Invasive Fish and Sea Urchins Drive the Status of Canopy Forming Macroalgae in the Eastern Mediterranean
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
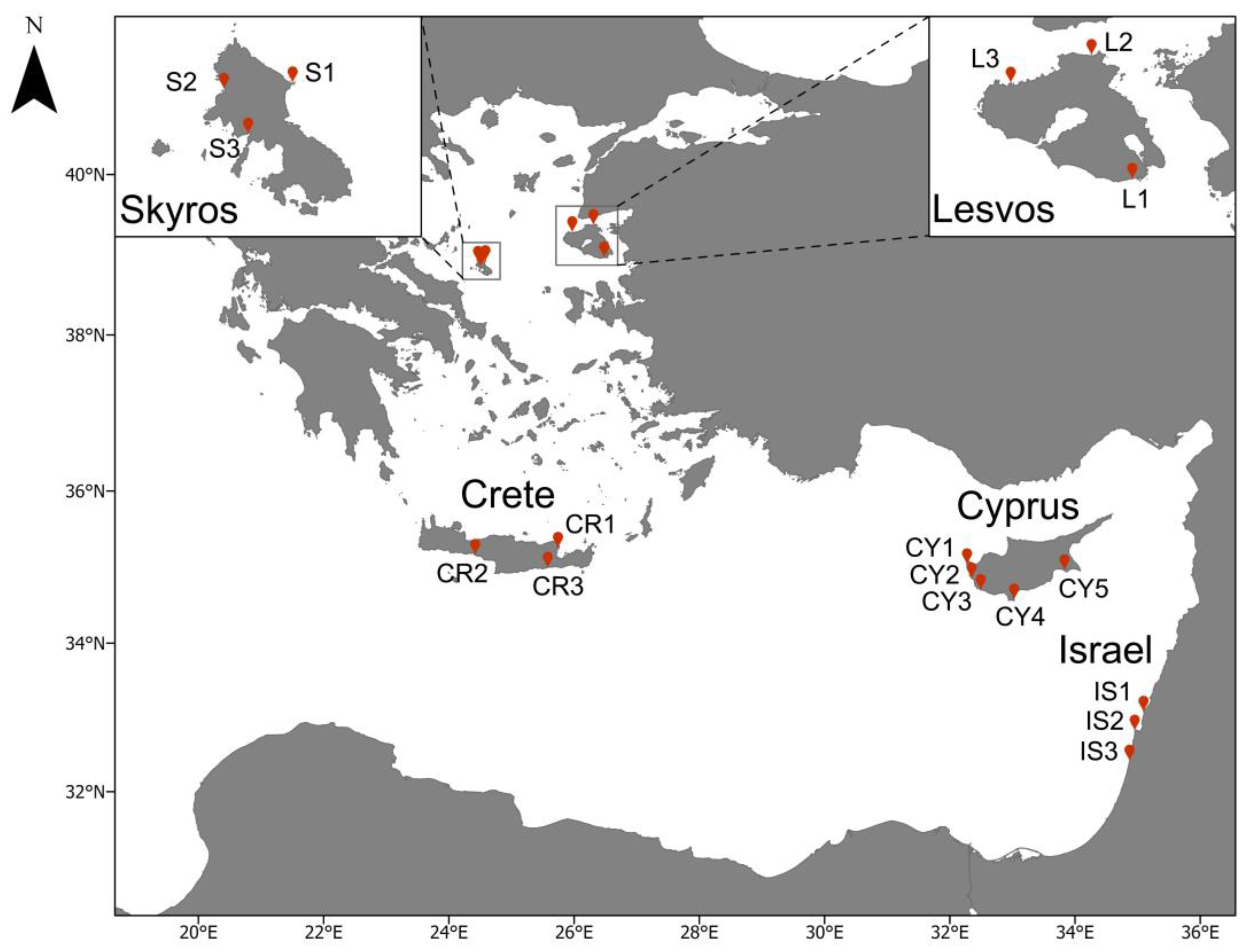
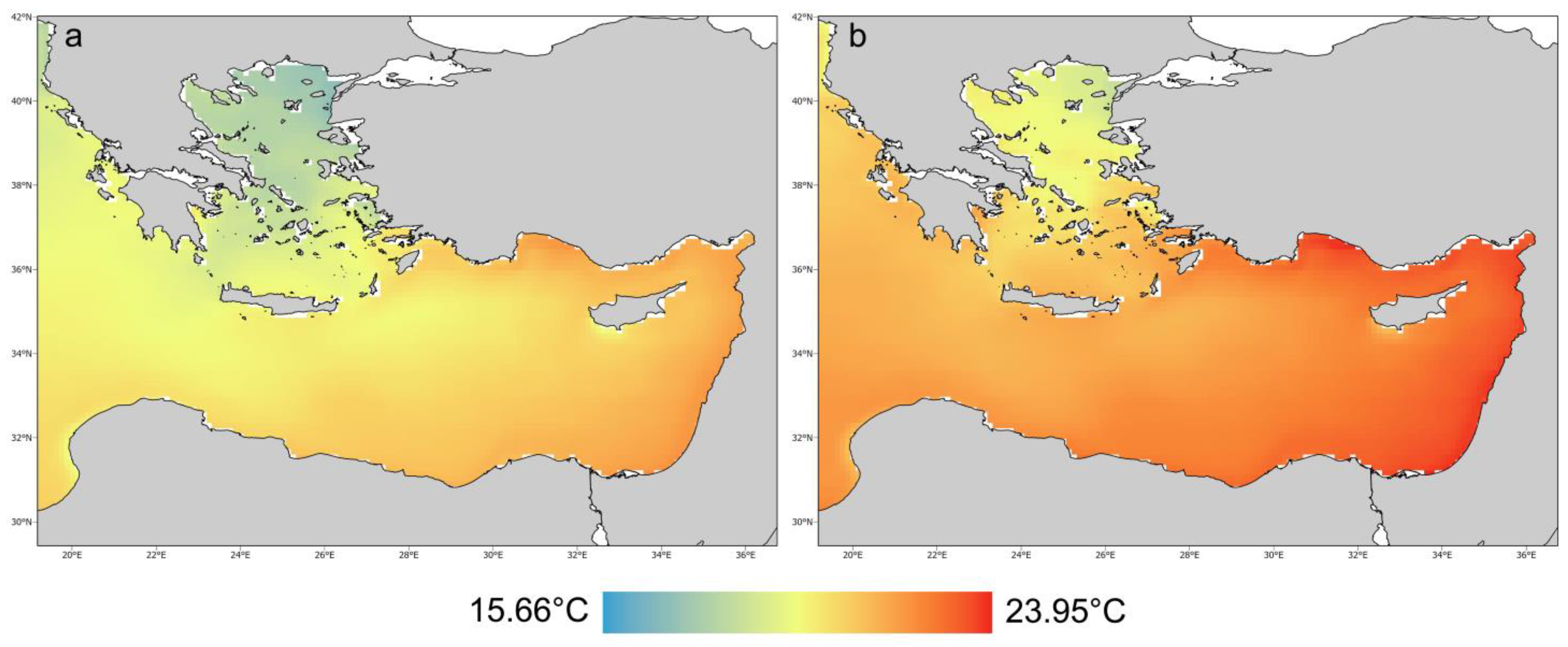
2.1. Study Area
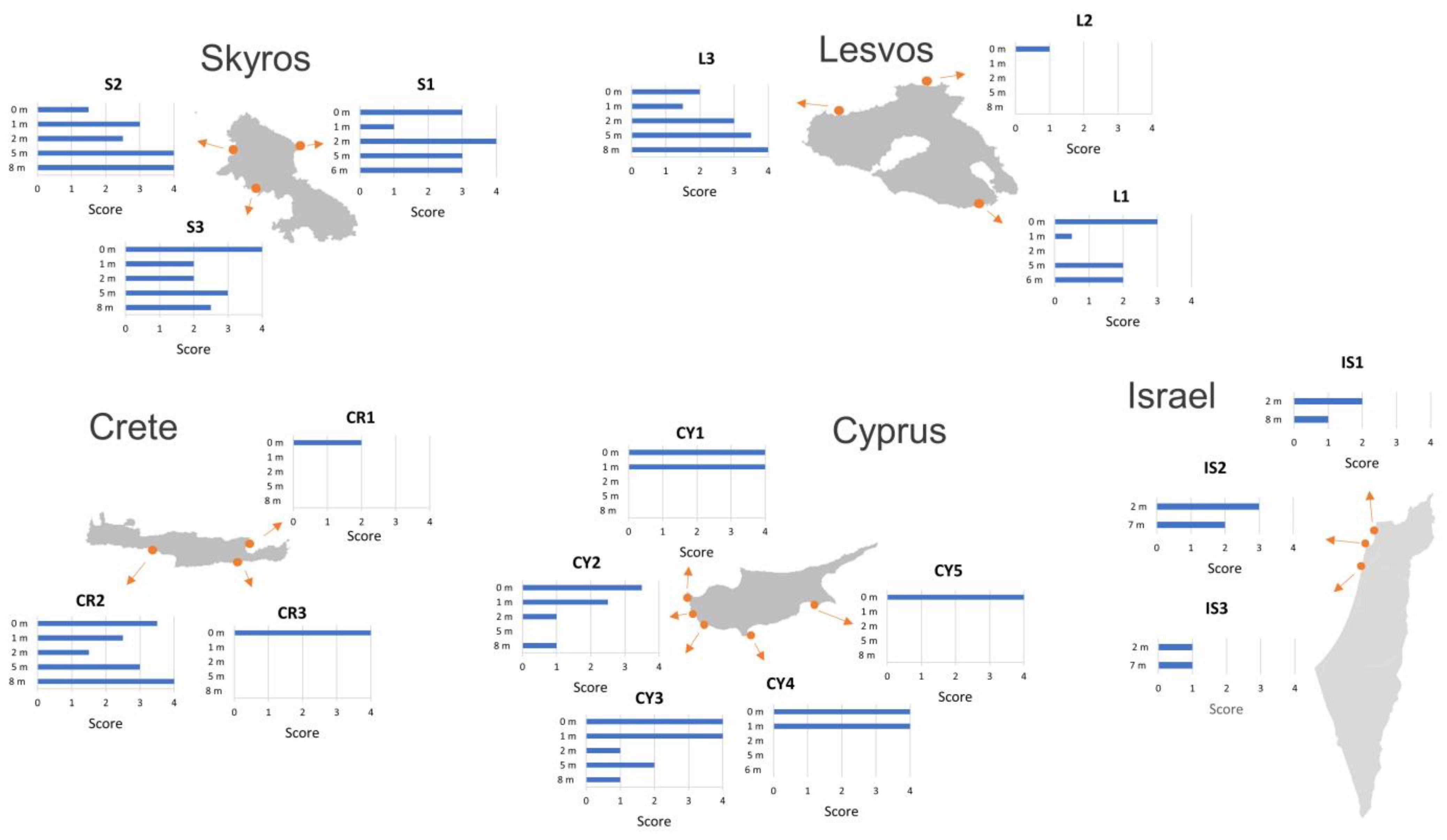
2.2. Ecological Status of Macroalgal Communities
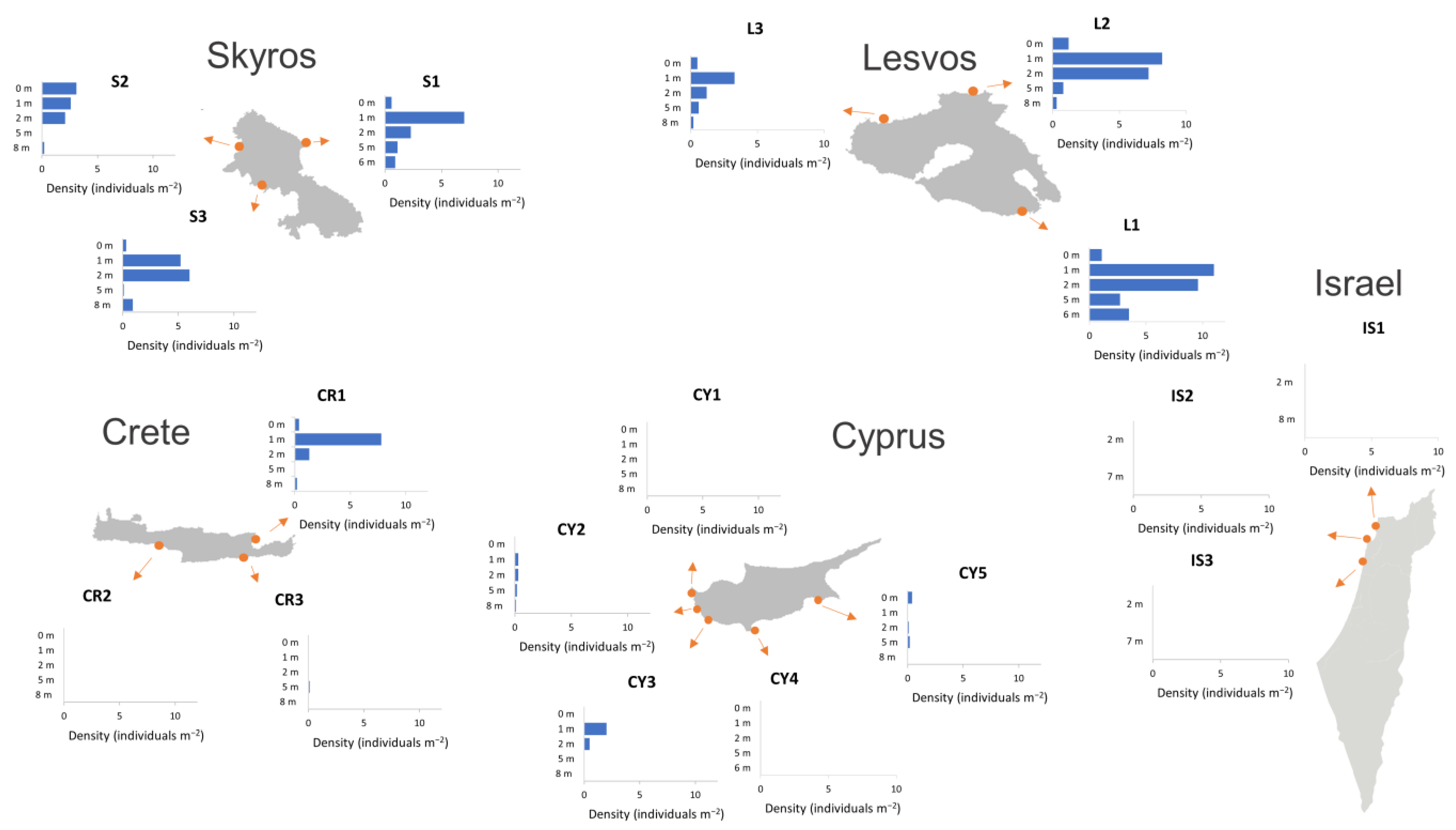
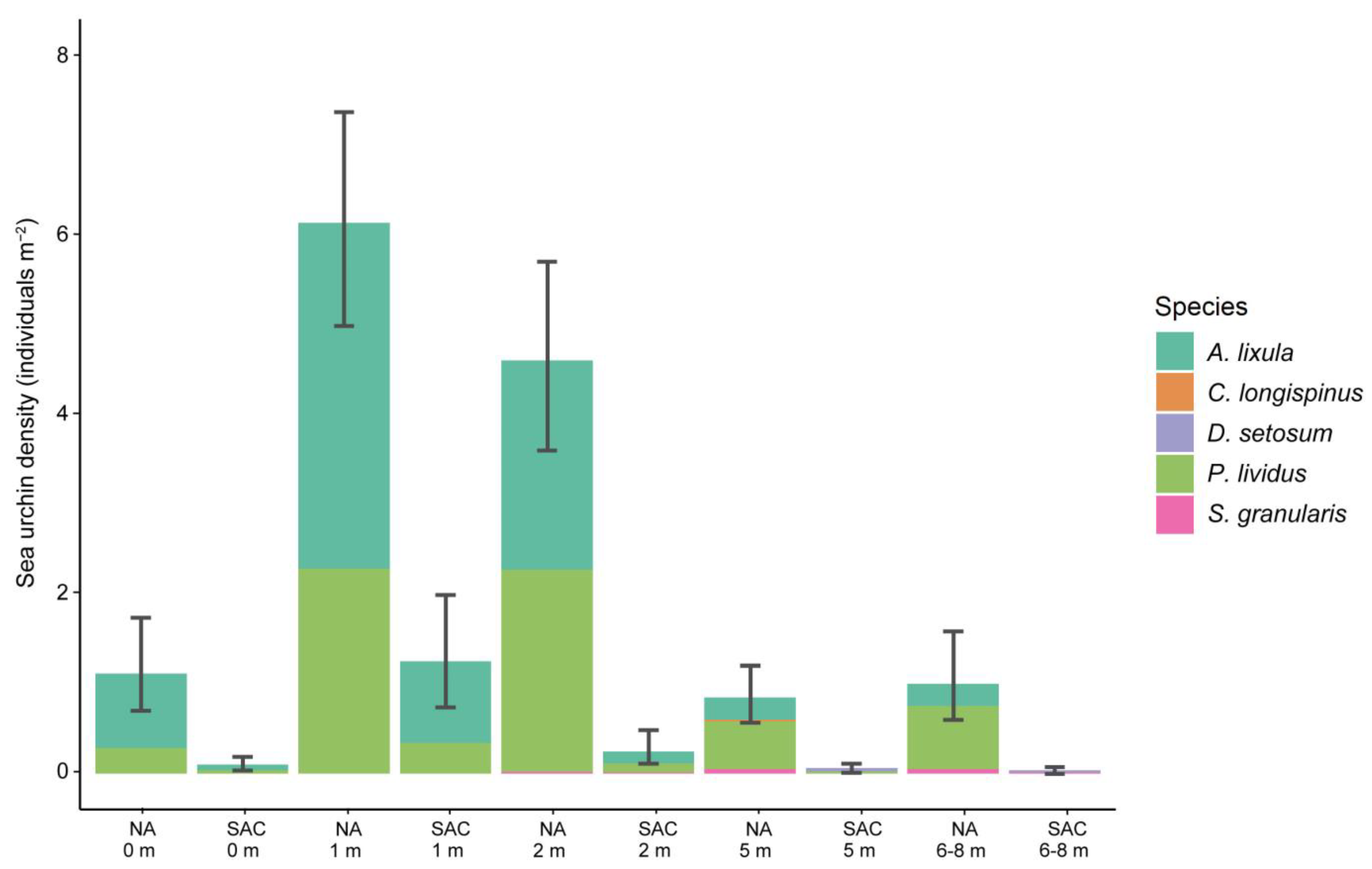
2.3. Sea Urchins Densities Estimations
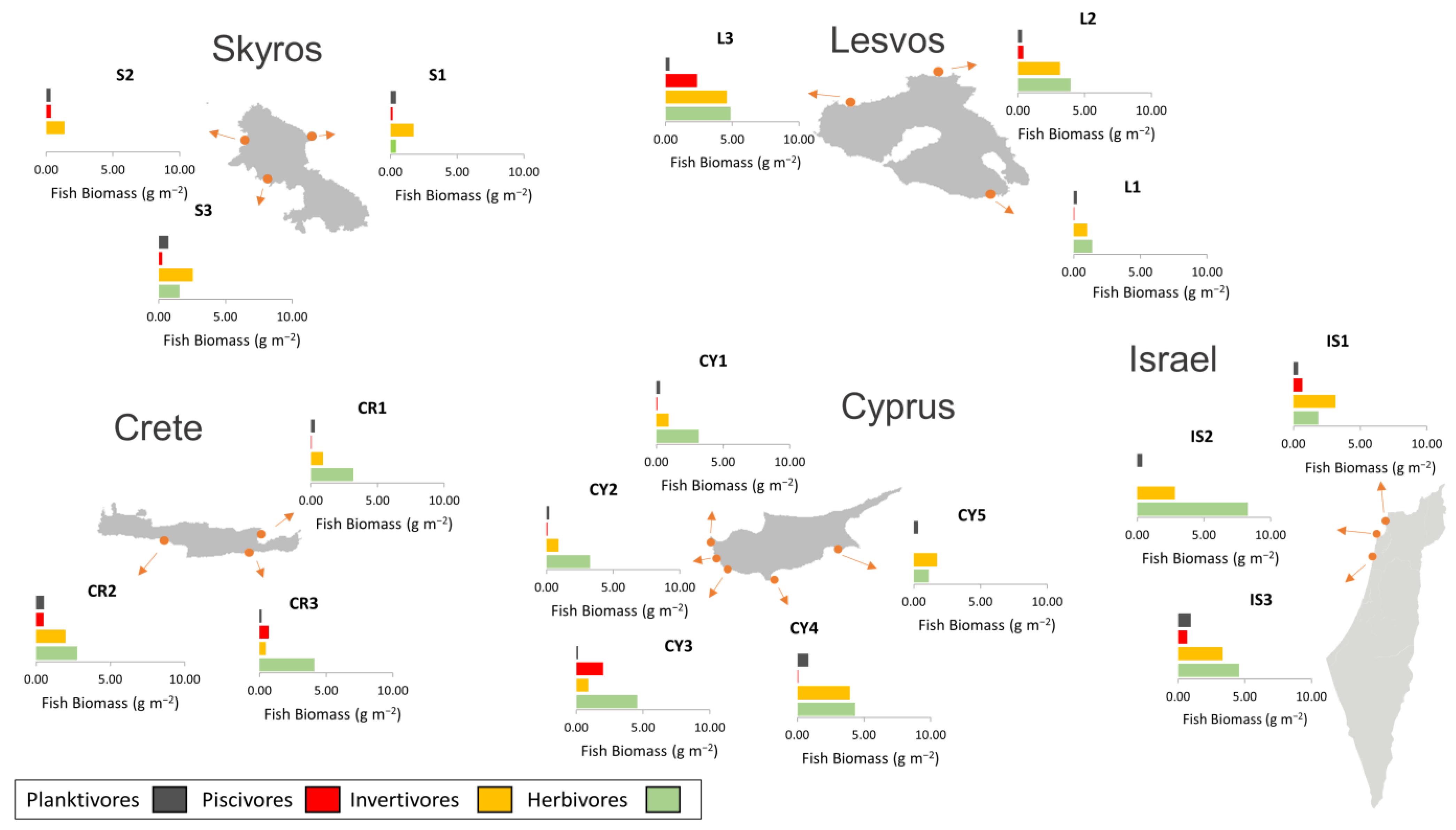
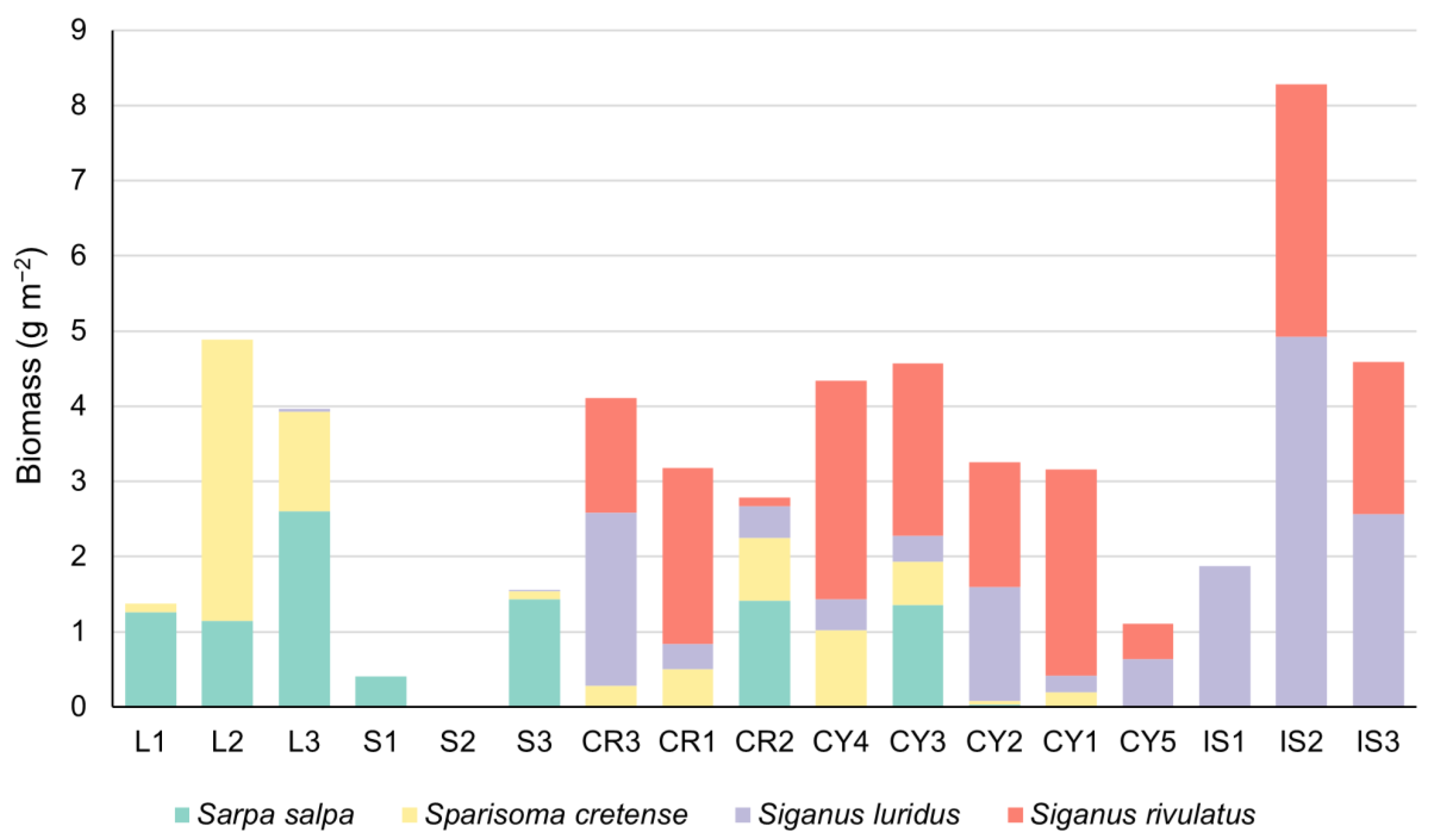
2.4. Fish Biomass Estimations
2.5. Modelling Canopy Algae Presence
3. Results
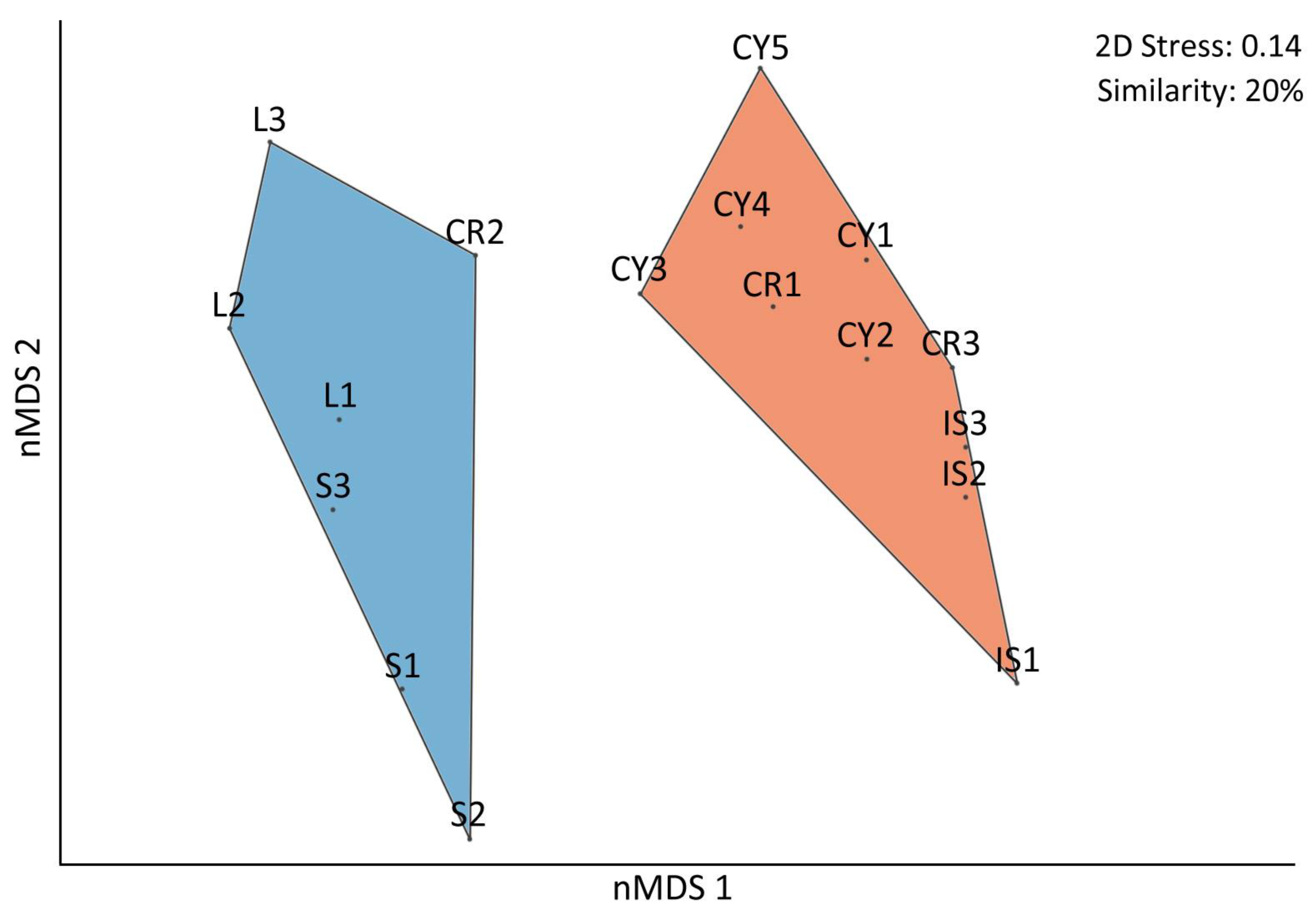
3.1. Macroalgal Communities’ Ecological Status
3.2. Sea Urchin Density
3.3. Fish Biomass
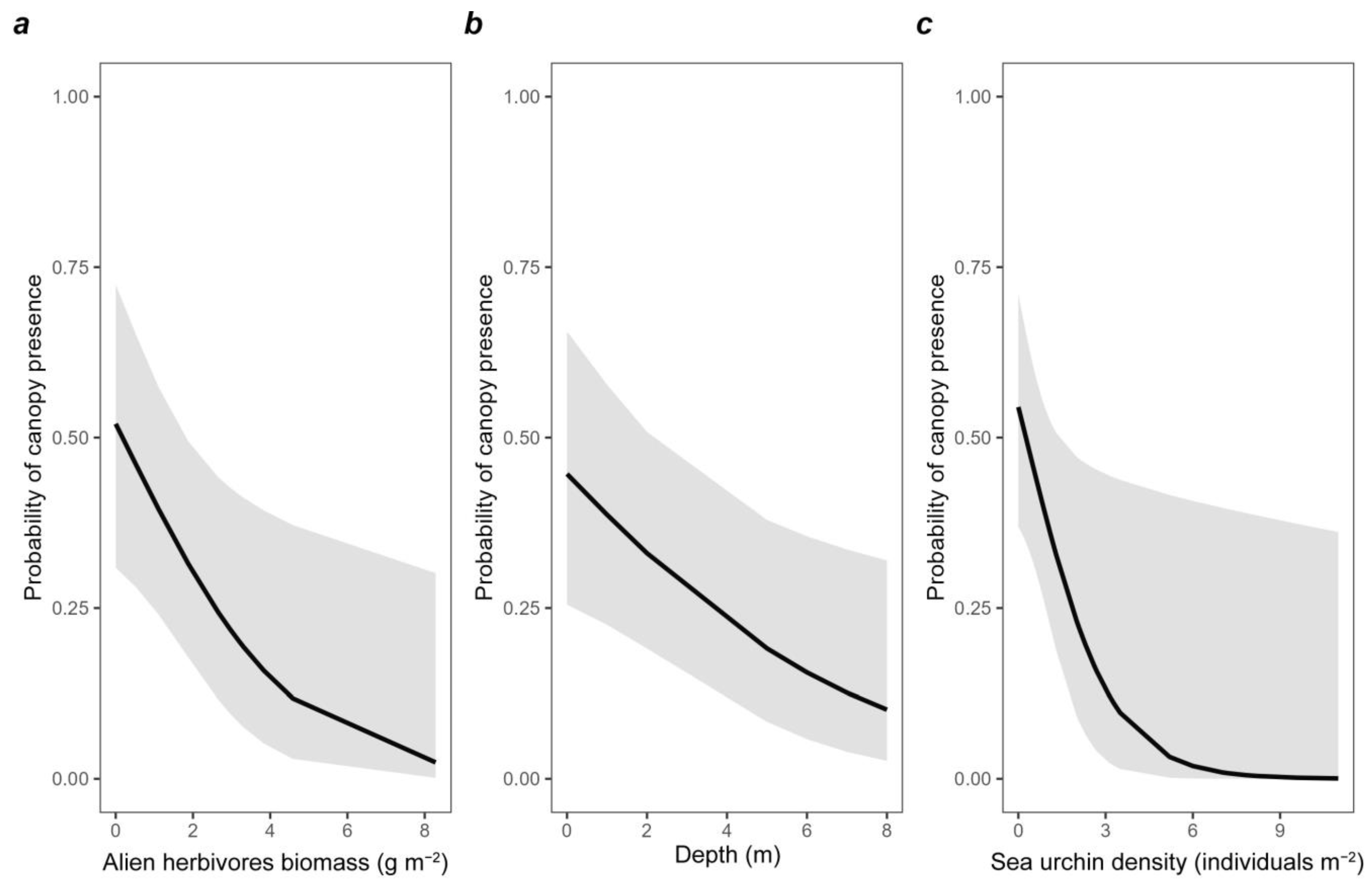
3.4. Modeling Canopy Algae Presence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bevilacqua, S.; Airoldi, L.; Ballesteros, E.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Boero, F.; Bulleri, F.; Cebrian, E.; Cerrano, C.; Claudet, J.; Colloca, F.; et al. Mediterranean Rocky Reefs in the Anthropocene: Present Status and Future Concerns. In Advances in Marine Biology; Sheppard, C., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK; Oxford, UK; San Diego, CA, USA; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 89, pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, J.; Fragkopoulou, E.; Frade, D.; Neiva, J.; Oliveira, A.; Abecasis, D.; Faugeron, S.; Serrão, E.A. A fine-tuned global distribution dataset of marine forests. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, E.; Ballesteros, E.; Dendrinos, P.; Di Franco, A.; Ferretti, F.; Foley, D.; Fraschetti, S.; Friedlander, A.; Garrabou, J.; Güçlüsoy, H.; et al. The structure of Mediterranean rocky reef ecosystems across environmental and human gradients, and conservation implications. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulleri, F.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Acunto, S.; Cinelli, F.; Hawkins, S.J. The Influence of Canopy Algae on Vertical Patterns of Distribution of Low-Shore Assemblages on Rocky Coasts in the Northwest Mediterranean. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 267, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheminée, A.; Pastor, J.; Bianchimani, O.; Thiriet, P.; Sala, E.; Cottalorda, J.-M.; Dominici, J.-M.; Lejeune, P.; Francour, P. Juvenile Fish Assemblages in Temperate Rocky Reefs Are Shaped by the Presence of Macro-Algae Canopy and Its Three-Dimensional Structure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheminée, A.; Sala, E.; Pastor, J.; Bodilis, P.; Thiriet, P.; Mangialajo, L.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Francour, P. Nursery value of Cystoseira forests for Mediterranean rocky reef fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 442, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomidi, M.; Katsanevakis, S.; Borja, A.; Braeckman, U.; Damalas, D.; Galparsoro, I.; Mifsud, R.; Mirto, S.; Pascual, M.; Pipitone, C.; et al. Assessment of goods and services, vulnerability, and conservation status of European seabed biotopes: A stepping stone towards ecosystem-based marine spatial management. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2012, 13, 49–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineur, F.; Arenas, F.; Assis, J.; Davies, A.J.; Engelen, A.H.; Fernandes, F.; Malta, E.J.; Thibaut, T.; Van Nguyen, T.U.; Vaz-Pinto, F.; et al. European seaweeds under pressure: Consequences for communities and ecosystem functioning. J. Sea Res. 2015, 98, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquete, C.; Piroddi, C.; Drakou, E.G.; Gurney, L.; Katsanevakis, S.; Charef, A.; Egoh, B. Current status and future prospects for the assessment of marine and coastal ecosystem services: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0067737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, G.; Asnaghi, V.; Chiantore, M.; Thrush, S.; Povero, P.; Vassallo, P.; Petrillo, M.; Paoli, C. The Effect of Cystoseira Canopy on the Value of Midlittoral Habitats in NW Mediterranean, an Emergy Assessment. Ecol. Modell. 