High Chromosomal Reorganization and Presence of Microchromosomes in Chactidae Scorpions from the Brazilian Amazon
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Karyotype Analysis
2.2. Probes
2.3. Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
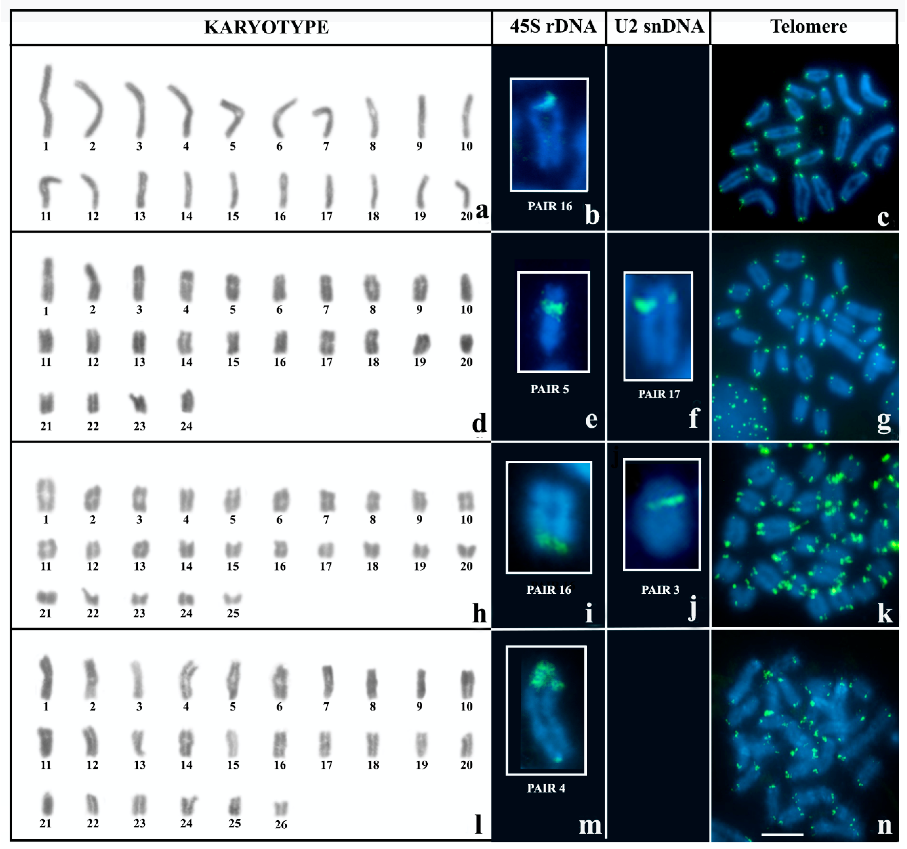
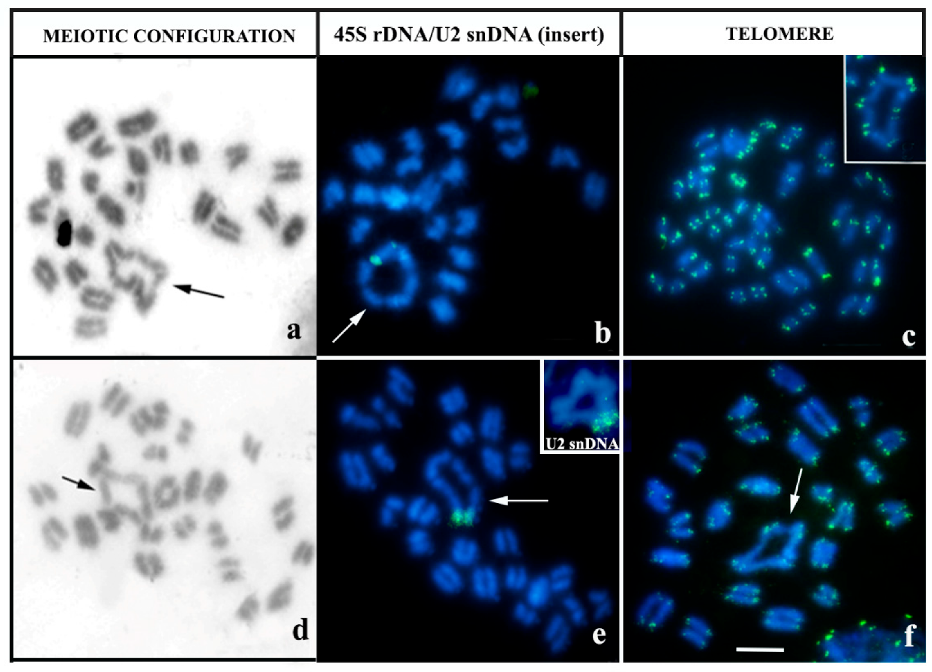
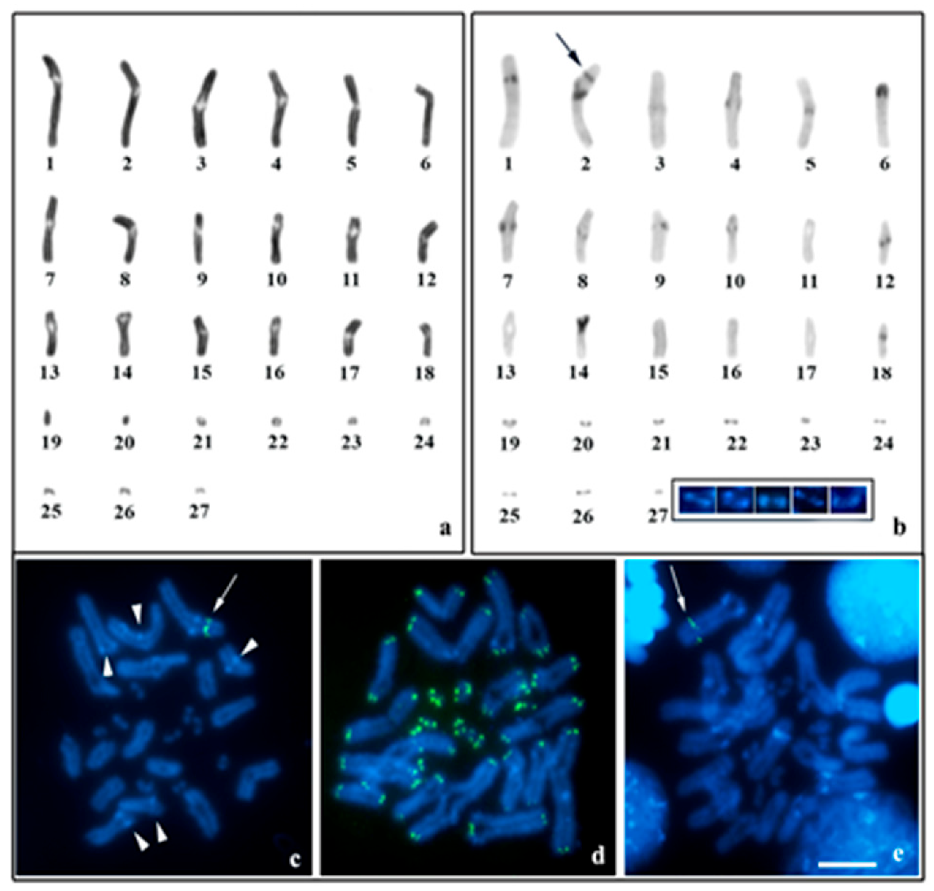
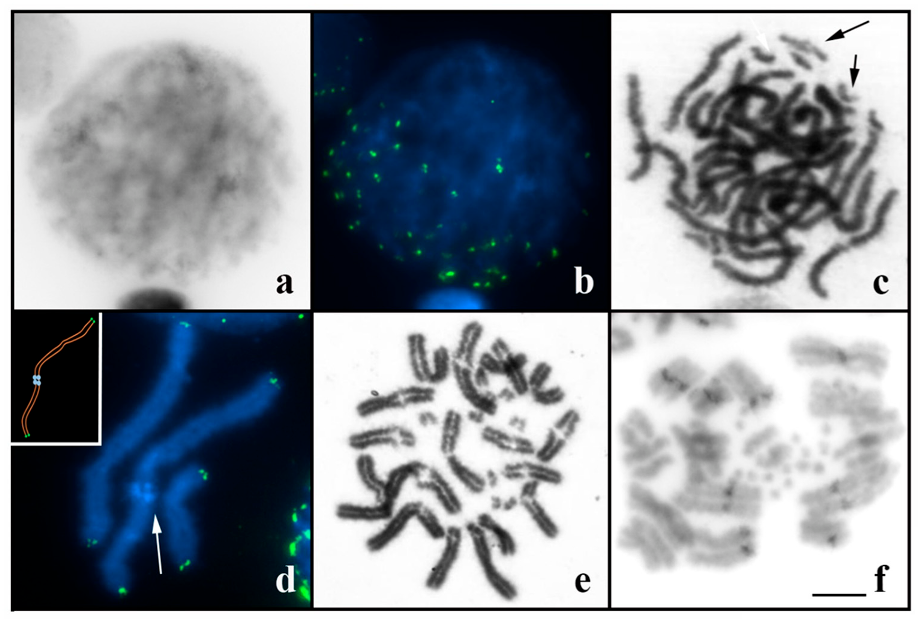
3. Results
3.1. Karyotype and Repetitive DNA Mapping in Brotheas
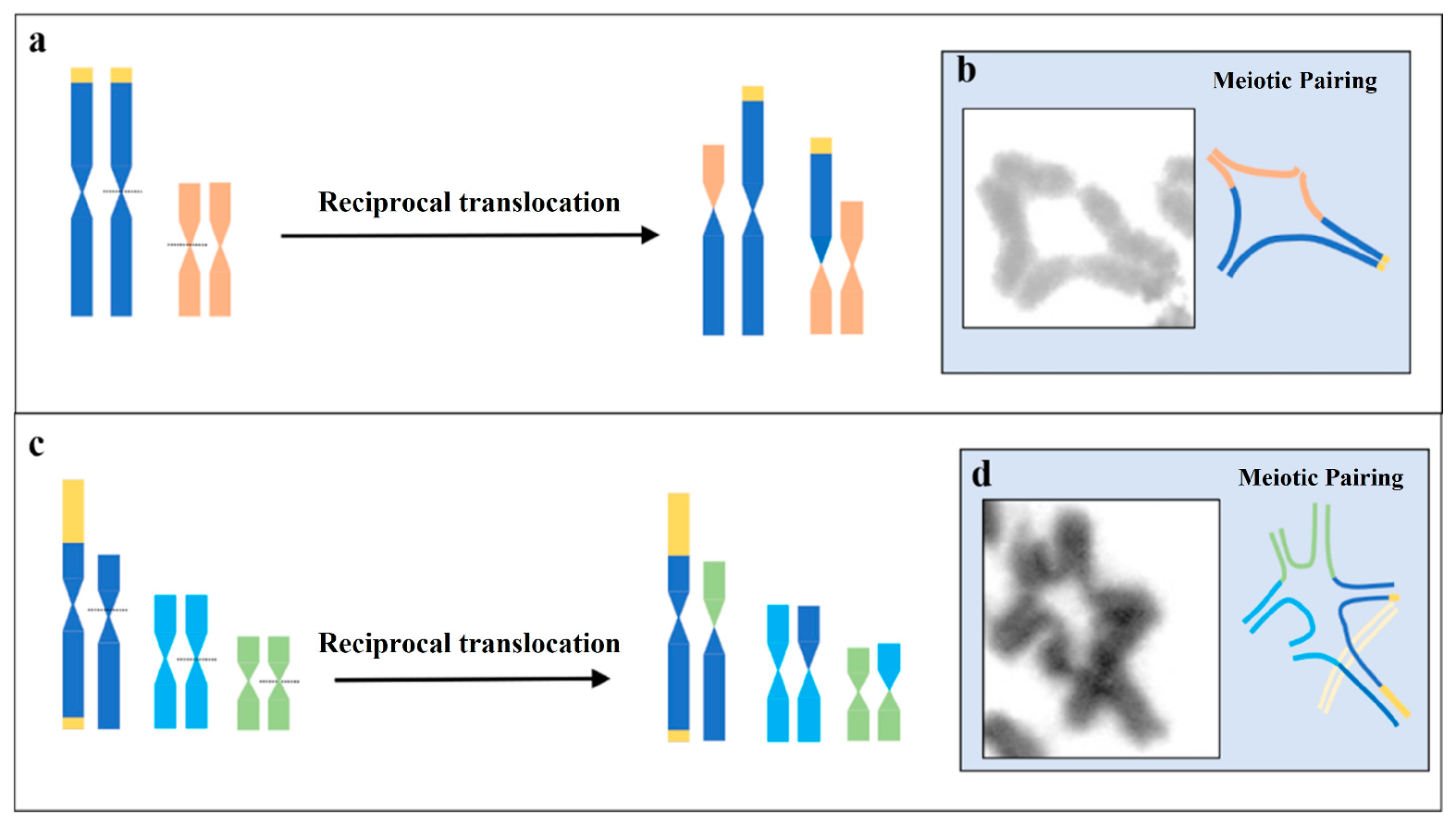
3.2. Multi-Chromosomal Meiotic Associations in Brotheas
3.3. Neochactas parvulus
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparative Karyotype Analysis of B. silvestris and B. paraensis
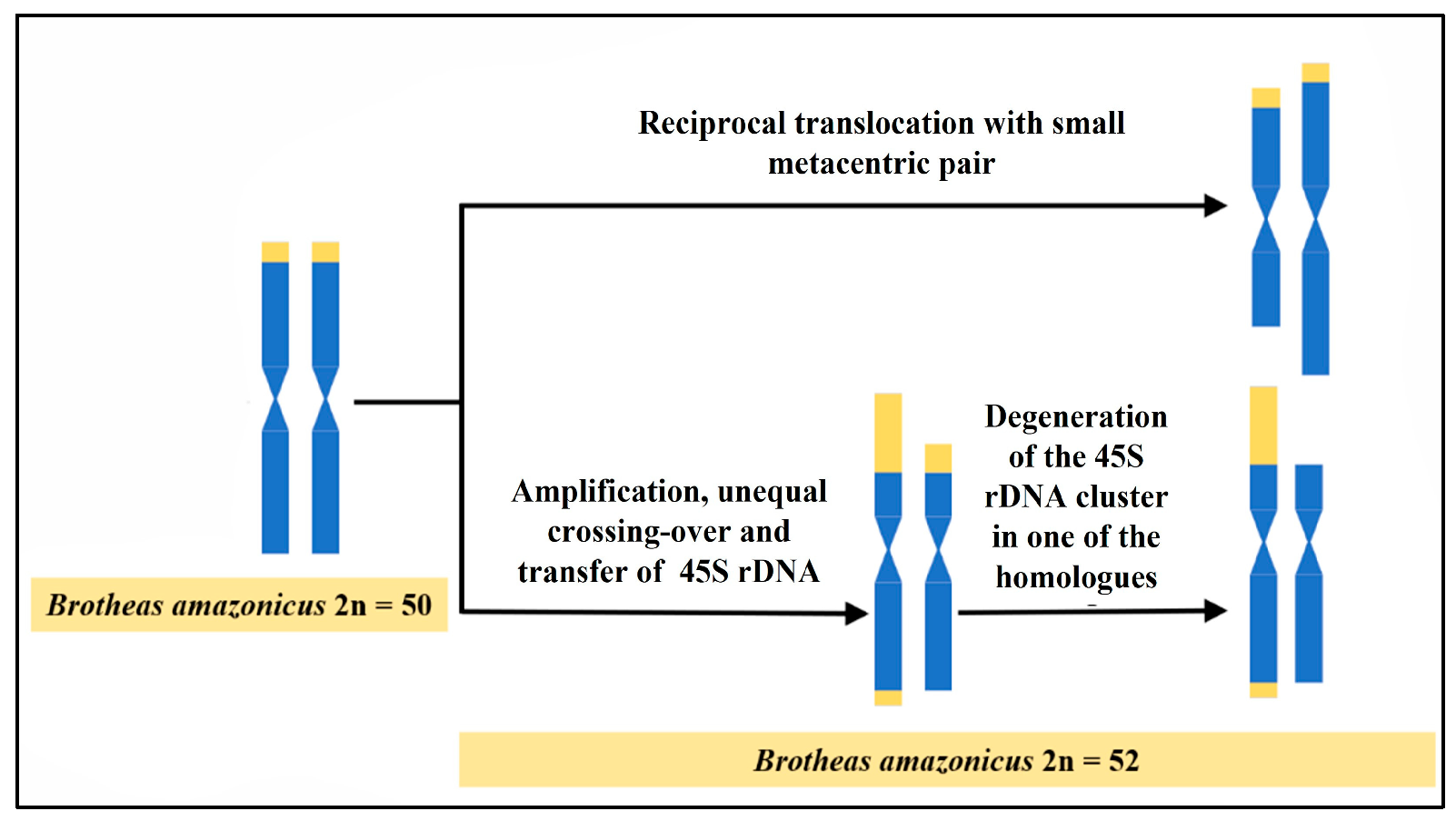
4.2. Cytogenetic Diversity in B. amazonicus
4.3. Bimodal Karyotype in N. parvulus
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Scorpion Files. Available online: http://scorpion-files.blogspot.com/ (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Plíšková, J.; Kovařík, F.; Košulič, O.; Štáhlavský, F. Description of a New species of Heterometrus Ehrenberg, 1828 (Scorpiones: Scorpionidae) from Thailand with remarks about the utilization of cytogenetic data in taxonomy of the genus. Ann. Zool. 2016, 66, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, B.R.R.; Milhomem-Paixão, S.S.R.; Noronha, R.C.R.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Costa, M.J.R.; Pardal, P.P.O.; Coelho, J.S.; Pieczarka, J.C. Karyotype diversity and chromosomal organization of repetitive DNA in Tityus obscurus (Scorpiones, Buhidae). BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adilardi, R.S.; Ojanguren-Affilastro, A.A.; Martí, D.A.; Mola, L.M. Chromosome puzzle in the southernmost populations of the medically important scorpion Tityus bahiensis (Perty 1833) (Buthidae), a polymorphic species with striking structural rearrangements. Zoo. Anz. 2020, 288, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harewood, L.; Fraser, P. The impact of chromosomal rearrangements on regulation of gene expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R76–R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Baurens, F.; Hervouet, C.; Salmon, F.; Delos, J.; Labadie, K.; Perdereau, A.; Mournet, P.; Blois, L.; Dupouy, M.; et al. Chromosome reciprocal translocations have accompanied subspecies evolution in bananas. Plant J. 2020, 104, 1698–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Herrera, A.; Castresana, J.; Robinson, T.J. Is mammalian chromosomal evolution driven by regions of genome fragility? Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glugoski, L.; Giuliano-Caetano, L.; Moreira-Filho, O.; Vicari, M.R.; Nogaroto, V. Co-located hAT transposable element and 5S rDNA in an interstitial telomeric sequence suggest the formation of Robertsonian fusion in armored catfish. Gene 2018, 650, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argueso, J.L.; Westmoreland, J.; Mieczkowski, P.A.; Gawel, M.; Petes, T.D.; Resnick, M.A. Double-strand breaks associated with repetitive DNA can reshape the genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11845–11850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delprat, A.; Negre, B.; Puig, M.; Ruiz, A. The transposon Galileo generates natural chromosomal inversions in Drosophila by ectopic recombination. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelfo, A.; Fachinetti, D. Keeping the centromere under control: A promising role for DNA methylation. Cells 2019, 8, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, N.; Beckmann, R.; Cate, J.H.; Dinman, J.D.; Dragon, F.; Ellis, S.R.; Lafontaine, D.L.; Lindahl, L.; Liljas, A.; Lipton, J.M.; et al. A new system for naming ribosomal proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 24, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochorová, J.; Garcia, S.; Gálvez, F.; Symonová, R.; Kovařík, A. Evolutionary trends in animal ribosomal DNA loci: Introduction to a new online database. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, V.F.; Carvalho, L.S.; Cella, D.M.; Schneider, M.C. Location of 45S ribosomal genes in mitotic and meiotic chromosomes of Buthid scorpions. Zoolog. Sci. 2014, 31, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šťáhlavský, F.; Štundlová, J.; Lowe, G.; Stockmann, M.; Kovařík, F. Application of cytogenetic markers in the taxonomy of flat rock scorpions (Scorpiones: Hormuridae), with the description of Hadogenes weygoldti sp. n. Zool. Anz. 2018, 273, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, B.R.R.; Noronha, R.C.R.; Costa, M.J.R.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Pieczarka, J.C. Meiosis in the scorpion Tityus silvestris: New insights into achiasmatic chromosomes. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio04352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štundlová, J.; Šmíd, J.; Nguyen, P.; Šťáhlavský, F. Cryptic diversity and dynamic chromosome evolution in Alpine scorpions (Euscorpiidae: Euscorpius). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 134, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šťáhlavský, F.; Nguyen, P.; Sadílek, D.; Štundlová, J.; Just, P.; Haddad, C.R.; Koç, H.; Ranawana, K.B.; Stockmann, M.; Yağmur, E.A.; et al. Evolutionary dynamics of rDNA clusters on chromosomes of buthid scorpions (Chelicerata: Arachnida). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 131, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilardi, R.S.; Ojanguren-Affilastro, A.A.; Mattoni, C.I.; Mola, L.M. Male and female meiosis in the mountain scorpion Zabius fuscus (Scorpiones, Buthidae): Heterochromatin, rDNA and TTAGG telomeric repeats. Genetica 2015, 143, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, G.; Martínez, J.; Méndez, I. Karyotype studies in cultivars of Agave tequilana Weber. Caryologia 2008, 61, 144–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mckain, M.R.; Wickett, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ayyampalayam, S.; Mccombie, W.R.; Chase, M.W.; Pires, J.C.; DE Pamphilis, C.W.; Leebens-Mack, J. Phylogenomic analysis of transcriptome data elucidates co-occurrence of a paleopolyploid event and the origin of bimodal karyotypes in Agavoideae (Asparagaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, M.; Vaio, M.; Dreissig, S.; Schubert, V.; Houben, A.; Pedrosa-Harand, A. Together but different: The subgenomes of the bimodal Eleutherine karyotypes are differentially organized. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 7, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, R.E.; Kiazim, L.; Skinner, B.; Fonseka, G.; Joseph, S.; Jennings, R.; Larkin, D.M.; Griffin, D.K. Patterns of microchromosome organization remain highly conserved throughout avian evolution. Chromosoma 2018, 128, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcqueen, H.A.; Siriaco, G.; Bird, A.P. Chicken microchromosomes are hyperacetylated, early replicating, and gene rich. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, B.M.; Robertson, L.B.W.; Tempest, H.G.; Langley, E.J.; Ioannou, D.; Fowler, K.E.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; Hall, A.D.; Griffin, D.K.; Völker, M. Comparative genomics in chicken and Pekin duck using FISH mapping and microarray analysis. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaschenz, R.; Livernois, A.M.; Rao, S.; Ezaz, T.; Deakin, J.E. Immunofluorescent staining reveals hypermethylation of microchromosomes in the central bearded dragon, Pogona vitticeps. Mol. Cytogenet. 2015, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, J.E.; Ezaz, T. Understanding the Evolution of Reptile Chromosomes through Applications of Combined Cytogenetics and Genomics Approaches. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2019, 157, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.C.; Zacaro, A.A.; Pinto-Da-Rocha, R.; Candido, D.M.; Cella, D.M. A comparative cytogenetic analysis of 2 Bothriuridae species and overwiew of the chromosome data of Scorpion. J. Hered. 2009, 100, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, V.F.; Carvalho, L.S.; Carvalho, M.A.; Schneider, M.C. Insights into the origin of the high variability of multivalent-meiotic associations in holocentric chromosomes of Tityus (Archaeotityus) scorpions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A. Contribution to the knowledge of cytology of two species of Brazilian scorpions: Opisthacantus manauarensis, Ferreira, 1967 (Scorpiones, Scorpionidae) and Bothriurus asper araguaie (Scorpiones, Bothriuridae). An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1968, 40, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço, W.R. Scorpiones. In ADIS, J. (org.). Amazonian Arachnida and Miryapoda: Identification Keys to All Classes, Orders, Families, Some Genera and List of Know Terrestrial Species; Pensoft Publishes: Moscow, Russia, 2002; pp. 399–438. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, A.T. A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 1972, 75, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirov, I.; Khrustaleva, L.; Van Laere, K.; Soloviev, A.; Meeus, S.; Romanov, D.; Fesenko, I. DRAWID: User-friendly java software for chromosome measurements and idiogram drawing. Comp. Cytogenet. 2017, 11, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levan, A.; Fredga, K.; Sandberg, A.A. Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromossomes. Hereditas 1964, 52, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, W.L.; Bedbrook, J.R. Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 1979, 7, 1869–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahara, K.; Marec, F.; Traut, W. TTAGG Telomeric repeats in chromosomes of some insects and other arthropods. Chromosome Res. 1999, 7, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgan, D.J.; Mclauchlan, A.; Wilson, G.D.F.; Livingston, S.P.; Edgecombe, G.D.; Macaranas, J.; Cassis, G.; Gray, M.R. Histone H3 and U2 snRNA DNA sequences and arthropod molecular evolution. Austral. J. Zool. 1998, 46, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-De-Mello, D.C.; Marec, F. Universal fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) protocol for mapping repetitive DNAs in insects and other arthropods. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2021, 296, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, C.M. Cytogenetics of Australian scorpions. II. Chromosome polymorphism in species of Urodacus (family Scorpionidae). Genome 1989, 32, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höffer, H.; Wollsscheid, E.; Gasnier, T. The relative abundance of Brotheas amazonicus (Chactidae, Scorpiones) in different habitat types of a central amazon rainforest. J. Arachnol. 1996, 24, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Frade, L.F.D.S.; Almeida, B.R.R.; Milhomem-Paixão, S.S.R.; Ready, J.S.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Pieczarka, J.C.; Noronha, R.C.R. Karyoevolution of Crenicichla heckel 1840 (Cichlidae, Perciformes): A process mediated by inversions. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio041699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, P.; Ferro, J.M.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Cardozo, D.E.; Blasco-Zúñiga, A.; Silva, J.B.; Marciano, E., Jr.; Costa, M.A.; Orrico, V.G.D.; Solé, M.; et al. Chromosome evolution in Lophyohylini (Amphibia, Anura, Hylinae). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Chen, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, R.; Li, Q.; Han, Y.; Li, Z. Comparative chromosomal localization of 45S and 5S rDNA sites in 76 purple-fleshed sweet potato cultivars. Plants 2020, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, M.S.; DE Souza, M.J.; Loreto, V. Chromosomal evolution of rDNA and H3 histone genes in representative Romaleidae grasshoppers from northeast Brazil. Mol. Cytogenet. 2013, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.V.; Cruz, C.; Hull, R.M.; Keller, M.A.; Ralser, M.; Houseley, J. Regulation of ribosomal DNA amplification by the TOR pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9674–9679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ma, L.; Yang, F.; Fei, S.Z.; Li, L. 45S rDNA regions are chromosome fragile sites expressed as gaps in vitro on metaphase chromosomes of root-tip meristematic cells in Lolium spp. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazaux, B.; Catalan, J.; Veyrunes, F.; Douzery, E.J.; Britton-Davidian, J. Are ribosomal DNA clusters rearrangement hotspots?: A case study in the genus Mus (Rodentia, Muridae). BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H. Chromosome dynamics regulating genomic dispersion and alteration of Nucleolus Organizer Regions (NORs). Cells 2020, 9, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, R.C.R.; DE Almeida, B.R.R.; DA Costa, M.J.R.