Mammaliicoccus spp. from German Dairy Farms Exhibit a Wide Range of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Non-Wildtype Phenotypes to Several Antibiotic Classes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3. Results
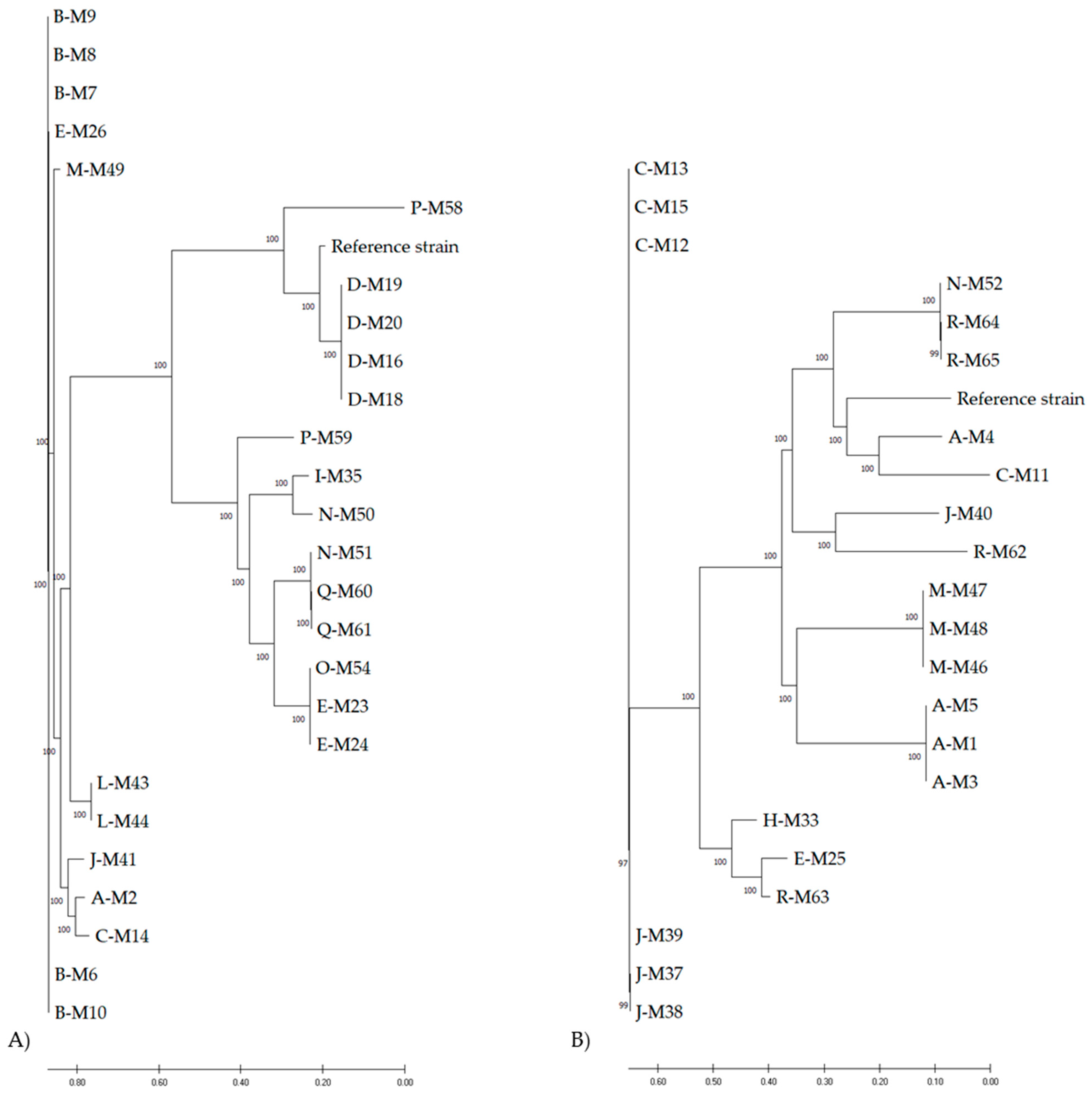
3.1. Phylogeny
3.2. AMR Genes
3.3. Phenotypic AMR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nemeghaire, S.; Argudín, M.A.; Feßler, A.T.; Hauschild, T.; Schwarz, S.; Butaye, P. The ecological importance of the Staphylococcus sciuri species group as a reservoir for resistance and virulence genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhaiyan, M.; Wirth, J.S.; Saravanan, V.S. Phylogenomic analyses of the Staphylococcaceae family suggest the reclassification of five species within the genus Staphylococcus as heterotypic synonyms, the promotion of five subspecies to novel species, the taxonomic reassignment of five Staphylococcus species to Mammaliicoccus gen. nov., and the formal assignment of Nosocomiicoccus to the family Staphylococcaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5926–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, G.K. Genomic epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus sciuri carrying a SCCmec-mecC hybrid element. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 79, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.M.; Paterson, G.K.; Holden, M.T.G.; Ba, X.; Rolo, J.; Morgan, F.J.E.; Pichon, B.; Kearns, A.; Zadoks, R.N.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. A novel hybrid SCCmec-mecC region in Staphylococcus sciuri. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 69, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazandi, M.; Al-Farha, A.A.; Coombs, G.W.; O’Dea, M.; Pang, S.; Trott, D.J.; Aviles, R.R.; Hemmatzadeh, F.; Venter, H.; Ogunniyi, A.D.; et al. Genomic characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus sciuri causing bovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitt, A.; Lienen, T.; Wichmann-Schauer, H.; Tenhagen, B.A. The occurrence of methicillin-resistant non-aureus staphylococci in samples from cows, young stock, and the environment on German dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 4604–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.M.S.; de Leon, C.; Silva, N.; Raso, T.F.; Serafini, P.P.; Givisiez, P.E.N.; Gebreyes, W.A.; Oliveira, C.J.B. Staphylococcus sciuri as a Reservoir of mecA to Staphylococcus aureus in Non-Migratory Seabirds from a Remote Oceanic Island. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miragaia, M. Factors Contributing to the Evolution of mecA-Mediated beta-lactam Resistance in Staphylococci: Update and New Insights From Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnitt, A.; Lienen, T.; Wichmann-Schauer, H.; Cuny, C.; Tenhagen, B.A. The Occurrence and Distribution of Livestock-Associated Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 on German Dairy Farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 11806–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneke, C.; Brendebach, H.; Uelze, L.; Borowiak, M.; Malorny, B.; Tausch, S.H. Species-Specific Quality Control, Assembly and Contamination Detection in Microbial Isolate Sequences with AQUAMIS. Genes 2021, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the Problem of Comparing Whole Bacterial Genomes across Different Sequencing Platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Haft, D.H.; Prasad, A.B.; Slotta, D.J.; Tolstoy, I.; Tyson, G.H.; Zhao, S.; Hsu, C.H.; McDermott, P.F.; et al. Validating the AMRFinder Tool and Resistance Gene Database by Using Antimicrobial Resistance Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in a Collection of Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00483-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority. Technical specifications on the harmonised monitoring and reporting of antimicrobial resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in food-producing animals and food. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Prola, K.; Prevost, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Pathogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heilmann, C.; Ziebuhr, W.; Becker, K. Are coagulase-negative staphylococci virulent? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Buck, J.; Ha, V.; Naushad, S.; Nobrega, D.B.; Luby, C.; Middleton, J.R.; De Vliegher, S.; Barkema, H.W. Non-aureus Staphylococci and Bovine Udder Health: Current Understanding and Knowledge Gaps. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienen, T.; Schnitt, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Maurischat, S.; Tenhagen, B.A. Genomic Distinctions of LA-MRSA ST398 on Dairy Farms From Different German Federal States With a Low Risk of Severe Human Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 575321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienen, T.; Schnitt, A.; Cuny, C.; Maurischat, S.; Tenhagen, B.-A. Phylogenetic Tracking of LA-MRSA ST398 Intra-Farm Transmission among Animals, Humans and the Environment on German Dairy Farms. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitt, A.; Tenhagen, B.A. Risk Factors for the Occurrence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Dairy Herds: An Update. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 17, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, T.; Schwarz, S.; Ding, Y.; Shen, J.; Lv, Y. Cfr-mediated linezolid-resistance among methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from infections of humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuny, C.; Arnold, P.; Hermes, J.; Eckmanns, T.; Mehraj, J.; Schoenfelder, S.; Ziebuhr, W.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fessler, A.T.; et al. Occurrence of cfr-mediated multiresistance in staphylococci from veal calves and pigs, from humans at the corresponding farms, and from veterinarians and their family members. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisblum, B. Erythromycin Resistance by Ribosome Modification. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclercq, R. Mechanisms of Resistance to Macrolides and Lincosamides: Nature of the Resistance Elements and Their Clinical Implications. Clin Infect Dis 2002, 34, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, S.; Feßler, A.T.; Loncaric, I.; Wu, C.; Kadlec, K.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J. Antimicrobial Resistance among Staphylococci of Animal Origin. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Sanz, E.; Haro-Moreno, J.M.; Jensen, S.O.; Roda-García, J.J.; López-Pérez, M. The Resistome and Mobilome of Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus sciuri C2865 Unveil a Transferable Trimethoprim Resistance Gene, Designated dfrE, Spread Unnoticed. mSystems 2021, 6, e0051121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granados-Chinchilla, F.; Rodriguez, C. Tetracyclines in Food and Feedingstuffs: From Regulation to Analytical Methods, Bacterial Resistance, and Environmental and Health Implications. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 1315497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendlandt, S.; Kadlec, K.; Fessler, A.T.; Schwarz, S. Identification of ABC transporter genes conferring combined pleuromutilin-lincosamide-streptogramin A resistance in bovine methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Hung, W.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Tsai, J.C.; Chiu, H.C.; Hsueh, P.R.; Teng, L.J. A novel fusidic acid resistance determinant, fusF, in Staphylococcus cohnii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Isolate | Species | Not Associated AMR 1 Genes | AMR Phenotype 2 and Associated AMR Genes | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHL | CIP | CLI | GEN | ERY | FOX | FUS | KAN | LZD | MUP | PEN | RIF | STR | SMX | SYN | TET | TIA | VAN | TMP | |||
| A-M2 | M. sciuri | fexA | erm(B); lnu(A) | aac(6’)-Ie;aph(2’’)-Ia | erm(B) | mecA | aac(6’)-Ie;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | tet(L);tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||
