Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and Expression of a Receptor for Activated Protein Kinase C1 (RACK1) Gene in Exopalaemon carinicauda Zoea Larvae under Aroclor 1254 Stress
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Shrimps’ Maintenance and Exposure
2.2. Cloning the ORF Fragment of EcRACK1
2.3. Sequence Analysis of EcRACK1
2.4. Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
3. Results
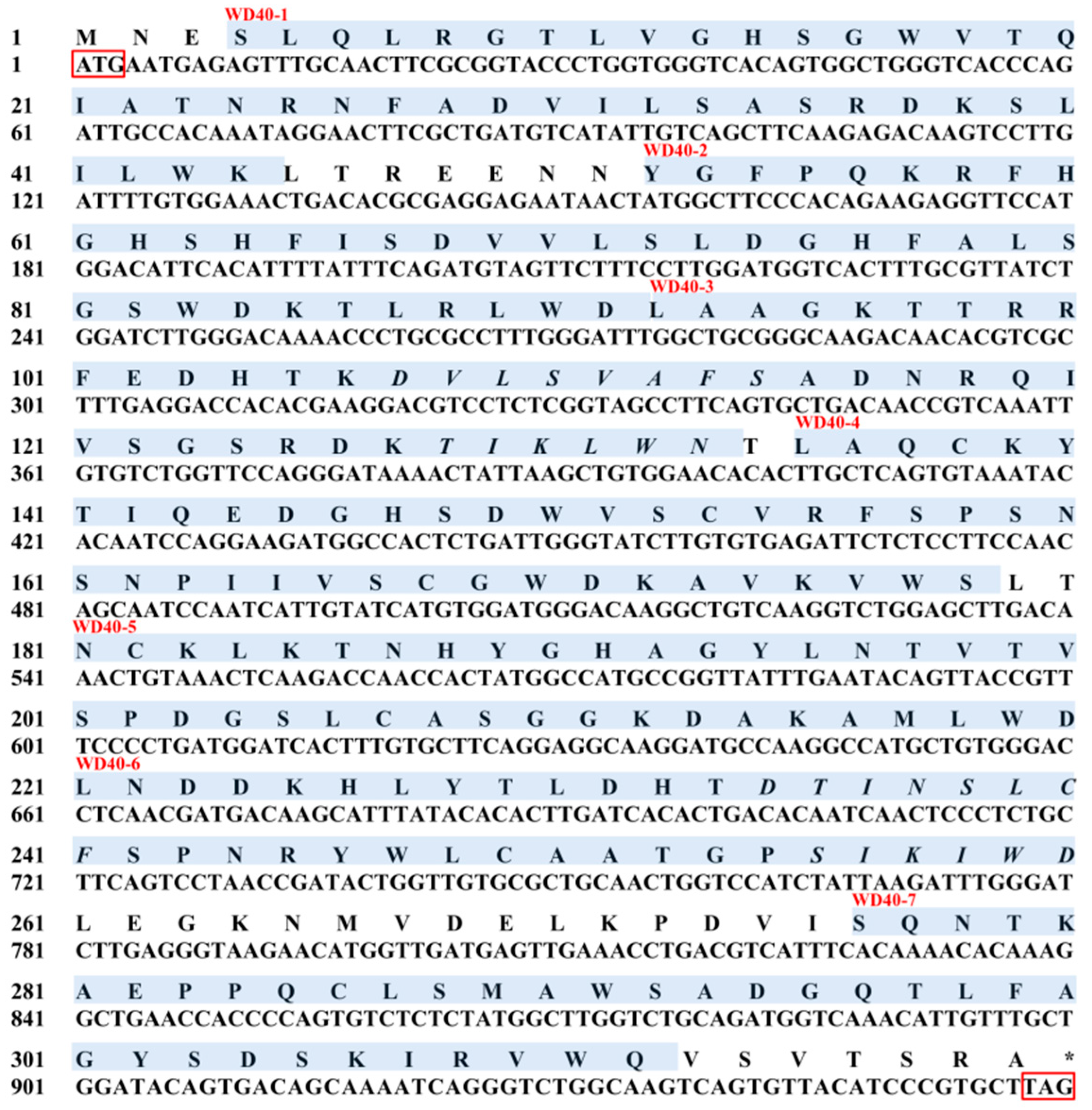
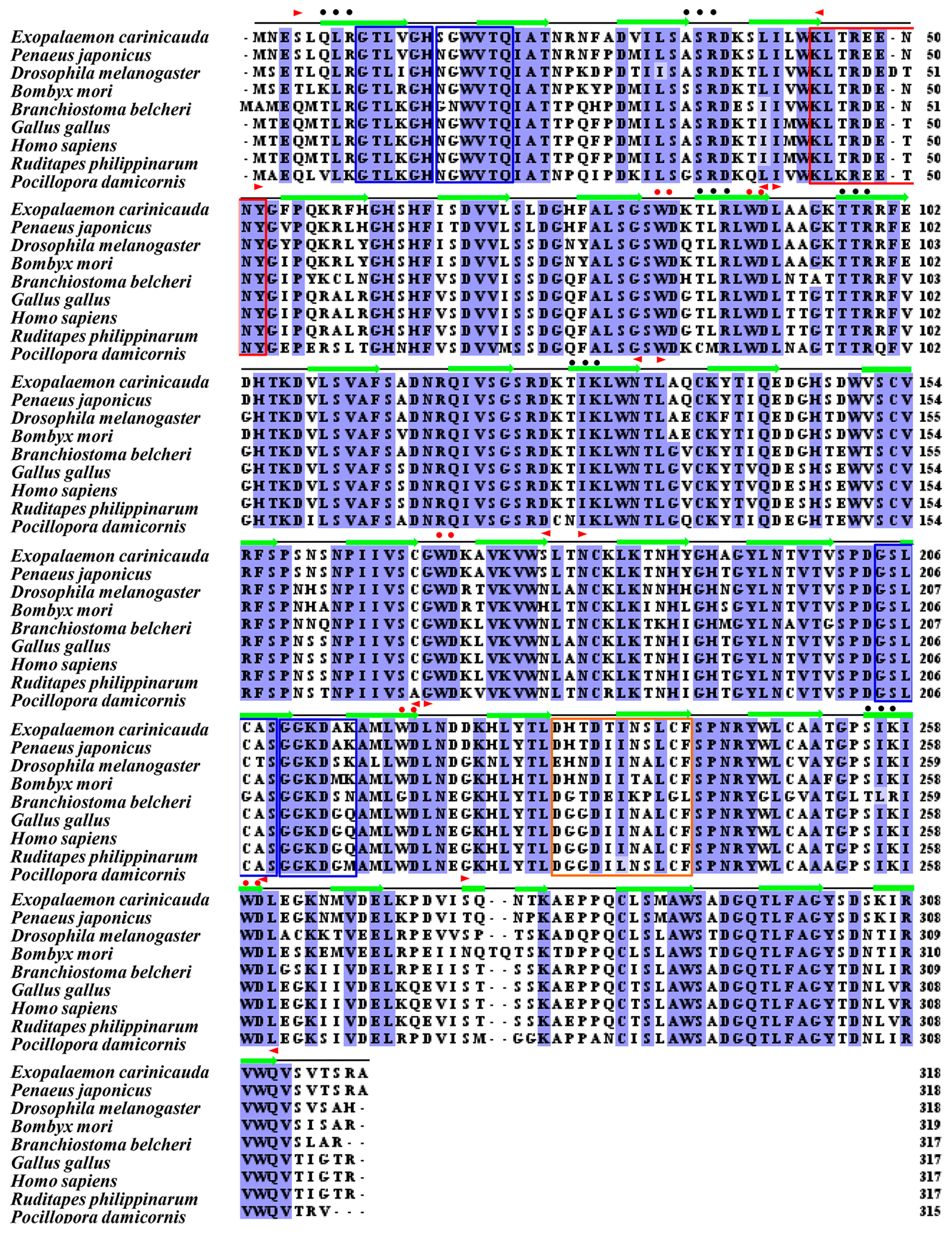
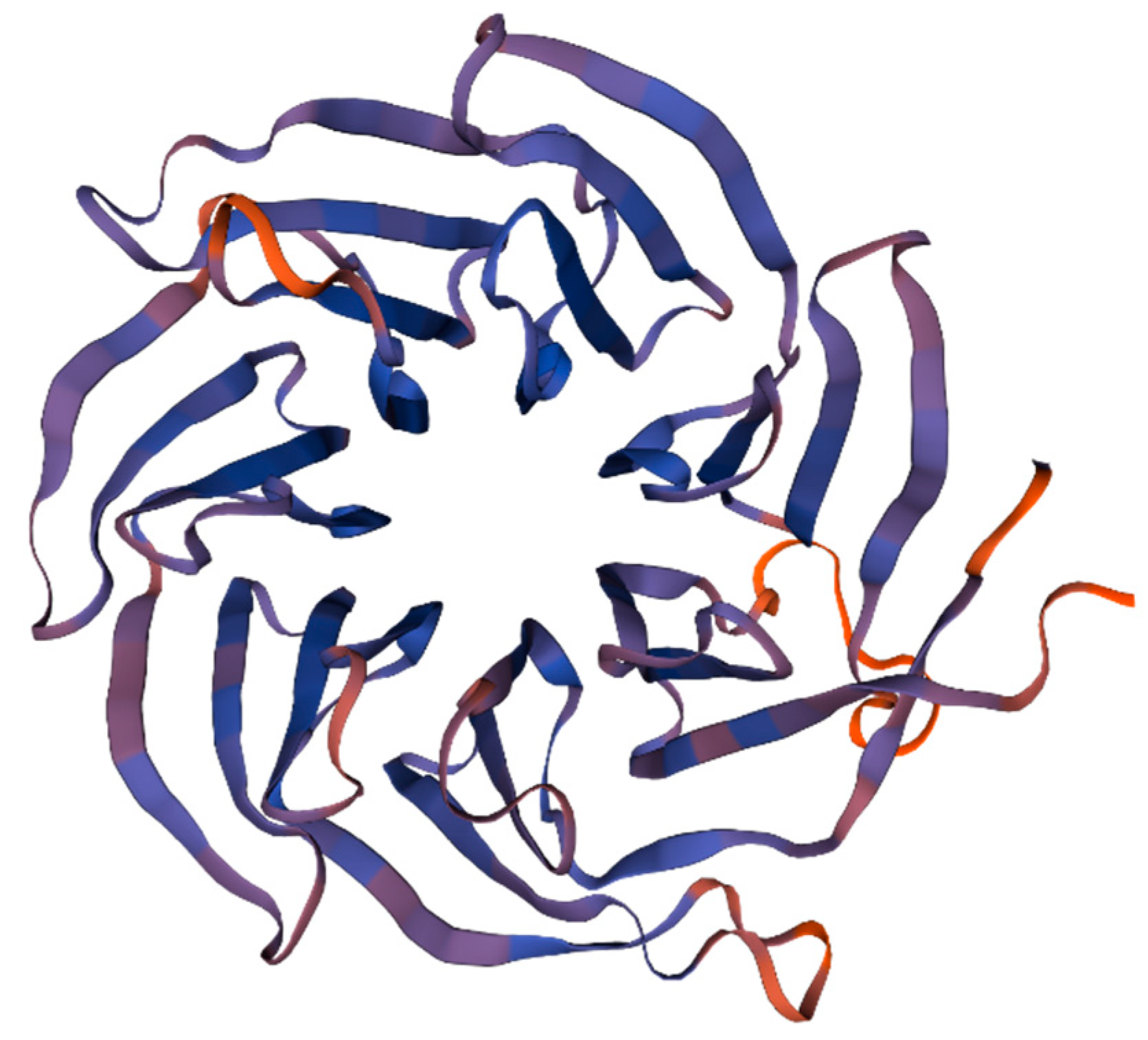
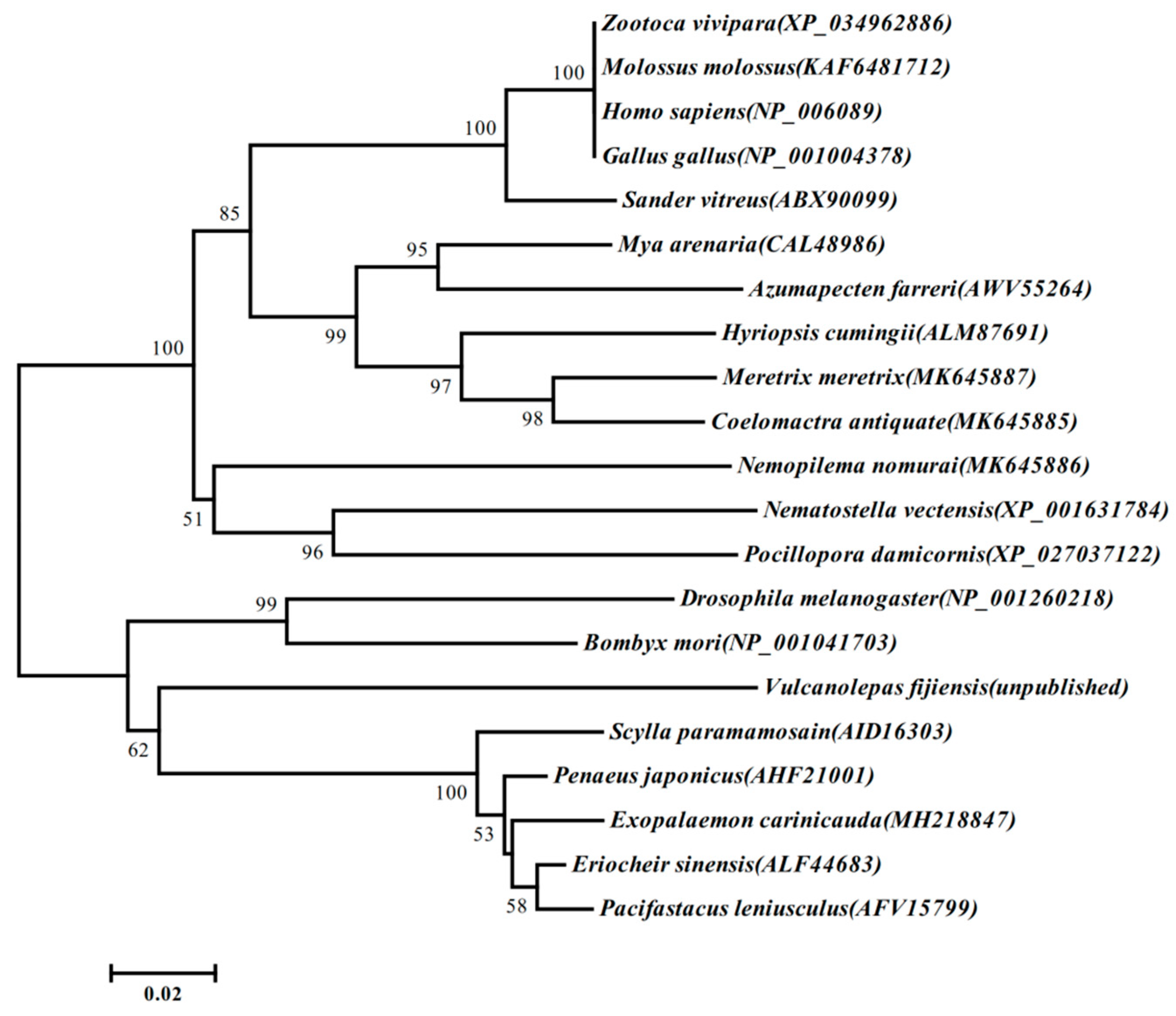
3.1. Sequence and Characterization of EcRACK1
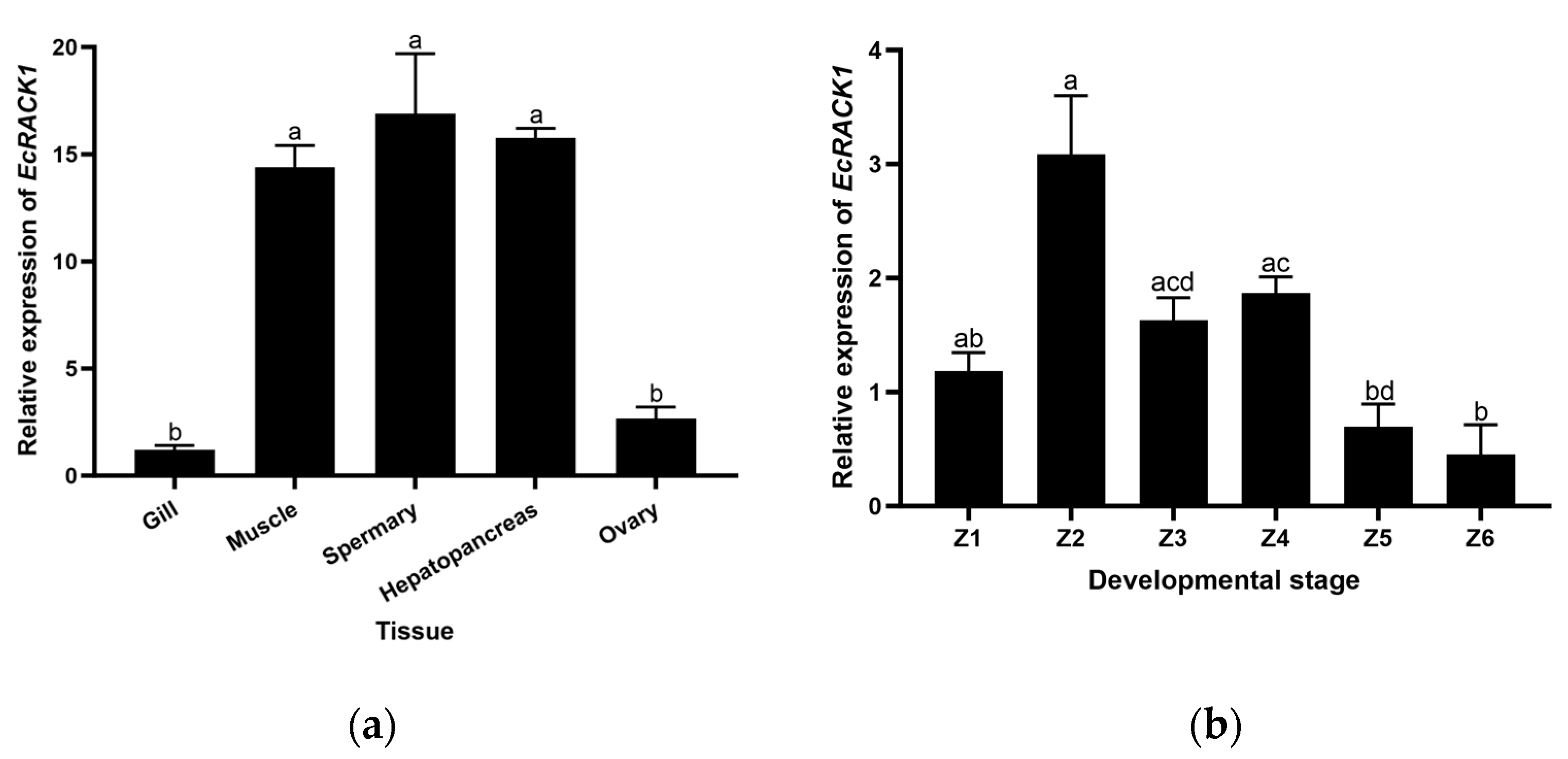
3.2. Specific Expression Patterns of EcRACK1
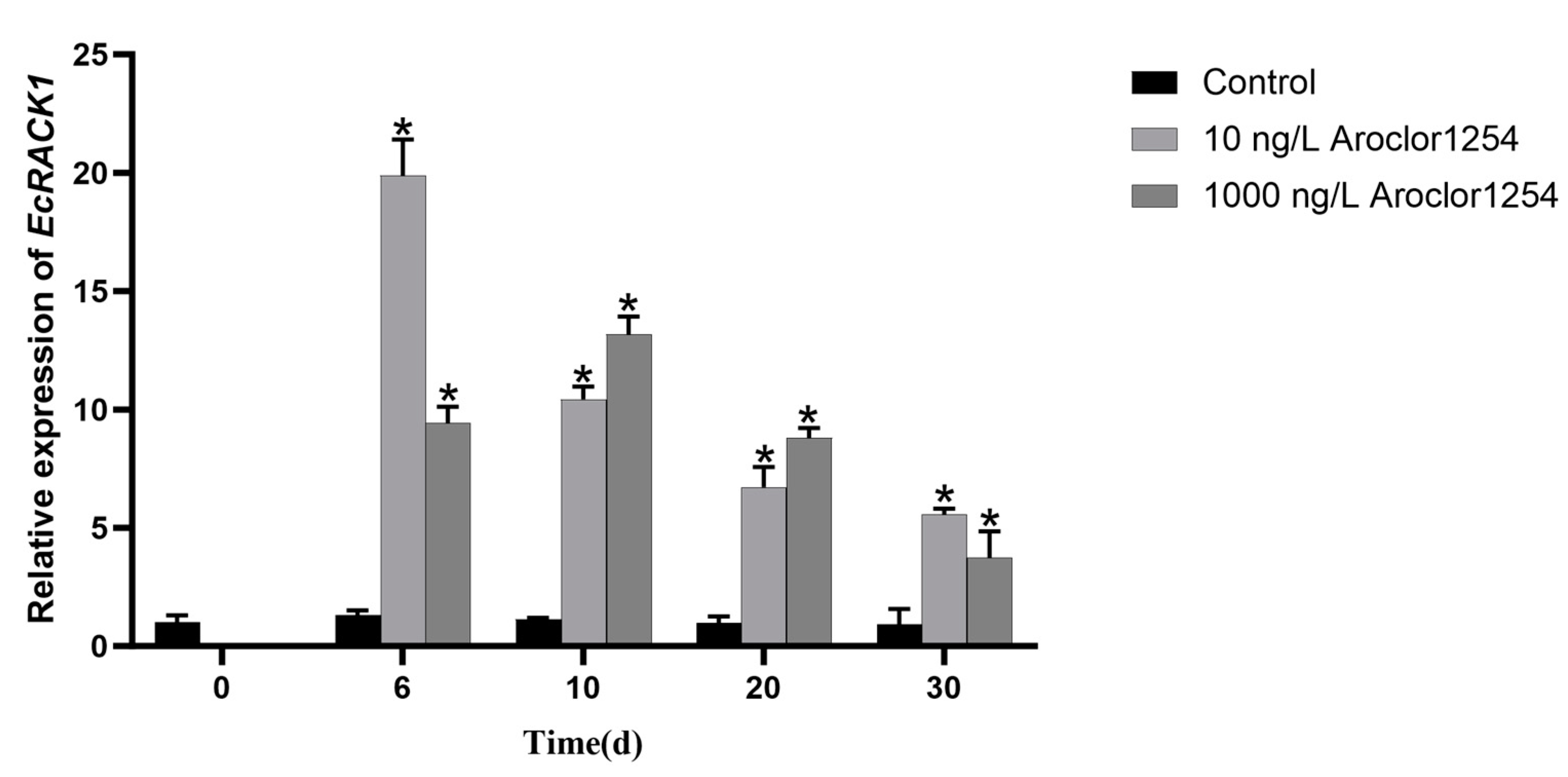
3.3. Expression Analysis of EcRACK1 under Aroclor 1254 Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, D.R.; Ron, D.; Kiely, P.A. RACK1, A multifaceted scaffolding protein: Structure and function. Cell Commun. Signal. 2011, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Peng, R.; Mu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ming, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y. Rack1 regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines by NF-κB in diabetic nephropathy. Open Med. 2022, 17, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCahill, A.; Warwicker, J.; Bolger, G.B.; Houslay, M.D.; Yarwood, S.J. The RACK1 scaffold protein: A dynamic cog in cell response mechanisms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 62, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Li, X.Y.; Cai, Y.; He, C.; Li, S.; Xie, C.; Xiong, Z.; Ge, Z.; Lu, N.; et al. Downregulation of tumor suppressor RACK1 by Helicobacter pylori infection promotes gastric carcinogenesis through the integrin β-1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2019, 450, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Tabata, K.; Twu, W.I.; Twu, W.I.; Rahman, M.S.; Kim, H.S.; Yu, J.B.; Jee, M.H.; Bartenschlager, R.; Jang, S.K. RACK1 mediates rewiring of intracellular networks induced by hepatitis C virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 5, e1008021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lan, R.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Bi, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Integrin β3, a RACK1 interacting protein, is critical for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection and NF-κB activation in Marc-145 cells. Virus Res. 2020, 282, 197956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.C.; Chou, C.C.; Chen, Y.K.; Tsai, S.; Hsieh, F.M.; Liu, H.J.; Hseu, T.H. Structure and genomic organization of porcine RACK1 gene. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Gene Struct. Expr. 1999, 1489, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korchak, H.M.; Kilpatrick, L.E. Roles for βII-protein kinase C and RACK1 in positive and negative signaling for superoxide anion generation in differentiated HL60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8910–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, D.; Jiang, Z.; Yao, L.; Vagts, A.; Diamond, I.; Gordon, A. Coordinated movement of RACK1 with activated βIIPKC. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27039–27046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, M.; Shor, B.; Caporaso, A.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Hu, L. Cpc2, a fission yeast homologue of mammalian RACK1 protein, interacts with Ran1 (Pat1) kinase to regulate cell cycle progression and meiotic development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 4016–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, S.J.; Steele, M.R.; Scotland, G.; Houslay, M.D.; Bolger, G.B. The RACK1 signaling scaffold protein selectively interacts with the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5 isoform. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 14909–14917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.Y.; Conroy, K.B.; Machleder, E.M.; Cartwright, C.A. RACK1, a receptor for activated C kinase and a homolog of the β subunit of G proteins, inhibits activity of src tyrosine kinases and growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 3245–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Pan, L.Q.; Miao, J.J.; Liu, T. Identification of interacting proteins with aryl hydrocarbon receptor in scallop Chlamys farreri by yeast two hybrid screening. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Lu, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Jiang, Z.; Wan, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. RACK1, a novel hPER1-interacting protein. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.J.; Pan, L.Q.; Liu, N.; Xu, C.Q.; Zhang, L. Molecular cloning of CYP4 and GSTpi homologues in the scallop Chlamys farreri, and its expression in response to Benzo[a]pyrene exposure. Mar. Genom. 2011, 4, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siah, A.; Masson, R.; Loup, B.; Bultelle, F.; Pellerin, J.; Leboulenger, F.; Danger, J.M. Receptor activated C kinase is down-regulated in the male gonad of the marine bivalve mollusc Mya arenaria exposed to tributyltin (TBT). Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 83, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Guo, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Qi, P. The receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) mediating immune response in thick shell mussel Mytilus coruscus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 85, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, G.; Zhu, L.; Chen, F.; Zar, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Wei, Y.; Xue, R.; Gong, C. Integrin beta and receptor for activated protein kinase C are involved in the cell entry of Bombyx mori cypovirus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3703–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Song, L. The receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) functions in hematopoiesis through JNK activation in Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 57, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. Molecular cloning and characterization of a receptor for activated protein kinase C1 (RACK1) from Chinese white shrimp; Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saelee, N.; Tonganunt-Srithaworn, M.; Wanna, W.; Phongdara, A. Receptor for Activated C Kinase-1 protein from Penaeus monodon (Pm-RACK1) participates in the shrimp antioxidant response. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Söderhäll, I.; Cerenius, L.; Söderhäll, K. Antilipopolysaccharide factor interferes with white spot syndrome virus replication in vitro and in vivo in the crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10365–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Wu, H.; Wei, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, H. Responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis to bacterial challenges by metabolomics and proteomics. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Geng, X.; Gao, L. Characterization of the RACK1 gene of Aips cerana cerana and its role in adverse environmental stresses. