Simple Summary
Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis are the most common species of Enterococcus spp. genus involved in human pathology. They are known for their increasing resistance to vancomycin, an antibiotic that blocks synthesis of Gram-positive bacteria’s cell wall. Other species of Enterococcus spp. (E. casseliflavus, E. gallinarum, E. durans, E. avium, E. raffinosus) are less common in human infections, and thus, their importance in the medical field is still uncertain. In this study, we analyzed the non-faecalis non-faecium Enterococci strains isolated from a tertiary care hospital in Romania for one year. Among a total of 658 Enterococcus isolates, 58 strains proved to be non-faecalis non-faecium Enterococci and met the inclusion criteria of our study. These species were isolated more frequently from mixed etiology infections with E. coli from the surgical ward. To put our results into perspective, a brief review of literature was performed in which we used 39 case reports involving non-faecalis non-faecium Enterococci. The emerging numbers of non-faecalis non-faecium Enterococci infections pose a danger to human health systems, due to their ability to easily acquire antibiotic resistance genes. To our knowledge, this study represents the first non-faecalis non-faecium Enterococci group analysis from Eastern Europe.
Abstract
(1) Background: This paper aims to provide a description of non-faecalis non-faecium enterococci isolated from a tertiary care hospital in Romania and to briefly review the existing literature regarding the involvement of Enterococcus raffinosus, Enterococcus durans and Enterococcus avium in human infections and their antimicrobial resistance patterns; (2) Methods: We retrospectively analyzed all Enteroccocus species isolated from the “Prof. Dr. O. Fodor” Regional Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology from Cluj-Napoca during one year focusing on non-faecalis non-faecium Enterococci. A brief review of the literature was performed using case reports involving Enterococcus raffinosus, Enterococcus durans and Enterococcus avium; (3) Results: Only 58 out of 658 Enteroccocus isolates were non-faecalis non-faecium and met the inclusion criteria. These species were isolated more often (p < 0.05) from the surgical ward from mixed etiology infections with E. coli. In our review, we included 39 case reports involving E. raffinosus, E. durans and E. avium; (4) Conclusions: Isolation of non-faecalis non-faecium enterococci displays an emerging trend with crucial healthcare consequences. Based on the analysis of the case reports, E. avium seems to be involved more often in neurological infections, E. durans in endocarditis, while E. raffinosus displays a more heterogenous distribution.
1. Introduction
Based on rigorous criteria, the World Health Organization (WHO) elaborated in 2016 a list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria that should represent the top priority for global academic and corporate effort and funding into developing new antibiotics to fight the related infections. Among the Gram-positive bacteria, the highest priority was given to vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, followed closely by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [1]. Although enterococci were known as commensals of the human gut as well as potential pathogens for decades, the publication of the WHO list led to a renewed interest in researching the Enterococcus faecium (E. faecium) and Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis) species, as they represent approximately 90% of the isolated enterococci in human infectious pathology [2,3].
With these two species being highly researched by the scientific community, it was noticed that other clinically significant species of the Enterococcus spp. genus were cultured from human biological specimens, notably E. casseliflavus, E. gallinarum, E. durans, E. avium, E. raffinosus and E. mundtii [4]. As these species are less frequent, they are collectively known as “non-faecalis non-faecium enterococci”, or simply “other enterococci (OE)”. These Enterococcus species were found in meat products and animal feces, carrying transmittable resistance genes for multiple antibiotics. It was also demonstrated that strains isolated from non-human sources can pass these genes to human strains, contributing to the overall burden of antibiotic-resistant infections [5].
The increasing resistance to vancomycin appears to be one of the greatest threats to public health, as this antibiotic is sometimes used as a last choice in infections with multiple resistant Gram-positive bacteria [6]. Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic that acts by binding to a key component of the Gram-positive bacteria’s cell wall, leading to a blockage in its synthesis and increasing its susceptibility to external factors.
The first vancomycin-resistant enterococci were discovered in 1988. Subsequently, it was found out that vancomycin resistance is achieved through a bacterium’s use of alternative cell wall synthesis pathways that are minimally influenced by the presence of the antibiotic in the environment [7]. Six phenotypes of vancomycin resistance have been described, namely vanA, vanB, vanC, vanD, vanE and vanG. Of these, vanA (resistance to both vancomycin and teicoplanin) and vanB (resistance to vancomycin but susceptibility to teicoplanin) are the most clinically significant ones, as they are coded by plasmid genes that may be transmitted horizontally (even to other genera, such as S. aureus). Meanwhile, vanC is coded by chromosomal genes, being described as intrinsic vancomycin resistance. E. casseliflavus and E. gallinarum are known to possess vanC non-transmittable genes [8].
Plasmid transmission of vanA resistance is a well-researched subject in E. faecalis and E. faecium. However, in recent years, nosocomial outbreaks of OE with the vanA vancomycin resistance phenotype were reported in the literature [9].
As little is known about the importance of OE isolates in human specimens and their antibiotic resistance profile, as well as the impact they have on overall morbidity and mortality, we propose a study that adds information to the general knowledge regarding their distribution among hospitalized patients, focusing on Enterococcus raffinosus, Enterococcus durans and Enterococcus avium.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was a longitudinal retrospective analysis of all enterococcus species isolated in the Regional Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology “Prof. Dr. O. Fodor” Cluj-Napoca, Romania, during a period of one year. We included the strains isolated from samples collected from the gastroenterology and hepatology department, surgery department and internal medicine department.
2.1. Strain Isolation, Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Sample processing followed the hospital’s protocol, using specific media: sheep blood agar (bioMérieux, Marcy–l’ Étoile, France), Brilliance™ UTI Agar (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham MA, USA). The strains were identified to the species level using a Vitek® 2 Compact (bioMérieux, Marcy–l’ Étoile, France) GP card and with the antibiotic susceptibility performed using Vitek® 2 Compact (bioMérieux, Marcy–l’ Étoile, France) AST P592 card.