| B-M6 | M. sciuri | erm(B) | erm(B) | mecA | sal(A) | ||||||||||||||||
| B-M7 | M. sciuri | aadD1 | lnu(A) | mecA | tet(L) | sal(A) | dfrK | ||||||||||||||
| B-M8 | M. sciuri | aadD1 | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | tet(L) | sal(A) | dfrK | |||||||||||||
| B-M9 | M. sciuri | aadD1 | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | tet(L) | sal(A) | dfrK | |||||||||||||
| B-M10 | M. sciuri | erm(B) | erm(B) | mecA | sal(A) | ||||||||||||||||
| C-M14 | M. sciuri | bleO | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | tet(L) | sal(A) | dfrK | ||||||||||||
| D-M16 | M. sciuri | fexA | mecA | mecA | tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||
| D-M18 | M. sciuri | fexA | mecA | mecA | tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||
| D-M19 | M. sciuri | fexA | mecA | mecA | tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||
| D-M20 | M. sciuri | fexA | mecA | mecA | tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||
| E-M23 | M. sciuri | mecA | str | tet(L);tet(M) | sal(A) | ||||||||||||||||
| E-M24 | M. sciuri | mecA | tet(L);tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||||
| E-M26 | M. sciuri | mecA | tet(L);tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||||
| I-M35 | M. sciuri | mecA | tet(L);tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||||
| J-M41 | M. sciuri | fexA | erm(45); lnu(A) | erm(45) | mecA | mecA | sal(A) | ||||||||||||||
| L-M43 | M. sciuri | lnu(A) | aac(6’)-Ie;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | aac(6’)-Ie;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | tet(L);tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||
| L-M44 | M. sciuri | lnu(A) | aac(6’)-Ie;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | aac(6’)-Ie;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | tet(L);tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||
| M-M49 | M. sciuri | fexA | lnu(A) | erm(B) | blaZ;mecA;mecC2 | tet(M) | sal(A) | ||||||||||||||
| N-M50 | M. sciuri | erm(B) | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | erm(B) | mecA | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | tet(L) | sal(A) | ||||||||||||
| N-M51 | M. sciuri | aadD1 | fexA | mecA | tet(L) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||
| O-M54 | M. sciuri | mecA | str | tet(K);tet(M) | sal(A) | ||||||||||||||||
| P-M58 | M. sciuri | spd | lnu(A) | mecA | mecA | tet(M) | sal(A) | ||||||||||||||
| P-M59 | M. sciuri | aadD1 | lnu(A) | mecA | tet(M) | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||
| Q-M60 | M. sciuri | fexA | mecA | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||||
| Q-M61 | M. sciuri | fexA | mecA | sal(A) | |||||||||||||||||
| Isolate | Species | Not Associated AMR 1 Genes | AMR Phenotype 2 and Associated AMR Genes | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHL | CIP | CLI | GEN | ERY | FOX | FUS | KAN | LZD | MUP | PEN | RIF | STR | SMX | SYN | TET | TIA | VAN | TMP | |||
| A-M1 | M. lentus | mph(C) | erm(B) | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | erm(B) | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | tet(L) | dfrG;dfrK | ||||||||||||
| A-M3 | M. lentus | mph(C) | erm(B) | erm(B) | mecA | str | dfrG | ||||||||||||||
| A-M4 | M. lentus | erm(B) | erm(B) | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | tet(L) | dfrK | ||||||||||||||
| A-M5 | M. lentus | mph(C) | erm(B) | erm(B) | mecA | str | dfrG | ||||||||||||||
| C-M11 | M. lentus | catA;lnu(A); mph(C) | mecA | str | dfrG | ||||||||||||||||
| C-M12 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | mecA | str | dfrG | |||||||||||||
| C-M13 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | mecA | str | dfrG | |||||||||||||
| C-M15 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | mecA | str | dfrG | |||||||||||||
| E-M25 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | mecA | mecA | tet(K);tet(M) | dfrG | ||||||||||||||
