Genetically Engineered Goats as Efficient Mammary Gland Bioreactors for Production of Recombinant Human Neutrophil Peptide 1 Using CRISPR/Cas9
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Plasmid Construction and In Vitro transcription
2.3. Preparation and Injection of One-Cell Embryos
2.4. Genome Editing Analysis
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Analysis
2.7. Antibacterial Activity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Generation of HNP1-Expressing Goats
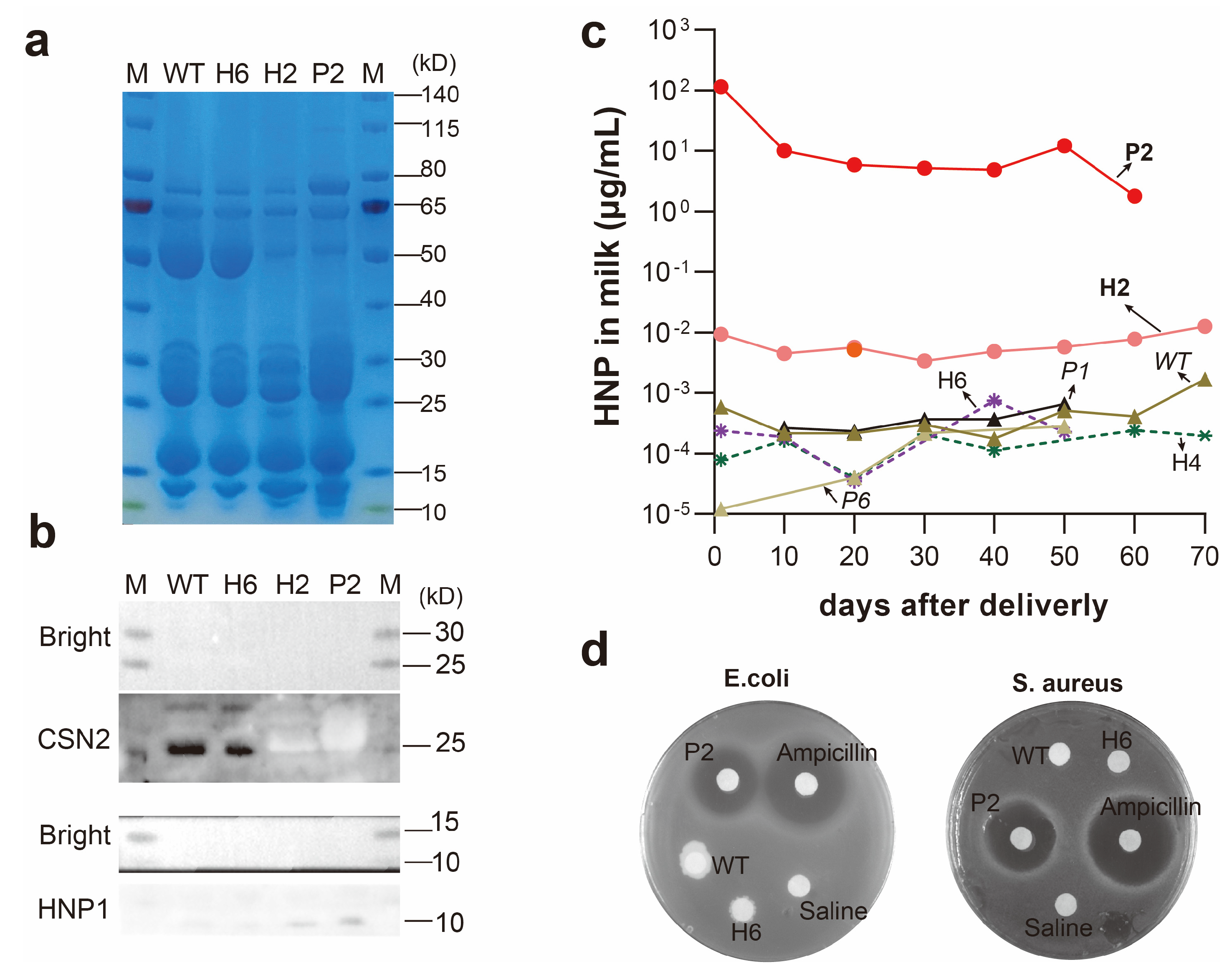
3.2. Production of HNP1 in Milk
3.3. Quantification of HNP1 Levels
3.4. Antibacterial Activity of HNP1 Milk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Bai, L.; Fan, J.; Liu, E. Expression systems and species used for transgenic animal bioreactors. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 580463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Cai, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H.; Yu, G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, A.; et al. Expression of active recombinant human lactoferrin in the milk of transgenic goats. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 57, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platenburg, G.J.; Kootwijk, E.P.; Kooiman, P.M.; Woloshuk, S.L.; Nuijens, J.H.; Krimpenfort, P.J.; Pieper, F.R.; de Boer, H.A.; Strijker, R. Expression of human lactoferrin in milk of transgenic mice. Transgenic Res. 1994, 3, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokkones, E.; Fromm, S.H.; Kareem, B.N.; Klungland, H.; Olstad, O.K.; Hogset, A.; Iversen, J.; Bjoro, K.; Gautvik, K.M. Human parathyroid hormone as a secretory peptide in milk of transgenic mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 1995, 59, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.H.; Birck-Wilson, E.; Allard, G.; Masiello, N.; Day, M.; Murphy, K.P.; Paragas, V.; Silver, S.; Moody, M.D. Purification and characterization of a recombinant version of human α-fetoprotein expressed in the milk of transgenic goats. Protein Expr. Purif. 2004, 38, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maga, E.A.; Shoemaker, C.F.; Rowe, J.D.; Bondurant, R.H.; Anderson, G.B.; Murray, J.D. Production and processing of milk from transgenic goats expressing human lysozyme in the mammary gland. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Huang, Y.; Baldassarre, H.; Wang, B.; Lazaris, A.; Leduc, M.; Bilodeau, A.S.; Bellemare, A.; Côté, M.; Herskovits, P.; et al. Recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase from milk of transgenic animals to protect against organophosphate poisoning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13603–13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kling, J. First US approval for a transgenic animal drug. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiguzel, C.; Iqbal, O.; Demir, M.; Fareed, J. European community and US-FDA approval of recombinant human antithrombin produced in genetically altered goats. Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. 2009, 15, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Doudna, J.A. CRISPR technology: A decade of genome editing is only the beginning. Science. 2023, 379, eadd8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.D.; Scott, D.A.; Weinstein, J.A.; Ran, F.A.; Konermann, S.; Agarwala, V.; Li, Y.; Fine, E.J.; Wu, X.; Shalem, O.; et al. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A Programmable Dual-RNA–Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. Science. 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adli, M. The CRISPR tool kit for genome editing and beyond. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.D.; Lander, E.S.; Zhang, F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell 2014, 157, 1262–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Wan, Y.; Xu, D.; Cui, L.; Deng, M.; Zhang, G.; Jia, R.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Deng, K.; et al. Generation and evaluation of Myostatin knock-out rabbits and goats using CRISPR/Cas9 system. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Lei, A.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, W.; Zhu, H.; Dong, Z.; Niu, Y.; Shi, B.; Cai, B.; et al. Generation of gene-modified goats targeting MSTN and FGF5 via zygote injection of CRISPR/Cas9 system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Meng, C.; Gui, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Efficient and Specific Generation of MSTN-Edited Hu Sheep Using C-CRISPR. Genes 2023, 14, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Niu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, H.; Kou, Q.; Lei, A.; Zhao, X.; Yan, H.; Cai, B.; Shen, Q.; et al. Multiplex gene editing via CRISPR/Cas9 exhibits desirable muscle hypertrophy without detectable off-target effects in sheep. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Yuan, L.; Deng, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Lai, L. Efficient Generation of Myostatin Gene Mutated Rabbit by CRISPR/Cas9. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Guo, R.; Deng, M.; Liu, Z.; Pang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F. Efficient generation of CLPG1-edited rabbits using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Reprod. Domest. Anim. Zuchthyg. 