2019, 404, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari Novoa, E.; Guiry, M. Reinstatement of the Genera Gongolaria Boehmer and Ericaria Stackhouse (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyceae). Not. Algarum 2020, 172, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament; Council of the European Union. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. Off. J. Eur. Union 2000, 327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Gubbay, S.; Sanders, N.; Haynes, T.; Janssen, J.A.M.; Rodwell, A.; Nieto, A.; García Criado, M.; Beal, S.; Borg, J.; Kennedy, M.; et al. European Red List of Habitats. Part 1; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cormaci, M.; Furnari, G. Changes of the Benthic Algal Flora of the Tremiti Islands (Southern Adriatic) Italy. In Sixteenth International Seaweed Symposium; Kain, J.M., Brown, M.T., Lahaye, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Pannacciulli, F.; Bulleri, F.; Moschella, P.S.; Airoldi, L.; Relini, G.; Cinelli, F. Predicting the Consequences of Anthropogenic Disturbance: Large-Scale Effects of Loss of Canopy Algae on Rocky Shores. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 214, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibaut, T.; Blanfune, A.; Boudouresque, C.-F.; Verlaque, M. Decline and Local Extinction of Fucales in French Riviera: The Harbinger of Future Extinctions? Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanfuné, A.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Verlaque, M.; Thibaut, T. The Fate of Cystoseira Crinita, a Forest-Forming Fucale (Phaeophyceae, Stramenopiles), in France (North Western Mediterranean Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 181, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, F.P.; Strain, E.M.A.; Piccioni, E.; De Clerck, O.; Sarà, G.; Airoldi, L. Status of Vulnerable Cystoseira Populations along the Italian Infralittoral Fringe, and Relationships with Environmental and Anthropogenic Variables. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilov, G.; Peleg, O.; Yeruham, E.; Garval, T.; Vichik, A.; Raveh, O. Alien turf: Overfishing, overgrazing and invader domination on southeastern Levant reef ecosystems. Aquat. Conserv. 2018, 28, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilov, G.; Peleg, O.; Guy-Haim, T.; Yeruham, E. Community dynamics and ecological shifts on Mediterranean vermetid reefs. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 160, 105045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, M.; Ballesteros, E. Shallow Cystoseira (Fucales: Ochrophyta) Assemblages Thriving in Sheltered Areas from Menorca (NW Mediterranean): Relationships with Environmental Factors and Anthropogenic Pressures. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Prieto, C.; Polo Albertí, L. Effects of the Sewage Pollution in the Structure and Dynamics of the Community of Cystoseira Mediterranea (Fucales, Phaeophyceae). Sci. Mar. 1996, 60, 253–263. [Google Scholar]
- Mangialajo, L.; Chiantore, M.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Loss of Fucoid Algae along a Gradient of Urbanisation, and Structure of Benthic Assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 358, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidis, S.; Rindi, F.; Cebrian, E.; Fraschetti, S.; Nasto, I.; Taskin, E.; Bianchelli, S.; Papathanasiou, V.; Kosmidou, M.; Caragnano, A.; et al. Effects of natural and anthropogenic stressors on fucalean brown seaweeds across different spatial scales in the Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 658417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, M.; Cebrian, E.; Tomas, F.; Ballesteros, E. Pollution Impacts and Recovery Potential in Three Species of the Genus Cystoseira (Fucales, Heterokontophyta). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdura, J.; Santamaría, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Smale, A.D.; Cefalì, E.M.; Golo, R.; Caralt, S.; Vergés, A.; Cebrian, E. Local-scale climatic refugia offer sanctuary for a habitat-forming species during a marine heatwave. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrat, M.; Comeau, S.; Verdura, J.; Alliouane, S.; Spennato, G.; Priouzeau, F.; Romero, G.; Mangialajo, L. Climate change and species facilitation affect the recruitment of macroalgal marine forests. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, E.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Harmelin-Vivien, M. Fishing, Trophic Cascades, and the Structure of Algal Assemblages: Evaluation of an Old but Untested Paradigm. Oikos 1998, 82, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumi, S.; Cebrian, E.; Kokkoris, G.D.; Ballesteros, E.; Sala, E. Relationships between Fish, Sea Urchins and Macroalgae: The Structure of Shallow Rocky Sublittoral Communities in the Cyclades, Eastern Mediterranean. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergés, A.; Tomas, F.; Cebrian, E.; Ballesteros, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Spiegel, D.; Sala, E. Tropical Rabbitfish and the Deforestation of a Warming Temperate Sea. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruham, E.; Shpigel, M.; Abelson, A.; Rilov, G. Ocean warming and tropical invaders erode the fitness of a key herbivore. Ecology 2020, 101, e02925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falace, A.; Kaleb, S.; De La Fuente, G.; Asnaghi, V.; Chiantore, M. Ex Situ Cultivation Protocol for Cystoseira amentacea Var. Stricta (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) from a Restoration Perspective. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdura, J.; Sales, M.; Ballesteros, E.; Cefalì, M.E.; Cebrian, E. Restoration of a Canopy-Forming Alga Based on Recruitment Enhancement: Methods and Long-Term Success Assessment. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, G.; Chiantore, M.; Asnaghi, V.; Kaleb, S.; Falace, A. First Ex Situ Outplanting of the Habitat-Forming Seaweed Cystoseira Amentacea Var. Stricta from a Restoration Perspective. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Ceccherelli, G. Effect of Sea Urchin Human Harvest in Promoting Canopy Forming Algae Restoration. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 219, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, F.; Mačić, V.; Bartolini, F.; Pey, A.; Laurent, M.; Mangialajo, L. Optimizing Canopy-Forming Algae Conservation and Restoration with a New Herbivorous Fish Deterrent Device. Restor. Ecol. 2020, 28, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardi, P.I.; Varkitzi, I.; Tsiamis, K.; Orfanidis, S.; Koutsoubas, D.; Falace, A.; Salomidi, M. Early development of Gongolaria montagnei (Fucales, Phaeophyta) germlings under laboratory conditions, with a view to enhancing restoration potential in the Eastern Mediterranean. Bot. Mar. 2022, 65, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poore, A.G.B.; Campbell, A.H.; Coleman, R.A.; Edgar, G.J.; Jormalainen, V.; Reynolds, P.L.; Sotka, E.E.; Stachowicz, J.J.; Taylor, R.B.; Vanderklift, M.A.; et al. Global Patterns in the Impact of Marine Herbivores on Benthic Primary Producers. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulleri, F.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Cinelli, F. Grazing by the Sea Urchins Arbacia Lixula L. and Paracentrotus Lividus Lam. in the Northwest Mediterranean. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 241, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, P.; Dulčić, J. Relationships among Predatory Fish, Sea Urchins and Barrens in Mediterranean Rocky Reefs across a Latitudinal Gradient. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 63, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privitera, D.; Chiantore, M.; Mangialajo, L.; Glavic, N.; Kozul, W.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Inter- and Intra-Specific Competition between Paracentrotus Lividus and Arbacia Lixula in Resource-Limited Barren Areas. J. Sea Res. 2008, 60, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaviri, C.; Vega Fernández, T.; Fanelli, G.; Badalamenti, F.; Gianguzza, P. Leading Role of the Sea Urchin Arbacia Lixula in Maintaining the Barren State in Southwestern Mediterranean. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 2505–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnetta, D.; Badalamenti, F.; Ceccherelli, G.; Di Trapani, F.; Bonaviri, C.; Gianguzza, P. Role of Two Co-Occurring Mediterranean Sea Urchins in the Formation of Barren from Cystoseira Canopy. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2015, 152, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirintanis, K.; Sini, M.; Doumas, O.; Trygonis, V.; Katsanevakis, S. Assessment of Grazing Effects on Phytobenthic Community Structure at Shallow Rocky Reefs: An Experimental Field Study in the North Aegean Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2018, 503, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Verlaque, M. Chapter 26—Paracentrotus lividus. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Lawrence, J.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 43, pp. 447–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergés, A.; Alcoverro, T.; Ballesteros, E. Role of Fish Herbivory in Structuring the Vertical Distribution of Canopy Algae Cystoseira spp. in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 375, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, F.; Bartolini, F.; Pey, A.; Laurent, M.; Martins, G.M.; Airoldi, L.; Mangialajo, L. Threats to Large Brown Algal Forests in Temperate Seas: The Overlooked Role of Native Herbivorous Fish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, F.; Bartolini, F.; Airoldi, L.; Mangialajo, L. Reduction of Herbivorous Fish Pressure Can Facilitate Focal Algal Species Forestation on Artificial Structures. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 138, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, O.; Tsirintanis, K.; Lioupa, V.; Katsanevakis, S. The Neglected Role of Omnivore Fish in the Overgrazing of Mediterranean Rocky Reefs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 673, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariche, M.; Letourneur, Y.; Harmelin-Vivien, M. Temporal Fluctuations and Settlement Patterns of Native and Lessepsian Herbivorous Fishes on the Lebanese Coast (Eastern Mediterranean). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2004, 70, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumi, S. Distribution Patterns of the Invasive Herbivore Siganus Luridus (Rüppell, 1829) and Its Relation to Native Benthic Communities in the Central Aegean Sea, Northeastern Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. 2014, 35, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, E.; Azzurro, E.; Bariche, M.; Cartes, J.E.; Maynou, F. Depicting the Novel Eastern Mediterranean Food Web: A Stable Isotopes Study Following Lessepsian Fish Invasion. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 2163–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Yildirim, D.; Ballesteros, E. Alien Marine Fishes Deplete Algal Biomass in the Eastern Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomidi, M.; Giakoumi, S.; Gerakaris, V.; Issaris, Y.; Sini, M.; Tsiamis, K. Setting an ecological baseline prior to the bottom-up establishment of a marine protected area in Santorini island, Aegean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2016, 17, 720–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruham, E.; Rilov, G.; Shpigel, M.; Abelson, A. Collapse of the Echinoid Paracentrotus Lividus Populations in the Eastern Mediterranean—Result of Climate Change? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marras, S.; Cucco, A.; Antognarelli, F.; Azzurro, E.; Milazzo, M.; Bariche, M.; Butenschön, M.; Kay, S.; Di Bitetto, M.; Quattrocchi, G.; et al. Predicting Future Thermal Habitat Suitability of Competing Native and Invasive Fish Species: From Metabolic Scope to Oceanographic Modelling. Conserv. Physiol. 2015, 3, cou059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Tempera, F.; Teixeira, H. Mapping the Impact of Alien Species on Marine Ecosystems: The Mediterranean Sea Case Study. Divers. Distrib. 2016, 22, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirintanis, K.; Azzurro, E.; Crocetta, F.; Dimiza, M.; Froglia, C.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Langeneck, J.; Mancinelli, G.; Rosso, A.; Stern, N.; et al. Bioinvasion impacts on biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human health in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2022, 17, 308–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleri, F.; Cucco, A.; Dal Bello, M.; Maggi, E.; Ravaglioli, C.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L. The role of wave-exposure and human impacts in regulating the distribution of alternative habitats on NW Mediterranean rocky reefs. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 201, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, A.; Guinda, X.; Juanes, J.A.; Ramos, E.; Echavarri-Erasun, B.; De La Hoz, C.F.; Degraer, S.; Kerckhof, F.; Bojanić, N.; Rousou, M.; et al. The role of physical variables in biodiversity patterns of intertidal macroalgae along European coasts. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2017, 97, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidis, S. Temperature Responses and Distribution of Macroalgae Belonging to the Warm-temperate Mediterranean-Atlantic Distribution Group. Bot. Mar. 1991, 34, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, N.; Ballesteros, E. Depth distribution of canopy-forming algae of the order Fucales is related to their photosynthetic features. Mar Ecol. 2021, 42, e12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellan, G.; Angeletti, L.; Montagna, P.; Taviani, M. Drawing the borders of the mesophotic zone of the Mediterranean Sea using satellite data. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, E.; Garrabou, J.; Hereu, B.; Zabala, M.; Cebrian, E.; Sala, E. Deep-water stands of Cystoseira zosteroides C. Agardh (Fucales, Ochrophyta) in the Northwestern Mediterranean: Insights into assemblage structure and population dynamics. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereu, B.; Mangialajo, L.; Ballesteros, E.; Thibaut, T. On the occurrence, structure and distribution of deep-water Cystoseira (Phaeophyceae) populations in the Port-Cros National Park (north-western Mediterranean). Eur. J. Phycol. 2008, 43, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, F.; Falace, A.; Alongi, G.; Buia, M.C.; Neiva, J.; Appolloni, L.; Marletta, G.; Russo, G.F. The Lush Fucales Underwater Forests off the Cilento Coast: An Overlooked Mediterranean Biodiversity Hotspot. Plants 2023, 12, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiamis, K.; Salomidi, M.; Kytinou, E.; Issaris, Y.; Gerakaris, V. On two new records of rare Cystoseira taxa (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) from Greece (Eastern Mediterranean). Bot. Mar. 2016, 59, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Zervakis, V.; Josey, S.A.; Peneva, E.L.; Struglia, M.V.; Stanev, E.V.; Theocharis, A.; Lionello, P.