Three Copies of zbed1 Specific in Chromosome W Are Essential for Female-Biased Sexual Size Dimorphism in Cynoglossus semilaevis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.3. Experimental Samples
2.4. DNA Extraction, RNA Extraction, and cDNA Synthesis
2.5. Identification of Three Multi-Copy Genes of Cs-zbed1 Gene and dPCR
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis of ZBED Family
2.7. Expression Patterns of zbed1
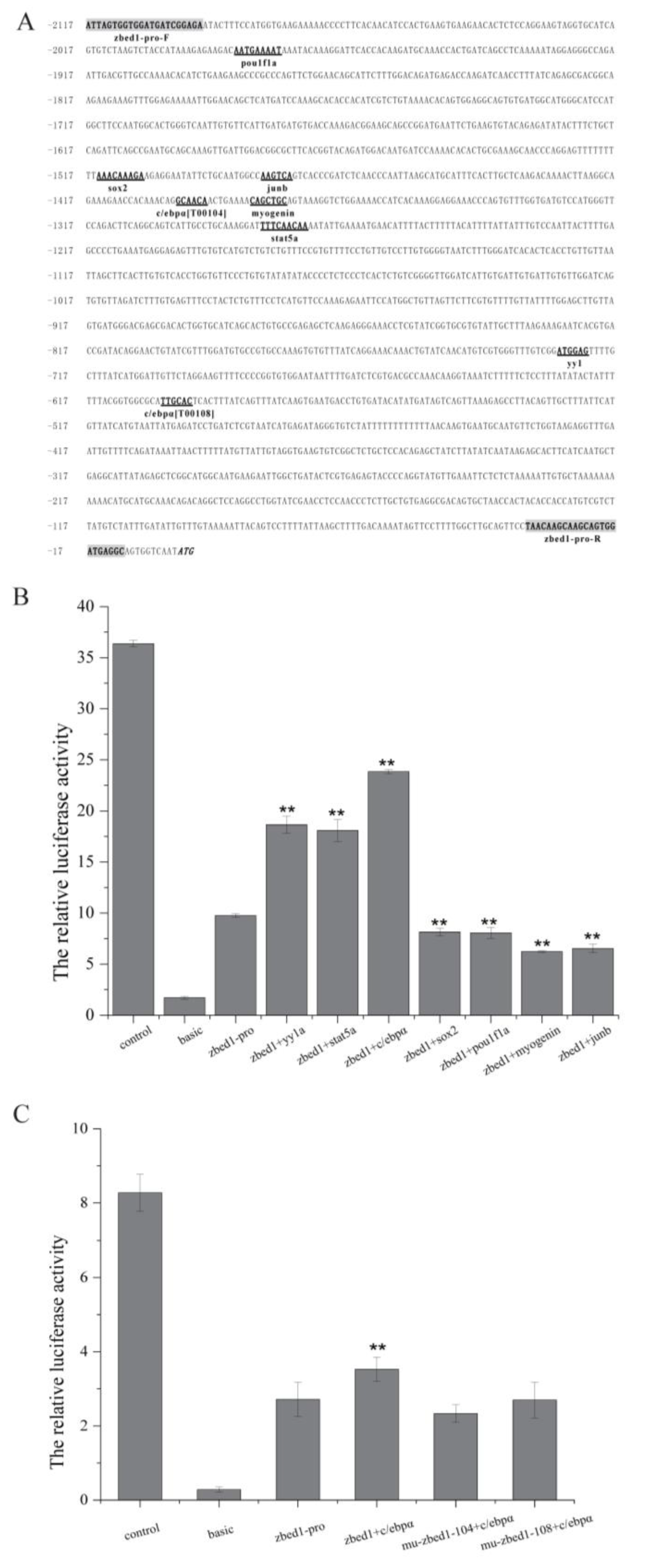
2.8. Promoter Activity Analysis of zbed1
2.9. Design and Transfection of RNAi in Female C. semilaevis Brain Cell Lines
3. Results
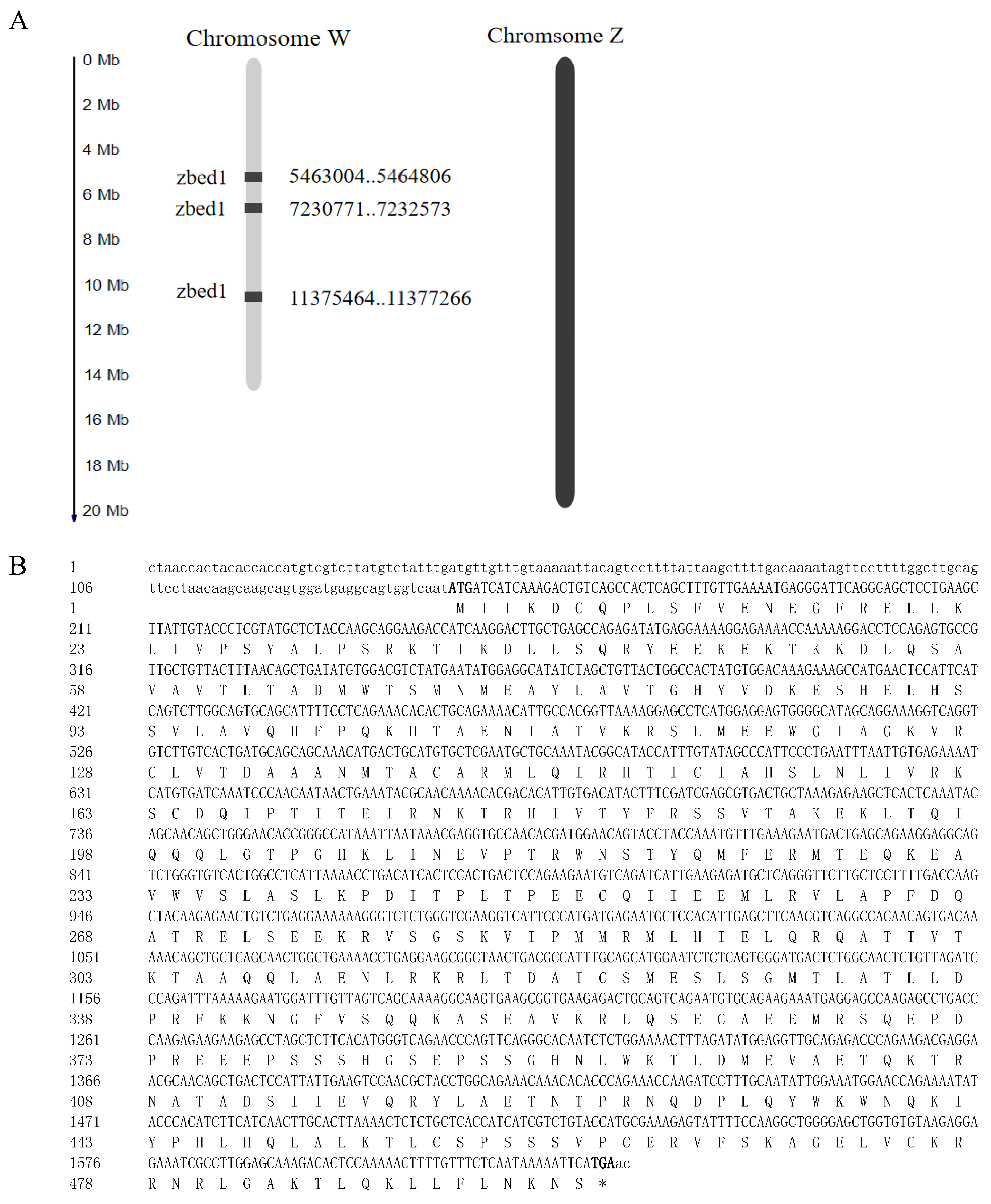
3.1. Multiple Copies of zbed1 on W Chromosome and Phylogenetic Tree of ZBED Family
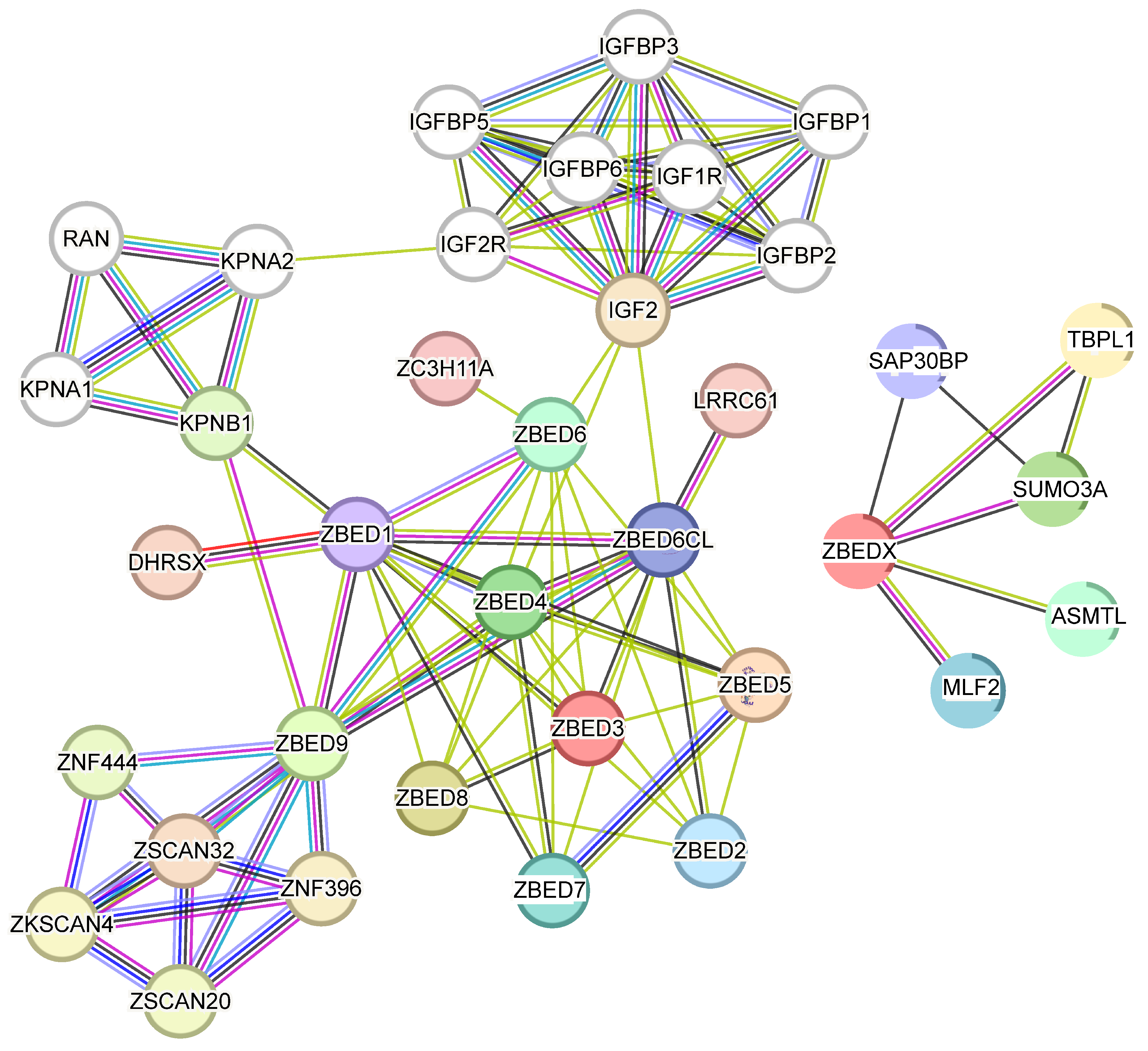
3.2. Interaction Network Analysis of ZBEDs
3.3. The Expression of zbed1 in Different Tissues and at Different Developmental Stages
3.4. Knock-Down Effects on zbed1 and Other Related Genes by RNAi Transfection in Brain Cells
3.5. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of zbed1 Promoter Activity and Transcription Factor Sites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cox, R.M.; Butler, M.A.; John-Alder, H.B. The evolution of sexual size dimorphism in reptiles. In Sex, Size and Gender Roles: Evolutionary Studies of Sexual Size Dimorphism; Fairbairn, D.J., Blanckenhorn, W.U., Székely, T., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenfors, P.; Gittleman, J.L.; Jones, K.E. Sexual size dimorphism in mammals. In Sex, Size and Gender Roles: Evolutionary Studies of Sexual Size Dimorphism; Fairbairn, D.J., Blanckenhorn, W.U., Székely, T., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Székely, T.; Lislevand, T.; Figuerola, J. Sexual size dimorphism in birds. In Sex, Size and Gender Roles: Evolutionary Studies of Sexual Size Dimorphism; Fairbairn, D.J., Blanckenhorn, W.U., Székely, T., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Badyaev, A.V. Growing apart: An ontogenetic perspective on the evolution of sexual size dimorphism. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Q.; Shi, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, N. Effects of long-term sex steroid hormones (estradiol and testosterone)-supplemented feeds on the growth performance of Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.M.; Stenquist, D.S.; Calsbeek, R. Testosterone, growth and the evolution of sexual size dimorphism. J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 1586–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millington, J.W.; Brownrigg, G.P.; Chao, C.; Sun, Z.; Basner-Collins, P.J.; Wat, L.W.; Hudry, B.; Miguel-Aliaga, I.; Rideout, E.J. Female-biased