Characterization of New Tropicoporus Species (Basidiomycota, Hymenochaetales, Hymenochaetaceae) Discovered in Tamil Nadu, India
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Macro- and Micro-Taxonomic Characteristic Analyses
2.2. PCR Amplification and Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
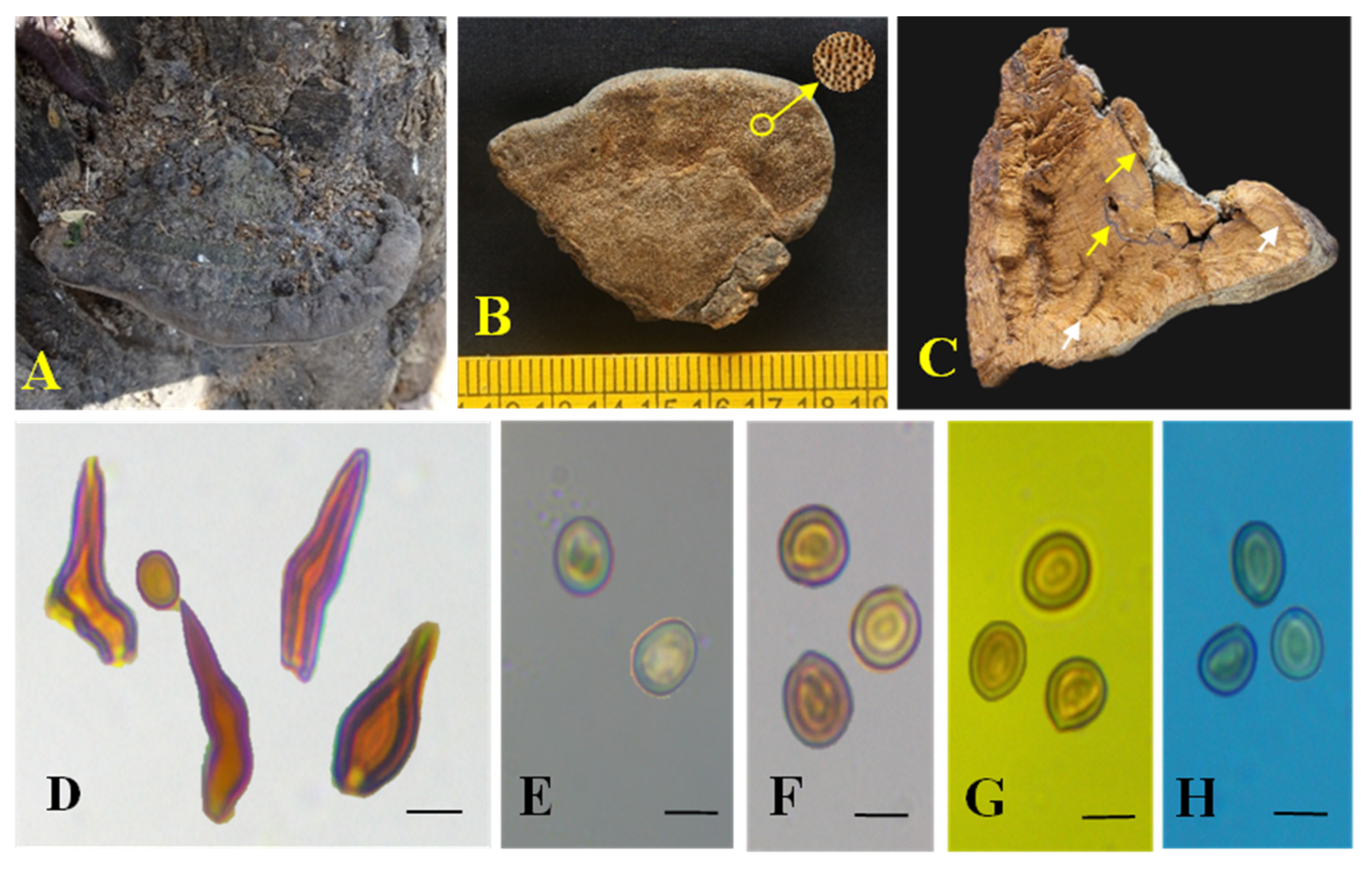
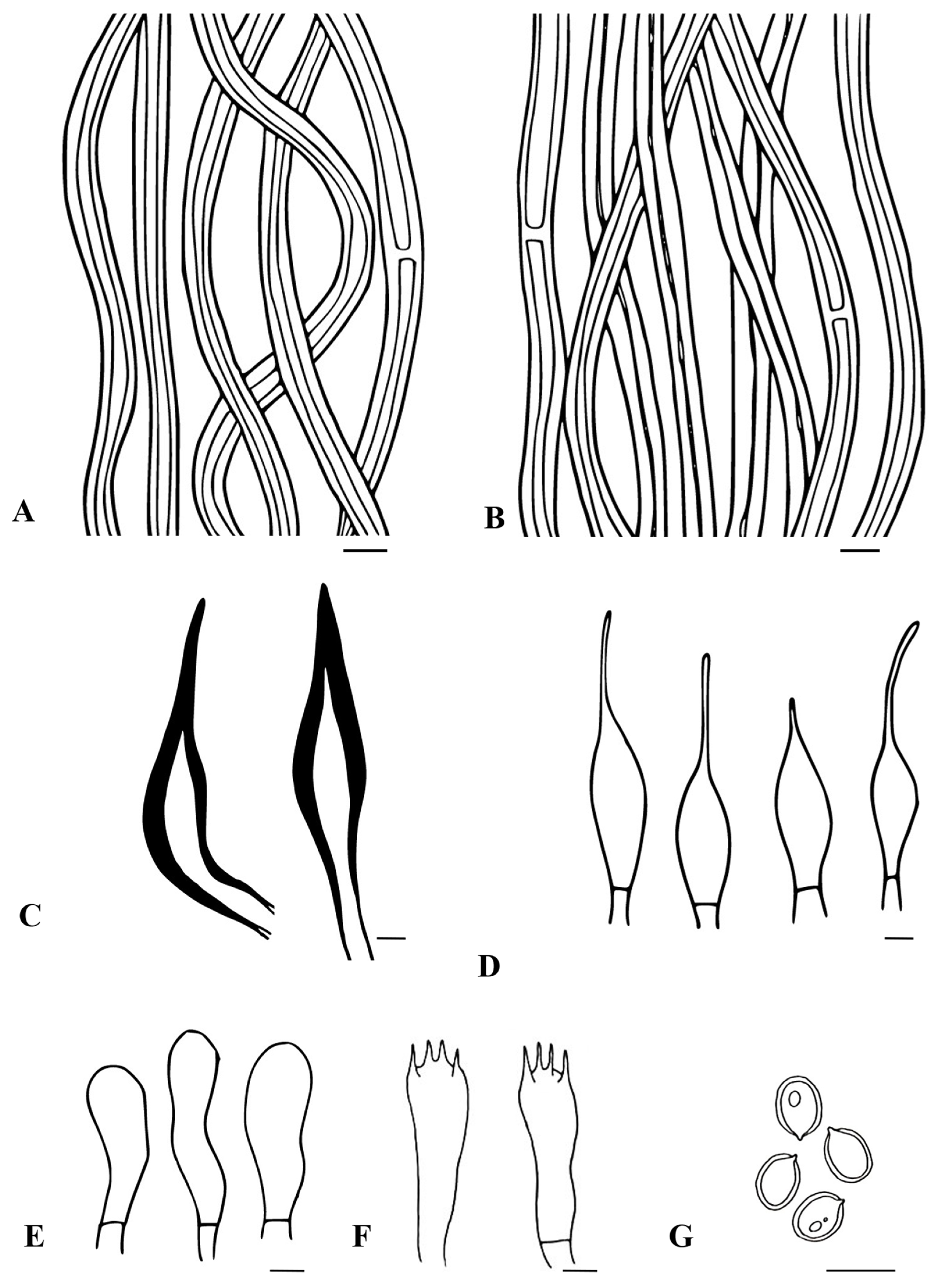
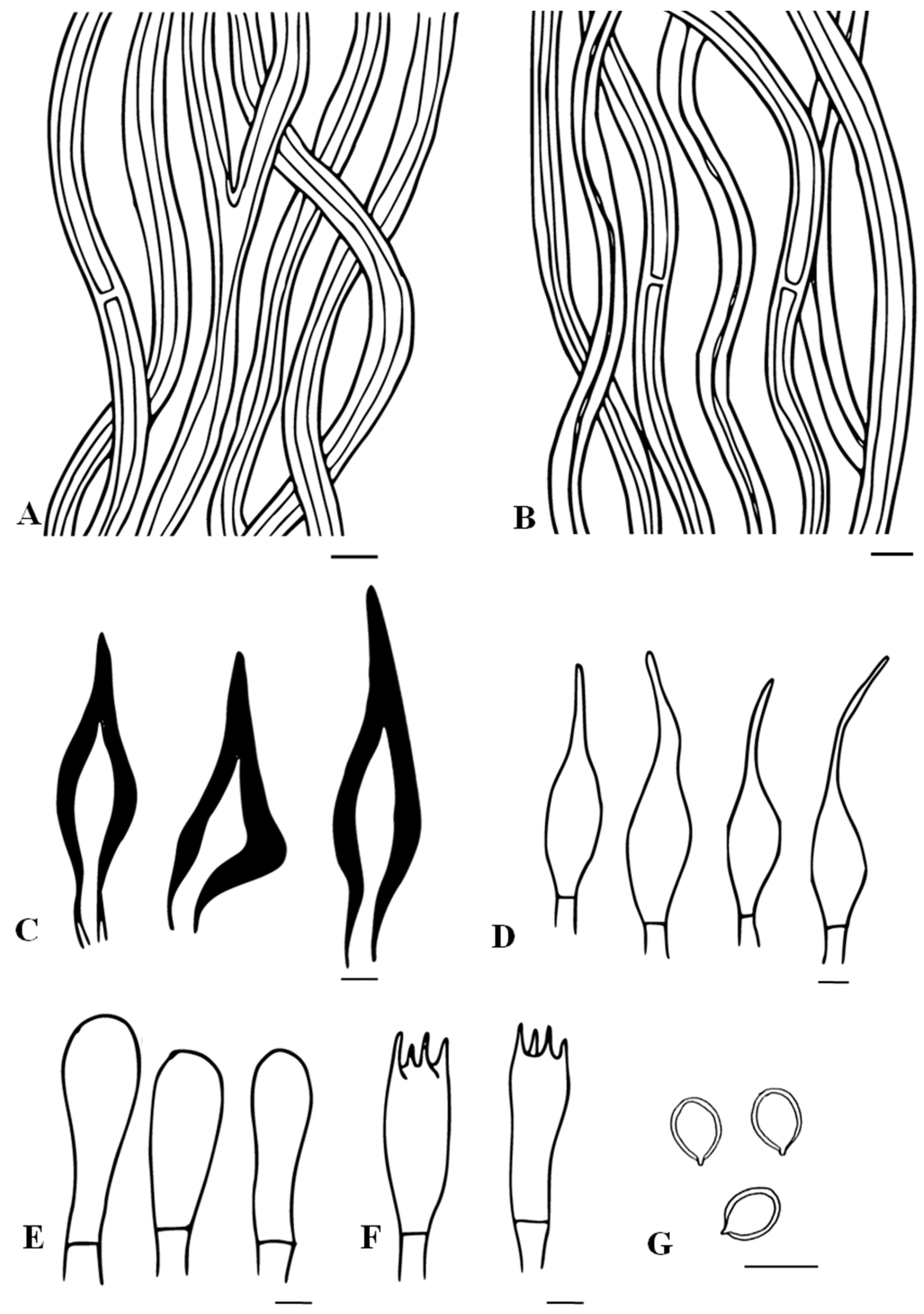
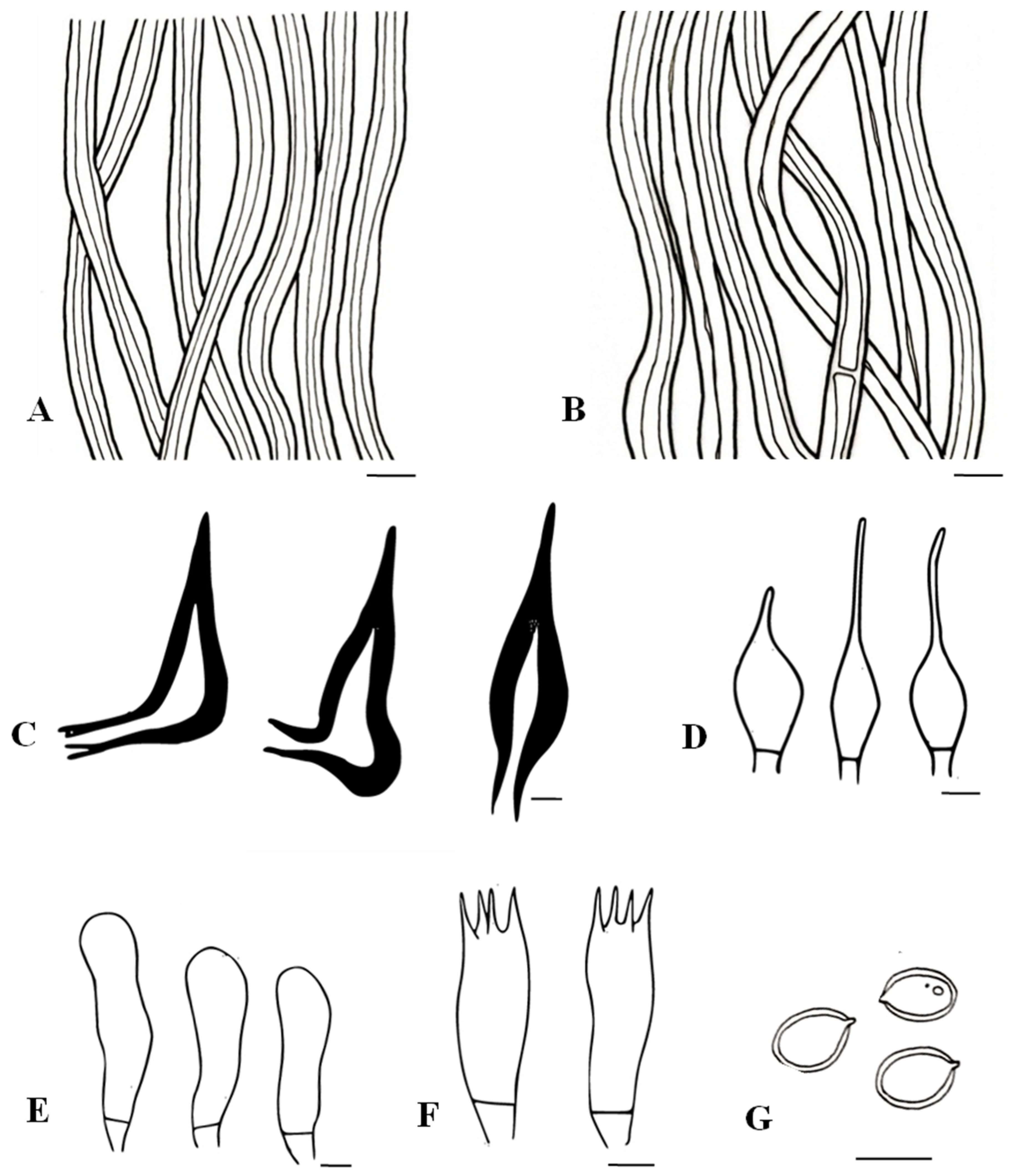
3.2. Taxonomic Characters of the Three New Species of Tropicoporus
4. Discussion
| 1 | Basidiomes resupinate to effused-reflexed | 2 |
| 1 | Basidiomes distinctly pileate | 8 |
| 2 | Basidiomes annual to biennial | 3 |
| 2 | Basidiomes perennial | 6 |
| 3 | Basidiospores cyanophilic | T. tenuis |
| 3 | Basidiospores acyanophilic | 4 |
| 4 | Basidiome resupinate to effused reflexed, pileal surface tomentose to hispid basidiospores > 3 μm in length | T. excentrodendri |
| 4 | Basidiome resupinate, basidiospores < 3 μm in length | 5 |
| 5 | Dissepiments lacerate, context layer present between tube layers | T. hainanicus |
| 5 | Dissepiments entire, context layer absent between tube layers | T. boehmeriae |
| 6 | Basidiomes resupinate, cystidioles present | 7 |
| 6 | Basidiomes cushion-shaped, cystidioles absent | T. ravidus |
| 7 | Pores 10–12/mm, basidiospores < 3 μm wide | T. minor |
| 7 | Pores 6–8/mm, basidiospores > 3 μm wide | T. zuzanae |
| 8 | Hyphal system strictly dimitic | T. lineatus |
| 8 | Hyphal system mono-dimitic, dimitic in trama | 9 |
| 9 | Basidiomes uncracked | 10 |
| 9 | Basidiomes cracked to rimose | 13 |
| 10 | Pilear surface warted; Pores always >5/mm | 11 |
| 10 | Pilear surface glabrous; Pores < 5/mm | 12 |
| 11 | Pilear surface azonate with warts, obtuse margin, context duplex without blackline | T. natarajanii |
