Post-Irradiation Thymic Regeneration in B6C3F1 Mice Is Age Dependent and Modulated by Activation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Irradiation of Mice and Sample Preparation
2.2. Preparation of Thymocytes for Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Histological Analysis of Thymus and Femur
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
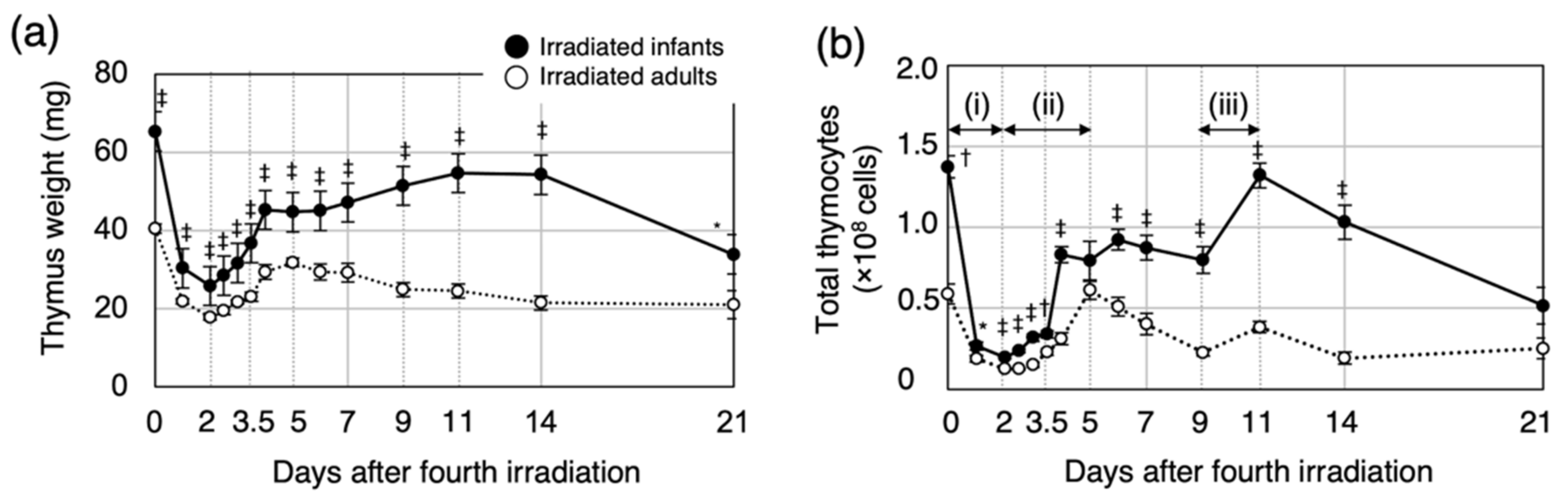
3.1. Post-Irradiation Cell Dynamics during Thymic Regeneration Differ Depending on Age at Exposure
3.2. Proliferation of Immature Thymocytes Plays a Key Role in Thymic Regeneration in Mice Irradiated during Infancy
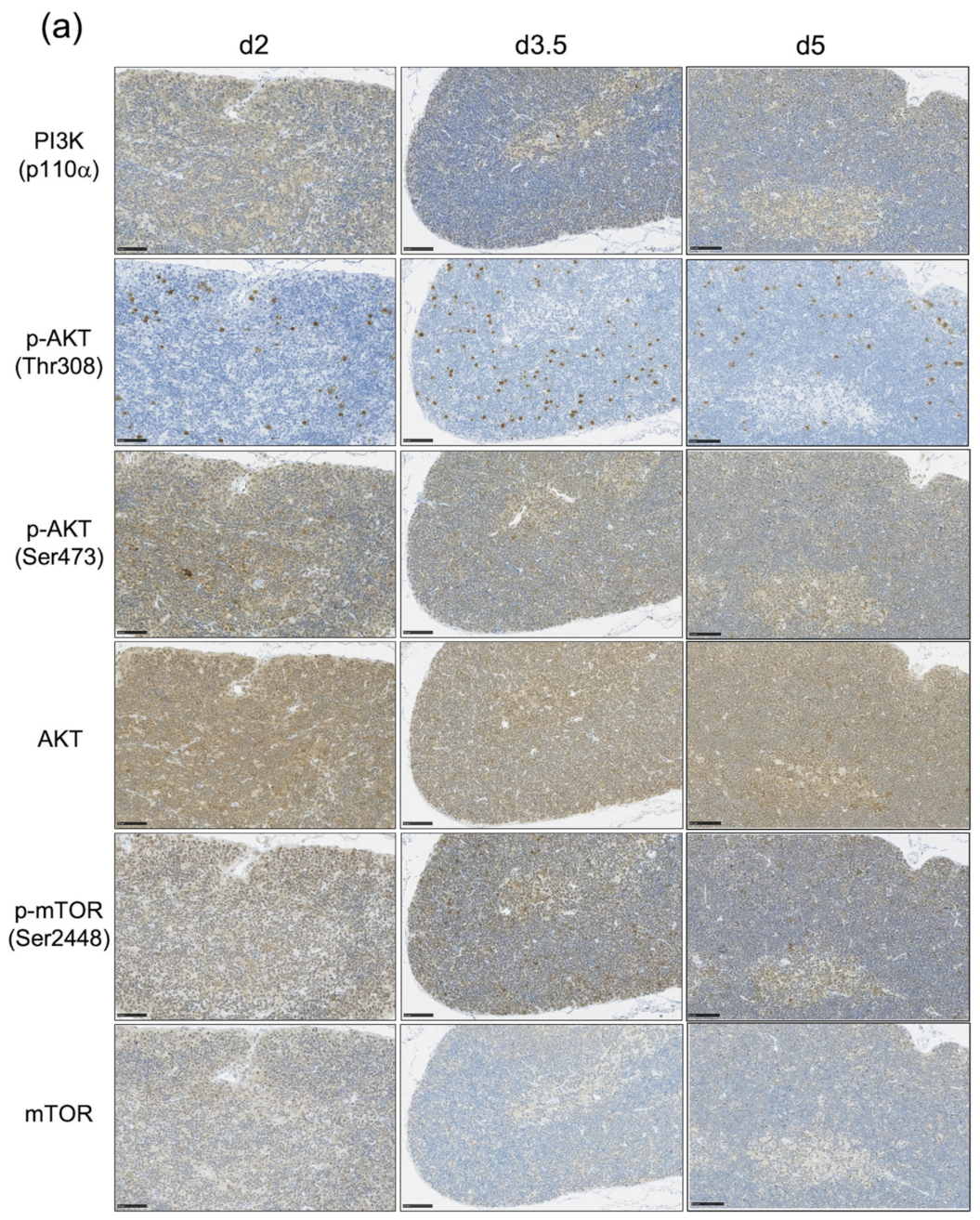
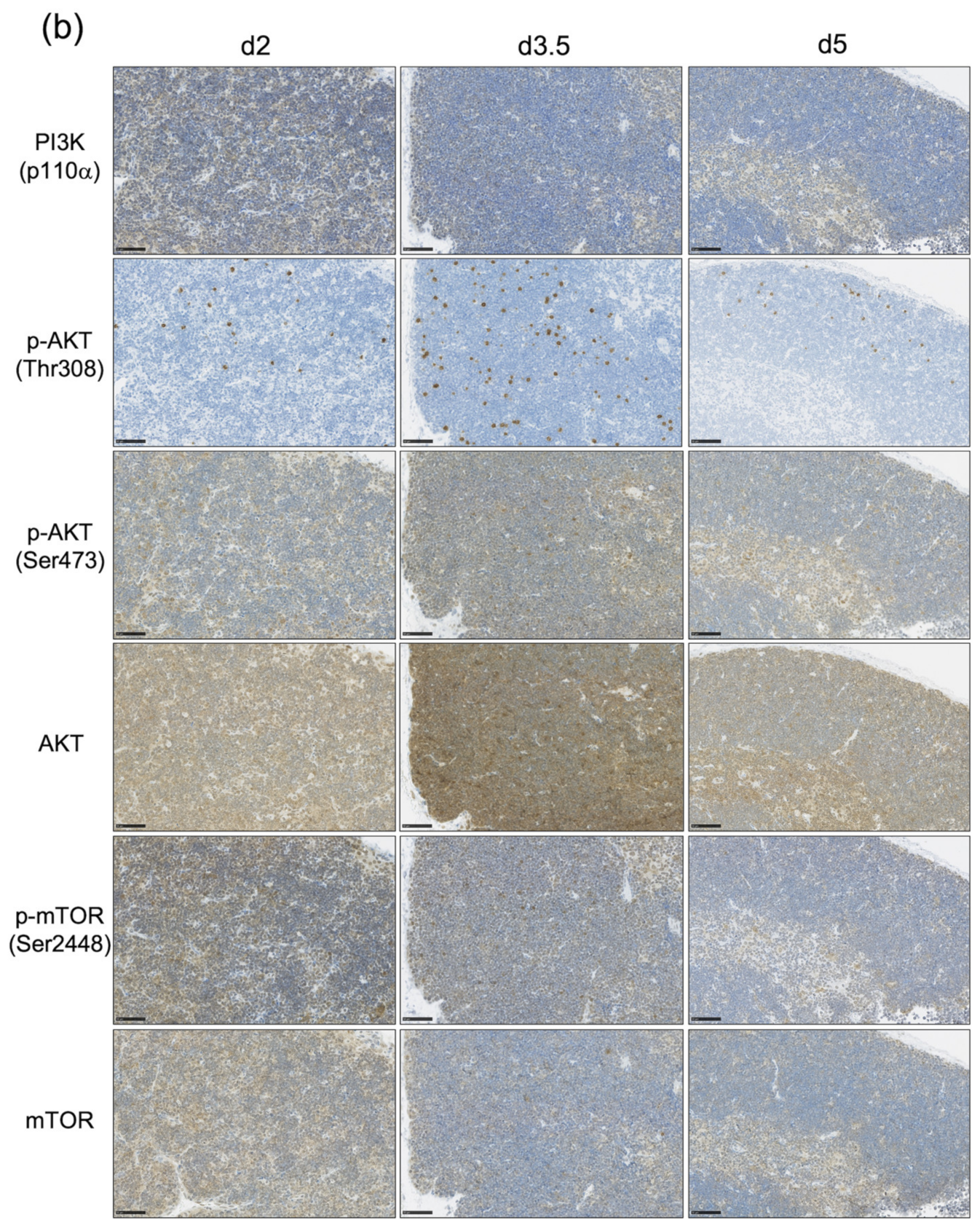
3.3. The Impact of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway on Cell Proliferation and Cell Survival Varies by Age at Exposure and with the Phase of Post-Exposure Thymic Regeneration
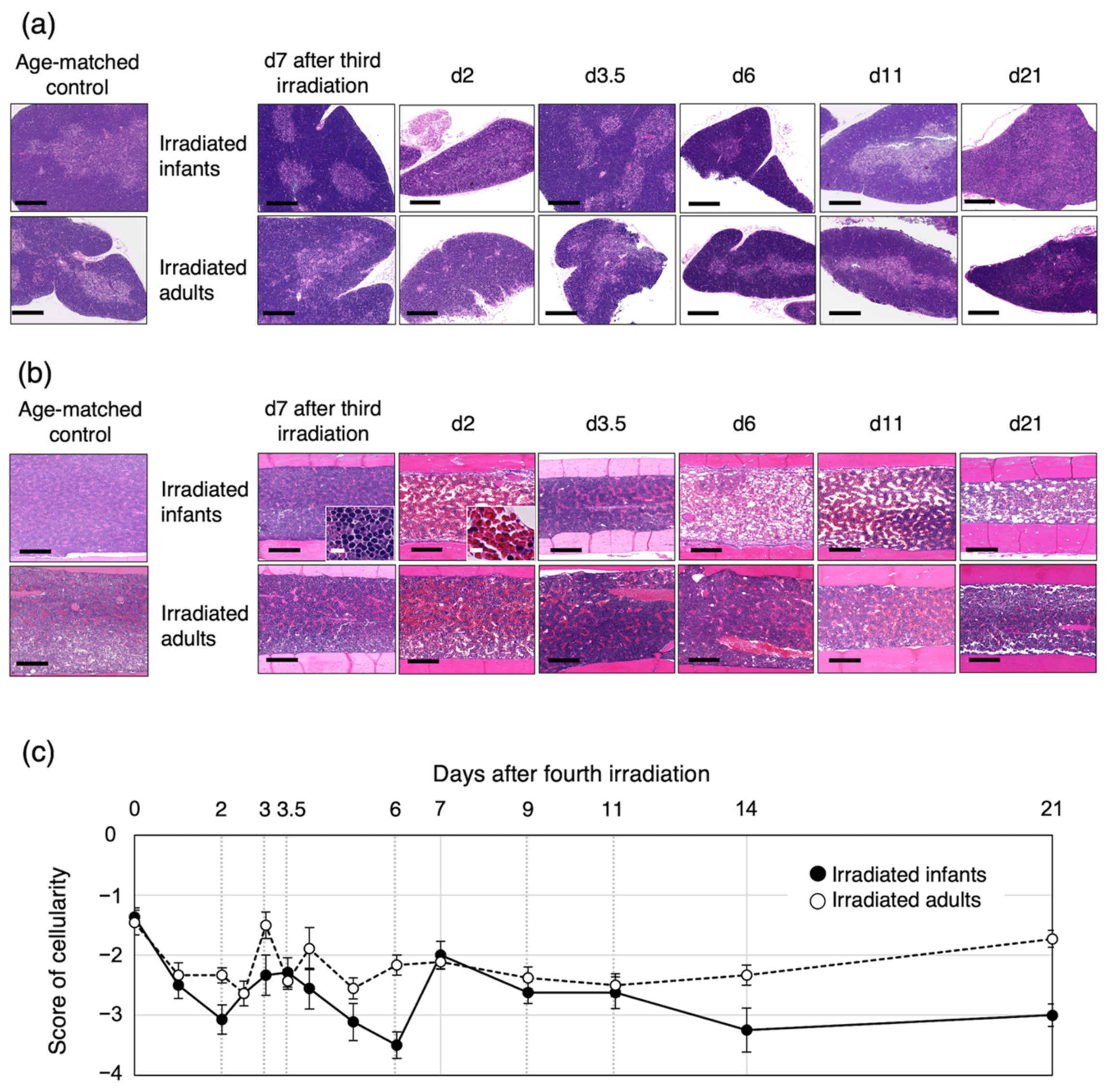
3.4. Bone-Marrow Injury after the Fourth Irradiation Is More Severe in Irradiated Infants Than in Irradiated Adults
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brody, A.S.; Frush, D.P.; Huda, W.; Brent, R.L. American Academy of Pediatrics Section on, R. Radiation risk to children from computed tomography. Pediatrics 2007, 120, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richardson, D.; Sugiyama, H.; Nishi, N.; Sakata, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Grant, E.J.; Soda, M.; Hsu, W.L.; Suyama, A.; Kodama, K.; et al. Ionizing radiation and leukemia mortality among Japanese Atomic Bomb Survivors, 1950–2000. Radiat. Res. 2009, 172, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.L.; Preston, D.L.; Soda, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Funamoto, S.; Kodama, K.; Kimura, A.; Kamada, N.; Dohy, H.; Tomonaga, M.; et al. The incidence of leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma among atomic bomb survivors: 1950–2001. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyoshi-Imamura, T.; Kakinuma, S.; Kaminishi, M.; Okamoto, M.; Takabatake, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Imaoka, T.; Nishimura, M.; Murakami-Murofushi, K.; Shimada, Y. Unique Characteristics of Radiation-Induced Apoptosis in the Postnatally Developing Small Intestine and Colon of Mice. Radiat. Res. 2010, 181, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Sawa, Y.; Blyth, B.J.; Tsuruoka, C.; Nogawa, H.; Shimada, Y.; Kakinuma, S. Radiation Exposure Enhances Hepatocyte Proliferation in Neonatal Mice but