upregulation of insulin pathway activity mediates the sex difference in Drosophila body size plasticity. eLife 2021, 10, e58341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, W.R. Sex chromosomes and the evolution of sexual dimorphism. Evolution 1984, 38, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; McClusky, R.; Chen, J.; Beaven, S.W.; Tontonoz, P.; Arnold, A.P.; Reue, K. The number of x chromosomes causes sex differences in adiposity in mice. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, K.; Carrier, D.R.; Adler, F.R.; Ostrander, E.A.; Lark, K.G. Interaction between the X chromosome and an autosome regulates size sexual dimorphism in Portuguese Water Dogs. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1820–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Alvarado, J.; Goffinet, J.; Michael, V.; Liberti, W., 3rd; Hatfield, J.; Gardner, T.; Pearson, J.; Mooney, R. Neural dynamics underlying birdsong practice and performance. Nature 2021, 599, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottebohm, F.; Arnold, A.P. Sexual dimorphism in vocal control areas of the songbird brain. Science 1976, 194, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agate, R.J.; Grisham, W.; Wade, J.; Mann, S.; Wingfield, J.; Schanen, C.; Palotie, A.; Arnold, A.P. Neural, not gonadal, origin of brain sex differences in a gynandromorphic finch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4873–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Bing, J.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S. Erbin and ErbB2 play roles in the sexual differentiation of the song system nucleus HVC in bengalese finches (Lonchura Striata var. domestica). Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, N.D.; Ghosh, S.M.; Shingleton, A.W. Sex-specific weight loss mediates sexual size dimorphism in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawala, A.; Gould, A.P. The sex of specific neurons controls female body growth in Drosophila. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2002252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawala, A.; Gould, A.P. Sex-lethal in neurons controls female body growth in Drosophila. Fly 2018, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, P.; Wiberg, R.A.W.; Papachristos, K.; Scofield, D.G.; Tellgren-Roth, C.; Immonen, E. Y-Linked Copy Number Polymorphism of Target of Rapamycin Is Associated with Sexual Size Dimorphism in Seed Beetles. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mank, J.E.; Hall, D.W.