Dynamic Role of Exosome microRNAs in Cancer Cell Signaling and Their Emerging Role as Noninvasive Biomarkers
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
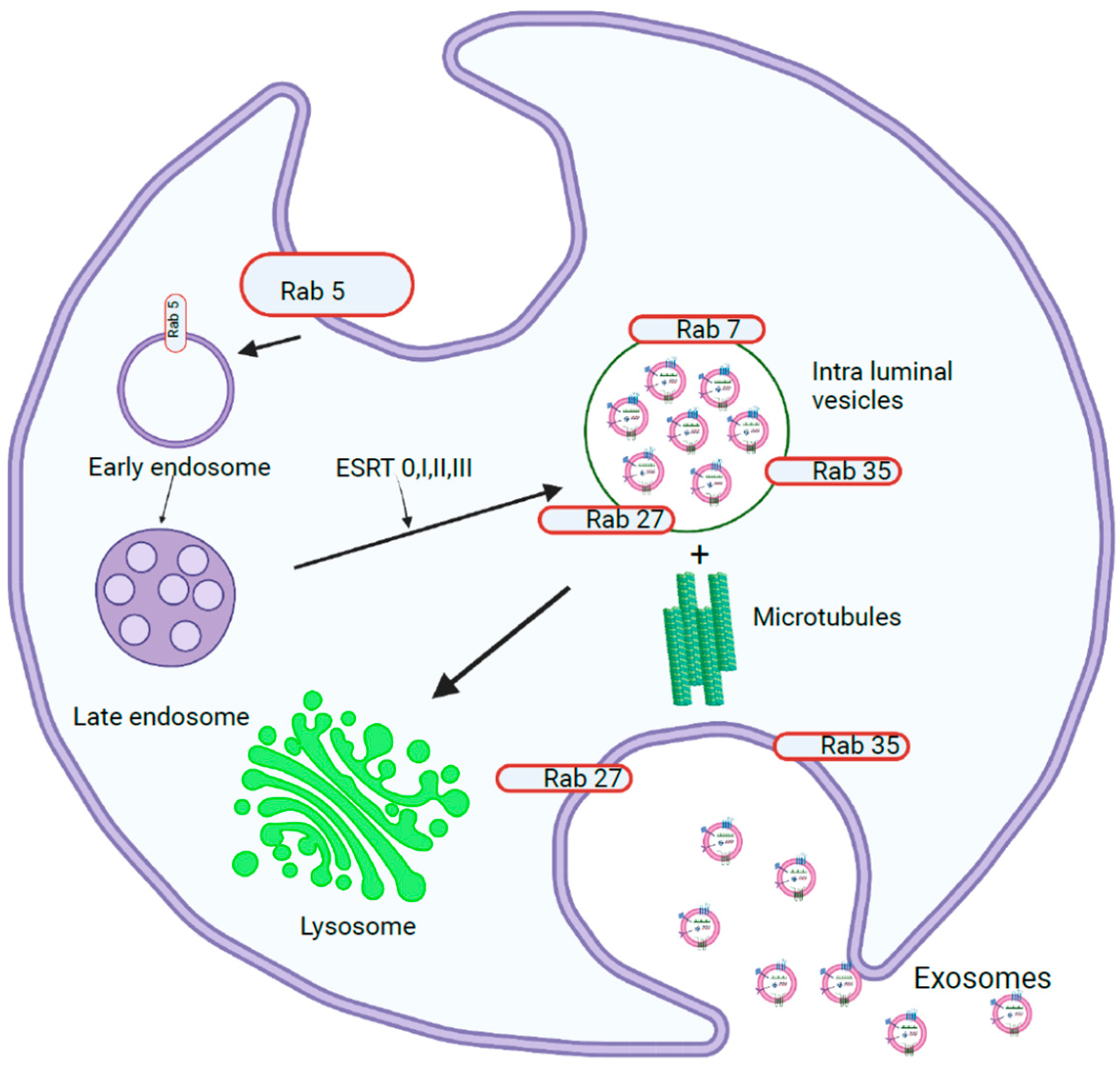
1.1. Exosome Biogenesis
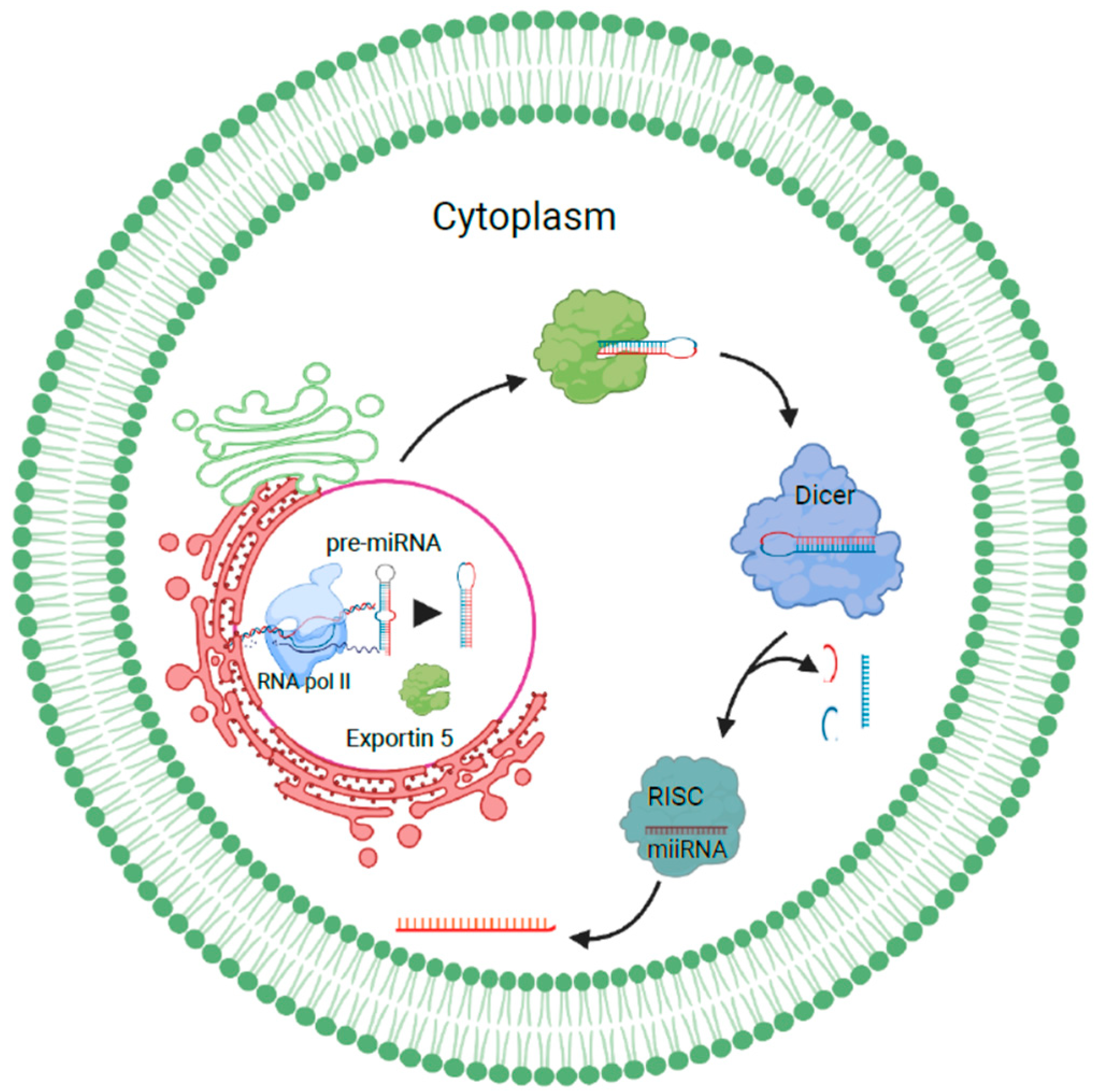
1.1.1. miRNA Sorting and Release of Exosomes
1.1.2. Role of Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins in Sorting RNAs into Exosomes
1.1.3. Exosome Release into Extracellular Space
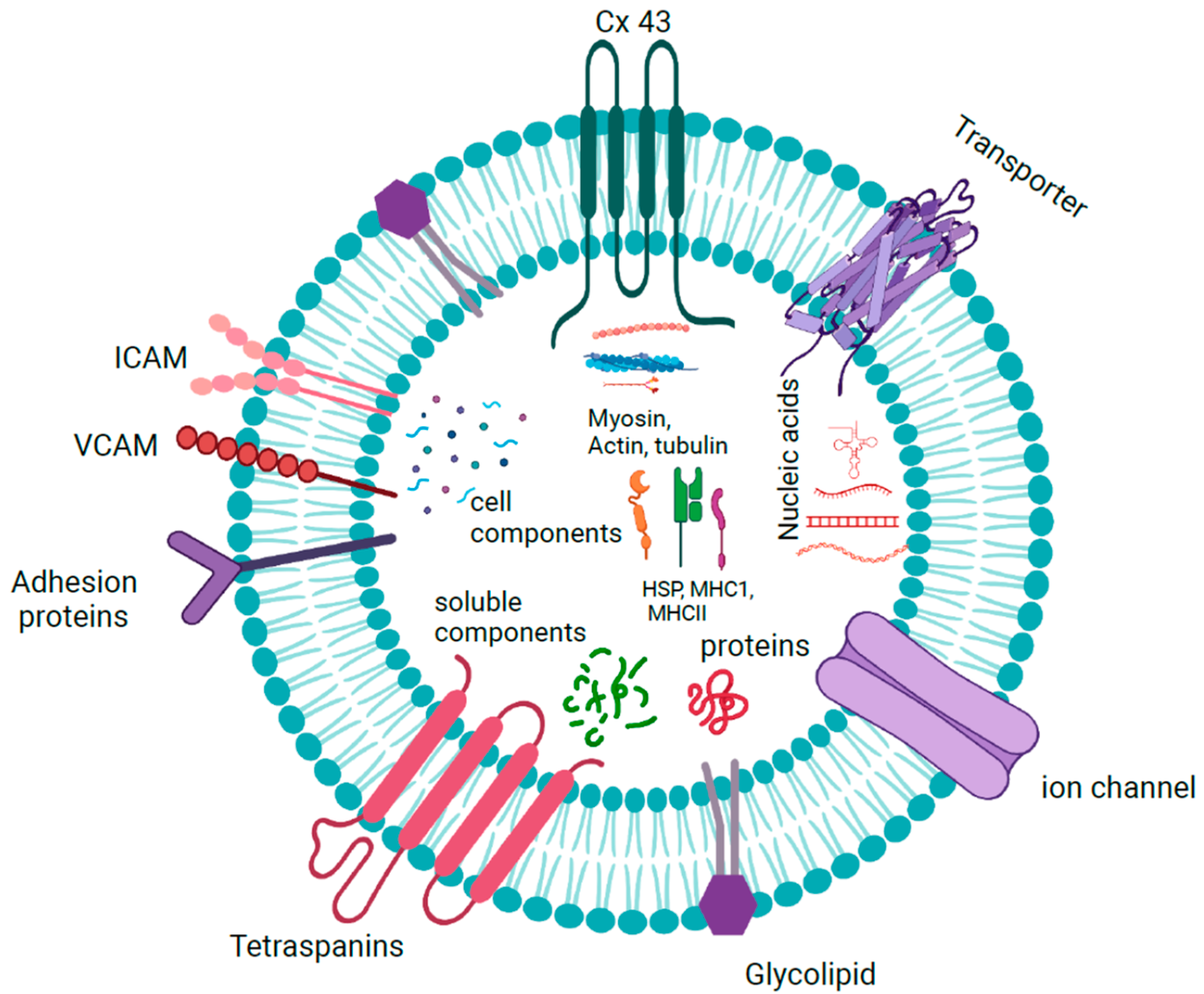
1.1.4. Exosome Cargoes
1.1.5. Exosomes in Cancer
1.2. Liver Cancer
1.2.1. Exosomal miRNA Signaling in Liver Cancer
1.2.2. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Liver Cancer
1.2.3. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Chemoresistance in Liver Cancer
1.2.4. Anticancer Effects of Exosomal miRNAs in Liver Cancer
1.3. Colorectal Cancer
1.3.1. Role of Exosomal miRNA in Cell Signaling in Colorectal Cancer
1.3.2. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Colorectal Cancer
1.3.3. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer
1.3.4. Anticancer Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Colorectal Cancer
1.4. Breast Cancer
1.4.1. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Signaling Pathways in Breast Cancer
1.4.2. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Breast Cancer
1.4.3. Association of Exosomal miRNAs with Hormone Receptor Status in Breast Cancer
1.4.4. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Chemo- and Radioresistance in Breast Cancer
1.4.5. Anticancer Effects of Exosomal miRNAs on Breast Cancer
1.5. Prostate Cancer
1.5.1. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Cell Signaling in Prostate Cancer
1.5.2. Role of Urinary Exosomal miRNAs in Prostate Cancer
1.5.3. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Osteoblastic Modulation in Prostate Cancer
1.5.4. Role of Exosomal miRNAs in Castration-/Chemoresistance in Prostate Cancer
1.5.5. Exosomal miRNAs as Tumor Suppressor in Prostate Cancer
2. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheta, M.; Taha, E.A.; Lu, Y.; Eguchi, T. Extracellular Vesicles: New Classification and Tumor Immunosuppression. Biology 2023, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willms, E.; Cabañas, C.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J.A.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicle Heterogeneity: Subpopulations, Isolation Techniques, and Diverse Functions in Cancer Progression. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Lin, L.; Sha, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, W.; et al. Regulation of exosome production and cargo sorting. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, R.O.; He, M. Unlocking the Power of Exosomes for Crossing Biological Barriers in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: From biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, A.; Ferrari, P.; Biava, P.M. Exosomes and Cell Communication: From Tumour-Derived Exosomes and Their Role in Tumour Progression to the Use of Exosomal Cargo for Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2021, 13, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, M.; Okada, F. Exosomes and Their Role in Cancer Progression. Yonago Acta Med. 2019, 62, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larios, J.; Mercier, V.; Roux, A.; Gruenberg, J. ALIX- and ESCRT-III-dependent sorting of tetraspanins to exosomes. J. Cell. Biol. 2020, 219, e201904113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; Carter, D.R.F.; Clayton, A.; Lambert, D.W.; Raposo, G.; Vader, P. Challenges and directions in studying cell-cell communication by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.T.; Wang, Y.K.; Tseng, Y.J. Exosomal Proteins and Lipids as Potential Biomarkers for Lung Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.V.; da Rosa Soares, A.; Ramalho, J.; Máximo Carvalho, C.; Cardoso, M.H.; Pintado, P.; Carvalho, A.S.; Beck, H.C.; Matthiesen, R.; Zuzarte, M.; et al. LAMP2A regulates the loading of proteins into exosomes. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, J.; Mi, S. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, T.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, C.; Li, W. The role of Exosomal miRNAs in cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ala, U. Competing Endogenous RNAs, Non-Coding RNAs and Diseases: An Intertwined Story. Cells 2020, 9, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zietzer, A.; Hosen, M.R.; Wang, H.; Goody, P.R.; Sylvester, M.; Latz, E.; Nickenig, G.; Werner, N.; Jansen, F. The RNA-binding protein hnRNPU regulates the sorting of microRNA-30c-5p into large extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1786967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Li, H.; Li, N.; Singh, R.N.; Bishop, C.E.; Chen, X.; Lu, B. MEX3C interacts with adaptor-related protein complex 2 and involves in miR-451a exosomal sorting. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Corbett, A.L.; Taatizadeh, E.; Tasnim, N.; Little, J.P.; Garnis, C.; Daugaard, M.; Guns, E.; Hoorfar, M.; Li, I.T.S. Challenges and opportunities in exosome research-Perspectives from biology, engineering, and cancer therapy. APL Bioeng. 2019, 3, 011503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Breyne, K.; Ughetto, S.; Laurent, L.C.; Breakefield, X.O. RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, F.; Zhang, D.; Qi, S.; Liu, Y. Metabolites as extracellular vesicle cargo in health, cancer, pleural effusion, and cardiovascular diseases: An emerging field of study to diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Biomed. Pharm. 2023, 157, 114046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, M. Exosomes: Revisiting their role as “garbage bags”. Traffic 2019, 20, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela-Eirin, M.; Varela-Vazquez, A.; Rodríguez-Candela Mateos, M.; Vila-Sanjurjo, A.; Fonseca, E.; Mascareñas, J.L.; Eugenio Vázquez, M.; Mayan, M.D. Recruitment of RNA molecules by connexin RNA-binding motifs: Implication in RNA and DNA transport through microvesicles and exosomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso-Quezada, J.; Ayala-Mar, S.; González-Valdez, J. The role of lipids in exosome biology and intercellular communication: Function, analytics and applications. Traffic 2021, 22, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Anca, M.; Fenoglio, C.; Buccellato, F.R.; Visconte, C.; Galimberti, D.; Scarpini, E. Extracellular Vesicles in Multiple Sclerosis: Role in the Pathogenesis and Potential Usefulness as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Tools. Cells 2021, 10, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzanowska, J.; Semira, C.; Costa-Silva, B. DNA in extracellular vesicles: Biological and clinical aspects. