Bio-Characterization and Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Exopolysaccharides in Biofilm-Producing Cyanobacteria Isolated from Soil Crust: Exploring the Potential of Microalgal Biomolecules
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Identification of Cyanobacteria in the Biological Soil Crust
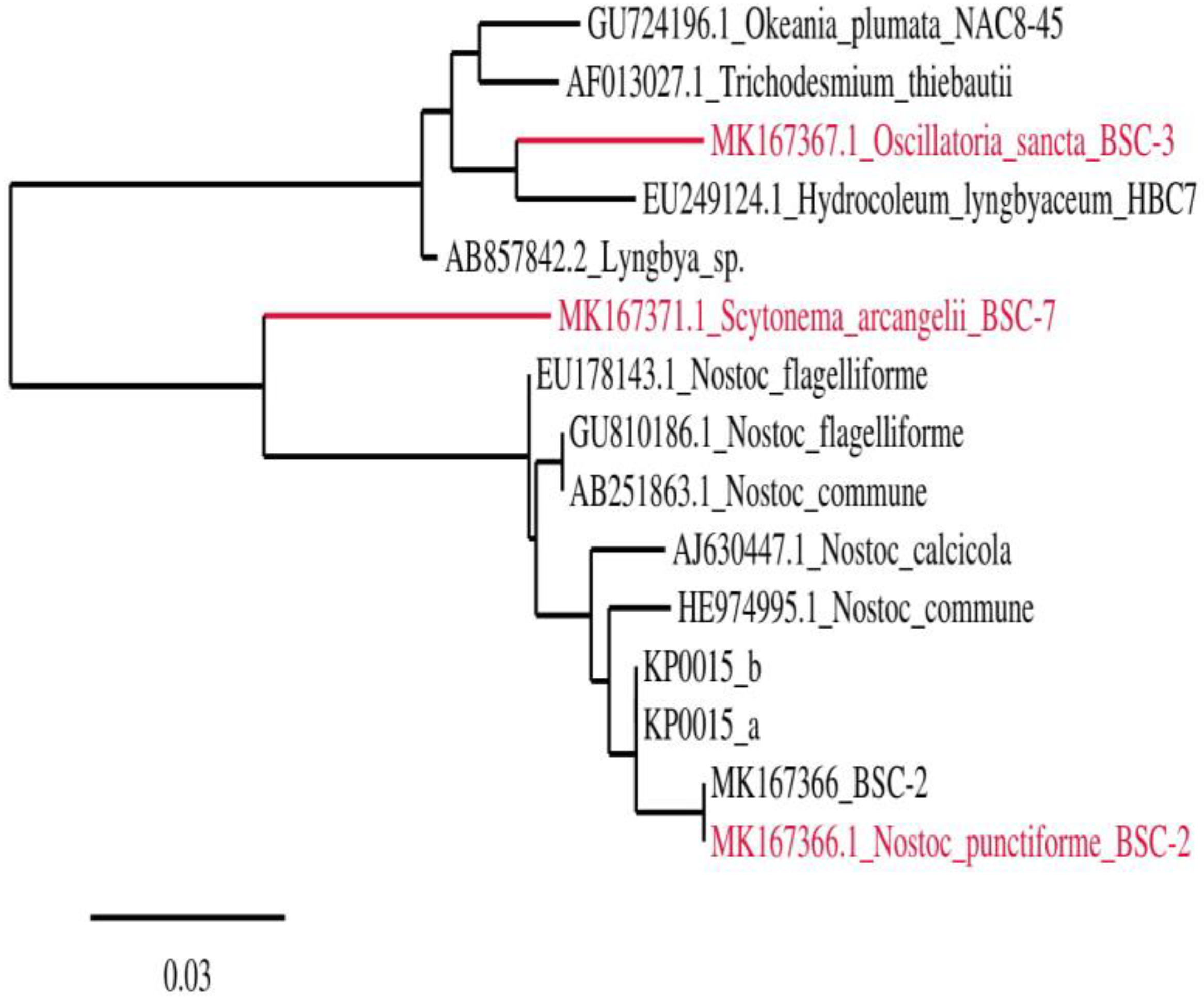
2.2. Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Exopolysaccharide Extraction
2.4. Protein and Carbohydrate Analyses of EPS
2.5. Physical Characterization of EPS
2.5.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.5.2. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
2.5.3. Antioxidant Assay
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl Assay (DPPH)
Ferric Ion Reducing Antioxidant Power Assay (FRAP)
2.5.4. Flocculation Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
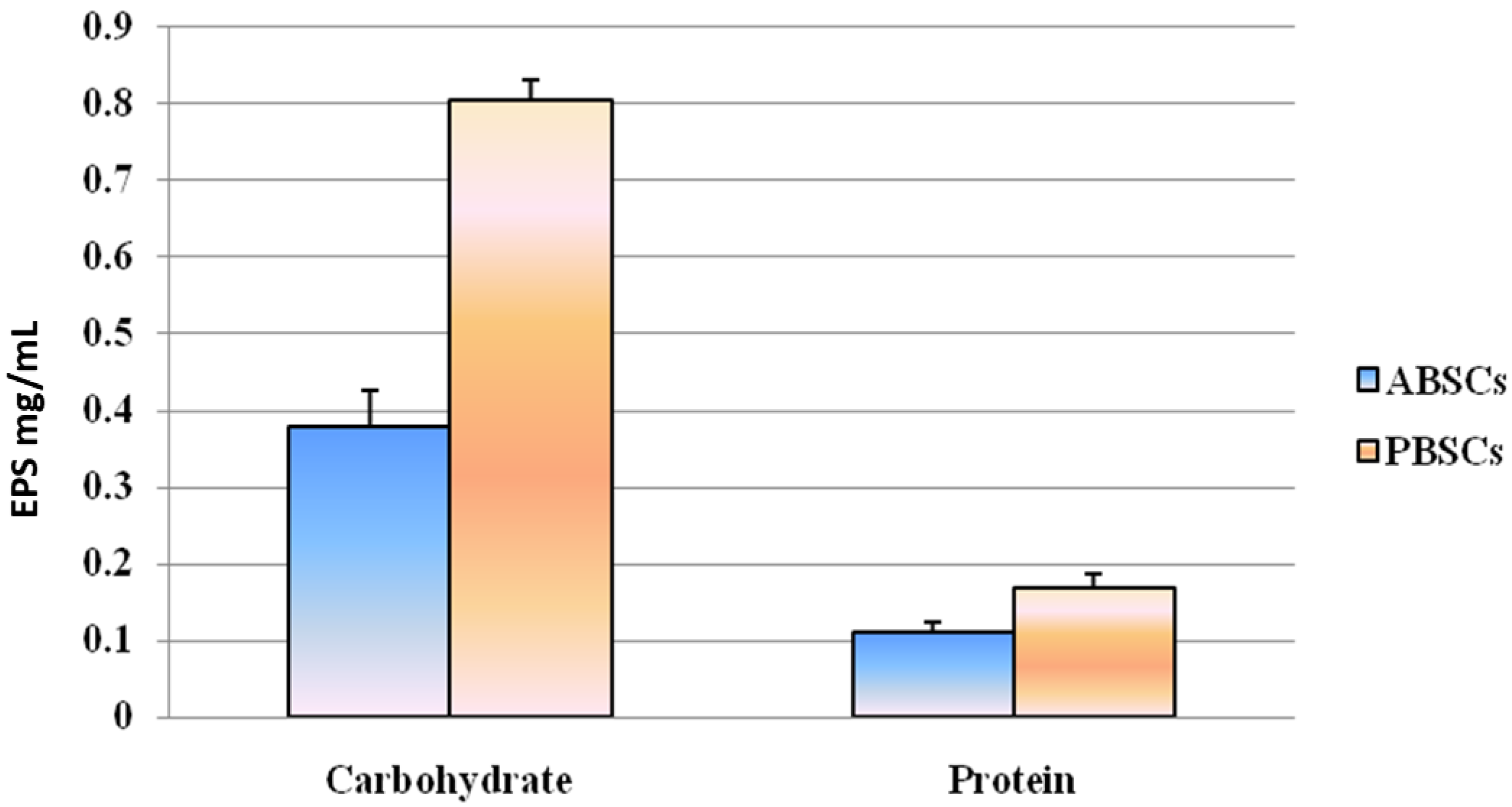
3.1. Protein and Carbohydrate Analyses of EPSs
3.2. FTIR
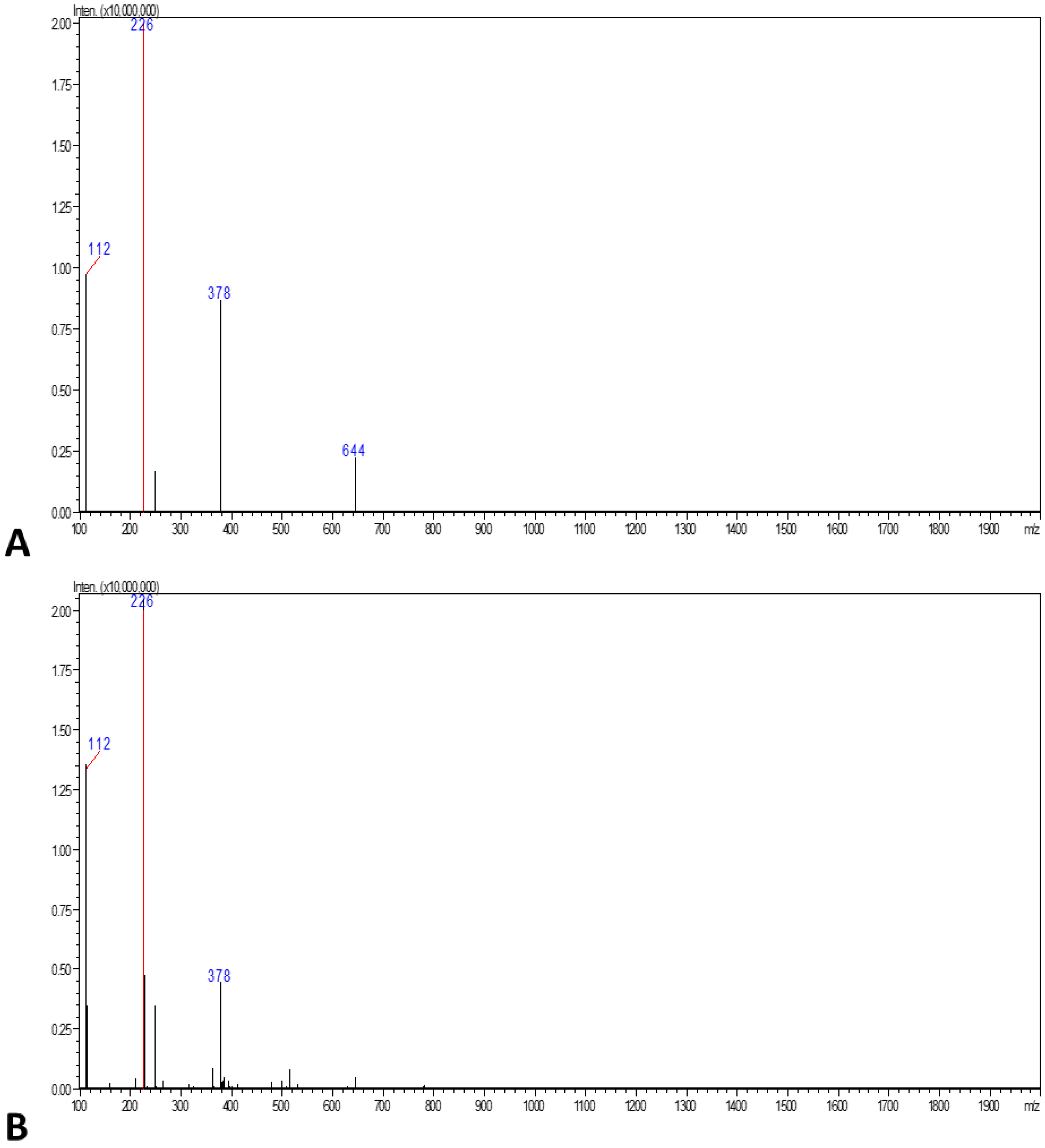
3.3. LC-MS
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
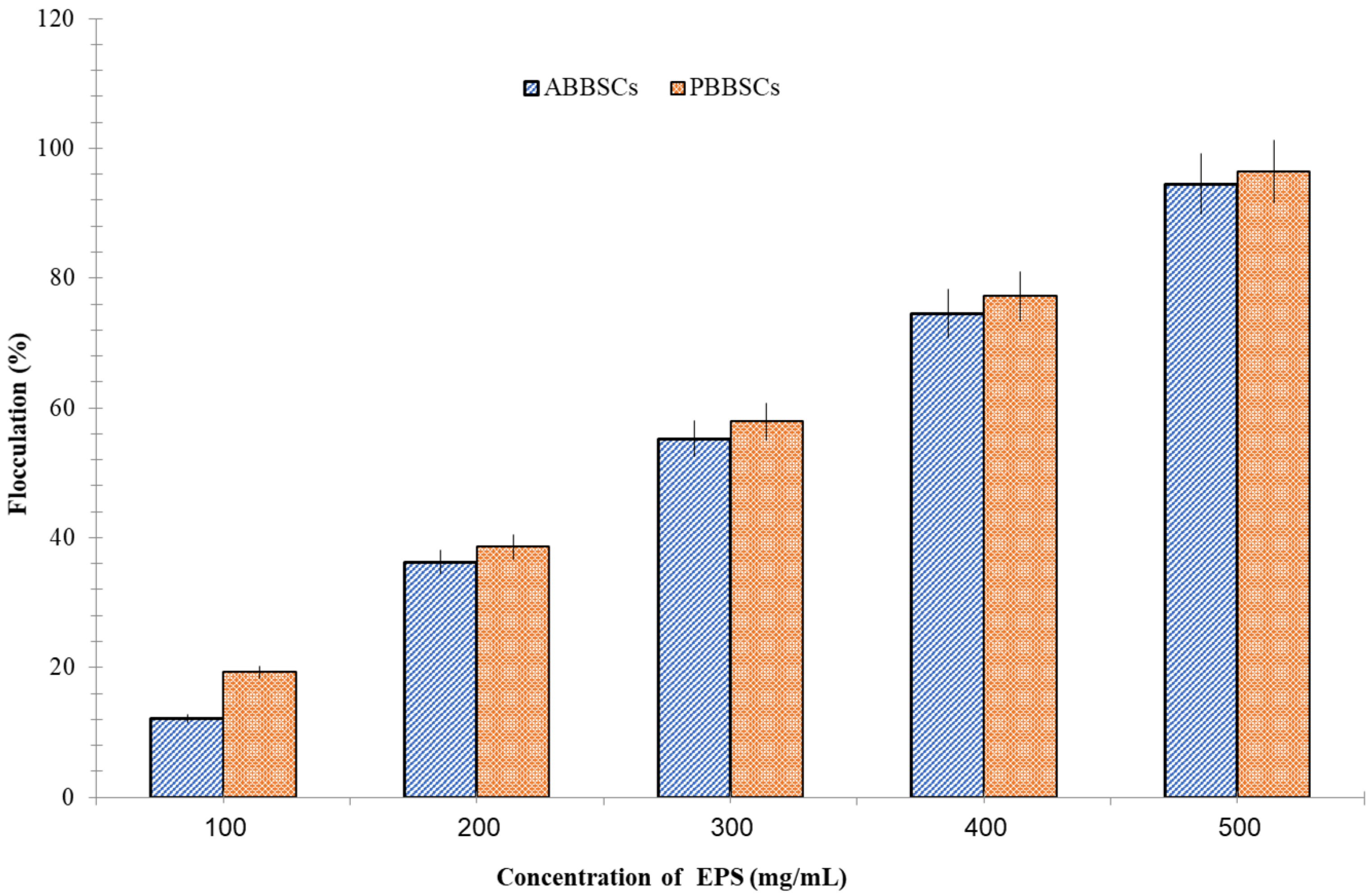
3.5. Flocculation Property
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhagobaty, R.K.; Joshi, S.R. Fungal endophytes of five medicinal plants prevalent in the traditionally preserved ‘Sacred forests’ of Meghalaya, India. For. Sci. Technol. 2011, 7, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth, M.; Muruganantham, P.; Jeevanantham, G.; Hussain, J.M.; Balaguru, B.; Ahamed, A.K. Distribution of cyanobacteria in biological soil crusts in sacred groves forest of Ariyalur and Pudukottai districts, Tamil Nadu, India. Res. J. Life Sci. Bioinform. Pharm. Chem. Sci. 2017, 3, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Vinoth, M.; Sivasankari, S.; Ahamed, A.K.K.; Al-Arjani, A.B.F.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Baskar, K. Biological soil crust (BSC) is an effective biofertilizer on Vigna mungo (L.). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.; Madamwar, D. Partial characterization of extracellular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: Ecological function and impact on soil aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Ray, A.; Garg, N.; Madamwar, D. Characterization of the extracellular polysaccharide produced by a marine cyanobacterium, Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142, and its exploitation toward metal removal from solutions. Curr. Microbiol. 2000, 40, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Noda, H.; Amano, H.; Zhuaug, C.; Mizuno, T.; Ito, H. Antitumor activity and immunological properties of marine algal polysaccharides, especially fucoidan, prepared from Sargassumthunbergii of Phaeophyceae. Anticancer Res. 1993, 13, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero, A.; Muro-Pastor, A.M.; Flores, E. Nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Das, S. Screening, production, optimization and characterization of cyanobacterial polysaccharide. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1971–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. The oxidative damage theory of aging. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 2, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, R.; Shah, N.P.; Tao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, H. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of exopolysaccharides from Bifidobacterium bifidum WBIN03 and Lactobacillus plantarum R315. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7334–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentão, P.; Fernandes, E.; Carvalho, F.; Andrade, P.B.; Seabra, R.M.; Bastos, M.L. Antioxidative properties of cardoon (Cynaracardunculus L.) infusion against superoxide radical, hydroxyl radical, and hypochlorous acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4989–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.W. Novel and established applications of microbial polysaccharides. Trends Biotech. 