Simple Summary
Serum levels of MGP, Gas6, vitamin K1, and EGFR were not significantly changed in response to the first cycle of chemotherapy. We found a strong correlation between MGP and VitK1 serum values, and a moderate negative correlation between VitK1 and EGFR in pre-treatment patients. The post-treatment value of EGFR is a strong independent factor that correlates positively with the Gas6 post-treatment values.
Abstract
Background: Vitamin K-dependent proteins (VKDPs) and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are involved in lung cancer progression. Therefore, we aimed to study the serum concentration of Matrix Gla protein (MGP), Growth Arrest-specific 6 (Gas6), and EGFR before and after the first cycle of chemotherapy and to investigate how MGP, Gas6, and EGFR are modified after one cycle of chemotherapy. Methods: We performed an observational study on twenty patients diagnosed with lung cancer, by assessing the serum concentration of vitaminK1 (VitK1), MGP, Gas6, and EGFR using the ELISA technique before and after three weeks of the first cycle of chemotherapy. Patients were evaluated using RECIST 1.1 criteria. Results: Serum levels of MGP, Gas6, EGFR, and VK1 before and after treatment were not changed significantly. Regarding the pre-treatment correlation of the MGP values, we found a strong positive relationship between MGP and VK1 pre-treatment values (r = 0.821, 95%CI 0.523; 0.954, p < 0.001). Furthermore, there was a moderately negative correlation between VK1 and EGFR pre-treatment values, with the relationship between them being marginally significant (r = −0.430, 95%CI −0.772; 0.001, p = 0.058). Post-treatment, we found a strong positive relationship between MGP and VK1 post-treatment values (r = 0.758, 95%CI 0.436; 0.900, p < 0.001). We also found a moderate positive relationship between Gas6 and EGFR post-treatment values, but the correlation was only marginally significant (r = 0.442, p = 0.051).
1. Introduction
The deaths caused by lung cancer represented about 18% of the total number of deaths worldwide in 2020, for both sexes and all ages. Lung cancers are divided into two main groups: small-cell carcinoma (SCLC, representing 13% of all cases) and non-small-cell carcinoma (NSCLC, representing 83% of all cases) [1,2,3,4,5]. Molecular profiling further classifies NSCLC into adenocarcinoma (ADC) and its variants, squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC), large-cell lung carcinoma (LCLC), and other types (salivary gland-type tumors, sarcomatous carcinomas, and not otherwise specified) [6]. Originating in the bronchial mucous glands, ADC is the most common type of NSCLC, representing the most common subtype of lung cancer in non-smokers [7].
Located in various tissues such as bones, blood vessels, or the heart, 17 vitamin K-dependent proteins have been identified until now [8]. The VKDPs are well known for their involvement in coagulation by factors II, VII, IX, and X. The VKDPs become active through the carboxylation process, which occurs in the liver (for the coagulation factors mentioned earlier) or peripherally, within the blood vessels [5]. The gamma-glutamyl carboxylase enzyme is needed for the full functionality of VKDPs and acts in a vitamin K-dependent manner, both hepatically and extrahepatically [6].
In recent years, the involvement of the VKDPs in lung cancer has become intensely studied, with recent studies reporting especially the role in tumor progression of Gas6 and MGP [7,8]. Furthermore, the role of EGFR in lung cancer is better established as it is already a targeted therapy [9].
MGP is a 10-kDa calcium-binding matrix protein that is secreted and contains several post-translationally modified-carboxyl-glutamic acid residues resulting from vitamin K-dependent carboxylation [4] In vitro, MGP links its Gla residues to calcium and hydroxyapatite to function as a critical regulator/inhibitor of mineralization [10].
High circulating levels of MGP in tumors have been linked to tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis in breast cancer, glioblastoma [11], primary renal-cell carcinomas, prostate carcinomas, and testicular germ-cell tumors [12]. Furthermore, it was observed that osteosarcoma patients that developed lung metastases had high serum levels of MGP at diagnosis. The MGP action of favoring metastasis spread can be explained by its effects of altering endothelial adhesion and the tumor cell’s extravasation ability and by modulating metalloproteinase activities [13]. In NSCLC, it was observed that MGP gene expression could promote macrophage recruitment, neovascularization, and tumor growth [14].
