Simple Summary
Pelodiscus sinensis is an important aquatic economic species in China with sexual dimorphism. All-male breeding is becoming a research hotspot. Here, comparative transcriptome analyses of female, male, and pseudo-female gonads were performed. We found that the differences between males and pseudo-females were mainly related to steroid hormone synthesis at the transcriptome level. When it comes to the sox family genes, sox3 may have a role in the process of sex reversal from male to pseudo-female, when sox8 and sox9 were inhibited by exogenous estrogen.
Abstract
The Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis shows obvious sexual dimorphism. The economic and nutrition value of male individuals are significantly higher than those of female individuals. Pseudo-females which are base to all-male breeding have been obtained by estrogen induction, while the gene function and molecular mechanism of sex reversal remain unclear in P. sinensis. Here, comparative transcriptome analyses of female, male, and pseudo-female gonads were performed, and 14,430 genes differentially expressed were identified in the pairwise comparison of three groups. GO and KEGG analyses were performed on the differentially expressed genes (DEGs), which mainly concentrated on steroid hormone synthesis. Furthermore, the results of gonadal transcriptome analysis revealed that 10 sex-related sox genes were differentially expressed in males vs. female, male vs. pseudo-female, and female vs. pseudo-female. Through the differential expression analysis of these 10 sox genes in mature gonads, six sox genes related to sex reversal were further screened. The molecular mechanism of the six sox genes in the embryo were analyzed during sex reversal after E2 treatment. In mature gonads, some sox family genes, such as sox9 sox12, and sox30 were highly expressed in the testis, while sox1, sox3, sox6, sox11, and sox17 were lowly expressed. In the male embryos, exogenous estrogen can activate the expression of sox3 and inhibit the expression of sox8, sox9, and sox11. In summary, sox3 may have a role in the process of sex reversal from male to pseudo-female, when sox8 and sox9 are inhibited. Sox family genes affect both female and male pathways in the process of sex reversal, which provides a new insight for the all-male breeding of the Chinese soft-shelled turtle.
1. Introduction
Pelodiscus sinensis, known as the Chinese soft-shelled turtle, is widely distributed in many freshwater areas, such as rivers and lakes in China, Korea, Russia, Thailand, Vietnam, and Japan [1]. This turtle shows obvious sexual dimorphism: males have a larger size, faster growth rate, and wider and thicker calipash than females. Furthermore, the male juvenile is more popular for aquaculture practices because it is priced higher than the female juvenile. Therefore, all-male breeding of P. sinensis by using sex control approaches has become important [2].
In aquaculture, unisexual offspring cannot be obtained by controlling the incubation temperature during the embryo development of P. sinensis. In addition, some studies have identified ZZ/ZW micro-sex chromosomes in P. sinensis, which is significantly different from the typical temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) in Trachemys scripta [3,4,5]. Sex-specific markers have been developed to accurately identify the genetic sex of a turtle by using RAD-Seq technology [1]. These studies suggest that genetic sex determination can be used for P. sinensis. Pseudo-female turtles (∆ZZ) with a female phenotype and male genotype can be obtained by using estradiol (E2) to induce male embryos (ZZ) in the sex determination stage to differentiate into physiological females [6]. The pseudo-female turtle is used as the female parent (∆ZZ) and the male turtle is used as the male parent (ZZ) when they reach sexual maturity. All their offspring should be males (ZZ). Therefore, it is important to study the sex determination mechanism of P. sinensis for the all-male aquaculture of this species.
Unlike the typical TSD mechanism of turtles such as T. scripta, the sex determination mechanism of P. sinensis is a more complex process that involves genes and hormones [7,8]. Estrogen is a gonadal steroid hormone that plays a key role in female sex determination in vertebrates [9]. E2 can induce the expression of cyp19a1 in an embryo, promote ovary development, and even induce the sex reversal of P. sinensis [10]. Some sex-specific genes commonly found in other species, such as dmrt1 [11,12], cyp19a1 [13], foxl2 [14], and rspo1 [6,15], have been reported in the preliminary studies of P. sinensis. These genes were not only directly involved in the sex determination of P. sinensis but also affected by exogenous E2, which was significantly changed during the sex determination period [6,10,13,14,16]. These studies have not formed a systematic molecular mechanism, and further analysis will provide a new understanding for the sex differentiation and reversal of P. sinensis.
A series of SRY-related high-mobility group (HMG)-box (SOX) transcription factors with an HMG box DNA-binding domain are called sox family genes, which play important roles in embryonic development, neurogenesis, and other aspects [17]. Sry was the first sox transcription factor to be identified, and it is involved in male sex determination in mammals. When sry is absent, male XY mice develop into females [18]. Sox9 was specifically expressed in the early stage of gonadal differentiation in male P. sinensis embryos, and it is an important gene involved in male sex determination in vertebrates [19]. The loss of sox9 resulted in the reversal from male to female in mice [20]. In vertebrates, sox3 inhibited the expression of sox9 in the ovaries and promoted ovary development and even directly activated the transcription of cyp19 [21,22,23]. In addition, sry can inhibit the expression of sox3 and promote the expression of sox9, ensuring that mice can be differentiated into males [24]. Other sox genes are also involved in sex differentiation and gonadal development [25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. To date, the interaction between sex-related sox genes and estrogen in the sex differentiation and reversal of P. sinensis has not yet been elucidated.
With the rapid development of omics research, high-throughput and high-sensitivity second-generation transcriptome sequencing technologies have been widely used to breed aquaculture animals, such as Cynoglossus semilaevis [32] and Oreochromis niloticus [33]. Currently, transcriptome studies on P. sinensis mainly focus on growth and immunity [34,35], and there is a lack of transcriptome studies on gonad differentiation and sex reversal. In this study, firstly, a comparative transcriptome analysis was performed using the gonadal tissues of E2-induced pseudo-female and female and male P. sinensis. The expression profiles of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the gonads of P. sinensis were established. Candidate genes and signaling pathways related to gonad differentiation and development were analyzed. Then, the differential expressions of significantly different sox family genes in pseudo-female, female, and male gonads were analyzed. The sox genes which may be involved in gonad development and function maintenance during the sex reversal were further screened and their expression patterns were analyzed after E2 treatment. These results provided transcriptome resources for analyzing the molecular mechanism of gonad differentiation and sex reversal of P. sinensis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
The procedures in this study were performed according to the Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection of Laboratory Animal Centre of the Yangtze River Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (Wuhan, China; ID Number: 20200118).
