Intersex Plays a Role in Microbial Homeostasis in the Brown Planthopper
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Expression Validation by Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.3. RNA Interference
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscope Analysis
2.5. Differential Expression Analysis Based on RNA-seq
2.6. Bacterial Community Characterization by Illumina Sequencing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
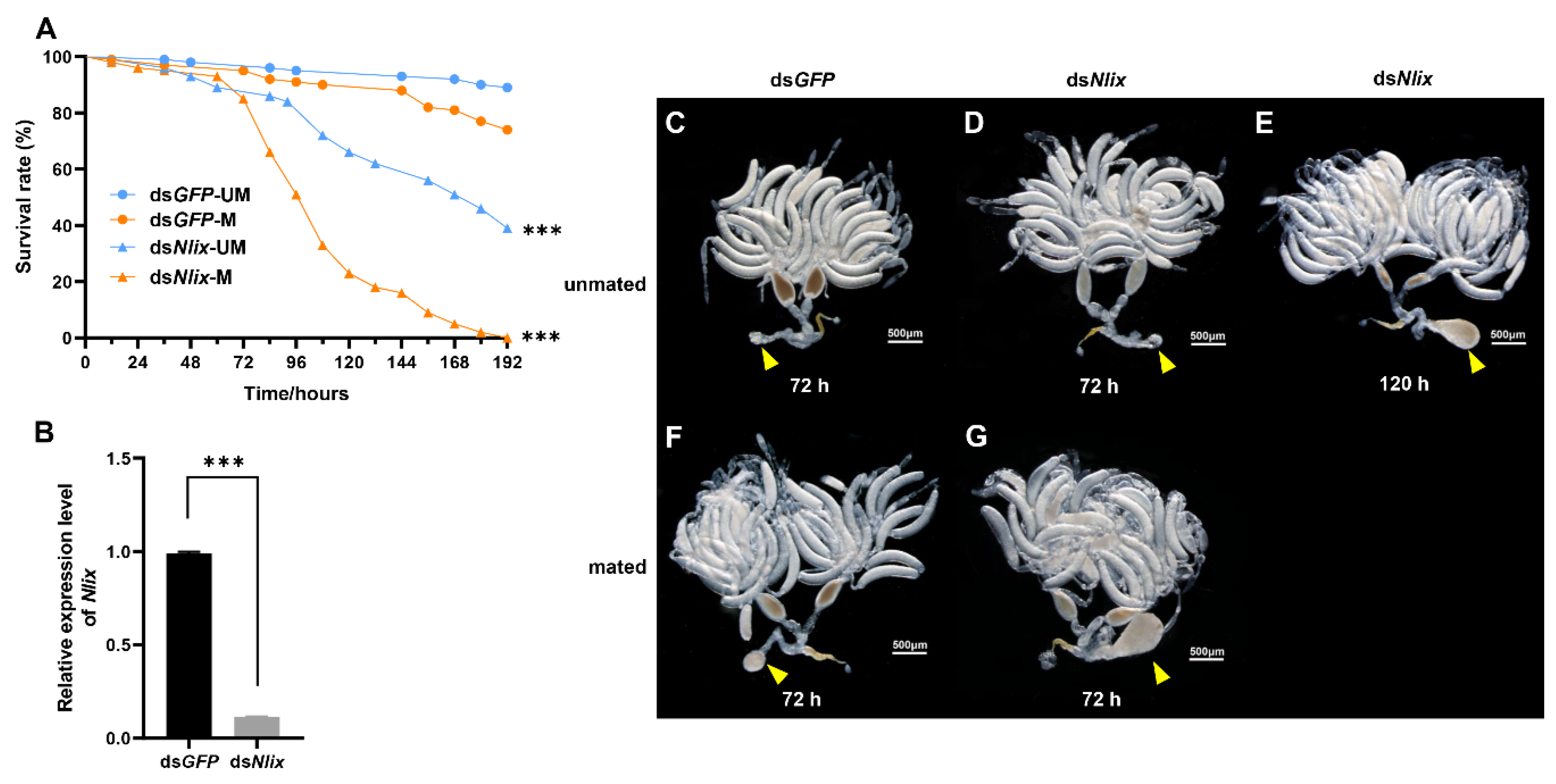
3.1. Effects of Nlix Knockdown on the Survival and Copulatory Bursa Development of BPH Female Adults
3.2. Electron Microscopy Observations
3.3. Expression of Defense Response Genes Regulated by dsNlix Treatment
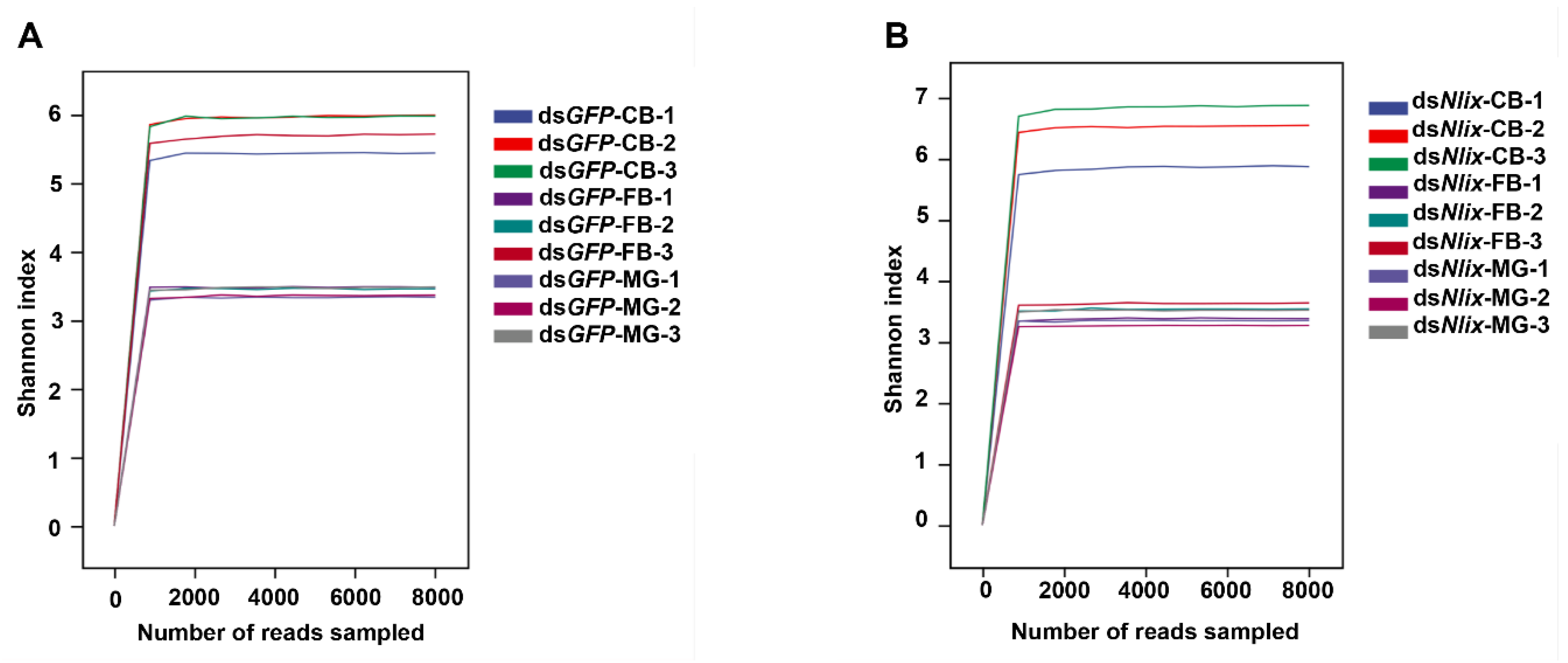
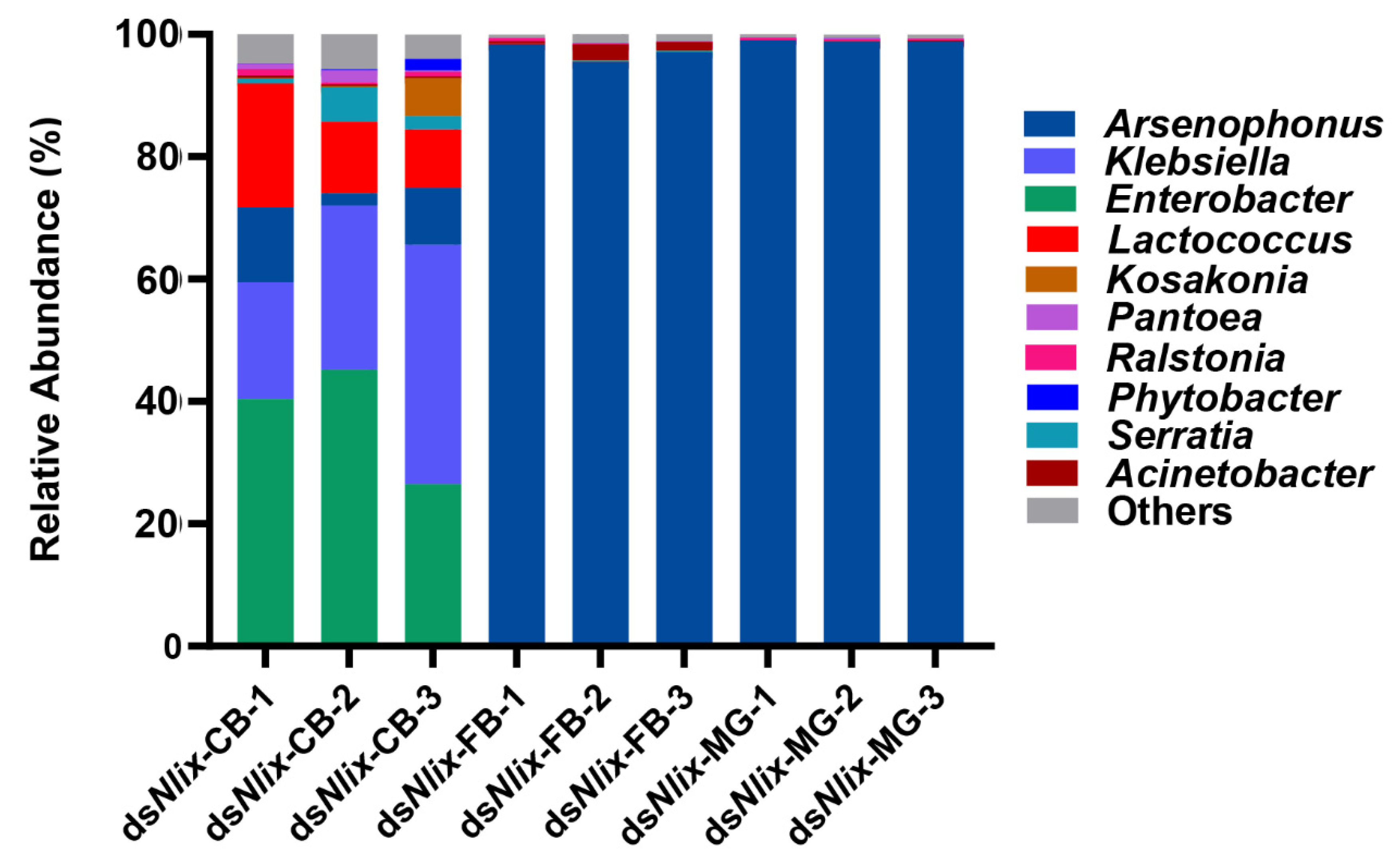
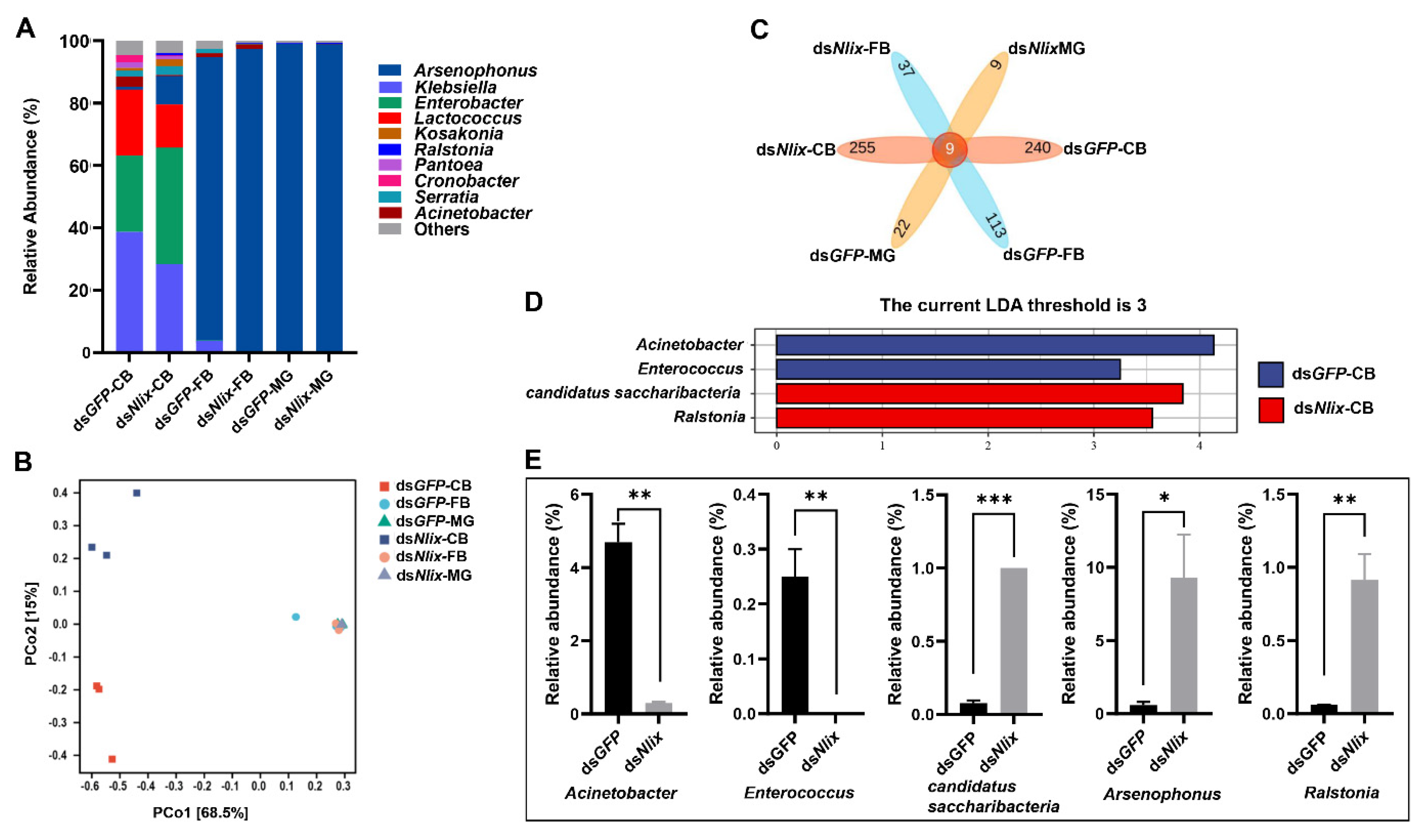
3.4. Microbial Community Compositions in Copulatory Bursa, Fat Body, and Midgut
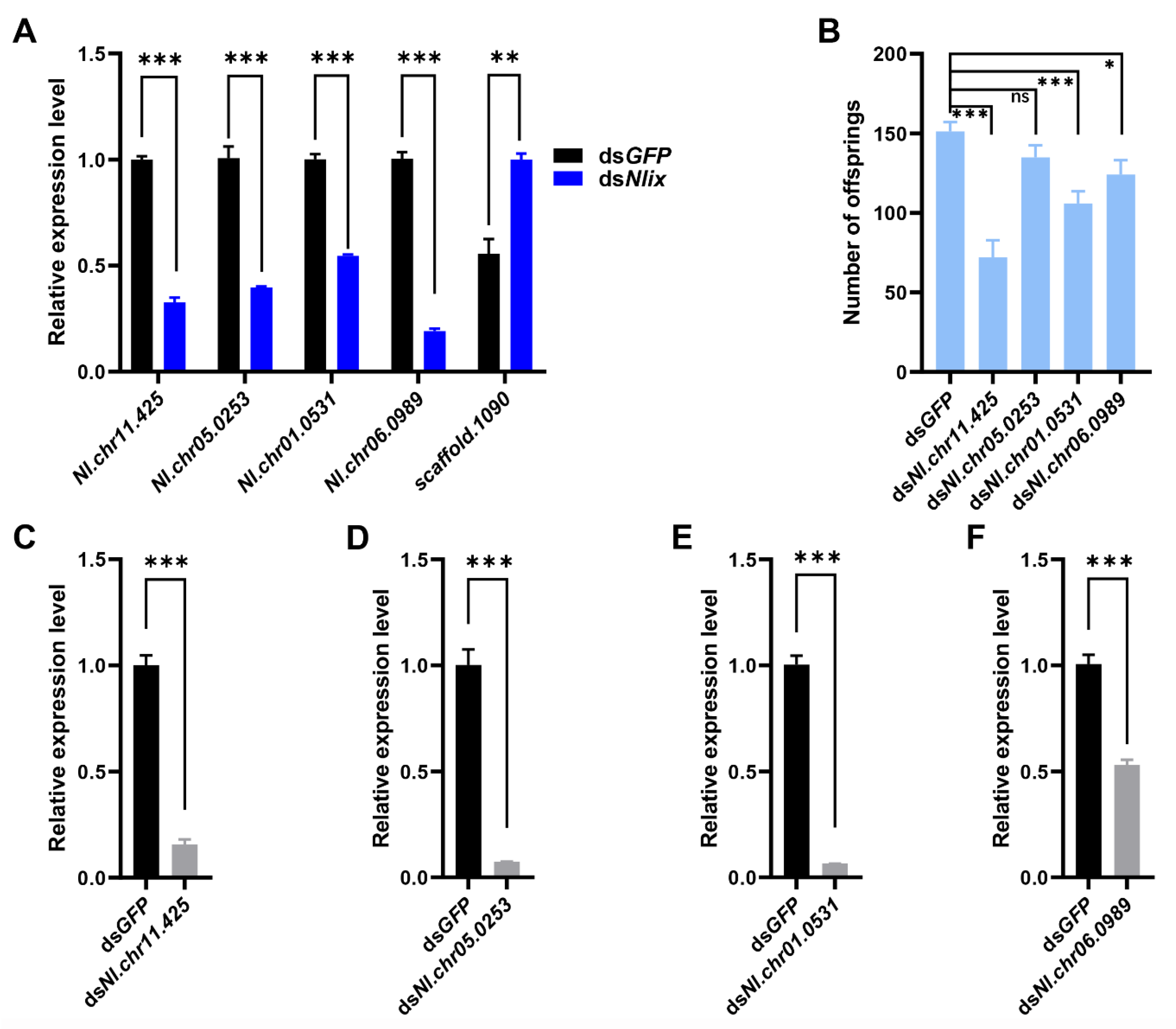
3.5. The Nlix Gene Was Associated with Shifted Microbial Communities of BPH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Primer Name | Sequence (5’-3’) * | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Nlix-RNAi-F-1 | T7-TTCTGGATTGAACAGTGGCAAT | Nlix-1 dsRNA synthesis |
| Nlix -RNAi-R-1 | T7-CAATGTTTCTCTTAGTTGACCG | |
| Nlix -RNAi-F-2 | T7-AATAATTTGGTGGACGTTGG | Nlix-2 dsRNA synthesis |
| Nlix -RNAi-R-2 | T7-AGGGTTCTGAATGTTGTGTG | |
| Nl.chr11.425-RNAi-F | T7-CGAGTTCTTTCCCGATAAGT TTGTGCATGTCTCCATACAA | Nl.chr11.425 dsRNA synthesis |
| Nl.chr11.425-RNAi-R | T7-TTGTGCATGTCTCCATACAA | |
| Nl.chr06.0989-RNAi-F | T7-CTGCCGGATATGTCATACAA | Nl.chr06.0989 dsRNA synthesis |
