The Hypothalamus of the Beaked Whales: The Paraventricular, Supraoptic, and Suprachiasmatic Nuclei
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Hypothalamus of Toothed Whales: Very Little Data
1.2. On the Neuroanatomy of the Beaked Whales
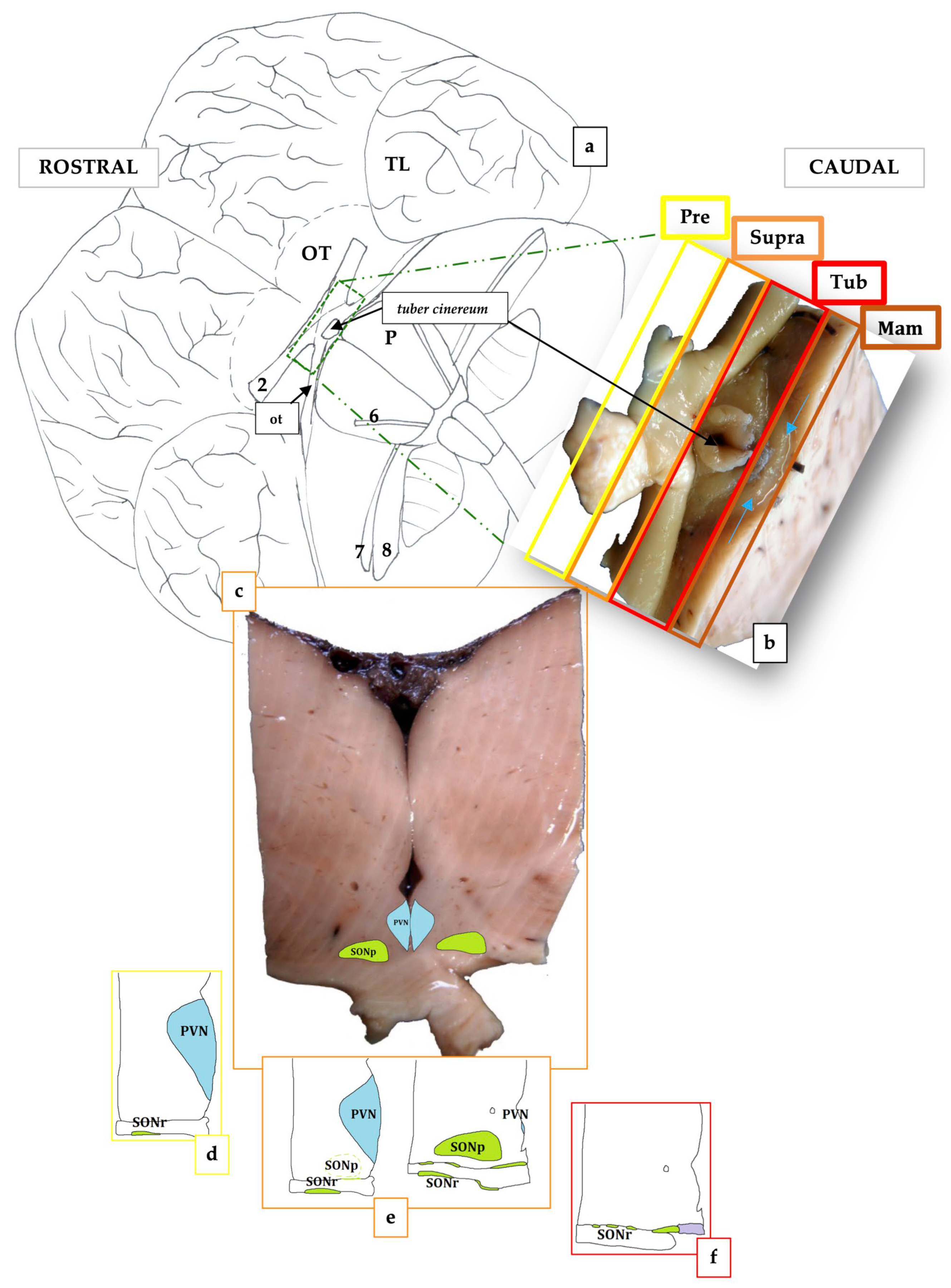
2. Materials and Methods
Specificity of the Antibodies