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhou, A.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, P. The Significance of Exosomal RNAs in the Development, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Gastric Cancer. Genes 2021, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskeh, M.D.A.; Entezari, M.; Mirzaei, S.; Zabolian, A.; Saleki, H.; Naghdi, M.J.; Sabet, S.; Khoshbakht, M.A.; Hashemi, M.; Hushmandi, K.; et al. Emerging role of exosomes in cancer progression and tumor microenvironment remodeling. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Luo, G.; Fang, Y.; et al. Exosomes: A New Pathway for Cancer Drug Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 743556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Ji, A.; Qiang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ding, Y. Exosomal miR-665 as a novel minimally invasive biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80666–80678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Eun, J.W.; Baek, G.O.; Seo, C.W.; Ahn, H.R.; Kim, S.S.; Cho, S.W.; Cheong, J.Y. Serum Exosomal MicroRNA, miR-10b-5p, as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lai, Y.; Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Weng, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Ye, Y. Human. umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-451a represses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting ADAM10. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1408–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fründt, T.; Krause, L.; Hussey, E.; Steinbach, B.; Köhler, D.; von Felden, J.; Schulze, K.; Lohse, A.W.; Wege, H.; Schwarzenbach, H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of miR-16, miR-146a, miR-192 and miR-221 in Exosomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver Cirrhosis Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-21 contributes to tumor progression by converting hepatocyte stellate cells to cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, R.; Qin, L. Exosomal miR-93 promotes proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting TIMP2/TP53INP1/CDKN1A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, L. Exosomal miR-452-5p Induce M2 Macrophage Polarization to Accelerate Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting TIMP3. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 1032106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhi, X.; Chen, E.J.; Wei, T.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Hu, L.Q.; Zhao, B.; Feng, X.H.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes promote tumor self-seeding in hepatocellular carcinoma by transferring miRNA-25-5p to enhance cell motility. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4964–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Shang, L.R.; Luo, Y.W.; Lin, Y.F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.M. Hepatoma cell-secreted exosomal microRNA-103 increases vascular permeability and promotes metastasis by targeting junction proteins. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1459–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, Y.; Noda, T.; Okumura, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Iwagami, Y.; Yamada, D.; Tomimaru, Y.; Akita, H.; Gotoh, K.; Takeda, Y.; et al. Serum exosomal miR-638 is a prognostic marker of HCC via downregulation of VE-cadherin and ZO-1 of endothelial cells. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.; Tong, R.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. High-metastatic cancer cells derived exosomal miR92a-3p promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of low-metastatic cancer cells by regulating PTEN/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6529–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Niu, L.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, P.; et al. Exosomal MiR-1290 Promotes Angiogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Targeting SMEK1. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 6617700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Liu, M.; Qu, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, T.; Wen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Min, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, L.; Tao, R.; Yan, L.; Song, H. Hypoxia-induced exosomes promote hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis via miR-1273f transfer. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 385, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zai, H.; Jiang, W.; Yao, Y.; Ou, Z.; Zhu, Q. miR-126 in Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Hepatoblastoma Cells Promotes the Tumorigenesis of Hepatoblastoma through Inducing the Differentiation of BMSCs into Cancer Stem Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 6744715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Jin, X.H.; Li, M.; Wang, F.W.; Huang, W.J.; Yun, J.P.; Xu, R.H.; Cai, Q.Q.; Xie, D. Acidic Microenvironment Up-Regulates Exosomal miR-21 and miR-10b in Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Promote Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Feng, D.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Causes Liver Cancer Cells to Release Exosomal miR-23a-3p and Up-regulate Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Macrophages. Hepatology 2019, 70, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, X.; Tang, B.; Liu, F.; Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Jing, Y.; Huang, F.; Jin, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. mTOR/miR-145-regulated exosomal GOLM1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma through augmented GSK-3β/MMPs. J. Genet. Genom. 2019, 46, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, P. miR-660-5p-loaded M2 macrophages-derived exosomes augment hepatocellular carcinoma development through regulating KLF3. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugawa, K.; Yoshizumi, T.; Mano, Y.; Itoh, S.; Harada, N.; Ikegami, T.; Kohashi, K.; Oda, Y.; Mori, M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression through downregulation of exosomal miR-150-3p. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Yue, S.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Pu, M.; et al. Loss of exosomal miR-320a from cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to HCC proliferation and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 397, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Lv, H.; Lv, G.