Ammonia Stress Disturbs Moult Signaling in Juvenile Swimming Crab Portunus trituberculatus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Survival and Moulting Experiment
2.3. Sample Collection for Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
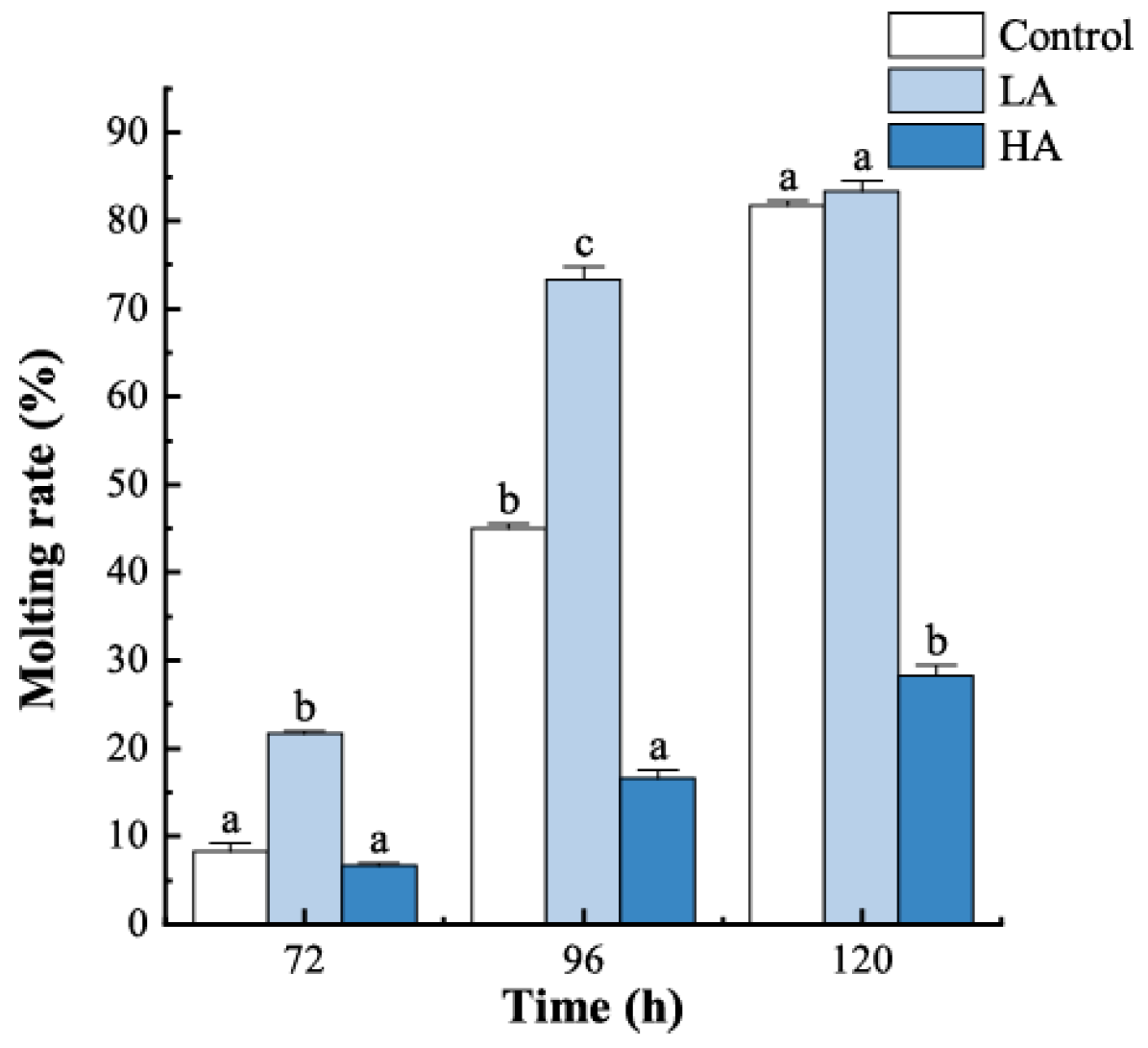
3.1. Survival and Molting
3.2. MIH Expression
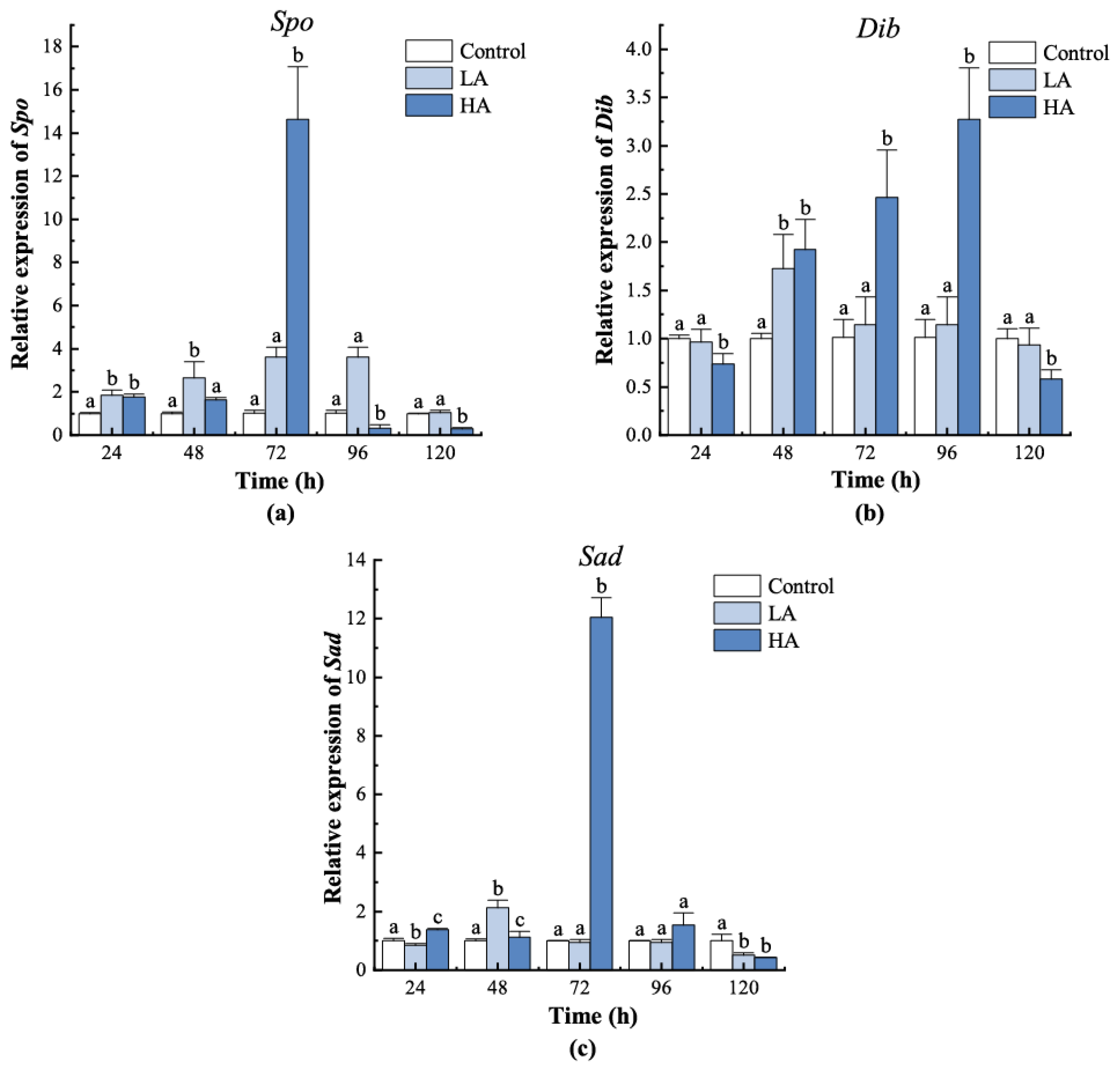
3.3. Expression of the Halloween Genes
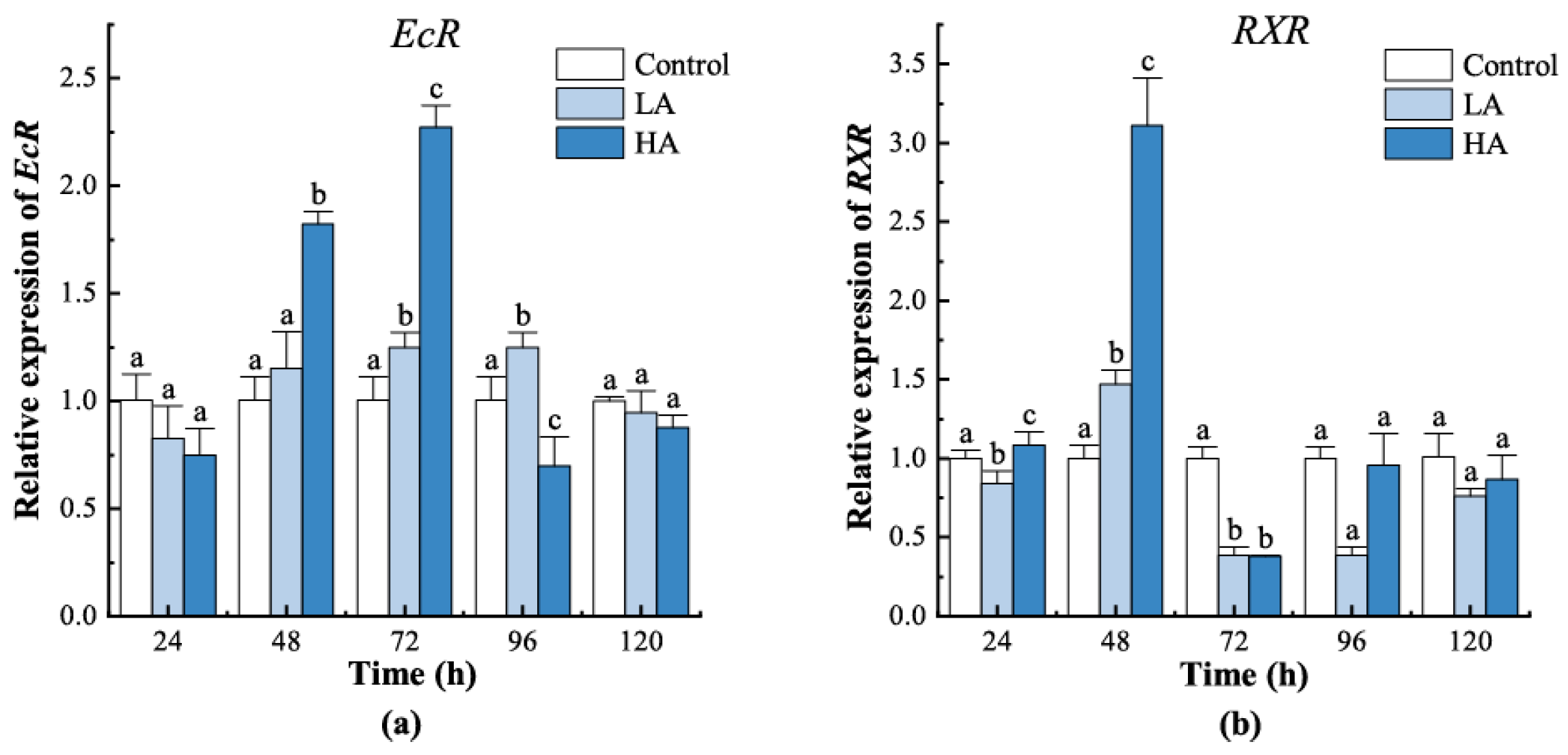
3.4. Expression of Ecdysteroid Receptors
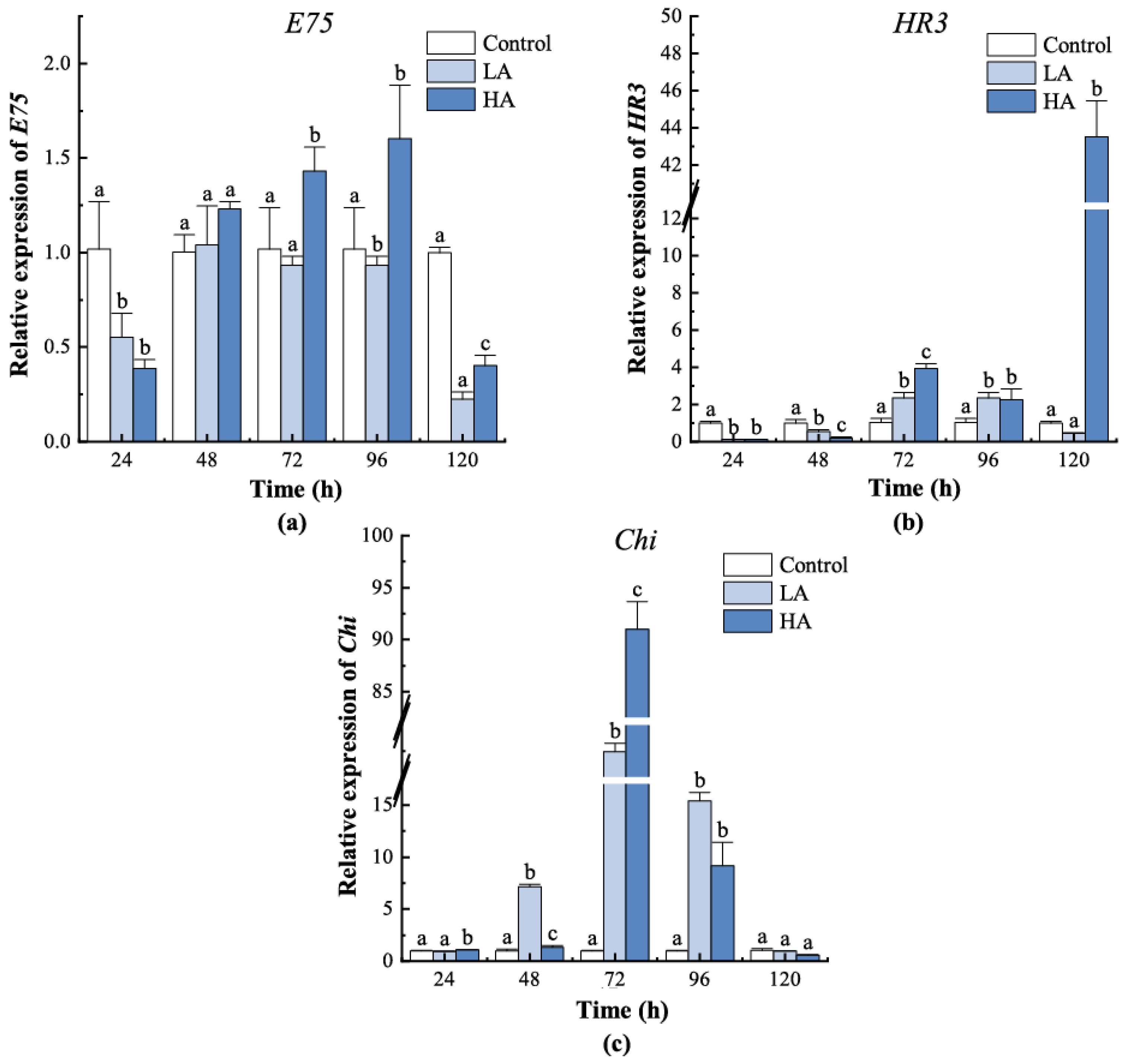
3.5. Expression of Ecdysteroid-Responsive Genes
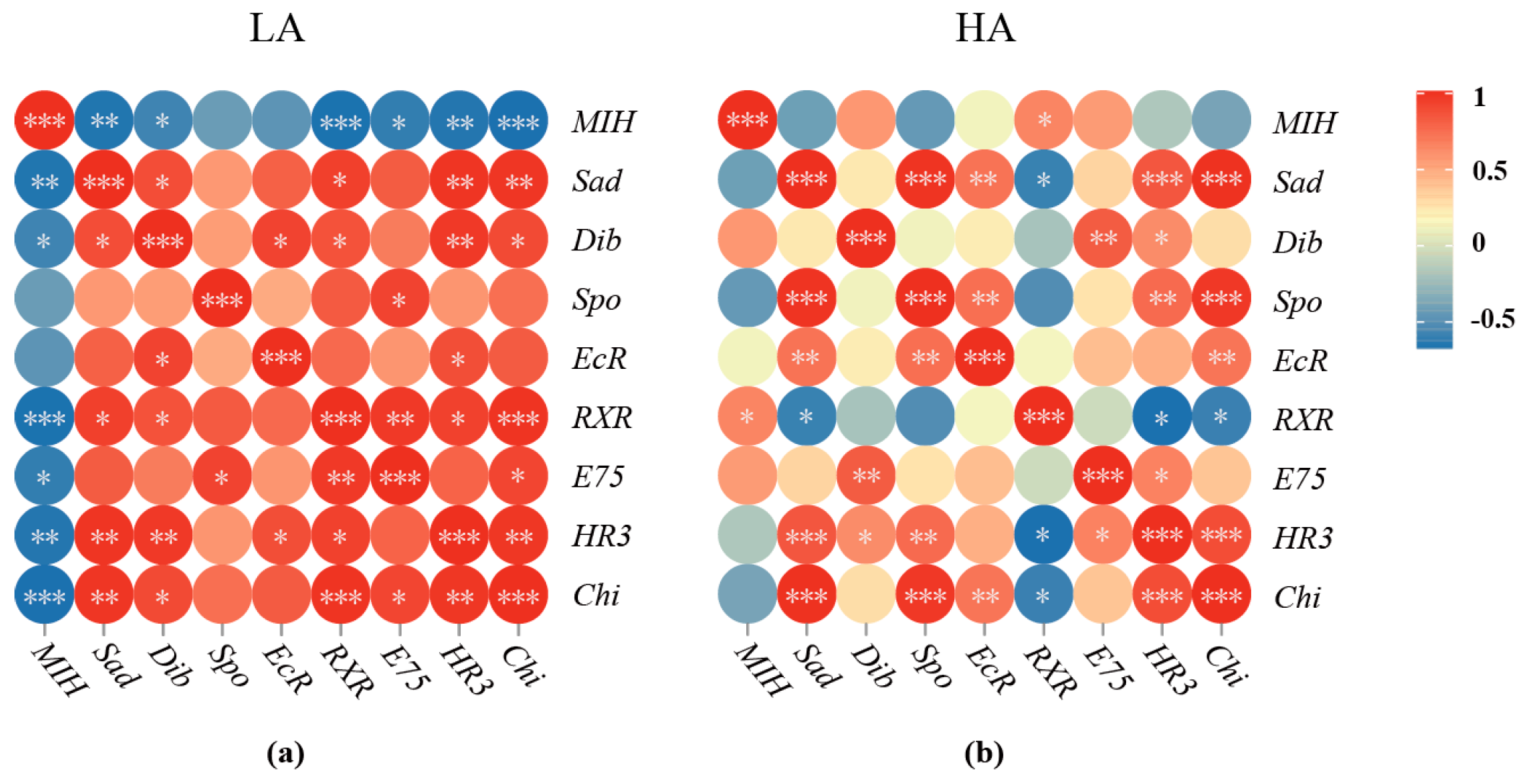
3.6. Correlation between the Expression of All the Detected Genes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, A.; Yang, S.; Song, Y. Marine Crabs in China Sea; Marine Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 194–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Meng, X. Identification of Neuropeptides Using Long-Read RNA-Seq in the Swimming Crab Portunus Trituberculatus, and Their Expression Profile Under Acute Ammonia Stress. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 910585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucking, C. A Broader Look at Ammonia Production, Excretion, and Transport in Fish: A Review of Impacts of Feeding and the Environment. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2017, 187, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, N.; Zeng, C. Toxic Effects of Ammonia, Nitrite, and Nitrate to Decapod Crustaceans: A Review on Factors Influencing Their Toxicity, Physiological Consequences, and Coping Mechanisms. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Jiang, L.X.; Li, Y.L.; Li, J.; Wang, R.J. The Effect of Ammonia-N and Sulfureted Hydrogen in the Growth and Ecdysis of Portunus trituberculatus Larvae. J. Qingdao Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2007, 24, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, S.; Ma, S. Effects of Salinity on Growth, Molt and Energy Utilization of Juvenile Swimming Crab Portunus Trituberculatus. J. Fish. Sci. China 2013, 19, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Zeng, C. Subchronic Exposure to Nitrite, Potassium and Their Combination on Survival, Growth, Total Haemocyte Count and Gill Structure of Juvenile Blue Swimmer Crabs, Portunus pelagicus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.Y.; Wang, H.H.; Lin, Z.G. Effect of Ammonia and Nitrite on Vigour, Survival Rate, Moulting Rate of the Blue Swimming Crab Portunus Pelagicus Zoea. Aquac. Int. 2011, 19, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, L.L.; Fotedar, R.; Shelley, C.C. Effects of Acute and Chronic Toxicity of Unionized Ammonia on Mud Crab, Scylla Serrata (Forsskal, 1755) Larvae. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.G.; Kim, S.G.; Jee, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Bai, S.C.; Kang, J.C. Effects of Ammonia and Nitrite on Survival, Growth and Moulting in Juvenile Tiger Crab, Orithyia Sinica (Linnaeus). Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Ilouz, O.; Manor, R.; Sagi, A.; Khalaila, I. Transcriptional Silencing of Vitellogenesis-Inhibiting and Molt-Inhibiting Hormones in the Giant Freshwater Prawn, Macrobrachium Rosenbergii, and Evaluation of the Associated Effects on Ovarian Development. Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covi, J.A.; Chang, E.S.; Mykles, D.L. Conserved Role of Cyclic Nucleotides in the Regulation of Ecdysteroidogenesis by the Crustacean Molting Gland. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 152, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Zmora, N.; Katayama, H.; Tsutsui, N. Crustacean Hyperglycemic Hormone (CHH) Neuropeptides family: Functions, Titer, and Binding to Target Tissues. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 166, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asazuma, H.; Nagata, S.; Nagasawa, H. Inhibitory Effect of Molt-Inhibiting Hormone on Phantom Expression in the Y-Organ of the Kuruma Prawn, Marsupenaeus japonicus. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 72, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Mu, C.; Wang, C. Effects of Dietary Cholesterol Levels on the Growth, Molt Performance, and Immunity of Juvenile Swimming Crab, Portunus trituberculatus. Isr. J. Aquac.