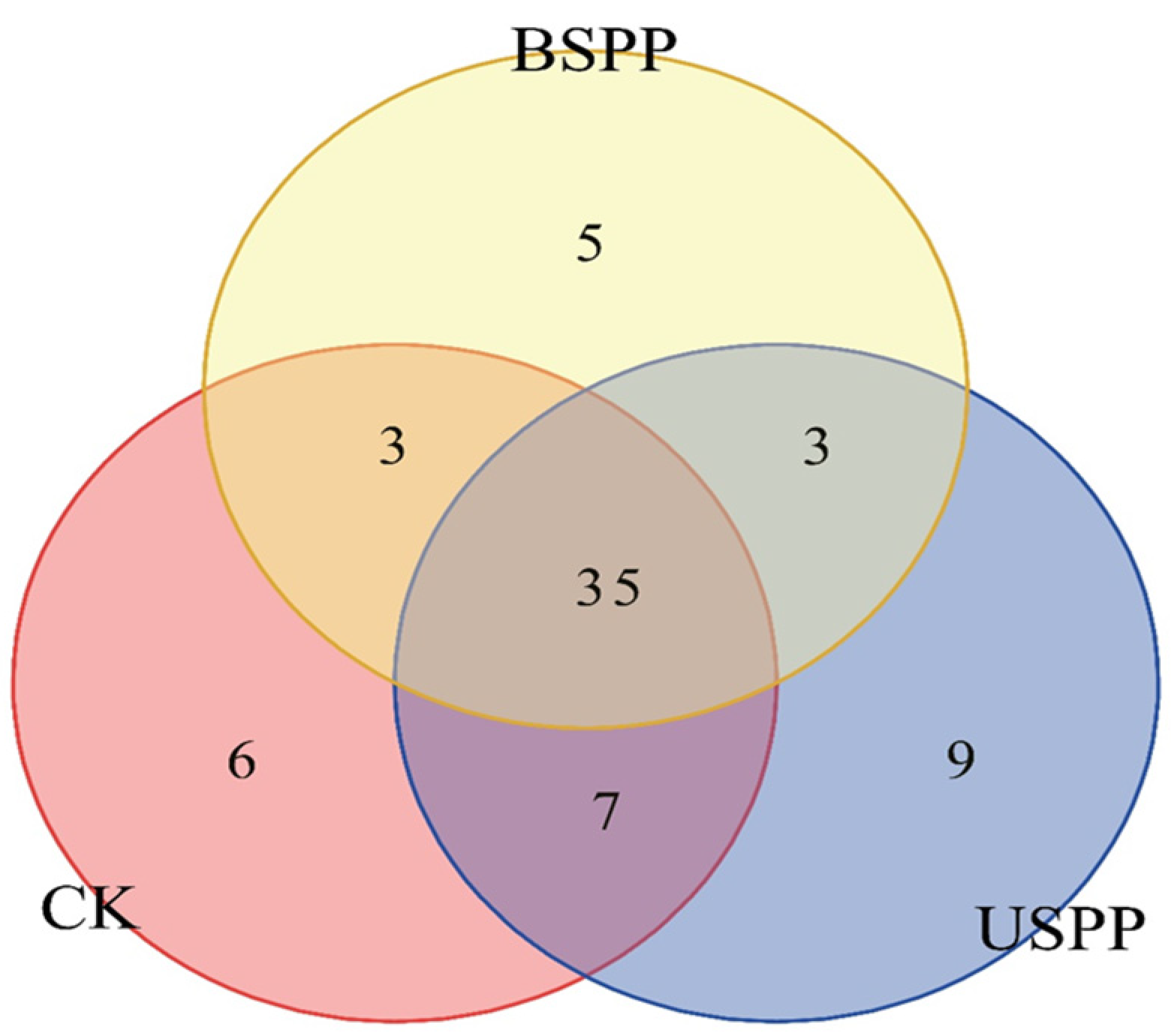
3.1. Insect Species Composition in Different Areas of the PV Power Station
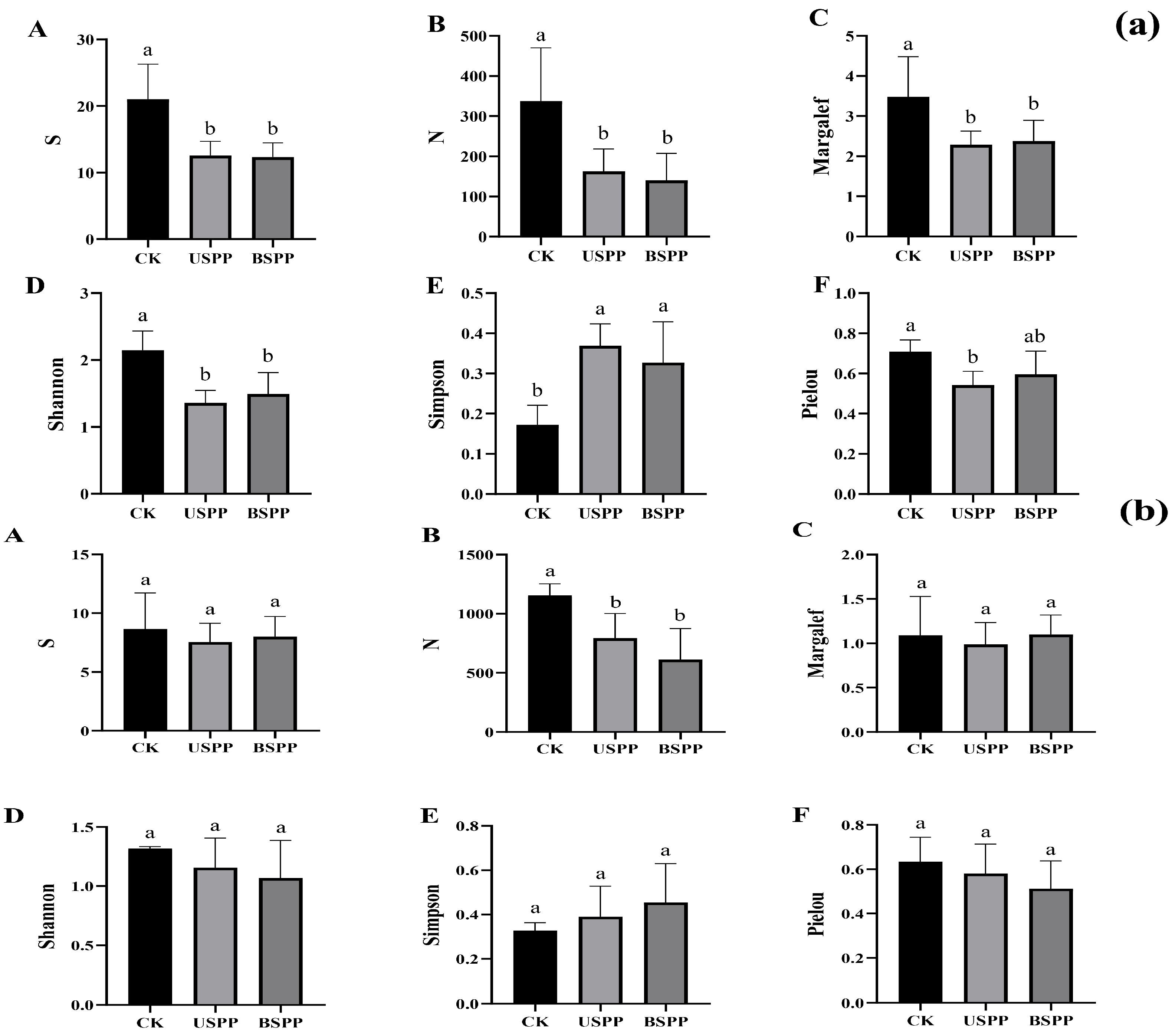
3.2. Insect Diversity in Different Areas of the PV Power Station
3.2.1. Diversity of Insects in Different Areas of the PV Power Station
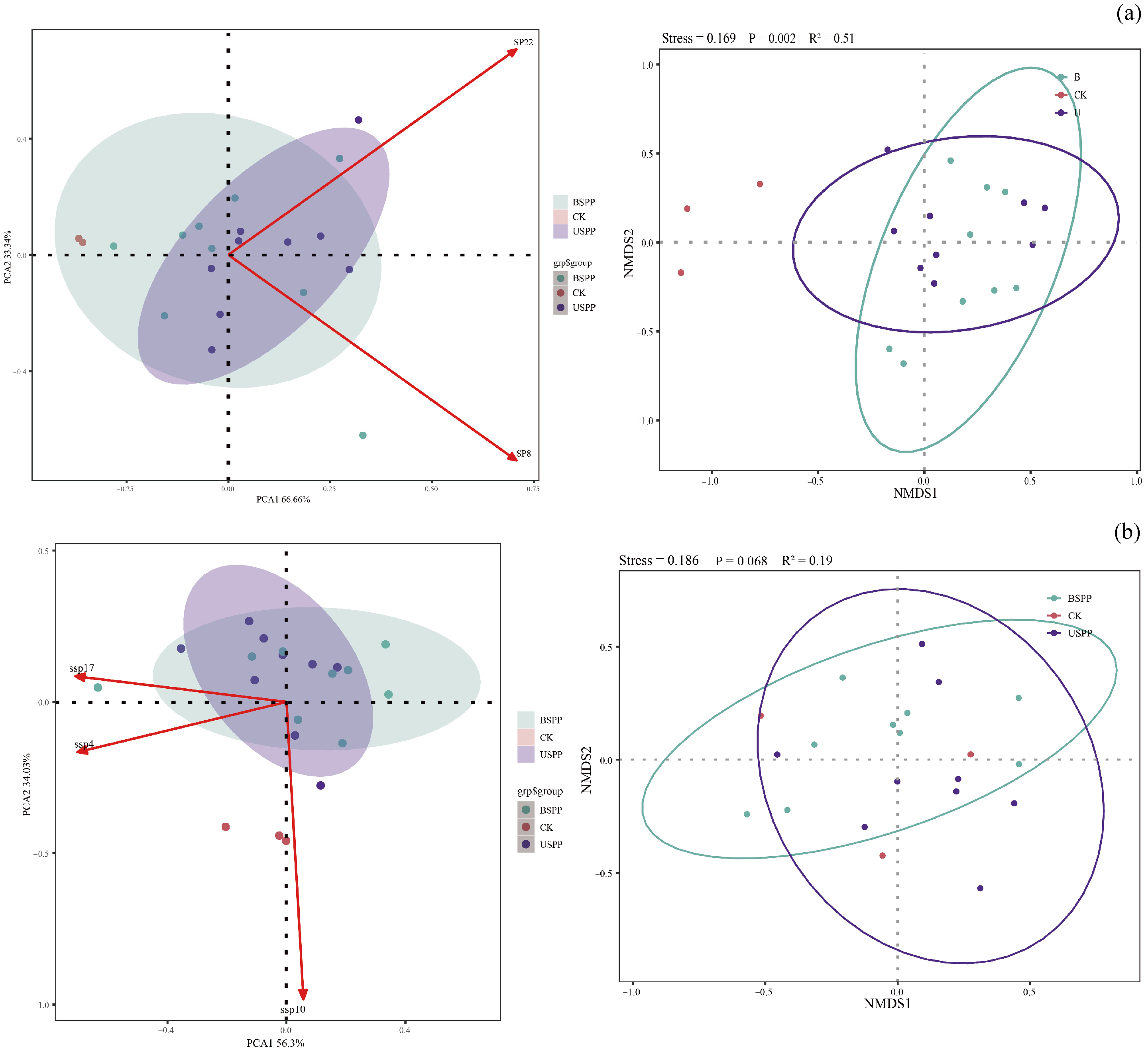
3.2.2. Composition in Different Regions of PV Power Station
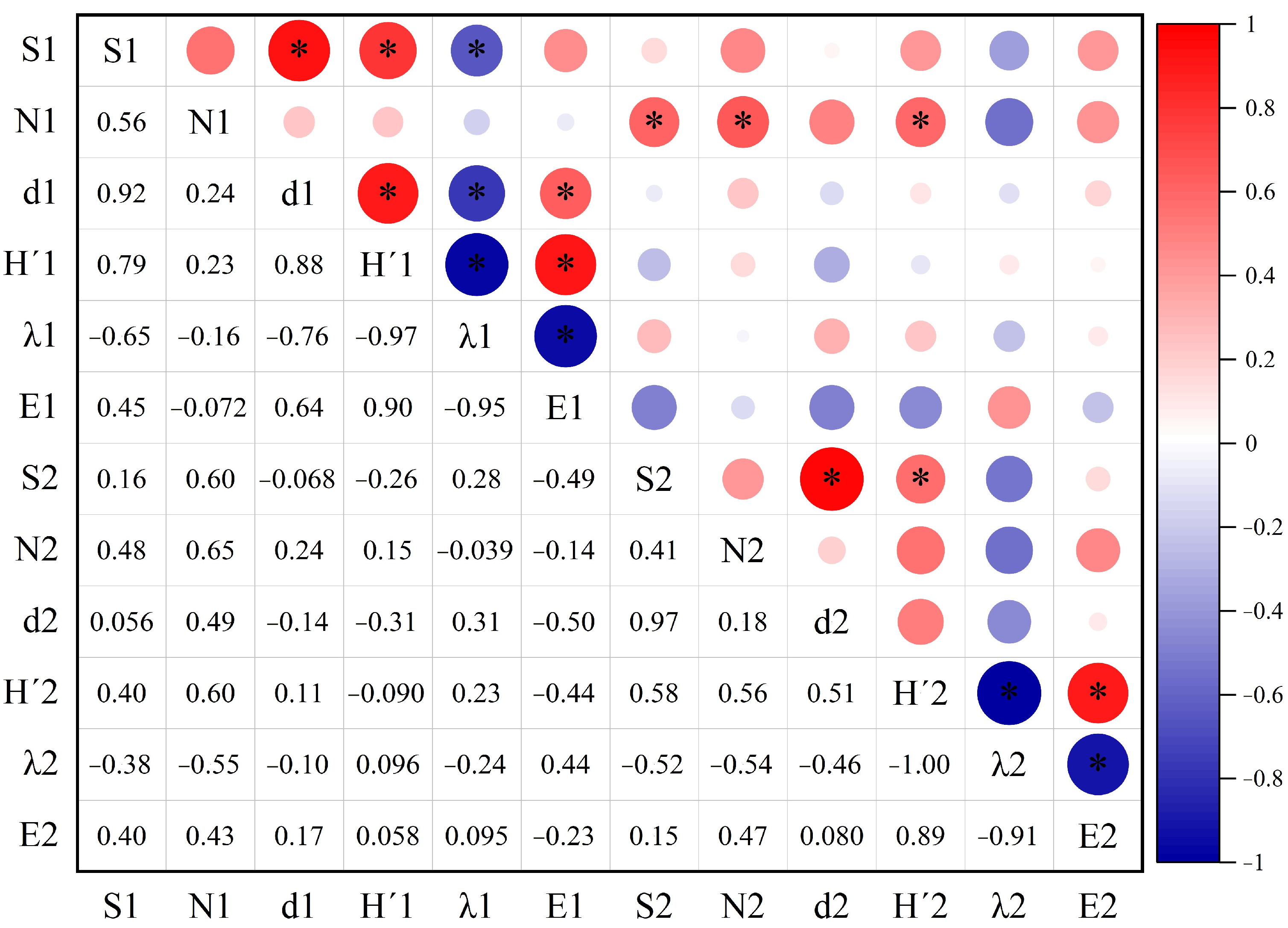
3.2.3. Correlation Analysis Between Predatory and Phytophagous Insect Diversity in Different Areas of the PV Power Station
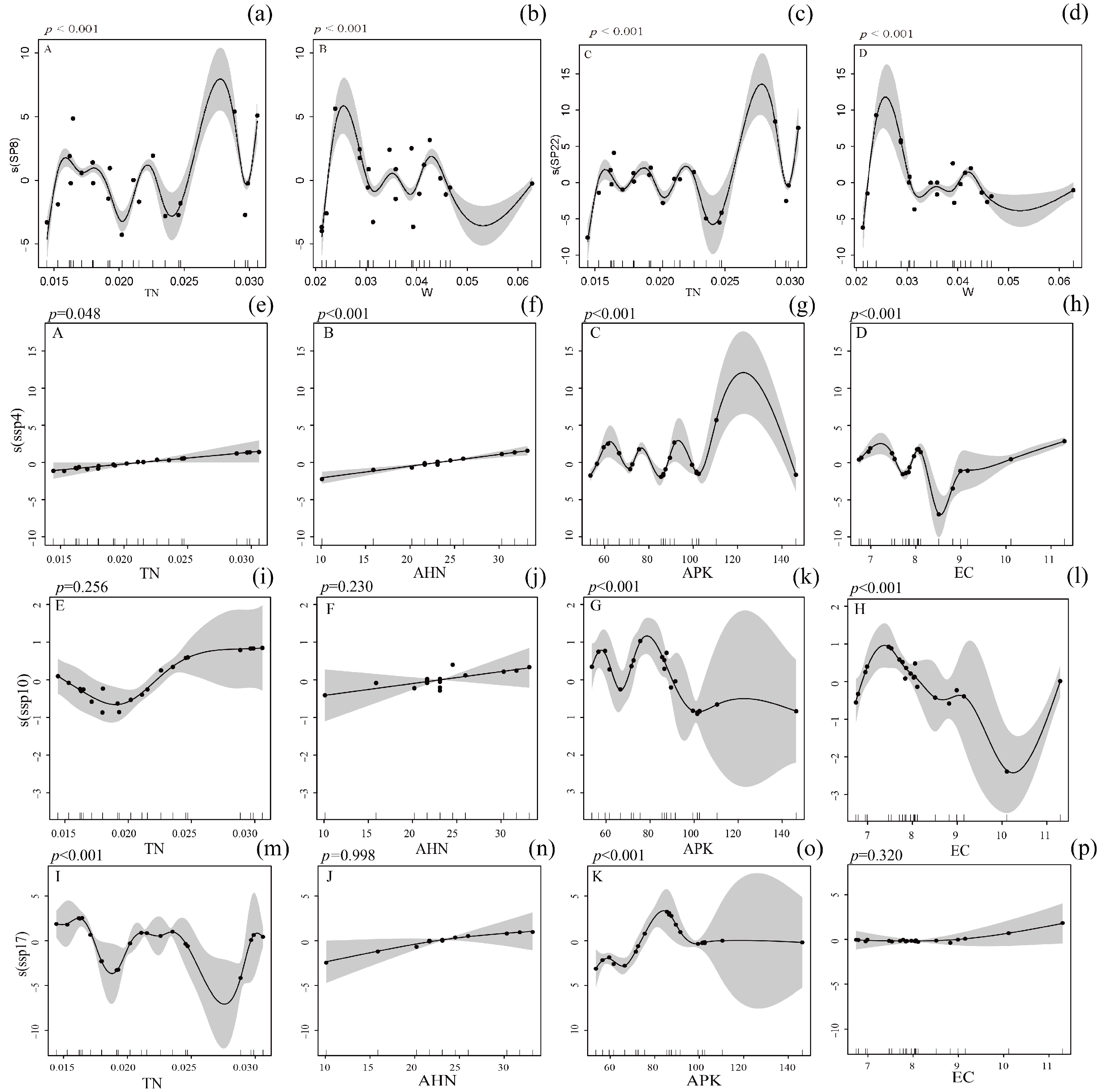
3.3. Response of Insect Diversity to Environmental Factors in PV Power Station
3.4. Response of Insect Community Diversity in PV Power Station to Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of PV Power Station on Insect Diversity
4.2. Impact of Environmental Factors in PV Power Station on Insect Community Diversity
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PV | photovoltaic |
| USPP | under solar photovoltaic panels |
| BSPP | between solar photovoltaic panels |
| CK | outside the photovoltaic power station (control) |
| S1 | species richness of predatory insects |
| N1 | abundance of predatory insects |
| d1 | Margalef richness index of predatory insects |
| H’1 | Shannon–Wiener diversity index of predatory insects |
| λ1 | Simpson dominance index of predatory insects |
| E1 | Pielou evenness index of predatory insects |
| S2 | Species richness of phytophagous insects |
| N2 | abundance of phytophagous insects |
| d2 | Margalef richness index of phytophagous insects |