| 11 | Basidiomes with infrequent warts, acute margin and homogenous context | T. cleistanthicola |
| 12 | Pilear surface indistinctly zonate, margin obtuse | T. pannaensis |
| 12 | Pilear surface broadly zonate, margin acute | T. maritimus |
| 13 | Pilear surface frequently warted with deep cracks at maturity, stratified tube with intermittent context | T. xerophyticus |
| 13 | Pilear surface cracked, lacks warts, stratified tubes without intermittent context | 14 |
| 14 | Pilear surface fulvous, velvety and cyanopilous basidiospores | T. rudis |
| 14 | Pilear surface smooth to glabrous or sulcate and acyanophilous basidiospores | 15 |
| 15 | Context duplex with black line | T. pseudoindicus |
| 15 | Context homogenous | 16 |
| 16 | Absence of cystidioles | T. subramanii |
| 16 | Presence of cystidioles | 17 |
| 17 | Obtuse margin, cystidiole more than 25 µm in length, hymenial setae not exceeding 20 µm in length | T. tamilnaduensis |
| 17 | Acute margin, cystidiole not exceeding 25 µm in length, hymenial setae more than 20 µm in length | 18 |
| 18 | Basidiomes with radially cracked, sulcate, crusted pilear surface | T. subindicus |
| 18 | Basidiomes with glabrous, irregularly cracked pilear surface without crust | T. indicus |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wagner, T.; Fischer, M. Proceeding towards a natural classification of the worldwide taxa Phellinus s.l. and Inonotus s.l. and phylogenetic relationships of allied genera. Mycologia 2002, 94, 998–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.C. Hymenochaetaceae (Basidiomycota) in China. Fungal Divers. 2010, 45, 131–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Dai, Y.C.; Hattori, T.; Yu, T.W.; Wang, D.M.; Parmasto, E.; Chang, H.Y.; Shih, S.Y. Species clarification for the medicinally valuable ‘sanghuang’ mushroom. Bot. Stud. 2012, 53, 135–149. [Google Scholar]
