Simple Summary
The genus Ranunculus (buttercup) includes over 600 species, some of which are endangered, e.g., Illyrian Buttercup. Knowledge of the reproductive biology of such species may be crucial for conservation action. For this purpose, six species with different reproduction modes (nonclonal reproducing sexually by seeds only, clonal propagating by seeds and additionally vegetatively and apomictic) were observed. Selected features related to the efficiency of sexual reproduction were described: pollen viability, number of fruit set, seed viability and germination. It has been shown that in clonal species, which include the Illyrian Buttercup, the efficiency of sexual reproduction is lower compared to nonclonal species. The results will support conservation action taken for this species.
Abstract
Generative processes have been evaluated in six European buttercup species in order to verify the hypothesis that the reproduction efficiency of clonal species is lower than that of nonclonal ones. The study covered common species (Ficaria verna, Ranunculus auricomus, R. bulbosus, R. cassubicus, R. lanuginosus) and the endangered R. illyricus. The following properties have been assessed: pollen viability (staining method), pollen grain germination and the pollen-tube elongation in pistil tissues (fluorescence microscopy), seed formation efficiency, seed viability (tetrazolium test) and germination ability by introducing factors interrupting dormancy (low temperature and gibberellin application). Additionally, the pistil morphology was documented for R. bulbosus, R. illyricus and R. cassubicus using SEM techniques. It was demonstrated that the reproductive efficiency, expressed as the production of viable seeds able to germinate, was significantly higher in the species reproducing sexually (especially in R. lanuginosus) compared to the clonal ones. However, the complexity observed leads to separation of an additional group (cluster) of apomictic species: R. auricomus and R. cassubicus, distinguished by the lowest pollen viability and a low ability of the seeds to germinate. In the vegetatively reproducing R. illyricus, the seed formation efficiency was just 13.2% despite the having highest number of pistils in its flowers. The developed seeds of this species observed in our experiment were viable, but in general effective methods to stimulate their germination have not been proposed yet. Here, the first comparative study concerning the biology of sexual reproduction of R. illyricus is presented in the context of its decreasing distribution in natural habitats.
1. Introduction
There are two modes of reproduction in plants: generative using seeds and vegetative (clonal) using bulbs, stolons or tubers. Numerous plant species are able to produce offspring both in vegetative and sexual ways, and the balance between the two reproductive modes may vary widely across and within the species. The problem of the trade-off between the resources allocated to vegetative versus generative reproduction within a plant has been investigated over recent decades [1,2,3]. The shares of sexual and clonal progeny may vary and depend on ecological or genetic factors that limit one or the other reproductive mode [4]. A question worth answering is to what extent the efficiency of sexual reproduction depends on the genetically determined reproduction mode.
An interesting choice for such investigations is the Ranunculus (buttercups) genus, which comprises about 600 species prevalent in both hemispheres, mainly in the subtropics and temperate zones [5]. Taking into account its taxonomic diversity, this genus is divided into 20 sections [6]. These are annual or perennial herbaceous plants growing in a variety of habitats, from damp meadows through forests up to xerothermic grasslands and mountain areas, as well as in streams and water reservoirs [5,7]. In the previous systematics, the genus Ranunculus also included representatives of the contemporary genus Ficaria [8,9].
Buttercups are characterized by different reproduction modes. They comprise species reproducing only generatively—self-fertilizing species or self-incompatible species—and those that have developed effective ways of vegetative reproduction [10,11,12]. There are species developing tubers in the axils of lower leaves (Ficaria verna Huds.), aboveground and underground stolons (R. asiaticus L., R. cymbalaria Pursch, R. repens L.), shoots rooting in the nodes (R. flammula L., R. hederaceus L., R. reptans L.), and other permanent underground storage organs (R. asiaticus, R. illyricus L., R. nigrescens Freyn, F. verna) [6]. Some species are optionally apomictic, asexually reproducing via seeds, for example, R. auricomus L. or R. kuepferi Greuter & Burdet [13,14,15,16,17]. Different strategies preventing self-pollination have been described in cross-pollinated species, such as protogyneous or protandrous flowers [11,18,19]. Both forms of temporal separation of gender phases have been described in Ranunculus, especially among the alpine species. Protogyny appeared to be more common and was described for alpine species of New Zealand, USA, lowland populations of R. acris L. and R. repens in the United Kingdom [18] and cultivated R. asiaticus [20]. Protandry of different degrees was reported for Ficaria verna [18] and New Zealand populations of R. acris and R. flammula [21].
The effectiveness of the sexual reproduction noted for Ranunculus species varies significantly and results from a proper course of successive stages: production of pollen, pollination, fertilization, seeds’ development, their viability and their ability to germinate. The course of these processes is affected by abiotic environmental factors, such as temperature [22,23,24], light [25] or water [26], as well as the presence of pollinators, which is the case for the self-compatible species Ranunculus adoneus A. Gray [22].
The regular course of generative processes depends not only on the availability of pollen, but also on its quality; for self-incompatible species, a precondition for seed formation is pollen of a different genotype [11] high viability. In the case of buttercups, studies have also looked at the size and viability of pollen grains in apomictic species [17,20,27,28,29]. Izmaiłow [16] conducted research on the apomictic complex of R. auricomus, and showed that a change in the plants ploidy level clearly reduced pollen viability and ability to germinate by ca. 30% and 75% in triploids and diploids, respectively.
