Comparative Mitogenome Analyses Uncover Mitogenome Features and Phylogenetic Implications of the Parrotfishes (Perciformes: Scaridae)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.2. Sequence Assembly, Annotation, and Analyses
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Features of Mitochondrial Genomes
3.2. Nucleotide Composition of the Parrotfish Mitogenomes and Unusual AT Skew of Calotomus Species
3.3. Protein-Coding Genes
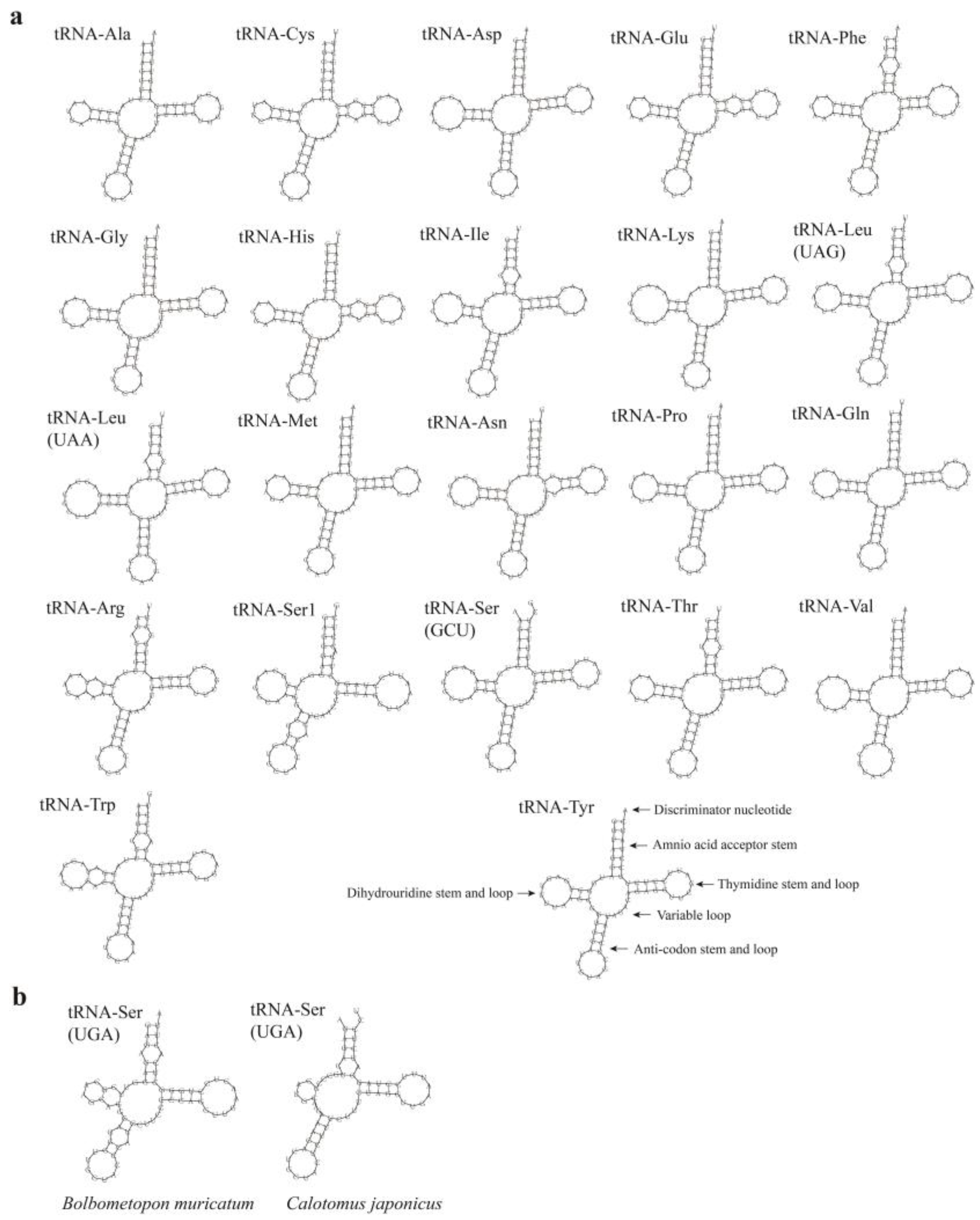
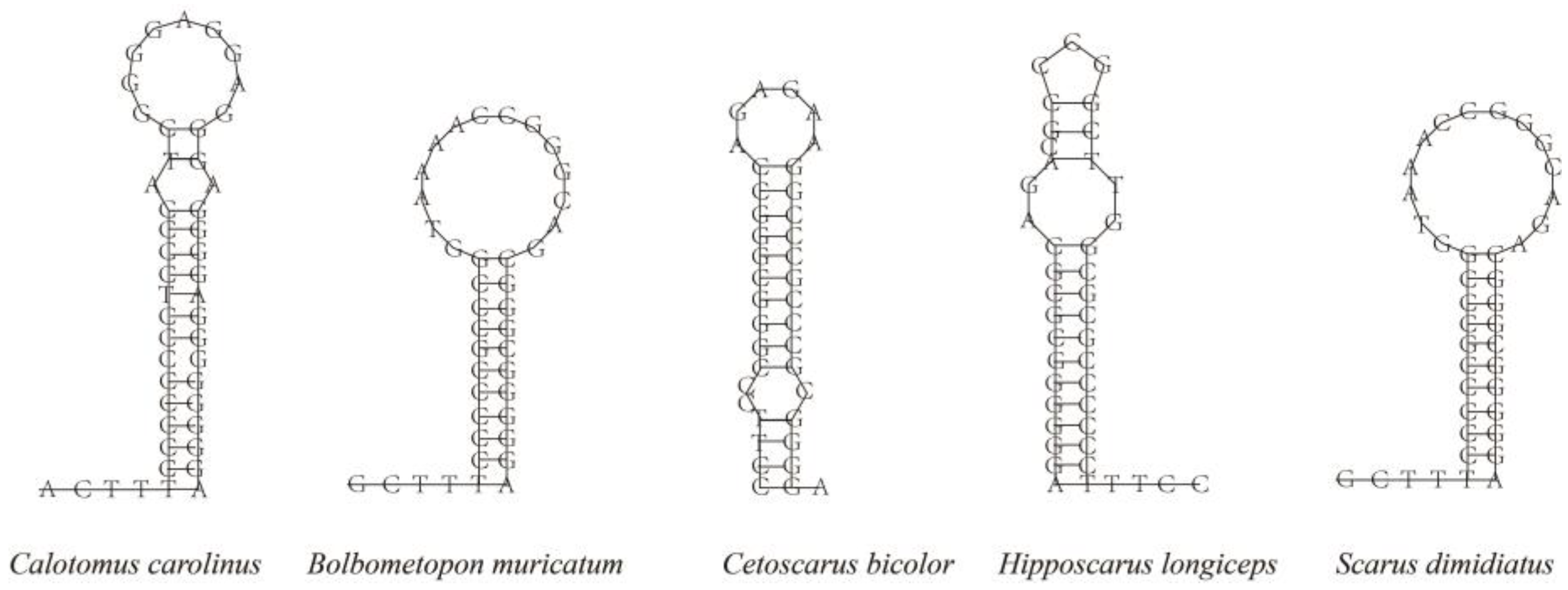
3.4. Gene Rearrangement and Secondary Structure of tRNAs
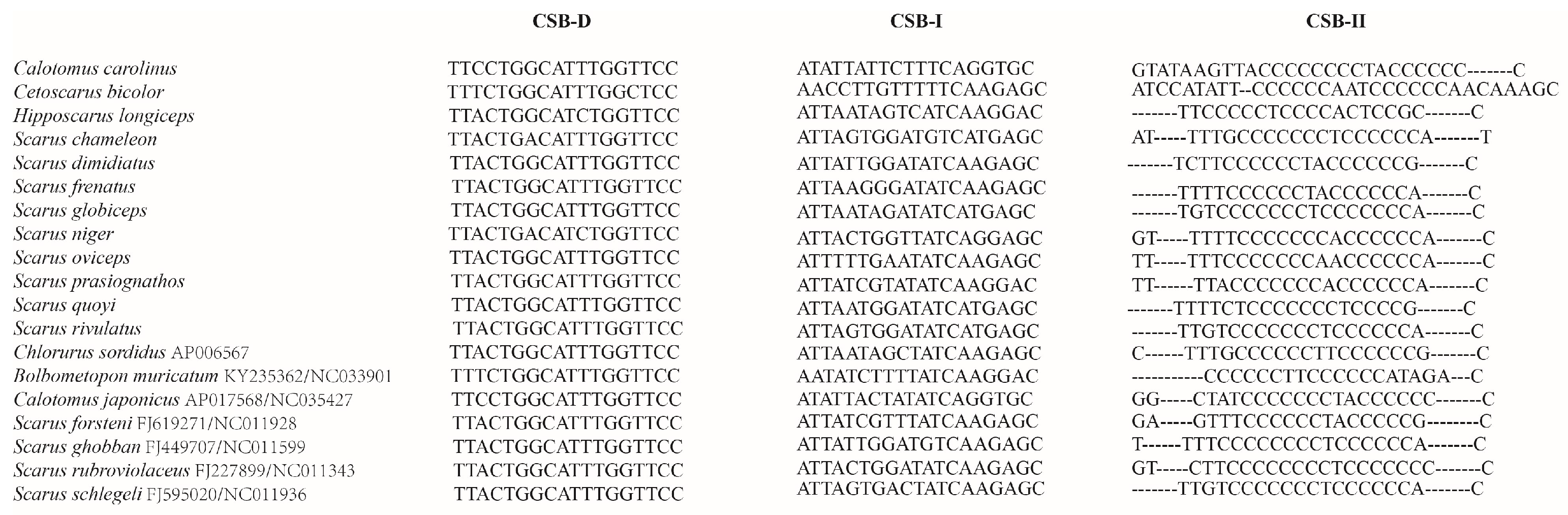
3.5. Overlaps and Non-Coding Intergenic Spacers
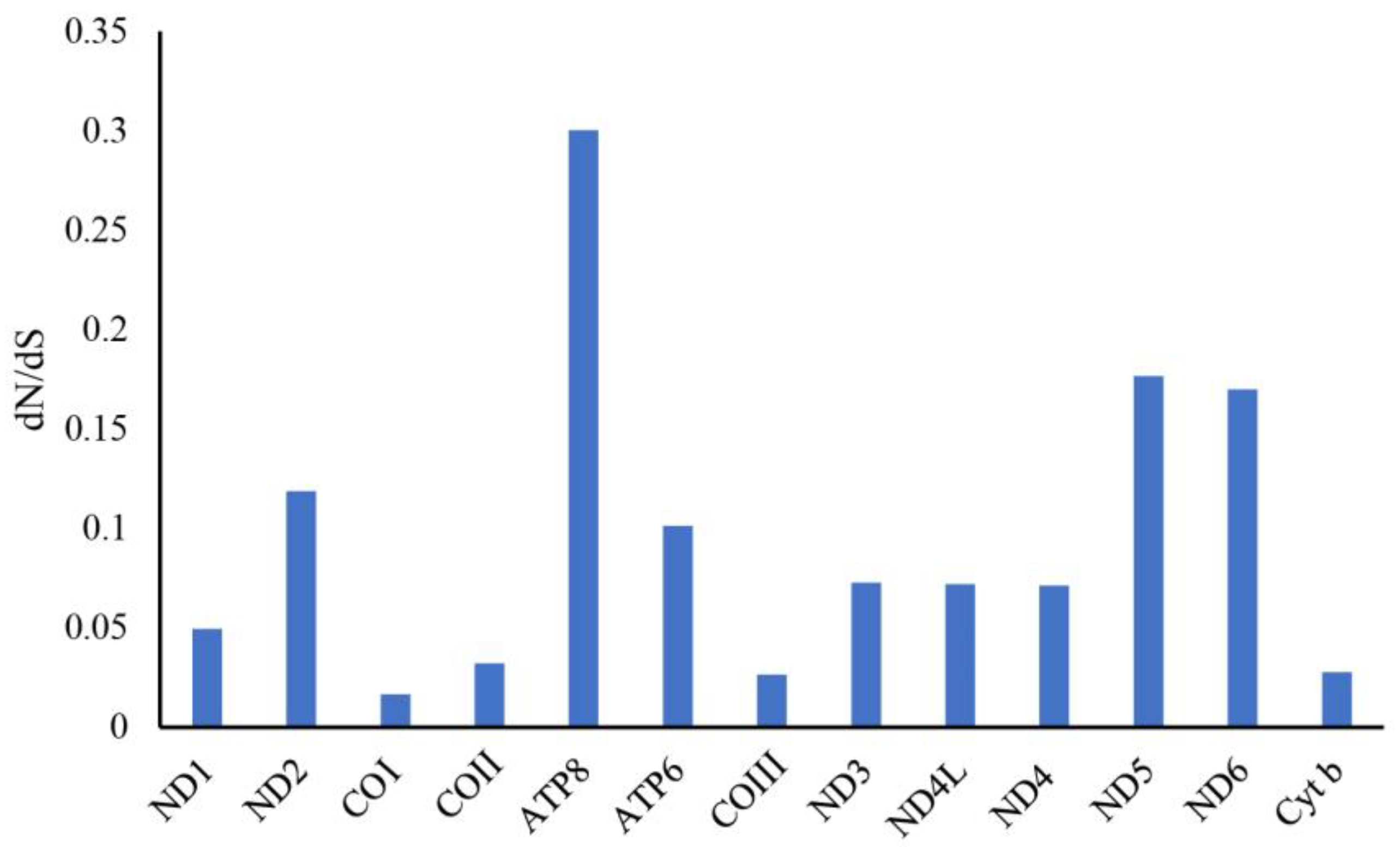
3.6. Non-Synonymous and Synonymous Substitutions
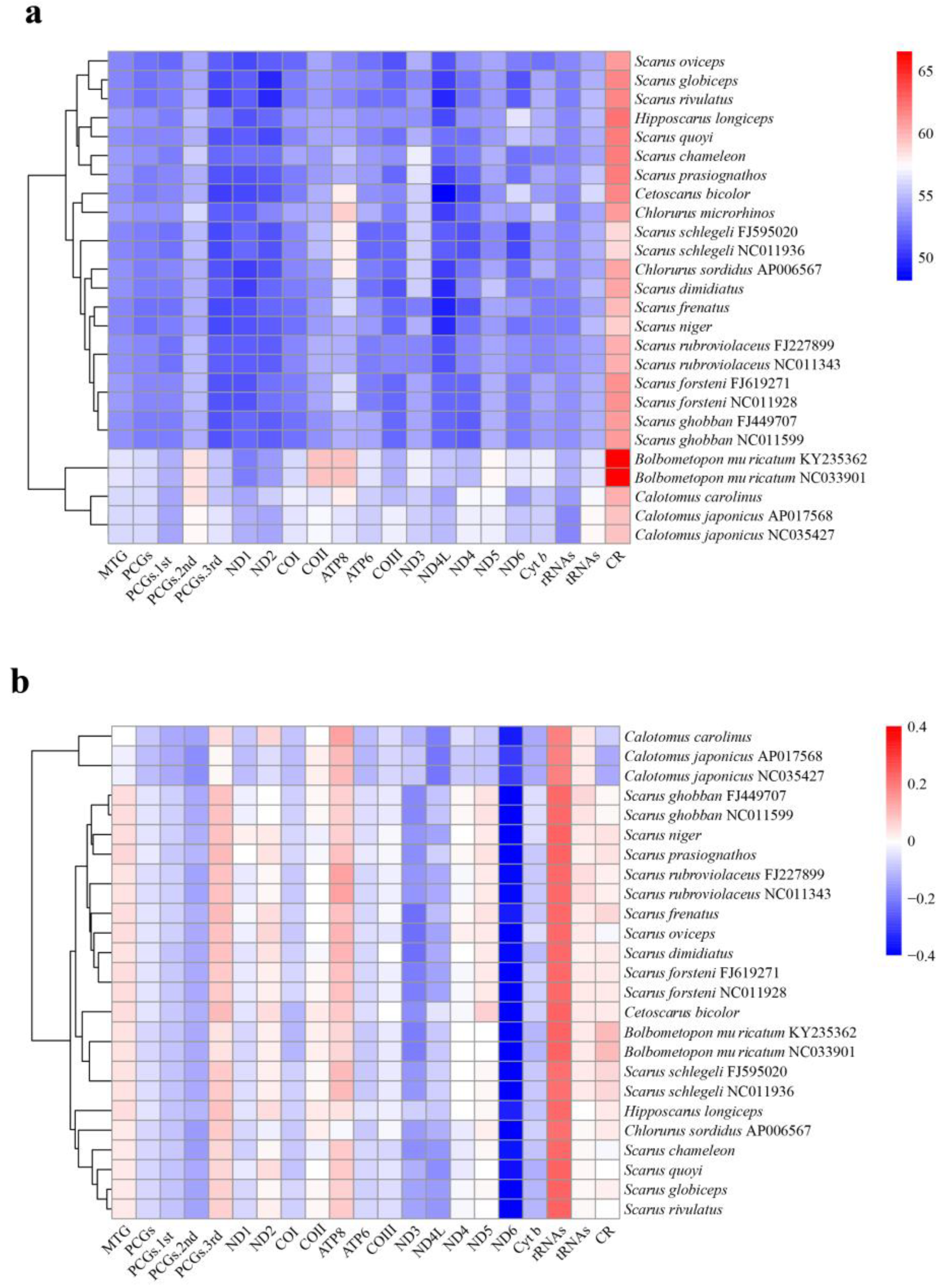
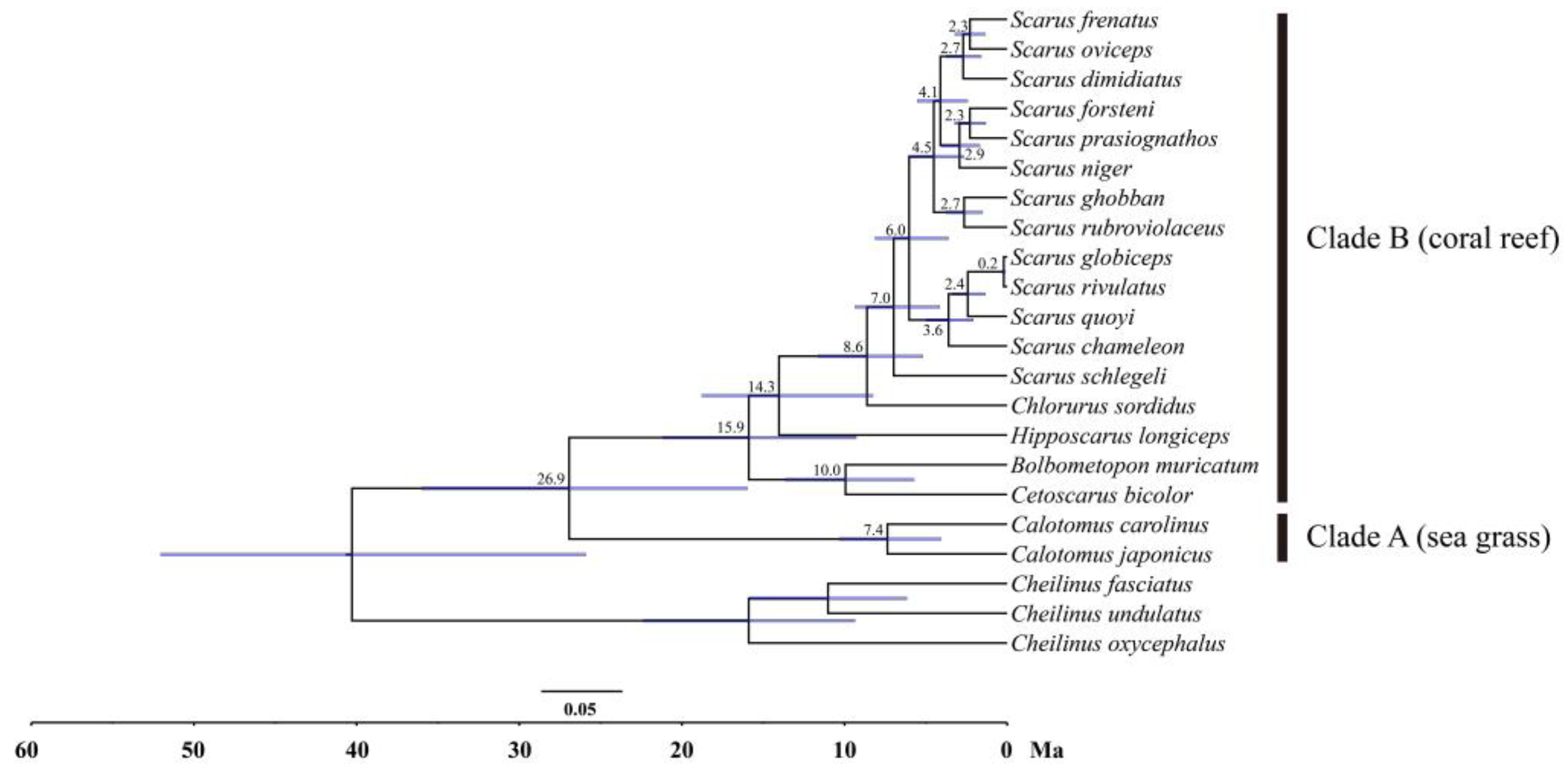
3.7. Phylogenetic Relationships of the Parrotfishes
3.8. Divergence Time Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Satoh, T.P.; Miya, M.; Mabuchi, K.; Nishida, M. Structure and variation of the mitochondrial genome of fishes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avise, J.C.; Arnold, J.; Ball, R.M.; Bermingham, E.; Lamb, T.; Neigel, J.E.; Reeb, C.A.; Saunders, N.C. Intraspecific Phylogeography: The Mitochondrial DNA Bridge between Population Genetics and Systematics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 489–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species; Harvard University Press: Harvard, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography: Retrospect and prospect. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 36, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Takeshima, H.; Endo, H.; Ishiguro, N.B.; Inoue, J.G.; Mukai, T.; Satoh, T.P.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Mabuchi, K.; et al. Major patterns of higher teleostean phylogenies: A new perspective based on 100 complete mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2003, 26, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, J.G.; Miya, M.; Lam, K.; Tay, B.-H.; Danks, J.A.; Bell, J.; I Walker, T.I.; Venkatesh, B. Evolutionary Origin and Phylogeny of the Modern Holocephalans (Chondrichthyes: Chimaeriformes): A Mitogenomic Perspective. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.L.; Ksepka, D.T.; Mitchell, K.J.; Tennyson, A.J.D.; Thomas, D.B.; Pan, H.; Zhang, G.; Rawlence, N.J.; Wood, J.R.; Bover, P.; et al. Mitogenomes Uncover Extinct Penguin Taxa and Reveal Island Formation as a Key Driver of Speciation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.