Selective Loss of MATR3 in Spinal Interneurons, Upper Motor Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Neurons in a MATR3 S85C Knock-In Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Tissue Preparation
2.3. Immunofluorescence on Cryosections
2.4. Immunofluorescence on Paraffin Sections
2.5. Imaging Spinal Motor Neurons and Interneurons and Quantification
2.6. Hippocampal Neurons with Reduced MATR3 Staining Quantification
2.7. Cortical Neurons with Reduced MATR3 Staining Quantification
2.8. Upper Motor Neuron Quantification
2.9. Quantification of IBA1 and GFAP Staining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
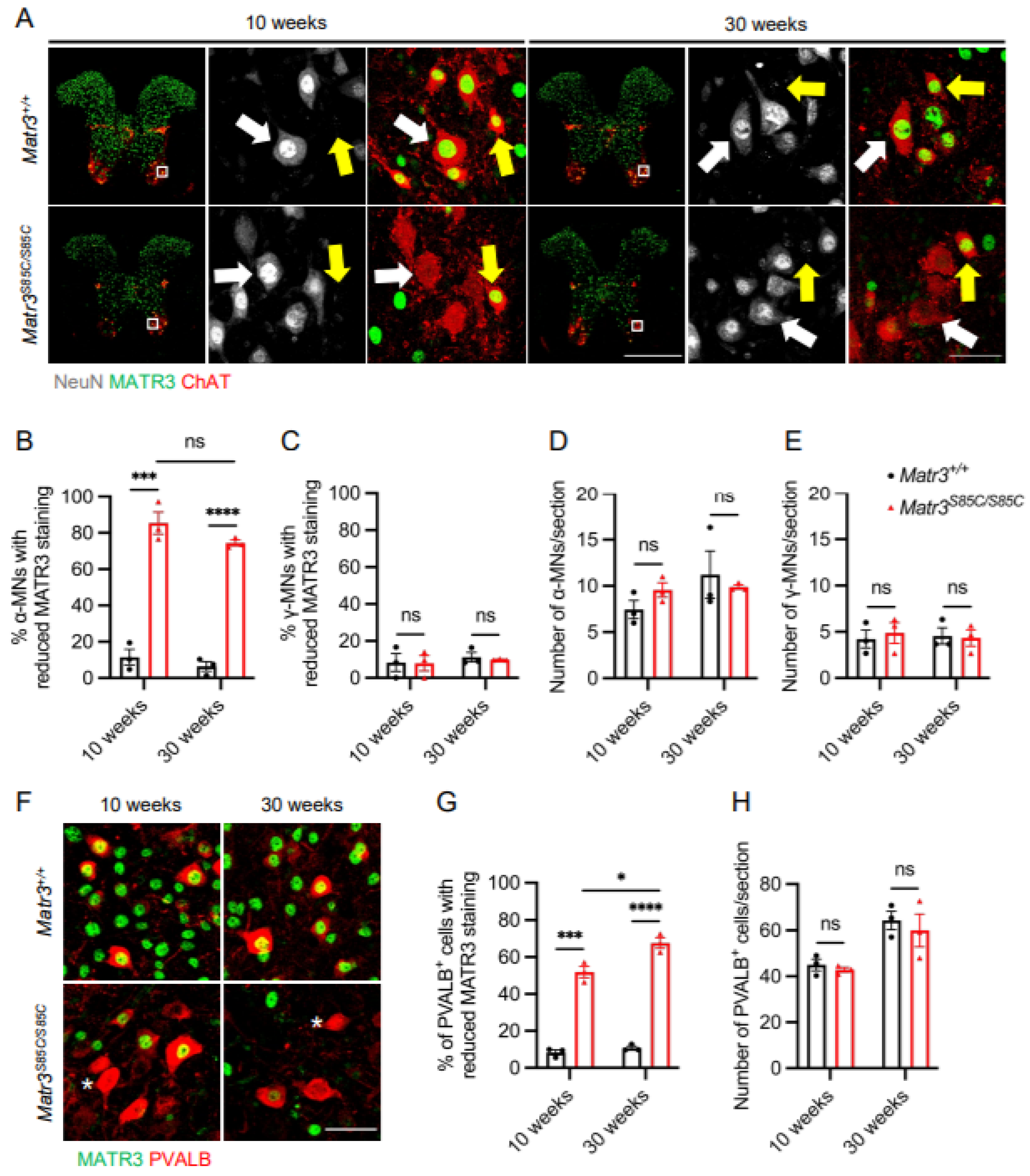
3.1. Selective Loss of MATR3 in α-Motor Neurons and Interneurons in the Spinal Cord of Matr3S85C/S85C Mice
3.2. Selective Loss of MATR3 in the Subsets of Upper Motor Neurons in the Cortex of Matr3S85C/S85C Mice
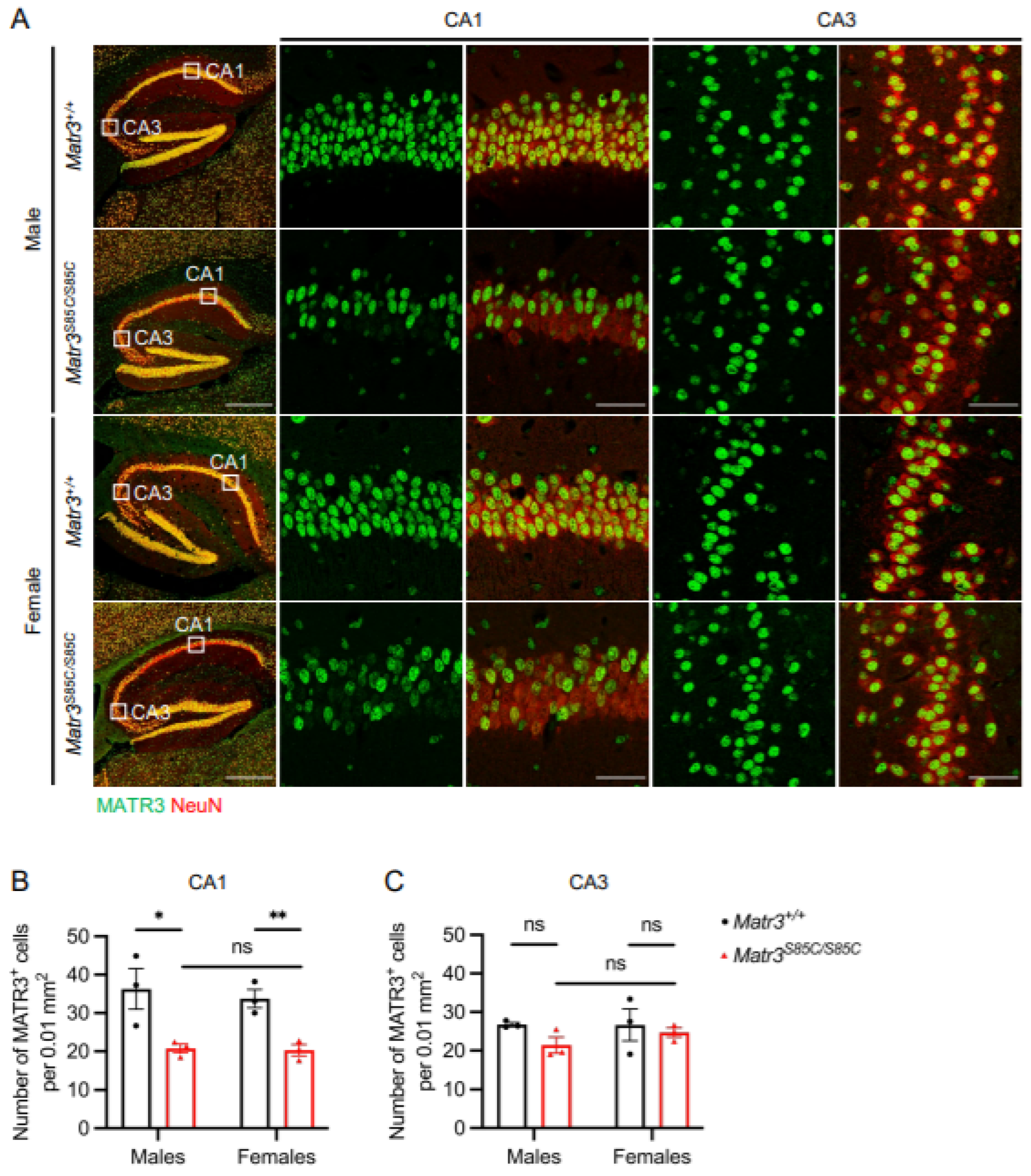
3.3. Selective Loss of MATR3 in the Subsets of Hippocampal Neurons of Matr3S85C/S85C Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowland, L.P.; Shneider, N.A. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi, S.; Stauffer, J.E.; Schulte, D.J.; Ravits, J. Neuropathology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Its Variants. Neurol. Clin. 2015, 33, 855–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stephens, B.; Navarrete, R.; Guiloff, R.J. Ubiquitin Immunoreactivity in Presumed Spinal Interneurones in Motor Neurone Disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2001, 27, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamatina, A.; Yang, J.H.; Brenner-Morton, S.; Bikoff, J.B.; Fang, L.; Kintner, C.R.; Jessell, T.M.; Sweeney, L.B. Differential Loss of Spinal Interneurons in a Mouse Model of ALS. Neuroscience 2020, 450, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabé, R.; Aimond, F.; Gosset, P.; Scamps, F.; Raoul, C. How Degeneration of Cells Surrounding Motoneurons Contributes to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Cells 2020, 9, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, M.; Sampathu, D.M.; Kwong, L.K.; Truax, A.C.; Micsenyi, M.C.; Chou, T.T.; Bruce, J.; Schuck, T.; Grossman, M.; Clark, C.M.; et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Science 2006, 314, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Pattamatta, A.; Zu, T.; Reid, T.; Bardhi, O.; Borchelt, D.R.; Yachnis, A.T.; Ranum, L.P.W. C9orf72 BAC Mouse Model with Motor Deficits and Neurodegenerative Features of ALS/FTD. Neuron 2016, 90, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rei, N.; Rombo, D.M.; Ferreira, M.F.; Baqi, Y.; Müller, C.E.