- Vlasák, J.; Li, H.J.; Zhou, L.W.; Dai, Y.C. A further study on Inonotus linteus complex (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota) in tropical America. Phytotaxa 2013, 124, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.W.; Vlasák, J.; Decock, C.; Assefa, A.; Stenlid, J.; Abate, D.; Wu, S.H.; Dai, Y.C. Global diversity and taxonomy of the Inonotus linteus complex (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota): Sanghuangporus gen. nov., Tropicoporus excentrodendri and T. guanacastensis gen. et spp. nov., and 17 new combinations. Fungal Divers. 2015, 77, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Qin, W.M.; Euatrakool, O.; Zhou, L.W. Tropicoporus boehmeriae sp. nov. (Hymenochaetaceae, Basidiomycota) from Thailand, a new member of the Inonotus linteus complex. Phytotaxa 2015, 231, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, G.; Silveira, A.O.; Antonelli, Z.I.; Yurchenko, E. Tropicoporus stratificans sp. nov. (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota) from southern Brazil. Phytotaxa 2016, 245, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.A.; Lawrence, D.P.; Baumgartner, K. Role of basidiomycete fungi in the grapevine trunk disease esca. Plant Pathol. 2019, 69, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-Montoya, C.A.; Costa-Rezende, D.H.; Ferreira-Lopes, V.; Borba-Silva, M.A.; Popoff, O.F. Tropicoporus drechsleri (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota), a new species in the “Inonotus linteus” complex from Northern Argentina. Phytotaxa 2018, 338, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, L.W.; Vlasak, J.; Dai, Y.C. Global diversity and systematics of Hymenochaetaceae with poroid hymenophore. Fungal Divers. 