2.2. Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
A database was generated using Microsoft Excel with the following variables: age, gender, diagnosis, sample type, number of hospitalization days, discharge status (recovered/deceased), Enterococcus species, associated bacteria or fungi if present, antimicrobial resistance profile and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). All information was gathered from the hospital’s electronic database.
To better understand the relation between the Enterococcus species, pathology and antimicrobial resistance, the samples were initially divided into three groups: E. faecalis, E. faecium and OE. The above-mentioned variables were presented distinctly for each group and an analysis of the differences between them was performed using the appropriate statistical tests. Regarding the antimicrobial resistance, the OE group was further divided into the vanC and non-vanC groups. The comparison between these groups was performed using the appropriate statistical tests for each variable.
For the OE species, the multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) index was determined, representing the ratio between the number of antibiotics that an isolate is resistant to and the total number of antibiotics the organism is tested for. The MAR index was compared using the Kruskal–Wallis test for independent groups. A pair-wise comparison test between the MAR indexes of each species was also performed using the Bonferroni correction for multiple tests for the adjustment of the significance values. The statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0.
2.3. Brief Review Protocol
In order to provide a more comprehensive image regarding the involvement of E. rafinosus, E. durans and E. avium in human pathology, we performed a brief review. We searched relevant articles on PubMed, Cochrane library electronic database and Med Nar, up to 15 December 2020. We considered the following terms included in the studies title or abstract: “enterococcus”, “rafinosus”, “durans” and “avium” combined with the operator “AND” along with “human”, “infection” and “diagnostic”. The search was performed by two individual researchers and the results were confronted afterwards. We excluded studies written in languages other than English, French or Spanish.
3. Results
Although we initially found 658 isolates of Enterococcus involved in human infections, 319 (representing 48.48%) were excluded because they were not identified using the automated system Vitek® 2 Compact (bioMérieux, Marcy-l’ Étoile, France). From the remaining isolates, 126 (37.16%) were E. faecalis, 155 (45.72%) were E. faecium and 58 (17.10%) were OE.
3.1. Descriptive Analysis of Enterococcus Species
A descriptive analysis was performed, focusing on the main characteristics of the patients, sample type, associated microorganisms and underlying conditions.
Table 1 contains the characteristics of the patients infected by the OE as well as a comparison between the species regarding age, gender, department, mortality and days of hospitalization. The mean age of the patients infected with OE was 64.33 years. More OE strains were isolated from male patients (n = 33) than female patients (n = 25). OE strains isolated from surgery/intensive care units (n = 43) were more common than those isolated from gastroenterology (n = 11) and internal medicine (n = 4) departments. Fatal infections with OE were declared in 29.3% of the cases.

Table 1.
Patient characteristics according to other Enterococci species.
OE strains were isolated from six urine samples, while three strains were isolated from urinary catheters. In total, 10 out of 58 OE strains were isolated from bile cultures, but only 7 of them from patients who underwent invasive gallbladder procedures. Puncture fluid cultures proved positive for 11 OE strains. The distribution of OE strains among other samples is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Distribution of other Enterococci among different samples.
Mixed etiology infections involving one or two species of enterococci in association with other bacteria or fungi were further evaluated. Table 3 presents bacterial and fungal strains associated with OE. E. faecium was associated with OE in eight infections, while E. faecalis co-infections were proved in five cases. Klebsiella spp. proved to be the most common Gram-negative bacteria isolated from OE co-infections (n = 20). Candida albicans infections were also reported in nine cases of OE infections.

Table 3.
Association of different bacteria and fungi with other Enterococci (number of associations and percentage for each species described).
The main diagnoses of the patients presenting an infection with OE are given in Table 4 (number and percentage of patients for each disease included in the study). Cirrhosis and bloodstream infections proved to be the most common underlying conditions in patients with OE infection.

Table 4.
Several underlying conditions associated with other Enteroccocus infections.
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing in Other Enterococci
E. gallinarum and E. casseliflavus are two species of OE that harbor the vanC gene; however, regarding the resistance to glycopeptides, the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of E. gallinarum for Teicoplanin equaled 1 mg/L for one strain and <0.5 mg/L for 30 strains. The MIC of E. casseliflavus for Teicoplanin equaled 1 mg/L for one strain and <0.5 mg/L for 2 strains. The MICs values for Tigecycline measured less than 0.12 mg/L for all tested strains of OE. Other antimicrobial susceptibility results for the OE in this study are presented in Figure 1.
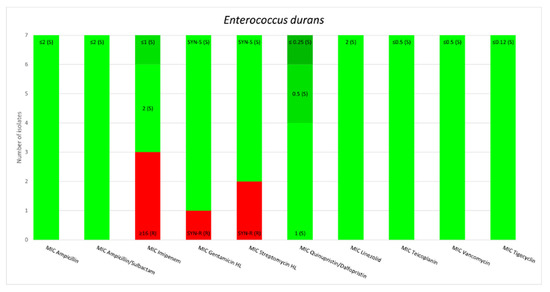
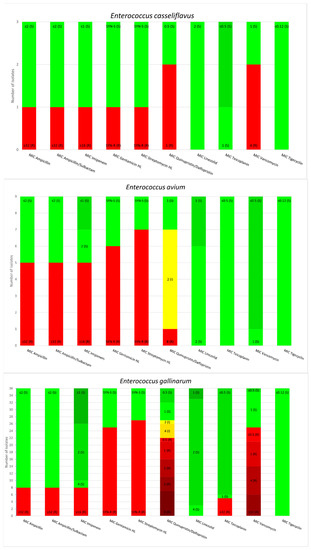
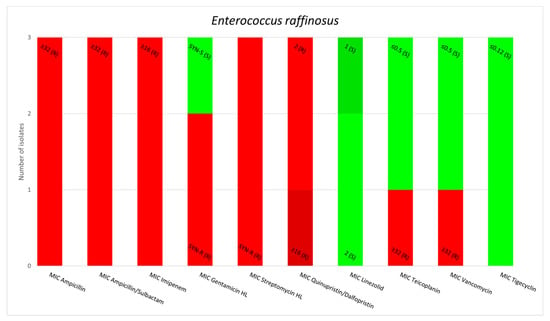
Figure 1.