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Sebastião, A.M.; Vaz, S.H. Hippocampal Synaptic Dysfunction in the SOD1G93A Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Reversal by Adenosine A2AR Blockade. Neuropharmacology 2020, 171, 108106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prell, T.; Grosskreutz, J. The Involvement of the Cerebellum in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2013, 14, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgrader, P.; Dey, R.; Berezney, R. Molecular Cloning of Matrin 3. A 125-Kilodalton Protein of the Nuclear Matrix Contains an Extensive Acidic Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9893–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.O.; Pioro, E.P.; Boehringer, A.; Chia, R.; Feit, H.; Renton, A.E.; Pliner, H.A.; Abramzon, Y.; Marangi, G.; Winborn, B.J.; et al. Mutations in the Matrin 3 Gene Cause Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, M.B.; Attig, J.; Bellora, N.; Konig, J.; Hallegger, M.; Kayikci, M.; Eyras, E.; Ule, J.; Smith, C.W. Nuclear Matrix Protein Matrin3 Regulates Alternative Splicing and Forms Overlapping Regulatory Networks with PTB. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, Y.; Oshima, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Reyes, C.J.; Costa Cruz, P.H.; Shibuya, T.; Kawahara, Y. Matrin3 Binds Directly to Intronic Pyrimidine-Rich Sequences and Controls Alternative Splicing. Genes Cells 2017, 22, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kao, C.S.; van Bruggen, R.; Kim, J.R.; Chen, X.X.L.; Chan, C.; Lee, J.; Cho, W.I.; Zhao, M.; Arndt, C.; Maksimovic, K.; et al. Selective Neuronal Degeneration in MATR3 S85C Knock-in Mouse Model of Early-Stage ALS. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalancette-Hebert, M.; Sharma, A.; Lyashchenko, A.K.; Shneider, N.A. Gamma Motor Neurons Survive and Exacerbate Alpha Motor Neuron Degeneration in ALS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8316–E8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Bruggen, R.; Maksimovic, K.; You, J.; Tran, D.D.; Lee, H.J.; Khan, M.; Kao, C.S.; Kim, J.R.; Cho, W.; Chen, X.X.L.; et al. MATR3 F115C Knock-in Mice Do Not Exhibit Motor Defects or Neuropathological Features of ALS. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 568, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allodi, I.; Montañana-Rosell, R.; Selvan, R.; Löw, P.; Kiehn, O. Locomotor Deficits in a Mouse Model of ALS Are Paralleled by Loss of V1-Interneuron Connections onto Fast Motor Neurons. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossaini, M.; Cano, S.C.; van Dis, V.; Haasdijk, E.D.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; Holstege, J.C.; Jaarsma, D. Spinal Inhibitory Interneuron Pathology Follows Motor Neuron Degeneration Independent of Glial Mutant Superoxide Dismutase 1 Expression in SOD1-ALS Mice. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 70, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ince, P.; Stout, N.; Shaw, P.; Slade, J.; Hunziker, W.; Heizmann, C.W.; Baimbridge, K.G. Parvalbumin and Calbindin D-28k in the Human Motor System and in Motor Neuron Disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1993, 19, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B.; Guiloff, R.J.; Navarrete, R.; Newman, P.; Nikhar, N.; Lewis, P. Widespread Loss of Neuronal Populations in the Spinal Ventral Horn in Sporadic Motor Neuron Disease. A Morphometric Study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 244, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyamurthy, A.; Johnson, K.R.; Matson, K.J.E.; Dobrott, C.I.; Li, L.; Ryba, A.R.; Bergman, T.B.; Kelly, M.C.; Kelley, M.W.; Levine, A.J. Massively Parallel Single Nucleus Transcriptional Profiling Defines Spinal Cord Neurons and Their Activity during Behavior. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2216–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, F.J.; Jonas, P.C.; Sapir, T.; Hartley, R.; Berrocal, M.C.; Geiman, E.J.; Todd, A.J.; Goulding, M. Postnatal Phenotype and Localization of Spinal Cord V1 Derived Interneurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 493, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiernan, M.C.; Vucic, S.; Cheah, B.C.; Turner, M.R.; Eisen, A.; Hardiman, O.; Burrell, J.R.; Zoing, M.C. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Lancet 2011, 377, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozdinler, P.H.; Benn, S.; Yamamoto, T.H.; Güzel, M.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Macklis, J.D. Corticospinal Motor Neurons and Related Subcerebral Projection Neurons Undergo Early and Specific Neurodegeneration in HSOD1G93A Transgenic ALS Mice. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4166–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arlotta, P.; Molyneaux, B.J.; Chen, J.; Inoue, J.; Kominami, R.; Macklis, J.D. Neuronal Subtype-Specific Genes That Control Corticospinal Motor Neuron Development in Vivo. Neuron 2005, 45, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohlfart, G.; Swank, R.L. Pathology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Fiber Analysis of the Ventral Roots and Pyramidal Tracts of the Spinal Cord. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1941, 46, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobue, G.; Matsuoka, Y.; Mukai, E.; Takayanagi, T.; Sobue, I.; Hashizume, Y. Spinal and Cranial Motor Nerve Roots in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and X-Linked Recessive Bulbospinal Muscular Atrophy: Morphometric and Teased-Fiber Study. Acta Neuropathol. 1981, 55, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholudeva, L.V.; Abraira, V.E.; Satkunendrarajah, K.; McDevitt, T.C.; Goulding, M.D.; Magnuson, D.S.K.; Lane, M.A. Spinal Interneurons as Gatekeepers to Neuroplasticity after Injury or Disease. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, J.; Genc, B.; Klessner, J.; Ozdinler, H. Retrograde Labeling, Transduction and Genetic Targeting Allow Cellular Analysis of Corticospinal Motor Neurons: Implications in Health and Disease. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grad, L.I.; Rouleau, G.A.; Ravits, J.; Cashman, N.R. Clinical Spectrum of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a024117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, M.; Jara, J.H.; Kocak, N.; Rylaarsdam, L.E.; Kim, K.D.; Bigio, E.H.; Hande Özdinler, P. Mitochondria, ER, and Nuclear Membrane Defects Reveal Early Mechanisms for Upper Motor Neuron Vulnerability with Respect to TDP-43 Pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiihashi, G.; Ito, D.; Yagi, T.; Nihei, Y.; Ebine, T.; Suzuki, N. Mislocated FUS Is Sufficient for Gain-of-Toxic-Function Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Phenotypes in Mice. Brain 2016, 139, 2380–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegorzewska, I.; Bell, S.; Cairns, N.J.; Miller, T.M.; Baloh, R.H. TDP-43 Mutant Transgenic Mice Develop Features of ALS and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18809–18814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machts, J.; Vielhaber, S.; Kollewe, K.; Petri, S.; Kaufmann, J.; Schoenfeld, M.A. Global Hippocampal Volume Reductions and Local CA1 Shape Deformations in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidi, F.; Karavasilis, E.; Rentzos, M.; Velonakis, G.; Zouvelou, V.; Xirou, S.; Argyropoulos, G.; Papatriantafyllou, I.; Pantolewn, V.; Ferentinos, P.; et al. Hippocampal Pathology in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Selective Vulnerability of Subfields and Their Associated Projections. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 84, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidi, F.; Karavasilis, E.; Velonakis, G.; Ferentinos, P.; Rentzos, M.; Kelekis, N.; Evdokimidis, I.; Bede, P. The Clinical and Radiological Spectrum of Hippocampal Pathology in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, J.; Maksimovic, K.; Lee, J.; Khan, M.; Masuda, R.; Park, J. Selective Loss of MATR3 in Spinal Interneurons, Upper Motor Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Neurons in a MATR3 S85C Knock-In Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Biology 2022, 11, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020298
You J, Maksimovic K, Lee J, Khan M, Masuda R, Park J. Selective Loss of MATR3 in Spinal Interneurons, Upper Motor Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Neurons in a MATR3 S85C Knock-In Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Biology. 2022; 11(2):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020298
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Justin, Katarina Maksimovic, Jooyun Lee, Mashiat Khan, Rintaro Masuda, and Jeehye Park. 2022. "Selective Loss of MATR3 in Spinal Interneurons, Upper Motor Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Neurons in a MATR3 S85C Knock-In Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis" Biology 11, no. 2: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020298
APA StyleYou, J., Maksimovic, K., Lee, J., Khan, M., Masuda, R., & Park, J. (2022). Selective Loss of MATR3 in Spinal Interneurons, Upper Motor Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Neurons in a MATR3 S85C Knock-In Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Biology, 11(2), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020298