2022, 113, 1–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, V.X.; de Oliveira, V.R.T.; de Lima-Junior, N.C.; Oliveira-Filho, J.R.C.; Santos, C.; Lima, N.; Gibertoni, T.B. Taxonomy and phylogenetic analysis reveal one new genus and three new species in Inonotus s.l. (Hymenochaetaceae) from Brazil. Cryptogam. Mycol. 2022, 43, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Wang, X.W.; Li, G.J.; Deng, C.-Y.; Rossi, W.; Leonardi, M.; Liimatainen, K.; Kekki, T.; Niskanen, T.; Smith, M.E.; et al. Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions on genera and species of fungal taxa. Fungal Divers. 2024, 1717–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaseelan, S.; Kezo, K.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Yang, E.; Zhao, C.; Elgorban, A.M.; Tibpromma, S.; Kaliyaperumal, M. New species of Tropicoporus (Basidiomycota, Hymenochaetales, Hymenochaetaceae) from India, with a key to Afro-Asian Tropicoporus species. MycoKeys 2024, 102, 29–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crous, P.W.; Jurjević, Z.; Balashov, S.; De la Peña-Lastra, S.; Mateos, A.; Pinruan, U.; Rigueiro-Rodríguez, A.; Osieck, E.R.; Altés, A.; Czachura, P.; et al. Fungal Planet description sheets: 1614–1696. Fungal Syst. Evol. 2024, 13, 183–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornerup, A.; Wanscher, J.H. Methuen Handbook of Colour, 3rd ed.; Eyre Methuen: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh tissue. Phytochem. Bull. Bot. Soc. Am. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Góes-Neto, A.; Loguercio-Leite, C.; Guerrero, R.T. DNA extraction from frozen field-collected and dehydrated herbarium fungal basidiome: Performance of SDS and CTAB-based methods. Biotemas 2005, 18, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edler, D.; Klein, J.; Antonelli, A.; Silvestro, D. raxmlGUI 2.0: A graphical interface and toolkit for phylogenetic analyses using RAxML. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, T.; Fischer, M. Natural groups and a revised system for the European poroid Hymenochaetales (Basidiomycota) supported by nLSU rDNA sequence data. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryvarden, L. The genus Inonotus a synopsis. Synop. Fungorum 2005, 21, 1–149. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.R. Hymenochaetaceae of India; Botanical Survey of India: Kolkata, India, 1995; 219p. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.R.; Das, K.; Mishra, D. The genus Inonotus and its related species in India. Mycosphere 2013, 4, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.M.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhou, L.W.; Decock, C.; Vlasák, J.; Dai, Y.C. Phylogeny and taxonomy of the Inonotus linteus complex. Fungal Divers. 2013, 58, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
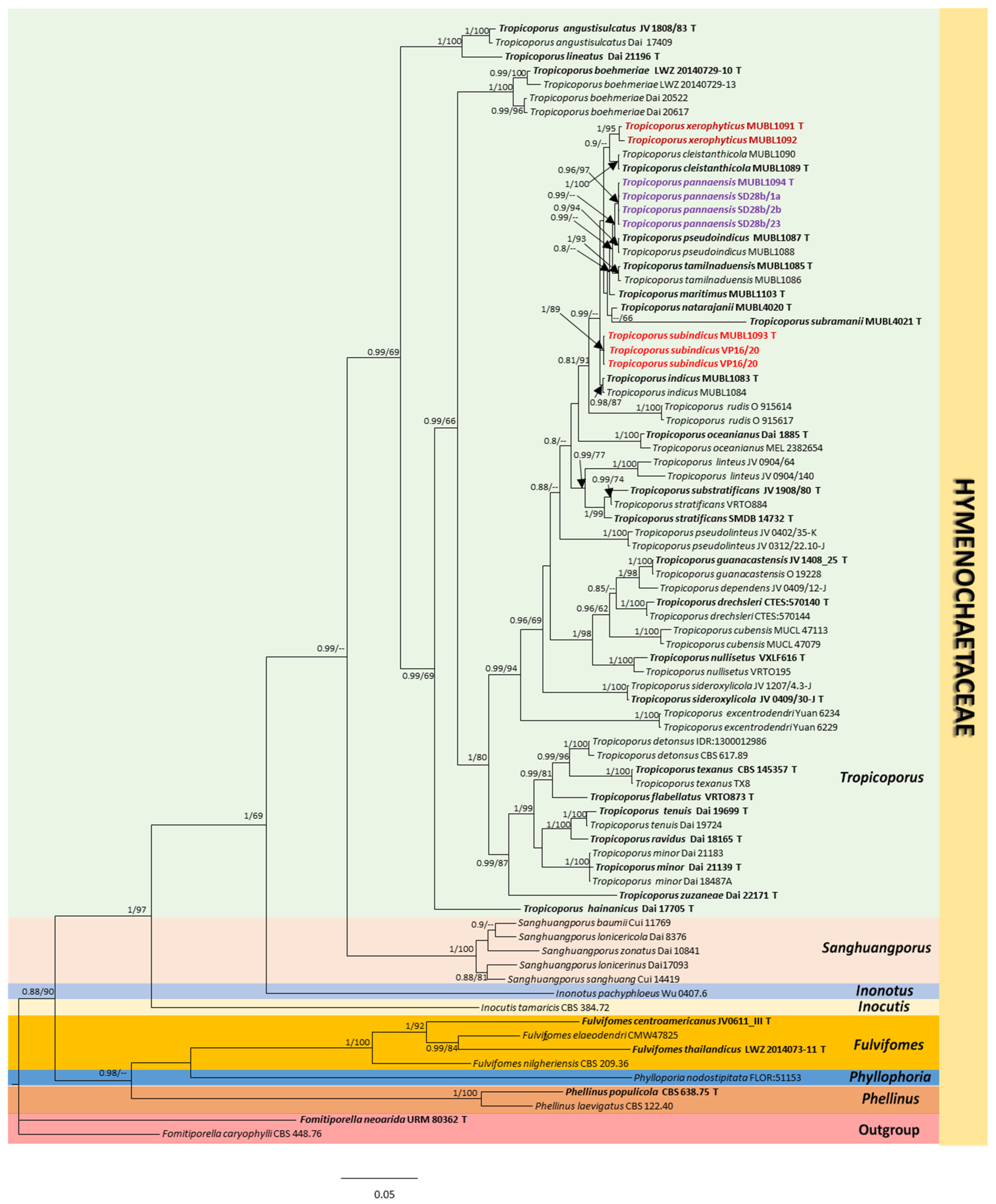


| Species | Strain Numbers | Geographical Locations | Accession Numbers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | LSU | |||
| Fomitiporella caryophylli | CBS 448.76 | India | AY558611 | AY059021 |
| F. neoarida t | URM 80362 | Brazil | KM211294 | KM211286 |
| Fulvifomes centroamericanus t | JV0611_III | Guatemala | KX960763 | KX960764 |
| F. elaeodendri | CMW47825 | South Africa | MH599094 | MH599134 |
| F. nilgheriensis | CBS 209.36 | USA | AY558633 | AY059023 |
| F. thailandicus t | LWZ 2014073-11 | Thailand | KR905672 | KR905665 |
| Inocutis tamaricis | CBS 384.72 | - | AY558604 | MH872221 |
| Inonotus pachyphloeus | Wu 0407.6 | Taiwan | KP030785 | KP030770 |
| Phellinus laevigatus | CBS 122.40 | USA | MH856059 | MH867554 |
| P. populicola t | CBS 638.75 | Finland | MH860960 | MH872729 |
| Phylloporia nodostipitata | FLOR:51153 | Brazil | KJ639057 | KJ631414 |
| Sanghuanporus baumii | Cui 11769 | China | MF772784 | MF772803 |
