Forensic Application of Stable Isotopes to Distinguish between Wild and Captive Turtles
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Stable Isotope Analysis
2.3. Statistical Comparisons
2.4. Predictive Model
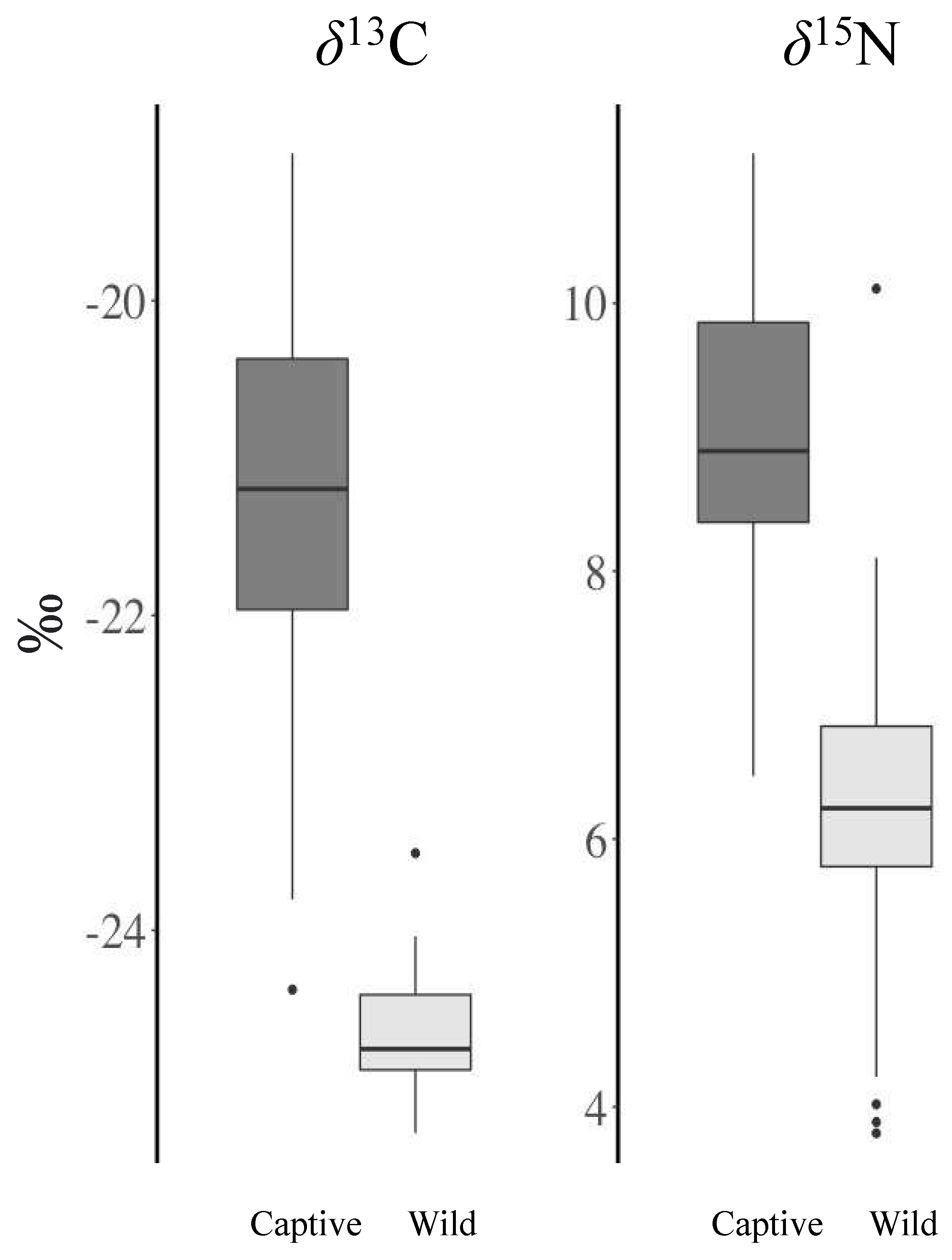
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Comparisons
3.2. Predictive Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyons, J.A.; Natusch, D.J.D. Wildlife Laundering through Breeding Farms: Illegal Harvest, Population Declines and a Means of Regulating the Trade of Green Pythons (Morelia viridis) from Indonesia. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 3073–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, C.B.; Iverson, J.B.; Rhodin, A.G.J.; van Dijk, P.P.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Kuchling, G.; Berry, K.H.; Bertolero, A.; Bjorndal, K.A.; Blanck, T.E.G.; et al. Turtles and Tortoises Are in Trouble. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R721–R735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC. World Wildlife Crime Report; UNODC: Vienna, Austria, 2016; p. 9-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, R.; Dawnay, N.; McEwing, R. Wildlife DNA Forensics—Bridging the Gap between Conservation Genetics and Law Enforcement, Endanger. Species Res. 2009, 9, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natusch, D.J.D.; Carter, J.F.; Aust, P.W.; Tri, N.V.; Tinggi, U.; Mumpuni; Riyanto, A.; Lyons, J.A. Serpent’s Source: Determining the Source and Geographic Origin of Traded Python Skins Using Isotopic and Elemental Markers. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 209, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B. Stable Isotope Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 521. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, K.A. Tracing Origins and Migration of Wildlife Using Stable Isotopes: A Review. Oecologia 1999, 120, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, G.J.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A. Global Application of Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes to Wildlife Forensics. Oecologia 2005, 143, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammershøj, M.; Pertoldi, C.; Asferg, T.; Møller, T.B.; Kristensen, N.B. Danish Free-Ranging Mink Populations Consist Mainly of Farm Animals: Evidence from Microsatellite and Stable Isotope Analyses. J. Nat. Conserv. 2005, 13, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempson, J.B.; Power, M. Use of Stable Isotopes to Distinguish Farmed from Wild Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2004, 13, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigouin, A.; Pinedo-Vasquez, M.; Nasi, R.; Poole, C.; Horne, B.; Lee, T.M. Priorities for the Trade of Less Charismatic Freshwater Turtle and Tortoise Species. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.T.; Willey, L.L. Status and Conservation of the Wood Turtle in the Northeastern United States; Technical Report Submitted to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service; 2015; 271p, Available online: https://rcngrants.org/sites/default/files/datasets/RCN2011-02v2.