Antitumor Efficacy of EGFR-Targeted Recombinant Immunotoxin in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Flow Cytometry Apoptosis Assay
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.7. In Vivo Xenograft Tumor Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
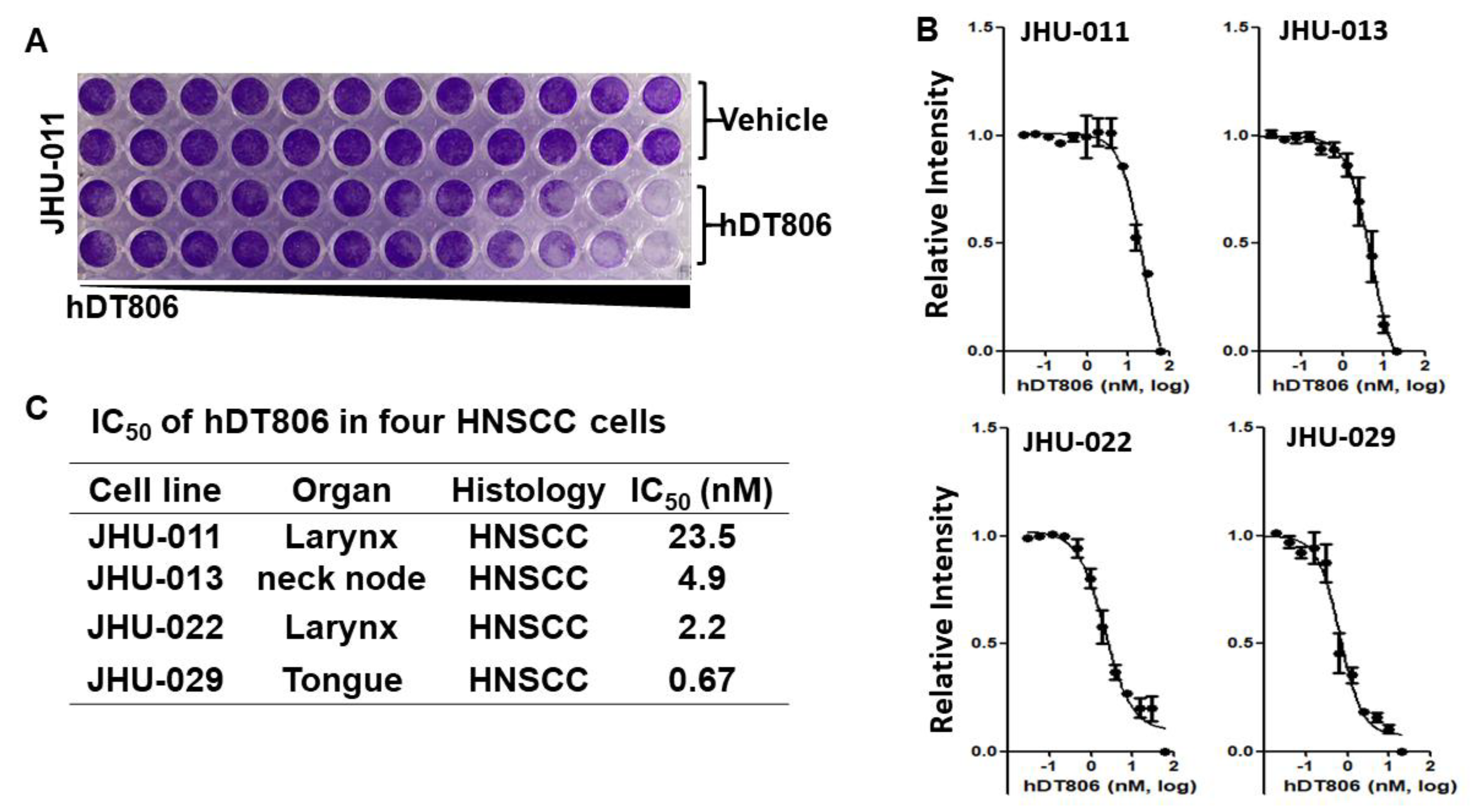
3.1. hDT806 Renders Potent Inhibition in Cell Viability and Proliferation of Human HNSCC Cell Lines
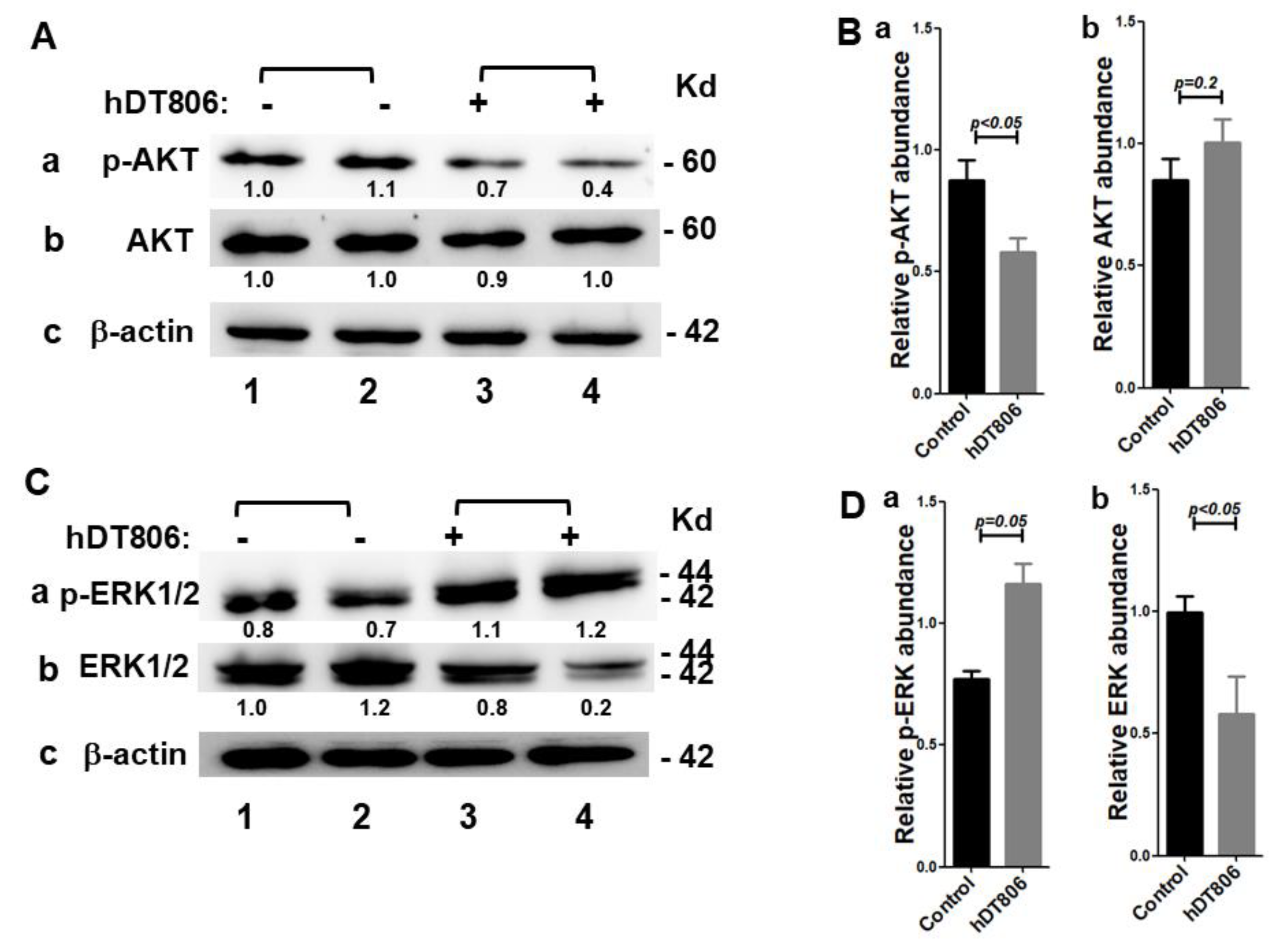
3.2. hDT806 Decreases EGFR Protein Levels and Disrupts Its Downstream Effectors in HNSCC Cells
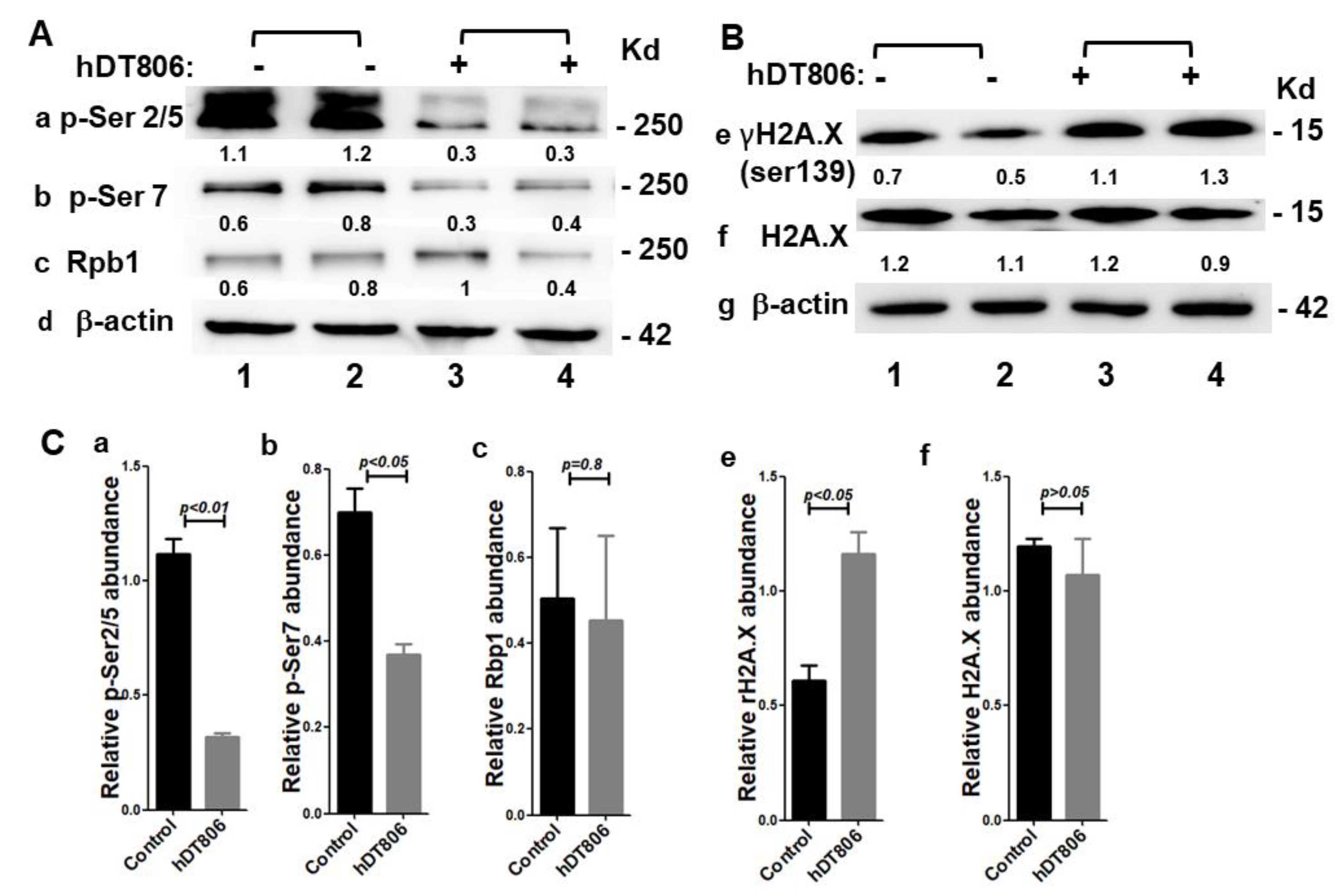
3.3. hDT806 Affects Transcription by Inhibiting RNA Polymerase II Phosphorylation in HNSCC Cells
3.4. hDT806 Induces DNA Damage Responses in HNSCC Cells
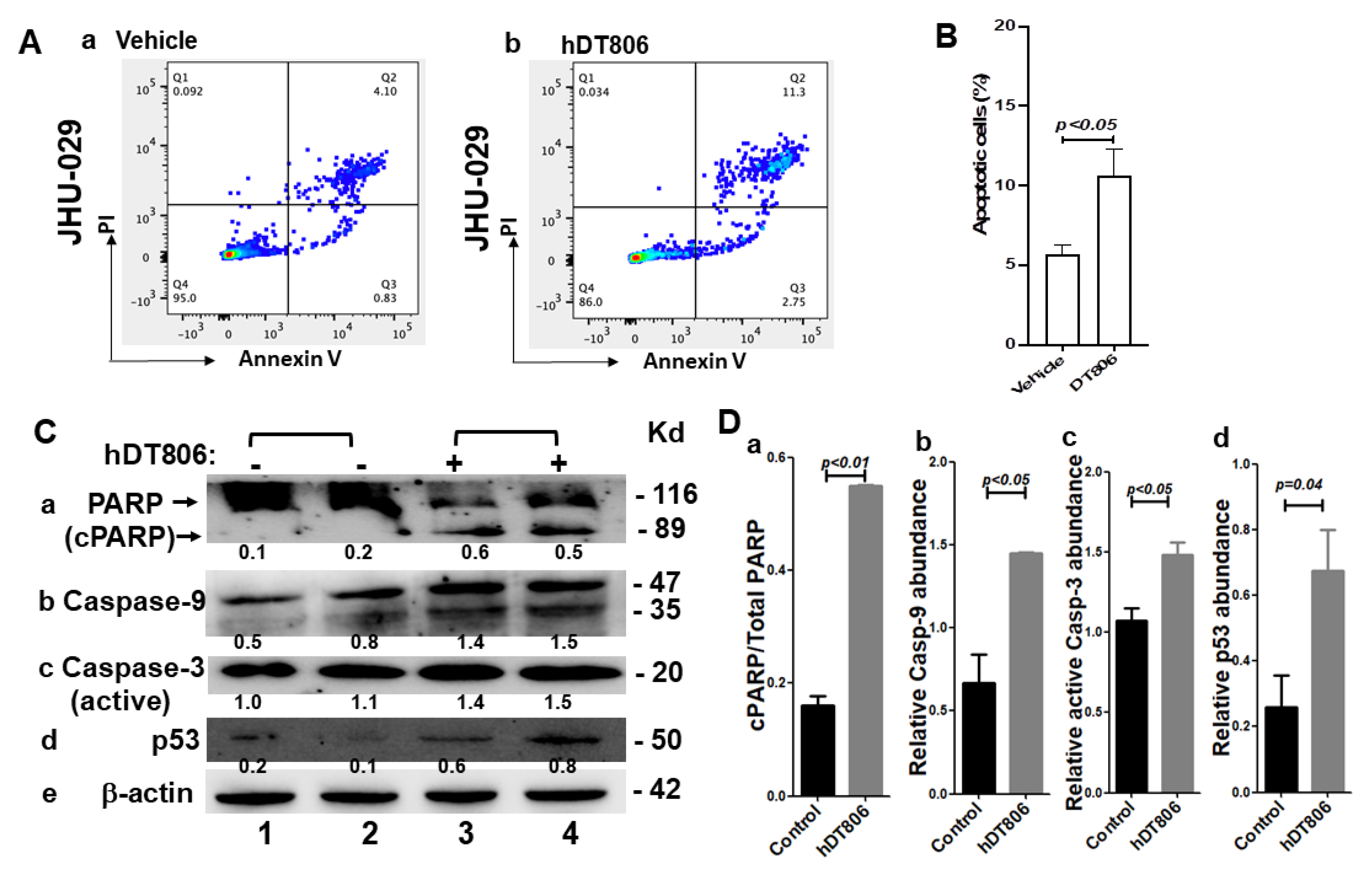
3.5. hDT806 Activates Apoptosis Pathways and Induces Apoptosis in HNSCC Cells
3.6. In Vivo hDT806 Administration Inhibits the Growth of JHU-029 Tumors in a Mouse Model Involving Apoptosis Induction and Growth Inhibition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourad, M.; Jetmore, T.; Jategaonkar, A.A.; Moubayed, S.; Moshier, E.; Urken, M.L. Epidemiological Trends of Head and Neck Cancer in the United States: A SEER Population Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 2562–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, K.; Eid, R.; Haddad, F.G.; Khalife-Saleh, N.; Kourie, H.R. New developments in the management of head and neck cancer—Impact of pembrolizumab. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, S.; Su, L.; Tighiouart, M.; Saba, N.; Zhang, H.; Shin, D.M.; Chen, Z. Distinctive E-cadherin and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in metastatic and nonmetastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Predictive and prognostic correlation. Cancer 2008, 113, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin Grandis, J.; Melhem, M.F.; Gooding, W.E.; Day, R.; Holst, V.A.; Wagener, M.M.; Drenning, S.D.; Tweardy, D.J. Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byeon, H.K.; Ku, M.; Yang, J. Beyond EGFR inhibition: Multilateral combat strategies to stop the progression of head and neck cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duvic, M.; Kuzel, T.M.; Olsen, E.A.; Martin, A.G.; Foss, F.