Seed Germination Ecology of Chenopodium album and Chenopodium murale
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seed Description
2.2. General Seed Germination Procedure
2.3. Effect of Temperature and Light on Germination
2.4. Effect of Salt Stress on Germination
2.5. Effect of Osmotic Stress on Germination
2.6. Effect of pH on Germination
2.7. Effect of Initial High Temperature on Weed Germination
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Temperature and Light on Germination
3.2. Effect of Salt Stress on Germination
3.3. Effect of Osmotic Stress on Germination
3.4. Effect of Initial Temperature on Germination
3.5. Effect of pH on Germination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krak, K.; Vít, P.; Belyayev, A.; Douda, J.; Hreusová, L.; Mandák, B. Allopolyploid origin of Chenopodium album s. str. (Chenopodiaceae): A molecular and cytogenetic insight. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coquillat, M. Sur les plantes les plus communes a’ la surface du globe. Bull. Mens. Soc. Linn. Lyon 1951, 20, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.C. Weeds, Weedicides, and Weed Control-Principle and Practice; Agro Botanical Publishers: Bikaner, India, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Narayan, R. Phenotypic plasticity of Chenopodium murale across contrasting habitat conditions in peri-urban areas in Indian dry tropics: Is it indicative of its invasiveness? Plant Ecol. 2012, 213, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, E.H.; Brown, E. Final results of the Duval buried seed experiment. J. Agric. Res. 1946, 72, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Bana, M.L.; Kaushik, R.A.; Bana, R.S.; Dhakar, M.K. Integrated weed management in cauliflower cv. ‘Pusa Snowball K-1’. Ann. Agric. Res. 2012, 33, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa, A.A.; Zulfiqar, U.; Sadia, S.; Bhowmik, P.; Chauhan, B.S. A global perspective on the biology, impact and management of Chenopodium album and Chenopodium murale: Two troublesome agricultural and environmental weeds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5357–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.K.; Yadav, D.S.; Sood, P.; Rahi, S.; Arya, K.; Thakur, S.K.; Lal, R.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, J.; Dass, A.; et al. Post-Emergence Herbicides for Effective Weed Management, Enhanced Wheat Productivity, Profitability and Quality in North-Western Himalayas: A ‘Participatory-Mode’ Technology Development and Dissemination. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K. Weed Science: Basics and Applications, 1st ed.; Jain Brothers Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt, C.F.; Meissner, R.; van Wyk, L.J. Allelopathic effects of Chenopodium album L. and Chenopodium polyspermum L. on another weed and two crop species. South Afr. J. Plant Soil 1997, 14, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, J.R.; Dabgar, Y.B. Allelopathic effects of Chenopodium album L. on Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 346–348. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, H.; Tamada, T. Association of beet necrotic yellow vein virus with isolates of Polymyxa betp Keskin. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 52, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, H.; Ui, T. Host range of Polymyxa betp Keskin strains in rhizomania-infested soils of sugar beet fields in Japan. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 52, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.A.; Whitham, T.G. Evolutionary reduction of complex life cycles: Loss of host-alternation in Pemphigus (Homoptera: Aphididae). Evolution 1988, 42, 717–728. [Google Scholar]
- De Waele, D.; Jordaan, E.M.; Basson, S. Host status of seven weed species and their effects on Ditylenchus destructor infestation on peanut. J. Nematol. 1990, 22, 292–296. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, M.; Smith, H.G.; Hallsworth, P.B. The host range of beet yellowing viruses among common arable weed species. Plant Pathol. 1994, 43, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélair, G.; Benôit, D.L. Host suitability of 32 common weeds to Meloidogyne hapla in organic soils of southwestern Quebec. J. Nematol. 1996, 28, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, E.H.C.; Dingley, J.M. New plant disease records in New Zealand: Miscellaneous fungal pathogens III. N. Z. J. Bot. 1996, 34, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillaspie, A.G., Jr.; Ghabrial, S.A. First report of peanut stunt cucumovirus naturally infecting Desmodium sp. Plant Dis. 1998, 82, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodehouse, R.P. Hayfever Plants; Hafner Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury, J.M. Poisonous Plants of the United States and Canada; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Schmutz, E.R.; Freeman, B.N.; Reed, R.E. Livestock-Poisoning Plants of Arizona; The University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Everist, S.L. Poisonous Plants of Australia; Angus & Robertson: Sydney, Australia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Heap, I. The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. 2021. Available online: http://www.weedscience.org (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Solymosi, P.; Lehoczki, E. Characterization of a triple (atrazine-pyrazon-pyridate) resistant biotype of common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album L.). J. Plant Physiol. 1989, 4, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencill, W.K.; Foy, C.L. Distribution of triazine-resistant smooth pigweed (Amaranthus hybridus) and common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) in Virginia. Weed Sci. 1988, 36, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, R.D.; Dominguez, C.; Tena, M. Characterization of triazine-resistant biotypes of common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album), hairy fleabane (Conyza bonaeriensis), and yellow foxtail (Setaria glauca) found in Spain. Weed Sci. 1989, 37, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagood, E.S., Jr. Control of triazine-resistant smooth pigweed (Amaranthus hybridus) and common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) in no-till corn (Zea mays). Weed Technol. 