| H’2 | Shannon–Wiener diversity index of phytophagous insects |
| λ2 | Simpson dominance index of phytophagous insects |
| E2 | Pielou evenness index of phytophagous insects |
| S | species richness |
| N | abundance |
| d | Margalef richness index |
| H’ | Shannon–Wiener diversity index |
| λ | Simpson dominance index |
| E | Pielou evenness index |
| pH | soil pH |
| OM | soil organic matter |
| TN | total nitrogen |
| TP | total phosphorus |
| TK | total potassium |
| AHN | alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen |
| AP | available potassium |
| APK | available phosphorus |
| EC | electrical conductivity of soil leachate |
| W | soil water content |
| EMF | electromagnetic field intensity |
| Db | noise level |
| Sp | vegetation species richness |
| H | vegetation height |
| C | vegetation coverage |
| F | vegetation frequency |
| B | vegetation biomass |
| D | vegetation density |
Appendix A
References
- Smith, J.A.; Doe, R.B.; Brown, C.D. Global expansion of photovoltaic power: Ecological trade-offs and solutions. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.H.; Ning, N. Development Status and Trends of China’s Solar-Plus-Storage Industry. Sino-Glob. Energy 2020, 25, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Solar energy potential and large-scale photovoltaic deployment in Northwest China. Renew. Energy 2021, 170, 44–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, R.R.; Easter, S.B.; Murphy-Mariscal, M.L.; Maestre, F.T.; Tavassoli, M.; Allen, E.B.; Barrows, C.W.; Belnap, J.; Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Ravi, S.; et