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Avise, J.C. Sex chromosomes and male ornaments: A comparative evaluation in ray-finned fishes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poissant, J.; Davis, C.S.; Malenfant, R.M.; Hogg, J.T.; Coltman, D.W. QTL mapping for sexually dimorphic fitness-related traits in wild bighorn sheep. Heredity 2012, 108, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, P.; Lian, J.; Hu, Q.; Sun, B.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Epigenetic modification and inheritance in sexual reversal of fish. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, C.R.; Hirst, A.G.; Atkinson, D. Selection for increased male size predicts variation in sexual size dimorphism among fish species. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20192640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Chen, S. Transcriptomics analysis revealing candidate networks and genes for the body size sexual dimorphism of Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2018, 18, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, R.; Chen, S. Identification of crucial factors involved in Cynoglossus semilaevis sexual size dimorphism by GWAS and demonstration of zbed1 regulatory network by DAP-seq. Genomics 2022, 114, 110376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, N.; Takahashi, M.; Hirose, F. Identification of a human homologue of the DREF transcription factor with a potential role in regulation of the histone H1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22928–22938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, D.; Sano, Y.; Adachi, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Osada, H.; Takahashi, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Osumi, T.; Hirose, F. hDREF regulates cell proliferation and expression of ribosomal protein genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, G. ZBED1/DREF: A transcription factor that regulates cell proliferation. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, T.D.D.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X.S.; Maia-Silva, D.; Hur, S.K.; de Almeida, L.M.N.; Preall, J.B.; Koo, P.K.; Vakoc, C.R. ZBED2 is an antagonist of interferon regulatory factor 1 and modifies cell identity in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11471–11482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghizadeh, M.; Akhmedov, N.B.; Yamashita, C.K.; Gribanova, Y.; Theendakara, V.; Mendoza, E.; Nelson, S.F.; Ljubimov, A.V.; Farber, D.B. ZBED4, a BED-type zinc-finger protein in the cones of the human retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3580–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markljung, E.; Jiang, L.; Jaffe, J.D.