Minimum inhibitory concentrations patterns in E. gallinarum, E. avium, E. raffinosus, E. casseliflavus and E. durans.
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Other Enterococci
OE were organized based on their intrinsic resistance to glycopeptides into vanC and non-vanC enterococci. Both vanC and non-vanC strains were statistically significant isolated more frequently from surgical wards than from clinical wards (p = 0.012). Table 5 contains the differences related with different epidemiologic criteria and microbial association criteria between OE with vanC pattern and non-vanC from our study.

Table 5.
Comparison of vanC enterococci with non-vanC enterococci distribution.
The comparison between OE, E. faecalis and E. faecium is presented in Table 6. OE are statistically significant isolated more frequently from polymicrobial infections than E. faecalis (p = 0.026) and E. faecium (p = 0.001). E. coli infections proved statistical significance in association with OE rather than E. faecium (p < 0.001).

Table 6.
Comparison between other Enterococci and E. faecalis and E. faecium.
The MAR index was studied for each strain of Enterococcus. E. faecium and E. raffinosus emerged as the most resistant species, with a MAR index above 0.6. A pair-wise comparison of the MAR indices and their statistical analysis are presented in Figure 2 and Table 7.
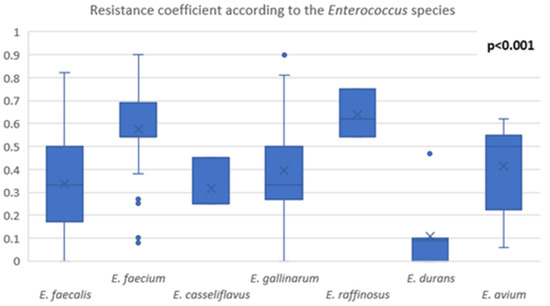
Figure 2.
Comparison of MAR index among Enterococcus species.

Table 7.
Pairwise comparison of the MAR index of the Enterococcus species.
3.4. Brief Review of the Literature Concerning E. raffinosus, E. durans and E. avium
Based on the protocol described above we included 39 case reports, 16 cases involving E. avium, 13 cases involving E. durans and 10 cases involving E. raffinosus. A summary of the case reports included in this brief review, organized based on the infection sites, is presented in Figure 3.
4. Discussion
Other Enterococci (OE) represent an often-forgotten group of human pathogens. Due to do the difficulty in isolating and diagnosing these bacteria, they remained for a long time in the shadow of more common pathogens from the Enterococcus genus, such as E. faecalis and E. faecium. Over the past decade, this dogma has changed drastically and once the automatic devices for isolation and detection became available worldwide, a surge of OE started to be reported. However, until recently, they remained an incidental finding without much knowledge regarding their pathogenicity [8,10].
Our work presents, to our knowledge, the first Eastern European extended report of OE isolated from human samples. We were able to isolate 58 strains belonging to 5 species of OE: E. gallinarum (36 strains), E. caselliflavus (3 strains), E. avium (9 strains), E. durans (7 strains) and E. raffinosus (3 strains).
Regarding the sample from where the strains were isolated, E. gallinarum was the only OE species isolated from the urine (nine strains), stool (two strains) and central venous catheter (one strain); moreover, E. avium was the only species isolated from the lower respiratory tract of a patient admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. Other products, such as bile, blood, pus, ascites and other fluids, presented a more prominent diversity regarding the isolates. However, regarding the bile culture, we observed that out of the twenty isolates of OE, fifteen were after an invasive procedure to the biliary tract. This was observed in other studies too, and currently, invasive procedures to the biliary tract represent a risk factor for infections with digestive tropism [11,12].
Another relevant observation represented the associations of OE with other pathogens, bacteria and fungi. OE are associated with a second pathogen in 84.48% of the cases, with Klebsiella pneumoniae representing the most common associated bacteria and Candida albicans the most common associated fungus. Thus, OE seem to be solely involved in human infections only in rare occasions. This may be another reason why these pathogens were isolated so rarely until recently and why their role in human infections is not clear [13,14,15,16].
The associated conditions of the patients with an isolated OE were cirrhosis, cholelithiasis, sepsis and malignancies (colon, stomach, pancreatic and bile ducts). These associations are not new and there are several reports that can further support these findings. Regarding the mechanism, some studies describe the involvement of vascular dilatation and permeation along with bacterial translocation like in cirrhosis. In colon cancer, enterococcus infections seem to be present due to alterations in the mucosa. However, none of the existing studies focus on OE so we are lacking information regarding their involvement, similarities and differences with E. faecalis and E. faecium [8,16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
Antimicrobial resistance patterns observed in our studies align with the existing information. None of the strains were resistant to linezolid and tigecycline, which remain two of the antibiotics used as a last resort in infections with VRE [8,23]. E. raffinosus strains were particularly resistant, displaying susceptibility only to linezolid, tigecycline, teicoplanin and vancomycin. This phenotype has the potential to become a real public health issue considering the ability of E. raffinosus to acquire circulating resistance genes, such as vanA or vanB, especially in some healthcare settings with high antimicrobial pressure, such as the intensive care units [9,24,25]. E. avium strains also presented a clinically relevant level of resistance similar to E. raffinosus. However, some of these strains were susceptible to ampicillin, ampicillin/sulbactam, imipenem, gentamicin, streptomycin and quinupristin/dalfopristin, which means that in contrast to E. raffinosus, infections caused by E. avium have more therapeutic options. The third OE species that does not display an intrinsic resistance phenotype to vancomycin, E. durans, has been found to be the most sensitive out of the three. The only resistances we observed in our study were to imipenem, gentamicin and streptomycin. All these findings are consistent with the information existing in literature and sustain the movement of developing new antibiotics [3,5,26,27].