For the reproductive success of a species, the formation of seeds that are alive and able to germinate is crucial. In many Ranunculaceae species at the time of diaspore dispersal, seed dormancy is determined by an undeveloped embryo or the structure of the seed coat [30,31,32]. Tiwari et al. [33] identified the dormancy of seeds in buttercups as an endogenous type resulting from underdevelopment of the embryo or physiological state. The natural ability of buttercup seeds to germinate varies across species, from 30% in R. testiculatus Crantz [34], to 50% in the case of R. cortusifolius Willd. [35], to even 96% for R. peltatus subsp. baudotii (Godron) Meikle ex C.D.K. Cook [30]. There are many ways in which the dormancy of seeds can be interrupted, and this effect has been studied for several buttercup species. Most commonly, seeds are exposed to low or high temperatures and growth regulators [30,34,35,36,37].
The aim of our research was to verify the hypothesis that the clonal species of Ranunculus exhibit limited effectiveness of generative reproduction (assessed based on pollen viability, number of pistils per flower, efficiency of fruit set, viability of seeds and ability of seeds to germinate) compared to nonclonal ones. Special attention was paid to Ranunculus illyricus—a rare species protected in some central European countries, the biology of which has not yet been studied and reported in detail.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
Six species from the Ranunculaceae family, including five buttercups and one lesser celandine, were studied. The species come from a temperate climate, but from a range of habitats, and they differ in terms of their reproduction modes (Table 1 and Table 2). They are common in Central and Eastern Europe, with the exception of xerothermic R. illyricus, which is endangered in some countries in Europe including Poland [38,39,40].

Table 1.
Systematics affiliation, ploidy level, reproduction mode and breeding system of investigated Ficaria verna and Ranunculus species.

Table 2.
Locality and date of plant material collection of Ficaria verna and Ranunculus species.
Species reproducing only by seeds are regarded as nonclonal, while those that produces vegetative offspring using bulbs, tubers, rhizomes or stolons are called clonal [43]. Based on this criterion, our own observations (Table 2) and the literature, R. lanuginosus [6], R. bulbosus [12], R. auricomus [14,16] and R. cassubicus [44,45,46] were classified as nonclonal species.
The second group—clonal—was represented by Ranunculus illyricus and Ficaria verna, which are perennial geophytes producing underground clusters of tuberous roots. Ficaria verna was previously included in genus Ranunculus as R. ficaria [9]. In Central Europe, one can also come across the tetraploid Ficaria verna subsp. bulbifera Á. Löve & D. Löve, which additionally produces descendant tubers in leaf axils [9,47].
The test material comprised flowers and achenes collected from randomly selected individuals in their natural habitats (Table 2), except for R. illyricus, which was gathered from a collection at the Faculty of Biotechnology and Horticulture of the University of Agriculture in Kraków. Cultivated plants represented natural resources from one of the two known localities in Poland [39,48,49] and were grown in thermal, light, moisture and edaphic conditions in line with Ellenberg indicator values [50]. The research material was obtained at the optimum times for flowering and fruiting, which were different for each species (Table 2). Specimens in populations did not bloom synchronously, hence it was possible to collect at the same time flowers with open anthers, to assess the viability of pollen, and overblown flowers (flowers with a wilting corolla), to examine pollination effectiveness and pollen-tube elongation.
For every species, 30 and at least 50 (50–132) flowers or multiple fruits were collected in 2017 and 2019, respectively, each from a separate individual. The taxa chosen for the research form an apocarpous gynoecium, from which a spherical cluster of single seed fruits (achenes) develops. The effectiveness of pollination and fruit set were observed in the conditions of open—pollination of plants in natural stands (in situ)— or in the case of R. illyricus, an outdoor collection (ex situ).
Table 1 presents the systematic division of the genus into sections following Tutin et al. [6], the chromosome number and breeding system in accordance with PLADIAS [19], and the reproduction type according to Erikson [41], Sarukhán and Harper [12], Troll [42], and Tutin et al. [6].
2.2. Pollen Quality and Pistil Morphology
Anthers and pistils were excised from the flowers to assess pollen quality, germination and pistil morphology. Pollen viability was evaluated using the indirect staining method [51] on the collection day. The assessment was conducted in three repetitions. A single repetition involved a mixture of pollen collected from 10 flowers, each coming from a separate plant. In total, 300 grains of pollen were assessed in each repetition using a Zeiss Axio Imager M2 microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). Photographs were taken using an EOS 450D digital camera (CANON, Tokyo, Japan). At the same time, the diameters of pollen grains were measured using computer graphics program AxioVision 4.8 in three repetitions with 30 grains of pollen each.
Pistils from overblown flowers from the middle part of the receptacle were fixed in FAA (formalin, glacial acetic acid, ethyl alcohol 1:1:8 v/v/v) for 10–12 h, and then macerated in a 30% NaOH solution for two to three hours and cleared with a 6% H2O2 solution. Next, pistil tissues were stained with aniline blue for three hours [52] and squeezed between microscopic slides. The observations of pollination, pollen germination and the pollen-tube growth from the stigma to the ovary were conducted in fluorescent ultraviolet light with a wavelength of about 356 nm, using a Zeiss Axio Imager M2 microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). in the fluorescence mode. This allowed for an assessment of the percentage of pollinated pistils, and among them, the share of pistils with germinating and nongerminating pollen. There were at least 50 pistils per species analyzed.
