Glucocorticoids and Their Receptor Isoforms: Roles in Female Reproduction, Pregnancy, and Foetal Development
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Glucocorticoids and the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis
2. Functions of Glucocorticoids
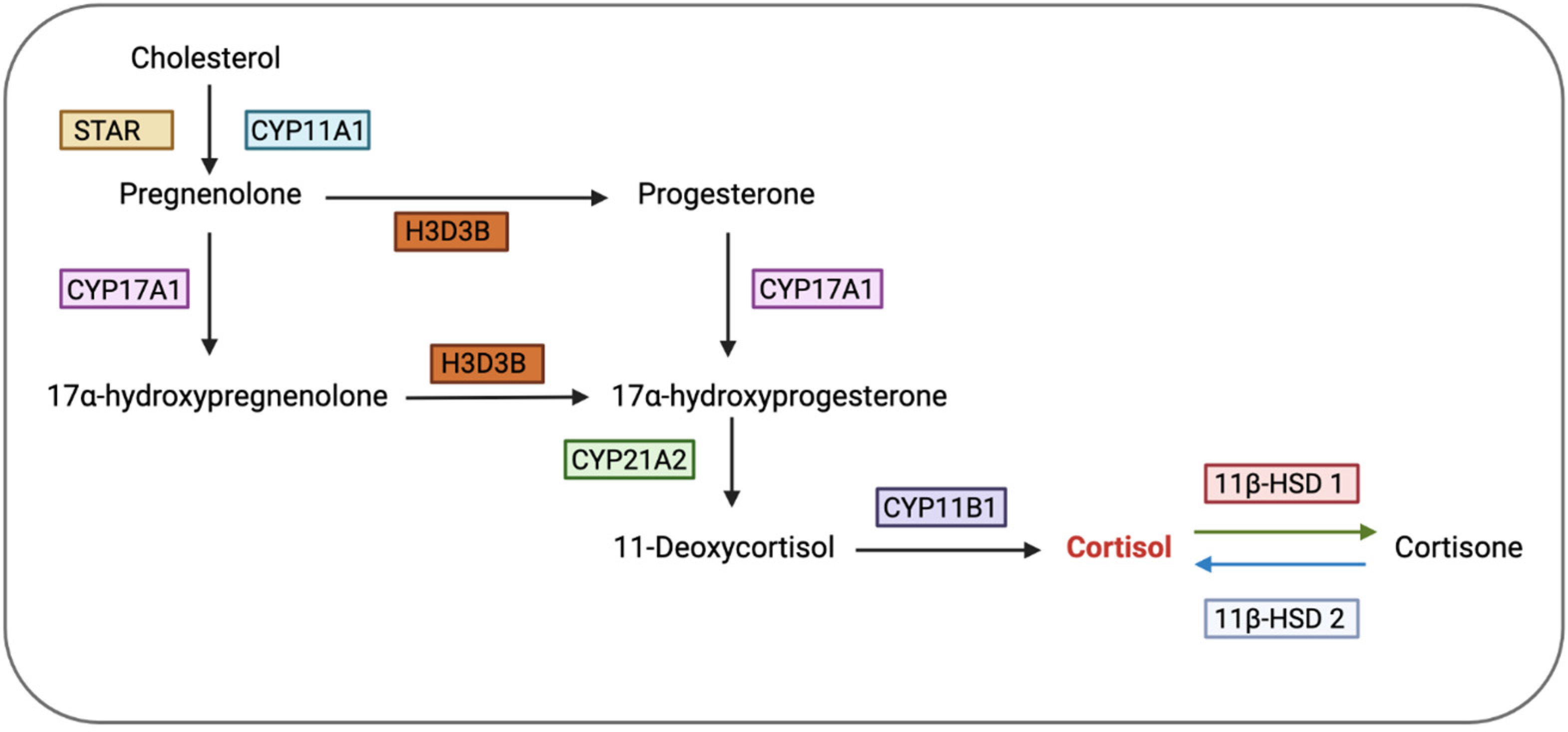
3. Glucocorticoid Bioavailability
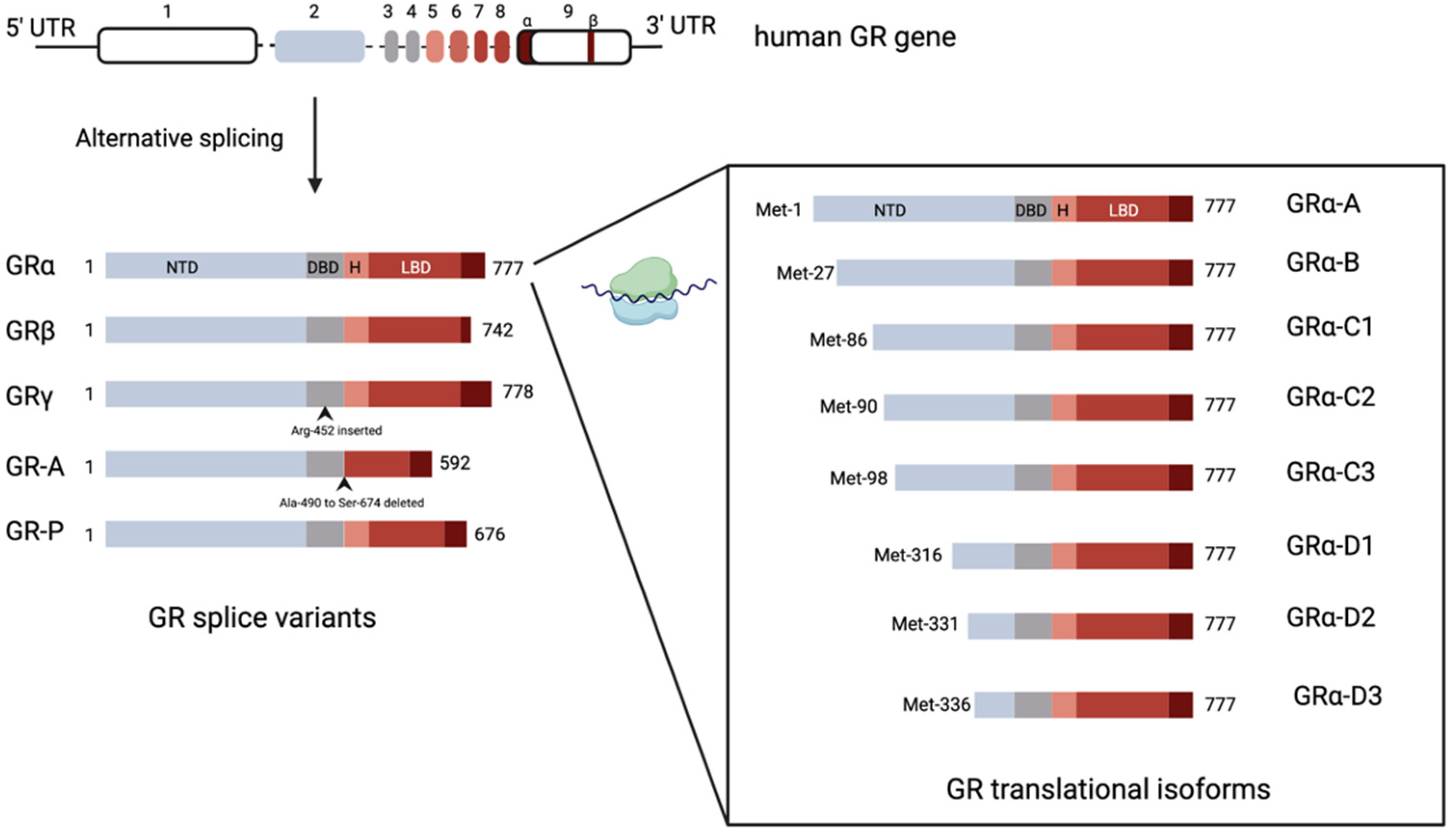
4. Glucocorticoid Receptors
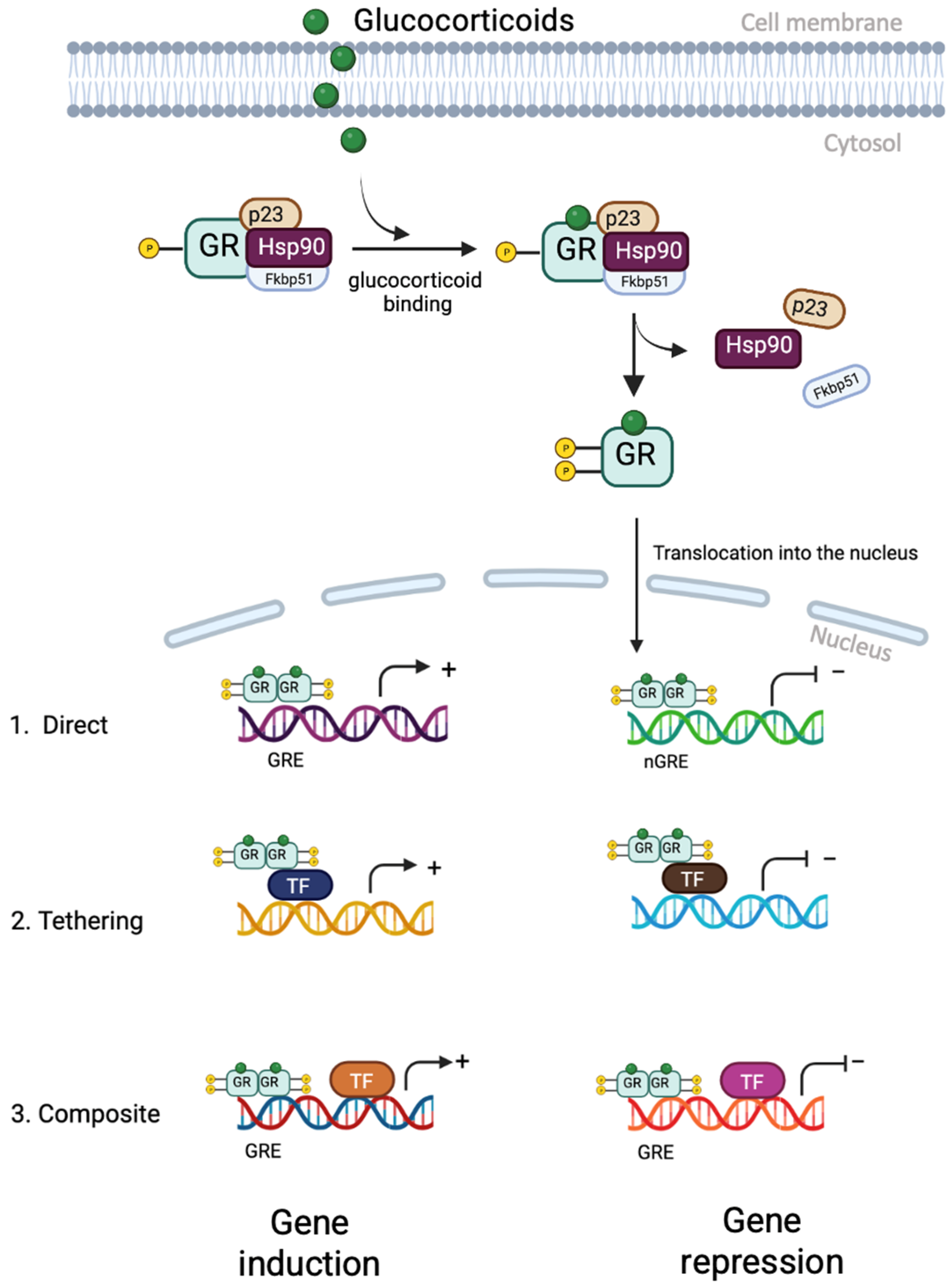
5. Glucocorticoid Receptor Signalling
6. Glucocorticoids on Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal Axis
7. Effect of Glucocorticoids on Reproductive Organs
7.1. Ovary
7.1.1. Dual Role of Glucocorticoids in the Ovary
7.1.2. Glucocorticoid Receptor Isoforms in the Ovary
7.2. Uterus
GR Isoforms in the Uterus
8. Pregnancy and Parturition
Effect of Excess Cortisol on Myometrial Contractility during Parturition
9. Foetus
9.1. Sex Differences
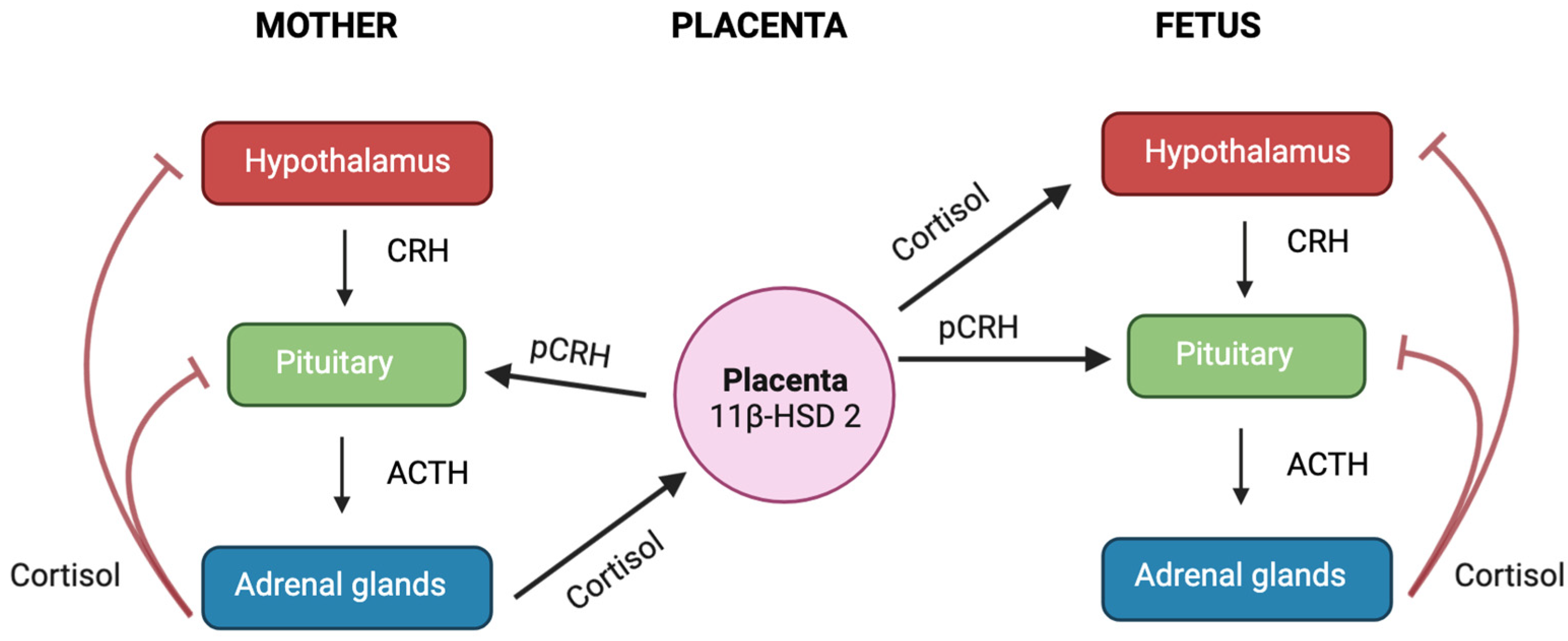
9.2. Glucocorticoid Receptor Isoform in the Placenta
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oakley, R.H.; Cidlowski, J.A. Cellular Processing of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene and Protein: New Mechanisms for Generating Tissue-specific Actions of Glucocorticoids. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3177–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, S.; Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. A General Introduction to Glucocorticoid Biology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Vale, W.W. The role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in neuroendocrine responses to stress. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, G. Regulation of Pituitary ACTH Secretion during Chronic Stress. Front. Neuroendocr. 1994, 15, 321–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawchenko, P. Evidence for a local site of action for glucocorticoids in inhibiting CRF and vasopressin expression in the paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res. 1987, 403, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munck, A.; Guyre, P.M.; Holbrook, N.J. Physiological Functions of Glucocorticoids in Stress and Their Relation to Pharmacological Actions. Endocr. Rev. 1984, 5, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exton, J.H. Regulation of Gluconeogenesis by Glucocorticoids. Monogr. Endocrinol. 1979, 12, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefsky, J.M. Effect of dexamethasone on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation of isolated rat adipocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1975, 56, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, L.M.; Manchem, V.P.; Leedom, T.A.; Rivard, A.L.; McKay, R.A.; Bao, D.; Neroladakis, T.; Monia, B.P.; Bodenmiller, D.M.; Cao, J.X.-C.; et al. Reduction of Hepatic and Adipose Tissue Glucocorticoid Receptor Expression With Antisense Oligonucleotides Improves Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia in Diabetic Rodents Without Causing Systemic Glucocorticoid Antagonism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marver, D.; Ackermann, D.; Gresko, N.; Carrel, M.; Loffing-Cueni, D.; Habermehl, D.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.; Rossier, B.C.; Loffing, J.; De Matteo, R.; et al. Evidence of corticosteroid action along the nephron. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1984, 246, F111–F123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, F.; Stewart, P.M. Cortisol metabolism in hypertension. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 20, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, M.N.; Sternberg, E.M. Glucocorticoid regulation of inflammation and its functional correlates: From HPA axis to glucocorticoid receptor dysfunction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1261, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desrivières, S.; Lourdusamy, A.; Müller, C.; Ducci, F.; Wong, C.P.; Kaakinen, M.; Pouta, A.; Hartikainen, A.-L.; Isohanni, M.; Charoen, P.; et al. Glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1) gene polymorphisms and onset of alcohol abuse in adolescents. Addict. Biol. 2010, 16, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Fentress, H.M.; Hoversten, M.T.; Zhang, L.; Hebda-Bauer, E.K.; Watson, S.J.; Seasholtz, A.F.; Akil, H. Early-Life Forebrain Glucocorticoid Receptor Overexpression Increases Anxiety Behavior and Cocaine Sensitization. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, P.L.; Ertsey, R.; Gonzales, L.W.; Gonzales, J. Transcriptional regulation of human pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C by glucocorticoids. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1996, 14, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grier, D.G.; Halliday, H.L. Effects of Glucocorticoids on Fetal and Neonatal Lung Development. Treat. Respir. Med. 2004, 3, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busada, J.T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid Action During Development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 125, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ahmet, A.; Ward, L.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Mandelcorn, E.D.; Leigh, R.; Brown, J.P.; Cohen, A.; Kim, H. A practical guide to the monitoring and management of the complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busillo, J.M.; Cidlowski, J.A. The five Rs of glucocorticoid action during inflammation: Ready, reinforce, repress, resolve, and restore. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Topete, D.; Cidlowski, J.A. One Hormone, Two Actions: Anti- and Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 2015, 22, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinenov, Y.; Rogatsky, I. Glucocorticoids and the innate immune system: Crosstalk with the Toll-like receptor signaling network. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 275, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besedovsky, H.; Del Rey, A.; Klusman, I.; Furukawa, H.; Arditi, G.M.; Kabiersch, A. Cytokines as modulators of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1991, 40, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, A.; Brown, E.S.; Bove, R.; Vaidya, A.; Gelfand, J. Glucocorticoids for therapeutic immunosuppression: Clinical pearls for the practicing neurologist. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 430, 120004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauci, A.S.; Dale, D.C.; Balow, J.E. Glucocorticosteroid Therapy: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Considerations. Ann. Intern. Med. 1976, 84, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settipane, G.A.; Pudupakkam, R.; McGowan, J.H. Corticosteroid effect on immunoglobulins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1978, 62, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, G.L. Plasma steroid-binding proteins: Primary gatekeepers of steroid hormone action. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, R13–R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaides, N.C.; Galata, Z.; Kino, T.; Chrousos, G.P.; Charmandari, E. The human glucocorticoid receptor: Molecular basis of biologic function. Steroids 2010, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, D.W.; Cidlowski, J.A. Specificity and sensitivity of glucocorticoid signaling in health and disease. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.Z.; Wardell, S.E.; Burnstein, K.L.; Defranco, D.; Fuller, P.J.; Giguere, V.; Hochberg, R.B.; McKay, L.; Renoir, J.-M.; Weigel, N.L.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology. LXV. The Pharmacology and Classification of the Nuclear Receptor Superfamily: Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone, and Androgen Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevyver, S.; Dejager, L.; Libert, C. Comprehensive Overview of the Structure and Regulation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 671–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamberger, C.M.; Bamberger, A.M.; de Castro, M.; Chrousos, G.P. Glucocorticoid receptor beta, a potential endogenous inhibitor of glucocorticoid action in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moalli, P.A.; Pillay, S.; Krett, N.L.; Rosen, S.T. Alternatively spliced glucocorticoid receptor messenger RNAs in glucocorticoid-resistant human multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3877–3879. [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Weinberger, C.; Ong, E.S.; Cerelli, G.; Oro, A.; Lebo, R.; Thompson, E.B.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Evans, R.M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature 1985, 318, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, R.H.; Sar, M.; Cidlowski, J.A. The Human Glucocorticoid Receptor β Isoform: Expression, biochemical properties, and putative function. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9550–9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, T.; Manoli, I.; Kelkar, S.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.A.; Chrousos, G.P. Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) β has intrinsic, GRα-independent transcriptional activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 381, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Cruz-Topete, D.; Oakley, R.H.; Xiao, X.; Cidlowski, J.A. Human Glucocorticoid Receptor β Regulates Gluconeogenesis and Inflammation in Mouse Liver. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, C.; Levy, A.; Hancock, J.; Lightman, S.; Norman, M. Insertion of an Amino Acid in the DNA-Binding Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor as a Result of Alternative Splicing. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 4283–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.W.; Davis, J.; White, A.; Clark, A.J. Glucocorticoid receptor structure and function in glucocorticoid-resistant small cell lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 3276–3280. [Google Scholar]
- Meijsing, S.H.; Pufall, M.A.; So, A.Y.; Bates, D.L.; Chen, L.; Yamamoto, K.R. DNA binding site sequence directs glucocorticoid receptor structure and activity. Science 2009, 324, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Chollier, M.; Watson, L.C.; Cooper, S.B.; Pufall, M.A.; Liu, J.S.; Borzym, K.; Vingron, M.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Meijsing, S.H. A naturally occuring insertion of a single amino acid rewires transcriptional regulation by glucocorticoid receptor isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17826–17831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.J.; Poolman, T.M.; Williamson, A.J.K.; Wang, Z.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A.; Whetton, A.D.; Brass, A.; Matthews, L.C.; Ray, D.W. Glucocorticoid receptor isoforms direct distinct mitochondrial programs to regulate ATP production. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaitan, D.; DeBold, C.R.; Turney, M.K.; Zhou, P.; Orth, D.N.; Kovacs, W.J. Glucocorticoid receptor structure and function in an adrenocorticotropin-secreting small cell lung cancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 1995, 9, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.Z.; Cidlowski, J.A. Translational Regulatory Mechanisms Generate N-Terminal Glucocorticoid Receptor Isoforms with Unique Transcriptional Target Genes. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Corticosteroids: Mechanisms of action in health and disease. Rheum. Dis. Clin. 2016, 42, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, W.B.; Toft, D.O. Steroid Receptor Interactions with Heat Shock Protein and Immunophilin Chaperones. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 306–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surjit, M.; Ganti, K.P.; Mukherji, A.; Ye, T.; Hua, G.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Widespread negative response elements mediate direct repression by agonist-liganded glucocorticoid receptor. Cell 2011, 145, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogatsky, I.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Glucocorticoid modulation of cytokine signaling. Tissue Antigens 2006, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaleon, M.; Steane, S.E.; McMahon, K.; Cuffe, J.S.; Moritz, K.M. Placental O-GlcNAc-transferase expression and interactions with the glucocorticoid receptor are sex specific and regulated by maternal corticosterone exposure in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneweg, F.L.; Karst, H.; de Kloet, E.R.; Joëls, M. Mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors at the neuronal membrane, regulators of nongenomic corticosteroid signalling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 350, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, R.A.; Witchell, S.F.; DeFranco, D.B. Cooperativity and complementarity: Synergies in non-classical and classical glucocorticoid signaling. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 2819–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayroldi, E.; Cannarile, L.; Migliorati, G.; Nocentini, G.; Delfino, D.V.; Riccardi, C.; Lee, J.; Machin, M.; Russell, K.E.; Pavlidis, S.; et al. Mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids: Genomic and nongenomic interference with MAPK signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4805–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, J.; Mikics, É.; Makara, G.B. The effects of non-genomic glucocorticoid mechanisms on bodily functions and the central neural system. A critical evaluation of findings. Front. Neuroendocr. 2008, 29, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, V.; Walsh, D.; Mainprice, B.; Bousquet, J.; Harvey, B. Rapid non-genomic inhibition of ATP-induced Cl− secretion by dexamethasone in human bronchial epithelium. J. Physiol. 2002, 545, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttgereit, F.; Scheffold, A. Rapid glucocorticoid effects on immune cells. Steroids 2002, 67, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Kimoto, T.; Tanabe, N.; Hattori, T.-A.; Yasumatsu, N.; Kawato, S. Corticosterone acutely prolonged N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated Ca2+ elevation in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, S.; Malcher-Lopes, R.; Halmos, K.C.; Tasker, J.G. Nongenomic Glucocorticoid Inhibition via Endocannabinoid Release in the Hypothalamus: A Fast Feedback Mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 4850–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Kuriyama, H. Glucocorticoids inhibit acetylcholine-induced current in chromaffin cells. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1989, 257, C906–C912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, P.Y. Glucocorticoid regulation of the serotonergic system of the brain. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol. 1976, 15, 251–265. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.-A.; Chen, Y.-Z. Nongenomic Effect of Glucocorticoid on the Release of Arginine Vasopressin from Hypothalamic Slices in Rats. Neuroendocrinology 1995, 62, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and Function of the MAPKs and Their Substrates, the MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, P.P.; Blenis, J. ERK and p38 MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases: A Family of Protein Kinases with Diverse Biological Functions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 320–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruscoli, S.; Di Virgilio, R.; Donato, V.; Velardi, E.; Baldoni, M.; Marchetti, C.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. Genomic and non-genomic effects of different glucocorticoids on mouse thymocyte apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 529, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxtall, J.D.; Van Hal, P.T.W.; Choudhury, Q.; Gilroy, D.; Flower, R.J. Different glucocorticoids vary in their genomic and non-genomic mechanism of action in A549 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, A.-Q.; Qiu, J.; Xiao, L.; Chen, Y.-Z. Rapid activation of JNK and p38 by glucocorticoids in primary cultured hippocampal cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 80, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Z.; Lin, W.; Chen, Y.Z. Inhibition of ATP-induced calcium influx in HT4 cells by glucocorticoids: Involvement of protein kinase A. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi-Moghadam, A.; Simoncini, T.; Yang, Z.; Limbourg, F.P.; Plumier, J.C.; Rebsamen, M.C.; Liao, J.K. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Acute cardiovascular protective effects of corticosteroids are mediated by non-transcriptional activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nat. Med. 2007, 8, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbach, V.; Verriere, V.; Grumbach, Y.; Bousquet, J.; Harvey, B. Rapid anti-secretory effects of glucocorticoids in human airway epithelium. Steroids 2006, 71, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, F.J.; Johnstone, T.B.; Corpuz, M.L.; Kazarian, A.G.; Mohajer, N.N.; Tliba, O.; Panettieri RAJr Koziol-White, C.; Roosan, M.R.; Ostrom, R.S. Glucocorticoids rapidly activate cAMP production via Gαs to initiate non-genomic signaling that contributes to one-third of their canonical genomic effects. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, K.F.; LaVigne, J.E.; Brust, T.F.; Seifert, R.; Dessauer, C.W.; Watts, V.J.; Ostrom, R.S. Physiological roles of mammalian transmembrane adenylyl cyclase isoforms. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 815–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumlin, J.A.; Lea, J.P.; Swanson, C.E.; Smith, C.L.; Edge, S.S.; Someren, J.S. Aldosterone and dexamethasone stimulate calcineurin activity through a transcription-independent mechanism involving steroid receptor-associated heat shock proteins. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marchetti, M.C.; Di Marco, B.; Cifone, G.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. Dexamethasone-induced apoptosis of thymocytes: Role of glucocorticoid receptor–associated Src kinase and caspase-8 activation. Blood 2003, 101, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartis, D.; Boldizsár, F.; Kvell, K.; Szabó, M.; Pálinkás, L.; Németh, P.; Monostori, É.; Berki, T. Intermolecular relations between the glucocorticoid receptor, ZAP-70 kinase, and Hsp-90. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagklis, T.; Ravanos, K.; Makedou, K.; Kourtis, A.; Rousso, D. Common features and differences of the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis in male and female. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2014, 31, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, S.D.; Wierman, M.E.; Shupnik, M.A.; Chin, W.W. Molecular Biology of the Pituitary Gonadotropins. Endocr. Rev. 1990, 11, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.S.; Pangas, S.A. The ovary: Basic biology and clinical implications. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whirledge, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. A Role for Glucocorticoids in Stress-Impaired Reproduction: Beyond the Hypothalamus and Pituitary. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4450–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraghty, A.C.; Kaufer, D. Glucocorticoid regulation of reproduction. In Glucocorticoid Signaling: From Molecules to Mice to Man; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 253–278. [Google Scholar]
- Whirledge, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoids and Reproduction: Traffic Control on the Road to Reproduction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, M.; Pertuiset, B.F.; Moguilewsky, M.; Magdelenat, H.; Martin, P.M. Steroid receptors in the central nervous system. Implications in neurology. Rev. Neurol. 1984, 140, 233–248. [Google Scholar]
- Chandran, U.R.; Attardi, B.; Friedman, R.; Dong, K.W.; Roberts, J.L.; DeFranco, D.B. Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated repression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone promoter activity in GT1 hypothalamic cell lines. Endocrinology 1994, 134, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A.C.; Attardi, B.; DeFranco, D.B. Glucocorticoid repression of the reproductive axis: Effects on GnRH and gonadotropin subunit mRNA levels. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 256, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, C.L.; Moriarty, G.C.; Wahl, L.M.; Naor, Z.; Catt, K.J. Preparation of Gonadotroph-Enriched Cell Populations From Adult Rat Anterior Pituitary Cells By Centrifugal Elutriation. Endocrinology 1982, 111, 1421–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.W.; Leung, P.C. The expression, regulation and signal transduction pathways of the mammalian gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2000, 78, 1029–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya-Núñez, G.; Conn, P. Transcriptional regulation of the GnRH receptor gene by glucocorticoids. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2003, 200, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilen, S.M.; Szabo, M.; Strasser, G.A.; McAndrews, J.M.; Ringstrom, S.J.; Schwartz, N.B. Corticosterone selectively increases follicle-stimulating hormone beta-subunit messenger ribonucleic acid in primary anterior pituitary cell culture without affecting its half-life. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 3802–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takumi, K.; Iijima, N.; Higo, S.; Ozawa, H. Immunohistochemical analysis of the colocalization of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor and glucocorticoid receptor in kisspeptin neurons in the hypothalamus of female rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 531, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, E.; Stephens, S.B.Z.; Chaing, S.; Munaganuru, N.; Kauffman, A.S.; Breen, K.M. Corticosterone Blocks Ovarian Cyclicity and the LH Surge via Decreased Kisspeptin Neuron Activation in Female Mice. Endocrinology 2015, 157, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubuka, T.; Morgan, K.; Pawson, A.J.; Osugi, T.; Chowdhury, V.S.; Minakata, H.; Tsutsui, K.; Millar, R.P.; Bentley, G.E. Identification of Human GnIH Homologs, RFRP-1 and RFRP-3, and the Cognate Receptor, GPR147 in the Human Hypothalamic Pituitary Axis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, I.J.; Bartolini, D.; Conductier, G.; Henry, B.A. Stress Increases Gonadotropin Inhibitory Hormone Cell Activity and Input to GnRH Cells in Ewes. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4339–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrenkohl, L.R. Prenatal Stress Reduces Fertility and Fecundity in Female Offspring. Science 1979, 206, 1097–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, E.W.; Crissman, J.W.; Liberacki, A.B.; Clements, C.M.; Breslin, W.J. Assessment of adult and neonatal reproductive parameters in Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to propylene glycol monomethyl ether vapors for two generations. Toxicol. Sci. 1999, 50, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, C.; Chevins, P. Prenatal stress reduces fertility of male offspring in mice, without affecting their adult testosterone levels. Horm. Behav. 1989, 23, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rensis, F.; Scaramuzzi, R.J. Heat stress and seasonal effects on reproduction in the dairy cow—A review. Theriogenology 2003, 60, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, B.; Tam-Dafond, L.; Jenni-Eiermann, S.; Arlettaz, R.; Schaub, M.; Jenni, L. Modulation of the adrenocortical response to acute stress with respect to brood value, reproductive success and survival in the Eurasian hoopoe. Oecologia 2013, 173, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.D.; French, S.S. Stress-Induced Tradeoffs in a Free-Living Lizard across a Variable Landscape: Consequences for Individuals and Populations. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, S.W.; Mitchell, C.A. Seismic stress effects on reproductive structures of tomato, potato, and marigold. HortScience 1985, 20, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobel, C.J.; Goldstein, A.; Barrett, E.S. Psychosocial Stress and Pregnancy Outcome. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 51, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, E.J.H.; de Medina, P.G.R.; Huizink, A.C.; Bergh, B.R.H.V.D.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Visser, G.H.A. Prenatal maternal stress: Effects on pregnancy and the (unborn) child. Early Hum. Dev. 2002, 70, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beals, K.A.; Meyer, N.L. Female Athlete Triad Update. Clin. Sports Med. 2007, 26, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, D.E. Altered hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis function in young female athletes: Implications and recommendations for management. Treat. Endocrinol. 2005, 4, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marilus, R.; Dickerman, Z.; Kaufman, H.; Varsano, I.; Laron, Z. Addison’s disease associated with precocious sexual development in a boy. Acta Pædiatrica 1981, 70, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadik, Z.; Cooper, M.; Chen, M.; Stern, N. Cushing’s disease presenting as pubertal arrest. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 1993, 6, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kinouchi, R.; Matsuzaki, T.; Iwasa, T.; Gereltsetseg, G.; Nakazawa, H.; Kunimi, K.; Kuwahara, A.; Yasui, T.; Irahara, M. Prepubertal exposure to glucocorticoid delays puberty independent of the hypothalamic Kiss1-GnRH system in female rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2012, 30, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killian, D.B.; Kiesling, D.O.; Wulff, F.P.; Stewart, A. Effects of Adrenalectomy and Glucocorticoids on Puberty in Gilts Reared in Confinement. J. Anim. Sci. 1987, 64, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.T.; Waddell, B.J. Increased Fetal Glucocorticoid Exposure Delays Puberty Onset in Postnatal Life. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politch, J.A.; Herrenkohl, L.R. Prenatal ACTH and corticosterone: Effects on reproduction in male mice. Physiol. Behav. 1984, 32, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politch, J.A.; Herrenkohl, L.R. Effects of prenatal stress on reproduction in male and female mice. Physiol. Behav. 1984, 32, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benešová, O.; Pavlík, A. Perinatal treatment with glucocorticoids and the risk of maldevelopment of the brain. Neuropharmacology 1989, 28, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, T.; Morohashi, K.-I. Gene regulation of steroidogenesis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 53, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Choi, Y.; Brännström, M.; Akin, J.W.; Curry, T.E.; Jo, M. Cortisol/glucocorticoid receptor: A critical mediator of the ovulatory process and luteinization in human periovulatory follicles. Hum. Reprod. 2023, 38, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Simerman, A.; Cho, M.; Singh, P.; Briton-Jones, C.; Hill, D.; Grogan, T.; Elashoff, D.; Clarke, N.J.; Chazenbalk, G.D.; et al. 21-Hydroxylase-Derived Steroids in Follicles of Nonobese Women Undergoing Ovarian Stimulation for In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Positively Correlate With Lipid Content of Luteinized Granulosa Cells (LGCs) as a Source of Cholesterol for Steroid Synthesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiston, A.L.; Obeyesekere, V.R.; Smith, R.E.; Krozowski, Z.S. Cloning and tissue distribution of the human 1 lβ-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 enzyme. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1994, 105, R11–R17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benediktsson, R.; Yau, J.L.W.; Low, S.; Brett, L.P.; Cooke, B.E.; Edwards, C.R.W.; Seckl, J.R. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the rat ovary: High expression in the oocyte. J. Endocrinol. 1992, 135, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, J.; Ricketts, M.; Whorwood, C.; Stewart, P. Ontogeny and sexual dimorphic expression of mouse type 2 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1997, 127, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, M.M.; Naessen, T.; Kirilovas, D.; Chaika, A.; Nosenko, J.; Mogilevkina, I.; Rockwood, A.L.; Carlström, K.; Bergquist, J. Steroid Profiles in Ovarian Follicular Fluid from Regularly Menstruating Women and Women after Ovarian Stimulation. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, K.; Holmes, M.; Seckl, J.; Clemmer, J.S.; Pruett, W.A.; Coleman, T.G.; Hall, J.E.; Hester, R.L.; Rossier, B.C.; Baker, M.E.; et al. 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases: Intracellular Gate-Keepers of Tissue Glucocorticoid Action. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1139–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetsuka, M.; Thomas, F.J.; Thomas, M.J.; Anderson, R.A.; Mason, J.I.; Hillier, S.G. Differential expression of messenger ribonucleic acids encoding 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase types 1 and 2 in human granulosa cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 2006–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen, L.C.; Bøtkjær, J.A.; Østrup, O.; Petersen, K.B.; Andersen, C.Y.; Grøndahl, M.L.; Englund, A.L.M. Two waves of transcriptomic changes in periovulatory human granulosa cells. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 35, 1230–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fateh, M.; Ben-Rafael, Z.; Benadiva, C.A.; Mastroianni, L., Jr.; Flickinger, G.L. Cortisol levels in human follicular fluid. Fertil. Steril. 1989, 51, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nteeba, J.; Sanz-Fernandez, M.V.; Rhoads, R.P.; Baumgard, L.H.; Ross, J.W.; Keating, A.F. Heat Stress Alters Ovarian Insulin-Mediated Phosphatidylinositol-3 Kinase and Steroidogenic Signaling in Gilt Ovaries. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 92, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosden, R.G.; Hunter, R.H.F.; Telfer, E.; Torrance, C.; Brown, N. Physiological factors underlying the formation of ovarian follicular fluid. Reproduction 1988, 82, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune, J.E. Ovarian Follicular Growth and Development in Mammals. Biol. Reprod. 1994, 50, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, F.; Kong, Q.-Q.; Ning, S.-F.; Yuan, H.-J.; Lian, H.-Y.; Luo, M.-J.; Tan, J.-H. Stresses on Female Mice Impair Oocyte Developmental Potential:Effects of Stress Severity and Duration on Oocytes at the Growing Follicle Stage. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 23, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.-J.; Han, X.; He, N.; Wang, G.-L.; Gong, S.; Lin, J.; Gao, M.; Tan, J.-H. Glucocorticoids impair oocyte developmental potential by triggering apoptosis of ovarian cells via activating the Fas system. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Wang, J.-Z.; Li, J.-J.; Wei, D.-L.; Sui, H.-S.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Zhou, P.; Tan, J.-H. Maternal Restraint Stress Diminishes the Developmental Potential of Oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 84, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.Y. Effect of glucocorticoids on spontaneous and follicle-stimulating hormone induced oocyte maturation in mouse oocytes during culture. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 85, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Merris, V.; Van Wemmel, K.; Cortvrindt, R. In vitro effects of dexamethasone on mouse ovarian function and pre-implantation embryo development. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 23, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Sun, G.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, H.-J.; Zhu, S.; Jiao, G.-Z.; Luo, M.-J.; Tan, J.-H. Mechanisms for the species difference between mouse and pig oocytes in their sensitivity to glucorticoids. Biol. Reprod. 2017, 96, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-G.; Chen, W.-Y.; Li, P.S. Effects of glucocorticoids on maturation of pig oocytes and their subsequent fertilizing capacity in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlet, D.; Ille, N.; Ertl, R.; Alves, B.; Gastal, G.; Paiva, S.; Gastal, M.; Gastal, E.; Aurich, C. Glucocorticoid metabolism in equine follicles and oocytes. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2016, 59, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-H.; Yang, B.-Q.; Hu, Y.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, L.-X.; Zhou, J.-C.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Lu, C.-L.; Ma, X. Dexamethasone altered steroidogenesis and changed redox status of granulosa cells. Endocrine 2014, 47, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-J.; Li, P.S. Dexamethasone Inhibits Luteinizing Hormone-Induced Synthesis of Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein in Cultured Rat Preovulatory Follicles. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 64, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.E.; Pester, L.A.; Curtis, P.; Shaw, R.W.; Edwards, C.R.W.; Cooke, B.A. Direct inhibition of ovarian steroidogenesis by Cortisol and the modulatory role of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Clin. Endocrinol. 1993, 38, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.N.; Whirledge, S. Stress and the HPA Axis: Balancing Homeostasis and Fertility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, M.; Frydman, N.; Duquenne, C.; N′ Tumba-Byn, T.; Benachi, A.; Habert, R.; Rouiller-Fabre, V.; Livera, G. Dexamethasone induces germ cell apoptosis in the human fetal ovary. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, e1890–e1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasson, R.; Amsterdam, A. Pleiotropic anti-apoptotic activity of glucocorticoids in ovarian follicular cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasson, R.; Shinder, V.; Dantes, A.; Land, A.; Amsterdam, A. Activation of multiple signal transduction pathways by glucocorticoids: Protection of ovarian follicular cells against apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 311, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiyama, J.; Nishimura, R.; Lee, H.-Y.; Sakumoto, R.; Tetsuka, M.; Acosta, T.J.; Skarzynski, D.J.; Okuda, K. Cortisol Is a Suppressor of Apoptosis in Bovine Corpus Luteum. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rae, M.T.; Price, D.; Harlow, C.R.; Critchley, H.O.; Hillier, S.G. Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated regulation of MMP9 gene expression in human ovarian surface epithelial cells. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 92, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, J.R.; Nakamura, K.; Erickson, G.F. Rat ovary glucocorticoid receptor: Identification and characterization. Steroids 1982, 39, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rae, M.T.; Niven, D.; Critchley, H.O.D.; Harlow, C.R.; Hillier, S.G. Antiinflammatory Steroid Action in Human Ovarian Surface Epithelial Cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 4538–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tetsuka, M.; Milne, M.; Simpson, G.; Hillier, S. Expression of 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase, Glucocorticoid Receptor, and Mineralocorticoid Receptor Genes in Rat Ovary. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, A.E.; Papageorghiou, A.T. Potential significance of physiological and pharmacological glucocorticoids in early pregnancy. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2008, 14, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čikoš, Š.; Babeľová, J.; Špirková, A.; Burkuš, J.; Kovaříková, V.; Šefčíková, Z.; Fabian, D.; Koppel, J. Glucocorticoid receptor isoforms and effects of glucocorticoids in ovulated mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 100, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, R.H.; Webster, J.C.; Sar, M.; Parker Jr, C.R.; Cidlowski, J.A. Expression and subcellular distribution of the β-isoform of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 5028–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhen, T.; Grissom, S.; Afshari, C.; Cidlowski, J.A. Dexamethasone blocks the rapid biological effects of 17β-estradiol in the rat uterus without antagonizing its global genomic actions. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1849–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.C.; Dey, S.K. Role of Histamine in Implantation: Dexamethasone Inhibits Estradiol-Induced Implantation in the Rat. Biol. Reprod. 1980, 22, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whirledge, S.; Xu, X.; Cidlowski, J.A. Global Gene Expression Analysis in Human Uterine Epithelial Cells Defines New Targets of Glucocorticoid and Estradiol Antagonism. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 89, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmowski, W.P.; Ding, J.; Shen, J.; Rana, N.; Fernandez, B.; Braun, D. Apoptosis in endometrial glandular and stromal cells in women with and without endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2001, 16, 1802–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, C.; Torres, M.; Galleguillos, C.; Sovino, H.; Boric, M.A.; Fuentes, A.; Johnson, M.C. Nuclear factor κB pathway and interleukin-6 are affected in eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis. Reproduction 2009, 137, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meno, C.; Saijoh, Y.; Fujii, H.; Ikeda, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Toyoda, Y. Left–right asymmetric expression of the TGFβ-family member lefty in mouse embryos. Nature 1996, 381, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Naidu, D.; Hearing, P.; Handwerger, S.; Tabibzadeh, S. LEFTY, a Member of the Transforming Growth Factor-β Superfamily, Inhibits Uterine Stromal Cell Differentiation: A Novel Autocrine Role. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjappa, M.K.; Medrano, T.I.; Lydon, J.P.; Bigsby, R.M.; Cooke, P.S. Maximal Dexamethasone Inhibition of Luminal Epithelial Proliferation Involves Progesterone Receptor (PR)- and Non-PR-Mediated Mechanisms in Neonatal Mouse Uterus. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 92, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, K.; Venkatakrishnan, R.; Salker, M.S.; Lucas, E.S.; Shaheen, F.; Kuroda, M.; Blanks, A.; Christian, M.; Quenby, S.; Brosens, J.J. Induction of 11β-HSD 1 and Activation of Distinct Mineralocorticoid Receptor- and Glucocorticoid Receptor-Dependent Gene Networks in Decidualizing Human Endometrial Stromal Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dunk, C.; Croy, A.B.; Lye, S.J. To serve and to protect: The role of decidual innate immune cells on human pregnancy. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 363, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.S.; Schumacher, A. The T helper type 17/regulatory T cell paradigm in pregnancy. Immunology 2016, 148, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinketova, K.; Mourdjeva, M.; Oreshkova, T. Human Decidual Stromal Cells as a Component of the Implantation Niche and a Modulator of Maternal Immunity. J. Pregnancy 2016, 2016, 8689436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whirledge, S.D.; Oakley, R.H.; Myers, P.H.; Lydon, J.P.; DeMayo, F.; Cidlowski, J.A. Uterine glucocorticoid receptors are critical for fertility in mice through control of embryo implantation and decidualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15166–15171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.A.; Jin, M.; Yu, D.; Moldenhauer, L.M.; Davies, M.J.; Hull, M.L.; Norman, R.J. Corticosteroid therapy in assisted reproduction—Immune suppression is a faulty premise. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Bogdan, A.; Balassa, T.; Csabai, T.; Szekeres-Bartho, J. (Eds.) The decidua—The maternal bed embracing the embryo—Maintains the pregnancy. In Seminars in Immunopathology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bartmann, C.; Segerer, S.E.; Rieger, L.; Kapp, M.; Sütterlin, M.; Kämmerer, U. Quantification of the Predominant Immune Cell Populations in Decidua Throughout Human Pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2013, 71, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, T.A.; Saunders, P.T.K.; Moffett-King, A.; Groome, N.P.; Critchley, H.O.D. Steroid Receptor Expression in Uterine Natural Killer Cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quenby, S.; Kalumbi, C.; Bates, M.; Farquharson, R.; Vince, G. Prednisolone reduces preconceptual endometrial natural killer cells in women with recurrent miscarriage. Fertil. Steril. 2005, 84, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, C.; Riboldi, E.; Ippolito, A.; Sica, A. Molecular and epigenetic basis of macrophage polarized activation. Semin. Immunol. 2015, 27, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, C.; Mjösberg, J.; Matussek, A.; Geffers, R.; Matthiesen, L.; Berg, G.; Sharma, S.; Buer, J.; Ernerudh, J. Gene Expression Profiling of Human Decidual Macrophages: Evidence for Immunosuppressive Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, J.; Möttönen, M.; Komi, J.; Alanen, A.; Lassila, O. Phenotypic characterization of human decidual macrophages. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 131, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiruchelvam, U.; Maybin, J.A.; Armstrong, G.M.; Greaves, E.; Saunders, P.T.K.; Critchley, H.O.D. Cortisol regulates the paracrine action of macrophages by inducing vasoactive gene expression in endometrial cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 99, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.; Yamamoto, S.; Bryant-Greenwood, G. Relaxin Modulates Proinflammatory Cytokine Secretion from Human Decidual Macrophages. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 85, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaks, V.; Birnberg, T.; Berkutzki, T.; Sela, S.; BenYashar, A.; Kalchenko, V.; Mor, G.; Keshet, E.; Dekel, N.; Neeman, M.; et al. Uterine DCs are crucial for decidua formation during embryo implantation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3954–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matasić, R.; Dietz, A.B.; Vuk-Pavlović, S. Dexamethasone inhibits dendritic cell maturation by redirecting differentiation of a subset of cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 66, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigler, M.B.; Egli, S.B.; Hysek, C.M.; Hoenger, G.; Schmied, L.; Baldin, F.S.; Marquardsen, F.A.; Recher, M.; Liechti, M.E.; Hess, C.; et al. Stress-Induced In Vivo Recruitment of Human Cytotoxic Natural Killer Cells Favors Subsets with Distinct Receptor Profiles and Associates with Increased Epinephrine Levels. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busillo, J.M.; Azzam, K.M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoids Sensitize the Innate Immune System through Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 38703–38713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutsatsou, P.; Sekeris, C.E. Steroid Receptors in the Uterus: Implications in Endometriosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 997, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Gyomorey, S.; Lye, S.J.; Gibb, W.; Challis, J.R. Effect of labor on glucocorticoid receptor (GRTotal, GRα, and GRβ) proteins in ovine intrauterine tissues. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. JSGI 2003, 10, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, M. The physiological roles of placental corticotropin releasing hormone in pregnancy and childbirth. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 69, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linton, E.A.; Perkins, A.V.; Woods, R.J.; Eben, F.; Wolfe, C.D.; Behan, D.P.; Potter, E.; Vale, W.W.; Lowry, P.J. Corticotropin releasing hormone-binding protein (CRH-BP): Plasma levels decrease during the third trimester of normal human pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Laurent, L.; King, S.; Vaillancourt, C. Effects of prenatal maternal stress on serotonin and fetal development. Placenta 2015, 48, S66–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, J.R.; Sloboda, D.M.; Alfaidy, N.; Lye, S.J.; Gibb, W.; Patel, F.A. Prostaglandins and mechanisms of preterm birth. Reproduction 2002, 124, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, P.; Myatt, L.; Sun, K. Roles of glucocorticoids in human parturition: A controversial fact? Placenta 2014, 35, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.B.M.; Flint, A.P.F.; Turnbull, A.C. Mechanism Of Action Of Glucocorticoids In Induction Of Ovine Parturition: Effect On Placental Steroid Metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 1975, 66, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, J.R.; Lye, S.J.; Gibb, W.; Whittle, W.; Patel, F.; Alfaidy, N. Understanding preterm labor. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 943, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggins, G.C.; Grieves, S. Possible Role for Prostaglandin F2α in Parturition in Sheep. Nature 1971, 232, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyomorey, S.; Lye, S.; Gibb, W.; Challis, J. Fetal-to-maternal progression of prostaglandin H(2) synthase-2 expression in ovine intrauterine tissues during the course of labor. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 62, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challis, J.R.; Matthews, S.G.; Gibb, W.; Lye, S.J. Endocrine and paracrine regulation of birth at term and preterm. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 514–550. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Sun, K. Induction of Amnion Epithelial Apoptosis by Cortisol via tPA/Plasmin System. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4487–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Lu, J.; Li, W.; Zuo, R.; Myatt, L.; Sun, K. Autophagic Degradation of Collagen 1A1 by Cortisol in Human Amnion Fibroblasts. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, V.; Liu, D.; Billett, E.; Kirk, S. Amniotic membrane collagen content and type distribution in women with preterm premature rupture of the membranes in pregnancy. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1997, 104, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, P.D.; Garite, T.J.; Porto, M.; Glynn, L.; Chicz-DeMet, A.; Dunkel-Schetter, C.; Sandman, C.A. Placental corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), spontaneous preterm birth, and fetal growth restriction: A prospective investigation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 191, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, J.; Matthews, S.; Van Meir, C.; Ramirez, M. Current topic: The placental corticotrophin-releasing hormone-adrenocorticotrophin axis. Placenta 1995, 16, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, I.; Day, J.; Brummer, V.; Horwell, D.; Morgan, H. Betamethazone Induction Of Labour. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 1977, 32, 580–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwosu, U.C.; Wallach, E.E.; Bolognese, R.J. Initiation of labor by intraamniotic cortisol instillation in prolonged human pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1976, 47, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, J.; Radin, T. The effect of corticosteroid administration on uterine activity and preterm labor in high-order multiple gestations. Obstet. Gynecol. 1995, 85, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, N.; Rosenlöcher, F.; Stalder, T.; Linke, J.; Distler, W.; Morgner, J.; Kirschbaum, C. Impact of Antenatal Synthetic Glucocorticoid Exposure on Endocrine Stress Reactivity in Term-Born Children. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3538–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, P.L.; Ballard, R.A. Scientific basis and therapeutic regimens for use of antenatal glucocorticoids. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1995, 173, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liggins, G.C. Premature parturition after infusion of corticotrophin or cortisol into foetal lambs. J. Endocrinol. 1968, 42, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Blanco, A.; Diago, V.; De La Cruz, V.S.; Hervás, D.; Cháfer-Pericás, C.; Vento, M. Can stress biomarkers predict preterm birth in women with threatened preterm labor? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 83, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, V.E.; Smith, R.; Giles, W.B.; Clifton, V.L. Endocrine Regulation of Human Fetal Growth: The Role of the Mother, Placenta, and Fetus. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 141–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Class, Q.A.B.; Lichtenstein, P.; Långström, N.; D’Onofrio, B.M. Timing of Prenatal Maternal Exposure to Severe Life Events and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: A Population Study of 2.6 Million Pregnancies. Psychosom. Med. 2011, 73, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Cutfield, W.; Hofman, P.; Hanson, M.A. The fetal, neonatal, and infant environments—The long-term consequences for disease risk. Early Hum. Dev. 2005, 81, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J. The developmental origins of chronic adult disease. Acta Pædiatrica 2004, 93, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.R.; Cuffe, J.S.; Moritz, K.M. Short- and long-term effects of exposure to natural and synthetic glucocorticoids during development. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2012, 39, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erni, K.; Shaqiri-Emini, L.; La Marca, R.; Zimmermann, R.; Ehlert, U. Psychobiological Effects of Prenatal Glucocorticoid Exposure in 10-Year-Old-Children. Front. Psychiatry 2012, 3, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huh, S.Y.; Andrew, R.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Kleinman, K.P.; Seckl, J.R.; Gillman, M.W. Association between umbilical cord glucocorticoids and blood pressure at age 3 years. BMC Med. 2008, 6, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuffe, J.; Dickinson, H.; Simmons, D.; Moritz, K. Sex specific changes in placental growth and MAPK following short term maternal dexamethasone exposure in the mouse. Placenta 2011, 32, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, B.A.; Moritz, K.M.; Roberts, C.T.; Walker, D.W.; Dickinson, H. The Placental Response to Excess Maternal Glucocorticoid Exposure Differs Between the Male and Female Conceptus in Spiny Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 85, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, L.