1989, 3, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, J.S.; LeBaron, H.M. Significance and distribution of herbicide resistance. Weed Technol. 1990, 4, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G.; Harvey, R.G. Triazine-resistant common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album L.) control in field corn (Zea mays L.). Weed Technol. 1993, 7, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, S.; Phillips, W.H., II; Kalnay, P. Long-term control of perennial broadleaf weeds and triazine-resistant common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) in no-till corn (Zea mays). Weed Technol. 1997, 11, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechant, E.; de Marez, T.; Vroman, G.; Hermann, O.; Legrand, G.; Misonne, J.F.; Bulcke, R. Distribution of metamitron-resistant Chenopodium album L. in Belgian sugar beet. Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2010, 75, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanizadeh, H.; Harrington, K.C. Cross-resistance to auxinic herbicides in dicamba-resistant Chenopodium album. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 60, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, C.; Huang, H.; Wei, S. First report of molecular basis of resistance to imazethapyr in common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album). Weed Sci. 2017, 68, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, B.S.; Johnson, D.E. The role of seed ecology in improving weed management strategies in the tropics. Adv. Agron. 2010, 105, 221–262. [Google Scholar]
- Travlos, I.; Gazoulis, I.; Kanatas, P.; Tsekoura, A.; Zannopoulos, S.; Papastylianou, P. Key factors affecting weed seeds’ germination, weed emergence, and their possible role for the efficacy of false seedbed technique as weed management practice. Front. Agron. 2020, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, B.E. Evaluation of the Water Potentials of Solutions of Polyethylene Glycol 8000. Plant Physiol. 1983, 72, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Dong, L.Y. Factors affecting seed germination and seedling emergence of Asia Minor bluegrass (Polypogon fugax). Weed Sci. 2015, 63, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bana, R.S.; Singh, T.; Louhar, G. Ecological weed management approaches for wheat under rice–wheat cropping system. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 4, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, H.J.; Karssen, C.M. Seasonal periodicity in germination of seeds of Chenopodium album L. Ann. Bot. 1993, 72, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, S. Comparative germination and emergence ecology of two populations of common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) from Iran and Denmark. Weed Sci. 2011, 59, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bana, R.S.; Singh, D.; Nain, M.S.; Kumar, H.; Kumar, V.; Sepat, S. Weed control and rice yield stability studies across diverse tillage and crop establishment systems under on-farm environments. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Liu, X.; Khan, M.A.; Gul, B. Effects of salt and water stress on the seed germination of Chenopodium glaucum L. Pak. J. Bot. 2004, 36, 793–800. [Google Scholar]