For R. bulbosus, R. illyricus and R. cassubicus, additional documentation was prepared for pistil pollination and morphology using the SEM technique. The material was fixed in FAA, dehydrated in ethyl alcohol and dried in vacuum. The dried tissues were sputter-coated with gold and viewed under a Phenom™ ProX Desktop SEM electron microscope (ThermoFisher Scientific™, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Efficiency of Seed Formation, Their Viability and Ability to Germinate
The efficiency of seed (single seed fruit) formation expressed as percentage was calculated as the number of ripe achenes per the number of pistils.
Seed viability was assessed using the tetrazolium method [53] in the year 2019. The achenes were soaked in water for 24 h, and then, after removing the pericarp, in a tetrazolium solution for the same period of time. The viability was evaluated for 15 to 58 seeds per species.
Seed material was also evaluated in terms of its ability to germinate using the blotter test in Petri dishes under a 16/8 h photoperiod and a temperature of 20 ± 2 °C [54]. The influence of factors interrupting seed dormancy was examined for a few variants: 4-week low-temperature stratification, pre-sowing conditioning with gibberellic acid (GA3), and a combination of both factors. Each treatment (and control) involved four Petri dishes (repetitions) with 25 seeds from each species.
In the stratification treatment, the seeds were kept at a low temperature (4 °C) for a period of four weeks. Application of gibberellin consisted of soaking seeds in a GA3 solution at a concentration of 1.0 × 10−3 mM for 24 h before sowing. Seeds that did not undergo this treatment were soaked in water for the same time and were used as control. The number of germinated seeds was evaluated after 4 weeks.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed with STATISTICA v. 13.3. Quantitative variables (efficiency of fruit set, germination of seeds per plate, number of pistils per flower, pollen diameter, pollen viability per sample) were tested for the normality of distribution and the homogeneity of variance. The normality of data in groups (species or clusters) was tested by a means of the Shapiro–Wilk test. The homogeneity of variance in groups (species or clusters) was tested by employing the Levene test. When comparing the groups with anormal distribution and homogeneity of variance, parametric tests (ANOVA) were used. However, when comparing the groups characterized by the lack of a normal distribution or the lack of homogeneity of variance, nonparametric tests (Kruskal–Wallis test) were applied. The null hypothesis tested stated that there were no differences between the groups (species or clusters), and the rejection of the null hypothesis allowed accepting the alternative hypothesis implying the existence of differences between the groups. Details of the tests used are provided in the captions of tables or figures. To assess the relationship between qualitative data, multiway contingency tables and the chi-squared test were used. The null hypothesis stated that there was no association between the group (species or cluster) and the parameter (viability of seeds). After rejection of the null hypothesis, it was possible to accept the alternative hypothesis that there was a relationship between the group and the parameter (viability of seeds). Additionally, cluster analyses were carried out to divide the species into groups of similar characteristics (Euclidean distance, Ward’s method). The significance level was α = 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Pollen Quality and Pistil Morphology
The pollen of the species studied in our work differed in its viability, from 38% for R. auricomus to 91% for R. bulbosus (Table 3, Figure 1a–c). As far as size is concerned, pollen grains were similar to each other across the species (Table 3).

Table 3.
Traits of generative reproduction of investigated Ficaria verna and Ranunculus species. Values represent means of parameter ±SE; letters indicate differences between species according to statistical analysis for each parameter, separately. Based on chi-squared analysis, it can be only stated that clusters differ from each other.
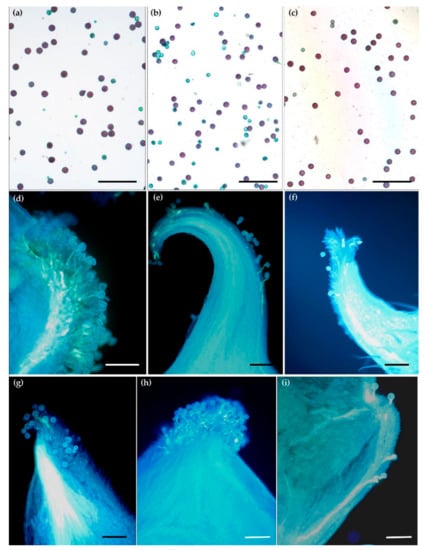
Figure 1.
Pollen grains’ viability and germination for Ranunculus species. Pollen grains’ viability for (a) R. illyricus, (b) Ficaria verna, (c) R. bulbosus after Alexander method staining: red—alive, green—dead. (d–i) Pollen grains’ and pollen tubes’ growth in fluorescent ultraviolet light after aniline blue staining; (d)—germinating pollen grains on stigma of F. verna, (e) R. lanuginosus, (f) R. auricomus, (g) R. illyricus, (h,i) R. bulbosus, bar = 200 μm.
The SEM-aided observation revealed differences in the morphology of pistils across the species studied in our research (Figure 2). The differences concerned the pistil shape and the presence of ovary hairs: in R. illyricus, the ovary was glabrous (Figure 2a,d), single long hairs were present at the base of the R. bulbosus ovary (Figure 2b,e), whereas in R. cassubicus, a hairy ovary was observed (Figure 2c,f). Distinct differences were also noticed on the surface covered with papillae (stigma). A straight pistil of R. illyricus was covered with papillae up to about one-third of its height (Figure 2d). In the case of R. bulbosus, papillae concentrated only around the top part of the pistil (Figure 2e), while R. cassubicus had papillae unilaterally covering the bent upper part of the pistil up to the ovary (Figure 2f).