2.2. Sample Collection
Two-year-old P. sinensis, 3 males (mean weight 1075 ± 126 g, recorded as M-1, M-2, and M-3), 3 females (mean weight 816 ± 72 g, recorded as F-1, F-2, and F-3), and 3 pseudo-females (mean weight 929 ± 77g, female phenotype and male genotype, recorded as PF-1, PF-2, and PF-3), were collected from Anhui Xijia Agricultural Development Co. Ltd. (Bengbu, Anhui Province, China). The pseudo-female turtles were obtained by treating the eggs with 30 mg/mL E2 at the stage 12 of embryo development which was the critical period of sex differentiation [36]. The biological sex and genetic sex of juvenile turtles were identified by phenotypic and sex-specific markers, respectively after they were cultured in greenhouse for 8 months [37]. The treated embryos at gonadal differentiation period (stage 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17 of embryonic development) were collected [36], and the sex of the embryos was identified using sex-specific markers. [1]. All turtles were anesthetized with 0.05% MS-222 (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), and the gonad tissues were collected and stored in liquid nitrogen.
2.3. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation and Transcriptome Sequencing
The total RNA was extracted from the gonads by using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The RNA quality was monitored using 1.5% agarose gels. The RNA purity was checked with the NanoPhotometer® spectrophotometer (Implen, Westlake Village, CA, USA). The RNA integrity was tested with the RNA Nano 6000 Assay Kit of the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Then, RNA concentration was measured using the Qubit® RNA Assay Kit in Qubit® 3.0 Fluorometer (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The NEBNext® UltraTM RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA) was used to generate the sequencing libraries, and the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 System was used to assess library quality. The libraries were sequenced on an Illumina Hiseq X Ten platform, and 150 bp paired-end reads were obtained. The raw reads were filtered to remove the low-quality reads and reads with the adapter and N content more than 10% and obtain clean reads. Then, FastQC v1.2 was used to evaluate the quality of the sequencing data.
2.4. Identification of the Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
The clean reads were aligned to the P. sinensis reference genome (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/?term=Pelodiscus+sinensis, PRJNA221645, Pelsin_1.0) by using the software Tophat2 v2.1.1 [38] and mapped to the coding sequences with bowtie2 v2.2.2 [39]. The gene and transcript expression levels were calculated using fragments per kilobase of transcripts per million bases [40] values in RSEM with default settings [41]. By using fragments per kilobase per million bases (FPKM) transformation, the paired-end reads from the same fragment were used as a fragment to obtain gene and transcription levels. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to detect the similarity detection of three biological repeats. The DEGs were identified using R package DEseq2 [42], with false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 and log2FC (fold change (condition 2/condition 1) > 1 or log2FC < −1. The upregulated DEGs showed FDR < 0.05 and log2FC > 1, and the downregulated DEGs, FDR < 0.05 and log2FC < −1.
2.5. GO and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
GOseq v1.22 was used for the GO enrichment analysis, which is based on the algorithm of hypergeometric distribution. The GO term of FDR < 0.05 was considered as a significantly enriched term. The KEGG enrichment analysis was used as a hypergeometric test to identify significantly enriched pathways relative to the annotated genes. KOBAS v3.0 was used for the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. A pathway with FDR < 0.05 was defined as significantly enriched with DEGs.
2.6. Validation of the Transcriptome with RT-qPCR
To verify the accuracy of the transcriptomic data, 13 DEGs related to gonadal differentiation and development were randomly selected for RT-qPCR. All the selected DEGs showed significantly different expressions in different samples. Gapdh was used as the endogenous reference gene, and RT-qPCR primers for the selected DEGs were designed using Primer Premier 5 (Table S1). The HiScript® III 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (+gDNA wiper) (Vazyme, Wuhan, China) was used to synthesize the template cDNA. The ChamQTM Universal SYBR® qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme, Wuhan, China) was used to establish the reaction system (total volume, 20 μL): 10 μL of 2 × Master Mix, 0.4 μL of each primer (total, 10 μM), 1 μL of template cDNA, and 8.2 μL of RNase-free ddH2O. The reaction was performed using the QuantStudio® 5 Real-Time PCR Instrument (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and the qPCR program was as follows: 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 34 s. The relative gene expression levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method [43], and log2 (fold change) was used for comparison with the RNA-seq data. The Duncan method of SPSS 22 was used for the significance analysis.
2.7. Expression Patterns of Sox Family Genes during Sex Reversal
To our knowledge, sox family genes play important roles in sex differentiation. Ten sex-related sox family genes were screened from the transcriptomic data on the basis of p < 0.05 and log2FC > 1 or log2FC < −1 to analyze their molecular functions in sex reversal. Furthermore, the expression patterns of the identified genes were analyzed in the male, female, and pseudo-female gonads. Next, six sox genes with significantly different expressions between pseudo-female and female or male were screened, and qPCR was used to detect the expression levels of the selected genes during E2-induced embryonic sex reversal.
3. Results
3.1. Quality Assessment of the Sequencing Data
The study was conducted according to the experimental process (Figure 1A). Transcriptome sequencing was performed using the gonads of the female (F), male (M), and pseudo-female (PF) of P. sinensis (Table 1). The number of clean reads in all samples ranged from 42,130,694 to 50,909,630. The GC content of each sample was between 48% and 51%. Q30 bases were more than 92%, indicating high sequencing quality. The clean reads were aligned to the reference genome of P. sinensis, and the results showed that 67.34–72.69% of the clean reads were successfully mapped (Table 2). The similarity between the three biological replicates was tested by principal component analysis, and the results showed good similarity between the samples (Figure 1B). These results showed that the sequencing data can be further analyzed.