- Koyro, H.W.; Eisa, S.S. Effect of salinity on composition, viability and germination of seeds of Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Plant Soil 2008, 302, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.X.; Chen, S.S.; Xu, D.S.; Lan, H.Y. Plant growth and responses of antioxidants of Chenopodium album to long-term NaCl and KCl stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 60, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.X.; Chen, S.S.; Xu, D.S.; Lan, H. Effect of three salts on germination and seedling survival of dimorphic seeds of Chenopodium album. Botany 2010, 88, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L. A contribution to our information on grass burning. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1939, 36, 270–282. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, P.A. Soil management in shifting cultivation areas. In Properties and Management of Soils in the Tropics; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 346–412. [Google Scholar]


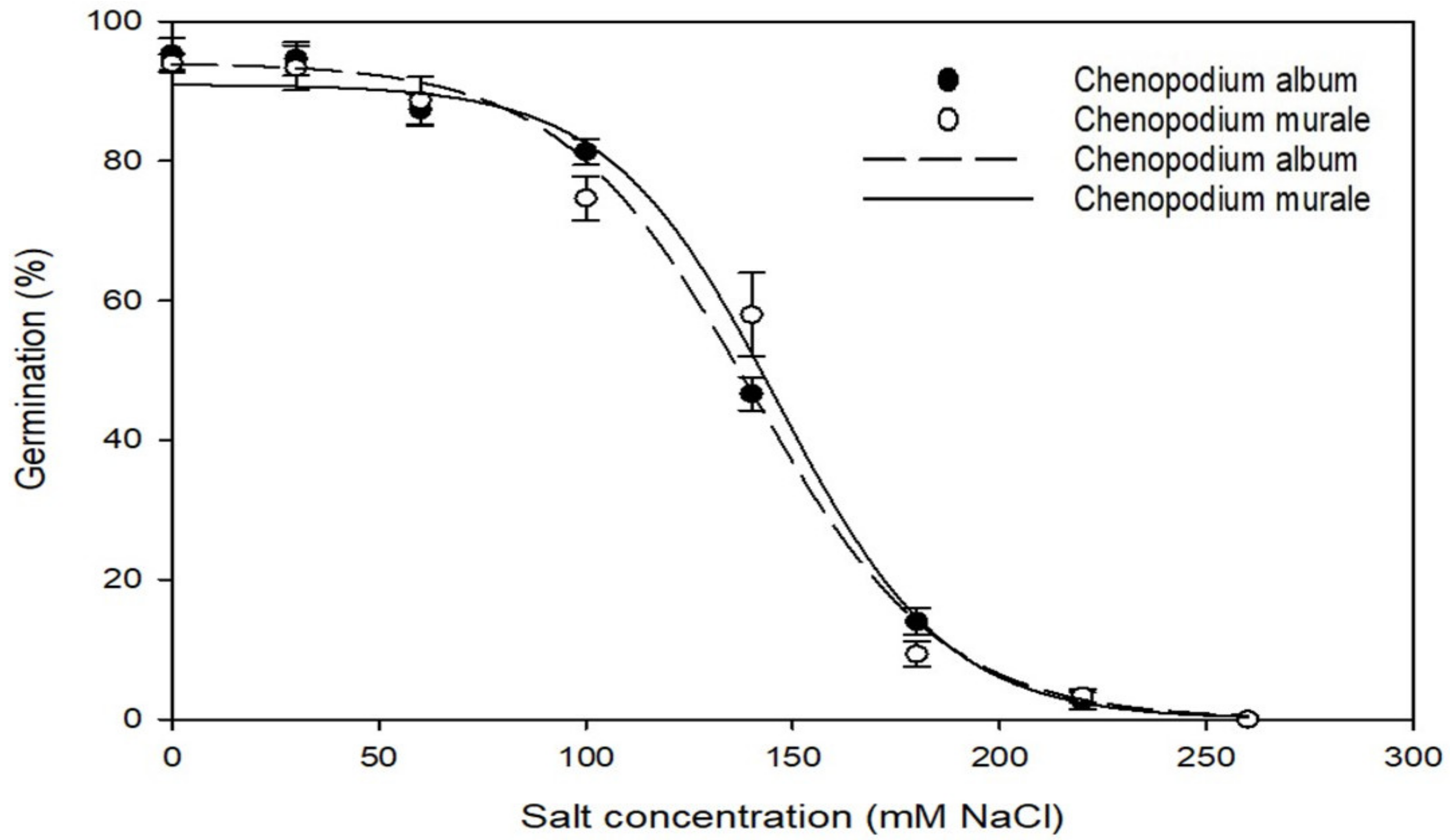
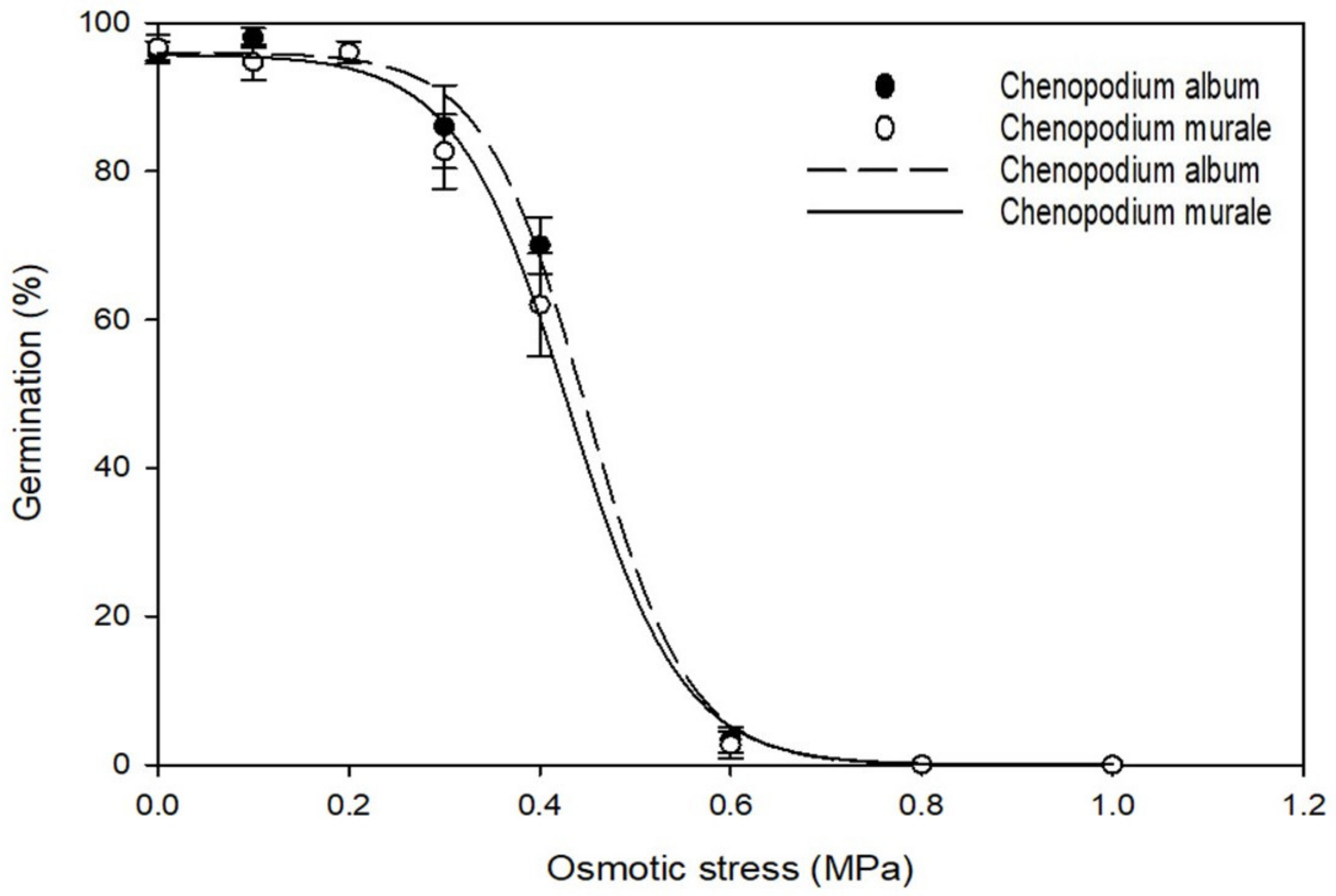


| Species | Parameter | Maximum Germination (a) | Germination Rate (b) | GR50 * (X50) | R2 | Standard Error of Estimate (Se) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chenopodium album | Osmotic stress (MPa) | 96 | −0.053 | 0.44 | 0.99 | 2.49 |
| Salt concentration (mM NaCl) | 94.1 | −22.98 | 139.89 | 0.99 | 2.07 | |
| Initial temperature (°C) | 98.3 | −1.67 | 80.15 | 1.0 | 0.21 | |
| Chenopodium murale | Osmotic stress (MPa) | 95.7 | −0.058 | 0.43 | 0.99 | 2.42 |
| Salt concentration (mM NaCl) | 91.0 | −20.32 | 146.31 | 0.99 | 5.25 | |
| Initial temperature (°C) | 96.7 | −0.87 | 79.3 | 1 | 0.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bana, R.S.; Kumar, V.; Sangwan, S.; Singh, T.; Kumari, A.; Dhanda, S.; Dawar, R.; Godara, S.; Singh, V. Seed Germination Ecology of Chenopodium album and Chenopodium murale. Biology 2022, 11, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111599
Bana RS, Kumar V, Sangwan S, Singh T, Kumari A, Dhanda S, Dawar R, Godara S, Singh V. Seed Germination Ecology of Chenopodium album and Chenopodium murale. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111599
Chicago/Turabian StyleBana, Ram Swaroop, Vipin Kumar, Seema Sangwan, Teekam Singh, Annu Kumari, Sachin Dhanda, Rakesh Dawar, Samarth Godara, and Vijay Singh. 2022. "Seed Germination Ecology of Chenopodium album and Chenopodium murale" Biology 11, no. 11: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111599
APA StyleBana, R. S., Kumar, V., Sangwan, S., Singh, T., Kumari, A., Dhanda, S., Dawar, R., Godara, S., & Singh, V. (2022). Seed Germination Ecology of Chenopodium album and Chenopodium murale. Biology, 11(11), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111599