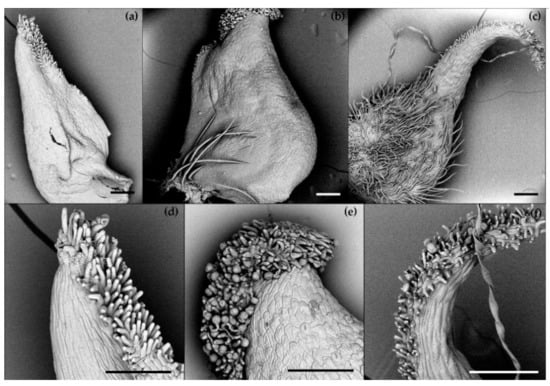
Figure 2.
Pistil morphology of Ranunculus species, SEM; (a,d)—R. illyricus, (b,e)—R. bulbosus, (c,f)—R. cassubicus; bar = 200 μm.
Despite the different dates of flowering across the species, both in the case of the natural sites and in the collection, the pollination (in the open-field conditions) was effective because the majority of the observed stigmas were covered with pollen (Table 4, Figure 1d–i). There were numerous germinating pollen grains observed on stigma of all the species. For the majority of the species (not in R. illyricus), a single pollen tube entering the ovary was also seen.

Table 4.
Pollination effectiveness and pollen-tube elongation in pistil tissues of investigated Ficaria verna and Ranunculus species.
3.2. Seeds’ Formation Efficiency, Their Viability and Ability to Germinate
The number of pistils per single flower varied across the species studied here (Table 3); extreme values were noted for two clonal species and ranged from 12 per flower for F. verna to 146 for R. illyricus. The species differed in terms of the effectiveness of fruit setting. The fruit set per flower estimated for R. bulbosus was 64%, while for R. illyricus it was only 11%. In this case, the clonal species were less effective than the other species, but also differed from each other. The highest viability of seeds was noted for R. illyricus and the lowest for F. verna. The species differed significantly in terms of the ability of seeds to germinate, with the best result observed for R. lanuginosus and R. bulbosus (Table 3, Figure 3). The species also responded in different ways to dormancy-breaking factors.
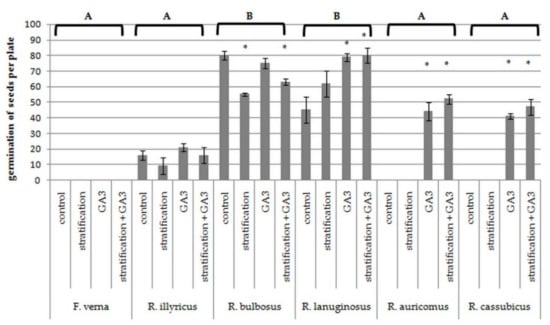
Figure 3.
Ability of seeds to germinate after exposure to low temperature and GA3 treatment. Letters indicate differences between species according to Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s test with α = 0.05. * indicate differences between each treatment and control according to U-Mann–Whitney test with α = 0.05 separately for each species.
Germination did not improve in the case of F. verna and R. illyricus, while for the germination of R. auricomus and R. cassubicus L., application of GA3 was crucial. GA3 also significantly improved germination of R. lanuginosus seeds. Low temperature decreased the germination ability of R. bulbosus (Figure 3). The combined action of the dormancy breakers did not improve germination parameters compared to the effect of either of the factors separately.
The species exhibited a variety of features, however, in order to decide if reproduction traits allow for distinguishing separate species groups, a cluster analysis was carried out based on pollen diameter and viability per sample, number of pistils per flower, efficiency of fruit set per flower, viability of seeds, and their ability to germinate per plate.
3.3. Cluster Analysis
Our cluster analysis formed four groups at 2.0 Euclidean distance. Cluster 1 with R. bulbosus and R. lanuginosus, taxa that reproduce only sexually, is characterized by the highest viability of pollen, highest ability of seeds to germinate, highest number of pistils per flower, highest efficiency of fruit set and high viability of seeds (Table 5, Figure 4). Cluster 2, comprising R. auricomus and R. cassubicus, is distinguished by the lowest pollen viability accompanied by a low ability of seeds to germinate and a medium number of pistils per flower. The clonal species belong to separate clusters. R. illyricus, which forms cluster 3, had the highest number of pistils per flower and the lowest efficiency of fruit set, and developed the most viable seeds, which germinated with difficulties. Cluster 4 with F. verna is characterized by high pollen viability, the lowest number of pistils per flower, and set seeds of low viability, which did not germinate.

Table 5.
Values of traits of generative reproduction in clusters (mean ± SE). Statistical test used is mentioned. Letters indicate differences between clusters according to statistical analysis for each parameter, separately. In the case of chi-squared analysis, it can be only stated that clusters differ from each other.
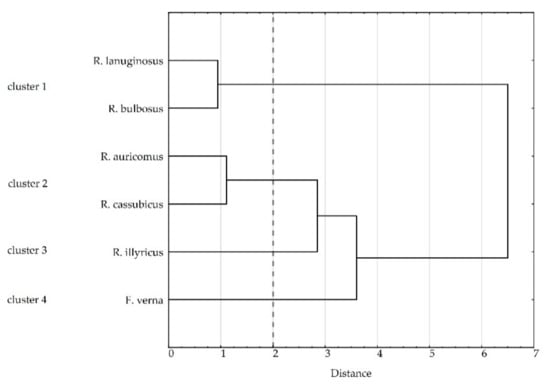
Figure 4.
