Evolutionary Shift of Insect Diapause Strategy in a Warming Climate: An Intra-Population Evidence from Asian Corn Borer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Location and Host Plant Cultivation
2.2. Assessment of ACB Voltinism
2.2.1. ACB Moth Collection
2.2.2. ACB Infestation and Diapause Survey
2.2.3. Modeling Incidence of Diapause
2.3. Phenology
2.3.1. Modeling First Moth Flights
2.3.2. Modelling and Predicting Second and Third Flights
3. Results
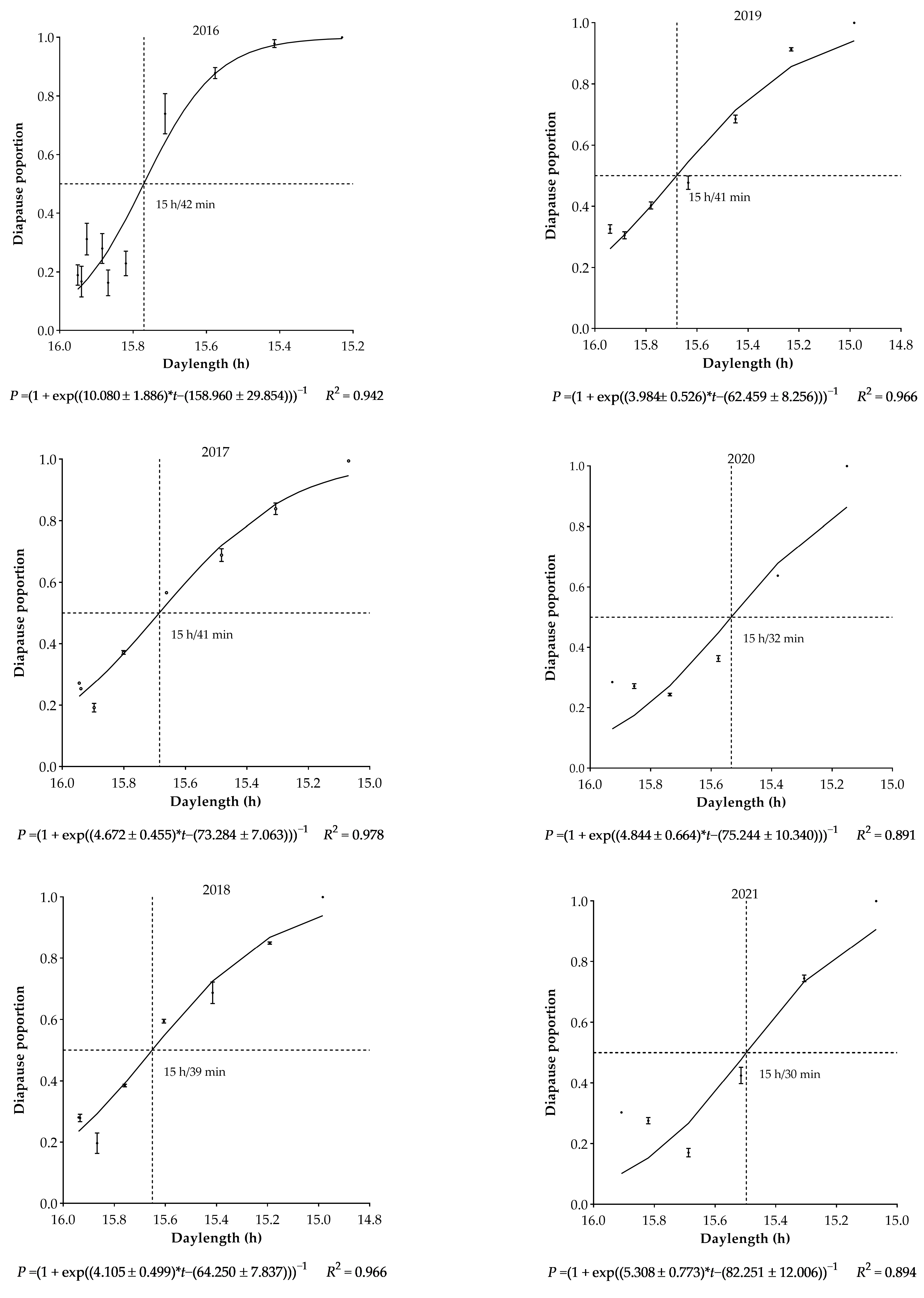
3.1. Intra-Population Variation of Diapause
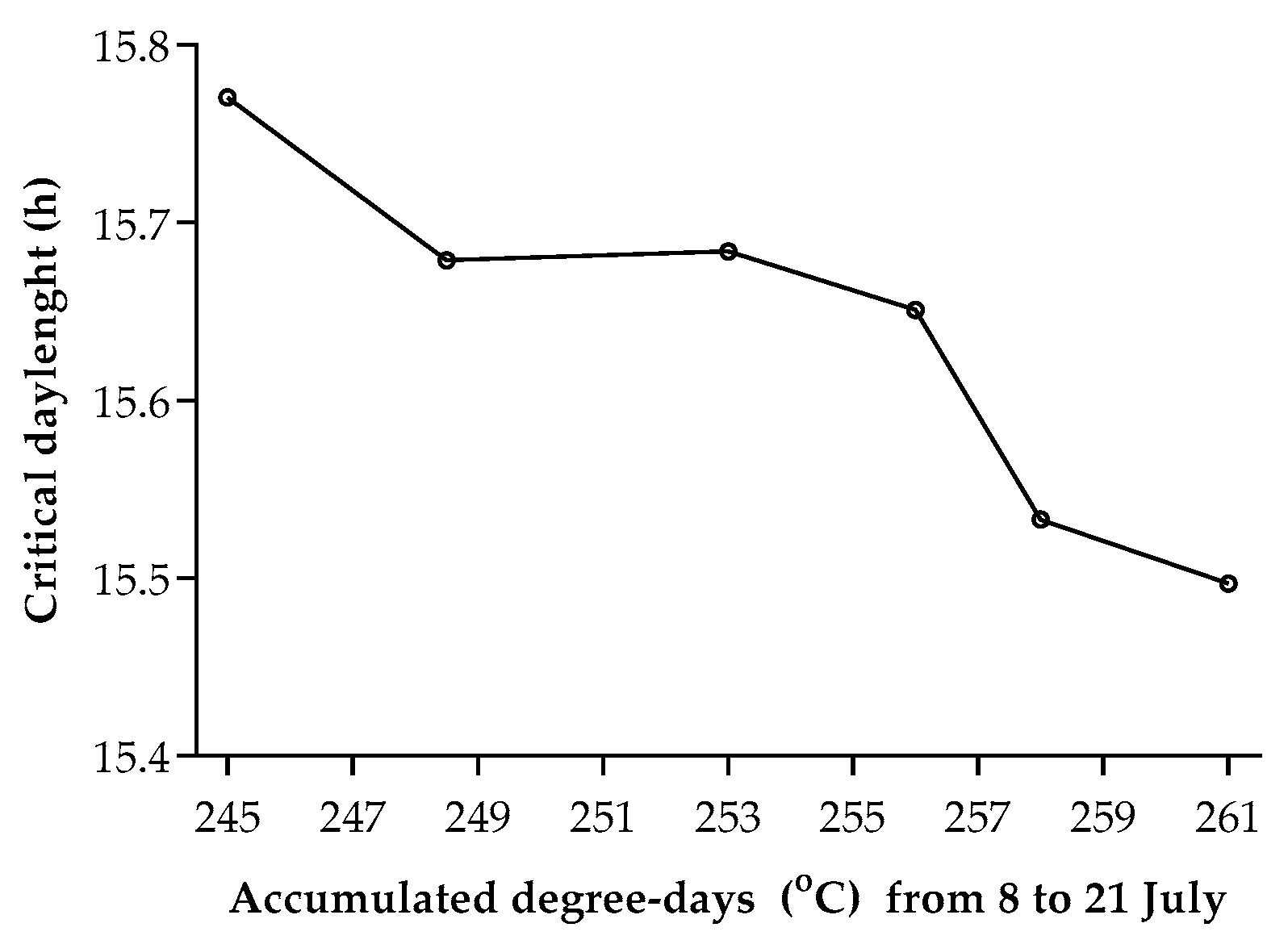
3.2. Climate-Induced Population Diapause Shift
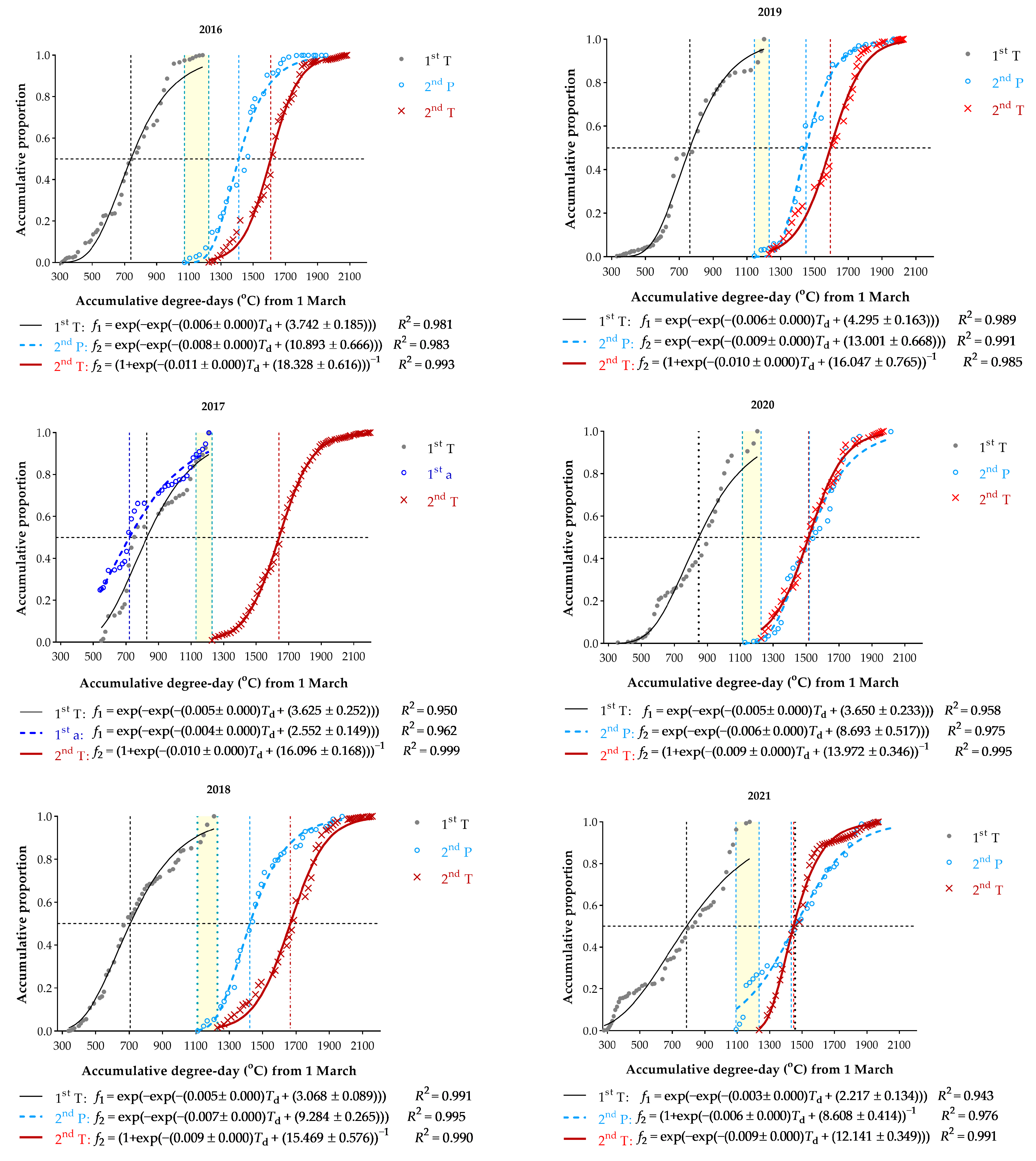
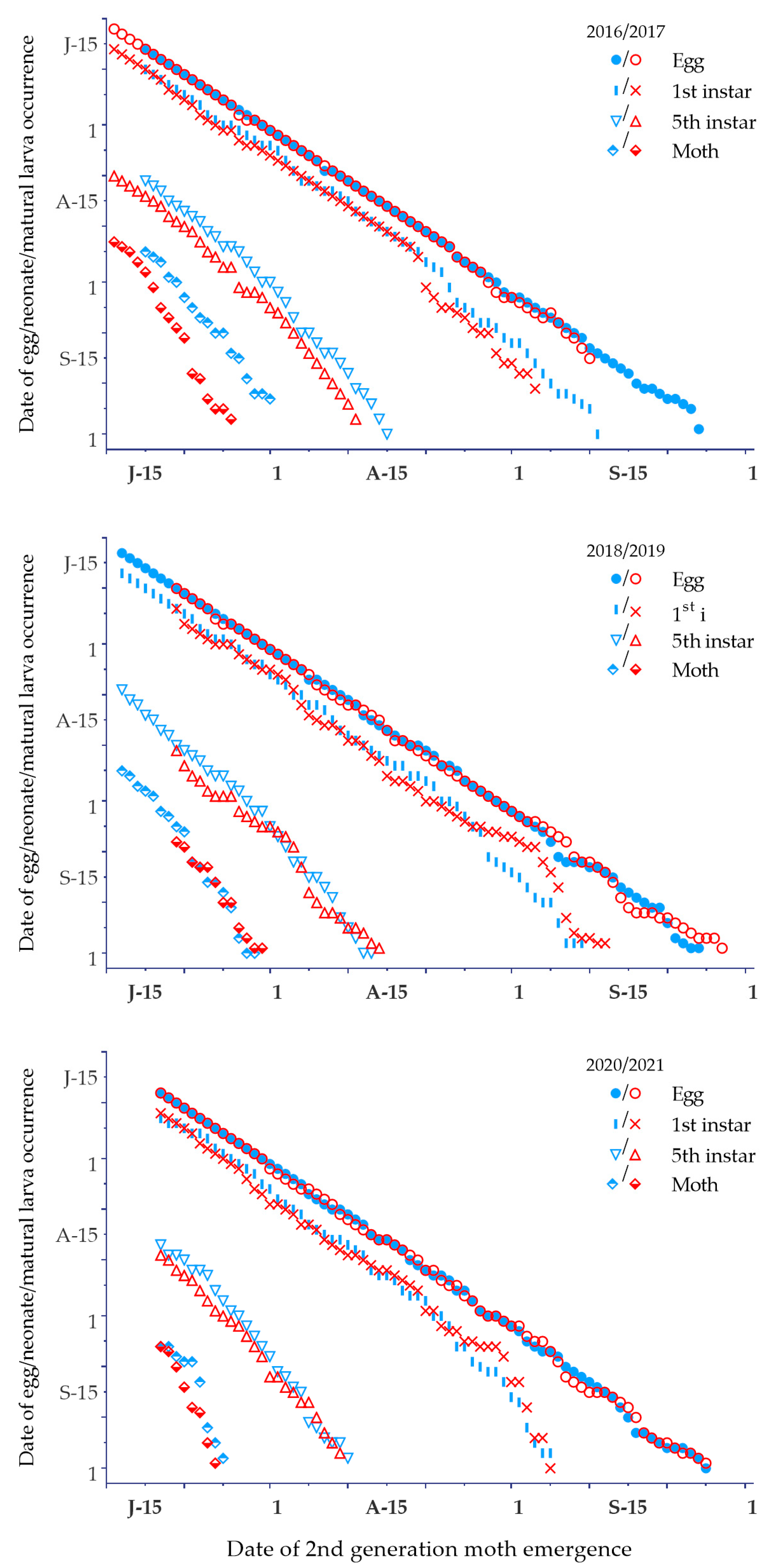
3.3. Spring Moth Emergence
3.4. Phenological Plasticity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, G.; Ma, C.S. Potential distribution of invasive crop pests under climate change: Incorporating mitigation responses of insects into models. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 49, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, C.D.; Hemming, D.; Baker, R.; Everatt, M.; Eyre, D.; Korycinska, A. A novel approach for exploring climatic factors limiting current pest distributions: A case study of Bemisia tabaci in north-west Europe and assessment of potential future establishment in the United Kingdom under climate change. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.P.; Ragland, G.J.; Assour, L.; Powell, T.H.Q.; Hood, G.R.; Emrich, S.; Nosil, P.; Feder, J.L. Experimental evidence of genome-wide impact of ecological selection during early stages of speciation-with-gene-flow. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.S.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, F.; Chang, X.Q.; Xing, K.; Zhu, L.; Ma, G.; Yang, H.P.; Rudolf, V.H.W. Climate warming promotes pesticide resistance through expanding overwintering range of a global pest. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Guillen, R.A.; Cordoba-Aguilar, A.; Hansson, B.; Ott, J.; Wellenreuther, M. Evolutionary consequences of climate-induced range shifts in insects. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2016, 91, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tito, R.; Vasconcelos, H.L.; Feeley, K.J. Global climate change increases risk of crop yield losses and food insecurity in the tropical Andes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, e592–e602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C.; Ryrholm, N.; Stefanescu, C.; Hill, J.K.; Thomas, C.D.; Descimon, H.; Huntley, B.; Kaila, L.; Kullberg, J.; Tammaru, T.; et al. Poleward shifts in geographical ranges of butterfly species associated with regional warming. Nature 1999, 399, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altermatt, F. Climatic warming increases voltinism in European butterflies and moths. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Vertedor, D.; Ferrero-García, J.J.; Torres-Vila, L.M. Global warming affects phenology and voltinism of Lobesia botrana in Spain. Agric. For. Entomol. 