1998, 16, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikachary, T.V. Cyanophyta; Indian Council of Agricultural Research: New Delhi, India, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgarand, S.M.; Theriot, E.C. Phylogeny of Aulacoseira (Bacillariophyta) based on molecules and morphology. J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, R.G. Analysis of sugars found in glycoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1966, 8, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mistry, B.D. A Handbook of Spectroscopic Data Chemistry; Oxford Book Company: Jaipur, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, H.J.; Lin, Y.H.; Yang, L.L.; Lee, M.H. Antioxidant activities of trypsin inhibitor, a 33 KDa root storage protein of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam cv. Tainong 57). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2978–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.; Strain, J. Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: Direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ormsby, A.A. The impacts of global and national policy on the management and conservation of sacred groves of India. Hum. Ecol. 2011, 39, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankari, S.; Vinoth, M.; Ravindran, D.; Baskar, K.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Abd_Allah, E.F. Efficacy of red light for enhanced cell disruption and fluorescence intensity of phycocyanin. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belnap, J.; Weber, B.; Büdel, B. Biological soil crusts as an organizing principle in dryland. In Biological Soil Crusts: An Organizing Principle in Drylands; Weber, B., Büdel, B., Belnap, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Chapter 1; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira-Grez, B.; Tam, K.; Cross, A.T.; Yong, J.W.H.; Kumaresan, D.; Nevill, P.; Farrell, M.; Whiteley, A.S. The bacterial microbiome associated with arid biological soil crusts and the biogeochemical influence of biological soil crusts upon the underlying soil. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delattre, C.; Pierre, G.; Lsoche, C.; Michaud, P. Production, extraction and characterization of microalgal and cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1159–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polysaccharides: Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility; Dumitriu, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaprakasam, S.; Mani, V.; Balasubramaniyan, N.; Abraham, D.R. Cyanobacterial Phytochromes in Optogenetics. In Epigenetics to Optogenetics—A New Paradigm in the Study of Biology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vinoth, M.; Jeevanantham, G.; Muruganantham, P.; Hussain, J.M.; Ahamed, A.K. Characterization and estimated diversity of cyanobacteria in biological soil crust in sacred grove forest of Tamil Nadu, India. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Roncero-Ramos, B.; Muñoz-Martín, M.A.; Chamizo, S.; Fernández-Valbuena, L.; Mendoza, D.; Perona, E.; Cantón, Y.; Mateo, P. Polyphasic evaluation of key cyanobacteria in biological soil crusts from the most arid region in Europe. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.F.; Ratnayake, R.R.; Meerajini, K.; Kumara, K.L.W. Antioxidant properties in some selected cyanobacteria isolated from freshwater bodies of Sri Lanka. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 4, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Hu, J.; Zhu, L. Self-flocculation as an efficient method to harvest microalgae: A mini-review. Water 2021, 13, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Philippis, R.; Vincenzini, M. Exocellular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria and their possible applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 22, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Mathivanan, K.; Govindarajan, R.K.; Uthaya Chandirika, J.; Govindasamy, C. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by bioluminescent bacteria: Characterization and evaluation of its antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Int. Nano. Lett. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamizo, S.; Mugnai, G.; Rossi, F.; Certini, G.; Philippis, R.D. Cyanobacteria inoculation improves soil stability and fertility on different textured soils: Gaining insights for applicability in soil restoration. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S. Cyanobacteria: A vital bio-agent in eco-restoration of degraded lands and sustainable agriculture. Clim. Chang. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 2, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Redmile-Gordon, M.A.; Evershed, R.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; White, R.P.; Goulding, K.W.T. Soil organic matter and the extracellular microbial matrix show contrasting responses to C and N availability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-García, V.; Ríos-Leal, E.; Calderón-Domínguez, G.; Cañizares-Villanueva, R.O.; Olvera-Ramírez, R. Detection, isolation, and characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by a strain of phormidium 94a isolated from an arid zone of Mexico. Biotech. Bioeng. 2004, 85, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattar, J.I.S.; Singh, D.P.; Jindal, N.; Kaur, N.; Singh, Y.; Rahi, P.; Gulati, A. Isolation and characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by the cyanobacteriumLimnothrixredekei PUPCCC116. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaki, J.; Matsui, Y.; Kojima, H.; Nakajima, S.; Kamei, K.; Tamesada, M. Structural analysis of monocyte activation constituents in cultured mycelia of Cordycepssinensis. Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.D. Isolation, structure, and cholesterol esterase inhibitory activity of a polysaccharide, PSA, from Cordycepssinensis. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2010, 53, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, B.; Nampoothiri, K.M. Production, purification and structural characterization of an exopolysaccharide produced by a probiotic Lactobacillus Plantarum MTCC 9510. Arch. Microbiol. 