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Artale, V.; et al. Changes in the oceanography of the Mediterranean Sea and their link to climate variability. In Developments in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Lionello, P., Malanotte-Rizzoli, P., Boscolo, R., Eds.; Elesevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 4, pp. 227–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambler, N. The Mediterranean Sea—Primary Productivity. In The Mediterranean Sea; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, F.; Valiente, J.A.; Palau, J.L. Sea Surface Temperature in the Mediterranean: Trends and Spatial Patterns (1982–2016). In Meteorology and Climatology of the Mediterranean and Black Seas; Vilibić, I., Horvath, K., Palau, J., Eds.; Pageoph Topical Volumes; Birkhäuser: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, K.; Tanhua, T.; Chiggiato, J.; Velaoras, D.; Josey, S.A.; Lafuente, J.G.; Vargas-Yáñez, M. The forcings of the Mediterranean Sea and the physical properties of its water masses. In Oceanography of the Mediterranean Sea; Schroeder, K., Chiggiato, J., Eds.; Elesevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Proctor, R.; Flather, R.A. A two-dimensional tidal model for the Mediterranean Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 16223–16239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Sanna, A. Mediterranean wave climate variability and its links with NAO and Indian Monsoon. Clim. Chang. 2005, 25, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E.U. Copernicus Marine Service Information. Available online: https://marine.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Thibaut, T.; Blanfuné, A.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Personnic, S.; Ruitton, S.; Ballesteros, E.; Bellan-Santini, D.; Bianchi, C.N.; Bussotti, S.; Cebrian, E.; et al. An Ecosystem-Based Approach to Assess the Status of Mediterranean Algae-Dominated Shallow Rocky Reefs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sini, M.; Vatikiotis, K.; Thanopoulou, Z.; Katsoupis, C.; Maina, I.; Kavadas, S.; Karachle, P.K.; Katsanevakis, S. Small-scale coastal fishing shapes the structure of shallow rocky reef fish in the Aegean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmelin, J.G.; Bachet, F.; Garcia, F. Mediterranean Marine Reserves: Fish Indices as Tests of Protection Efficiency. Mar. Ecol. 1995, 16, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutopoulos, D.K.; Stergiou, K.I. Length–Weight and Length–Length Relationships of Fish Species from the Aegean Sea (Greece). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. World Wide Web Electronic Publication. 2021. Available online: https://www.fishbase.se/search.php (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Clarke, K.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed.; PRIMER-E Ltd Plymouth: London, UK, 2001; pp. 1–172. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Soft. 2015, 67, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolker, B.M.; Brooks, M.E.; Clark, C.J.; Geange, S.W.; Poulsen, J.R.; Stevens, M.H.H.; White, J.-S.S. Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends. Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://socialsciences.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Books/Companion/ (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- O’brien, R.M. A Caution Regarding Rules of Thumb for Variance Inflation Factors. Qual. Quant. 2007, 41, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, F. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models. R Package Version 0.4.6. 2022. Available online: http://florianhartig.github.io/DHARMa/ (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Stoffel, M.A.; Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H. partR2: Partitioning R2 in generalized linear mixed models. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Lüdecke, D. sjPlot: Data Visualization for Statistics in Social Science. R Package Version 2.8.14. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=sjPlot (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Auguie, B. egg: Extensions for ‘ggplot2’: Custom geom, custom themes, plot alignment, labelled panels, symmetric scales, and fixed panel size. R Package Version 0.4 5. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/egg/ (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. RStudio; PBC: Boston, MA USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Katsanevakis, S.; Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Zenetos, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Invading the Mediterranean Sea: Biodiversity Patterns Shaped by Human Activities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragkousis, M.; Sini, M.; Koukourouvli, N.; Zenetos, A.; Katsanevakis, S. Invading the Greek Seas: Spatiotemporal Patterns of Marine Impactful Alien and Cryptogenic Species. Diversity 2023, 15, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevault, F.; Somot, S.; Beuvier, J. A Regional Version of the NEMO Ocean Engine on the Mediterranean Sea: NEMOMED8 User’s Guide; Technical Note107, Groupe de Météorologie Grande Echelle et Climat; Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques: Toulouse, France, 2009; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Boada, J.; Arthur, R.; Alonso, D.; Pagès, J.F.; Pessarrodona, A.; Oliva, S.; Ceccherelli, G.; Piazzi, L.; Romero, J.; Alcoverro, T. Immanent conditions determine imminent collapses: Nutrient regimes define the resilience of macroalgal communities. Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 20162814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarra, S.; Livanou, E.; Varkitzi, I.; Lagaria, A.; Assimakopoulou, G.; Pagou, K.; Ignatiades, L. Phytoplankton Dynamics in the Aegean Sea. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Barceló, D., Andrey, G., Kostianoy, G.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, A.M.; Micheli, C. Ecological Function of Phenolic Compounds from Mediterranean Fucoid Algae and Seagrasses: An Overview on the Genus Cystoseira sensu lato and Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilov, G.; David, N.; Guy-Haim, T.; Golomb, D.; Arav, R.; Filin, S. Sea level rise can severely reduce biodiversity and community net production on rocky shores. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulas, M.; Silverman, J.; Guy-Haim, T.; Noe, S.; Rilov, G. Thermal vulnerability of the Levantine endemic and endangered habitat-forming macroalga, Gongolaria rayssiae: Implications for reef carbon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 862332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilley, S.A.; Schiel, D.R. Community effects following the deletion of a habitat-forming alga from rocky marine shores. Oecologia 2006, 148, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, L.; Balata, D.; Beck, W.M. The Gray Zone: Relationships between habitat loss and marine diversity and their applications in conservation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiel, R.D.; Lilley, A.S. Impacts and negative feedbacks in community recovery over eight years following removal of habitat-forming macroalgae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 407, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, P.G.; Steger, J.; Bošnjak, M.; Dunne, B.; Guifarro, Z.; Turapova, E.; Hua, Q.; Kaufman, D.S.; Rilov, G.; Zuschin, M. Native biodiversity collapse in the eastern Mediterranean. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2021, 288, 20202469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rilov, G.; Fraschetti, S.; Gissi, E.; Pipitone, C.; Badalamenti, F.; Tamburello, L.; Menini, E.; Goriup, P.; Mazaris, A.D.; Garrabou, J.; et al. A fast-moving target: Achieving marine conservation goals under shifting climate and policies. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, F.P.; D’Agostaro, R.; Milazzo, M.; Chemello, R. The invasive Asparagopsis taxiformis hosts a low diverse and less trophic structured molluscan assemblage compared with the native Ericaria brachycarpa. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 166, 105279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, F.P.; D’Agostaro, R.; Milazzo, M.; Badalamenti, F.; Musco, L.; Mikac, B.; Brutto, S.L.; Chemello, R. The invasive seaweed Asparagopsis taxiformis erodes the habitat structure and biodiversity of native algal forests in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 173, 105515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro Goldberg, D.; Rilov, G.; Villéger, S.; Belmaker, J. Predation cues lead to reduced foraging of invasive Siganus rivulatus in the Mediterranean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 678848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Tsirintanis, K.; Sini, M.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Koukourouvli, N. Aliens in the Aegean—A sea under siege (ALAS). Res. Ideas Outcomes 2020, 6, e53057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Site | Average SST (°C) | Average Annual Maximum SST (°C) | Average Annual Minimum SST (°C) | Average ZSD (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS1 | 23.4 | 30.3 | 16.8 | 21.4 |
| IS2 | 23.4 | 30.4 | 16.8 | 17.8 |
| IS3 | 23.4 | 30.4 | 16.7 | 20.0 |
| CY1 | 22.5 | 29.6 | 16.5 | 25.6 |
| CY2 | 22.4 | 29.6 | 16.5 | 28.6 |
| CY3 | 22.3 | 29.2 | 16.4 | 27.3 |
| CY4 | 22.0 | 28.4 | 16.6 | 26.9 |
| CY5 | 22.5 | 29.2 | 16.5 | 28.2 |
| CR1 | 20.8 | 27.2 | 15.1 | 25.7 |
| CR2 | 20.9 | 26.9 | 15.3 | 27.6 |
| CR3 | 21.2 | 27.4 | 15.7 | 27.3 |
| S1 | 19.3 | 27.4 | 13.9 | 20.9 |
| S2 | 19.4 | 27.3 | 14.0 | 22.8 |
| S3 | 19.3 | 27.1 | 13.9 | 23.2 |
| L1 | 19.5 | 25.7 | 14.9 | 22.3 |
| L2 | 18.9 | 25.6 | 14.4 | 20.7 |
| L3 | 18.9 | 25.4 | 14.5 | 22.4 |
| Status | 4 (Very Good) | 3 (Good) | 2 (Moderate) | 1 (Low) | 0 (Very Low) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cover Type | Arborescent perennial ≥50% | Arborescent perennial 5 to 50% | Shrubby ≥50% | Shrubby 5 to 50% | Turf Encrusting |
| Predictors | β Estimates | Odds Ratios | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1.46 | 4.30 | 2.15 | 0.031 |
| Alien Herbivores | −0.46 | 0.63 | −2.25 | 0.024 |
| Depth | −0.25 | 0.78 | −2.33 | 0.020 |
| Sea urchins | −0.69 | 0.50 | −2.06 | 0.039 |
| N site | 17 | |||
| Observations | 76 | |||
| Marginal R2/Conditional R2 | 0.352/0.364 | |||
| Log-likelihood | −40.291 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaou, A.; Tsirintanis, K.; Rilov, G.; Katsanevakis, S. Invasive Fish and Sea Urchins Drive the Status of Canopy Forming Macroalgae in the Eastern Mediterranean. Biology 2023, 12, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060763
Nikolaou A, Tsirintanis K, Rilov G, Katsanevakis S. Invasive Fish and Sea Urchins Drive the Status of Canopy Forming Macroalgae in the Eastern Mediterranean. Biology. 2023; 12(6):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060763
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaou, Athanasios, Konstantinos Tsirintanis, Gil Rilov, and Stelios Katsanevakis. 2023. "Invasive Fish and Sea Urchins Drive the Status of Canopy Forming Macroalgae in the Eastern Mediterranean" Biology 12, no. 6: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060763
APA StyleNikolaou, A., Tsirintanis, K., Rilov, G., & Katsanevakis, S. (2023). Invasive Fish and Sea Urchins Drive the Status of Canopy Forming Macroalgae in the Eastern Mediterranean. Biology, 12(6), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060763