| Nl.chr06.0989-RNAi-R | T7-GACGAGACCAAGAGAGTTTT | |
| Nl.chr01.0531-RNAi-F | T7-CACGAACATCTCTAACCGAT | Nl.chr01.0531 dsRNA synthesis |
| Nl.chr01.0531-RNAi-R | T7-CCATTGAAGGGATAGACGAG | |
| Nl.chr05.0253-RNAi-F | T7-ACACAGCAGTTGATGGTAAT | Nl.chr05.0253 dsRNA synthesis |
| Nl.chr05.0253-RNAi-R | T7-GCTTTCCAAGGAAAAGCTAC | |
| QNlix -F-1 | GACAACCGAATATGCCAGGACAG | RT-qPCR for Nlix-1 |
| QNlix -R-1 | AGTTGACCGACAAGAGATTTGACT | |
| QNlix -F-2 | ACTCTCAAAACAGCGGCCA | RT-qPCR for Nlix-2 |
| QNlix -R-2 | TTCCTTGGTTCAGGCACTCC | |
| QNl.chr11.425-RNAi-F | TCGTTTTGGATCGAAGGGCA | RT-qPCR for Nl.chr11.425 |
| QNl.chr11.425-RNAi-R | AACGGGTTCATGTTTTGGCG | |
| QNl.chr06.0989-RNAi-F | GTGGCACAATCCAATCACCG | RT-qPCR for Nl.chr06.0989 |
| QNl.chr06.0989-RNAi-R | TACCATCCGCACTGGAGTTG | |
| QNl.chr01.0531-RNAi-F | CACGAACATCTCTAACCGAT | RT-qPCR for Nl.chr01.0531 |
| QNl.chr01.0531-RNAi-R | CCATTGAAGGGATAGACGAG | |
| QNl.chr05.0253-RNAi-F | CAGTCCAATGCTCCCCTGAG | RT-qPCR for Nl.chr05.0253 |
| QNl.chr05.0253-RNAi-R | ACAACGAGCGGCTGTTAGAA | |
| Qscaffold.1090-RNAi-R | GACTGCAGTGAAAGACCCGA | RT-qPCR for scaffold.1090 |
| Qscaffold.1090-RNAi-R | CGATCAACCAGGATGCCAGA | |
| QNl18S-F | CGCTACTACCGATTGAA | RT-qPCR for 18s |
| QNl18S-R | GGAAACCTTGTTACGACTT |
References
- Hurst, G.D.; Jiggins, F.M. Male-killing bacteria in insects: Mechanisms, incidence, and implications. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stouthamer, R.; Breeuwer, J.A.; Hurst, G.D. Wolbachia Pipientis: Microbial manipulator of arthropod reproduction. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 1999, 53, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.E. Nutritional interactions in insect-microbial symbioses: Aphids and their symbiotic bacteria Buchnera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, A.E. Phloem-sap feeding by animals: Problems and solutions. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldhaar, H.; Straka, J.; Krischke, M.; Berthold, K.; Stoll, S.; Mueller, M.J.; Gross, R. Nutritional upgrading for omnivorous carpenter ants by the endosymbiont Blochmannia. BMC Biol. 2007, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shigenobu, S.; Watanabe, H.; Hattori, M.; Sakaki, Y.; Ishikawa, H. Genome sequence of the endocellular bacterial symbiont of aphids Buchnera sp. APS. Nature 2000, 407, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliver, K.M.; Moran, N.A.; Hunter, M.S. Variation in resistance to parasitism in aphids is due to symbionts not host genotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12795–12800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliver, K.M.; Russell, J.A.; Moran, N.A.; Hunter, M.S. Facultative bacterial symbionts in aphids confer resistance to parasitic wasps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piel, J. A polyketide synthase-peptide synthetase gene cluster from an uncultured bacterial symbiont of Paederus beetles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14002–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cirimotich, C.M.; Dong, Y.; Clayton, A.M.; Sandiford, S.L.; Souza-Neto, J.A.; Mulenga, M.; Dimopoulos, G. Natural microbe-mediated refractoriness to plasmodium infection in Anopheles gambiae. Science 