Gas6 has a molecular weight of 75 kDa and a length of 721 amino acids [15]. Gas6 has many physiological roles, of which tissue repair, inflammation, cell survival, proliferation, and migration are worth mentioning [16]. In terms of its role in lung diseases, Gas6/AXL signaling has been shown to reduce alveolar inflammation and acute ischemia-reperfusion injury [17].
In lung ADC, the Gas6-stimulated phosphorylation of the AXL [a tyrosine kinase receptor (RTK) with oncogenic potential and transforming activity] is enhanced [18]. Gas6, derived from CAFs (carcinoma-associated fibroblasts), may promote the migration of AXL-expressing lung cancer cells during chemotherapy. Given that patients with tumor AXL- and stromal Gas6-positive tumors had significantly lower five-year disease-free survival rates than the double negative group, it was concluded that Gas6 is involved in poor clinical outcomes [19]. Therefore, AXL/Gas6 might represent prognostic biomarkers for identifying cases at high risk of post-operative death [20]. Ultimately, it was observed that high AXL mRNA expression [21] and low expression of long noncoding RNA Gas6-AS1 [22] may predict poor prognosis in patients with NSCLC.
EGFR, also known as ERBB1 [Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor 1] and HER1 (Human EGFR related 1), is an RTK and a crucial component of several cell signaling pathways. Its binding to ligands (EGF and TGF-) activates three major downstream signaling pathways (RAS/RAF/MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and JAK/STAT), stimulating mitosis and inhibiting apoptosis. The RAS/RAF/MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and JAK/STAT pathways play important roles in normal cell growth, proliferation, survival, and differentiation [23].
EGFR gene mutations and protein overexpression are associated with lung cancer, especially with NSCLC [23]. EGFR and KRAS (Kristen rat sarcoma virus) mutations are frequently found in lung ADCs [24]. Secondary mutations in EGFR (such as T790M) or upregulation of the MET kinase are found in over 50% of resistant tumors [25]. The importance of EGFR in lung cancers supports the concept of “oncogene addiction” [26]. Patients with EGFR mutations benefit from treatment with EGFR-TKIs (e.g., Gefitinib and Erlotinib) for less than one year, after which there appears to be a resistance-conferring mutation in EGFR and drug resistance develops [23], especially following treatment with Gefitinib [27]. Resistance to EGFR-TKIs is inevitable due to various mechanisms (secondary mutation, activation of alternative pathways, aberrance of the downstream pathways, impairment of the EGFR-TKIs-mediated apoptosis pathway, histologic transformation, etc.) [23]. The genetic or pharmacological inhibition of AXL could prevent or overcome the acquired resistance to EGFR TKIs and restore sensitivity to erlotinib in tumor models, identifying AXL as a promising therapeutic target. Combining treatments with multiple targets may prove superior efficacy [25].
Considering the role of these three molecules in lung cancer pathology, the main goal of this study was to assess their serum concentration before and after treatment and investigate how MGP, Gas6, EGFR, and VK1 are modified after one cycle of chemotherapy.
2. Materials and Methods
All procedures were approved by the ethics committee of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hațieganu Cluj-Napoca (406/11 August 2017) prior to the start of experiments. The study was conducted at the Amethyst Radiotherapy Cluj (612/6 August 2020) and the Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. Ion Chiricuță from Cluj-Napoca (185/15 July 2020). All subjects included have signed an informed consent.
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
We conducted an observational study in which twenty patients diagnosed with lung cancer were included. We compared in this group the serum levels of MGP, Gas6, VK1, and EGFR before and after one cycle of chemotherapy. The inclusion criteria for this study were defined by patients with lung cancer, regardless of the stage of the disease, before one cycle of chemotherapy. The lung cancer diagnosis was based on thoracic computer tomography (CT) imaging, lung biopsy puncture, and pathological examination.
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
Age under 18, administration of vitamin K supplements treatment with anticoagulants, vitamin D antagonists, calcium, calcium antagonists, bisphosphonates, or corticosteroid drugs in the last six months were excluded from the study.