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Su, B.; Guo, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Wu, Z.; Wu, W. CAF-Released Exosomal miR-20a-5p Facilitates HCC Progression via the LIMA1-Mediated β-Catenin Pathway. Cells 2022, 11, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Qiu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, G.; Li, X. Exosomal MiR-744 Inhibits Proliferation and Sorafenib Chemoresistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PAX2. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 7209–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, G.; Chen, L.; Xia, C.; Wang, W.; Qi, J.; Li, A.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. MiR-199a-modified exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve hepatocellular carcinoma chemosensitivity through mTOR pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, G.; Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz-Ojeda, P.; Schmid, T.; Boix, L.; Moreno, M.; Sapena, V.; Praena-Fernández, J.M.; Castell, F.J.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M.; Reig, M.; Brüne, B.; et al. miR-200c-3p, miR-222-5p, and miR-512-3p Constitute a Biomarker Signature of Sorafenib Effectiveness in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Su, R.; Sun, K.; Hu, Y.; Yang, F.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect against liver fibrosis via delivering miR-148a to target KLF6/STAT3 pathway in macrophages. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Liu, J.B.; Lin, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.J.; Shi, Y.; Jia, C.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Yu, F.; Wang, H.M.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-15a from mesenchymal stem cells impedes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via downregulation of SALL4. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Z.; Gu, H.; Ding, S.; Ji, Y. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-secreted exosomal microRNA-205-5p exerts inhibitory effect on the progression of liver cancer through regulating CDKL3. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 225, 153549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Kan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, S.; Feng, W.; Gao, S. Engineered exosome-mediated delivery of functionally active miR-26a and its enhanced suppression effect in HepG2 cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Huang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, K.; Zhou, C.; Yu, L.; Peng, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Exosome-depleted MiR-148a-3p derived from Hepatic Stellate Cells Promotes Tumor Progression via ITGA5/PI3K/Akt Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, L.; Piontek, K.; Sakaguchi, M.; Selaru, F.M. Exosome miR-335 as a novel therapeutic strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Shi, C.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Exosomal microRNA-618 derived from mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the progression of hepatic fibrosis by targeting Smad4. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 5915–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Xin, R.; Dong, W. Decreased serum exosomal miR-320a expression is an unfavorable prognostic factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519896144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, P.; Li, M.; Wu, Y. The Predictive Efficacy of Serum Exosomal microRNA-122 and microRNA-148a for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Smart Healthcare. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5914541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, W.H.; Xiong, L.K.; Guo, D.L. Exosomal miR-9-3p suppresses HBGF-5 expression and is a functional biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva Med. 2018, 109, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ding, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Yin, T.; Han, S.; Geng, J.; Sun, W. Downregulation of serum exosomal miR-320d predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, P.; Xiang, R.; Yang, S. Exosomal miR-451a Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting LPIN1. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhen, S.; Yu, Q.; Gong, Z. HCV-E2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by stimulating mast cells to secrete exosomal shuttle microRNAs. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladabaum, U.; Dominitz, J.A.; Kahi, C.; Schoen, R.E. Strategies for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Zhang, H.; Tian, R.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tian, J.; Cui, Y.; Ren, S.; Zuo, X.; et al. Exosomal EPHA2 derived from highly metastatic breast cancer cells promotes angiogenesis by activating the AMPK signaling pathway through Ephrin A1-EPHA2 forward signaling. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4127–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Leng, K.; Xu, Y.; Mei, L.; Han, P.; Zhang, B.; Yao, K.; Li, C.; et al. Colorectal cancer-derived exosomal miR-106b-3p promotes metastasis by down-regulating DLC-1 expression. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2020, 134, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Peng, J.; Huang, D.; Sun, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, W.; et al. miRNA-99b-5p suppresses liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by down-regulating mTOR. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24448–24462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, B.; Hao, T. Up-regulation of mir-10b predicate advanced clinicopathological features and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2932–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, C.; Cheng, M.; Jin, C.; Duan, Q.; Xu, D.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ren, B.; et al. Exosomal miR-6803-5p as potential diagnostic and prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 4113–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, Q.; Huang, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-128-3p Promotes Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting FOXO4 via TGF-β/SMAD and JAK/STAT3 Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 568738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Lan, X.; Song, F.; Sun, J.; Zhou, K.; Liu, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Cancer-derived exosomal miR-25-3p promotes pre-metastatic niche formation by inducing vascular permeability and angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Song, W. miR-424-5p promotes the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by directly targeting SCN4B. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.H.; Tian, D.; Yang, Z.C.; Li, J.L. Exosomal miR-21 promotes proliferation, invasion and therapy resistance of colon adenocarcinoma cells through its target PDCD4. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uratani, R.; Toiyama, Y.; Kitajima, T.; Kawamura, M.; Hiro, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Mohri, Y.; Mori, T.; et al. Diagnostic Potential of Cell-Free and Exosomal MicroRNAs in the Identification of Patients with High-Risk Colorectal Adenomas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Shang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Jing, J.; Fang, Y. Exosomal miR-224-5p from Colorectal Cancer Cells Promotes Malignant Transformation of Human Normal Colon Epithelial Cells by Promoting Cell Proliferation through Downregulation of CMTM4. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5983629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohmen, J.; Semaan, A.; Kobilay, M.; Zaleski, M.; Branchi, V.; Schlierf, A.; Hettwer, K.; Uhlig, S.; Hartmann, G.; Kalff, J.C.; et al. Diagnostic Potential of Exosomal microRNAs in Colorectal Cancer. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Dou, R.; Wei, C.; Liu, K.; Shi, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Xiong, B. Tumor-derived exosomal microRNA-106b-5p activates EMT-cancer cell and M2-subtype TAM interaction to facilitate CRC metastasis. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2088–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Zhou, F.; Nie, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. Hypoxic colorectal cancer-secreted exosomes deliver miR-210-3p to normoxic tumor cells to elicit a protumoral effect. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Li, J.; Hong, Z.; Jia, F.; He, Y.; Yuan, L. The role of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-431-5p in survival and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. Mutagenesis 2022, 37, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Mi, Y.; Guan, B.; Zheng, B.; Wei, P.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, A.; Wang, X.; Gu, C.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Zeng, B.; Chen, C.; Ji, P.; Wu, J.; Quan, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-183-5p promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by regulation of FOXO1. Aging 2020, 12, 8352–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Ye, A.; Ye, W.; Liao, X.; Qin, G.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Luo, H.; Yi, M.; Xian, L.; et al. Cancer-secreted exosomal miR-21-5p induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability by targeting KRIT1. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Yu, C.H.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, S.Z.; Yu, W.Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q. Exosomal miR-1229 derived from colorectal cancer cells promotes angiogenesis by targeting HIPK2. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, R.; Liu, K.; Yang, C.; Zheng, J.; Shi, D.; Lin, X.; Wei, C.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. EMT-cancer cells-derived exosomal miR-27b-3p promotes circulating tumour cells-mediated metastasis by modulating vascular permeability in colorectal cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ge, H.; Liu, Y. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-93-5p from cancer-associated fibroblasts confer radioresistance in colorectal cancer cells by downregulating FOXA1 and upregulating TGFB3. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J. Exosomal miR-590-3p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers radioresistance in colorectal cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Wei, C.; Xia, S.; Qiao, Z.; Zhang, X.W.; Yu, B.; Zhou, J.; Wang, R. Exosomal miR-625-3p secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts in colorectal cancer promotes EMT and chemotherapeutic resistance by blocking the CELF2/WWOX pathway. Pharm. Res. 2022, 186, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Geng, Y.; Xue, F.; Zhang, J. Colorectal cancer cell-derived exosomes containing miR-10b regulate fibroblast cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Bull. Cancer 2018, 105, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lai, Q.; Fang, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Gu, C.; Chen, J.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomal miR-17-5p promotes colorectal cancer aggressive phenotype by initiating a RUNX3/MYC/TGF-β1 positive feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 2020, 491, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Si, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, S.; Qu, X.; Yu, X. Exosomal miR-146a-5p and miR-155-5p promote CXCL12/CXCR7-induced metastasis of colorectal cancer by crosstalk with cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Sun, W.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Ba, Y. Plasma Exosomal miRNA Expression Profile as Oxaliplatin-Based Chemoresistant Biomarkers in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bian, Z.; Yao, S.; Fei, B.; Zhou, L.; Yin, Y.; Huang, Z. A panel of serum exosomal microRNAs as predictive markers for chemoresistance in advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2019, 84, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, M. Novel exosomal miR-46146 transfer oxaliplatin chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wei, S. EVs delivery of miR-1915-3p improves the chemotherapeutic efficacy of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2021, 88, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.H.; Kuo, W.W.; Shih, H.N.; Cheng, S.F.; Yang, C.K.; Chen, M.C.; Tu, C.C.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Liao, P.H.; Huang, C.Y. FOXC1 Regulation of miR-31-5p Confers Oxaliplatin Resistance by Targeting LATS2 in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Ren, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, D. Exosomal miR-548c-5p Regulates Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth and Invasion Through HIF1A/CDC42 Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 9875–9885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.; Baghaei, K.; Hajivalili, M.; Zali, M.R.; Ebtekar, M.; Amani, D. The anti-tumor effects of CT-26 derived exosomes enriched by MicroRNA-34a on murine model of colorectal cancer. Life Sci. 2022, 290, 120234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangiri, B.; Khalaj-Kondori, M.; Asadollahi, E.; Purrafee Dizaj, L.; Sadeghizadeh, M. MSC-Derived exosomes suppress colorectal cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via miR-100/mTOR/miR-143 pathway. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 627, 122214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tong, H.X.; Yang, H.; Liu, W.F.