not in Adult Mice. Radiat. Res. 2017, 188, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyoshi, K.; Takabatake, T.; Shinagawa, M.; Kadono, K.; Daino, K.; Imaoka, T.; Kakinuma, S.; Nishimura, M.; Shimada, Y. Age Dependence of Hematopoietic Progenitor Survival and Chemokine Family Gene Induction after Gamma Irradiation in Bone Marrow Tissue in C3H/He Mice. Radiat. Res. 2014, 181, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.S.; Brown, M.B. A quantitative dose-response study of lymphoid-tumor development in irradiated C 57 black mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1952, 13, 185–208. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, Y.; Nishimura, M.; Kakinuma, S.; Okumoto, M.; Shiroishi, T.; Clifton, K.H.; Wakana, S. Radiation-associated loss of heterozygosity at the Znfn1a1 (Ikaros) locus on chromosome 11 in murine thymic lymphomas. Radiat. Res. 2000, 154, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma, S.; Nishimura, M.; Sasanuma, S.; Mita, K.; Suzuki, G.; Katsura, Y.; Sado, T.; Shimada, Y. Spectrum of Znfn1a1 (Ikaros) inactivation and its association with loss of heterozygosity in radiogenic T-cell lymphomas in susceptible B6C3F1 mice. Radiat. Res. 2002, 157, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Takabatake, T.; Kakinuma, S.; Amasaki, Y.; Nishimura, M.; Imaoka, T.; Yamauchi, K.; Shang, Y.; Miyoshi-Imamura, T.; Nogawa, H.; et al. Complicated biallelic inactivation of Pten in radiation-induced mouse thymic lymphomas. Mutat. Res. 2010, 686, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyth, B.J.; Kakinuma, S.; Sunaoshi, M.; Amasaki, Y.; Hirano-Sakairi, S.; Ogawa, K.; Shirakami, A.; Shang, Y.; Tsuruoka, C.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Genetic Analysis of T Cell Lymphomas in Carbon Ion-Irradiated Mice Reveals Frequent Interstitial Chromosome Deletions: Implications for Second Cancer Induction in Normal Tissues during Carbon Ion Radiotherapy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsuyama, M.; Hirokawa, K. Radiation-induced-thymic lymphoma occurs in young, but not in old mice. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 74, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunaoshi, M.; Amasaki, Y.; Hirano-Sakairi, S.; Blyth, B.J.; Morioka, T.; Kaminishi, M.; Shang, Y.; Nishimura, M.; Shimada, Y.; Tachibana, A.; et al. The effect of age at exposure on the inactivating mechanisms and relative contributions of key tumor suppressor genes in radiation-induced mouse T-cell lymphomas. Mutat. Res. 2015, 779, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, S.; Winandy, S. Ikaros Regulates Notch Target Gene Expression in Developing Thymocytes. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 6265–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemarié, M.; Bottardi, S.; Mavoungou, L.; Pak, H.; Milot, E. IKAROS is required for the measured response of NOTCH target genes upon external NOTCH signaling. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntilla, M.M.; Koretzky, G.A. Critical roles of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in T cell development. Immunol. Lett. 2008, 116, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, L.; Chiang, L.; Kang, C.; Winoto, A. The role of the PI3K-AKT kinase pathway in T-cell development beyond the β checkpoint. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 3200–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boniver, J.; Declève, A.; Lieberman, M.; Honsik, C.; Travis, M.; Kaplan, H.S. Marrow-thymus interactions during radiation leukemogenesis in C57BL/Ka mice. Cancer Res. 1981, 42, 390–392. [Google Scholar]
- Hays, E.F.; Bristol, G.C.; McDougall, S.; Klots, J.L.; Kronenberg, M. Development of lymphoma in the thymus of AKR mice treated with the lymphomagenic virus SL 3-3. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 4225–4230. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, H.S.; Brown, M.B.; Paull, J. Influence of postirradiation thymectomy and of thymic implants on lymphoid tumor incidence in C57BL mice. Cancer Res. 1953, 13, 677–680. [Google Scholar]
- Muto, M.; Kubo, E.; Sado, T. Development of prelymphoma cells committed to thymic lymphomas during radiation-induced thymic lymphomagenesis in B10 mice. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 3469–3472. [Google Scholar]
- Morioka, T.; Blyth, B.J.; Imaoka, T.; Nishimura, M.; Takeshita, H.; Shimomura, T.; Ohtake, J.; Ishida, A.; Schofield, P.; Gro-sche, B.; et al. Establishing the Japan-Store house of animal radiobiology experiments (J-SHARE), a large-scale necropsy and histopathology archive providing international access to important radiobiology data. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Cai, H.; Li, Q.; Du, Z.; Tan, W.S. Effects of telomerase activity and apoptosis on ex vivo expansion of cord blood CD34+ cells. Cell Proliferat. 