2010, 192, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnanelli, F.M.; Papini, P.; Trifoni, M.; Vegliò, F. Biosorption of metal ions on Arthrobacter sp.: Biomass characterization and biosorption modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, E.M.; Afroz, R.; Mottalib, N.; Hossain, I.; Islam, A.; Gan, S.H.; Khalil, I. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of methanolic extract of BAU Kul (Ziziphusmauritiana), an improved variety of fruit from Bangladesh. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.F.; Raanan, H.; Dai, G.Z.; Oren, N.; Berkowicz, S.; Murik, O.; Kaplan, A.; Qiu, B.S. Reading and surviving the harsh conditions in desert biological soil crust: The cyanobacterial viewpoint. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuab036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, L.; M’sakni, N.H.; Ben Ouada, H.; Bacha, H.; Roudesli, S. Partial characterization of extracellular polysaccharides produced by cyanobacteriumArthrospiraplatensis. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2009, 14, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, K.; Selva, R.; Chandrika, J.U.; Govindarajan, R.K.; Srinivasan, R.; Annadurai, G.; Duc, P.A. Biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria: Synthesis, calcination, and characterization. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unban, K.; Puangkhankham, N.; Kanpiengjai, A.; Govindarajan, R.K.; Kalaimurugan, D.; Khanongnuch, C. Improvement of polymer grade L-lactic acid production using Lactobacillus rhamnosus SCJ9 from low-grade cassava chips by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Processes 2020, 8, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, R.K.; Mathivanan, K.; Khanongnuch, C.; Srinivasan, R.; Unban, K.; Deepak, A.C.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Alarjani, K.M.; Al Qahtany, F.S. Tannin acyl-hydrolase production by Bacillus subtilis KMS2-2: Purification, characterization, and cytotoxicity studies. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, R.K.; Khanongnuch, C.; Mathivanan, K.; Shyu, D.J.; Sharma, K.P.; De Mandal, S. In-vitro biotransformation of tea using tannase produced by Enterobacter cloacae 41. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3235–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challouf, R.; Trabelsi, L.; Ben Dhieb, R.; El Abed, O.; Yahia, A.; Ghozzi, K.; Ben Ammar, J.; Omran, H.; Ben Ouada, H. Evaluation of cytotoxicity and biological activities in extracellular polysaccharides released by cyanobacterium, Arthrospiraplatensis. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
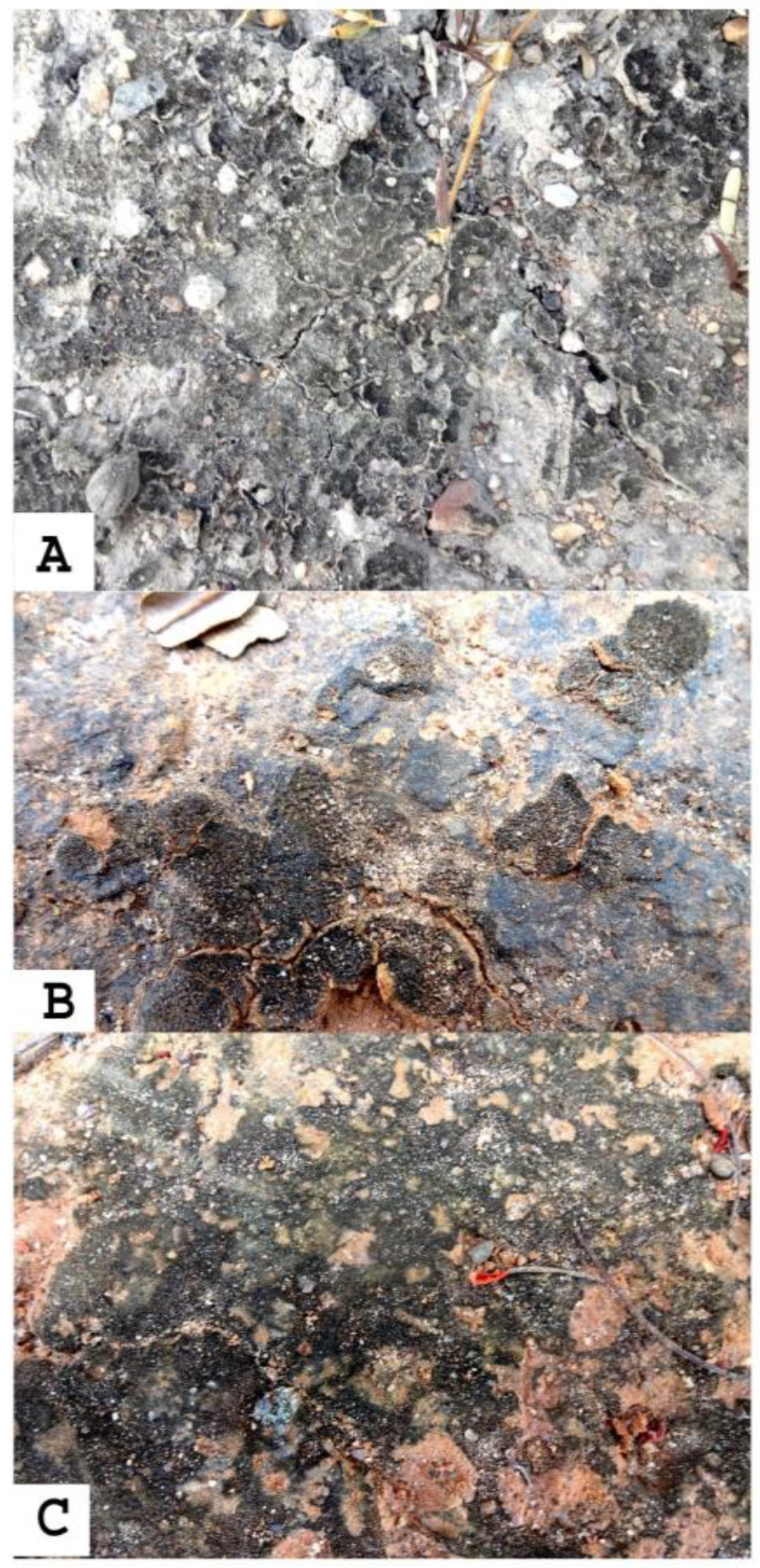





| S.NO | Cyanobacterial Species | Types of Biological Soil Crust | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABBSCs | PBBSCs | ||
| 1. | Anabaena sp. | − | + |
| 2. | Gloeocapsarupestris Kutz. | − | |
| 3. | Hapalosiphonbaroni West, W., and G., S. | + | − |
| 4. | Lyngbyakasyapii Ghose. | + | − |
| 5. | Lyngbyalachneri (Zimm.) Geitler. | + | − |
| 6. | Lyngbyarivularianum Gom. | + | − |
| 7. | Microcoleusacutissimus Gardner. | + | + |
| 8. | Microcystisaeruginosa Kutz. | + | + |
| 9. | Microcystis sp. | − | − |
| 10. | Nostocpunctiforme | − | + |
| 11. | Oscillatoria sancta (Kutz.) Gom. | + | − |
| 12. | Phormidiumfoveolarum Gom. | − | + |
| 13. | Phormidiumabronema Skuja. | − | + |
| 14. | Phormidiumangustissimum West, W., and G., S. | − | + |
| 15. | Phormidiumbohneri Sohmidle. | + | − |
| 16. | Phormidiumfoveolarum Gom. | + | − |
| 17. | Phormidium sp. | − | + |
| 18. | Phormidiumtenue (Menegh.) Gom. | − | + |
| 19. | Phormidiumusterii Schmidle. | − | + |
| 20. | Scytonemaarcangeli | + | − |
| 21. | Scytonemajulianum (Kutz.) Menegh. | + | − |
| 22. | Scytonemamillei Born. | + | − |
| 23. | Scytonemapseudopunctatum Skuja. | + | − |
| 24. | Scytonemaschmidtii Gom. | + | − |
| 25. | Scytonema sp. | + | − |