| H-M33 | M. lentus | aadD1;mph(C) | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | mecA | tet(L) | dfrK | |||||||||||||
| J-M37 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | mecA | tet(L) | dfrG | |||||||||||||
| J-M38 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | mecA | tet(L) | dfrG | |||||||||||||
| J-M39 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | lnu(A) | mecA | mecA | str | tet(K) | dfrG | ||||||||||||
| J-M40 | M. lentus | mph(C);spd | fexA | erm(B) | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | erm(B) | aac(6’)-Ie;aadD1;aph(2’’)-Ia | mecA | str | tet(L);tet(M) | dfrK | ||||||||||
| M-M46 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | erm(43) | erm(43) | mecA | mecA | str | tet(K);tet(M) | ||||||||||||
| M-M47 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | erm(43) | erm(43) | mecA | mecA | str | tet(K);tet(M) | ||||||||||||
| M-M48 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | erm(43) | erm(43) | mecA | mecA | str | tet(K);tet(M) | ||||||||||||
| N-M52 | M. lentus | mph(C) | fexA | cfr | mecA | dfrG | |||||||||||||||
| R-M62 | M. lentus | mmph(C) | fexA | erm(43); lnu(A) | erm(43) | blaZ; mecA;mecC2 | str | tet(K);tet(M) | dfrG | ||||||||||||
| R-M63 | M. lentus | aadD1;bleO;cfr;mph(C) | fexA | mecA | mecA | str | tet(K) | dfrG | |||||||||||||
| R-M64 | M. lentus | mph(C) | mecA | mecA | str | tet(K) | dfrG | ||||||||||||||
| R-M65 | M. lentus | mph(C) | mecA | str | tet(K) | dfrG | |||||||||||||||
| Isolate | Species | Not Associated AMR 1 Genes | AMR Phenotype 2 and Associated AMR Genes | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHL | CIP | CLI | GEN | ERY | FOX | FUS | KAN | LZD | MUP | PEN | RIF | STR | SMX | SYN | TET | TIA | VAN | TMP | |||
| D-M17 | M. sp. | mecA | |||||||||||||||||||
| E-M21 | M. sp. | mph(C) | msr(A) | ||||||||||||||||||
| E-M22 | M. sp. | mph(C) | msr(A) | mecA | |||||||||||||||||
| F-M27 | M. vitulinus | fexA;lnu(A) | str | tet(K); tet(M) | |||||||||||||||||
| G-M28 | M. sp. | mecA | |||||||||||||||||||
| G-M30 | M. sp. | mecA | |||||||||||||||||||
| G-M31 | M. sp. | mecA | |||||||||||||||||||
| H-M32 | M. sp. | lnu(A) | mecA | ||||||||||||||||||
| H-M34 | M. sp. | mecA | |||||||||||||||||||
| I-M36 | M. sp. | mecA | str | ||||||||||||||||||
| K-M42 | M. sp. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| M-M45 | M. sp. | lnu(A) | mecA | ||||||||||||||||||
| O-M53 | M. sp. | mecA | |||||||||||||||||||
| P-M55 | M. sp. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| P-M56 | M. sp. | lnu(A) | mecA | ||||||||||||||||||
| P-M57 | M. sp. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lienen, T.; Schnitt, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Maurischat, S.; Tenhagen, B.-A. Mammaliicoccus spp. from German Dairy Farms Exhibit a Wide Range of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Non-Wildtype Phenotypes to Several Antibiotic Classes. Biology 2022, 11, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020152
Lienen T, Schnitt A, Hammerl JA, Maurischat S, Tenhagen B-A. Mammaliicoccus spp. from German Dairy Farms Exhibit a Wide Range of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Non-Wildtype Phenotypes to Several Antibiotic Classes. Biology. 2022; 11(2):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020152
Chicago/Turabian StyleLienen, Tobias, Arne Schnitt, Jens Andre Hammerl, Sven Maurischat, and Bernd-Alois Tenhagen. 2022. "Mammaliicoccus spp. from German Dairy Farms Exhibit a Wide Range of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Non-Wildtype Phenotypes to Several Antibiotic Classes" Biology 11, no. 2: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020152
APA StyleLienen, T., Schnitt, A., Hammerl, J. A., Maurischat, S., & Tenhagen, B.-A. (2022). Mammaliicoccus spp. from German Dairy Farms Exhibit a Wide Range of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Non-Wildtype Phenotypes to Several Antibiotic Classes. Biology, 11(2), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020152