2013, 46, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Lesche, R.; Li, D.M.; Liliental, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Gavrilova, N.; Mueller, B.; Liu, X.; Wu, H. PTEN modulates cell cycle progression and cell survival by regulating phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5,-trisphosphate and Akt/protein kinase B sig-naling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6199–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kandel, E.S.; Skeen, J.; Majewski, N.; Cristofano, D.A.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Feliciano, C.S.; Gartel, A.; Hay, N. Activation of Akt/Protein Kinase B Overcomes a G2/M Cell Cycle Checkpoint Induced by DNA Damage. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 7831–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porritt, H.E.; Gordon, K.; Petrie, H.T. Kinetics of steady-state differentiation and mapping of intrathymic-signaling envi-ronments by stem cell transplantation in nonirradiated mice. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min, H.; Montecino-Rodriguez, E.; Dorshkind, K. Reduction in the developmental potential of intrathymic T cell progenitors with age. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.G.; Parsons, M.; Bonnard, M.; Chan, V.S.; Yeh, W.C.; Woodgett, J.R.; Ohashi, P.S. Protein kinase B regulates T lymphocyte survival, nuclear factor kappaB activation, and Bcl-X(L) levels in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juntilla, M.M.; Wofford, J.A.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Rathmell, J.C.; Koretzky, G.A. Akt1 and Akt2 are required for alphabeta thymocyte survival and differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12105–12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, M.; Han, Z.C. Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/AKT in radiation responses. Histol. Histopathol. 2004, 19, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Ding, Z.; Hawke, D.; Xing, D.; Jiang, B.; Mills, G.B.; Lu, Z. AKT-dependent phosphorylation of Niban regulates nucleophosmin- and MDM2-mediated p53 stability and cell apoptosis. Embo Rep. 2012, 13, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z. Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression by Growth Factor-Induced Cell Signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rössig, L.; Jadidi, A.S.; Urbich, C.; Badorff, C.