-E.; Breeschoten, T.; Timmermans, M.J.T.N.; Nadein, K.; Xue, H.-J.; Bai, M.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.-K.; Vogler, A.P. The phylogeny of Galerucinae (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and the performance of mitochondrial genomes in phylogenetic inference compared to nuclear rRNA genes. Cladistics 2018, 34, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, M.J.; Herniou, E.A.; Russell, R.B.; Littlewood, D.T.J. Changes in mitochondrial genetic codes as phylogenetic characters: Two examples from the flatworms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11359–11364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dong, X.-L.; Wang, Z.-M.; Miao, X.-G.; Wang, S.-Y.; Kong, X.-Y. Complete mitogenome sequences of four flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes) reveal a novel gene arrangement of L-strand coding genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zou, H.; Hua, C.-J.; Li, W.-X.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Al-Misned, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Wang, G.-T. Mitochondrial Architecture Rearrangements Produce Asymmetrical Nonadaptive Mutational Pressures That Subvert the Phylogenetic Reconstruction in Isopoda. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1797–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, P.F. The Ecology of Fishes on Coral Reefs; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Parenti, P.; Randall, J.E. Checklist of the species of the families Labridae and Scaridae: An update. Smithiana Bull. 2011, 13, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gobalet, K.W. Cranial Specializations of Parrotfishes, Genus Scarus (Scarinae, Labridae) for Scraping Reef Surfaces. In Biology of Parrotfishes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Choat, J.H. A functional analysis of grazing in parrotfishes (family Scaridae): The ecological im-plications. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1989, 28, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R. Direct estimate of bioerosion by two parrotfish species, Chlorurus gibbus and C. sordidus, on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Biol. 1995, 121, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.M.; Wainwright, P.C. Herbivore abundance and grazing intensity on a Caribbean coral reef. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 87, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Hoey, A.S.; Hughes, T.P. Human activity selectively impacts the ecosystem roles of parrotfishes on coral reefs. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2012, 279, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurber, R.V.; Burkepile, D.E.; Correa, A.M.S.; Thurber, A.R.; Shantz, A.A.; Welsh, R.; Pritchard, C.; Rosales, S. Macroalgae Decrease Growth and Alter Microbial Community Structure of the Reef-Building Coral, Porites astreoides. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, N.C.; Pennino, M.G.; Lopes, P.F.D.M.; Carvalho, A.R. Multiple management strategies to control selectivity on parrotfishes harvesting. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 134, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, T.; Burkepile, D.; Ruttenberg, B.; Paddack, M. Herbivory and the resilience of Caribbean coral reefs: Knowledge gaps and implications for management. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 520, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, C. Geographic Variation in the Species Composition of Parrotfish (Labridae: Scarini) in the South China Sea. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.M.; Kench, P.S. Parrotfish erosion underpins reef growth, sand talus development and island building in the Maldives. Sediment. Geol. 2016, 341, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggertsen, L.; Goodell, W.; Cordeiro, C.A.M.M.; Mendes, T.C.; Longo, G.O.; Ferreira, C.E.L.; Berkström, C. Seascape Configuration Leads to Spatially Uneven Delivery of Parrotfish Herbivory across a Western Indian Ocean Seascape. Diversity 2020, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, B.J.; Cronn, R.; Liston, A.; Pilgrim, K.; Schwartz, M.K. Mitochondrial genome sequences illuminate maternal lineages of conservation concern in a rare carnivore. BMC Ecol. 2011, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johri, S.; Fellows, S.R.; Solanki, J.; Busch, A.; Livingston, I.; Mora, M.F.; Tiwari, A.; Cantu, V.A.; Goodman, A.; Morris, M.; et al. Mitochondrial genome to aid species delimitation and effective conservation of the Sharpnose Guitarfish (Glaucostegus granulatus). Meta Gene 2020, 24, 100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, K.; Miya, M.; Satoh, T.P.; Westneat, M.W.; Nishida, M. Gene Rearrangements and Evolution of tRNA Pseudogenes in the Mitochondrial Genome of the Parrotfish (Teleostei: Perciformes: Scaridae). J. Mol. Evol. 2004, 59, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, K. Complete mitochondrial genome of the parrotfish Calotomus japonicus (Osteichthyes: Scaridae) with implications based on the phylogenetic position. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2016, 1, 643–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Hsu, H.-H.; Jang-Liaw, N.-H. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence for the green humphead parrotfish Bolbometopon muricatum. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2017, 9, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streelman, J.T.; Alfaro, M.; Westneat, M.W.; Bellwood, D.R.; Karl, S.A. Evolutionary History of the Parrotfishes: Biogeography, Ecomorphology, and Comparative Diversity. Evolution 2002, 56, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.L.; Fessler, J.L.; Alfaro, M.E.; Streelman, J.T.; Westneat, M.W. Phylogenetic relationships and the evolution of regulatory gene sequences in the parrotfishes. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 49, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choat, J.H.; Klanten, O.S.; Van Herwerden, L.; Robertson, D.R.; Clements, K.D. Patterns and processes in the evolutionary history of parrotfishes (Family Labridae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 107, 529–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M.; et al. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A Mitochondrial Genome Database of Fish with an Accurate and Automatic Annotation Pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE7: New and Improved Tools for Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xie, Z.; Salemi, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. An index of substitution saturation and its application. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2003, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView Version 4: A Multiplatform Graphical User Interface for Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic Analysis by Maximum Likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Drummond, A.J. Tracer v1.7. 2014. Available online: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Bellwood, D.R.; Schultz, O. A Review of the Fossil Record of the Parrotfishes (Labroidei: Scaridae) with a Description of a New Calotomus Species from the Middle Miocene (Badenian) of Austria. Ann. Nat. Mus. Wien 1990, 92, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Bellwood, D.R. A new fossil fish Phyllopharyngodon longipinnis gen. et sp. nov. (family labridae) from the Eocene, Monte Bolca, Italy. Studi Ric. Sui Giacimenti Terziari Bolca 1990, 6, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, G.; Gutman, G.A. Slipped-strand mispairing: A major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taanman, J.-W. The mitochondrial genome: Structure, transcription, translation and replication. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta BBA-Bioenergies 1999, 1410, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Valerio, A.; Austin, A.D.; Dowton, M.; Johnson, N.F. The first mitochondrial genome for the wasp superfamily Platygastroidea: The egg parasitoid Trissolcus basalis. Genome 2012, 55, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodovalho, C.D.M.; Lyra, M.L.; Ferro, M.; Bacci, M., Jr. The Mitochondrial Genome of the Leaf-Cutter Ant Atta laevigata: A Mitogenome with a Large Number of Intergenic Spacers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbisà, E.; Tanzariello, F.; Reyes, A.; Pesole, G.; Saccone, C. Mammalian mitochondrial D-loop region structural analysis: Identification of new conserved sequences and their functional and evolutionary implications. Gene 1997, 205, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-S.; Wu, J.-H.; Huang, S.-P. The taxonomy and phylogeny of the cyprinid genus Opsariichthys Bleeker (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) from Taiwan, with description of a new species. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2009, 86, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Hsu, K.; Wu, J.; Chiu, Y.; Lin, H.; Ju, Y. Population genetic diversity and structure of Rhinogobius candidianus (Gobiidae) in Taiwan: Translocation and release. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemi, M. Nucleotide substitution models. Practice: The Phylip and Tree-Puzzle software packages. In The Phylogenetic Handbook a Practical Approach to Phylogenetic Analysis and Hypothesis Testing; Salemi, M., Vandamme, A.-M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Brabec, J.; Scholz, T.; Králová-Hromadová, I.; Bazsalovicsová, E.; Olson, P.D. Substitution saturation and nuclear paralogs of commonly employed phylogenetic markers in the Caryophyllidea, an unusual group of non-segmented tapeworms (Platyhelminthes). Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Jiang, H.; Bo, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; He, S. Comparative mitochondrial genome analysis of Neodontobutis hainanensis and Perccottus glenii reveals conserved genome organization and phylogeny. Genomics 2020, 112, 3862–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francino, M.P.; Ochman, H. Strand asymmetries in DNA evolution. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.; Lobry, J. Asymmetric substitution patterns: A review of possible underlying mutational or selective mechanisms. Gene 1999, 238, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, C. A study on the correlation of nucleotide skews and the positioning of the origin of replication: Different modes of replication in bacterial species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 6816–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charneski, C.A.; Honti, F.; Bryant, J.M.; Hurst, L.D.; Feil, E.J. Atypical AT Skew in Firmicute Genomes Results from Selection and Not from Mutation. PLOS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liao, T.-Y.; Arai, R.; Zhao, L. Sinorhodeus microlepis, a new genus and species of bitterling from China (Teleostei: Cyprinidae: Acheilognathinae). Zootaxa 2017, 4353, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Yang, W.-T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, Y.; Gui, J.-F. Unusual AT-skew of Sinorhodeus microlepis mitogenome provides new insights into mitogenome features and phylogenetic implications of bitterling fishes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiklejohn, C.D.; Montooth, K.L.; Rand, D.M. Positive and negative selection on the mitochondrial genome. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellwood, D.R. A phylogenetic study of the parrotfish family Scaridae (Pisces: Labroidea), with a revision of genera. Rec. Aust. Museum, Suppl. 1994, 20, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.E.J.; Rosen, B.R. Implications of paucity of corals in the Paleogene of SE Asia: Plate tectonics or Centre of Origin? In Biogeography and Geological Evolution of SE Asia; Backhuys Publishers: Laiden, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 165–195. [Google Scholar]