2010, 12, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckli, S.; Hirschi, M.; Spirig, C.; Calanca, P.; Rotach, M.W.; Samietz, J. Impact of climate change on voltinism and prospective diapause induction of a global pest insect—Cydia pomonella (L.). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbauer, M.J.; Kriticos, D.J.; Lukacs, Z.; Clarke, A.R. Modelling a forest lepidopteran: Phenological plasticity determines voltinism which influences population dynamics. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 198, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, A.M.; Appelberg, G.; Harding, S.; Barring, L. Spatio-temporal impact of climate change on the activity and voltinism of the spruce bark beetle, Ips typographus. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, C.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Huey, R.B.; Sheldon, K.S.; Ghalambor, C.K.; Haak, D.C.; Martin, P.R. Impacts of climate warming on terrestrial ectotherms across latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6668–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braune, E.; Richter, O.; Sondgerath, D.; Suhling, F. Voltinism flexibility of a riverine dragonfly along thermal gradients. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Sun, J.R.; Shi, W.P.; Harwood, J.D.; Monticelli, L.S.; Tan, X.L.; Chen, J.L. Effects of field simulated warming on feeding behavior of Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) and host defense systems. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.L.; Tan, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.X.; Zhang, Y.; Harwood, J.D.; Chen, J.L. Effects of simulated climate warming on the population dynamics of Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) and its parasitoids in wheat fields. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 3252–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, L.J.; Macfadyen, S.; Hoffmann, A.A. Predicting the effects of climate change on natural enemies of agricultural pests. Biol. Control 2010, 52, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, C.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Tigchelaar, M.; Battisti, D.S.; Merrill, S.C.; Huey, R.B.; Naylor, R.L. Increase in crop losses to insect pests in a warming climate. Science 2018, 361, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Yu, Z.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Siemann, E.; Wan, S.; Ding, J. Elevated temperature reduces wheat grain yield by increasing pests and decreasing soil mutualists. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalin, P. Diapause induction and termination in a commonly univoltine leaf beetle (Phratora vulgatissima). Insect Sci. 2011, 18, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koštál, V. Insect photoperiodic calendar and circadian clock: Independence, cooperation, or unity? J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 538–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, M.J.; Tauber, C.A. Insect seasonality: Diapause maintenance, termination, and postdiapause development. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1976, 21, 81–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, M.J.; Tauber, C.A.; Masaki, S. Seasonal Adaptations of Insects; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; p. 411. [Google Scholar]