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Akt-dependent phosphorylation of p21(Cip1) regulates PCNA binding and proliferation of endothelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 5644–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viglietto, G.; Motti, M.L.; Bruni, P.; Melillo, R.M.; D’Alessio, A.; Califano, D.; Vinci, F.; Chiappetta, G.; Tsichlis, P.; Bellacosa, A.; et al. Cytoplasmic relocalization and inhibition of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 by PKB/Akt-mediated phosphorylation in breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, I.; Yakes, M.F.; Rojo, F.; Shin, N.; Bakin, A.V.; Baselga, J.; Arteaga, C.L. PKB/Akt mediates cell-cycle progression by phosphorylation of p27(Kip1) at threonine 157 and modulation of its cellular localization. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zubovitz, J.; Petrocelli, T.; Kotchetkov, R.; Connor, M.K.; Han, K.; Lee, J.; Ciarallo, S.; Catzavelos, C.; Beniston, R.; et al. PKB/Akt phosphorylates p27, impairs nuclear import of p27 and opposes p27-mediated G1 arrest. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, J.A.; Cheng, M.; Roussel, M.F.; Sherr, C.J. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis and subcel-lular localization. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3499–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinsella, S.; Dudakov, J.A. When the Damage Is Done: Injury and Repair in Thymus Function. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, T.; Nishikawa, S.; Ohno, N.; Akiyama, N.; Tamakoshi, M.; Yoshida, H.; Nishikawa, S. Expression and function of the interleukin 7 receptor in murine lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 9125–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, L.; Nolla, H.; Suzuki, A.; Mak, T.W.; Winoto, A. Normal development is an integral part of tumorigenesis in T cell-specific PTEN-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kops, G.; Weaver, B.A.A.; Cleveland, D.W. On the road to cancer: Aneuploidy and the mitotic checkpoint. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzot, D. Complex and segmental uniparental disomy (UPD): Review and lessons from rare chromosomal complements. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 38, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LaFave, M.C.; Sekelsky, J. Mitotic Recombination: Why? When? How? Where? PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winandy, S.; Wu, P.; Georgopoulos, K. A dominant mutation in the Ikaros gene leads to rapid development of leukemia and lymphoma. Cell 1995, 83, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.H.; Nichogiannopoulou, A.; Wu, L.; Sun, L.; Sharpe, A.H.; Bigby, M.; Georgopoulos, K. Selective defects in the development of the fetal and adult