| S. lonicericola | Dai 8376 | China | JQ860308 | MF772805 |
| S. lonicerinus | Dai 17093 | China | MF772788 | MF772807 |
| S. sanghuang | Cui 14419 | China | MF772789 | MF772810 |
| S. zonatus | Dai 10841 | China | JQ860306 | KP030775 |
| Tropicoporus angustisulcatus | Dai 17409 | Brazil | MZ484584 | MZ437417 |
| T. angustisulcatus t | JV 1808/83 | French Guiana | MZ484585 | MZ437418 |
| T. boehmeriae | LWZ 20140729-13 | Thailand | KT223641 | MT319394 |
| T. boehmeriae | Dai 20522 | China | MZ484586 | MZ437419 |
| T. boehmeriae | Dai 20617 | China | MZ484587 | MZ437420 |
| T. boehmeriae t | LWZ 20140729-10 | Thailand | KT223640 | MT319393 |
| T. cleistanthicola | MUBL1090 | India | OR272291 | OR272336 |
| T. cleistanthicola t | MUBL1089 | India | OR272292 | OR272337 |
| T. cubensis | MUCL 47113 | Cuba | JQ860324 | KP030777 |
| T. cubensis | MUCL 47079 | Cuba | JQ860325 | KP030776 |
| T. dependens | JV 0409/12-J | USA | KC778777 | MF772818 |
| T. detonsus | CBS 617.89 | - | AF534077 | AY059037 |
| T. detonsus | IDR 1300012986 | USA | KF695121 | KF695122 |
| T. drechsleri | CTES:570144 | Argentina | MG242437 | MG242442 |
| T. drechslerit | CTES:570140 | Argentina | MG242439 | MG242444 |
| T. excentrodendri | Yuan 6234 | China | KP030791 | - |
| T. excentrodendri | Yuan 6229 | China | KP030789 | - |
| T. flabellatus t | VRTO873 | Brazil | MT908376 | MT906643 |
| T. guanacastensis | O 19228 | Costa Rica | KP030794 | - |
| T. guanacastensis t | JV 1408_25 | Costa Rica | KP030793 | KP030778 |
| T. hainanicus t | Dai 17705 | China | MZ484588 | MZ437421 |
| T. indicus | MUBL1084 | India | OR272294 | OR272339 |
| T. indicus t | MUBL1083 | India | OR272293 | OR272338 |
| T. lineatus t | Dai 21196 | Malaysia | MZ484594 | MZ437426 |
| T. linteus | JV 0904/64 | USA | JQ860322 | JX467701 |
| T. linteus | JV 0904/140 | USA | JQ860323 | KP030780 |