2.3. Sample Preparation and Determination
Blood samples obtained from freshly drawn blood were centrifuged and stored at −80 °C. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for human VK1, Gas6, MGP, and EGFR was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions (MyBioSource, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
Optical density was determined using a microplate reader (Stat Fax) set to 450 nm and then the concentration of human VK1, human Gas6, human MGP, and human EGFR were calculated.
These assays have high sensitivity and specificity for detection of VK1, Gas6, MGP, and EGFR. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between these parameters and analogs was observed.
The second blood sample was obtained after approximately three weeks from the first cycle of chemotherapy, and the parameters were detected using the same methods. Moreover, common blood analyses were evaluated, including complete blood count, creatinine, urea, total bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, gamma glutamyl transferase, calcium, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, potassium, sodium, magnesium, and glucose.
CT Evaluation
Of a total of twenty patients included in this group, five had to be removed due to a lack of available pretreatment data. Using contrast-enhanced thoracic CT, we have compared the evolution of the remaining fifteen lung cancer patients before and after therapy. The interval between the initial scan and control ranged from 1 to 7 months, with an average of 3.07 and a standard deviation of 1.49 months. Patients were evaluated using RECIST 1.1 criteria, which is the gold standard for assessment of treatment response in solid tumors [28].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables were presented as mean and standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range, and categorical variables were presented as frequency and percentages. We performed descriptive and inferential statistical analysis to summarize the characteristics of the study population. To evaluate the proportion between nominal variables, we applied the Fisher exact test. The results of the Shapiro-Wilk normality test showed a non-Gaussian distribution; therefore, we continued to use non-parametric tests. We analyzed the strength of a linear relationship between VK1, Gas6, MGP, and EGFR using Spearman’s rank-order correlation test. To compare patients’ general characteristics, we employed the Mann-Whitney U test. To compare patients’ laboratory characteristics pre- and post-treatment, we employed the Wilcoxon matched pair signed rank test. The individual impacts of several confounding factors on the variance of continuous variables were assessed by building multivariate regression models. The quality of the model was described by using the accuracy of prediction and R squared. The predictors in the final regression equations were accepted according to a repeated backward-stepwise algorithm (inclusion criteria p < 0.05, exclusion criteria p > 0.10) in order to obtain the most appropriate theoretical model to fit the collected data. Data analysis was performed using SPSS v. 26.0 (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, Chicago, IL, USA). A p value of < 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Study Group
The twenty patients included in our study had a median age of 64.5 [59.75–73.5] years, and most of them were men (80%). Male patients in this study were older than the female patients, but no significant statistical difference was observed (65.5 vs. 59 years, p = 0.178). Four patients (20%) were non-smokers, five (25%) were former smokers, and eleven (55%) were current smokers.
There were no statistically significant differences in the gender distribution of smoker status (p = 0.958).
From the point of view of histopathological type of cancer, most of our study group patients presented adenocarcinoma (ten patients, 50%), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (six patients, 30%), and small cell lung cancer (four patients, 20%).
As for chemotherapy, most of the adenocarcinoma patients were treated with pemetrexed and carboplatin (five patients, 25%), and the squamous cell carcinoma patients with carboplatin (four patients, 20%) (Figure 1).
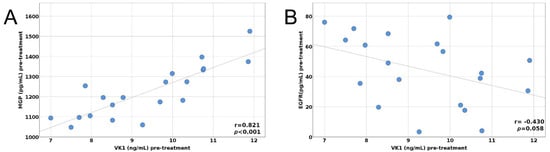
Figure 1.
(A) Pre-treatment correlation between MGP and VitK1, (B) Pre-treatment correlation between EGFR and VitK1.
3.2. Biochemical and Hematological Parameters
We wanted to assess the general status of our patients before and after the chemotherapeutic treatment. The post-treatment values of white blood cells (WBC) were significantly lower compared to pre-treatment (5.2 vs. 8.13 × 109/L; p = 0.007). We also observed a significant rise in total bilirubin and calcium levels in the post-treatment group, 0.51 vs. 0.41 mg/dL (p = 0.014) and 9.5 vs. 9.3 mg/dL (p = 0.019), respectively (Table 1).

Table 1.
General laboratory characteristics pre- and post-treatment.
In addition, serum levels of Gas6, EGFR, VK1, and MGP were compared in patients before and after chemotherapeutical treatment. The pre-treatment values of Gas6, EGFR, VK1, and MGP were slightly higher compared to the post-treatment values, but without reaching significant statistical differences (Table 2).