- Stalhandske, S.; Gotthard, K.; Leimar, O. Winter chilling speeds spring development of temperate butterflies. J. Anim. Ecol. 2017, 86, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.J.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, C.; Xue, F.S. Optimal low temperature and chilling period for both summer and winter diapause development in Pieris melete: Based on a similar mechanism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalhandske, S.; Lehmann, P.; Pruisscher, P.; Leimar, O. Effect of winter cold duration on spring phenology of the orange tip butterfly, Anthocharis cardamines. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 5509–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wei, X.T.; Xiao, H.J.; He, H.M.; Xia, Q.W.; Xue, F.S. Diapause induction and termination in Hyphantria cunea (Drury) (Lepidoptera: Arctiinae). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xia, Q.W.; Fu, S.; Wu, X.F.; Xue, F.S. Effect of photoperiod and temperature on the intensity of pupal diapause in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2014, 104, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.W.; Cai, W.Q. A preliminary report on the photoperiodic response of the Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) in Jiangsu. Acta Entomol. Sin. 1964, 13, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.R.; He, K.L. Asian Corn Borer and Its Integrated Management; Golden Shield Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.Q. Evolution of Voltine Biotypes of Asian Corn Borer and Their Response to Climate Warming. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, D.R. On the photoperiodic reactions in different voltinism ecotypes of Asian corn borer. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 2000, 27, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.L.; Chen, C.; Xiao, L.; Xia, Q.W.; Hu, L.T.; Xue, F.S. Geographical variation and inheritance of the photoperiodic response controlling larval diapause in two distinct voltine ecotypes of the Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis. Physiol. Entomol. 2013, 38, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Q.; Zhang, H.G.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L. Effects of photoperiod and temperature on diapause induction in Ostrinia furnacalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2013, 56, 996–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.W.; Chen, C.; Tu, X.Y.; Yang, H.Z.; Xue, F.S. Inheritance of photoperiodic induction of larval diapause in the Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis. Physiol. Entomol. 2012, 37, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.D.; Chen, S.X.; Qin, J.G. Vertical distribution of Ostrinia furnacalis. Plant Prot. Technol. Ext. 2002, 22, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, H.K.; Bai, S.X.; Gu, Z.L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.Q.; Li, A.