| T. maritimus t | MUBL1103 | India | PP378327 | PP378328 |
| T. minor t | Dai 21139 | China | MZ484592 | MZ437424 |
| T. minor | Dai 18487A | China | MZ484590 | MZ437422 |
| T. minor | Dai 21183 | China | MZ484593 | MZ437425 |
| T. natarajanii t | MUBL4020 | India | OP003881 | - |
| T. nullisetus | VRTO195 | Brazil | MN795118 | MN812254 |
| T. nullisetus t | VXLF616 | Brazil | MN795129 | MN812261 |
| T. oceanianus t | Dai 18859 | Australia | PP034280 | - |
| T. oceanianus | MEL 2382654 | Australia | KP013017 | KP013017 |
| T. pannaensis | SD28b/1a | India | OR520889 | OR520892 |
| T. pannaensis | SD28b/2b | India | OR520890 | OR520891 |
| T. pannaensis | SD28b/23 | India | OR520916 | OR520917 |
| T. pannaensis t | MUBL1094 | India | OR515276 | OR515277 |
| T. pseudoindicus | MUBL1088 | India | OR272296 | OR272341 |
| T. pseudoindicus t | MUBL1087 | India | OR272295 | OR272340 |
| T. pseudolinteus | JV 0312/22.10-J | Venezuela | KC778780 | - |
| T. pseudolinteus | JV0402/35-K | Venezuela | KC778781 | MF772820 |
| T. ravidus t | Dai 18165 | China | MZ484595 | MZ437427 |
| T. rudis | O 915614 | Rwanda | KP030796 | - |
| T. rudis | O 915617 | Tanzania | KP030797 | MH101016 |
| T. sideroxylicola | JV 1207/4.3-J | USA | KC778783 | - |
| T. sideroxylicola t | JV 0409/30-J | USA | KC778782 | - |
| T. stratificans t | SMDB 14732 | Brazil | KM199689 | - |
| T. stratificans | VRTO884 | Brazil | MN795124 | MN812266 |
| T. subindicus | VP16/20 | India | OR520914 | OR520915 |
| T. subindicus | VP16/23 | India | OR520912 | OR520913 |
| T. subindicus t | MUBL1093 | India | OR519719 | OR519722 |
| T. subramanii t | MUBL4021 | India | OP003882 | - |
| T. substratificans t | JV 1908/80 | French Guiana | MZ484597 | MZ437429 |
| T. tamilnaduensis | MUBL1086 | India | - | OR272344 |
| T. tamilnaduensis t | MUBL1085 | India | OR272297 | OR272343 |