2019, 54, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ouyang, H.; Xie, Z.; Yao, C.; Guo, N.; Li, M.; Jiao, H.; Pang, D. Efficient Generation of Myostatin Mutations in Pigs Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Hwang, I.S.; Choi, H.; Hwang, J.H.; Hwang, J.S.; Lee, D.G. The novel biological action of antimicrobial peptides via apoptosis induction. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, W.E., Jr.; McDougall, B.; Tran, D.; Selsted, M.E. Anti-HIV-1 activity of indolicidin, an antimicrobial peptide from neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 63, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehlbaum, P.; Bulet, P.; Chernysh, S.; Briand, J.P.; Roussel, J.P.; Letellier, L.; Hetru, C.; Hoffmann, J.A. Structure-activity analysis of thanatin, a 21-residue inducible insect defense peptide with sequence homology to frog skin antimicrobial peptides. PNAS 1996, 93, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolatchiev, A.; Baturin, V.; Bazikov, I.; Maltsev, A.; Kunitsina, E. Effect of antimicrobial peptides HNP-1 and hBD-1 on Staphylococcus aureus strains in vitro and in vivo. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. Recombinant production of antimicrobial peptides in Escherichia coli: A review. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 80, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, S.; Wei, W.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, N.; Jin, Y.; et al. Recombinant HNP-1 Produced by Escherichia coli Triggers Bacterial Apoptosis and Exhibits Antibacterial Activity against Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0086021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazgier, M.; Lubkowski, J. Expression and purification of recombinant human alpha-defensins in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Wan, Y.; Guo, R.; Deng, M.; Deng, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F. Generation of beta-lactoglobulin knock-out goats using CRISPR/Cas9. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Du, J.; Yun, S.; Xue, C.; Yao, Y.; Rao, S. Recent advances in CRISPR-Cas9-based genome insertion technologies. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadros, R.M.; Miura, H.; Harms, D.W.; Akatsuka, H.; Sato, T.; Aida, T.; Redder, R.; Richardson, G.P.; Inagaki, Y.; Sakai, D.; et al. Easi-CRISPR: A robust method for one-step generation of mice carrying conditional and insertion alleles using long ssDNA donors and CRISPR ribonucleoproteins. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Ying, W.; Hu, X.; Dai, P.; Meng, F.; Shi, L.; Sun, Y.; Yao, N.; et al. Tild-CRISPR Allows for Efficient and Precise Gene Knockin in Mouse and Human Cells. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 526–536.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarnall, M.T.N.; Ioannidi, E.I.; Schmitt-Ulms, C.; Krajeski, R.N.; Lim, J.; Villiger, L.