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.Y. Population dynamics and major damage region of Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis in Dehong Prefecture of Yunnan Province. Plant Prot. 2016, 42, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.F.; Chen, P.; Wang, R.; Lian, M.L.; Xia, Z.H. The influence of photoperiod and temperature on the diapause of the Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée). Acta Entomol. Sin. 1984, 27, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Chen, C.; Xiao, L.; He, H.; Xue, F. Inheritance of diapause in crosses between the northernmost and the southernmost strains of the Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Xie, W.M.; Yang, G.H. A preliminary study on the ecotypes of Ostrina furnacalis in North China. J. Maize Sci. 1992, 1, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.H.; Zhang, J.X. A preliminary study on the diapause ratios of different generations of the natural population of Asian corn borer in Beijing. Acta Agric. Univ. Pekin. 1983, 1, 107–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Li, J.P.; Wang, Y.S. Preliminary study on voltinism types of Ostrinia furnacalis (ACB). Maize Sci. 1995, 3, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.Q.; Wang, L.X.; Zhang, T.T.; Bai, S.X.; Wang, K.Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Hutchison, W.D. Voltine ecotypes of the Asian corn borer and their response to climate warming. Insects 2021, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikten, C.; Skoda, S.R.; Hunt, T.E.; Molina-Ochoa, J.; Foster, J.E. Genetic variation and inheritance of diapause induction in two distinct voltine ecotypes of Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2011, 104, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, B.S.; Sumerford, D.V.; Hellmich, R.L. Geographic and voltinism differentiation among North American Ostrinia nubilalis (European corn borer) mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase haplotypes. J. Insect Sci. 2004, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvin, D.D.; Song, P.Z. Variability in postdiapause development periods of geographically separate Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) populations in Pennsylvania. Environ. Entomol. 1994, 23, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, K.S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Coates, B.S. Influence of voltine ecotype and geographic distance on genetic and haplotype variation in the Asian corn borer. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 10244–10257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showers, W.B.; Chiang, H.C.; Keaster, A.J.; Hill, R.E.; Reed, G.L.; Sparks, A.N.; Musick, G.J. Ecotypes of the European corn borer in North America. Environ. Entomol. 1975, 4, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.L.; Tang, J.J.; Chen, C.; He, H.M.; Gao, Y.L.; Xue, F.S. Diapause incidence and critical day length of Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis) populations exhibit a latitudinal cline in both pure and hybrid strains. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.R.; Ni, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L. Effects of photoperiod and temperature on diapause induction in Conogethes punctiferalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Insect Sci. 2014, 21, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D.S. Insect photoperiodism: Effects of temperature on the induction of insect diapause and diverse roles for the circadian system in the photoperiodic response. Entomol. Sci. 2014, 17, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D.S. The temperature-compensated photoperiodic clock ‘programming’ development and pupal diapause in the flesh-fly, Sarcophaga argyrostoma. J. Insect Physiol. 1971, 17, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Jiang, X.F.; Luo, L.Z. Effects of photoperiod and temperature on diapause induction in the beet webworm Loxostege sticticalis Linnaeus (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2009, 52, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.L.; Xue, F.S.; Wang, G.H.; Han, R.D.; Ge, F. Photoperiodic response of diapause induction in the pine caterpillar, Dendrolimus punctatus. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2005, 117, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T. Geographic variation in critical photoperiod for diapause induction and its temperature dependence in Hyphantria cunea Drury (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Oecologia 1997, 111, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, D.R. On the relationship between voltinism and development duration of Asian corn borer in Jilin Province. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 1999, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhang, R.; Gui, C.M.; Wang, Y.S. Research on biology of the Asian corn borer—I. Relationship between development and photoperiod response. Jilin Agric. Sci. 1980, 57, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cheu, S.P.; Chow, D.R.; Tung, H.F.; Lee, C.H. Yield reduction of corn caused by the European corn borer at different developmental stages. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 1964, 3, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.R.; Song, Y.Y.; Li, B.X.; Zhang, G.Y.; Gao, S.L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.S.; Xie, W.M.; et al. Studies on behavior of dispersal and possibility of migration in adult overwintering generation Asian corn borer by using release-and-recapture technique. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 1994, 21, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.R.; Song, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Zhang, G.Y.; Liu, Y. A release-and-recapture study on dispersal of adults of first and second generation Asian corn borer in north China. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 1995, 22, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.Y.; Cui, C.Y.; Wang, Y.W. Methodology for predicting and forecasting population density of Asian corn borer. J. Qiqihar Norm. Univ. 1979, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y. Control tactics for against Asian corn borer based on diapause site. Agric. Sci. Lett. 1952, 52, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.M. A study on the corn borers. Acta Entomol. Sin. 1959, 9, 528–539. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.M. Forecast and control of Asian corn borer in Jilin Province. J. Maize Sci. 1996, 4, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.J.; Yuan, Q.C.; Jin, S.F.; Gong, D.Y.; Wu, Z.Q.; Zhang, R.L. The forecast of emergence on the first generation adults of the corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée), by multi-variate equation. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 1986, 13, 78, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Lei, C.P.; Sun, H.; Zhang, T.S.; Dong, H.; Qian, H.T.; Cong, B. Effects of global warming on generations of Ostrinia furnacalis in Shenyang Region. J. Maize Sci. 2014, 22, 137–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, G.H.; Li, L.J.; Liu, H.W.; Wang, Y.Z. The occurrence of the Asian corn borer in Jilin Province. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 2005, 32, 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.D.; Chen, S.X.; Qin, J.G. Studies on correlation between the quantity of hibernant larva and the harm level of 1st generation of Asian corn borer. J. Zhangjiakou Agric. Coll. 2002, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.C.; Meng, X.W.; Wang, X.Q.; Li, F.S. A study on the interactions of microsporidia-Asian corn borer-corn in univotine ACB area of Northeastern China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1991, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.P.; Xie, W.M.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.S.; Yang, G.H. Key factors affecting long-term forecast of 1st Asian corn borer emergence size in Jilin Province: I. Relation of emergency size with natural enemy and overwinter population size. J. Maize Sci. 1995, 3, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.Y.; Liang, Y.C. A study on the technique for predicting and forecasting the population levels of corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) in Heilongjiang Province of China. In Proceedings of the XIV Symposium of the International Working Group on Ostrinia (IWGO), Beijing, China, September 1986; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, S.X.; Li, L.J.; Chen, L.L.; Chang, X.; Zhang, G.H. Generation distribution change of the Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) in Jilin Province. J. Plant Prot. 2015, 42, 978–984. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.X.; Li, D.S.; Luo, B.J.; Zhao, X.M.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, M.; Jiang, X.J.; He, K.L. The effectiveness of releasing different Trichogramma species to control the Asian corn borer. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 56, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.L.; Zhou, D.R.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wen, L.P.; Bai, S.X. On the damage and control tactics of Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) in sweet corn field. Acta Phys. Sin. 2002, 29, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.Y.; Liang, Y.C.; Zhang, G.Z. A study on the technique for predicting and forecasting the population levels of corn borer. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1985, 18, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Lin, E.; Ma, S.M.; Ju, H.; Guo, L.P.; Xiong, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.L. Adaptation of agriculture to warming in Northeast China. Clim. Chang. 