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J. Low expression of exosomal miR-150 predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients after surgical resections. Carcinogenesis 2022, 43, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.Y.; Gu, R.H.; Yan, B. Downregulation of exosome-encapsulated miR-548c-5p is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokutani, Y.; Uemura, M.; Munakata, K.; Okuzaki, D.; Haraguchi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Nishimura, J.; Hata, T.; Murata, K.; Takemasa, I.; et al. Down-Regulation of microRNA-132 is Associated with Poor Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Cui, M.; Zhang, H. miR-140-3p inhibits colorectal cancer progression and its liver metastasis by targeting BCL9 and BCL2. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 3358–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, P.P.; Huang, J.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Yuan, J.Z.; Ma, E.M.; Liu, X.; Bai, J. Reduced serum exosomal miR-874 expression predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 24, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wan, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, J.; Han, M.; Zhou, C. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNA-3940-5p Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Integrin α6. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, F.; Ying, Y.; Pan, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, H.; Zhan, X. MicroRNA-466 (miR-466) functions as a tumor suppressor and prognostic factor in colorectal cancer (CRC). Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 18, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, B.; Wang, Y. Exosome-Transmitted miR-506-3p Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Malignancy via Regulating GSTP1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Ge, Z.Z.; Qu, Y.Y.; Cao, Y.; Kang, Z.X. Downregulation of serum exosomal miR-150-5p is associated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 26, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Devasia, T.; Mariotto, A.B.; Yabroff, K.R.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, Z.; Talkhabi, M.; Taleahmad, S. Identification of potential microRNA diagnostic panels and uncovering regulatory mechanisms in breast cancer pathogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadirad, A.; Khodadadi, A.; Talaiezadeh, A.; Shohan, M.; Rashno, M.; Joudaki, N. Evaluation of miRNA-21-5p and miRNA-10b-5p levels in serum-derived exosomes of breast cancer patients in different grades. Mol. Cell. Probes 2022, 64, 101831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.J.; Yang, H.B.; Jing, J.F.; Jia, M.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Guo, F.; Gao, J.N. Identification of serum exosomal miR-148a as a novel prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 24, 7303–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Dong, X. Serum Exosomal miR-17-5p as a Promising Biomarker Diagnostic Biomarker for Breast Cancer. Clin. Lab. 2020, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueta, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tomiguchi, M.; Takeshita, T.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Iwase, H. Differential expression of exosomal miRNAs between breast cancer patients with and without recurrence. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69934–69944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Q. Cancer-derived exosomal miR-7641 promotes breast cancer progression and metastasis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qian, T.; Bao, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, H.; Xing, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Meng, X.; Wang, C.; et al. Circulating exosomal miR-363-5p inhibits lymph node metastasis by downregulating PDGFB and serves as a potential noninvasive biomarker for breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 2466–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Mo, F.; Song, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S. Exosomal hsa-miR-21-5p is a biomarker for breast cancer diagnosis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, K.; Ni, C.; Lv, Z.; Guan, D. Identification of exosomal miR-455-5p and miR-1255a as therapeutic targets for breast cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20190303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Mao, J.H.; Wang, B.Y.; Wang, L.X.; Wen, H.Y.; Xu, L.J.; Fu, J.X.; Yang, H. Exosomal miR-1910-3p promotes proliferation, metastasis, and autophagy of breast cancer cells by targeting MTMR3 and activating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020, 489, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Yang, S.; Zhou, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, S.; Feng, J. Microenvironment-induced TIMP2 loss by cancer-secreted exosomal miR-4443 promotes liver metastasis of breast cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5722–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lai, S.; Qu, F.; Li, Z.; Fu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhong, X.; Wang, C.; Li, H. CCL18 promotes breast cancer progression by exosomal miR-760 activation of ARF6/Src/PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Lowry, M.C.; Corcoran, C.; Martinez, V.G.; Daly, M.; Rani, S.; Gallagher, W.M.; Radomski, M.W.; MacLeod, R.A.; O’Driscoll, L. miR-134 in extracellular vesicles reduces triple-negative breast cancer aggression and increases drug sensitivity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32774–32789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H.; Yu, Q. Exosomal MicroRNA MiR-1246 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Drug Resistance by Targeting CCNG2 in Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Dou, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, P.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, M. Breast Cancer Exosome-Derived miR-425-5p Induces Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Like Properties in Human Mammary Fibroblasts by TGFβ1/ROS Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5266627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, L.; Gao, R.; Che, C.; Yang, G. Downregulation of exosomal miR-7-5p promotes breast cancer migration and invasion by targeting RYK and participating in the atypical WNT signalling pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Tao, X.; Shen, X. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes inhibit migration and invasion of breast cancer cells via miR-21-5p/ZNF367 pathway. Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, P.M.M.; Alkhilaiwi, F.; Cavalli, I.J.; Malheiros, D.; de Souza Fonseca Ribeiro, E.M.; Cavalli, L.R. Extracellular vesicles from triple-negative breast cancer cells promote proliferation and drug resistance in non-tumorigenic breast cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 172, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Fan, P.; Zhang, C.; Xie, J.; Gu, X.; Lei, S.