Cluster analysis of species based on pollen viability and diameter, number of pistils per flower, efficiency of fruit set, viability and seed germination (Euclidean distance, Ward’s method). Dashed line marks cut-off point (distance 2) and separation into 4 clusters.
4. Discussion
A comparative analysis of traits affecting sexual reproduction was carried out for five Ranunculus and one Ficaria species, out of which two are clonal perennials with two reproduction modes. The hypothesis to be verified assumed that the clonal species of Ranunculus have a limited effectiveness of generative reproduction compared to nonclonal ones. Our results confirmed this hypothesis, and additionally, the cluster analysis revealed that the relationships were more complex than expected. As a result, four groups of species (clusters) differing in their efficiency of sexual reproduction were separated.
The separation of clonal species from nonclonal species was confirmed, however, each of the clonal species constituted a separate group characterized by a low efficiency of generative reproduction expressed in the number of seeds capable of germination. Limitations to this efficiency appeared at different stages of generative reproduction: in R. illyricus, as a result of the low efficiency of fruit setting, and in F. verna, mainly following the formation of nonviable seeds. It was reported by Perje [55] that the low efficiency of sexual reproduction of F. verna was due to low viability of pollen unable to germinate on the stigmas. However, our investigation showed that pollen of this species was viable, germinated on the stigma and entered the ovary, in agreement with the report by Wcisło and Pogan [32].
In both clonal species, vegetative reproduction dominates, which relates to high allocation of resources to the production of vegetative propagules. Although these two species develop underground tubers, the mode of vegetative reproduction is different. Our observations of the R. illyricus plants in the collection revealed that the mother cluster of bulbs develops descendant clusters of bulbs (ramets) at the end of underground rhizomes for a few consecutive years. The underground clusters of tubers of R. illyricus are dedicated to new progeny, while the underground tubers of F. verna serve as a resource storage ensuring survival of the mother plant. Propagating bulbs of this species are formed on aboveground shoots in the axils of leaves.
Among the nonclonal species, two sister groups were distinguished: the first group comprised R. lanuginosus and R. bulbosus, whereas the second group included R. auricomus and R. cassubicus. This division is very interesting, because among the nonclonal species, a group of apomictic species has been separated [14,16] which were characterized by the lowest pollen viability accompanied by a low ability of seeds to germinate and a medium number of pistils per flower.
Our cluster analysis suggests that apomictic species are closer to the group of clonal species than sexual ones. The common feature of apomictic and clonal species is uniparental offspring developing without fertilization, copying favorable genotypes. However, in the case of apomixis, this process takes less input energy: resource allocation is similar to that of sexually reproducing species with genetically diversified progeny. Although facultative apomixis restricts recombination and reduces the evolutionary potential of the species, it maintains the fertility of individuals and is advantageous for colonization [56]. Apomixis could also support the fitness of a population under unfavorable environmental conditions [57].
Interestingly, the four clusters separated here coincide with the sections described within the genus Ranunculus by Tutin et al. [6] (Table 1) based on morphological traits. Similarly, studies [58] on the morphological and genetic diversity of apomictic and sexual Cenchrus species have shown that the apomictic species were clustered together separately from the sexual species. Moreover, the genetic distinctiveness was also evident from the assessed morphological features.
4.1. Seed Germination
The seed germination behavior is one of crucial traits in the life history of the plant species. According to the data available, different species of buttercups have different requirements for treatments breaking dormancy and stimulating germination [30,34,35,36]. It was shown [37] that the use of a low temperature is the most effective way to interrupt dormancy in species from the Ranunculaceae family growing in temperate climate and mountain areas. We have presented two groups of species that were distinguished in terms of the ability of seeds to germinate and their reaction to the applied factors breaking dormancy (Figure 3). One group included clonal and nonclonal facultative apomictic species, the seeds of which germinated worse than the seeds of sexual species. Neither GA3 nor low-temperature treatments improved the germination abilities of the clonal species, while gibberellin significantly increased the germination ability of the apomictic species.
Gibberellin, a natural phytohormone, is known for its ability to reduce seed dormancy time and successfully stimulate the seed germination of other plants. Gibberellin is an antagonist of abscisic acid, and both hormones are crucial for germination control [59,60,61]. Their proportions, and hence the seed germination ability, may be considerably modified by external factors, such as temperature [62]. Consequently, low- or high-temperature treatments are often used to stimulate germination [63]. Low temperature is the most typical factor controlling the physiological dormancy of seeds of plants in temperate climates [60]. Prechilling has been shown on numerous occasions to be effective in breaking seed dormancy for such species [64,65,66].
The seeds of the remaining nonclonal species in our experiment were characterized by a much greater ability to germinate, although the response of these species to the factors used was different. R. lanuginosus reacted like apomictic species, and GA3 was beneficial for seed germination. The reaction of xerothermic R. bulbosus seeds to stratification, which negatively affected the ability to germinate, was thought-provoking. Most likely, the plant was brought into secondary dormancy due to low temperature, a phenomenon already described for annual winter [67], some xerothermic [68,69] or desert species [70]. This mechanism may be important in preventing early germination of seeds in summer or early fall, when the conditions are not suitable for the development of new plant generations.
4.2. Pollen-Tube Development
Microscopic observations confirmed that there had been no restrictions on pollination both in the flowers from natural sites and from the collection (Figure 1d–i). Most of the pistils were pollinated in all the species under investigation and pollen germinated on stigmas profusely.