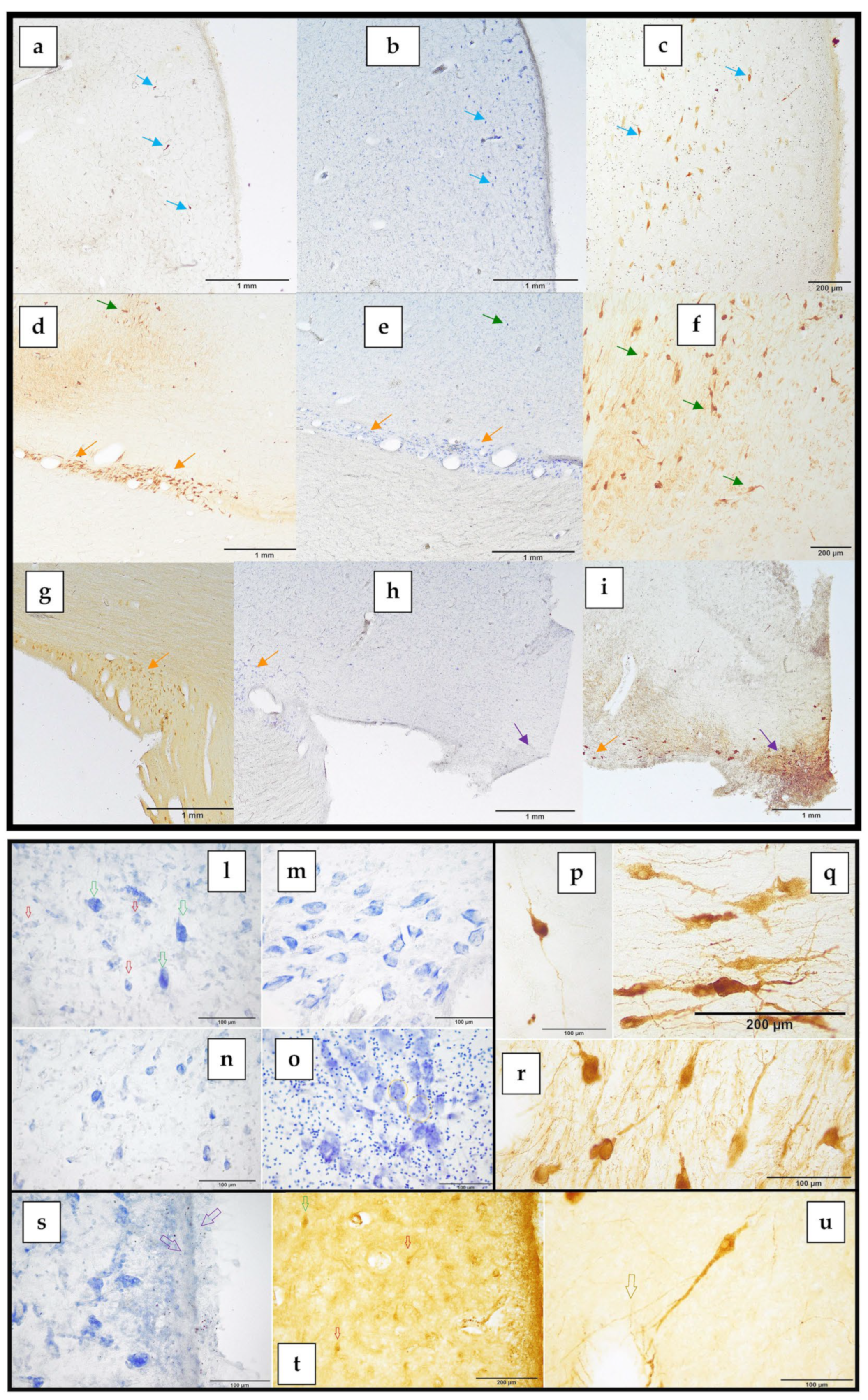
3. Results
3.1. The Hypothalamus of the Toothed Whales
- Preoptic (Pre), rostral to the optic chiasm;
- Supraoptic or anterior (Supra), dorsal to the optic chiasm;
- Tuberal (Tub), dorsal to the tuber cinereum;
- Mammillary (Mam), dorsal to the rudimentary mammillary bodies.