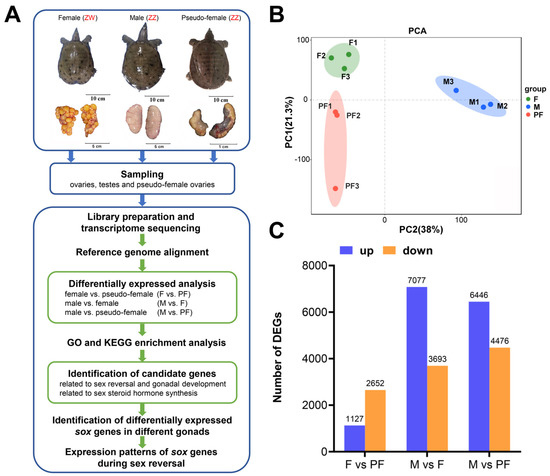
Figure 1.
Experimental design and data analysis. (A) Diagram of the experiment. (B) Principal component analysis between three sets of data. (C) The number of DEGs in the three comparisons of P. sinensis. Up-regulated DEGs (blue), and down-regulated DEGs (orange) are presented by a histogram. Filter threshold is FDR < 0.05, log2FoldChange > 1 or log2FC < −1.

Table 1.
Summary of the sequencing data quality.

Table 2.
Summary of the clean reads mapped to the reference genome.
3.2. Analysis of DEGs
The pairwise comparisons of F and PF, M and F, and M and PF were used to identify the DEGs. Genes with |log2FC| ≥ 1 and FDR < 0.05 were determined to be DEGs. In the present study, a total of 14,430 DEGs were obtained from the three comparisons after filtration. In F vs. PF, 1127 upregulated DEGs and 2652 downregulated DEGs were identified in the female (Figure 1C). According to the results of M vs. F, 7077 DEGs were upregulated in the male and 3693 DEGs were upregulated in the female. When compared with PF, M showed 6446 upregulated and 4476 downregulated DEGs. Of the 14,430 DEGs, 3017 and 975 sex different genes were specifically expressed in the males and females. In addition, 147 genes expressed in only the pseudo-female but not in both female and male were screened (Table S2).
3.3. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
To investigate the potential functions of genes in P. sinensis, the DEGs were annotated in the GO database. In F vs. PF, 55, 29, and 41 GO terms were significantly enriched in biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF), respectively. In M vs. F, 63, 46, and 74 GO terms were significantly enriched in BP, CC, and MF, respectively. In M vs. PF, 86, 43, and 57 GO terms were significantly enriched in BP, CC, and MF, respectively (Table S3). The significantly enriched GO terms related to sexual reversal can be found in F vs. PF and M vs. PF, of which the DEGs enriched in BP were mainly associated with metabolism and cell cycle, such as metabolic process (GO: 0008152), primary metabolic process (GO: 0044238), and DNA replication (GO: 0006260) (Figure 2). On the other hand, reproduction (GO: 0000003), reproductive process (GO: 0022414), and other reproductive activities were significantly enriched between males and females (Figure S1). The three groups were all significantly enriched in terms related to chromosome replication, catalytic activity, and molecular binding.
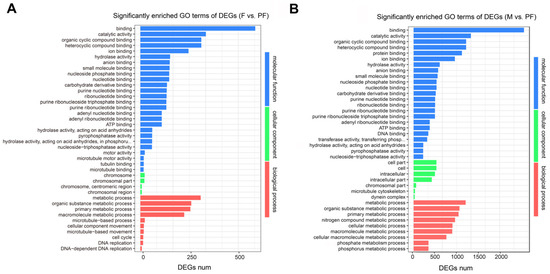
Figure 2.
Significantly enriched GO terms of DEGs comparison among the groups. (A) F vs. PF. (B) M vs. PF. Statistical significance GO terms were determined based on FDR < 0.05. The x-axis indicates the number of genes, and the y-axis indicates the second-level GO term.
KEGG enrichment analysis was performed to reveal the functional characteristics of the DEGs. In this study, a total of 340 signaling pathways were found, and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis (ko00940) was only significantly enriched between males and females. Indole alkaloid biosynthesis (ko00901) and betalain biosynthesis (ko00965) were only enriched between males and pseudo-females (Table S4). In F vs. PF, 1652 DEGs were mainly involved in cell cycle (ko04110), cell cycle—yeast (ko04111), and meiotic—yeast (ko04113) (Figure 3A). In M vs. PF, 3469 DEGs were observed in 335 signaling pathways, and gap junction (ko04540), phosphatidylinositol signaling system (ko04070), and purine metabolism (ko00230) were the most prominent (Figure 3B). Furthermore, most DEGs were enriched in cell cycle (ko04110), cell cyclic–yeast (ko04111), and oocyte meiosis (ko04114) in M vs. F (Figure S2). Among these pathways, those involved in physiological activities, such as cell cycle (ko04110) and purine metabolism (ko00230), were significantly enriched. However, great differences existed in the pathways involved in the synthesis and metabolism of steroid hormones between males and pseudo-females. Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 (ko00980), drug metabolism–cytochrome P450 (ko00982), and other steroid metabolic pathways were significantly enriched in the pseudo-females. Reproductive-related pathways such as oocyte meiosis (ko04114), meiosis–yeast (ko04113), and progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation (ko04914) were significantly enriched in the males and females.
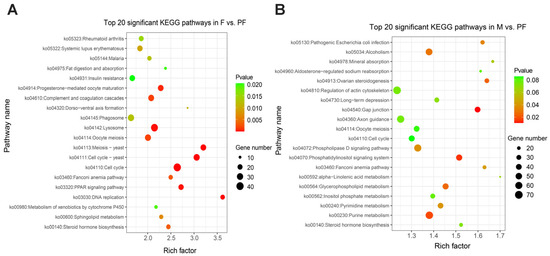
Figure 3.
Top 20 KEGG enrichment significant pathways. (A) Female vs. Pseudo-female. (B) Male vs. Pseudo-female. Rich factor is the ratio of DEGs and back genes in the pathway, the closer p value is to zero, the more significant is the enrichment.