-Bamidgeh 2015, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, R.; Niwa, Y.S. Enzymes for Ecdysteroid Biosynthesis: Their Biological Functions in Insects and Beyond. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, I.; Kenny, N.; Hui, J.; Hering, L.; Mayer, G. Halloween Genes in Panarthropods and the Evolution of the Early Moulting Pathway in Ecdysozoa. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Zhu, D.; Tang, J.; Xie, X.; Qiu, X. Cloning and expression analysis of ecdysteroid receptor(EcR) in Portunus trituberculatus. J. Fish. China 2013, 37, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Ge, Q.Q.; Cui, Y.T.; Ma, L.; Li, J. Cloning of E75 Gene and Expression Analysis of E75, ECR and RXR During Different Molting Stages of Exopalaemon carinicauda. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2018, 39, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Tao, T.; Shen, X.; Zhu, D. Role of Halloween Genes in Ecdysteroids Biosynthesis of the Swimming Crab (Portunus Trituberculatus): Implications from RNA Interference and Eyestalk Ablation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 199, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Garcia-Carreño, F.L.; Muhlia-Almazán, A.; Peregrino-Uriarte, A.B.; Yépiz-Plascencia, G.; Córdova-Murueta, J.H. Cuticular Chitin Synthase and Chitinase mRNA of Whiteleg Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei during the Molting Cycle. Aquaculture 2012, 330–333, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.T. Effects of Temperature, Salinity, Dissolved Oxygen, Ammonia-N and Nitrite-N on the Molting of Scylla paramamosain. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.F. Chronic Toxicity of Ammonia-N, Nitrire-N and Salinity on Development of the Embryo and Larva of Portunus trituberculatus. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mykles, D.L. Ecdysteroid Metabolism in Crustaceans. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Yu, K.; Shu, L.; Ye, H.; Li, S.; Zeng, C. Evaluating the Effects of Temperature, Salinity, Starvation and Autotomy on Molting Success, Molting Interval and Expression of Ecdysone Receptor in Early Juvenile Mud Crabs, Scylla paramamosain. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 464, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikapitiya, C.; Kim, W.S.; Park, K.; Kwak, I.S. Identification of Potential Markers and Sensitive Tissues for Low or High Salinity Stress in an Intertidal Mud Crab (Macrophthalmus Japonicus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.H.; Tan, B.P.; Mai, K.S.; Chi, K.S.; Liu, H.Y.; Dong, X.H.; Yang, Q.H. Dentification of Differentially Expressed Genes in Hepatopancreas of White Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei Induced by Long-Term Low-Salinity Stress. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2013, 43, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, F.; Pan, L.; Xie, P.; Zheng, D.; Li, J. Immune Responses and Expression of Immune-Related Genes in Swimming Crab Portunus Trituberculatus Exposed to Elevated Ambient Ammonia-N Stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 157, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Jayasundara, N.; Ren, X.; Gao, B.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Meng, X. Physiological and Molecular Responses in the Gill of the Swimming Crab Portunus Trituberculatus During Long-Term Ammonia Stress. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 797241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Tao, T.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, D. The Nuclear Receptor E75 from the Swimming Crab, Portunus Trituberculatus: CDNA Cloning, Transcriptional Analysis, and Putative Roles on Expression of Ecdysteroid-Related Genes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 200, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Yao, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Aweya, J.J. Effects of Ammonia on Shrimp Physiology and Immunity: A Review. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2194–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Peña, M.D.C.; Moreira, M.D.G.B.S. Effect of Dietary Cellulose Level on Specific Dynamic Action and Ammonia Excretion of the Prawn Macrobrachium Rosenbergii (De Man 1879): Cellulose on SDA M. Rosenbergii. Aquac. Res. 2003, 34, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Kou, Y.Z. Effects of Ammonia on Growth and Molting of Penaeus Japonicus Juveniles. Aquaculture 1992, 104, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.L. A Preliminary Study on the Structure and Function of the Ecdysone Response Genes of the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and Their Regulation to Wnt Signal Pathway. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, P.; Li, J.T.; Li, J. Cloning and Expression of Molt-inhibiting Hormone Gene from Exopalaemon carinicauda under Environmental Stresses. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2015, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Webster, S.G. Dynamics of in Vivo Release of Molt-Inhibiting Hormone and Crustacean Hyperglycemic Hormone in the Shore Crab, Carcinus maenas. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 5545–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Pan, L.; Li, L.; Zheng, D. Molecular Cloning, Characterization and Recombinant Expression of Crustacean Hyperglycemic Hormone in White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Peptides 2014, 53, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, D.; Qi, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xie, X.; Shen, J. Molt-inhibiting hormone levels and ecdysteroid titer during a molt cycle of Portunus trituberculatus. ACTA Hydrobiol. Sin. 2013, 37, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewitz, K.F.; Gilbert, L.I. Daphnia Halloween Genes That Encode Cytochrome P450s Mediating the Synthesis of the Arthropod Molting Hormone: Evolutionary Implications. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iga, M.; Smagghe, G. Identification and Expression Profile of Halloween Genes Involved in Ecdysteroid Biosynthesis in Spodoptera littoralis. Peptides 2010, 31, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, E.; Badisco, L.; Verlinden, H.; Vandersmissen, T.; Van Soest, S.; Van Wielendaele, P.; Vanden Broeck, J. Role of the Halloween Genes, Spook and Phantom in Ecdysteroidogenesis in the Desert Locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Roegner, M.E.; Watson, R.D. Calcium Signaling and Regulation of Ecdysteroidogenesis in Crustacean Y-Organs. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2021, 314, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykles, D.L. Signaling Pathways That Regulate the Crustacean Molting Gland. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, T.A.J.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Xiang, J. Molecular Characterization and Effect of RNA Interference of Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) on E75 and Chitinase Gene Expression in Chinese Shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 153, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Lee, S.G.; Mykles, D.L. Ecdysteroid-Responsive Genes, RXR and E75, in the Tropical Land Crab, Gecarcinus Lateralis: Differential Tissue Expression of Multiple RXR Isoforms Generated at Three Alternative Splicing Sites in the Hinge and Ligand-Binding Domains. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2005, 242, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiu, S.H.K.; Hult, E.F.; Yagi, K.J.; Tobe, S.S. Farnesoic Acid and Methyl Farnesoate Production during Lobster Reproduction: Possible Functional Correlation with Retinoid X Receptor Expression. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 175, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-W.; Chang, E.S.; Mykles, D.L. Three Calpains and Ecdysone Receptor in the Land Crab Gecarcinus Lateralis: Sequences, Expression and Effects of Elevated Ecdysteroid Induced by Eyestalk Ablation. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 3177–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannas, B.R.; LeBlanc, G.A. Expression and Ecdysteroid Responsiveness of the Nuclear Receptors HR3 and E75 in the Crustacean Daphnia Magna. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 315, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechter, A.; Tom, M.; Yudkovski, Y.; Weil, S.; Chang, S.A.; Chang, E.S.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Berman, A.; Sagi, A. Search for Hepatopancreatic Ecdysteroid-Responsive Genes during the Crayfish Molt Cycle: From a Single Gene to Multigenicity. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 3525–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Jayasundara, N.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Gao, B.; Li, J.; Liu, P. Integrated Physiological, Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses of the Hepatopancreas of the Female Swimming Crab Portunus Trituberculatus under Ammonia Exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 113026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Pan, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Transcriptomic Response to Ammonia-N Stress in the Hepatopancreas of Swimming Crab Portunus trituberculatus. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Salinity Acclimation on the Growth Performance, Osmoregulation and Energy Metabolism of the Oriental River Prawn, Macrobrachium Nipponense (De Haan). Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnier, C.; Justou, C. Combined Effect of External Ammonia and Molt Stage on the Blue Shrimp Litopenaeus Stylirostris Physiological Response. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 309, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddiford, L.M.; Cherbas, P.; Truman, J.W. Ecdysone Receptors and Their Biological Actions. Vitam. Horm. 2000, 60, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.H.; Chang, E.S. Ecdysteroid Treatment Delays Ecdysis in the Lobster, Homarus americanus. Biol. Bull. 1991, 181, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.S.; Mykles, D.L. Regulation of Crustacean Molting: A Review and Our Perspectives. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.S. Comparative Endocrinology of Molting and Reproduction: Insects and Crustaceans. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1993, 38, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, L.I. Halloween Genes Encode P450 Enzymes That Mediate Steroid Hormone Biosynthesis in Drosophila Melanogaster. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Henrich, V.C. Arthropod Nuclear Receptors and Their Role in Molting: Arthropod Nuclear Receptors. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6128–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | CGAAACCTTCAACACTCCCG | GGGACAGTGTGTGAAACGCC |
| MIH | CCGCTGAATCTCACACCGAT | AAGGTTCCGCTGAGTTCCTG |
| E751 | CGAGAGCCTAGTGATGTA | ATGAGTGATGAGCGAGTA |
| HR3 | CTCACGAGGAGCTCTGGTTC | TGCGAGAATTTCCTGAATCC |
| EcR1 | TAAGTGATGACGACTCGGATGC | ACGAGCAAGCCTTTAGCAGTG |
| RXR 1 | AGCGTCAGAGGACAAAAGGC | TGGTCCAGTGGCTGCTCAT |
| Chi1 | CCCAGCCGATAGGAAGACC | CGCTGTCAGTATCATTCCGTTAG |
| Sad1 | CACGGCATTTTCAAGGAGA | AAGGCGTCATCCAGGCACT |
| Dib1 | TGCGAGTCTGCTTGAGGTG | AGCCATTGTCAGTGGGGAG |
| Spo1 | GGGACGAGCCCAATAAGTT | CTGGTGCTGAAAGGGATGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Shang, Y.; Yu, X.; Gao, B.; Lv, J.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Meng, X. Ammonia Stress Disturbs Moult Signaling in Juvenile Swimming Crab Portunus trituberculatus. Biology 2023, 12, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030409
Wang D, Liu X, Shang Y, Yu X, Gao B, Lv J, Li J, Liu P, Li J, Meng X. Ammonia Stress Disturbs Moult Signaling in Juvenile Swimming Crab Portunus trituberculatus. Biology. 2023; 12(3):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030409
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Daixia, Xiaochen Liu, Yan Shang, Xuee Yu, Baoquan Gao, Jianjian Lv, Jitao Li, Ping Liu, Jian Li, and Xianliang Meng. 2023. "Ammonia Stress Disturbs Moult Signaling in Juvenile Swimming Crab Portunus trituberculatus" Biology 12, no. 3: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030409
APA StyleWang, D., Liu, X., Shang, Y., Yu, X., Gao, B., Lv, J., Li, J., Liu, P., Li, J., & Meng, X. (2023). Ammonia Stress Disturbs Moult Signaling in Juvenile Swimming Crab Portunus trituberculatus. Biology, 12(3), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030409