Table 2.
Specific laboratory characteristics pre- and post-treatment.
Further, pre-treatment and post-treatment correlations between MGP, Gas6, EGFR, and VK1 are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
MGP pre- and post-treatment correlations.
The pre- and post-treatment correlations between MGP, Gas6, EGFR, and VK1 are depicted in Figure 1A,B and Figure 2A,B.
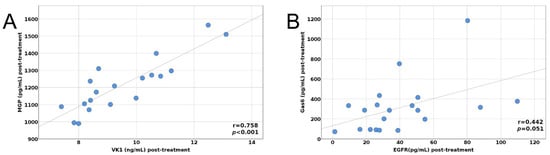
Figure 2.
(A) Post-treatment correlation between MGP and VitK1, (B) Post-treatment correlation between Gas6 and EGFR.
Furthermore, multivariate linear regression was employed to evaluate the independent predictor factors of Gas6 in our patients’ groups (Table 4). The predictors in the final regression equations were accepted according to a repeated backward-stepwise algorithm to obtain the most appropriate theoretical model to fit the collected data. Our results highlighted that VK1 is a predictor factor for Gas6 post-treatment values. Additionally, age and smoking influence the post-treatment values of Gas6. This model seems to be a good fit, explaining 89.4% of the Gas6 variance (adjusted R2 = 0.894).

Table 4.
Multivariate linear regression for Gas6 post-treatment values.
A multivariate linear regression was performed (Table 5) to identify the independent predictor factors of MGP post-treatment values in our study group. Our analysis showed that pre-treatment values of various parameters, like MGP and VK1, were predictor factors for MGP post-treatment values. Furthermore, age and smoking influence the post-treatment values of MGP. This model explains 53% of the MGP variance (adjusted R2 = 0.530).

Table 5.
Multivariate linear regression for MGP post-treatment values.
Finally, we used a multivariate linear regression to identify the independent predictor factors of Gas6 post-treatment values in the study group. Our results showed that the independent factors that influenced the Gas6 values after treatment were MGP and EGFR (R2 = 0.405) (Table 6).

Table 6.
Post-treatment values for Gas 6 after multivariate linear regression.
According to RECIST 1.1 criteria, one patient (6.66%) had a complete remission and one (6.66%) had an unknown complete remission with persistent imaging abnormalities. Four patients (26.67%) had a partial response, and eight (53.33%) showed minimal disease progression or amelioration. There was only one (6.66%) case of significant disease progression. According to the RECIST 1.1 criteria regarding the response to treatment, there was no significant difference in serum levels of MGP, Gas6, vitamin K1 and EGFR after one cycle of chemotherapy.
4. Discussion
Based on the main histopathological types, lung cancers are divided into two main groups: small-cell carcinoma (13 % of the cases) and non-small-cell carcinoma (83 % of the cases). Non-small-cell lung carcinoma is further subdivided into adenocarcinoma and its variants, squamous cell carcinoma, and large-cell lung carcinoma, as well as salivary gland-type tumors and sarcomatous carcinomas [1,3].
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of non-small-cell carcinoma and the most common subtype of lung cancer in non-smokers, originating in the bronchial mucous glands [29].
In our study, adenocarcinoma represented the most frequent type of lung cancer, encountered in 50% of patients. This is correlated with the fact that most patients were non-smokers or former smokers. Despite its significant advances, chemotherapy in adenocarcinoma leaves most patients’ survival at an abysmal level [30,31,32,33,34].
Carboplatin was mostly used in our study (in total, in fifteen patients, 75%), and pemetrexed in five patients (25% of cases). Similar to our documentation from the scientific literature [35,36,37], the combination most commonly used was pemetrexed and carboplatin (five patients, 25%).
We observed a significant rise in total bilirubin, illustrating the impairment of hepatic function after the chemotherapy. During cancer chemotherapy, the drug-related toxicity can be unpredictable and alter the hepatic function and the drug clearance. A bilirubin level greater than 5.0 mg/dl is generally regarded as an absolute contraindication to administering cytotoxic chemotherapy [38].