In all the species except Ranunculus illyricus, there were bundles of pollen tubes growing from the stigma towards the ovary where their growth was inhibited. Only for R. bulbosus was it possible to record a pollen tube entering the ovule (Table 4). In Ranunculus, which possess one ovule per carpel, a single pollen tube is sufficient for fertilization and fruit set. Our results corroborate those of Rendle and Murray [11] and Beruto et al. [20], who in the case of for Ranunculus also described large numbers of pollen grains capable of germinating, yet the growth of all but one pollen tube ceased and only that one tube reached the micropyle.
In the case of clonal Ficaria verna, for more than half of the specimens analyzed, numerous pollen tubes entering the ovary were observed. This contrasts with the results of Wcisło and Pogan [32] for this species, who reported only a few cases of single pollen tubes entering the ovary and only 7% of fruit set efficiency. The authors stated that the low efficiency of fruit set was a result of retarded growth of pollen tubes, and in consequence, a lack of fertilization in the majority of ovules. Our observations revealed a normal elongation of pollen tubes of F. verna corresponding to 25% of fruit set, but seed viability was only 7%. This means there must have been disturbances during the embryo development.
Different results were obtained for Ranunculus illyricus, in which numerous pollen grains remained ungerminated and no pollen tube entering the ovary was observed. In this case, mechanisms inhibiting pollen-tube growth probably appeared in the early stages of its growth. The relatively high number of pistils with ungerminated pollen grains of R. illyricus (54.5%) could also be a result of low viability of pollen (Table 3).
Ranunculus illyricus, which is a rare and endangered species in many countries, deserves special attention. Active conservation measures should take into account the fact that the fruit set of R. illyricus is low in ex situ conditions, perhaps owing to geitonogamy. It cannot be ruled out that this phenomenon also affects the wild population, but the biology of R. illyricus has not yet been investigated.
5. Conclusions
Our comparative analysis of reproductive traits of five Ranunulus species and Ficaria verna allowed for the distinguishing of four clusters of species, reproducing in sexual (cluster 1), clonal (cluster 2 and 3) and apomictic (cluster 4) modes. The clonal species, which belong to two separate clusters, were characterized by lower efficiency of sexual reproduction compared with the nonclonal species. However, within the nonclonal species, an additional group of apomictic species was separated. The new divisional clusters coincide with classical systematic sections identified within the genus Ranunculus by Tutin based on morphological criteria.
The reproductive efficiency, expressed as the development of viable seeds able to germinate, as well as the susceptibility of seeds to dormancy-breaking factors, varied across the species. Gibberellin treatments improved seed germination in contrast to low temperature, which inhibited germination of R. bulbosus seeds.
Great potential for sexual reproduction expressed by the number of pistils in Ranunculus illyricus flowers was limited by the relatively low viability of pollen and its poor performance in the style. The fruit set efficiency in R. illyricus was low, however, seeds were viable. It is important that methods of dormancy breaking should be developed to support future conservation efforts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.S., B.N.; methodology, D.K., E.S.; validation, E.S., D.K., B.N.; formal analysis, A.K., D.K.; investigation, D.K., E.S., B.N.; resources, K.T.; data curation, D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, D.K.; writing—review and editing, E.S., B.N., D.K., A.K., A.S.-S.; visualization, E.S., D.K.; supervision, E.S., B.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Poland (SUB/2021-050012-D011) to support the maintenance and development of the research potential of the Department of Botany, Physiology and Plant Protection.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank A. Kalisz for support in data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rautiainen, P.; Koivula, K.; Hyvärinen, M. The effect of within-genet and between-genet competition on sexual reproduction and vegetative spread in Potentilla anserina ssp. egedii. J. Ecol. 2004, 92, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Kim, J.G. The optimal balance between sexual and asexual reproduction in variable environments: A systematic review. J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 40, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Asexual and sexual reproductive strategies in clonal plants. Front. Biol. China 2007, 2, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, C.G.; Dorken, M.E.; Barrett, S.C. Ecological and evolutionary consequences of sexual and clonal reproduction in aquatic plants. Aquat. Bot. 2016, 135, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M. Angiospermae. Ordnung Ranunculales. Fam. Ranunculaceae. II. Systematic Part. In Die Natürliche Pflanzenfamilien, 2nd ed.; Hiepko, P., Ed.; Duncker & Humblot: Berlin, Germany, 1995; pp. 223–519. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Tutin, T.G.; Heywood, V.H.; Burges, N.A.; Valentine, D.H.; Walters, S.M.; Webb, D.A. Flora Europaea, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, M. Ranunculaceae. In The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants; Kubitzki, K., Rohwer, J.G., Bittrich, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 563–583. [Google Scholar]