To further evaluate the importance of OE, we divided them in two groups based on the intrinsic resistance to vancomycin. In this respect, the vanC group contains E. casseliflavus and E. gallinarum, while the non-vanC group contains E. raffinosus, E. durans and E. avium. We observed no significant difference between the two groups regarding age of the patients they infect, mortality, average length of hospitalization, association of Klebsiella spp. and E. coli and existing oncologic condition. However, non-vanC strains were isolated from the surgical ward significantly (p < 0.005) more often than vanC strains. We found no existing information in the literature to sustain this observation. We hypothesized that the antibiotic pressure from a surgical and critical care ward can select more resistant and diverse strains. Moreover, in our study, one additional factor that can explain these results was the hospital’s profile, being a gastroenterology and hepatology institute; most of the patients that required surgery involved an abdominal surgery, and thus, there is a higher chance of bacterial translocation [28,29].
To evaluate the implications of OE in human pathology, we compare them with the most recognized species of the genus, E. faecalis and E. faecium. There was no statistical difference between the groups concerning age, mortality, average length of hospitalization, association with Klebsiella spp. and Candida spp. and the surgical or clinical hospital ward. However, OE were isolated from mixed etiology microbial infections statistically more often than E. faecalis (p < 0.005) and E. faecium (p < 0.005). Additionally, the association of OE and E. coli was present statistically more often than E. faecium and E. coli (p < 0.005). These findings support the hypothesis that in our study, OE were isolated more often from the surgical ward due to the hospital’s profile (studies suggest the association of more than one microorganism in infections after abdominal surgery) [30,31].
The MAR index provides information regarding the antimicrobial resistance of each strain isolated. The statistical analysis performed revealed that E. faecium and E. raffinosus had significantly higher MAR indices than the other species. Although E. faecium is known to be highly resistant, our study showed that E. raffinosus has the potential to become a public health issue in the future regarding their antimicrobial resistance, despite the low prevalence of isolation of this pathogen in humans. However, these results must be considered with caution due to the low number of isolates. E. durans seems to be a less significant concern regarding the antimicrobial resistance, according to our results [32,33].
We further discuss the findings of our brief review focusing on E. avium, E. durans and E. raffinosus and some future perspectives.
4.1. Enterococcus avium
E. avium is a Gram-positive catalase negative streptococcus, commonly isolated from birds. In the past, E. avium was also known as group Q streptococcus [34]. Although it was described to cause bacteriemia and, thus, had the potential for other systemic infections, there are few case reports to date regarding the involvement of this pathogen in human infections [35].
In our review, we found only sixteen case reports describing the involvement of this bacterium in human pathology. Out of the sixteen cases, almost half of them presented a neurologic complication due to this bacterium: brain abscess or bacterial meningoencephalitis. We found three cases of brain abscess involving the temporal lobe and two cases of cerebellum abscess [36,37,38,39,40]. The association of chronic otitis media is common for all these cases. Although brain abscess represents less than 10% of all intracranial space-occupying lesions, due to the mortality rate described at about 25% in some studies and due to the unknown pathogenetic processes that may be involved, the association of E. avium and brain infections need to be further studied. Regarding the outcome of these cases, four of them survived and one patient died. The antimicrobial treatment in most of these cases was an association of a cephalosporin with vancomycin, metronidazole or amikacin. Escribano et al. described the association of linezolid and meropenem with a similar positive outcome [38].
Bacterial meningoencephalitis due to E. avium is described in only two cases, both with a positive outcome but without the association of chronic otitis media. This entity seems to involve a different pathogenetic process than the brain abscesses. Another relevant difference between brain abscess and bacterial meningoencephalitis relies around the age, with all the patients with brain abscess being less than 50 years old, while patients with bacterial meningoencephalitis were above 60 years old. However, this observation’s relevance is yet to be determined [41,42].
Regarding peritonitis, E. avium was involved in three out of the sixteen case reports [43,44,45]. Two cases involved patients around 60 years of age, with common risk factors being hypertension and peritoneal dialysis. Both patients were cured, but different treatment protocols were used. However, Ugur et al. described a pediatric case involving a female patient with several comorbidities which ultimately succumbed to the infection, despite the treatment with amikacin and vancomycin [45]. These observations suggest that E. avium may be more frequently involved than previously known in peritonitis in patients with peritoneal dialysis due to end stage kidney disease. Additionally, in cases with several other comorbidities or risk factors, E. avium seems to be able to produce a deadly infection.
Other cases reported E. avium as the causative agent in infections such as endocarditis, splenic and pancreatic abscess, osteomyelitis, bacteremia with a gastrointestinal starting point and even rare entities such as non-clostridial gas gangrene. All these findings presented an extraordinary heterogenicity concerning the infections caused by E. avium [46,47,48,49,50].
In the era of MALDI-TOF and other modern identification tools, we may be facing a real flood of new species and the real impact of E. avium on human health may become clearer.