In addition, in our study, we looked at serum levels of common laboratory parameters before and after treatment. We noticed a significant rise in calcium levels in the post-treatment group, which can illustrate the possible presence of bone metastases. Bone is a common site of metastatic cancer spread, mostly in adenocarcinoma, and can lead to pathological fractures, nerve root compression at the level of spinal cord vertebrae, or hypercalcemia of malignancy [39].
Cellular differentiation in cancer and tumor progression [40] has recently been linked to MGP expression. In addition, the same study proved that MGP might contribute to increased cancer resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs by augmenting the interaction of stromal cancerous cells with the extracellular matrix components [40]. It has also been shown that an increased expression of MGP is linked to the respective chemotherapeutic drugs [40,41].
In our study, MGP serum values were strongly correlated with VK1 values, only before therapy. Moreover, MGP decreased insignificantly after chemotherapy in our study. Since MGP is a marker for extrahepatic vitamin K insufficiency, we found that after the first chemotherapy cycle, patients had no deficiency in vitamin K.
It was observed that Gas6 is frequently overexpressed in lung cancer cells and is found in the plasma [42,43], and Gas6 is associated with cell growth of stromal cancerous cells and tumor progression [44]. Therapeutic agents targeting Gas6 and AXL have been developed, and promising results have been observed in both preclinical and clinical settings when such agents are used alone or in combination [45].
In contrast to Kanzaki et al.’s [19] murine models, where plasma levels of Gas6 and its expression in stromal cancerous cells increased after cisplatin chemotherapy, we found an insignificant decrease in serum level of Gas6 after the first chemotherapy cycle with cisplatin in our study Moreover, compared to the study of Nonagase et al. [46], the plasma Gas6 concentration after EGFR–tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) was increased. These contradictory results could be explained by the alterations induced by chemotherapy, which could influence the behavior of cancer cells. In the tumor stromal microenvironment, cancer-associated fibroblasts play an important role, and Gas6 could promote non-small cell lung cancer. In a murine model, Kanzaki et al. [19] found that Gas6 expression by cancer-associated fibroblasts was upregulated following cisplatin treatment. Moreover, Gas6 expression might be influenced by intratumoral hypoperfusion during chemotherapy. On the other hand, Gas6 expression is increased after serum starvation in a human lung CAF line. In clinical samples, stromal Gas6 expression increased after chemotherapy. Plasma samples were obtained from EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients before or after treatment with first or second-generation EGFR-TKIs in the study by Nanogase et al. [46].
In the current literature, EGFR gene mutations and protein overexpression are involved in the development and progression of lung cancer [23,47]. However, EGFR’s value as a prognostic biomarker for survival outcomes is not yet established. There are no consistent results regarding the predictive value of EGFR serum levels in lung cancer patients and, more importantly, its ability to predict therapeutic response to anti-EGFR drugs [48,49,50]. Mohan et al. [48] published a study in 2020 on the measurement of serum levels of EGFR mRNA expression, attempting to emphasize its value as a predictor of response to treatment and survival in non-small cell lung cancer types. In that study, most of the patients had advanced lung cancer (70.6%), and serum EGFR mRNA expression was considered a marker for predicting treatment response and survival outcomes in non-small-cell carcinoma [48]. Another study, which used an ELISA assay to measure and compare EGFR serum protein and circulating mRNA levels, found that both the protein serum level and gene expression of EGFR were higher in patients with lung cancer [51]. Our study found a moderately negative correlation between VK1 and EGFR pre-treatment values, the relationship between them being marginally significant.
To identify possible correlations between the post-treatment values of the parameters investigated, in our multivariate linear regression for Gas6 post-treatment value, we obtained a stronger correlation between the post-treatment values of Gas6 and EGFR. The increase of one unit of measurement of EGFR leads to an increase of the Gas6 value by 4.245 units (Table 6).
The study aimed not to highlight the variations compared to the general population, but to highlight the modification of the four parameters (Gas6, MGP, EGFR, and vitamin K) pre- and post-treatment and to underline the possible mechanisms associated with the treatment.