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 263, 110796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Pu, F.; Qin, J.; You, W.; Ke, C. Characterization of receptor of activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) and functional analysis during larval metamorphosis of the oyster Crassostrea angulata. Gene 2014, 537, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Xiao, S.; Yu, Z. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) from pearl oyster (Pinctada martensii) challenged with bacteria and exposed to cadmium. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardenne, F.; Loc’h, L.F.; Bodin, N. Persistent organic pollutants and trace metals in selected marine organisms from the Akanda National Park, Gabon (Central Africa). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 116009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, L.; Hong, L.; Wu, S.; Xie, W. Distributions of dissolved organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in China coastal waters. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Wan, M.M.; Lin, K.; Chen, Y.S.; Wang, R.; Tan, L.; Wang, J.T. Spatiotemporal distribution, source analysis and ecological risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in the Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 198, 115780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Shen, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.X. Seasonal and spatial distributions and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Yangtze Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe, S. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzofurans (PCDFs), and related compounds: Environmental and mechanistic considerations which support the development of toxic equivalency factors (TEFs). Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1990, 21, 51–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, M.; Lee, D.; Rhee, J. Effects of Polychlorinated Biphenyls on Survival, Growth, and Offspring Production of the Mysid Crustacean, Neomysis awatschensis. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2018, 10, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y. Detection of Four Types of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Antarctic Krill of Different Sexes in Different Periods. Master’s thesis, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Pan, L.; Miao, J. In vitro study of the effect of metabolism enzymes on benzo (a) pyrene-induced DNA damage in the scallop Chlamys farreri. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 42, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P. Q-Gene: Processing quantitative real-time RT–PCR data. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1439–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Chen, J.G. RACK1 genes regulate plant development with unequal genetic redundancy in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, S.O. Role of the Receptor for Activated C Kinase1A (RACK1a) in Hormone Auxin Mediated Root Development and Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Ph.D. Thesis, Howard University, Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guillemot, F.; Billault, A.; Auffray, C. Physical linkage of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein-related gene to the chicken major histocompatibility complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4594–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disatnik, M.H.; Hernandez-Sotomayor, S.M.; Jones, G.; Carpenter, G.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 binding to intracellular receptors for activated protein kinase C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.; Azadmanesh, K.; Shasaltaneh, M.D.; Mayahi, V.; Naghdi, N. The Implication of Androgens in the Presence of Protein Kinase C to Repair Alzheimer’s Disease-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction. Iran. Biomed. J. 2020, 24, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Gao, D.