al. Environmental impacts of utility-scale solar energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.S.; Page, T.; Moore-O’Leary, K.A. Pollinator conservation in solar energy landscapes: A review. Biol. Conserv. 2022, 265, 109425. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Duan, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Effects of different photovoltaic array constructions on natural restoration of desert grassland plant communities and soil physicochemical properties. Pratacultural Sci. 2023, 40, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q. Effects of Photovoltaic Panel Arrays on Plant Communities and Soil Characteristics in Degraded Songnen Grassland; University of Northeast Normal: Changchun, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.M. Effects of Magnetic Field and LED Light on the Biological Characteristics of the Diamondback Moth (Plutella xylostella); University of Yangzhou: Yangzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rosas, M.Y.; Peri, L.P.; Carrara, R.; Flores, G.E.; Pedrana, J.; Pastur, G.M. Potential biodiversity map of darkling beetles (Tenebrionidae): Environmental characterization, land-uses and analyses of protection areas in Southern Patagonia. J. Insect Conserv. 2019, 23, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorini, S.; Salvati, L.; SMasayuki, A.; Natsuko, K. Takata Tenebrionid beetles as proxy indicators of climate aridity in a Mediterranean area. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 38, 256–38261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, A. Ecological vulnerability of arid and semi-arid regions in Northwest China. J. Arid. Environ. 2019, 160, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- National Energy Administration (NEA). China Renewable Energy Development Report; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X. Effects of electromagnetic fields from solar farms on arthropod communities in desert ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 159123. [Google Scholar]
- Samways, M.J.; Barton, P.S.; Birkhofer, K.; Chichorro, F.; Deacon, C.; Fartmann, T.; Fukshima, C.S.; Gaigher, R.; Habel, J.C.; Hallmann, C.A.; et al. Solutions for humanity on how to conserve insects. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 242, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrou, H.; Wery, J.; Dufour, L.; Dupraz, C. Productivity and radiation use efficiency of lettuces grown in the partial shade of photovoltaic panels. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 44, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodsky, S.M.; Campbell, J.W.; Hernandez, R.R. Solar energy development impacts on bird biodiversity: A global meta-analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 033002. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agro-Chemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Magurran, A.E. Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement: 40th Anniversary Edition; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guisan, A.; Edwards, T.C.; Hastie, T. Generalized linear and generalized additive models in studies of species distributions: Setting the scene. Ecol. Model. 