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, K.; Garushyants, S.K.; Roberts, N.; et al. Drag-and-drop genome insertion of large sequences without double-strand DNA cleavage using CRISPR-directed integrases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, N.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Tong, Y.; Chen, J.; Cheng, G. Breeding and expression stability of human lactoferrin transgenic goat. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2012, 45, 2737–2742. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, R.R.; Melo, L.M.; de Figueirêdo Freitas, V.J. Production of recombinant proteins in milk of transgenic and non-transgenic goats. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol 2011, 54, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesino, R.; Toledo, J.R. The mammary gland: Bioreactor for the production of recombinant proteins. Biotecnol. Apl. 2006, 23, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
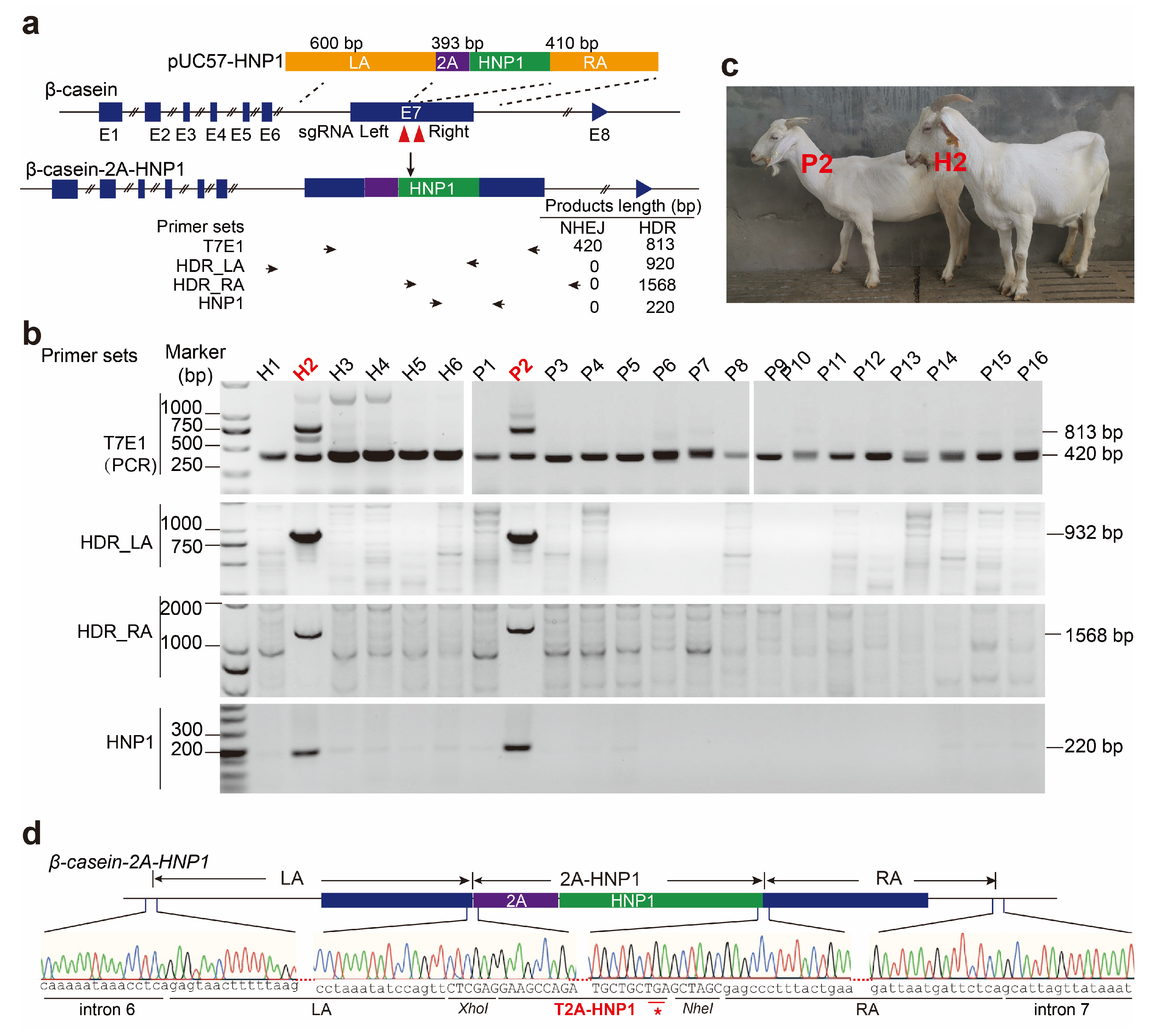
 indicating the cas9 cutting site.
indicating the cas9 cutting site.
 indicating the cas9 cutting site.
indicating the cas9 cutting site.
| Embryo No. | Recipient No. | Offspring No. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transferred/injected | Pregnant/total (%) | Live | CSN2 indels (%) | CSN2 bi-allelic indels (%) | HNP1 insertion (%) |
| 74/92 | 19/32 (59.38) | 22 | 21 (95.45) | 16 (72.73) | 2 (9.09) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Guo, R.; Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Wan, Y. Genetically Engineered Goats as Efficient Mammary Gland Bioreactors for Production of Recombinant Human Neutrophil Peptide 1 Using CRISPR/Cas9. Biology 2024, 13, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060367
Li D, Guo R, Chen F, Wang J, Wang F, Wan Y. Genetically Engineered Goats as Efficient Mammary Gland Bioreactors for Production of Recombinant Human Neutrophil Peptide 1 Using CRISPR/Cas9. Biology. 2024; 13(6):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060367
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongxu, Rihong Guo, Fang Chen, Jingang Wang, Feng Wang, and Yongjie Wan. 2024. "Genetically Engineered Goats as Efficient Mammary Gland Bioreactors for Production of Recombinant Human Neutrophil Peptide 1 Using CRISPR/Cas9" Biology 13, no. 6: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060367
APA StyleLi, D., Guo, R., Chen, F., Wang, J., Wang, F., & Wan, Y. (2024). Genetically Engineered Goats as Efficient Mammary Gland Bioreactors for Production of Recombinant Human Neutrophil Peptide 1 Using CRISPR/Cas9. Biology, 13(6), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060367