4.2. Enterococcus durans
E. durans is part of the normal flora of the gastrointestinal tract. It is one of the rarest species of Enterococcus involved in human pathology, with few case reports existing since its discovery in 1935 by Sherman and Wing [51]. This is due to the low virulence, with few pathogenic factors described. Similar to other species of the genus enterococcus, E. durans is positive for the group D antigen in the Lancefield classification system. It is immobile and does not use mannitol as a source of energy, unlike other enterococcus species, namely E. avium and E. raffinosus. Other relevant biochemical characteristics are the positive reaction for the arginine test and negative reactions for the arabinose, pyruvate, raffinose and sorbose tests. This pattern of sugar metabolism makes E. durans difficult to diagnose in the microbiology laboratory if there is no automatic diagnostic equipment available, such as Vitek2Compact or MALDI-TOF [52].
In our review, we included thirteen case reports with E. durans as the etiologic agent. More than half, eight out of thirteen cases selected, were represented by infective endocarditis [53,54,55,56,57,58,59]. E. durans seems to be able to impair both the mitral and tricuspid valve as well as the aortic valve. It can affect the native valve and the prosthetic valve in the same manner. Concerning the severity, both cases that involved the mitral valve had a poor outcome, regardless of the treatment regime that was used [53,59]. Other endocarditis sites of infection seem to be associated with a better outcome. However, due to the low number of cases published concerning E. durans endocarditis, it is hazardous to draw more relevant observations and conclusions.
Other types of infection that were associated with E. durans were bacteremia, gastritis, infection of the knee arthroplasty, and inflammatory pseudo-tumor of the liver [60,61,62,63]. There is one published case where E. durans was isolated from a screening sample for ante natal identification of Streptococcus agalactiae and one case where it was isolated from a bear bite wound [64,65]. These might suggest the presence of E. durans in other significant sites of the microbiome than previously known and may also signify that E. durans can be isolated from a much wider variety of samples.
4.3. Enterococcus raffinosus
The most enigmatic out of the three species approached in this paper, E. raffinosus, is also the most recently isolated. It is tellurite- and arginine-negative, but mannitol-, sorbose-, arabinose-, raffinose- and pyruvate-positive. This biochemical profile along with the species being immobile make identification very difficult in laboratories that do not have an automatic detection method available [66].
Over the past two decades, case reports involving E. raffinosus in different human pathologies started to emerge. In our brief review, we included ten case reports of E. raffinosus. Unlike E. avium and E. durans, which seem to have a specific infection site, with E. raffinosus, there is more evident heterogenicity concerning the type of infections it can cause. However, regarding endocarditis, we found three case reports that have E. raffinosus as the etiologic agent [25,67,68]. Even if the antimicrobial protocol was different in these three cases, all of them had a positive outcome. The remaining seven case reports from our brief review describe infections at different sites of the human body: endophthalmitis, sinusitis, urinary tract infection, vaginal infection, vertebral osteomyelitis, infected hematoma and decubital ulcer. Most of these infections were treated with teicoplanin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, but the other antibiotic regimes seem to offer similar results [69,70,71,72,73,74,75].
Another relevant issue that concerned E. raffinosus is the ability of this bacteria to harbor the vanA gene that gives resistance to glycopeptides. There have been several studies recently that described actual outbreaks of vanA E. raffinosus in different types of facilities, making this OE extremely dangerous for medical environment and even for the public health [9,76]. Being difficult to diagnose without proper equipment and having the ability to harbor the vanA gene and possibly other resistance genes, E. raffinosus may prove itself a dangerous bacterium to combat. This represents further proof, if needed, that OE are an actual issue of public health, and their identification and antimicrobial testing should represent a priority for clinical microbiologists in the future.
4.4. Limitations
Regarding the limitations of our study, the retrospective nature of the study and the relatively low number of OE identified represent some of the most relevant aspects. Additionally, identification to the species level was not performed using MALDI-TOF or another molecular tool, since it was not available in our facility. Considering the brief review, the low number of the case reports included and their heterogenicity may affect the outcome.
4.5. Future Perspective
Based on the existing information, OE have the potential to become a real threat to the human health. Additionally, from an epidemiologic point of view, we might be facing outbreaks of OE harboring different ARG in the near future. However, recent papers are focusing on the probiotic potential of the Enterococcus genus [77]. This topic remains controversial due to the lack of proper information regarding some Enterococcus species, other than E. faecalis and E. faecium. While E. durans was analyzed from the probiotic potential point of view, E. raffinosus and E. gallinarum remain into question [77,78]. Still, the use of Enterococcus as a probiotic agent seems to have spiked global interest, but further studies are needed, specifically for OE, before a definitive conclusion is made [78].
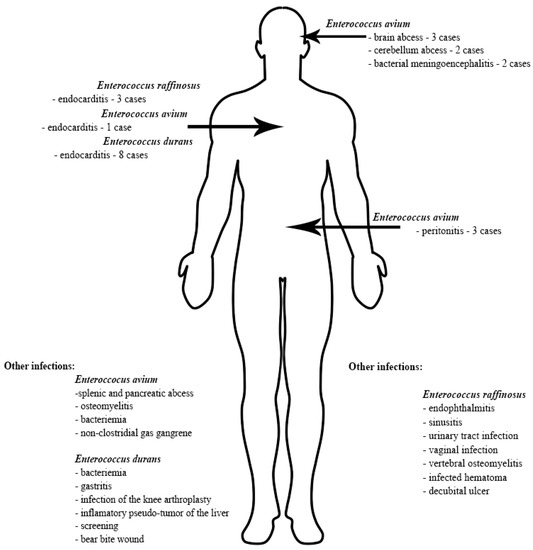
Figure 3.