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Heald, P.W.; Bacha, P.; Nichols, J.; Liepa, A. Quality-of-life improvements in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma patients treated with denileukin diftitox (ONTAK). Clin. Lymphoma 2002, 2, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Wilson, W.H.; White, J.D.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Giardina, S.; Waldmann, T.A.; Pastan, I. Phase I trial of recombinant immunotoxin anti-Tac(Fv)-PE38 (LMB-2) in patients with hematologic malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 1622–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, E.; Duvic, M.; Frankel, A.; Kim, Y.; Martin, A.; Vonderheid, E.; Jegasothy, B.; Wood, G.; Gordon, M.; Heald, P.; et al. Pivotal phase III trial of two dose levels of denileukin diftitox for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Tagraxofusp: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Liu, H.; Kim, Y.; Karras, N.; Pawlowska, A.; Toomey, D.; Kyono, W.; Gaynon, P.; Rosenthal, J.; Stein, A. First pediatric experience of SL-401, a CD123-targeted therapy, in patients with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: Report of three cases. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamimura, K.; Yokoo, T.; Abe, H.; Sakai, N.; Nagoya, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Miura, H.; Sakamaki, A.; Kamimura, H.; et al. Effect of Diphtheria Toxin-Based Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amit, D.; Matouk, I.J.; Lavon, I.; Birman, T.; Galula, J.; Abu-Lail, R.; Schneider, T.; Siegal, T.; Hochberg, A.; Fellig, Y. Transcriptional targeting of glioblastoma by diphtheria toxin-A driven by both H19 and IGF2-P4 promoters. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2012, 5, 124–135. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Lin, S.; Gu, X.; Pomper, M.G.; Wang, P.C.; Shan, L. A bivalent recombinant immunotoxin with high potency against tumors with EGFR and EGFRvIII expression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1764–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohseni, Z.; Sedighian, H.; Halabian, R.; Amani, J.; Behzadi, E.; Imani Fooladi, A.A. Potent in vitro antitumor activity of B-subunit of Shiga toxin conjugated to the diphtheria toxin against breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 899, 174057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yu, X.; Huang, S.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. The therapeutic potential of attenuated diphtheria toxin delivered by an adenovirus vector with survivin promoter on human lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2021, 22, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.K.; Burgess, A.W.; Clayton, A.H.; Scott, A.M. Targeting of a conformationally exposed, tumor-specific epitope of EGFR as a strategy for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2924–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrett, T.P.; Burgess, A.W.; Gan, H.K.; Luwor, R.B.; Cartwright, G.; Walker, F.; Orchard, S.G.; Clayton, A.H.A.; Nice, E.C.; Rothacker, J. Antibodies specifically targeting a locally misfolded region of tumor associated EGFR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5082–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Song, X.; Dong, Y.; Cai, H.; Walters, E.; Zhang, R.; Pang, X.; Xie, T.; Guo, Y.; Sridhar, R.; et al. Vitamin E succinate induces ceramide-mediated apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Xie, T.; Korotcov, A.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, X.; Shan, L.; Ji, H.; Sridhar, R.; Wang, P.; Califano, J.; et al. Salvianolic acid B inhibits growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo via cyclooxygenase-2 and apoptotic pathways. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2200–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, G.; Zhu, A.; Gu, X. Mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition-induced modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2021, 43, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feoktistova, M.; Geserick, P.; Leverkus, M. Crystal Violet Assay for Determining Viability of Cultured Cells. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 2016, pdb.prot087379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Guan, X.; Gu, X.; Xie, G. Probe-free allele-specific copy number detection and analysis of tumors. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 497, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, A.; Gu, X.; Xie, G. Inhibition of MEK suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth through independent MYC and BIM regulation. Cell Oncol. 2019, 42, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari, P.M.; Wheeler, D.L.; Grandis, J.R. Molecular target approaches in head and neck cancer: Epidermal growth factor receptor and beyond. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 19, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.J.; Johnson, D.E.; Grandis, J.R. EGFR-targeted therapies in the post-genomic era. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, H.L.; Poon, P.H.Y.; Su, Y.X.; Chan, J.Y.K.; Lo, K.W.; Yeung, C.K.; Liu, Y.; Wong, E.; Li, H.; Lau, C.W.; et al. Erlotinib sensitivity of MAPK1p.D321N mutation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. NPJ Genom. Med. 2020, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Allen, E.M.; Lui, V.W.; Egloff, A.M.; Goetz, E.M.; Li, H.; Johnson, J.T.; Duvvuri, U.; Bauman, J.E.; Stransky, N.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Genomic Correlate of Exceptional Erlotinib Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antignani, A.; Ho, E.C.H.; Bilotta, M.T.; Qiu, R.; Sarnvosky, R.; FitzGerald, D.J. Targeting Receptors on Cancer Cells with Protein Toxins. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateyak, M.K.; Kinzy, T.G. ADP-ribosylation of translation elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin in yeast inhibits translation and cell separation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 24647–24655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsin, J.P.; Manley, J.L. The RNA polymerase II CTD coordinates transcription and RNA processing. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2119–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.C.; Phatnani, H.P.; Haystead, T.A.; MacDonald, J.A.; Alam, S.M.; Greenleaf, A.L. C-terminal repeat domain kinase I phosphorylates Ser2 and Ser5 of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain repeats. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24957–24964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Dijk, L.K.; Boerman, O.C.; Kaanders, J.H.; Bussink, J. PET Imaging in Head and Neck Cancer Patients to Monitor Treatment Response: A Future Role for EGFR-Targeted Imaging. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3602–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toulany, M.; Kasten-Pisula, U.; Brammer, I.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Dittmann, K.; Baumann, M.; Dikomey, E.; Rodemann, H.P. Blockage of epidermal growth factor receptor-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT signaling increases radiosensitivity of K-RAS mutated human tumor cells in vitro by affecting DNA repair. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4119–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, K.; Almasan, A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation: A marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 920, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S.; Debatin, K.M. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4798–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, D.R.; Llambi, F. Cell Death Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a006080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, B.J.; Kelly, G.L.; Janic, A.; Herold, M.J.; Strasser, A. How does p53 induce apoptosis and how does this relate to p53-mediated tumour suppression? Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.C.; Gu, X.; Shan, L. Recombinant Immunotoxin Therapy of Glioblastoma: Smart Design, Key Findings, and Specific Challenges. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7929286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, C.T.; Wikstrand, C.J.; Bigner, D.D. EGFRvIII as a promising target for antibody-based brain tumor therapy. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2000, 17, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.W. EGFR-targeted therapy in malignant glioma: Novel aspects and mechanisms of drug resistance. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 3, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Wen, W.; Pendleton, K.P.; Lui, V.W.; Egloff, A.M.; Grandis, J.R. MAPK1E322K mutation increases head and neck squamous cell carcinoma sensitivity to erlotinib through enhanced secretion of amphiregulin. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 23300–23311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajput, M.; Singh, R.; Singh, N.; Singh, R.P. EGFR-mediated Rad51 expression potentiates intrinsic resistance in prostate cancer via EMT and DNA repair pathways. Life Sci. 2021, 286, 120031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Tallman, M.S.; Robak, T.; Coutre, S.; Wilson, W.H.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; FitzGerald, D.J.; Lechleider, R.; Pastan, I. Phase I trial of anti-CD22 recombinant immunotoxin moxetumomab pasudotox (CAT-8015 or HA22) in patients with hairy cell leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, M.; Beers, R.; Xiang, L.; Nagata, S.; Wang, Q.C.; Pastan, I. An immunotoxin with greatly reduced immunogenicity by identification and removal of B cell epitopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11311–11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cizeau, J.; Grenkow, D.M.; Brown, J.G.; Entwistle, J.; MacDonald, G.C. Engineering and biological characterization of VB6–845, an anti-EpCAM immunotoxin containing a T-cell epitope-depleted variant of the plant toxin bouganin. J. Immunother. 2009, 32, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollevoet, K.; Mason-Osann, E.; Liu, X.F.; Imhof-Jung, S.; Niederfellner, G.; Pastan, I. In vitro and in vivo activity of the low-immunogenic antimesothelin immunotoxin RG7787 in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2040–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harding, F.A.; Liu, A.D.; Stickler, M.; Razo, O.J.; Chin, R.; Faravashi, N.; Viola, W.; Graycar, T.; Yeung, V.P.; Aehle, W.; et