2002, 157, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2025. Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Grodsky, S.M.; Campbell, J.W.; Hernandez, R.R. Solar energy development impacts flower-visiting beetles and flies in the Mojave Desert. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 263, 109336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, R.; Vazquez, D.P.; Flores, G.E. Habitat specificity can blur the predictions of species–energy theory: A case study of tenebrionid beetles adapted to aridity. J. Arid. Environ. 2011, 75, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stork, N.E. How many species of insects and other terrestrial arthropods are there on Earth? Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, P.W.; Denno, R.F.; Eubanks, M.D.; Finke, D.L.; Kaplan, I. Insect Ecology: Behavior, Populations and Communities; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeman, R.L. The trophic-dynamic aspect of ecology. Ecology 1942, 23, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimm, S.L.; Lawton, J.H.; Cohen, J.E. Food web patterns and their consequences. Nature 1991, 350, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairston, N.G.; Smith, F.E.; Slobodkin, L.B. Community structure, population control, and competition. Am. Nat. 1960, 94, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.S.; Cagle, A.E.; Macknick, J.; Bloom, D.E.; Caplan, J.S.; Ravi, S. Effects of revegetation on soil physical and chemical properties in solar photovoltaic infrastructure. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodsky, S.M.; Hernandez, R.R. Reduced ecosystem services of desert plants from ground-mounted solar energy development. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkó, O.; Batáry, P. The role of insect diversity in ecosystem functioning. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tomanová, K.; Vácha, M. The effect of radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation (RF-EMR) from wireless communication on insects: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Environ. Health 2022, 37, 551–561. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, G.; McKenna, M.F.; Angeloni, L.M.; Crooks, K.R.; Fristrup, K.M.; Brown, E.; Warner, K.A.; Nelson, M.D.; White, C.; Briggs, J.; et al. synthesis of two decades of research documenting the effects of noise on wildlife. Biol. Rev. 2016, 91, 982–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.F.; Liu, S.Z.; Zhan, K.J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.L.; Liu, S.J.; Sun, T. Photovoltaic Conversion and Energy Transfer Effect of Desert Photovoltaic Field: A Case Study of Gulang Zhenfa Photovoltaic Field of Gansu. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 36, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.Y.; Du, L.T.; Pan, H.Z. Simulation of carbon and water fluxes of planted shrub ecosystem in desert steppe biome zone based on parameter optimization. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.Y.; Ma, L.; Qu, J.J.; Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; Tan, L.H.; Xiao, J.H. Effect of Large Photovoltaic Power Station on Microclimate of Desert Region in Gonghe Basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 37, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kalnay, E.; Motesharrei, S.; Rivas, J.; Kucharski, F.; DanieL, K.; Bach, E.; Zeng, N. Climate model shows large-scale wind and solar farms in the sahara wind and solar farms in the Sahara increase rain and vegetation. Science 2018, 361, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ban, L.; Yin, X.; Wei, S.; Sun, W.; Zhang, R. Insect Community Diversity in Photovoltaic Power Station and Its Response to Environmental Factors. Biology 2025, 14, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101388
Wang Y, Cheng Y, Ban L, Yin X, Wei S, Sun W, Zhang R. Insect Community Diversity in Photovoltaic Power Station and Its Response to Environmental Factors. Biology. 2025; 14(10):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101388
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ying, Yuanrun Cheng, Liping Ban, Xuewei Yin, Shuhua Wei, Wei Sun, and Rong Zhang. 2025. "Insect Community Diversity in Photovoltaic Power Station and Its Response to Environmental Factors" Biology 14, no. 10: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101388
APA StyleWang, Y., Cheng, Y., Ban, L., Yin, X., Wei, S., Sun, W., & Zhang, R. (2025). Insect Community Diversity in Photovoltaic Power Station and Its Response to Environmental Factors. Biology, 14(10), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101388