| T. tenuis | Dai 19724 | China | MZ484599 | MZ437431 |
| T. tenuis t | Dai 19699 | China | MZ484598 | MZ437430 |
| T. texanus | TX8 | USA | MN108123 | MN113949 |
| T. texanus t | CBS 145357 | USA | NR_168219 | NG_068906 |
| T.xerophyticus | MUBL1092 | India | OR515255 | OR515267 |
| T.xerophyticus t | MUBL1091 | India | OR515186 | OR515187 |
| T. zuzanae t | Dai 22171 | China | PP034282 | PP034284 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arumugam, E.; Murugadoss, R.; Gunaseelan, S.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Elgorban, A.M.; Rampelotto, P.H.; Kaliyaperumal, M. Characterization of New Tropicoporus Species (Basidiomycota, Hymenochaetales, Hymenochaetaceae) Discovered in Tamil Nadu, India. Biology 2024, 13, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100770
Arumugam E, Murugadoss R, Gunaseelan S, Karunarathna SC, Elgorban AM, Rampelotto PH, Kaliyaperumal M. Characterization of New Tropicoporus Species (Basidiomycota, Hymenochaetales, Hymenochaetaceae) Discovered in Tamil Nadu, India. Biology. 2024; 13(10):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100770
Chicago/Turabian StyleArumugam, Elangovan, Ramesh Murugadoss, Sugantha Gunaseelan, Samantha C. Karunarathna, Abdallah M. Elgorban, Pabulo Henrique Rampelotto, and Malarvizhi Kaliyaperumal. 2024. "Characterization of New Tropicoporus Species (Basidiomycota, Hymenochaetales, Hymenochaetaceae) Discovered in Tamil Nadu, India" Biology 13, no. 10: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100770
APA StyleArumugam, E., Murugadoss, R., Gunaseelan, S., Karunarathna, S. C., Elgorban, A. M., Rampelotto, P. H., & Kaliyaperumal, M. (2024). Characterization of New Tropicoporus Species (Basidiomycota, Hymenochaetales, Hymenochaetaceae) Discovered in Tamil Nadu, India. Biology, 13(10), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100770