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Z. Exosomal microRNA-503-3p derived from macrophages represses glycolysis and promotes mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in breast cancer cells by elevating DACT2. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scognamiglio, I.; Cocca, L.; Puoti, I.; Palma, F.; Ingenito, F.; Quintavalle, C.; Affinito, A.; Roscigno, G.; Nuzzo, S.; Chianese, R.V.; et al. Exosomal microRNAs synergistically trigger stromal fibroblasts in breast cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 28, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Q. Exosomal miR-500a-5p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through targeting USP28. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3932–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Sheng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, R.; Xiao, Q.; Shi, L.; Li, H.; Yin, C.; Luo, H.; Hao, C.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal miR-18b promotes breast cancer invasion and metastasis by regulating TCEAL7. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, K.; Mossahebi-Mohammadi, M.; Ghazimoradi, M.H.; Cho, W.C.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Babashah, S. Monocytes educated by cancer-associated fibroblasts secrete exosomal miR-181a to activate AKT signaling in breast cancer cells. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Stevic, I.; Pan, C.; Müller, V.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Different signatures of miR-16, miR-30b and miR-93 in exosomes from breast cancer and DCIS patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichelser, C.; Stückrath, I.; Müller, V.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Wikman, H.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Increased serum levels of circulating exosomal microRNA-373 in receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9650–9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtaz, C.J.; Reifschläger, L.; Strähle, L.; Feldheim, J.; Feldheim, J.J.; Schmitt, C.; Kiesel, M.; Herbert, S.L.; Wöckel, A.; Meybohm, P.; et al. Analysis of microRNAs in Exosomes of Breast Cancer Patients in Search of Molecular Prognostic Factors in Brain Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Shi, Z.; Cao, L.; Liu, J.; Pan, T.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J. Chemotherapy-elicited exosomal miR-378a-3p and miR-378d promote breast cancer stemness and chemoresistance via the activation of EZH2/STAT3 signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, T.; Tian, X.; Duan, X.; Zhang, C. Exosomal miR-1246 and miR-155 as predictive and prognostic biomarkers for trastuzumab-based therapy resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2020, 86, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Dong, C.; Ruan, X.; Yan, W.; Cao, M.; Pizzo, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, L.; Ren, X.; et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs Promote Breast Cancer Stemness by Targeting ONECUT2. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3608–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Hu, J.; Lu, P.; Cao, H.; Yu, C.; Li, X.; Qian, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Han, N.; et al. Exosome-transmitted miR-567 reverses trastuzumab resistance by inhibiting ATG5 in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.Z.; Ho, W.Y.; Yeap, S.K.; Ali, N.M.; Yong, C.Y.; Boo, L.; Alitheen, N.B. Exosomal-microRNA transcriptome profiling of Parental and CSC-like MDA-MB-231 cells in response to cisplatin treatment. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 233, 153854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, A.; de Miguel-Pérez, D.; Ortega, F.G.; García-Puche, J.L.; Robles-Fernández, I.; Exposito, J.; Martorell-Marugan, J.; Carmona-Sáez, P.; Garrido-Navas, M.D.C.; Rolfo, C.; et al. Exosomal miRNA profile as complementary tool in the diagnostic and prediction of treatment response in localized breast cancer under neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Leng, D. Detection significance of miR-3662, miR-146a, and miR-1290 in serum exosomes of breast cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jin, L.J.; Zhang, X.Y. Exosomal miRNA-205 promotes breast cancer chemoresistance and tumorigenesis through E2F1. Aging 2021, 13, 18498–18514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, X.; Yue, Q.; Cao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tian, J.; Lu, Y.; He, L.; Bai, J.; et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-16-5p restrains epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells via EPHA1/NF-κB signaling axis. Genomics 2022, 114, 110341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, B.; Wu, S.; Yang, W.; Luo, R.; Geng, S.; Xin, Z.; Jin, W.; Shen, X.; Gu, X.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-551b-3p from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells inhibits breast cancer progression via regulating TRIM31/Akt signaling. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 1797–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, X. Optimization of a method for the clinical detection of serum exosomal miR-940 as a potential biomarker of breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 956167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Exosome miR-134-5p restrains breast cancer progression via regulating PI3K/AKT pathway by targeting ARHGAP1. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 47, 4037–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaei-Poul, Y.; Shojaei, S.; Koochaki, A.; Ghanbarian, H.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S. Evaluating the influence of Human. Umbilical Cord. Mesenchymal Stem Cells-derived exosomes loaded with miR-3182 on metastatic performance of Triple Negative Breast Cancer cells. Life Sci. 2021, 286, 120015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, G.; Das, P.; Ranjan, P.; Valderrama, F.; Cieza-Borrella, C. Urinary extracellular vesicles miRNA-A new era of prostate cancer biomarkers. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1065757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagirath, D.; Yang, T.L.; Bucay, N.; Sekhon, K.; Majid, S.; Shahryari, V.; Dahiya, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Saini, S. microRNA-1246 Is an Exosomal Biomarker for Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, T.; Liang, M.; Du, M.; Xia, S.; Dittmar, R.; Wang, D.; See, W.; Costello, B.A.; Quevedo, F.; et al. Exosomal miR-1290 and miR-375 as prognostic markers in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endzeliņš, E.; Berger, A.; Melne, V.