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Dual functions of Rack1 in regulating Hedgehog pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 3082–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buoso, E.; Masi, M.; Galbiati, V.; Maddalon, A.; Iulini, M.; Kenda, M.; Dolenc, M.S.; Marinovich, M.; Corsini, E. Effect of estrogen-active compounds on the expression of RACK1 and immunological implications. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2081–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashio, R.; Sato, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Kageyama, T.; Satoh, Y.; Shinichiro, R.; Masuda, N.; Goshima, N.; Jiang, S.; Okayasu, I. Expression of RACK1 is a novel biomarker in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Lung Cancer 2010, 69, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, B.N.; Cheng, Y.K.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Shao, R.L.; Liu, R.D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. A novel Trichinella spiralis serine proteinase disrupted gut epithelial barrier and mediated larval invasion through binding to RACK1 and activating MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0011872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershner, L.; Welshhans, K. RACK1 regulates neural development. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Names | Sequences (5′–3′) | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| EcRACK1-F for ORF | ATGAATGAGAGTTTGCAACTTC | / |
| EcRACK1-R for ORF | CTAAGCACGGGATGTAACACT | |
| EcRACK1-qF | AGATTGCCACAAATAGGAACT | 2.0982 |
| EcRACK1-qR | GCACTGAAGGCTACCGAGA | |
| Ecβ-actin-qF | TGACGAAGACGCAACAGC | 1.9116 |