3.4. Screening of Candidate DEGs Related to Sex Reversal and Gonadal Development
In this study, sex-related GO terms and KEGG signaling pathways were screened out, e.g., meiotic cell cycle (GO: 0051321), sexual reproduction (GO: 0019953), steroid hormone biosynthesis (ko00140), ovarian steroidogenesis (ko04913), and progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation (ko04914) (Table S5). They were mainly related to reproductive activities, such as steroid hormone synthesis, gonadal development, oocyte maturation, gametogenesis, and binding. Twenty-eight candidate DEGs involved in gonadal development and sex reversal were mainly screened from steroid synthesis and gonadal development pathways and genes significantly expressed between pseudo-females and common sex types (Table 3). Some genes, such as corticosteroid 11-β-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 (hsd11b2) and 17-β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 7 (hsd17b7), were differentially expressed in steroid hormone biosynthesis. Some genes showed sex-specific expression patterns. Foxl2, fgf8, fgf9, bmp15, and gdf9 were highly expressed in the pseudo-females, and dmrt1, klhl10, theg, and fam71d were specifically expressed in the males. Moreover, Genes (wnt1, wnt2, rspo1, and rspo2) involved in wnt signaling pathway (ko04310) were highly expressed in the ovaries. Some sox family genes (sox1, sox2, sox3, sox11, sox12, and sox17) were highly expressed in the pseudo-female ovary, but the expression of sox30 was higher in the testis. Among them, sox17 was enriched in wnt signaling pathway of female pathway. A total of 17 sox family genes were obtained from the transcriptome data, most of which were differentially expressed in pseudo-female ovaries (Table S6). Sex-related sox genes will be further screened and analyzed for their roles in the sex reversal.

Table 3.
Candidate differentially expressed genes (DEGs) putatively related to steroid synthesis and gonadal development.
3.5. DEGs Were Verified with RT-qPCR
Ten sex-related DEGs were selected randomly from the candidate sex-related genes for RT-qPCR verification. Five genes (hsd3b, hsd11b2, hsd17b7, hsd17b8, cyp19a1) were involved in sex steroid hormone synthesis, three were sox family genes (sox3, sox17, sox30), and two female-specific genes (bmp15 and gdf9). The validation results were generally consistent with the transcriptomic data, which confirmed the reliability of the transcriptomic data (Figure 4).
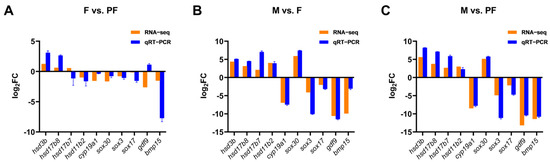
Figure 4.
Validation of the RNA-seq data by RT-qPCR. (A) F vs. PF. (B) M vs. F. (C) M vs. PF. The x-axis presents the gene name, and the y-axis presents a fold change in gene expression.
3.6. Identification of Sex-Related Sox Genes in Different Gonads
Of the sex-related sox family genes, sox1, sox2, sox3, sox6, sox8, sox9, sox11, sox12, sox17, and sox30 were screened on the basis of the transcriptomic data to analyze their molecular functions during E2-induced sex reversal of P. sinensis. The sex-related sox family genes were screened from the DEGs of F vs. PF and M vs. PF, on the basis of p < 0.05 and log2FC > 1 or log2FC < −1. The expression patterns of these genes were analyzed in the normal ovary, testis, and pseudo-female ovary (Figure 5). In this study, sox1, sox3, sox6, sox9, sox11, sox12, sox17, and sox30 showed sex specificity. The expression levels of sox9, sox12 and sox30 were higher in the testis than in the ovary, whereas sox1, sox3, sox6, sox11, and sox17 showed the opposite trend. No significant differences were observed in the expression levels of sox2, and sox8 in the females and males. Furthermore, the expression levels of sox3, sox8, sox11, and sox17 were significantly higher in the pseudo-female gonads than in the males and females, whereas the expression level of sox9 was significantly lower. The results suggest that these genes may play an important role in the development and maturation of pseudo-female gonads, even during sexual reversal and differentiation. Therefore, sox3, sox8, sox9, sox11, sox17, and sox30 were selected for further analyses during the sex reversal of exogenous estrogen treatment. These genes showed significant differences between pseudo-female ovary and testis.
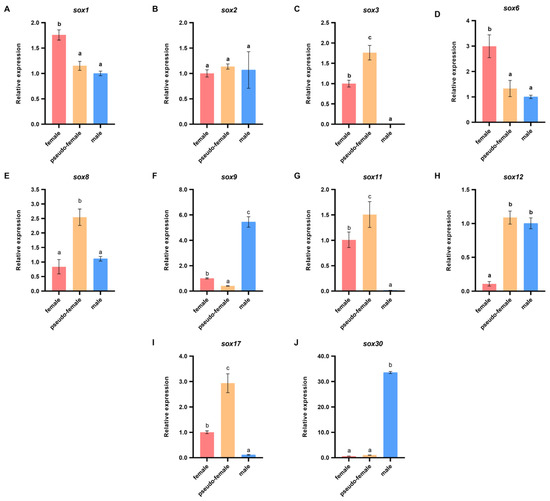
Figure 5.
Differential expressions of sex-related sox genes in different gonads of P. sinensis. (A) sox1. (B) sox2. (C) sox3. (D) sox6. (E) sox8. (F) sox9. (G) sox11. (H) sox12. (I) sox17. (J) sox30. Each value is presented as the mean ± SD of three repetitions. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc tests were used to analyze the means. Different letters indicate significant differences.