lymphoid system in mice with an Ikaros null mutation. Immunity 1996, 5, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, M.; Kakinuma, S.; Yamamoto, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Suzuki, G.; Sado, T.; Shimada, Y. Elevated interleukin 9 receptor expression and response to interleukins 9 and 7 in thymocytes during radiation induced T cell lymphomagenesis in B6C3F1 mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 198, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granadier, D.; Iovino, L.; Kinsella, S.; Dudakov, J.A. Dynamics of thymus function and T cell receptor repertoire breadth in health and disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, D.; Quang, C.; Ghysdael, J. Microenvironmental cues for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia development. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 271, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu-Raychaudhuri, S.; Abria, C.; Raychaudhuri, S.P. IL-9, a local growth factor for synovial T cells in inflammatory arthritis. Cytokine 2016, 79, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Kakinuma, S.; Amasaki, Y.; Nishimura, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shimada, Y. Aberrant activation of interleukin-9 receptor and downstream Stat3/5 in primary T-cell lymphomas in vivo in susceptible B6 and resistant C3H mice. In Vivo 2008, 22, 713–720. [Google Scholar]
- Gentil Dit Maurin, A.; Lemercier, C.; Collin-Faure, V.; Marche, P.N.; Jouvin-Marche, E.; Candeias, S.M. Developmental regulation of p53-dependent radiation-induced thymocyte apoptosis in mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 179, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dudakov, J.A.; Hanash, A.M.; Jenq, R.R.; Young, L.F.; Ghosh, A.; Singer, N.V.; West, M.L.; Smith, O.M.; Holland, A.M.; Tsai, J.J.; et al. Interleukin-22 drives endogenous thymic regeneration in mice. Science 2012, 336, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, H.; Fang, M.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Yu, J. Interleukin-22 secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts regulates the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer cells via the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 4077–4088. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, J.; Chunming, Z.; Binbin, G.; Na, S.; Shengxi, W.; Wei, S. IL-22 promotes the progression of breast cancer through reg-ulating HOXB-AS5. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 103601–103612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayasu, A.; Kakinuma, S.; Nishimura, M.; Shang, Y.; Sunaoshi, M.; Tsuruoka, C.; Ishihara, H.; Shimada, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Kinetics of cytokine mRNA and protein expression by plastic adherent cells in the thymus after split-dose irradiation. Cytokine 2018, 114, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, T.; Deguchi, Y.; Ohshima, D.; Takeda, W.; Ohtsuka, M.; Shichino, S.; Ueha, S.; Yamazaki, S.; Kawauchi, M.; Nakamura, E.; et al. Interleukin-11-expressing fibroblasts have a unique gene signature correlated with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Chen, C.; Deng, X.; Wang, F.; Song, S.; Cai, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Shi, M.; Ke, Q.; et al. IL-11 mediates the Radioresistance of Cervical Cancer Cells via the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4638–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sunaoshi, M.; Blyth, B.J.; Shang, Y.; Tsuruoka, C.; Morioka, T.; Shinagawa, M.; Ogawa, M.; Shimada, Y.; Tachibana, A.; Iizuka, D.; et al. Post-Irradiation Thymic Regeneration in B6C3F1 Mice Is Age Dependent and Modulated by Activation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway. Biology 2022, 11, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030449
Sunaoshi M, Blyth BJ, Shang Y, Tsuruoka C, Morioka T, Shinagawa M, Ogawa M, Shimada Y, Tachibana A, Iizuka D, et al. Post-Irradiation Thymic Regeneration in B6C3F1 Mice Is Age Dependent and Modulated by Activation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway. Biology. 2022; 11(3):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030449
Chicago/Turabian StyleSunaoshi, Masaaki, Benjamin J. Blyth, Yi Shang, Chizuru Tsuruoka, Takamitsu Morioka, Mayumi Shinagawa, Mari Ogawa, Yoshiya Shimada, Akira Tachibana, Daisuke Iizuka, and et al. 2022. "Post-Irradiation Thymic Regeneration in B6C3F1 Mice Is Age Dependent and Modulated by Activation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway" Biology 11, no. 3: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030449
APA StyleSunaoshi, M., Blyth, B. J., Shang, Y., Tsuruoka, C., Morioka, T., Shinagawa, M., Ogawa, M., Shimada, Y., Tachibana, A., Iizuka, D., & Kakinuma, S. (2022). Post-Irradiation Thymic Regeneration in B6C3F1 Mice Is Age Dependent and Modulated by Activation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway. Biology, 11(3), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030449