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Soboļevska, K.; Ābols, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Šantare, D.; Rudņickiha, A.; Lietuvietis, V.; et al. Detection of circulating miRNAs: Comparative analysis of extracellular vesicle-incorporated miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs in whole plasma of prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.F.; Li, R.; Kang, W.; Hao, X.K. Exosomal microRNA-141 is upregulated in the serum of prostate cancer patients. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Park, Y.H.; Jung, S.H.; Jang, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, Y.J. Urinary exosome microRNA signatures as a noninvasive prognostic biomarker for prostate cancer. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Zheng, Z.; Xue, D. Functional Implication of Exosomal miR-217 and miR-23b-3p in the Progression of Prostate Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 11595–11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Peng, R.; Fang, F.; Mao, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Dai, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Feng, N.; et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote prostate cancer progression via exosome-mediated miR-95 transfer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9729–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedemann, C.; Reinersmann, J.L.; Klinger, C.; Degener, S.; Dreger, N.M.; Roth, S.; Kaufmann, M.; Savelsbergh, A. Prostate Cancer-Associated miRNAs in Saliva: First Steps to an Easily Accessible and Reliable Screening Tool. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, T.Y.; Dou, M.; Ma, Y.B.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.D.; Chong, T.; Wang, Z.M.; Xue, L. miR-20b-5p is a novel biomarker for detecting prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, M.P.; Silva, A.H.; Cisilotto, J.; Rosolen, D.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. miR-425-5p as an exosomal biomarker for metastatic prostate cancer. Cell. Signal. 2021, 87, 110113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.J.; Pawlowski, T.; Catto, J.W.; Marsden, G.; Vessella, R.L.; Rhees, B.; Kuslich, C.; Visakorpi, T.; Hamdy, F.C. Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, A.; Fredsøe, J.; Sørensen, K.D.; Borre, M.; Evander, M.; Laurell, T.; Lilja, H.; Ceder, Y. High-Throughput and Automated Acoustic Trapping of Extracellular Vesicles to Identify microRNAs With Diagnostic Potential for Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 631021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawati, I.; Liu, M.C.; Hsieh, C.L.; Do, A.D.; Sung, S.Y. Targeting Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Using Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes for Therapeutic MicroRNA-let-7c Delivery. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2022, 27, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lu, X.; Yang, F.; Qin, L.; Yang, N.; Cai, P.; Han, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, H. The Expression of miR-205 in Prostate Carcinoma and the Relationship with Prognosis in Patients. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 1784791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, B.; Lin, L.; Zhu, Q.; Ye, L.; Li, T.; Li, F. Blood circulating exosomes carrying microRNA-423-5p regulates cell progression in prostate cancer via targeting FRMD3. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 2970–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Shin, H.; Moon, H.W.; Park, Y.H.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y. Urinary exosomal microRNA profiling in intermediate-risk prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albino, D.; Falcione, M.; Uboldi, V.; Temilola, D.O.; Sandrini, G.; Merulla, J.; Civenni, G.; Kokanovic, A.; Stürchler, A.; Shinde, D.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles release oncogenic miR-424 in experimental models and patients with aggressive prostate cancer. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, G.K.; Ramteke, A.; Birks, D.; Abouzeid Ali, H.E.; Venkataraman, S.; Agarwal, C.; Vibhakar, R.; Miller, L.D.; Agarwal, R.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; et al. Exosomal microRNA profiling to identify hypoxia-related biomarkers in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13894–13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Gao, X. Inhibition of cancer cell-derived exosomal microRNA-183 suppresses cell growth and metastasis in prostate cancer by upregulating TPM1. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, C.A.; Andahur, E.I.; Valenzuela, R.; Castellón, E.A.; Fullá, J.A.; Ramos, C.G.; Triviño, J.C. Exosomes from bulk and stem cells from human prostate cancer have a differential microRNA content that contributes cooperatively over local and pre-metastatic niche. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3993–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Yang, H.C.; Rhee, W.J. Simultaneous multiplexed detection of exosomal microRNAs and surface proteins for prostate cancer diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 146, 111749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, G.; Panio, A.; Cava, C.; Gallivanone, F.; Alini, M.; Strano, G.; Molfino, F.; Brioschi, L.; Viani, P.; Porro, D. Secreted miR-153 Controls Proliferation and Invasion of Higher Gleason Score Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foj, L.; Ferrer, F.; Serra, M.; Arévalo, A.; Gavagnach, M.; Giménez, N.; Filella, X. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal Urinary miRNAs in Prostate Cancer Detection and Prognosis. Prostate 2017, 77, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shim, J.S.; Han, B.H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.; Cho, I.J.; Kang, S.G.; Kang, J.Y.; Bong, K.W.; Choi, N. Hydrogel-based hybridization chain reaction (HCR) for detection of urinary exosomal miRNAs as a diagnostic tool of prostate cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryzgunova, O.E.; Zaripov, M.M.; Skvortsova, T.E.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Zaporozhchenko, I.A.; Morozkin, E.S.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Yurchenko, Y.B.; Voitsitskiy, V.E.; et al. Comparative Study of Extracellular Vesicles from the Urine of Healthy Individuals and Prostate Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdmann, J.; Markert, L.; Klinger, C.; Kaufmann, M.; Schork, K.; Turewicz, M.; Eisenacher, M.; Degener, S.; Dreger, N.M.; Roth, S.; et al. MicroRNAs from urinary exosomes as alternative biomarkers in the differentiation of benign and malignant prostate diseases. J. Circ. Biomark. 2022, 11, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Qin, S.; An, T.