- Braisier, M.D. An outline of sea grass communities. Paleontology 1975, 18, 681–702. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Sheykh, M.; Ahmadi, N.; Cao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, S.; Sha, J.; Jian, Z.; Windley, B.F.; Talebian, M. Permanent closure of the Tethyan Seaway in the northwestern Iranian Plateau driven by cyclic sea-level fluctuations in the late Middle Miocene. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2021, 564, 110172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomar, L.; Hallock, P. Changes in coral-reef structure through the Miocene in the Mediterranean province: Adaptive versus environmental influence. Geology 2007, 35, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletti, G.; Balmer, E.M.; Bialik, O.M.; Cannings, T.; Kroon, D.; Robertson, A.H.; Basso, D. Microfacies evidence for the evolution of Miocene coral-reef environments in Cyprus. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2021, 584, 110670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, R.; Bourget, J.; Håkansson, E.; Paumard, V.; Wilson, M.E. Middle Miocene tropical oligotrophic lagoon deposit sheds light on the origin of the Western Australian coral reef province. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2021, 576, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Goatley, C.H.R.; Bellwood, O. The evolution of fishes and corals on reefs: Form, function and interdependence. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 878–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Features | Start | Stop | Length/bp | Intergenic Nucleotide | Start Codon | Stop Codon | Anti-Codon | Strand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tRNAPhe | 1 | 69 | 69 | 0 | GAA | + * | ||
| 12S-rRNA | 70 | 1020 | 951 | 0 | + | |||
| tRNAVal | 1021 | 1093 | 73 | 0 | TAC | + | ||
| 16S-rRNA | 1094 | 2782 | 1689 | 0 | + | |||
| tRNALeu(UAA) | 2783 | 2855 | 73 | 0 | TAA | + | ||
| ND1 | 2856 | 3830 | 975 | 7 | ATG | TAA | + | |
| tRNAIle | 3838 | 3907 | 70 | 10 | GAT | + | ||
| tRNAMet | 3918 | 3986 | 69 | 6 | TTG | + | ||
| tRNAGln | 3993 | 4063 | 71 | 68 | CAT | − | ||
| ND2 | 4132 | 5176 | 1045 | 0 | ATG | TAG | + | |
| tRNATrp | 5177 | 5247 | 71 | 4 | TCA | + | ||
| tRNAAla | 5252 | 5322 | 71 | 5 | TGC | − | ||
| tRNAAsn | 5328 | 5400 | 73 | 41 | GTT | − | ||
| tRNACys | 5442 | 5507 | 66 | 9 | GCA | − | ||
| tRNATyr | 5517 | 5586 | 70 | 1 | GTA | − | ||
| COI | 5588 | 7138 | 1551 | 0 | GTG | TAA | + | |
| tRNASer (UGA) | 7139 | 7209 | 71 | 3 | TGA | − | ||
| tRNAAsp | 7213 | 7283 | 71 | 4 | GTC | + | ||
| COII | 7288 | 7978 | 691 | 0 | ATG | T | + | |