- Sell, P.D. Ranunculus ficaria L. sensu lato. Watsonia 1994, 20, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K.; Markham, B. Biological flora of the British Isles—Ranunculus ficaria L. J. Ecol. 1978, 66, 1011–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.M.; Hiscock, S.J. Evolution and Phylogeny of Self-Incompatibility Systems in Angiosperms. In Self-Incompatibility in Flowering Plants. Evolution, Diversity, and Mechanisms; Franklin-Tong, V.E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidenberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendle, H.; Murray, B.G. Breeding systems and pollen tube behaviour in compatible and incompatible crosses in New Zealand species of Ranunculus L. N. Z. J. Bot. 1988, 26, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarukhán, J.; Harper, J.L. Studies on plant demography: Ranunculus repens L., R. bulbosus L. and R. acris L.: I. Population flux and survivorship. J. Ecol. 1974, 61, 675–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosendai, A.C.; Hörandl, E. Cytotype stability, facultative apomixis and geographical parthenogenesis in Ranunculus kuepferi (Ranunculaceae). Ann. Bot. 2010, 105, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hörandl, E. Evolutionary implications of self-compatibility and reproductive fitness in the apomictic Ranunculus auricomus polyploid complex (Ranunculaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 2008, 169, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörandl, E.; Cosendai, A.C.; Temsch, E.M. Understanding the geographic distributions of apomictic plants: A case for a pluralistic approach. Plant Ecol. Divers. 2008, 1, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izmaiłow, R. Reproductive strategy in the Ranunculus auricomus complex (Ranunculaceae). Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 1996, 65, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schinkel, C.C.; Kirchheimer, B.; Dullinger, S.; Geelen, D.; De Storme, N.; Hörandl, E. Pathways to polyploidy: Indications of a female triploid bridge in the alpine species Ranunculus kuepferi (Ranunculaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2017, 303, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.M. Breeding systems of Australian Ranunculus in the alpine region. Nord. J. Bot. 1997, 17, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PLADIAS. Database of the Czech Flora and Vegetation. Available online: www.pladias.cz (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Beruto, M.; Rabaglio, M.; Viglione, S.; Van Labeke, M.C.; Dhooghe, E. Ranunculus. In Ornamental Crops. Handbook of Plant Breeding; Van Huylenbroeck, J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11, pp. 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.G.; Webb, C.J. The avoidance of interference between the presentation of pollen and stigmas in angiosperms I. Dichogamy. N. Z. J. Bot. 1986, 24, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, M.L.; Galen, C. Consequences of flower heliotropism for reproduction in an alpine buttercup (Ranunculus adoneus). Oecologia 1989, 78, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totland, Ø.; Alatalo, J.M. Effects of temperature and date of snowmelt on growth, reproduction, and flowering phenology in the arctic/alpine herb, Ranunculus glacialis. Oecologia 2002, 133, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Steinacher, G.; Landinig, U. Ranunculus glacialis L.: Successful reproduction at the altitudinal limits of higher plant life. Protoplasma 2010, 243, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galen, C.; Stanton, M.L. Sunny-side up: Flower heliotropism as a source of parental environmental effects on pollen quality and performance in the snow buttercup, Ranunculus adoneus (Ranunculaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2003, 90, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybka, V.; Duchoslav, M. Influence of water depth on growth and reproduction of Ranunculus lingua. Belg. J. Bot. 2007, 140, 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hörandl, E.; Dobeš, C.; Lambrou, M. Chromosomen-und Pollenuntersuchungen an österreichischen Arten des apomiktischen Ranunculus auricomus-Komplexes. Bot. Helv. 1997, 107, 195–209. [Google Scholar]
- Kallajxhiu, N.; Kapidani, G.; Naqellari, P.; Pupuleku, B.; Turku, S.; Gjeta, E. Palynological comparison of pollen grains of Ranunculus psilostachys with those of Ranunculus bulbosum and Ranunculus sardous. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2015, 4, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, K.; Urfan, M.; Tiwari, P. In Vitro Pollen Germination, Tube Growth and Pollen Viability of Some Angiospermic Taxa from Srinagar Valley (Garhwal Himalya). Int. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. Res. 2017, 4, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Carta, A.; Bedini, G.; Foggi, B.; Probert, R.J. Laboratory germination and seed bank storage of Ranunculus peltatus subsp. baudotii seed from the Tuscan Archipelago. Seed Sci. Technol. 2012, 40, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomizu, T.; Niimi, Y.; Wanatabe, E. Embryo development and seed germination of Hepatica nobilis Schreber var. japonica as affected by temperature after sowing. Sci. Hortic. 2004, 99, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wcisło, H.; Pogan, E. Cytoembryological aspects of reduced seed setting in Ranunculus ficaria L. subsp. bulbifer (Marsden-Jones) Lawalrée. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 1981, 50, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Tiwari, T.N.; Prasad, S.R. Seed dormancy in ornamental plants: A review. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 86, 580–592. [Google Scholar]
- Young, J.A.; Martens, E.; West, N.E. Germination of buttercup seeds. J. Range Manag. 1992, 45, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pérez-García, F. Effect of cryopreservation, gibberellic acid and mechanical scarification on the seed germination of eight endemic species from Canary Islands. Seed Sci. Technol. 2008, 36, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Khosh-Khui, M. Presence of double dormancy in Wild Persian Buttercup (Ranunculus asiaticus L.). Int. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 2, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Srivastava, N.; Sharma, V.; Dobriyal, A.K.; Kamal, B.; Gupta, S.; Jadon, V.S. Influence of pre-sowing treatments on in vitro seed germination of Ativisha (Aconitum heterophyllum Wall) of Uttarakhand. Biotechnology 2011, 10, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grulich, V. The Red List of vascular plants of the Czech Republic. Příroda 2017, 35, 75–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kaźmierczakowa, R.; Towpasz, K. Ranunculus illyricus L.—Jaskier illiryjski. In Polish Red Data Book of Plants—Pteridophytes and Flowering Plants, 3rd ed.; Kaźmierczakowa, R., Zarzycki, K., Mirek, Z., Eds.; Polish Academy of Sciences, Institute of Nature Conservation: Cracow, Poland, 2014; pp. 196–197. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Turis, P.; Kliment, J.; Feráková, V.; Dítě, D.; Eliáš, P.; Hrivnák, R.; Koštál, J.; Šuvada, R.; Mráz, P.; Bernátová, D. Red List of vascular plants of the Carpathian part of Slovakia. Thaiszia J. Bot. 2014, 24, 35–87. [Google Scholar]