3.7. Expression Patterns of Sox Genes in the Embryonic Sex Reversal after E2 Treatment
The expression patterns of sox3, sox8, sox9, sox11, sox17, and sox30 in the embryo were recorded during sex reversal after E2 treatment. In the female embryos treated with E2, the expression pattern of sox3 was significantly upregulated and peaked at stage 13 and then decreased, but it was still higher than that in the untreated embryo (p < 0.05, Figure 6). Sox8 and sox17 were definitely inhibited from stage 13, and their levels then remained low. Although the expression level of sox30 was significantly different at stage 13 and 17, it was not affected by E2 on the whole. No arresting changes were observed in the expression patterns of sox9, and sox11. In the male embryos, the expression level of sox3 was higher than that in the control, and it reached peaked at stage 15 and then decreased (Figure 7). However, sox8, sox9, and sox11 were dramatically inhibited during sex differentiation. During the differentiation of the primordial gonads into ovaries, the expression level of sox3 was obviously increased by exogenous estrogen. At this point, sox8, sox9, and sox11 were inhibited in the male embryos. It was suggested that sox3 may play an important role in the sex reversal from male to pseudo-female. No effect of exogenous estrogen on the expression level of sox30 was found in male embryos.
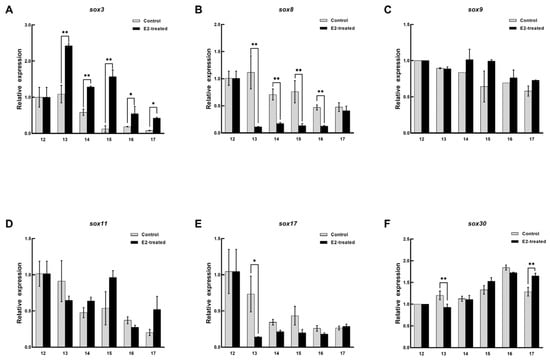
Figure 6.
Expression changes of six sox genes during the sex differentiation of female embryo after estradiol treatment. (A) sox3. (B) sox8. (C) sox9. (D) sox11. (E) sox17. (F) sox30. The x axis represents the embryonic development stage, and the y axis represents the relative expression level. Each value is presented as the mean ± SD of three repetitions. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc tests were used to analyze the means. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.
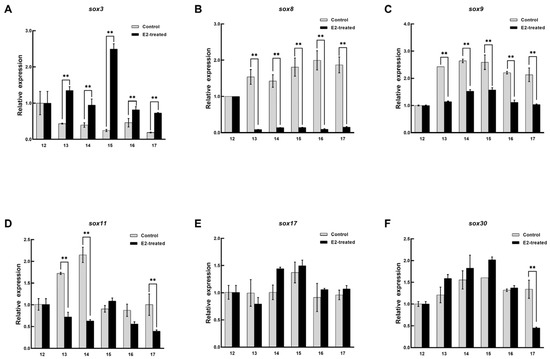
Figure 7.
Expression changes of six sox genes during the sex differentiation of male embryo after estradiol treatment. (A) sox3. (B) sox8. (C) sox9. (D) sox11. (E) sox17. (F) sox30. The x axis represents the embryonic development stage, and the y axis represents the relative expression level. Each value is presented as the mean ± SD of three repetitions. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc tests were used to analyze the means. ** p < 0.01.
4. Discussion
The research field of sex determination and gonadal development mechanism of P. sinensis is widely concerned because of the economic characteristics associated with significant sexual dimorphism. In order to obtain all-male offspring, the pseudo-females (∆ZZ) after sex reversal will be reproduced as the female parent. Pseudo-females resemble females in gonadal morphology. Our transcriptome results showed that pseudo-females were closer to females at mRNA level. During the sex differentiation of vertebrates, exogenous sex steroids can influence the phenotypic sex greatly [44] and sox family genes play a crucial role in the process. In this study, a comparative transcriptome analysis was performed using the gonadal tissues of P. sinensis males, females, and pseudo-females. The objective of this study was to identify DEGs in the gonads of the different sex types of P. sinensis. Differentially expressed genes between male and pseudo-female gonads may be the key genes during the sex reversal. Further, expression patterns of sox family genes were analyzed during sex reversal after E2 treatment to explore the role of sox family genes in sex reversal.
Sex steroid hormones, especially androgen and E2, play an important regulatory role in reproductive activities such as sex determination, gametogenesis, and storage in turtles and other vertebrates [45,46,47]. In the gonadal transcriptome of P. sinensis, cyp19a1, cyp11a, hsd3b, hsd11b2, and hsd17b7 were found to be significantly enriched in steroid hormone biosynthesis and ovarian steroid hormone genesis pathways. Previous studies have shown that star, cyp11a1, and hsd3b are closely related to gonadal development and gametogenesis in fish [45,48,49]. Hsd11b2 is involved in the synthesis of androgen 11-kT, and it plays an important role in the male sex differentiation of vertebrates such as Epinephelus coioides [50] and Cynoglossus semilaevis [51]. Hsd17b7 could convert estrone to E2 and played an important role in mouse embryonic development [52]. The expression levels of cyp11a, hsd3b, and hsd11b2 were observably higher in male P. sinensis than in the female, which was consistent with the results of Oryzias latipes [53]. However, the expression level of hsd17b7 was inconsistent with that reported in previous studies. The expression level of hsd17b7 was higher in the males than in the females and pseudo-females. This may be because, when cyp19a1 is inhibited, the male turtle upregulates the expression of hsd17b7 to maintain life activities. On the other hand, steroid biosynthesis pathways, such as steroid hormone biosynthesis (ko00140), ovarian steroidogenesis (ko04913), and progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation (ko04914), were enriched in pseudo-female, suggesting that the pseudo-females could maintain ovarian development and maturation through these pathways as females do.
In addition, several female-specific genes have been identified. Fgf9 is a downstream target of the male sex-determining gene sox9, and it participates in male sex determination by positive feedback regulation of sox9. However, fgf9 inhibits the activation of the wnt signaling pathway and expression of foxl2 [54]. Mice that lacked fgf9 showed sex reversal from male to female [55]. Our results show some differences: the expression levels of fgf8 and fgf9 were significantly higher in the pseudo-females than in the males and females. Some studies have shown that fgf8 and fgf9 promote follicular maturation during gonadal development [56]. Therefore, fgf8 and fgf9 may be key genes during estrogen-induced sex reversal of P. sinensis, but this needs further experimental verification.