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Wallerman, O.; Larhammar, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Saenz-Vash, V.; Gnirke, A.; et al. ZBED6, a novel transcription factor derived from a domesticated DNA transposon regulates IGF2 expression and muscle growth. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Liu, G.; Zhou, J.; Chen, P.; Sun, C.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Hou, L.; Yin, B.; Qiang, B.; et al. Zbed3 Is Indispensable for Wnt Signaling Regulation of Cortical Layers Formation in Developing Brain. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 31, 4078–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Yuan, L.; Hu, W.; Luo, Y.; Suo, L.; Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, G.; et al. Zinc-finger BED domain-containing 3 (Zbed3) is a novel secreted protein associated with insulin resistance in humans. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 275, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.W.; Sheu, J.C.; Tsai, H.J. Genomic Structure, Protein Character, Phylogenic Implication, and Embryonic Expression Pattern of a Zebrafish New Member of Zinc Finger BED-Type Gene Family. Genes 2023, 14, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaillon, O.; Aury, J.M.; Brunet, F.; Petit, J.L.; Stange-Thomann, N.; Mauceli, E.; Bouneau, L.; Fischer, C.; Ozouf-Costaz, C.; Bernot, A.; et al. Genome duplication in the teleost fish Tetraodon nigroviridis reveals the early vertebrate proto-karyotype. Nature 2004, 431, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, P.; Gong, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Wei, M.; Xu, X.; Xu, W. pitpβ_w Encoding Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Protein Is Involved in Female Differentiation of Chinese Tongue Sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 861763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, N.; Yang, Q.; Shi, R.; Li, X.; Cui, Z.; Cheng, J.; Chen, S. Potential Involvement of ewsr1-w Gene in Ovarian Development of Chinese Tongue Sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Animals 2022, 12, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Songlin, C.; Fengtao, G.; Liang, M.M.; Qiaomu, H.; Wentao, S.; Changwei, S.; WeiQun, L. SCAR-transformation of sex-specific SSR marker and its application in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semiliaevis). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2014, 22, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ortí, G.; Zhang, G.; Lu, G. A practical approach to phylogenomics: The phylogeny of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii) as a case study. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, D.; Moriuchi, T.; Osumi, T.; Hirose, F. Transcription Factor hDREF Is a Novel SUMO E3 Ligase of Mi2α. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11619–11634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, D.; Komori, H.; Higuchi, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Osumi, T.; Hirose, F. Human DNA replication-related element binding factor (hDREF) self-association via hATC domain is necessary for its nuclear accumulation and DNA binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7563–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.V.; Traynor, S.; Ditzel, H.J.; Gjerstorff, M.F. Human DREF/ZBED1 is a nuclear protein widely expressed in multiple cell types derived from all three primary germ layers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Law, R.D. Cell lineage of zebrafish blastomeres: III. Clonal analyses of the blastula and gastrula stages. Dev. Biol. 1985, 108, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Law, R.D. Cell lineage of zebrafish blastomeres: II. Formation of the yolk syncytial layer. Dev. Biol. 1985, 108, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.; Shih, J.; Fraser, S.E. Fate maps of the zebrafish embryo. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1995, 5, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strähle, U.; Blader, P. Early neurogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Guo, J.; Jiang, F.; Lu, J.; Ding, Y.; Li, A.; Liang, X.; Jia, W. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α is a crucial regulator of human fat mass and obesity associated gene transcription and expression. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 406909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Feng, B.; Li, S.; Mahboob, S.; Shao, C. Cloning and functional analysis of c/ebpα as negative regulator of dmrt1 in Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Gene 2021, 768, 145321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.; Cisternas, P.; Inestrosa, N.C. Role of Wnt Signaling in Central Nervous System Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2297–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Fu, X.H.; Zhou, D.; Li, J.M. The Role of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Disrupted Hippocampal Neurogenesis of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: A Potential Therapeutic Target? Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1319–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo, S.B.; Valenzuela-Bezanilla, D.; Mardones, M.D.; Varela-Nallar, L. Role of Wnt Signaling in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Health and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Peng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y. ADNP promotes neural differentiation by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Du, J.; Yu, Y.; Liang, N.; Liang, M.; Yao, G.; Cui, S.; Huang, H.; Sun, F. NGF promotes mouse granulosa cell proliferation by inhibiting ESR2 mediated down-regulation of CDKN1A. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 406, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, S. The linkage of cell cycle and DNA replication with growth difference in female Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis): Analysis from transcriptomic study and WGCNA. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 39, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Primers | Information | Sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Cs-SEX-F | sex detection | CCTAAATGATGGATGTAGATTCTGTC |
| Cs-SEX-R | sex detection | GATCCAGAGAAAATAAACCCAGG |
| zbed1-cds-F | CDS cloning | ATGATCATCAAAGACTGTCAGCC |
| zbed1-cds-R | CDS cloning | TCATGAATTTTTATTGAGAAACA |
| zbed1-pro-F | promoter cloning | AGATCTGCGATCTAAGTAAGCTATTAGTGGTGGATGATCGGAGA |
| zbed1-pro-R | promoter cloning | CAACAGTACCGGAATGCCAAGCTGCCTCATCCACTGCTTGCTTGTTA |
| zbed1-mu-c/ebpα104-F | promoter mutation | AAAGAACCACAAACAGCGATCAACT |
| zbed1-mu-c/ebpα104-R | promoter mutation | AGTTGATCGCTGTTTGTGGTTCTTT |
| zbed1-mu-c/ebpα108-F | promoter mutation | TGGCGCATACCAGTCACTTTATCAG |
| zbed1-mu-c/ebpα108-R | promoter mutation | CTGATAAAGTGACTGGTATGCGCCA |
| zbed1- site1 | RNAi site1 | GCAACAGCTGACTCCATTA |
| RNAi-NC | negative control (nc) | CTGAAGATCCGGCTCATCA |
| zbed1-qPCR-F | qPCR | CTCCAGAGTGCCGTTGC |
| zbed1-qPCR-R | qPCR | GTTCATGGCTTTCTTTGTCC |
| actin-F | qPCR | TTCCAGCCTTCCTTCCTT |
| actin-R | qPCR | TACCTCCAGACAGCACAG |
| esr2-qPCR-F | qPCR | GATTAGGAGAAGGTGGAGAAGG |
| esr2-qPCR-R | qPCR | GGTAACCAGAGGCATAGTCGTG |
| ccng1-qPCR-F | qPCR | AGTGACTACGCCAACACCAAAT |
| ccng1-qPCR-R | qPCR | GATGGTAGGCAGATGAGCGATT |
| ccndx-qPCR-F | qPCR | CCTTGTCCTTGCCTATCTC |
| ccndx-qPCR-R | qPCR | GACGCCTCAAAGTTGTTCT |
| piwill-qPCR-F | qPCR | CATCCAACTGTCGGCCAACTAT |
| piwill-qPCR-R | qPCR | TCGGCAATCTATTAGGCAGGAA |
| cdk4-qPCR-F | qPCR | CGCCAGTATGCAGTATGA |
| cdk4-qPCR-R | qPCR | TCTTGAGCAGAGCCACCT |
| cdk2-qPCR-F | qPCR | CACTGGTATCCCTCTGCC |
| cdk2-qPCR-R | qPCR | GAAGTCGGCGAGTTTGAT |
| cdk6-qPCR-F | qPCR | TACCACCCGAGACCATTA |
| cdk6-qPCR-R | qPCR | TAGATTCGAGCCAGACCA |
| tbp-qPCR-F | qPCR | AAACAGTAACAGGCTCCAC |
| tbp-qPCR-R | qPCR | TCCAGTTTACAGCCAAGAT |
| wnt7b-qPCR-F | qPCR | AGCAGCATTCACCTACGC |
| wnt7b-qPCR-R | qPCR | CTTCCAGCCTTCCTCTTG |