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Van der Merwe, N.; Vogel, J. 13C Content of Human Collagen as a Measure of Prehistoric Diet in Woodland North America. Nature 1978, 276, 815–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willey, L.L.; Akre, T.S.B.; Jones, M.T.; Brown, D.J.; Tamplin, J.W. Spatial Ecology and Seasonal Behavior in Biology and Conservation of the Wood Turtle; Jones, M.T., Willey, L.L., Eds.; Northeast Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies, Inc.: Petersburgh, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.T.; Willey, L.L.; Mays, J.D.; Akre, T.S.B.; Tamplin, J.W.; Gipe, K.D.; Burne, M.R.; Kleopfer, J.D.; Badje, A. Habitat in Biology and Conservation of the Wood Turtle; Jones, M.T., Willey, L.L., Eds.; Northeast Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies, Inc.: Petersburgh, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 81–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, J.B., III; Cutting, K.A.; Warren, J.M. Use of Stable Isotopes to Investigate Keratin Deposition in the Claw Tips of Ducks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aresco, M.J.; Travis, J.; MacRae, P.S.D. Trophic Interactions of Turtles in a North Florida Lake Food Web: Prevalence of Omnivory. Copeia 2015, 103, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.B., III; Kurle, C.M. Measuring the Realized Niches of Animals Using Stable Isotopes: From Rats to Bears. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 7, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2022. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Hopkins, J.B., III; Kock, P.L.; Ferguson, J.M.; Kalinokski, S.T. The changing anthropogenic diets of American black bears over the past century in Yosemite National Park. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, J.H. Habitat Use by Wood Turtles in Central Pennsylvania. J. Herpetol. 1992, 26, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class | Location | Sex | Season | δ13C | δ15N | Prob Wild |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Captive | ACF1 | F | Fall | −21.07 | 9.98 | 0.0002 |
| Captive | ACF2 | F | Fall | −22.61 | 8.73 | 0.0226 |
| Captive | ACF3 | F | Fall | −22.98 | 8.59 | 0.0610 |
| Captive | ACF3 | F | Fall | −20.27 | 8.62 | 0.0001 |
| Captive | ACF3 | F | Fall | −19.14 | 9.90 | 0.0000 |
| Captive | ACF4 | F | Fall | −20.26 | 9.47 | 0.0000 |
| Captive | ACF4 | F | Fall | −20.91 | 9.11 | 0.0002 |
| Captive | ACF4 | F | Fall | −20.48 | 8.26 | 0.0002 |
| Captive | ACF4 | F | Fall | −24.38 | 8.40 | 0.7187 |
| Captive | ACF4 | F | Fall | −23.62 | 7.47 | 0.4788 |
| Captive | ACF4 | F | Fall | −19.98 | 9.20 | 0.0000 |
| Captive | ACF2 | F | Spring | −19.55 | 10.45 | 0.0000 |
| Captive | ACF3 | F | Spring | −20.96 | 10.46 | 0.0001 |
| Captive | ACF4 | F | Spring | −19.61 | 10.84 | 0.0000 |
| Captive | ACF5 | F | Spring | −21.92 | 10.05 | 0.0012 |
| Captive | ACF6 | F | Spring | −21.10 | 8.97 | 0.0004 |
| Captive | ACF7 | F | Spring | −21.87 | 11.12 | 0.0004 |
| Captive | ACF7 | F | Spring | −21.38 | 10.92 | 0.0001 |
| Captive | ACF8 | F | Spring | −20.40 | 9.48 | 0.0000 |
| Captive | ACF9 | F | Spring | −21.25 | 8.79 | 0.0007 |
| Captive | ACF9 | F | Spring | −21.14 | 8.79 | 0.0005 |
| Captive | ACF9 | F | Spring | −20.46 | 8.97 | 0.0001 |
| Captive | ACF9 | F | Spring | −21.83 | 8.74 | 0.0032 |
| Captive | ACF9 | F | Spring | −22.54 | 6.80 | 0.1031 |
| Captive | ACF9 | F | Spring | −22.64 | 6.50 | 0.1632 |
| Captive | ACF9 | F | Spring | −22.40 | 7.05 | 0.0612 |
| Captive | ACF9 | F | Spring | −21.46 | 9.48 | 0.0006 |
| Captive | ACF9 | M | Fall | −21.26 | 8.82 | 0.0023 |
| Captive | ACF10 | M | Fall | −20.27 | 9.84 | 0.0001 |
| Captive | ACF11 | M | Fall | −23.80 | 8.12 | 0.7136 |
| Captive | ACF4 | M | Spring | −21.55 | 8.12 | 0.0090 |
| Captive | ACF11 | M | Spring | −19.89 | 8.41 | 0.0001 |
| Captive | ACF11 | M | Spring | −19.06 | 8.18 | 0.0000 |
| Captive | ACF11 | M | Spring | −21.82 | 10.34 | 0.0022 |
| Captive | ACF12 | M | Spring | −21.01 | 9.51 | 0.0006 |