2007, 84, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.L.; Yokozawa, M.; Xu, Y.L.; Hayashi, Y.; Zhang, Z. Climate changes and trends in phenology and yields of field crops in China, 1981-2000. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 138, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Yang, X.G.; Hubbard, K.G.; Lin, X.M. Maize potential yields and yield gaps in the changing climate of northeast China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 3441–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.C.; Chen, F.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Gao, Q.; Yang, X.L.; Yuan, L.X.; Zhang, F.S.; Mi, G.H. Modern maize hybrids in Northeast China exhibit increased yield potential and resource use efficiency despite adverse climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Y.L.; Lin, E.D. Climate change and its impacts in Northeast China. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2007, 23, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Zhang, F.; Lu, X.; Babendreier, D. Mass rearing and release of Trichogramma for biological control of insect pests of corn in China. Biol. Control 2014, 68, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.R.; Wen, L.P.; Song, Y.Y. Methodologies and criterions for evaluating maize resistance to the Asian corn borer. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2000, 31, 439–443. [Google Scholar]
- Tobin, P.C.; Nagarkatti, S.; Saunders, M.C. Phenology of grape berry moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in cultivated grape at selected geographic locations. Environ. Entomol. 2003, 32, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.M. Estimation of temperature threshold for development in Asian corn borer. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 1988, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Q.; Xin, Y.F. Studies on the persistent times and thermal constants of Asian maize borer Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) in different voltinism in Shenyang area. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2000, 31, 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Yang, K.J.; Zhao, C.J.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.W.; Li, X.N. The occurrence regularity of Ostrinia furnacalis in the midwest of Heilongjiang Province. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 2013, 7, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.P.; Lu, X.; Xie, W.M.; Wang, Y.S.; Yang, G.H. Key factors affecting long-term forecast of 1st Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis) emergency size in Jilin Province: II. Relation of emergency size with precipitation and overwinter population size. J. Maize Sci. 1995, 3, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, C.E.; Rice, M.E.; Calvin, D.D.; Van Duyn, J.W.; Shower, W.B.; Hutchison, W.D.; Witkowski, J.F.; Higgins, R.A.; Onstad, D.W.; Dively, G.P. European Corn Borer: Ecology and Management; North Central Regional Extension Publication No. 327; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.F. Study on Generation Spatial Pattern and Hardiness of Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) in Northeastern China; Shenyang Agricultural University: Shenyang, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Ge, Y.F.; Hu, X.; Dong, A.S.; Zou, C.S.; Yang, K.J.; Wang, L.Y. Occurrence of dynamics of Ostrinia furnacalis in Nengjiang region of Heilogjiang Province and the release of Trichogrmma dendrolimi for its control. Plant Prot. 2019, 45, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuthnot, K.D. Strains of the European corn borer in the United States. Tech. Bull. 1944, 869, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.Y.; Qin, Q.L.; Yang, Y.Z.; Huang, D.L. The effects of some factors on the diapause induction of Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2000, 20, 620–623. [Google Scholar]
- McLeod, D.G.R. Genetics of diapause induction and termination in the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), in southwestern Ontario. Can. Entomol. 1978, 110, 1351–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Xia, Q.W.; Chen, C.; Kuang, X.J.; Xue, F.S. Geographic variation in longevity and fecundity of the Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) (Lepidoptera, Crambidae). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 4160–4165. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Song, Y.Y.; He, K.L.; Gao, Y.X. Effects of different combinations of temperature and humidity on fecundity and longevity of the adult Asian corn borer. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1998, 41, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.B.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Dennehy, T.J.; Patin, A.L.; Bartlett, A.C. Development time and resistance to Bt crops. Nature 1999, 400, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.T. Biology and Genetic Analysis of Cry1Ab Resistant Asian Corn Borer (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae); Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Liu, K.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, M.; He, K. Evolutionary Shift of Insect Diapause Strategy in a Warming Climate: An Intra-Population Evidence from Asian Corn Borer. Biology 2023, 12, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060762
Wang L, Liu K, Zhao X, Zhang T, Yuan M, He K. Evolutionary Shift of Insect Diapause Strategy in a Warming Climate: An Intra-Population Evidence from Asian Corn Borer. Biology. 2023; 12(6):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060762
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lianxia, Kaiqiang Liu, Xiumei Zhao, Tiantao Zhang, Ming Yuan, and Kanglai He. 2023. "Evolutionary Shift of Insect Diapause Strategy in a Warming Climate: An Intra-Population Evidence from Asian Corn Borer" Biology 12, no. 6: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060762
APA StyleWang, L., Liu, K., Zhao, X., Zhang, T., Yuan, M., & He, K. (2023). Evolutionary Shift of Insect Diapause Strategy in a Warming Climate: An Intra-Population Evidence from Asian Corn Borer. Biology, 12(6), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060762