| Total | 15 | 10 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinoth, M.; Sivasankari, S.; Ahamed, A.K.K.; Alsamhary, K.I.; Al-enazi, N.M.; Abdel-Raouf, N.; Alharbi, R.M.; Govindarajan, R.K.; Ravi, G.; Alarjani, K.M.; et al. Bio-Characterization and Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Exopolysaccharides in Biofilm-Producing Cyanobacteria Isolated from Soil Crust: Exploring the Potential of Microalgal Biomolecules. Biology 2023, 12, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081065
Vinoth M, Sivasankari S, Ahamed AKK, Alsamhary KI, Al-enazi NM, Abdel-Raouf N, Alharbi RM, Govindarajan RK, Ravi G, Alarjani KM, et al. Bio-Characterization and Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Exopolysaccharides in Biofilm-Producing Cyanobacteria Isolated from Soil Crust: Exploring the Potential of Microalgal Biomolecules. Biology. 2023; 12(8):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081065
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinoth, Mani, Sivaprakasam Sivasankari, Abdul Kareem Khaleel Ahamed, Khawla Ibrahim Alsamhary, Nouf Mohammed Al-enazi, Neveen Abdel-Raouf, Reem Mohammed Alharbi, Rasiravathanahalli Kaveriyappan Govindarajan, Gangalla Ravi, Khaloud Mohammed Alarjani, and et al. 2023. "Bio-Characterization and Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Exopolysaccharides in Biofilm-Producing Cyanobacteria Isolated from Soil Crust: Exploring the Potential of Microalgal Biomolecules" Biology 12, no. 8: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081065
APA StyleVinoth, M., Sivasankari, S., Ahamed, A. K. K., Alsamhary, K. I., Al-enazi, N. M., Abdel-Raouf, N., Alharbi, R. M., Govindarajan, R. K., Ravi, G., Alarjani, K. M., & Sholkamy, E. N. (2023). Bio-Characterization and Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Exopolysaccharides in Biofilm-Producing Cyanobacteria Isolated from Soil Crust: Exploring the Potential of Microalgal Biomolecules. Biology, 12(8), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081065