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Martins, C.; Pieczarka, J.C. Meiotic analyses show adaptations to maintenance of fertility in X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5Y5 system of amazon frog Leptodactylus pentadactylus (Laurenti, 1768). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagómez, D.A.; Ayala-Valdovinos, M.A.; Galindo-García, J.; Sánchez-Chipres, D.R.; Mora-Galindo, J.; Taylor-Preciado, J.J. Extensive nonhomologous meiotic synapsis between normal chromosome axes of an rcp(3;6)(p14;q21) translocation in a hairless mexican boar. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 120, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornienko, O.S.; Gusachenko, A.M.; Vysotskaya, L.V. C-heterochromatin during synapsis and recombination in grey cockroach Nauphoeta cinerea spermatogenesis. Cell Tissue Biol. 2009, 3, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cruz, R.; Robles, P.; Steinberg, E.R.; Camats, N.; Brieño, M.A.; Garcia-Caldés, M.; Mudry, M.D. Pairing and recombination features during meiosis in Cebus paraguayanus (Primates: Platyrrhini). BMC Genet. 2009, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickler, D.; Kleckner, N. Meiotic chromosomes: Integrating structure and function. Ann. Rev. Genet. 1999, 33, 603–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganley, A.R.; Kobayashi, T. Highly efficient concerted evolution in the ribosomal DNA repeats: Total rDNA repeat variation revealed by whole-genome shotgun sequence data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.; Kovařík, A.; Leitch, A.R.; Garnatje, T. Cytogenetic features of rRNA genes across land plants: Analysis of the Plant rDNA database. Plant J. 2017, 89, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilardi, R.S.; Ojanguren-Affilastro, A.A.; Mola, L.M. Sex-Linked chromosome heterozygosity in males of Tityus confluens (Buthidae): A clue about the presence of sex chromosomes in scorpions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, R.S.T.; Gazoni, T.; Costa, M.A. Cytogenetics of warrior wasps (Vespidae: Synoeca) reveals intense evolutionary dynamics of ribosomal DNA clusters and an unprecedented number of microchromosomes in Hymenoptera. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2019, 126, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhtanov, V.A. Two types of highly ordered micro- and macrochromosome arrangement in metaphase plates of butterflies (Lepidoptera). Comp. Cytogenet. 