Infection localization of E. avium, E. raffinosus and E. durans [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75].
5. Conclusions
Despite the paucity of published articles and isolated strains from human infections, there is proof that OE can be involved in severe infections with potentially a deadly outcome. The fact that they can harbor antibiotic resistance genes and can easily acquire further ones only adds to the danger that these Enterococcus species pose. This prompts an urgent need for further studies that can help us isolate, understand and treat the various infections that the OE group can cause.
To our knowledge, this paper provides the first analysis of the OE group from Eastern Europe and represents a milestone in the research of this niche.
OE have been in the spotlight recently concerning E. gallinarum and E. casseliflavus due to their vancomycin resistance via the chromosomal vanC gene. However, this paper provides comprehensive information regarding the involvement of E. raffinosus, E. durans and E. avium in human infections and their treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization D.A.T. and L.M.J.; methodology D.A.T. and R.M.M.; software, A.B. and R.M.M.; validation C.A.C., I.A.C. and S.L.P.; formal analysis R.M.M. and A.B.; investigation, D.A.T.; resources, S.L.P. and A.B.; data curation, D.A.T. and A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, D.A.T.; writing—review and editing, C.A.C., I.A.C. and S.L.P.; visualization, A.B.; supervision, L.M.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the retrospective character of this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-K.; Lai, C.-C.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lin, S.-H.; Liao, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-T.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-I.; Hsueh, P.-R. Bacteremia caused by non-faecalis and non-faecium enterococcus species at a Medical center in Taiwan, 2000 to 2008. J. Infect. 2010, 61, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Li, G.; Wang, W. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterococcus Species: A Hospital-Based Study in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Perio, M.A.; Yarnold, P.R.; Warren, J.; Noskin, G.A. Risk Factors and Outcomes Associated with Non–Enterococcus faecalis, Non– Enterococcus faecium Enterococcal Bacteremia. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2006, 27, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignaroli, C.; Zandri, G.; Aquilanti, L.; Pasquaroli, S.; Biavasco, F. Multidrug-Resistant Enterococci in Animal Meat and Faeces and Co-Transfer of Resistance from an Enterococcus durans to a Human Enterococcus faecium. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogios, P.J.; Savchenko, A. Molecular mechanisms of vancomycin resistance. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlberg, E.; Umstätter, F.; Kleist, C.; Domhan, C.; Mier, W.; Uhl, P. Renaissance of vancomycin: Approaches for breaking antibiotic resistance in multidrug-resistant bacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 2020, 66, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, J.; Knezevich, A.; Luzzati, R.; di Bella, S. Clinical management of non-faecium non-faecalis vancomycin-resistant enterococci infection. Focus on Enterococcus gallinarum and Enterococcus casseliflavus/flavescens. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, S.; Fines-Guyon, M.; Nebbad, B.; Merle, J.C.; le Pluart, D.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Decousser, J.W.; Cattoir, V. First nosocomial outbreak of vanA-type vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus raffinosus in France. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 94, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, K.E. Enterococcal Genetics. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarsch, J.; Czigany, Z.; Heij, L.R.; Luedde, T.; van Dam, R.; Lang, S.A.; Ulmer, T.F.; Hornef, M.W.; Neumann, U.P. Bacterial bile duct colonization in perihilar cholangi-ocarcinoma and its clinical significance. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, Y.; Kato, J.; Kawamura, S.; Kojima, K.; Ohki, T.; Seki, M.; Tagawa, K.; Toda, N. Risk Factors for Acute Cholangitis Caused by Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sava, I.G.; Heikens, E.; Huebner, J. Pathogenesis and immunity in enterococcal infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, E.; van Tyne, D.; Gilmore, M.S. Pathogenicity of Enterococci. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin-Asif, H.; Ali, S.A. The Genus Enterococcus and Its Associated Virulent Factors. In Microorganisms; Blumenberg, M., Shaaban, M., Elgaml, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Cai, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, L.; Xuan, N.; Zhang, G. Clinical characteristics and risk factors in mixed-enterococcal blood-stream infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3397–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.C.; Zhang, Q.B.; Qiao, L. Pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7312–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellot, P.; Francés, R.; Such, J. Pathological bacterial translocation in cirrhosis: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and clinical implications. Liver Int. 2012, 33, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, C.V.; Taddei, A.; Amedei, A. The controversial role of Enterococcus faecalis in colorectal cancer. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1756284818783606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, J.A.G.; Varadarajalu, Y.; Liu, S.; Milikowski, C. Enterococcus Bacteremia A Manifestation of Colon Cancer? Available online: www.infectdis.com (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- Alexopoulou, A.; Agiasotelli, D.; Vasilieva, L.E.; Dourakis, S.P. Bacterial translocation markers in liver cirrhosis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, B.H.; Chung, G.E.; Myung, S.J.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, E.-C.; Lee, H.-S. Enterococcus: Not an innocent bystander in cirrhotic patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 28, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, K.; Bardossy, A.C.; Zervos, M. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci: Epidemiology, Infection Prevention, and Control. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2016, 30, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimoto, K.; Nomura, T.; Maruyama, H.; Tomita, H.; Shibata, N.; Arakawa, Y.; Ike, Y. First VanD-type vancomycin-resistant Enter-ococcus raffinosus isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3966–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasovich, A.; Ganaha, M.C.; Ebi, C.; García, R.D.; Blanco, M.; Lopardo, H. Endocarditis due to vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus raffinosus successfully treated with linezolid: Case report and review of literature. Rev. Argent Microbiol. 2009, 40, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Cercenado, E.; Onal, S.; Eliopoulos, C.T.; Rubin, L.G.; Isenberg, H.D.; Moeuering, R.C.; Eliopoulos, G.M. Characterization of Vancomycin Resistance in Enterococcus durans [Internet]. Available online: http://jac.oxfordjournals.org/ (accessed on 17 December 2021).