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Paravicini, T.M.; Campbell, S.; Dickinson, H.; Singh, R.R.; Gezmish, O.; Black, M.J.; Moritz, K.M. Prenatal Exposure to Dexamethasone in the Mouse Alters Cardiac Growth Patterns and Increases Pulse Pressure in Aged Male Offspring. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Meng, W.; Shang, H.; Li, S.; Sloboda, D.M.; Ehrlich, L.; Lange, K.; Xu, H.; Henrich, W.; Dudenhausen, J.W.; et al. Early Dexamethasone Treatment Induces Placental Apoptosis in Sheep. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 22, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, V.; Cuffe, J.; Moritz, K.; Cole, T.; Fuller, P.; Lu, N.; Kumar, S.; Chong, S.; Saif, Z. Review: The role of multiple placental glucocorticoid receptor isoforms in adapting to the maternal environment and regulating fetal growth. Placenta 2016, 54, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, V.E.; Gibson, P.G.; Giles, W.B.; Zakar, T.; Smith, R.; Bisits, A.M.; Kessell, C.G.; Clifton, V.L. Maternal Asthma Is Associated with Reduced Female Fetal Growth. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuffe, J.S.M.; Burgess, D.J.; O’Sullivan, L.; Singh, R.R.; Moritz, K.M. Maternal corticosterone exposure in the mouse programs sex-specific renal adaptations in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in 6-month offspring. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, S.L.; Bale, T.L. Prenatal Stress-Induced Increases in Placental Inflammation and Offspring Hyperactivity Are Male-Specific and Ameliorated by Maternal Antiinflammatory Treatment. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 2635–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.N.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Jefferies, A.J.; Anevska, K.; Moritz, K.M.; Wlodek, M.E. Sex-Specific Metabolic Outcomes in Offspring of Female Rats Born Small or Exposed to Stress During Pregnancy. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4104–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, T.; Grecian, S.M.; Reynolds, R.M. Sex differences in early-life programming of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in humans suggest increased vulnerability in females: A systematic review. J. Dev. Orig. Heal. Dis. 2017, 8, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, V.L. Sex and the Human Placenta: Mediating Differential Strategies of Fetal Growth and Survival. Placenta 2010, 31, S33–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mericq, V.; Medina, P.; Kakarieka, E.; Márquez, L.; Johnson, M.C.; Iñiguez, G. Differences in expression and activity of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and 2 in human placentas of term pregnancies according to birth weight and gender. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuffe, J.S.M.; Saif, Z.; Perkins, A.V.; Moritz, K.M.; Clifton, V.L. Dexamethasone and sex regulate placental glucocorticoid receptor isoforms in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 234, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simcock, G.; Kildea, S.; Elgbeili, G.; Laplante, D.P.; Cobham, V.; King, S. Prenatal maternal stress shapes children’s theory of mind: The QF2011 Queensland Flood Study. J. Dev. Orig. Heal. Dis. 2017, 8, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandman, C.A.; Glynn, L.M.; Davis, E.P. Is there a viability–vulnerability tradeoff? Sex differences in fetal programming. J. Psychosom. Res. 2013, 75, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, E.C.; Murphy, S.E.; Ramchandani, P.G.; Hill, J. Associations between biological markers of prenatal stress and infant negative emotionality are specific to sex. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 86, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, N.M.; Hodyl, N.A.; Murphy, V.E.; Osei-Kumah, A.; Wyper, H.; Hodgson, D.M.; Smith, R.; Clifton, V.L. Placental Cytokine Expression Covaries with Maternal Asthma Severity and Fetal Sex. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, Z.; Hodyl, N.; Hobbs, E.; Tuck, A.; Butler, M.; Osei-Kumah, A.; Clifton, V. The human placenta expresses multiple glucocorticoid receptor isoforms that are altered by fetal sex, growth restriction and maternal asthma. Placenta 2014, 35, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, Z.; Hodyl, N.; Stark, M.; Fuller, P.; Cole, T.; Lu, N.; Clifton, V. Expression of eight glucocorticoid receptor isoforms in the human preterm placenta vary with fetal sex and birthweight. Placenta 2015, 36, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, Z.; Dyson, R.M.; Palliser, H.K.; Wright, I.M.R.; Lu, N.; Clifton, V.L. Identification of Eight Different Isoforms of the Glucocorticoid Receptor in Guinea Pig Placenta: Relationship to Preterm Delivery, Sex and Betamethasone Exposure. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, V.L.; McDonald, M.; Morrison, J.L.; Holman, S.L.; Lock, M.C.; Saif, Z.; Meakin, A.; Wooldridge, A.L.; Gatford, K.L.; Wallace, M.J.; et al. Placental glucocorticoid receptor isoforms in a sheep model of maternal allergic asthma. Placenta 2019, 83, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akison, L.K.; Andersen IS, G.; Kent, N.L.; Steane, S.E.; Saif, Z.; Clifton, V.L.; Moritz, K.M. Glucocorticoid receptor isoform expression profile in the rat placenta and fetal liver in pregnancies exposed to periconceptional alcohol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 228A. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, I.; Kisich, K.; Hauk, P.J.; Vottero, A.; Chrousos, G.P.; Klemm, D.J.; Leung, D.Y. High Constitutive Glucocorticoid Receptor β in Human Neutrophils Enables Them to Reduce Their Spontaneous Rate of Cell Death in Response to Corticosteroids. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruver-Yates, A.L.; Cidlowski, J.A. Tissue-Specific Actions of Glucocorticoids on Apoptosis: A Double-Edged Sword. Cells 2013, 2, 202–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, C.L.; Walker, S.P.; Lappas, M.; Tong, S. Circulating RNA coding genes regulating apoptosis in maternal blood in severe early onset fetal growth restriction and pre-eclampsia. J. Perinatol. 2013, 33, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhaumik, S.; Lockett, J.; Cuffe, J.; Clifton, V.L. Glucocorticoids and Their Receptor Isoforms: Roles in Female Reproduction, Pregnancy, and Foetal Development. Biology 2023, 12, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081104
Bhaumik S, Lockett J, Cuffe J, Clifton VL. Glucocorticoids and Their Receptor Isoforms: Roles in Female Reproduction, Pregnancy, and Foetal Development. Biology. 2023; 12(8):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081104
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhaumik, Sreeparna, Jack Lockett, James Cuffe, and Vicki L. Clifton. 2023. "Glucocorticoids and Their Receptor Isoforms: Roles in Female Reproduction, Pregnancy, and Foetal Development" Biology 12, no. 8: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081104
APA StyleBhaumik, S., Lockett, J., Cuffe, J., & Clifton, V. L. (2023). Glucocorticoids and Their Receptor Isoforms: Roles in Female Reproduction, Pregnancy, and Foetal Development. Biology, 12(8), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081104