| Captive | ACF12 | M | Spring | −22.08 | 6.47 | 0.1368 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Fall | −24.82 | 4.22 | 0.9973 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Fall | −24.90 | 5.39 | 0.9936 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Fall | −24.75 | 6.23 | 0.9802 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Fall | −24.89 | 3.89 | 0.9984 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Fall | −24.04 | 7.31 | 0.7521 |
| Wild | FIELD2 | F | Fall | −24.61 | 4.02 | 0.9963 |
| Wild | FIELD2 | F | Fall | −24.57 | 6.47 | 0.9613 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.20 | 8.10 | 0.6866 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.71 | 5.75 | 0.9858 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.84 | 5.84 | 0.9889 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.60 | 6.63 | 0.9582 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.78 | 6.23 | 0.9812 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −25.29 | 10.11 | 0.8359 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −25.00 | 4.37 | 0.9981 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −25.00 | 3.80 | 0.9989 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.30 | 7.69 | 0.8047 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.88 | 7.56 | 0.9518 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.83 | 6.15 | 0.9847 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.61 | 4.57 | 0.9939 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.90 | 6.40 | 0.9837 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | F | Spring | −24.18 | 6.45 | 0.9063 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Fall | −24.15 | 6.16 | 0.9738 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Fall | −23.51 | 7.41 | 0.6998 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Fall | −24.93 | 6.39 | 0.9952 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Fall | −24.38 | 6.69 | 0.9757 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Spring | −24.76 | 6.49 | 0.9921 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Spring | −24.43 | 6.83 | 0.9756 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Spring | −24.87 | 5.91 | 0.9964 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Spring | −24.43 | 7.38 | 0.9600 |
| Wild | FIELD1 | M | Spring | −24.39 | 7.15 | 0.9637 |
| Wild | FIELD3 | M | Spring | −25.02 | 5.93 | 0.9975 |
| Wild | FIELD3 | M | Spring | −24.89 | 6.03 | 0.9962 |
| Wild | FIELD3 | M | Spring | −24.77 | 5.91 | 0.9954 |
| Wild | FIELD3 | M | Spring | −24.39 | 6.85 | 0.9722 |
| Wild | FIELD3 | M | Spring | −24.68 | 5.63 | 0.9956 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hopkins, J.B., III; Frederick, C.A.; Yorks, D.; Pollock, E.; Chatfield, M.W.H. Forensic Application of Stable Isotopes to Distinguish between Wild and Captive Turtles. Biology 2022, 11, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121728
Hopkins JB III, Frederick CA, Yorks D, Pollock E, Chatfield MWH. Forensic Application of Stable Isotopes to Distinguish between Wild and Captive Turtles. Biology. 2022; 11(12):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121728
Chicago/Turabian StyleHopkins, John B., III, Cheryl A. Frederick, Derek Yorks, Erik Pollock, and Matthew W. H. Chatfield. 2022. "Forensic Application of Stable Isotopes to Distinguish between Wild and Captive Turtles" Biology 11, no. 12: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121728
APA StyleHopkins, J. B., III, Frederick, C. A., Yorks, D., Pollock, E., & Chatfield, M. W. H. (2022). Forensic Application of Stable Isotopes to Distinguish between Wild and Captive Turtles. Biology, 11(12), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121728