| tRNALys | 7979 | 8052 | 74 | 1 | TTT | + | ||
| ATPase 8 | 8054 | 8221 | 168 | −16 | ATG | TAG | + | |
| ATPase 6 | 8206 | 8894 | 689 | 0 | CTG | TA | + | |
| COIII | 8895 | 9679 | 785 | 0 | ATG | TAA | + | |
| tRNAGly | 9680 | 9750 | 71 | 1 | TCC | + | ||
| ND3 | 9752 | 10103 | 352 | 0 | ATA | TAG | + | |
| tRNAArg | 10,104 | 10,172 | 69 | 0 | TCG | + | ||
| ND4L | 10,173 | 10,469 | 297 | −7 | ATG | TAA | + | |
| ND4 | 10,463 | 11,843 | 1381 | 0 | ATG | T | + | |
| tRNAHis | 11,844 | 11,912 | 69 | 2 | GTG | + | ||
| tRNASer (GCU) | 11,915 | 11,980 | 66 | 32 | GCT | + | ||
| tRNALeu (UAG) | 12,013 | 12,084 | 72 | 4 | TAG | + | ||
| ND5 | 12,089 | 13,930 | 1842 | −4 | ATG | TAA | + | |
| ND6 | 13,927 | 14,448 | 522 | 1 | ATG | TAA | − | |
| tRNAGlu | 14,450 | 14,522 | 73 | 64 | TTC | − | ||
| Cyt b | 14,587 | 15,727 | 1141 | 0 | ATG | T | + | |
| tRNAThr | 15,728 | 15,799 | 72 | 0 | TGT | + | ||
| tRNAPro | 15,800 | 15,872 | 73 | 0 | TGG | − | ||
| D-loop | 15,873 | 17,114 | 1242 | + |
| Base Composition (%) | CSB-D | CSB-I | CSB-II |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10.5 | 34.2 | 8.8 |
| T | 44.4 | 32.2 | 20.1 |
| G | 21.6 | 19.6 | 5.2 |
| C | 23.5 | 14.0 | 65.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Li, C.; Yu, D.; Wang, T.; Lin, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y. Comparative Mitogenome Analyses Uncover Mitogenome Features and Phylogenetic Implications of the Parrotfishes (Perciformes: Scaridae). Biology 2023, 12, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030410
Gao J, Li C, Yu D, Wang T, Lin L, Xiao Y, Wu P, Liu Y. Comparative Mitogenome Analyses Uncover Mitogenome Features and Phylogenetic Implications of the Parrotfishes (Perciformes: Scaridae). Biology. 2023; 12(3):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030410
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jiaxin, Chunhou Li, Dan Yu, Teng Wang, Lin Lin, Yayuan Xiao, Peng Wu, and Yong Liu. 2023. "Comparative Mitogenome Analyses Uncover Mitogenome Features and Phylogenetic Implications of the Parrotfishes (Perciformes: Scaridae)" Biology 12, no. 3: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030410
APA StyleGao, J., Li, C., Yu, D., Wang, T., Lin, L., Xiao, Y., Wu, P., & Liu, Y. (2023). Comparative Mitogenome Analyses Uncover Mitogenome Features and Phylogenetic Implications of the Parrotfishes (Perciformes: Scaridae). Biology, 12(3), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030410