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, L. MiR-145 detection in urinary extracellular vesicles increase diagnostic efficiency of prostate cancer based on hydrostatic filtration dialysis method. Prostate 2017, 77, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Fujita, K.; Tomiyama, E.; Hatano, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Wang, C.; Ishizuya, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Kato, T.; et al. MiR-30b-3p and miR-126-3p of urinary extracellular vesicles could be new biomarkers for prostate cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.X.; Diao, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Ye, Y.; Hao, X.K. Identification of Urinary Exosomal miRNAs for the Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.; Kaul, D.; Mavuduru, R.S.; Kakkar, N.; Bhatia, A. Urinary-exosomal miR-2909: A novel pathognomonic trait of prostate cancer severity. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 259, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, S.L.; Ma, Y.Y.; Diao, Y.J.; Yang, L.; Su, M.Q.; Li, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wang, J.; Lei, L.; et al. Exosomal miR-141-3p regulates osteoblast activity to promote the osteoblastic metastasis of prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 94834–94849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Hu, K.; Qiu, S.; Xie, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ni, S.; Zhang, L. Exosomes derived from PC-3 cells suppress osteoclast differentiation by downregulating miR-148a and blocking the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Dai, R.; Deng, N.; Su, W.; Liu, P. Exosomal miR-1275 Secreted by Prostate Cancer Cells Modulates Osteoblast Proliferation and Activity by Targeting the SIRT2/RUNX2 Cascade. Cell. Transpl. 2021, 30, 9636897211052977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Ochi, H.; Sunamura, S.; Kosaka, N.; Mabuchi, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Yao, K.; Kanda, H.; Ae, K.; Okawa, A.; et al. Cancer-secreted hsa-miR-940 induces an osteoblastic phenotype in the bone metastatic microenvironment via targeting ARHGAP1 and FAM134A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2204–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Tan, Z.; Yang, M.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L. PC-3-Derived Exosomes Inhibit Osteoclast Differentiation by Downregulating miR-214 and Blocking NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8650846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudova, E.A.; Kobelyatskaya, A.A.; Katunina, I.V.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Fedorova, M.S.; Guvatova, Z.G.; Nyushko, K.M.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Pavlov, V.S.; Savvateeva, M.V.; et al. Dynamic Profiling of Exosomal microRNAs in Blood Plasma of Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Front. Biosci. (Sch. Ed.) 2022, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagirath, D.; Liston, M.; Akoto, T.; Lui, B.; Bensing, B.A.; Sharma, A.; Saini, S. Novel, non-invasive markers for detecting therapy induced neuroendocrine differentiation in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, C.; Rani, S.; O’Driscoll, L. miR-34a is an intracellular and exosomal predictive biomarker for response to docetaxel with clinical relevance to prostate cancer progression. Prostate 2014, 74, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ding, M.; Su, Y.; Cui, D.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, S.; Jia, G.; Wang, X.; Ruan, Y.; et al. Loss of exosomal miR-146a-5p from cancer-associated fibroblasts after androgen deprivation therapy contributes to prostate cancer metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Bai, L.; Liao, R.; Zhao, J.; Guo, M.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; et al. MicroRNA-375 is a therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer through the PTPN4/STAT3 axis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1290–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Guan, H.; Mizokami, A.; Keller, E.T.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, J.; Hu, L.; Lu, Y.; et al. Exosome-derived microRNAs contribute to prostate cancer chemoresistance. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Gui, Q. Exosomal Circ-XIAP Promotes Docetaxel Resistance in Prostate Cancer by Regulating miR-1182/TPD52 Axis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 2021, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, S. Exosome-derived miR-27a produced by PSC-27 cells contributes to prostate cancer chemoresistance through p53. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannistraci, A.; Federici, G.; Addario, A.; Di Pace, A.L.; Grassi, L.; Muto, G.; Collura, D.; Signore, M.; De Salvo, L.; Sentinelli, S.; et al. C-Met/miR-130b axis as novel mechanism and biomarker for castration resistance state acquisition. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3718–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.; Yu, G.; Jia, Z.; Wang, X. Prostate carcinoma cell-derived exosomal MicroRNA-26a modulates the metastasis and tumor growth of prostate carcinoma. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 117, 109109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, G.; Gu, J.; Zhou, D.; Li, L.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T.; Wang, X. Cancer-associated fibroblast-secreted exosomal miR-423-5p promotes chemotherapy resistance in prostate cancer by targeting GREM2 through the TGF-β signaling pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Exosomal circRNA HIPK3 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and metastasis in prostate cancer by regulating miR-212/BMI-1 pathway. J. Biosci. 2021, 46, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y. Suppressive function of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-187 in prostate cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aseervatham, J. Dynamic Role of Exosome microRNAs in Cancer Cell Signaling and Their Emerging Role as Noninvasive Biomarkers. Biology 2023, 12, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050710
Aseervatham J. Dynamic Role of Exosome microRNAs in Cancer Cell Signaling and Their Emerging Role as Noninvasive Biomarkers. Biology. 2023; 12(5):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050710
Chicago/Turabian StyleAseervatham, Jaya. 2023. "Dynamic Role of Exosome microRNAs in Cancer Cell Signaling and Their Emerging Role as Noninvasive Biomarkers" Biology 12, no. 5: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050710
APA StyleAseervatham, J. (2023). Dynamic Role of Exosome microRNAs in Cancer Cell Signaling and Their Emerging Role as Noninvasive Biomarkers. Biology, 12(5), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050710




