Crystal Structure of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rho1 Reveals Its Evolutionary Relationship with Other Rho GTPases
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
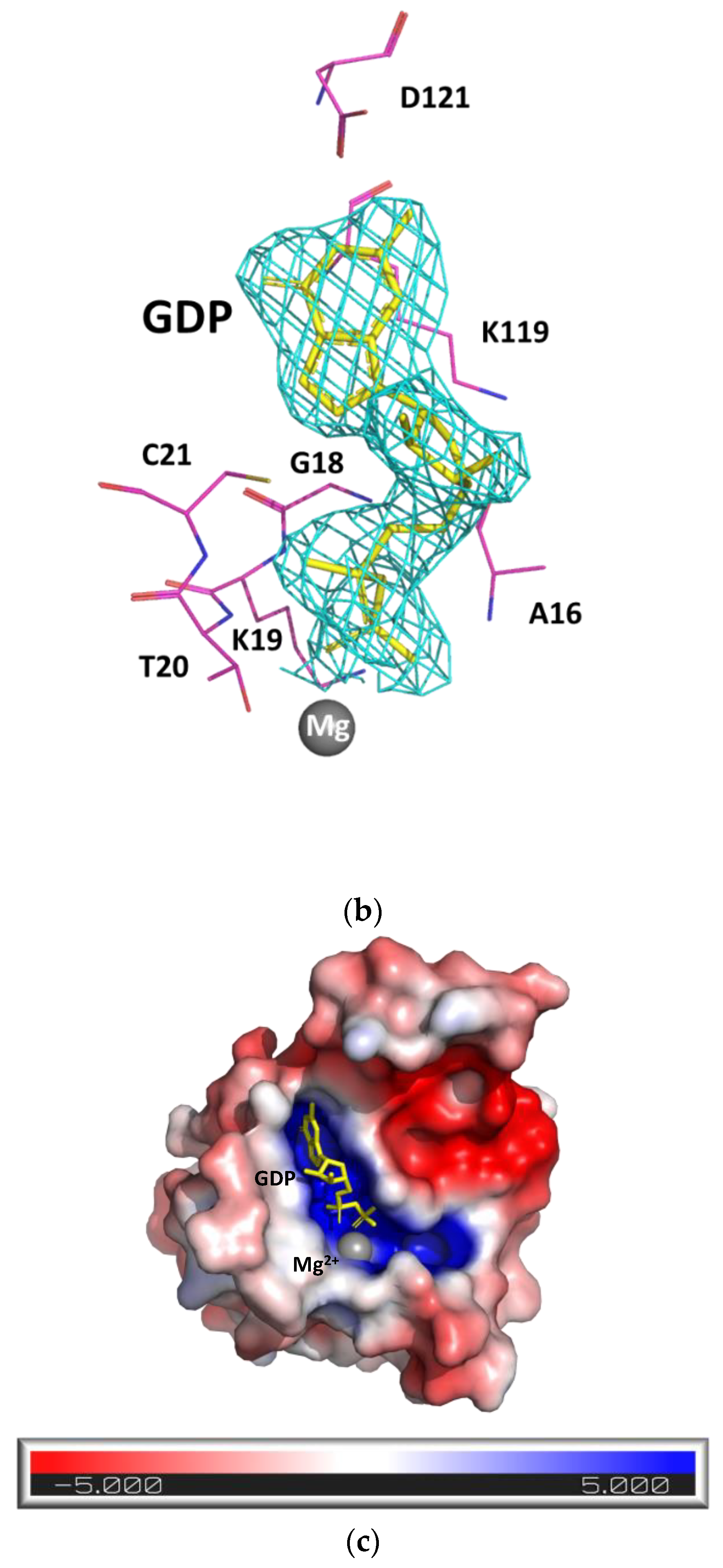
2.1. Structure of SpRho1–GDP Complex
2.2. Comparison of Rho Subfamily Protein Structures
2.3. Sequence Comparison of Rho Subfamily Proteins


2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of Rho Subfamily Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Protein Expression and Purification
4.2. Crystallization and Structure Determination
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beljan, S.; Bosnar, M.H.; Ćetković, H. Rho Family of Ras-Like GTPases in Early-Branching Animals. Cells 2020, 9, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, H.R.; Sanders, D.A.; McCormick, F. The GTPase superfamily: Conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature 1991, 349, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnoub, A.E.; Symons, M.; Campbell, S.; Der, C.J. Molecular Basis for Rho GTPase Signaling Specificity. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2004, 84, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longenecker, K.; Read, P.; Derewenda, U.; Dauter, Z.; Liu, X.; Garrard, S.; Walker, L.; Somlyo, A.V.; Nakamoto, R.K.; Somlyo, A.P.; et al. How RhoGDI binds Rho. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1999, 55, 1503–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hakoshima, T.; Shimizu, T.; Maesaki, R. Structural Basis of the Rho GTPase Signaling. J. Biochem. 2003, 134, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fort, P.; Blangy, A. The Evolutionary Landscape of Dbl-Like RhoGEF Families: Adapting Eukaryotic Cells to Environmental Signals. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1471–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ridley, A.J.; Schwartz, M.A.; Burridge, K.; Firtel, R.A.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Borisy, G.; Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.R. Cell Migration: Integrating Signals from Front to Back. Science 2003, 302, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wennerberg, K.; Der, C.J. Rho-family GTPases: It’s not only Rac and Rho (and I like it). J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ihara, K.; Muraguchi, S.; Kato, M.; Shimizu, T.; Shirakawa, M.; Kuroda, S.; Kaibuchi, K.; Hakoshima, T. Crystal Structure of Human RhoA in a Dominantly Active Form Complexed with a GTP Analogue. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9656–9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bery, N.; Keller, L.; Soulié, M.; Gence, R.; Iscache, A.-L.; Cherier, J.; Cabantous, S.; Sordet, O.; Lajoie-Mazenc, I.; Pedelacq, J.-D.; et al. A Targeted Protein Degradation Cell-Based Screening for Nanobodies Selective toward the Cellular RHOB GTP-Bound Conformation. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 1544–1558.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tnimov, Z.; Guo, Z.; Gambin, Y.; Nguyen, U.T.T.; Wu, Y.; Abankwa, D.; Stigter, A.; Collins, B.; Waldmann, H.; Goody, R.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Prenylated RhoA Interaction with Its Chaperone, RhoGDI. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26549–26562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jobichen, C.; Pal, K.; Swaminathan, K. Crystal structure of mouse RhoA:GTPγS complex in a centered lattice. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2012, 13, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Derewenda, U.; Liu, X.; Minor, W.; Nakamoto, R.K.; Somlyo, A.V.; Somlyo, A.P.; Derewenda, Z.S. Crystal structure of RhoA–GDP and its functional implications. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1997, 4, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristelly, R.; Gao, G.; Tesmer, J. Structural Determinants of RhoA Binding and Nucleotide Exchange in Leukemia-associated Rho Guanine-Nucleotide Exchange Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 47352–47362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, S.M.G.; Cerione, R.A. X-ray Crystal Structures Reveal Two Activated States for RhoC. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 6547–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Ihara, K.; Maesaki, R.; Kuroda, S.; Kaibuchi, K.; Hakoshima, T. An Open Conformation of Switch I Revealed by the Crystal Structure of a Mg2+-free Form of RHOA Complexed with GDP. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18311–18317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, A.; Ridley, A. Why three Rho proteins? RhoA, RhoB, RhoC, and cell motility. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 301, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.L.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem. J. 2000, 348, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorský, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Always look on the bright site of Rho: Structural implications for a conserved intermolecular interface. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nisimoto, Y.; Freeman, J.L.R.; Motalebi, S.A.; Hirshberg, M.; Lambeth, J.D. Rac Binding to p67. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18834–18841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnoub, A.E.; Der, C.J.; Campbell, S.L. The Insert Region of Rac1 Is Essential for Membrane Ruffling but Not Cellular Transformation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 2847–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zong, H.; Kaibuchi, K.; Quilliam, L.A. The Insert Region of RhoA Is Essential for Rho Kinase Activation and Cellular Transformation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 5287–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hancock, J.P.; Paterson, H.; MarshalIt, J. A Polybasic Domain or Palmitoylation Is Required in Addition to the CAAX Motif to Localize ~21’s to the Plasma Membrane. Cell 1990, 63, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelson, D.; Silletti, J.; Murphy, G.; D’Eustachio, P.; Rush, M.; Philips, M.R. Differential Localization of Rho GTPases in Live Cells: Regulation by Hypervariable Regions and RhoGDI Binding. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.Z.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequencealignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goujon, M.; McWilliam, H.; Li, W.Z.; Valentin, F.; Squizzato, S.; Paern, J.; Lopez, R. A new bioinformatics analysis tools frameworkat EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W695–W699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 7, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshberg, M.; Stockley, R.W.; Dodson, G.; Webb, M. The crystal structure of human rac1, a member of the rho-family complexed with a GTP analogue. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1997, 4, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.; Hoffman, G.R.; Manor, D.; Clardy, J.C.; Cerione, R.A. Structures of Cdc42 bound to the active and catalytically compromised forms of Cdc42GAP. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1998, 5, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadota, H.; Anraku, Y.; Botstein, D.; Ohya, Y. Conditional lethality of a yeast strain expressing human RHOA in place of RHO1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9317–9321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; Volume 276, pp. 307–326. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S007668799776066X (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.-W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, D60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, R.; Weyand, M.; Lammers, M.; Ishizaki, T.; Ahmadian, M.R.; Wittinghofer, A. Structural and mech-anistic insights into the interaction between Rho and mammalian Dia. Nature 2005, 435, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, M.; Kurokawa, K.; Sato, Y.; Yamagata, A.; Mimura, H.; Yoshikawa, A.; Sato, K.; Nakano, A.; Fukai, S. Structural basis for the Rho- and phosphoinositide-dependent localization of the exocyst subunit Sec3. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Unit Cell Parameters (Å, ◦) | a = 105.69, b = 66.35, c = 75.55, α = γ = 90, β = 112.78 |
|---|---|
| Space group | C2 |
| Data collection | |
| Resolution range (Å) | 50.00–2.78 (2.83–2.78) * |
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.5418 |
| Unique reflections | 12485 (617) |
| Completeness (%) Redundancy | 100.0 (99.8) 4.4 (4.4) |
| Overall (I/σ(I)) | 3.3 (2.8) |
| Rsym a CC 1/2 CC * | 19.0 (0.818) 0.952 (0.518) 0.988 (0.824) |
| Refinement and quality b | |
| Resolution range (Å) | 50–2.78 |
| Rwork c | 0.19 |
| Rfree d | 0.23 |
| Root mean square deviation | |
| Bond length (Å) | 0.010 |
| Bond angles (o) | 1.466 |
| Ramachandran statistics e Favored (%) | 95.38 |
| Outliers (%) | 0.29 f |
| MolProbity score | 2.00 |
| Clashscore (all atoms) | 6.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Xie, J.; Seetharaman, J. Crystal Structure of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rho1 Reveals Its Evolutionary Relationship with Other Rho GTPases. Biology 2022, 11, 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111627
Huang Q, Xie J, Seetharaman J. Crystal Structure of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rho1 Reveals Its Evolutionary Relationship with Other Rho GTPases. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111627
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qingqing, Jiarong Xie, and Jayaraman Seetharaman. 2022. "Crystal Structure of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rho1 Reveals Its Evolutionary Relationship with Other Rho GTPases" Biology 11, no. 11: 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111627
APA StyleHuang, Q., Xie, J., & Seetharaman, J. (2022). Crystal Structure of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rho1 Reveals Its Evolutionary Relationship with Other Rho GTPases. Biology, 11(11), 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111627