- Rasheed, M.; Iqbal, M.; Saddick, S.; Ali, I.; Khan, F.; Kanwal, S.; Ahmed, D.; Ibrahim, M.; Afzal, U.; Awais, M. Identification of Lead Compounds against Scm (fms10) in Enterococcus faecium Using Computer Aided Drug Designing. Life 2021, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.A.; Courvalin, P.; Reynolds, P.E. vanC Cluster of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus gallinarum BM4174 [Internet]. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/journal/aac (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Ahmed, M.O.; Baptiste, K.E. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci: A Review of Antimicrobial Resistance Mechanisms and Per-spectives of Human and Animal Health. Microbial. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaaki, A.; Al-Radi, O.O.; Khoja, A.; Alnawawi, A.; Alnawawi, A.; Maghrabi, A.; Altaf, A.; Aljiffry, M. Surgical site infection following abdominal surgery: A prospective cohort study. Can. J. Surg. 2019, 62, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emil, A.; Lital, K.B.; Eithan, A.; Tamar, M.; Alia, R.; Faris, N. Surgical site infections after abdominal surgery: Incidence and risk factors. A prospective cohort study. Infect. Dis. 2015, 47, 761–767. [Google Scholar]
- Fatoba, D.O.; Abia, A.L.K.; Amoako, D.G.; Essack, S.Y. Rethinking manure application: Increase in multidrug-resistant enterococcus spp. in agricultural soil following chicken litter application. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtula, V.; Jackson, C.R.; Farrell, E.G.; Barrett, J.B.; Hiott, L.M.; Chambers, P.A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterococcus spp. Isolated from Environmental Samples in an Area of Intensive Poultry Production. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 1020–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; Jones, D.; Farrow, J.A.E.; Kilpper-Balz, R.; Schleifer, K.H. Enterococcus avium nom. rev., comb, nov.; E. casseliflavus nom. rev., comb. nov.; E. durans nom. rev., comb. nov.; E. gallinarum comb. nov.; and E. malodoratus sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1986, 36, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Keating, M.R.; Iii, F.R.C.; Steckelberg, J.M. Bacteremia Due to Enterococcus avium Downloaded from [Internet]. Clinical Infectious Diseases. Available online: http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/ (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Park, S.-Y.; Park, K.-H.; Cho, Y.H.; Choi, S.-H. Brain Abscess Caused by Enterococcus avium: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Infect. Chemother. 2013, 45, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.; Dhawan, B.; Kapil, A.; Das, B.K.; Pandey, P.; Gupta, A. Brain abscess due to Enterococcus avium. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2005, 329, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solivera, J.; Vidal, E.; Rivin, E.; Lozano, J.; Escribano, J. Otogenic Cerebellar Abscess by Enterococcus avium, a Very Rare Infectious Agent. J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Central Eur. Neurosurg. 2013, 74, e155–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivan, Y.; Toy, M.A.; Karaoglan, I.; Namiduru, M.; Buyukhatipoglu, H. Enterococcus avium Cerebral abscess. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Kapil, A.; Das, K.; Dhawan, B. Enterococcus avium cerebellar abscess. Neurol. India 2005, 54, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; England, R.; Evans, M.; Soo, S.-S.; Venkatesan, P. Microbiologically confirmed meningoencephalitis due to Enterococcus avium: A first report. J. Infect. 2007, 54, e129–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, C.; Yazawa, S.; Matsuoka, F.; Ishihara, A.; Hayami, M.; Kawasaki, S. Bacterial meningoencephalitis in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis: Two case reports [Internet]. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. Available online: www.elsevier.com/locate/clineuro (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Chao, C.-T.; Yang, S.-Y.; Huang, J. Peritoneal Dialysis Peritonitis Caused by Enterococcus avium. Perit. Dial. Int. J. Int. Soc. Perit. Dial. 2013, 33, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapa, S.; Naramala, S.; Boken, D.; Moreno, A.; Konala, V.M. Peritonitis from Anaerobic Gram-positive Cocci Likely Due to Translocation of Bacteria from Gut in a Patient Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis. Cureus 2019, 11, e6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugur, A.R.; Findik, D.; Dagi, H.T.; Tuncer, I.; Peru, H. Enterococcus avium Peritonitis in a Child on Continuous Ambulatory Peri-toneal Dialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. J. Int. Soc. Perit. Dial. 2014, 34, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zylva, J.; Padley, J.; Badbess, R.; Dedigama, M. Multiorgan failure following gastroenteritis: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 34, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoyev, Z.; Anavekar, N.; Wilson, F.; Uslan, D.; Baddour, L.; Mookadam, F. Enterococcus avium endocarditis. Scandinavian. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 36, 876–878. [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth, T.A. ABCES SPLENIC Farnsworth. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.; Hangai, M.; Oda, T. Bacteremia with an Iliopsoas Abscess and Osteomyelitis of the Femoral Head Caused by Enterococcus avium in a Patient with End-stage Kidney Disease. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orimo, H.; Yamamoto, O.; Izu, K.; Murata, K.; Yasuda, H. Four Cases of Non-clostridial Gas Gangrene with Diabetes Mellitus. J. UOEH 2002, 24, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, J.M.; Wing, H.U. Streptococcus Durans, N. SP. J. Dairy Sci. 1937, 20, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.; Vancanneyt, M.; Descheemaeker, P.; Baele, M.; Van Landuyt, H.; Gordts, B.; Butaye, P.; Swings, J.; Haesebrouck, F. Differentiation and identification of Enterococcus durans, E. hirae and E. villorum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Shehri, M.; Zarak, M.; Sarwari, A. Late prosthetic valve infective endocarditis by Enterococcus durans. J. Global Infect. Dis. 2020, 12, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zala, A.; Collins, N. Enterococcus durans Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: A Previously Unreported Clinical Entity. Hear. Lung Circ. 2016, 25, e133–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallavollita, L.; Di Gioacchino, L.; Balestrini, F. Bioprosthetic Aortic Valve Endocarditis in Association with Enterococcus durans. Tex. Hear. Inst. J. 2016, 43, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakrishnan, R.; Rapose, A. Fatal Enterococcus durans aortic valve endocarditis: A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep. 2012, 2012, bcr0220125855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Jovanović, M.; Lavadinović, L.; Stošović, B.; Pelemiš, M. Enterococcus durans endocarditis in a patient with transpo-sition of the great vessels. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenzaka, T.; Takamura, N.; Kumabe, A.; Takeda, K. A case of subacute infective endocarditis and blood access infection caused by Enterococcus durans [Internet]. Available online: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2334/13/594 (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Mustafa, S.; Hatun, C.; Bugra, C.; Okan, G.; Hakan, L. Enterococcus durans Endocarditis. Am. J. Therap. 2017, 25, e663–e665. [Google Scholar]
- Jover Díaz, F.; Martín González, C.; Mayol Belda, M.J.; Cuadrado Pastor, J.M. Seudotumor inflamatorio hepático múltiple y bac-teriemia por Enterococcus durans. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 32, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zimaity, H.M.; Ramchatesingh, J.; Clarridge, J.; Abudayyeh, S.; Osato, M.S.; Graham, D.Y. Enterococcus gastritis. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 944–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labruyère, C.; Zeller, V.; Lhotellier, L.; Desplaces, N.; Léonard, P.; Mamoudy, P.; Marmor, S. Chronic infection of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: One-stage conversion to total knee arthroplasty. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2015, 101, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Anasetti, C.; Sandin, R.L.; Rolfe, N.; Greene, J.N. Development of daptomycin resistance in a bone marrow transplant patient with vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus durans. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2006, 12, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, V.; Franco, A.; Gherardi, G.; Marrollo, R.; Argentieri, A.V.; Pimentel de Araujo, F.; Carretto, E. η-hemolytic, multi-lancefield anti-gen-agglutinating Enterococcus durans from a pregnant woman, mimicking streptococcus agalactiae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2181–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kunimoto, D.; Rennie, R.; Citron, D.M.; Goldstein, E.J.C. Bacteriology of a Bear Bite Wound to a Human: Case Report. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3374–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; Facklam, R.R.; Farrow, J.A.E.; Williamson, R. Enterococcus raffinosus sp. nov., Enterococcus solitarius sp. nov. and Enterococcus pseudoavium sp. nov. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1989, 57, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, A.; Urban, C.; Rubin, D. Maneesha Ahluwalia -and. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus raffinosus Endocarditis A Case Report and Review of Literature. Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract. 2008, 16, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastroianni, A. Enterococcus raffinosus endocarditis. First case and literature review Prima segnalazione di endocardite da Enterococcus raffinosus e rassegna della letteratura. Infez Med. 2009, 17, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savini, V.; Catavitello, C.; Favaro, M.; Masciarelli, G.; Astolfi, D.; Balbinot, A.; Mauti, A.; Dianetti, J.; Fontana, C.; D’Amario, C.; et al. Enterococcus raffinosus sinusitis post-Aspergillus flavus paranasal infection, in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome: Report of a case and concise review of pertinent lit-erature. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 63, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, P.; Hollowoa, B.; Lala, N.; Thanendrarajan, S.; Matin, A.; Kothari, A.; Schinke, C. Enterococcus raffinosus Infection with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in a Multiple Myeloma Patient after Autologous Stem Cell Transplant. Hematol. Rep. 2017, 9, 7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, V.; Manna, A.; D’Antonio, F.; Talia, M.; Catavitello, C.; Balbinot, A.; Febbo, F.; Carlino, D.; Fioritoni, F.; Di Bonaventura, G.; et al. First report of vaginal infection caused by Entero-coccus raffinosus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 672–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, V.; Manna, A.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Catavitello, C.; Talia, M.; Balbinot, A.; Febbo, F.; D’Antonio, D. Multidrug-Resistant Enterococcus raffinosus From A Decubitus Ulcer: A Case Report. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2008, 7, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoe, J.A.T.; Witherden, I.R.; Settle, C. Vertebral Osteomyelitis Caused by Enterococcus raffinosus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1678–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyaldenhoven, B.S.; Schlieper, G.; Lütticken, R.; Reinert, R.R. Enterococcus raffinosus infection in an immunosuppressed patient: Case report and review of the literature. J. Infect. 2005, 51, e121–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-J.; Yang, K.-J.; Sun, C.-C.; Yeung, L. Traumatic endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus raffinosus and Enterobacter gergoviae. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalec, M.; Kedzierska, J.; Gajda, A.; Sadowy, E.; Wegrzyn, J.; Naser, S.; Skotnicki, A.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hryniewicz, W. Hospital outbreak of vancomycin-resistant enterococci caused by a single clone of Enterococcus raffinosus and several clones of Enterococcus faecium. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferchichi, M.; Sebei, K.; Boukerb, A.M.; Karray-Bouraoui, N.; Chevalier, S.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Connil, N.; Zommiti, M. Enterococcus spp.: Is It a Bad Choice for a Good Use—A Conundrum to Solve? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zommiti, M.; Chevalier, S.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Connil, N. Special Issue “Enterococci for Probiotic Use: Safety and Risk”: Editorial. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).