2019, 13, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, A.; Fontanetti, C.S.; Ferreira, A. The Chromosomes and the sex determining mechanism of Scaphura nigra (Orthoptera, Ensifera, Tettigoniidae, Phaneropterinae). J. Orthoptera Res. 2010, 19, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, V.G.; Maryańska-Nadachowska, A.; Shapoval, N.A.; Anokhin, B.A.; Shapoval, A.P. Cytogenetic characterization of eight Odonata species originating from the curonian spit (the Baltic Sea, Russia) using C-banding and FISH with 18S rDNA and Telomeric (TTAGG) Probes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2017, 153, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, M.G.; Bastos, C.E.M.C.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Pieczarka, J.C.; Vicari, M.R.; Noronha, R.C.R. Physical mapping of repetitive DNA suggests 2n reduction in Amazon turtles Podocnemis (Testudines: Podocnemididae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, T.F.A.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Aleixo, A.; Pinheiro, M.L.S.; O’brien, P.C.M.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Yang, F.; Suarez, P.; Pieczarka, J.C. Chromosome painting in Glyphorynchus spirurus (Vieillot, 1819) detects a new fission in Passeriformes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikulnath, K.; Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Matsuda, Y. Karyotype evolution in monitor lizards: Cross-species chromosome mapping of cDNA reveals highly conserved synteny and gene order in the Toxicofera clade. Chromosome Res. 2013, 21, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, H.T.; Maruyama, T.; Gojobori, T.; Inoue, Y.; Crozier, R.H. Theoretical bases for karayotype evolution. I. The Minimum–Interaction Hypothesis. Am. Nat. 1986, 128, 900–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisachov, A.P.; Trifonov, V.A.; Giovannotti, M.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Borodin, P.M. Immunocytological analysis of meiotic recombination in two anole lizards (Squamata, Dactyloidae). Comp. Cytogenet. 2017, 11, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscani, M.A.; Pigozzi, M.I.; Bressa, M.J.; Papeschi, A.G. Synapsis with and without recombination in the male meiosis of the leaf-footed bug Holhymenia rubiginosa (Coreidae, Heteroptera). Genetica 2007, 132, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.C.; Mattos, V.F.; Carvalho, L.S.; Cella, D.M. Organization and behavior of the synaptonemal complex during achiasmatic meiosis of four buthid scorpions. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 144, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, D.W. Origin and evolution of avian microchromosomes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2002, 96, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosa, C.G. On chromosome uniformity, bimodality and evolution in the tribe Aloineae (Asphodelaceae). Caryologia 2005, 58, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibiapino, A.; Báez, M.; García, M.A.; Costea, M.; Stefanović, S.; Pedrosa-Harand, A. Karyotype asymmetry in Cuscuta L. subgenus Pachystigma reflects its repeat DNA composition. Chromosome Res. 2022, 30, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilardi, R.S.; Ojanguren-Affilastro, A.A.; Rodríguez Gil, S.G.; Scioscia, C.L.; Mola, L.M. Meiotic studies in Brachistosternus alienus (Scorpiones; Bothriuridae). J. Arachnol. 2013, 41, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genus | Species | N | Locality | Geographic Coordinate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brotheas | B. amazonicus | 1 male, 1 female, 16 embryos | Manaus/AM | 3°06′10″ S/59°58′42″ O |
| 7 males, 5 females, 9 embryos | Parintins/AM | 2°38′15″ S/56°43′46″ O | ||
| B. silvestris | 3 males, 1 female, 19 embryos | Óbidos/PA | 1°54′16″ S/55°31′12″ O | |
| B. paraensis | 2 males, 1 female, 12 embryos | Óbidos/PA | 1°54′16″ S/55°31′12″ O | |
| Neochactas | N. parvulus | 2 males, 1 female | Óbidos/PA | 1°54′16″ S/55°31′12″ O |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida, B.; Malcher, S.; Costa, M.; Martins, J.; Procópio, R.; Noronha, R.; Nagamachi, C.; Pieczarka, J. High Chromosomal Reorganization and Presence of Microchromosomes in Chactidae Scorpions from the Brazilian Amazon. Biology 2023, 12, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12040563
Almeida B, Malcher S, Costa M, Martins J, Procópio R, Noronha R, Nagamachi C, Pieczarka J. High Chromosomal Reorganization and Presence of Microchromosomes in Chactidae Scorpions from the Brazilian Amazon. Biology. 2023; 12(4):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12040563
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida, Bruno, Stella Malcher, Marlyson Costa, Jonas Martins, Rudi Procópio, Renata Noronha, Cleusa Nagamachi, and Julio Pieczarka. 2023. "High Chromosomal Reorganization and Presence of Microchromosomes in Chactidae Scorpions from the Brazilian Amazon" Biology 12, no. 4: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12040563
APA StyleAlmeida, B., Malcher, S., Costa, M., Martins, J., Procópio, R., Noronha, R., Nagamachi, C., & Pieczarka, J. (2023). High Chromosomal Reorganization and Presence of Microchromosomes in Chactidae Scorpions from the Brazilian Amazon. Biology, 12(4), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12040563