Certain limitations of the present study should be considered. First, the sample size was relatively small, and the study design was observational. Another potential limitation was that serum MGP, Gas6, and EGFR levels were assessed only after the first cycle of chemotherapy. Further studies are required for the evaluation of these parameters after more than one cycle of chemotherapy. Moreover, different stages of the disease may influence the serum concentration of MGP, Gas6, and EGFR after the first dose of chemotherapy. Maybe these variations in tumor characteristics could be responsible for the fluctuation of biomarker values and their consequent non-significance.
However, the data obtained represents preliminary results that can offer new opportunities. According to the RECIST 1.1 criteria, there was no statistically significant difference in serum levels of MGP, Gas6, and EGFR after one cycle of chemotherapy. Our study was the first that evaluated the serum levels of those three proteins in lung cancer patients after one cycle of chemotherapy.
5. Conclusions
Lung cancer is a complex and heterogeneous disease that needs a multidisciplinary approach for diagnosis, classification, and therapy. The serum markers profiling cancer and targeted therapy represent the future main directions for efficient cancer therapy.
Between VKDPs, the pre-treatment values of MGP correlate strongly with the vitamin K1 level.
The post-treatment value of EGFR is a stronger independent factor that correlates positively with the Gas6 post-treatment values.
Our pilot study did not find any serum modification of these proteins in the serum samples after one dose of chemotherapy. Based on RECIST 1.1 criteria, these proteins (MGP, Gas6, and EGFR) could not be markers for response to treatment in patients treated with cisplatin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C. and A.G.D.; methodology, A.C.; validation, G.S., I.L. and A.M.C.; formal analysis, A.G.D., A.-M.C., Z.F., I.A.F.; investigation, A.G.D., A.-M.C., Z.F.; resources, A.M.C.; data curation, G.S., I.L. and A.M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C., A.G.D.; writing—review and editing, A.C., G.S., C.N.S.; supervision, I.L., G.S. and A.M.C. All authors contributed equally to this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant of the Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitization, CNCS/CCCDI—UEFISCDI, project number 2/2019 (DARKFOOD), within PNCDI III.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Globocan 2020. Lung Cancer. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/15-Lung-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Murtaza, M.; Dawson, S.J.; Tsui, D.W.; Gale, D.; Forshew, T.; Piskorz, A.M.; Parkinson, C.; Chin, S.F.; Kingsbury, Z.; Wong, A.S.; et al. Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature 2013, 497, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Parra-Cuentas, E.; Wistuba, I.I. Diagnosis and Molecular Classification of Lung Cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2016, 170, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Li, S. Vitamin K-dependent proteins involved in bone and cardiovascular health (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danziger, J. Vitamin K-dependent proteins, warfarin, and vascular calcification. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Connor, E.M.; Durack, E. Osteocalcin: The extra-skeletal role of a vitamin K-dependent protein in glucose metabolism. J. Nutr. Interm. Metab. 2017, 7, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Li, S. Role of emerging vitamin K-dependent proteins: Growth arrest-specific protein 6, Gla-rich protein and periostin (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Guo, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, H. Preliminary Study on the Biological Markers for I-IIb Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Based on a Serum-peptidomics. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 2019, 22, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.H.; Carrington, C.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H.W.; Ng, C.; Nam, H.; Park, A.; Stace, C.; West, W.; Mao, H.Q.; et al. Nanoparticle-mediated tumor cell expression of mIL-12 via systemic gene delivery treats syngeneic models of murine lung cancers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, R.; Ouyang, H.; Somerman, M.J.; McCauley, L.K.; Franceschi, R. Matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein is a key regulator of PTH-mediated inhibition of mineralization in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 4379–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brouwer, B.; Piscaer, I.; Von Der Thusen, J.H.; Grutters, J.C.; Schutgens, R.E.; Wouters, E.F.; Janssen, R. Should vitamin K be supplemented instead of antagonised in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levedakou, E.N.; Strohmeyer, T.G.; Effert, P.J.; Liu, E.T. Expression of the matrix Gla protein in urogenital malignancies. Int. J. Cancer 1992, 52, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandueta, C.; Ormazábal, C.; Perurena, N.; Martínez-Canarias, S.; Zalacaín, M.; Julián, M.S.; Grigoriadis, A.E.; Valencia, K.; Campos-Laborie, F.J.; Rivas, J.; et al. Matrix-Gla protein promotes osteosarcoma lung metastasis and associates with poor prognosis. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ruan, L.; Yang, Y.; Mei, Q. Analysis of gene expression changes associated with human carcinoma-associated fibroblasts in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, R.A.; Opperdoes, F.R.; Nicolaes, G.A.; Mulder, A.B.; Mulder, R. Understanding the functional difference between growth arrest-specific protein 6 and protein S: An evolutionary approach. Open Biol. 2014, 4, 140121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tondo, G.; Perani, D.; Comi, C. TAM Receptor Pathways at the Crossroads of Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 2387614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.K.; Wu, C.P.; Lin, J.Y.; Peng, S.C.; Lee, C.H.; Huang, K.L.; Shen, C.H. Gas6/Axl signaling attenuates alveolar inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by up-regulating SOCS3-mediated pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechertier, T.; Reynolds, L.E.; Kim, H.; Pedrosa, A.R.; Gómez-Escudero, J.; Muñoz-Félix, J.M.; Batista, S.; Dukinfield, M.; Demircioglu, F.; Wong, P.P.; et al. Pericyte FAK negatively regulates Gas6/Axl signalling to suppress tumour angiogenesis and tumour growth. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, R.; Naito, H.; Kise, K.; Takara, K.; Eino, D.; Minami, M.; Shintani, Y.; Funaki, S.; Kawamura, T.; Kimura, T.; et al. Gas6 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes migration of Axl-expressing lung cancer cells during chemotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, W.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, H.; Lim, Z.F.; Huang, M.; Deng, C.; Yu, X.; Su, H.; Komo, S.; et al. AXL-GAS6 expression can predict for adverse prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Kong, R.; Yin, D.D.; Zhang, E.B.; Xu, T.P.; De, W.; Shu, Y.Q. Low expression of long noncoding RNA GAS6-AS1 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with NSCLC. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, S.; Miki, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Mori, K.; Saito, M.; Niikawa, H.; Kondo, T.; Yamada-Okabe, H.; Sasano, H. Activation of AXL and antitumor effects of a monoclonal antibody to AXL in lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Fu, L. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, T.; Nakaoku, T.; Tsuta, K.; Tsuchihara, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Yoh, K.; Goto, K. Beyond ALK-RET, ROS1 and other oncogene fusions in lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, J.C.; Lin, L.; Olivas, V.; Au, V.; La Framboise, T.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Wang, X.; Levine, A.D.; Rho, J.K.; et al. Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, R.; Crombet, T.; de Leon, J.; Moreno, E. A view on EGFR-targeted therapies from the oncogene-addiction perspective. Front Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metro, M.; Crinò, L. Advances on EGFR mutation for lung cancer. TLCR 2012, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Persijn, E.L.; Gelderblom, H.; Bloem, J.L. RECIST revised: Implications for the radiologist. A review article on the modified RECIST guideline. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 20, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, D.J.; Wallen, J.M. Lung Adenocarcinoma; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519578/ (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Lokich, J.; Anderson, N. Carboplatin versus cisplatin in solid tumors: An analysis of the literature. Ann. Oncol. 1998, 9, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, H.; Akerley, W.; Devore, R. Paclitaxel, carboplatin and radiation therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncology 1998, 12, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Lück, H.J.; Roché, H. Weekly paclitaxel: An effective and well-tolerated treatment in patients with advanced breast cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 44, S15–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliotti, G.V.; Smit, E.; Bosquee, L.; O'Brien, M.; Ardizzoni, A.; Zatloukal, P.; Eberhardt, W.; Smid-Geirnaerdt, M.; de Bruin, H.G.; Dussenne, S.; et al. A phase II study of paclitaxel in advanced bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (EORTC trial 08956). Lung Cancer 2005, 50, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, G.M.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Maddaus, M.A.; Johnstone, D.W.; Johnson, E.A.; Harpole, D.H.; Gillenwater, H.H.; Watson, D.M.