3.2. The Paraventricular Nucleus of BWs
3.3. The Supraoptic Nucleus of BWs
3.4. The Suprachiasmatic Nucleus of BWs
3.5. Cytoarchitecture of the PVN and SON
- The magnocellular neurons present in both the PVN and the SON;
- The parvocellular neurons present exclusively in the PVN.
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paxinos, G. The Rat Nervous System, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, H.; Moser, N.; Huggenberger, S. The Mouse Hypothalamus. In Neuroanatomy of the Mouse: An Introduction; Schröder, H., Moser, N., Huggenberger, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 205–230. [Google Scholar]
- Dudás, B. Part I—Morphology of the human hypothalamus: Anatomy, blood supply, nuclei and pathways. In Atlas of the Human Hypothalamus; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaab, D.F. (Ed.) Chapter 8 Supraoptic and paraventricular nucleus (SON, PVN). In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Nederlands, 2003; Volume 79, pp. 163–237. [Google Scholar]
- Kupfermann, I. Hypothalamus and limbic system: Peptidergic neurons, homeostasis, and emotional behavior. In Principles of the Neural Science; Kandel, E.R., Schwartz, J.H., Jessell, T.M., Eds.; Elsiever: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Chapter 47; pp. 735–749. [Google Scholar]
- Saper, C.B. Hypothalamus. In The Human Nervous System; Paxinos, G., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Chapter 15; pp. 389–413. [Google Scholar]
- Vuppaladhadiam, L.; Ehsan, C.; Akkati, M.; Bhargava, A. Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Family: A Stress Hormone-Receptor System’s Emerging Role in Mediating Sex-Specific Signaling. Cells 2020, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibata, Y.; Okamura, H.; Tanaka, M.; Tamada, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Iijima, N.; Matsuda, T.; Munekawa, K.; Takamatsu, T.; Hisa, Y.; et al. Functional morphology of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1999, 20, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogenboom, R.; Kalsbeek, M.J.; Korpel, N.L.; de Goede, P.; Koenen, M.; Buijs, R.M.; Romijn, J.A.; Swaab, D.F.; Kalsbeek, A.; Yi, C.-X. Loss of arginine vasopressin- and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing neurons and glial cells in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C.A.; Finger, E.C. Chapter 7—The supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei in healthy aging and neurodegeneration. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Nederlands, 2021; Volume 180, pp. 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudsmit, E.; Hofman, M.A.; Fliers, E.; Swaab, D.F. The supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the human hypothalamus in relation to sex, age and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 1990, 11, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgane, P.J.; Jacobs, M.S.; McFarland, W.L. The anatomy of the brain of the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). Surface configurations of the telencephalon of the bottlenose dolphin with comparative anatomical observations in four other cetacean species. Brain Res. Bull. 1980, 5, 1–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelschläger, H.H.A.; Oelschläger, J.S. Brain. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals; Perrin, W.F., Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgane, P.; Jacobs, M. Comparative anatomy of the cetacean central nervous system. In Functional Anatomy of Marine Mammals; Harrison, R.J., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1972; Volume 1, pp. 117–244. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, L.A.; Patzke, N.; Bhagwandin, A.; Bux, F.; Fuxe, K.; Barber, G.; Siegel, J.M.; Manger, P.R. Organization and number of orexinergic neurons in the hypothalamus of two species of Cetartiodactyla: A comparison of giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) and harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2012, 44, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baird, R.W.; Webster, D.L.; Schorr, G.S.; McSweeney, D.J.; Barlow, J. Diel variation in beaked whale diving behavior. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2008, 24, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaldo de Quirós, Y.; Fernandez, A.; Baird, R.W.; Brownell, R.L.; Aguilar de Soto, N.; Allen, D.; Arbelo, M.; Arregui, M.; Costidis, A.; Fahlman, A.; et al. Advances in research on the impacts of anti-submarine sonar on beaked whales. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Brownson, R.H. Relative brain sizes and cortical surface areas in odontocetes. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1984, 172, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, S.; Carlin, K.; Van Alstyne, K.; Hanson, A.; Tarpley, R. Comparison of Dolphins’ Body and Brain Measurements with Four Other Groups of Cetaceans Reveals Great Diversity. Brain Behav. Evol. 2017, 88, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, L. A Comparison of Encephalization between Odontocete Cetaceans and Anthropoid Primates. Brain Behav. Evol. 1998, 51, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graïc, J.-M.; Peruffo, A.; Corain, L.; Finos, L.; Grisan, E.; Cozzi, B. The primary visual cortex of Cetartiodactyls: Organization, cytoarchitectonics and comparison with perissodactyls and primates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2022, 227, 1195–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, P.R.; Chanis, R.; Marino, L. Cortical complexity in cetacean brains. Anat. Record. Part A 2005, 287, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Brownson, R.H.; Van Alstyne, K.R.; Hauser, R.A. Higher neuron densities in the cerebral cortex and larger cerebellums may limit dive times of delphinids compared to deep-diving toothed whales. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchini, S.; Herráez, P.; Arbelo, M.; Espinosa de los Monteros, A.; Sierra, E.; Rivero, M.; Bombardi, C.; Fernández, A. Methodology and Neuromarkers for Cetaceans’ Brains. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acher, R.; Chauvet, J.; Chauvet, M.T. Isolation of Finback Whale Oxytocin and Vasopressin. Nature 1964, 201, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvet, J.; Chauvet, M.T.; Acher, R. The neurohypophysial hormones of mammals: Isolation and characterization of oxytocin and vasopressin from whale (Balaenoptera physalus L.). Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol. 1963, 45, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi, H.; Muramoto, K.; Ramachandran, J. Isolation and primary structure of adrenocorticotropin from several species of whale. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1978, 12, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünthal, E. Über den Primatencharakter des Gehirns von Delphinus delphis. Eur. Neurol. 1942, 105, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatschek, R.; Schlesinger, H. Der Hirnstamm des Delphins (Delphinus delphis L.). In Arbeiten aus dem neurologischen Institute (Institut für Anatomie und Physiologie des Zentralnervensystems) an der Wiener Universität. IX; Heft: Vienna, Austria, 1902; pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Jelgersma, G. Das Gehirn der Wassersäugetiere: Eine Anatomische Untersuchung; Johann Ambrosius Barth: Leipzig, Germany, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, R.B.R. Anatomie Comparèe des Mammifëres Domestiques. Tome 6: Neurologie 1 Systëme Nerveux Central; VIGOT: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Parent, A.; Carpenter, M. Carpenter’s Human Neuroanatomy, 9th ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, C.F. De cinerea cerebri substantia. In Exercitationes Academicae; Sommer: Leipzig, Germany, 1779; Volume 1, pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hofman, M.A.; Goudsmit, E.; Purba, J.S.; Swaab, D.F. Morphometric analysis of the supraoptic nucleus in the human brain. J. Anat. 1990, 172, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Ishunina, T.A.; Swaab, D.F. Vasopressin and oxytocin neurons of the human supraoptic and paraventricular nucleus: Size changes in relation to age and sex. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 4637–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federative International Programme for Anatomical Terminology (FIPAT). Terminologia Neuroanatomica. International Neuroanatomical Terminology; Dalhousie University Libraries: Halifax, NS, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, D.; Ramos, J.; Gonzalez, C.; Fernandez-Viadero, C. The supraoptic nucleus: A morphological and quantitative study in control and hypophysectomised rats. J. Anat. 1990, 169, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarro, A.; Tolivia, J.; Alvarez-Uría, M. Hamster supraoptic nucleus: Cytoarchitectural, morphometric, and three-dimensional reconstruction. Anat. Rec. 1994, 240, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delville, Y.; Koh, E.T.; Ferris, C.F. Sexual differences in the magnocellular vasopressinergic system in golden hamsters. Brain Res. Bull. 1994, 33, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature ICVGAN. Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria; World Association of Veterinary Anatomists (WAVA): Hanover, Germany; Ghent, Belgium; Columbia, MO, USA; Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Gagel, O. Zur Topik und feineren Histologie der vegetativen Kerne des Zwischenhirns. Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 1928, 87, 558–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, M.; Busch, J.R.; Jacobsen, C.; Lundemose, S.B.; Lynnerup, N.; Rath, M.F.; Banner, J. The accessory magnocellular neurosecretory system of the rostral human hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, C.B.; Lowell, B.B. The hypothalamus. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R1111–R1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelyane, N.M.S.; Marília, A.S.B.; Helder, H.A.M.; Melquisedec, A.D.S.; Lara, L.S.; Paulo, L.A.G.M.; Fernando, V.L.L.; Jeferson, S.C.; Ruthnaldo, R.M.L.; Judney, C.C.; et al. The Suprachiasmatic Nucleus and the Intergeniculate Leaflet of the Flat-Faced Fruit-Eating Bat (Artibeus planirostris): Retinal Projections and Neurochemical Anatomy. Front. Neuroanat. 2018, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.M.C. Dim Light at Night and Constant Darkness: Two Frequently Used Lighting Conditions That Jeopardize the Health and Well-being of Laboratory Rodents. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Swaab, D.F. The human pineal gland and melatonin in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, B.; Huggenberger, S.; Oelschläger, H. Chapter 6. Brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves. In The Anatomy of Dolphins. Insights into Body Structure and Function; Cozzi, B., Huggenberger, S., Oelschläger, H., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 197–304. [Google Scholar]
- Jais, A.; Brüning, J.C. Arcuate Nucleus-Dependent Regulation of Metabolism—Pathways to Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 43, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, E.A.; Robinson, A.G. Hypothalamic neurons secreting vasopressin and neurophysin. Kidney Int. 1976, 10, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Bellver, C.; Cadiz-Moretti, B.; Novejarque, A.; Martinez-Garcia, F.; Lanuza, E. Differential efferent projections of the anterior, posteroventral, and posterodorsal subdivisions of the medial amygdala in mice. Front. Neuroanat. 2012, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primary Antibody | Clonality Host Species Isotype | Species Reactivity | Dilution | NS | SA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Vasopressin Abcam Ab39363 | P R IgG | Reacts with: Rat, Pig | 1/500 | G (S-1000) | BaR (BA-1000) |
| Anti-CRF1/CRHR1 Abcam Ab59023 | P G IgG | Reacts with: Human Predicted to work with: Rat, Sheep, Chicken, Pufferfish, Rhesus monkey, African green | 1/100 | R (S-5000) | BaG (BA-9500) |
| PVNpar | PVNmag | SONmag | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thionine P | 49.23 ± 7.19 µm | 91.23 ± 15.19 µm | 87.05 ± 15.47 µm |
| Thionine A | 139.16 ± 29.66 µm2 | 496.65 ± 155.4 µm2 | 445.11 ± 142.81 µm2 |
| ADH P | - | 100.77 ± 16.74 µm | 100.37 ± 17.82 µm |
| ADH A | - | 508.78 ± 149.61 µm2 | 558.21 ± 176.48 µm2 |
| Thionine P CBW | - | 96.87 ± 14.79 µm | 89.02 ± 13.75 µm |
| Thionine A CBW | - | 532.72 ± 165.41 µm2 | 485.98 ± 128.94 µm2 |
| Thionine P BBW | - | 87.48 ± 14.45 µm | 86.25 ± 16.28 µm |
| Thionine A BBW | - | 472.6 ± 145.75 µm2 | 423.28 ± 128.94 µm2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sacchini, S.; Bombardi, C.; Arbelo, M.; Herráez, P. The Hypothalamus of the Beaked Whales: The Paraventricular, Supraoptic, and Suprachiasmatic Nuclei. Biology 2023, 12, 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101319
Sacchini S, Bombardi C, Arbelo M, Herráez P. The Hypothalamus of the Beaked Whales: The Paraventricular, Supraoptic, and Suprachiasmatic Nuclei. Biology. 2023; 12(10):1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101319
Chicago/Turabian StyleSacchini, Simona, Cristiano Bombardi, Manuel Arbelo, and Pedro Herráez. 2023. "The Hypothalamus of the Beaked Whales: The Paraventricular, Supraoptic, and Suprachiasmatic Nuclei" Biology 12, no. 10: 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101319
APA StyleSacchini, S., Bombardi, C., Arbelo, M., & Herráez, P. (2023). The Hypothalamus of the Beaked Whales: The Paraventricular, Supraoptic, and Suprachiasmatic Nuclei. Biology, 12(10), 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101319