| zbed1-taqman-F | Taqman primer | CTCTGGCAACTCTGTTAGATCC |
| zbed1-taqman-R | Taqman primer | GCTCTTGGCTCCTCATTTCT |
| zbed1-taqman-probe | Taqman probe | AAAGGCAAGTGAAGCGGTGAAGAGAC 5′6-FAM, 3′BHQ1 |
| myh6-taqman-F | Taqman primer | ACAAGTGGCTTCCTGTCTATG |
| myh6-taqman-R | Taqman primer | GCGTTATCGGAGATGGAGAAA |
| myh6-taqman-probe | Taqman probe | TAAGAAGAGAAGCGAGGCTCCACCTC 5′6-FAM, 3′BHQ1 |
| Name | Gene ID | Protein ID | Gene Length (bp) | ORF Length (bp) | Amino Acid Length (aa) | Chr | Location | No. of Exons | No. of Introns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| zbed1 | 103397026 | XP_016898185.1 | 1802 | 1491 | 496 | W | 5,463,004–5,464,806 | 3 | 2 |
| zbed1 | 103397195 | XP_016898198.1 | 1802 | 1491 | 496 | W | 11,375,464–11,377,266 | 3 | 2 |
| zbed1 | 107990198 | XP_016898129.1 | 1802 | 1491 | 496 | W | 7,230,771–7,232,573 | 3 | 2 |
| zbed1l | 103384517 | XP_016891160.2 | 1990 | 1537 | 511 | 10 | 2,017,183–2,0191,72 | 2 | 1 |
| zbed4 | 103382917 | XP_024912923.1 | 7442 | 3750 | 1249 | 8 | 26,160,975–26,168,416 | 3 | 2 |
| zbedx | 103384547 | XP_024914808.1 | 7167 | 2163 | 720 | 10 | 2,351,855–2,359,021 | 6 | 5 |
| zbedx | 103397244 | XP_008333685.2 | 52448 | 1161 | 386 | W | 13,905,364–13,957,811 | 2 | 1 |
| zbedx | 112486373 | XP_024908564.1 | 1318 | 1089 | 362 | W | 10,396,182–10,397,499 | 2 | 1 |
| zbedx | 103392902 | XP_024920030.1 | 69214 | 1550 | 499 | 17 | 6,577,362–6,646,575 | 7 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Mai, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, N. Three Copies of zbed1 Specific in Chromosome W Are Essential for Female-Biased Sexual Size Dimorphism in Cynoglossus semilaevis. Biology 2024, 13, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030141
Sun Y, Li X, Mai J, Xu W, Wang J, Zhang Q, Wang N. Three Copies of zbed1 Specific in Chromosome W Are Essential for Female-Biased Sexual Size Dimorphism in Cynoglossus semilaevis. Biology. 2024; 13(3):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030141
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yuqi, Xihong Li, Jiaqi Mai, Wenteng Xu, Jiacheng Wang, Qi Zhang, and Na Wang. 2024. "Three Copies of zbed1 Specific in Chromosome W Are Essential for Female-Biased Sexual Size Dimorphism in Cynoglossus semilaevis" Biology 13, no. 3: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030141
APA StyleSun, Y., Li, X., Mai, J., Xu, W., Wang, J., Zhang, Q., & Wang, N. (2024). Three Copies of zbed1 Specific in Chromosome W Are Essential for Female-Biased Sexual Size Dimorphism in Cynoglossus semilaevis. Biology, 13(3), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13030141