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Schilsky, R.L.; et al. Adjuvant paclitaxel plus carboplatin compared with observation in stage IB non-small-cell lung cancer: CALGB 9633 with the Cancer and Leukemia Group B, Radiation Therapy Oncology Group, and North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study Groups. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5043–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, I.; Nokihara, H.; Nomura, S.; Niho, S.; Sugawara, S.; Horinouchi, H.; Azuma, K.; Yoneshima, Y.; Murakami, H.; Hosomi, Y.; et al. Comparison of Carboplatin Plus Pemetrexed Followed by Maintenance Pemetrexed with Docetaxel Monotherapy in Elderly Patients with Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e196828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, V.; Patil, V.M.; Joshi, A.; Menon, N.; Chougule, A.; Mahajan, A.; Janu, A.; Purandare, N.; Kumar, R.; More, S.; et al. Gefitinib Versus Gefitinib Plus Pemetrexed and Carboplatin Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lin, L.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Shu, Y.; Shi, J.; Hu, Y.; et al. Camrelizumab plus carboplatin and pemetrexed versus chemotherapy alone in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CameL): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüll, B.; Scheithauer, W.; Kornek, G.V. Capecitabine as salvage therapy for a breast cancer patient with extensive liver metastases and associated impairment of liver function. Onkologie 2003, 26, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchuk, M.; Addison, C.L.; Clemons, M.; Kuchuk, I.; Wheatley-Price, P. Incidence and consequences of bone metastases in lung cancer patients. J. Bone Oncol. 2013, 2, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterzyńska, K.; Klejewski, A.; Wojtowicz, K.; Świerczewska, M.; Andrzejewska, M.; Rusek, D.; Sobkowski, M.; Kędzia, W.; Brązert, J.; Nowicki, M.; et al. The Role of Matrix Gla Protein (MGP) Expression in Paclitaxel and Topotecan Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowacka, M.; Sterzynska, K.; Andrzejewska, M.; Nowicki, M.; Januchowski, R. Drug resistance evaluation in novel 3D in vitro model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, M.; Sonobe, M.; Nakayama, E.; Kobayashi, M.; Kikuchi, R.; Kitamura, J.; Imamura, N.; Date, H. Higher expression of receptor tyrosine kinase Axl, and differential expression of its ligand, Gas6, predict poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 (Suppl. 3), S467–S476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, I.; Hafizi, S.; Stenhoff, J.; Hansson, K.; Dahlbäck, B. Analysis of Gas6 in human platelets and plasma. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auyez, A.; Sayan, A.E.; Kriajevska, M.; Tulchinsky, E. AXL Receptor in Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance: When Normal Functions Go Askew. Cancers 2021, 13, 4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Siemann, D.W. Therapeutic Targeting of the Gas6/Axl Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonagase, Y.; Takeda, M.; Azuma, K.; Hayashi, H.; Haratani, K.; Tanaka, K.; Yonesaka, K.; Ishii, H.; Hoshino, T.; Nakagawa, K. Tumor tissue and plasma levels of AXL and GAS6 before and after tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Dai, Y.; Chen, L.A. The Prediction Of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation And Prognosis Of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor By Serum Ferritin In Advanced NSCLC. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8835–8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, A.; Ansari, A.; Masroor, M.; Saxena, A.; Pandey, R.M.; Upadhyay, A.; Luthra, K.; Khilnani, G.C.; Jain, D.; Kumar, R.; et al. Measurement of Serum EGFR mRNA Expression is a Reliable Predictor of Treatment Response and Survival Outcomes in Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2020, 21, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Ventosa, E.Y.; Blanco-Prieto, S.; González-Piñeiro, A.L.; Rodríguez-Berrocal, F.J.; Piñeiro-Corrales, G.; Páez de la Cadena, M. Pretreatment levels of the serum biomarkers CEA, CYFRA 21-1, SCC and the soluble EGFR and its ligands EGF, TGF-alpha, HB-EGF in the prediction of outcome in erlotinib treated non-small-cell lung cancer patients. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghgoo, S.M.; Khosravi, A.; Mortaz, E.; Pourabdollah-Toutkaboni, M.; Seifi, S.; Sabour, S.; Allameh, A. Prognostic value of rare and complex mutations in EGFR and serum levels of soluble EGFR and its ligands in non-small cell lung carcinoma patients. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serilmez, M.; Özgür, E.; Karaman, S.; Gezer, U.; Duranyıldız, D. Detection of serum protein and circulating mRNA of cMET, HGF EGF and EGFR levels in lung cancer patients to guide individualized therapy. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 25, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).