- Erikson, J. Zür Biologie und Morphologie von Ranunculus illyricus. Bot. Zent. 1897, 72, 193. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Troll, W. Vergleichende Morphologie der Höheren Pflanzen; Verlag von Gebrüder Bortraeger: Berlin-Zehlendorf, Germany, 1943; pp. 2646–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Herben, T.; Tackenberg, O.; Klimešová, J. Reproduction by seed and clonality in plants: Correlated syndromes or independent strategies? J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 1696–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izmaiłow, R. Cytogenetic studies in the apomictic species Ranunculus cassubicus L. Acta Biol. Crac. Ser. Bot. 1970, 13, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Izmaiłow, R. Cyto-embryological studies in experimental hybrids of the apomictic species Ranunculus cassubicus L. Acta Biol. Crac. Ser. Bot. 1973, 16, 99–120. [Google Scholar]
- Paun, O.; Stuessy, T.F.; Hörandl, E. The role of hybridization, polyploidization and glaciation in the origin and evolution of the apomictic Ranunculus cassubicus complex. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towpasz, K. Ficaria verna Huds. ssp. calthifolia (Rchb.) Vel. in Poland. Fragm. Flor. Geobot Pol. 1971, 17, 215–219. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dembicz, J.; Kozub, Ł. Confirmation of Ranunculus illyricus (Ranunculaceae) locality in Skorocice (Małopolska Upland). Fragm. Flor. Geobot Pol. 2015, 22, 381–384. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Towpasz, K.; Cwener, A. New locality of Ranunculus illyricus (Ranunculaceae) in Poland. Fragm. Flor. Geobot Pol. 2002, 9, 370–372. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberg, H. Zeigerwerte der Gefässpflanzen Mitteleuropas. Scr. Geobot. 1974, 9, 1–166. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, M. P. Differential staining of aborted and non-aborted pollen. Stain Technol. 1969, 44, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.W. Staining and observing pollen tubes by means of fluorescence. Stain Technol. 1959, 34, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J. Tetrazolium Testing Handbook: Contribution No. 29 to the Handbook on Seed Testing, Revised 2000; AOSA: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- International Seed Testing Association (ISTA). International rules for seed testing. Seed Sci. Technol. 1999, 27, 1–333. [Google Scholar]
- Perje, A.M. Some causes of variation in Ranunculus ficaria L. Ark. Bot. Ser. 1952, 2, 251–264. [Google Scholar]
- Hörandl, E. The evolution of self-fertility in apomictic plants. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2010, 23, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syngelaki, E.; Daubert, M.; Klatt, S.; Hörandl, E. Phenotypic responses, reproduction mode and epigenetic patterns under temperature treatments in the Alpine plant species Ranunculus kuepferi (Ranunculaceae). Biology 2020, 9, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Saxena, S.; Rai, A.; Radhakrishna, A.; Kaushal, P. Ecological, genetic, and reproductive features of Cenchrus species indicate evolutionary superiority of apomixis under environmental stresses. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skubacz, A.; Daszkowska-Golec, A. Seed dormancy: The complex process regulated by abscisic acid, gibberellins, and other phytohormones that makes seed germination work. In Phytohormones—Signaling Mechanisms and Crosstalk in Plant Development and Stress Responses; El-Elsawi, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfield, S. Seed dormancy and germination. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R874–R878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Cheng, S.; Chen, Z.; Nie, G.; Xu, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Ye, J. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealing the potential mechanism of seed germination stimulated by exogenous gibberellin in Fraxinus hupehensis. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izydorczyk, C.; Nguyen, T.N.; Jo, S.; Son, S.; Tuan, P.A.; Ayele, B.T. Spatiotemporal modulation of abscisic acid and gibberellin metabolism and signalling mediates the effects of suboptimal and supraoptimal temperatures on seed germination in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, H.; Kirmizi, S.; Güleryüz, G.; Sakar, F. Germination requirements of Androsace villosa L. (Primulaceae). Acta Biol. Crac. Ser. Bot. 2011, 53, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadzadeh, S.; Zaefarian, F.; Rezvani, M. Effects of some chemical factors, prechilling treatments and interactions on the seed dormancy-breaking of two Papaver species. Weed Biol. Manag. 2015, 15, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, V.; Zaefarian, F.; Rezvani, M. Effect of pre-chilling and environmental factors on breaking seed dormancy and germination of three foxtail species. Acta Agric. Slov. 2015, 105, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, H.; Saadatian, B.; Aliverdi, A. Geographical variation in breaking the seed dormancy of Persian cumin (Carum carvi L.) ecotypes and their physiological responses to salinity and drought stresses. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 124, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekenian, M.R.; Willemsen, R.W. Germination characteristics of Raphanus raphanistrum. I. Laboratory studies. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1975, 102, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C. Delayed germination in seeds of Phacelia dubia var. dubia. Can. J. Bot. 1973, 51, 2481–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, K.K.; Allen, P.S.; Meyer, S.E. Secondary dormancy induction and release in Bromus tectorum seeds: The role of temperature, water potential and hydrothermal time. Seed Sci. Res. 2017, 27, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C. Ecological life cycle of Helenium amarum in central Tennessee. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1973, 100, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).