The SOX transcription factors play a vital role in the gonadal development of many animals [29]. Not all sox genes in P. sinensis have been found to be involved in sex determination, especially in the males [57]. In this study, sox9 and sox17 were enriched in cAMP signaling pathway (ko04024) and wnt signaling pathway (ko04310) related to gender determination, respectively. As a result of RT-qPCR, sox1, sox3, sox6, sox11, and sox17 exhibited female-specific expression in the gonads, whereas sox9, sox12, and sox30 exhibited male specificity. Among the male-specific genes, sox12 and sox30 exhibited different mRNA levels in pseudo-female ovaries. Sox30 was almost not expressed in both females and pseudo-females and was hardly affected by exogenous estradiol in the sex reversal of P. sinensis. It has been reported that the silencing of sox30 in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio) decreased the expression level of sox9 and significantly decreased serum testosterone [31]. Contrary to previous studies, the expression level of sox12 in pseudo-female was similar to that in male, but higher than that in female [58]. Researches in mice have also shown that sox12 can regulate gonad morphogenesis and germ cell differentiation [59]. All in all, sox12 and sox30 are male-specific genes involved in the maturation and maintenance of the testis in P. sinensis, and not involved in sex differentiation and sex reversal. It has been reported that sox9 is an important male sex-determining gene in P. sinensis [16]. Our study confirmed that estrogen inhibited the expression of sox9 in embryos.
Among the female-specific genes, sox1 and sox6 were highly expressed in the ovary with no difference between pseudo-female ovary and testis. Its expression pattern was consistent with that of Acipenser sinensis [60]. The mRNA expression level of sox17 was higher in the pseudo-females than in the females. However, sox17 was not affected by exogenous estrogen in the sex reversal, which was different from the increased sox17 expression level reported in Dicentrarchus labrax [30] during gonadal differentiation. These results suggest that the molecular functions of sox1, sox6, and sox17 may be related to ovarian development and maintenance rather than sex reversal.
The expression levels of sox3, sox8, and sox11 were higher in the pseudo-females than in the males and females. The expression level of sox3 increased in the embryos after E2 treatment, whereas sox8, sox9, and sox11 decreased during the sex differentiation period in the males. Previous studies have revealed that E2 can cause sex reversal in P. sinensis [13]. In this process, sox3 may promote the sex reversal of male to pseudo-female, and sox8, sox9 and sox11 were inhibited by E2. Interestingly, sox11 is female-specific but inhibited by estrogen during gonadal differentiation, suggesting that sox11 is related to ovarian development and does not participate in the sex differentiation of P. sinensis. Both sox8 and sox9 were inhibited by exogenous estrogen during sex reversal, but the expression level of sox8 was higher in the pseudo-female ovaries than in the males. The expression level of sox9 showed the opposite trend. Previous studies have showed that the cooperative functions of sox9 and sox8 play an important role in the maintenance of testicular function in mice [61]. Our results may indicate that sox8 promoted the development of pseudo-female ovaries, but this needs to be studied further.
In vertebrates, such as Xenopus laevis [21], Rana rugosa [23], and Mus musculus [24], sox3 inhibited the expression of sox9 in the ovaries, promoted the development of ovaries, and even directly activated the transcription of cyp19. Deletion and overexpression of sox3 can lead to sex reversal in Oryzias dancena [22]. Our studies showed that sox3 was increased by exogenous estrogen during sex differentiation in both female and male embryos. Therefore, it was speculated that sox3 may have a key role in the regulation of female sex differentiation in P. sinensis through the estrogen pathway.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, in this study, gonadal transcriptomic differences between E2-induced pseudo-female, male, and female P. sinensis were investigated, and sox family genes were analyzed after E2 treatment. The results showed that the pseudo-females were more similar to the females with respect to mRNA expression levels. The important genes during sex reversal were identified, especially sox3, sox8, and sox9, and they may play a vital role in the sex reversal of male to pseudo-female. Sox3 may promote male-to-female sex reversal, and sox8 and sox9 were inhibited by E2 during the sex reversal (Figure 8). This study provides a reference for further investigations of the molecular mechanism of sex regulation and all-male breeding of P. sinensis.
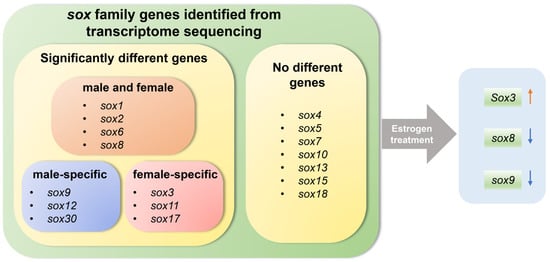
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram illustrating the role of sox genes in gonad and exogenous estrogen-induced gonadal development and sex reversal in Chinese soft-shelled turtle.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology11010083/s1, Table S1: Primer sequences used in this experiment; Table S2: Differentially expressed genes in the transcriptome; Table S3: GO enrichment analysis of DEGs; Table S4: KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs; Table S5: Significantly enriched GO terms and KEGG pathways related to sex; Table S6: Sox family genes identified form the transcriptome. Figure S1: Significantly enriched GO terms in M vs. F. Figure S2: Top 20 KEGG enrichment significant pathways in M vs. F.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W., G.Z. and H.L.; methodology, Y.W. and H.L.; validation, Y.W., X.L. and T.X.; formal analysis, Y.W.; investigation, Y.W., X.L., C.Q. and T.X.; resources, C.Q., G.Z. and H.L.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, X.L., T.X., G.Z. and H.L.; visualization, Y.W.; supervision, G.Z. and H.L.; project administration, H.L.; funding acquisition, G.Z. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Freshwater Aquatic Germplasm Resource Center (grant NO. FGRC18537) and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (grant NO. 2020TD33).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the appropriate Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection of Laboratory Animal Centre of the Yangtze River Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (Wuhan, China) (ID Number: 20200118).