al. A beta-lactamase with reduced immunogenicity for the targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics using antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazor, R.; King, E.M.; Onda, M.; Cuburu, N.; Addissie, S.; Crown, D.; Liu, X.-F.; Kishimoto, T.K.; Pastan, I. Tolerogenic nanoparticles restore the antitumor activity of recombinant immunotoxins by mitigating immunogenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E733–E742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Javan, B.; Shahbazi, M. Hypoxia-inducible tumour-specific promoters as a dual-targeting transcriptional regulation system for cancer gene therapy. Ecancermedicalscience 2017, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Tang, H.; Guo, W.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wan, X.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Use of the XRCC2 promoter for in vivo cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, G.; Shan, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, T.-C.; Gu, X. Antitumor Efficacy of EGFR-Targeted Recombinant Immunotoxin in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biology 2022, 11, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040486
Xie G, Shan L, Liu Y, Wu T-C, Gu X. Antitumor Efficacy of EGFR-Targeted Recombinant Immunotoxin in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biology. 2022; 11(4):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040486
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Guiqin, Liang Shan, Yuanyi Liu, Tzyy-Choou Wu, and Xinbin Gu. 2022. "Antitumor Efficacy of EGFR-Targeted Recombinant Immunotoxin in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Biology 11, no. 4: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040486
APA StyleXie, G., Shan, L., Liu, Y., Wu, T.-C., & Gu, X. (2022). Antitumor Efficacy of EGFR-Targeted Recombinant Immunotoxin in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biology, 11(4), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040486