| Ecβ-actin-qR | TCATCGCCGACATAAGAG |
| Names | Sequences (C–N) |
|---|---|
| WD40-1 | 4SLQLRGTLVGHSGWVTQIATNRNFADVILSASRDKSLILWK44 |
| WD40-2 | 52YGFPQKRFHGHSHFISDVVLSLDGHFALSGSWDKTLRLWD91 |
| WD40-3 | 92LAAGKTTRRFEDHTKDVLSVAFSADNRQIVSGSRDKTIKLWN133 |
| WD40-4 | 135LAQCKYTIQEDGHSDWVSCVRFSPSNSNPIIVSCGWDKAVKVWS178 |
| WD40-5 | 181NCKLKTNHYGHAGYLNTVTVSPDGSLCASGGKDAKAMLWD220 |
| WD40-6 | 223LNDDKHLYTLDHTDTINSLCFSPNRYWLCAATGPSIKIWD260 |
| WD40-7 | 276SQNTKAEPPQCLSMAWSADGQTLFAGYSDSKIRVWQ311 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Hu, J.; Guo, Y.; Shen, X. Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and Expression of a Receptor for Activated Protein Kinase C1 (RACK1) Gene in Exopalaemon carinicauda Zoea Larvae under Aroclor 1254 Stress. Biology 2024, 13, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030174
Cai Y, Hu J, Guo Y, Shen X. Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and Expression of a Receptor for Activated Protein Kinase C1 (RACK1) Gene in Exopalaemon carinicauda Zoea Larvae under Aroclor 1254 Stress. Biology. 2024; 13(3):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030174
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yuefeng, Jie Hu, Yepeng Guo, and Xin Shen. 2024. "Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and Expression of a Receptor for Activated Protein Kinase C1 (RACK1) Gene in Exopalaemon carinicauda Zoea Larvae under Aroclor 1254 Stress" Biology 13, no. 3: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030174
APA StyleCai, Y., Hu, J., Guo, Y., & Shen, X. (2024). Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and Expression of a Receptor for Activated Protein Kinase C1 (RACK1) Gene in Exopalaemon carinicauda Zoea Larvae under Aroclor 1254 Stress. Biology, 13(3), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030174