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw sequence data reported in this study were deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive (GSA) in National Genomics Data Center (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa/), China National Center for Bioinformation/Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences under BioProject PRJCA007752, with accession number CRA005737. The data presented in this study are also available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liang, H.W.; Wang, L.H.; Sha, H.; Zou, G.W. Development and Validation of Sex-Specific Markers in Pelodiscus Sinensis Using Restriction Site-Associated DNA Sequencing. Genes 2019, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.W.; Cao, L.H.; Li, X.; Tong, M.M.; Jiang, Y.L.; Li, Z.; Luo, X.Z.; Zou, G.W. Morphological differences analysis of three strains of Pelodiscus sinensis. Freshw. Fish. 2017, 47, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Tang, W.Q.; Sun, B.J.; Zeng, Z.G.; Valenzuela, N.; Du, W.G. Temperature-dependent sex determination ruled out in the Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) via molecular cytogenetics and incubation experiments across populations. Sex. Dev. 2015, 9, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kettlewell, J.R.; Anderson, R.C.; Bardwell, V.J.; Zarkower, D. Sexually dimorphic expression of multiple doublesex-related genes in the embryonic mouse gonad. Gene Expr. Patterns GEP 2003, 3, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagoshi, T.; Uno, Y.; Matsubara, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Nishida, C. The ZW micro-sex chromosomes of the Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis, Trionychidae, Testudines) have the same origin as chicken chromosome 15. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2009, 125, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.W.; Meng, Y.; Cao, L.H.; Li, X.; Zou, G.W. Effect of exogenous hormones on R-spondin 1 (RSPO1) gene expression and embryo development in Pelodiscus sinensis. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2019, 31, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Wan, Q.H.; Fang, S.G. Identification of sex using SBNO1 gene in the Chinese softshell turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis (Trionychidae). J. Genet. 2019, 98, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. The Effect of DMRT1 Gene on Male Gonadal Development in Pelodiscus sinensis. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Toyota, K.; Masuda, S.; Sugita, S.; Miyaoku, K.; Yamagishi, G.; Akashi, H.; Miyagawa, S. Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) Agonist Induces Ovarian Differentiation and Aberrant Mullerian Duct Development in the Chinese Soft-shelled Turtle, Pelodiscus sinensi. Zool. Stud. 2020, 59, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.S.; Cai, H.; Han, W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Sun, W.; Ge, C.T.; Qian, G.Y. Functional characterization of Cyp19a1 in female sexual differentiation in Pelodiscus sinensis. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2017, 47, 640–649. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Cai, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Bao, H.; Wang, L.; Ye, J.; Qian, G.; Ge, C. Dmrt1 is required for primary male sexual differentiation in Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shi, S.R.; Cai, H.; Mi, M.D.; Qian, G.Y.; Ge, C.T. Function Analysis of Dmrt1 in Male Sexual Differentiation in Pelodiscus sinensis. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2015, 45, 881–889. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.W.; Meng, Y.; Cao, L.H.; Li, X.; Zou, G.W. Expression and characterization of the cyp19a gene and its responses to estradiol/letrozole exposure in Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.L.; Diao, X.M.; Li, Y.; Zhai, X.L.; Zhou, C.L. Molecular cloning and expression of FOXL2 gene induced by exogenous hormone in the Pelodiscus sinensis. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2019, 43, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Sun, W.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, G.; Ge, C. Knockdown of R-spondin1 leads to partial sex reversal in genetic female Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2021, 309, 113788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, T.; Mi, M.D.; Yang, K.Z.; Qian, G.Y.; Ge, C.T. The effects of estrogen on gonadal differentiation and expressions of DMRT1 and SOX9 in Pelodiscus sinensis. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2014, 38, 467–473. [Google Scholar]
- Denny, P.; Swift, S.; Brand, N.; Dabhade, N.; Barton, P.; Ashworth, A. A conserved family of genes related to the testis determining gene, SRY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gubbay, J.; Collignon, J.; Koopman, P.; Capel, B.; Economou, A.; Münsterberg, A.; Vivian, N.; Goodfellow, P.; Lovell-Badge, R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature 1990, 346, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Chu, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, S.R.; Ge, C.T.; Qian, G.Y. The expression pattern of SOX9 gene during embryonic development and its expression changes in sex reversal in Pelodiscus sinensis. J. Fish. China 2014, 38, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.E.; Whitworth, D.J.; Qin, Y.; Agoulnik, A.I.; Agoulnik, I.U.; Harrison, W.R.; Behringer, R.R.; Overbeek, P.A. A transgenic insertion upstream of sox9 is associated with dominant XX sex reversal in the mouse. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyano, S.; Ito, M.; Takamatsu, N.; Takiguchi, S.; Shiba, T. The Xenopus Sox3 gene expressed in oocytes of early stages. Gene 1997, 188, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehana, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Myosho, T.; Suster, M.L.; Kawakami, K.; Shin, I.T.; Kohara, Y.; Kuroki, Y.; Toyoda, A.; Fujiyama, A.; et al. Co-option of Sox3 as the male-determining factor on the Y chromosome in the fish Oryzias dancena. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, Y.; Naruse, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakamura, M. Sox3: A transcription factor for Cyp19 expression in the frog Rana rugosa. Gene 2009, 445, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstrom, D.E.; Young, M.; Albrecht, K.H.; Eicher, E.M. Related function of mouse SOX3, SOX9, and SRY HMG domains assayed by male sex determination. Genesis 2000, 28, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartl, M.; Schories, S.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Nagao, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Bertin, C.; Mourot, B.; Schmidt, C.; Wilhelm, D.; Centanin, L.; et al. Sox5 is involved in germ-cell regulation and sex determination in medaka following co-option of nested transposable elements. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.M.; Owens, D.A.; Wang, L.; King, M.L. A novel role for sox7 in Xenopus early primordial germ cell development: Mining the PGC transcriptome. Development 2018, 145, dev155978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, M.K.; Takada, S.; Kennedy, C.L.; Scott, G.; Harada, S.; Ray, M.K.; Dai, Q.; Wilhelm, D.; de Kretser, D.M.; Eddy, E.M.; et al. Sox8 is a critical regulator of adult Sertoli cell function and male fertility. Dev. Biol. 2008, 316, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, J.C.; Wilhelm, D.; Davidson, T.L.; Knight, D.; Koopman, P. Sox10 gain-of-function causes XX sex reversal in mice: Implications for human 22q-linked disorders of sex development. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Liu, T.T.; Qiao, D.; Hu, Q.T.; Su, S.P. Identification and functional analysis of SOX transcription factors in the genome of the Chinese soft-shell turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 242, 110407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Martín, L.; Galay-Burgos, M.; Sweeney, G.; Piferrer, F. Different sox17 transcripts during sex differentiation in sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 299, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Senthilkumaran, B. Role of sox30 in regulating testicular steroidogenesis of common carp. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 204, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Gao, D.; Lu, J.; Sun, X. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals the Sexual Dimorphism of Gene Expression Patterns during Gonad Differentiation in the Half-Smooth Tongue Sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.J.; Wang, H.; Ji, X.S. Transcriptome Profiling and Analysis of Genes Associated with High Temperature-Induced Masculinization in Sex-Undifferentiated Nile Tilapia Gonad. Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 22, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Z.F.; Hu, Y.Z.; Tan, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.N.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.Q. Comparative Analysis Transcriptome of Spleen of Chinese Soft-shelled Turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2020, 39, 5449–5456. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Xu, X.J.; He, Z.Y.; Zheng, T.L.; Shao, J.Z. De novo transcriptome analysis reveals insights into different mechanisms of growth and immunity in a Chinese soft-shelled turtle hybrid and the parental varieties. Gene 2017, 605, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, C.; Zou, G.W.; Liang, H.W. Chinese Softshelled Turtle Pelodiscus sinensis: Embryonic Development and Embryo Staging. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2020, 36, 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Sha, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, G.B.; Zou, G.W.; Liang, H.W. MicroRNAs May Play an Important Role in Sexual Reversal Process of Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis. Genes 2021, 12, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B. Aligning short sequencing reads with Bowtie. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2010, 32, 11.7.1–11.7.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Chang, G.; Wu, N.; Ding, H.; Wang, H. Differential expression analysis and identification of sex-related genes by gonad transcriptome sequencing in estradiol-treated and non-treated Ussuri catfish Pseudobagrus ussuriensis. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, S.R.; Salati, A.P.; Jalali, A.H.; Falahatkar, B. Expression profile of star and cyp19 and plasma sex steroid during gonad development from previtellogenesis to early atresia in captive Sterlet sturgeon, Acipenser ruthenus. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2018, 35, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsu, Y.; Ichikawa, R.; Ikeuchi, T.; Kohno, S.; Guillette, L.J.J.; Iguchi, T. Molecular cloning and characterization of estrogen, androgen, and progesterone nuclear receptors from a freshwater turtle (Pseudemys nelsoni). Endocrinology 2008, 149, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; Rhen, T. Role for androgens in determination of ovarian fate in the common snapping turtle, Chelydra serpentina. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 281, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.J.; Lin, J.C.; Chung, B.C. Zebrafish cyp11a1 and hsd3b genes: Structure, expression and steroidogenic development during embryogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 312, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamoto, M.; Fukasawa, M.; Tanaka, S.; Shimamori, K.; Suzuki, A.; Matsuda, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nagahama, Y.; Shibata, N. Expression of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (hsd3b), star and ad4bp/sf-1 during gonadal development in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 176, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wang, Q.; Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Lin, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Natural sex change in mature protogynous orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides): Gonadal restructuring, sex hormone shifts and gene profiles. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 97, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.C.; Feng, B.; Shao, C.W.; Wang, Q. Molecular Characterization and Expression Patterns of hsd11b1l and hsd11b2 and Their Response to High Temperature Stress in Chinese Tongue Sole Cynoglossus semilaevis. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2021, 42, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Shehu, A.; Mao, J.; Gibori, G.B.; Halperin, G.B.; Le, J.; Devi, Y.S.; Merrill, B.; Kiyokawa, H.; Gibori, G. Prolactin receptor-associated protein/17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 7 gene (Hsd17b7) plays a crucial role in embryonic development and fetal survival. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2268–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Li, G. Comparison of Gonadal Transcriptomes Uncovers Reproduction-Related Genes with Sexually Dimorphic Expression Patterns in Diodon hystrix. Animals 2021, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kobayashi, A.; Sekido, R.; DiNapoli, L.; Brennan, J.; Chaboissier, M.C.; Poulat, F.; Behringer, R.R.; Lovell-Badge, R.; Capel, B. Fgf9 and Wnt4 act as antagonistic signals to regulate mammalian sex determination. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cen, C.H.; Chen, M.; Jiang, L.; Hou, X.H.; Gao, F. The regulation of gonadal somatic cell differentiation during sex determination in mice. Acta Physiol. Sin. 2020, 72, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Price, C.A. Mechanisms of fibroblast growth factor signaling in the ovarian follicle. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 228, R31–R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Li, Y.P. Roles of SOX Transcription Factors on Fate Decision of Germ Cells. Chin. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 41, 961–966. [Google Scholar]
- Anitha, A.; Senthilkumaran, B. Role of sox family genes in teleostean reproduction-an overview. Reprod. Breed. 2021, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Arsenault, M.; Ng, E.T.; Longmuss, E.; Chau, T.C.; Hartwig, S.; Koopman, P. SOX4 regulates gonad morphogenesis and promotes male germ cell differentiation in mice. Dev. Biol. 2017, 423, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Hu, Y.C.; Han, J.L.; Xiao, K.; Liu, X.Q.; Tan, C.; Zeng, Q.K.; Du, H.J. Genome-wide analysis of the Chinese sturgeon sox gene family: Identification, characterisation and expression profiles of different tissues. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 96, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrionuevo, F.; Georg, I.; Scherthan, H.; Lécureuil, C.; Guillou, F.; Wegner, M.; Scherer, G. Testis cord differentiation after the sex determination stage is independent of Sox9 but fails in the combined absence of Sox9 and Sox8. Dev. Biol. 2009, 327, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).