2011, 332, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hayatsu, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Nagayama, A.; Tago, K.; Fukatsu, T. Symbiont-mediated insecticide resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.F.; Guo, Z.J.; Riegler, M.; Xi, Z.Y.; Liang, G.W.; Xu, Y.J. Gut symbiont enhances insecticide resistance in a significant pest, the oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Microbiome 2017, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dillon, R.; Charnley, K. Mutualism between the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria and its gut microbiota. Res. Microbiol 2002, 153, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Segal, D.; Ringo, J.M.; Hefetz, A.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I.; Rosenberg, E. Commensal bacteria play a role in mating preference of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20051–20056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, Z.S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.Y.; Cheng, D.F. The divergence in bacterial components associated with Bactrocera dorsalis across developmental stages. Front. Microbiol 2018, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwong, W.K.; Moran, N.A. Gut microbial communities of social bees. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.Z.; Sun, J.T.; Wang, L.T.; Shu, X.H.; Guo, Y.; Keiichiro, M.; Zhu, Y.X.; Bing, X.L.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Hong, X.Y. Recent infection by Wolbachia alters microbial communities in wild Laodelphax striatellus populations. Microbiome 2020, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, E.M.; Lee, K.A.; Seo, Y.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, J.H.; Oh, B.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, W.J. Coordination of multiple dual oxidase-regulatory pathways in responses to commensal and infectious microbes in drosophila gut. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvell, H.; Engström, Y. A multilayered defense against infection: Combinatorial control of insect immune genes. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, T.; Liu, G.; Kang, D.; Ekengren, S.; Steiner, H.; Hultmark, D. A family of peptidoglycan recognition proteins in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13772–13777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.M.; Li, H.J.; Ren, L.; Cheng, D.F. Microbial communities in different developmental stages of the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis, are associated with differentially expressed peptidoglycan recognition protein-encoding genes. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2019, 85, e00803-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.X.; Yu, L.L.; Fan, H.W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.J.; Xi, Y.; Berthold, K.; Zhu, Z.R.; et al. Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.Q.; Guo, J.S.; Li, D.T.; Yu, Y.; Hagoort, J.; Moussian, B.; Zhang, C.X. Three-dimensional reconstruction of a whole insect reveals its phloem sap-sucking mechanism at nano-resolution. eLife 2021, 10, e62875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, K. Nutritional physiology of the brown rice planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stal (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). II. Essential amino acids for nymphal development. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1985, 20, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.W.; Noda, H.; Xie, H.Q.; Suetsugu, Y.; Zhu, Q.H.; Zhang, C.X. Genomic analysis of an ascomycete fungus from the rice planthopper reveals how it adapts to an endosymbiotic lifestyle. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2623–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.W.; Lu, J.B.; Ye, Y.X.; Yu, X.P.; Zhang, C.X. Characteristics of the draft genome of “Candidatus Arsenophonus nilaparvatae”, a facultative endosymbiont of Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Sci. 2016, 23, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Wang, T.Z.; Zhu, H.F.; Pan, H.B.; Yu, X.P. Diversity and dynamics of microbial communities in brown planthopper at different developmental stages revealed by high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Yu, N.; Xu, X.X.; Liu, Z.W. Community structure, dispersal ability and functional profiling of microbiome existing in fat body and ovary of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Xie, Y.C.; Li, H.J.; Zhuo, J.C.; Zhang, C.X. Pleiotropic roles of the orthologue of the drosophila melanogaster intersex gene in the brown planthopper. Genes 2021, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, K.; Huang, Y.P. Intersex regulates female external genital and imaginal disc development in the silkworm. Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2019, 108, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Yang, J.J.; Huo, Z.J.; Wang, S.L.; Wu, Q.J.; Zhou, X.G.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.J. Characteristic and functional study of intersex, a gene related to female fertility in Bemisia tabaci. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett-Engele, C.M.; Siegal, M.L.; Manoli, D.S.; Williams, B.C.; Li, H.; Baker, B.S. Intersex, a gene required for female sexual development in Drosophila, is expressed in both sexes and functions together with doublesex to regulate terminal differentiation. Development 2002, 129, 4661–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.J.; Xue, J.; Lu, B.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhuo, J.C.; He, S.F.; Ma, X.F.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Fan, H.W.; Xu, J.Y.; et al. Two insulin receptors determine alternative wing morphs in planthoppers. Nature 2015, 519, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, J.C.; Hu, Q.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Jo, S.B.; Zhang, C.X. Identification and functional analysis of the doublesex gene in the sexual development of a hemimetabolous insect, the brown planthopper. Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2018, 102, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramette, A. Multivariate analyses in microbial ecology. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, A.E. Multiorganismal insects: Diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebollar, E.A.; Hughey, M.C.; Medina, D.; Harris, R.N.; Ibáñez, R.; Belden, L.K. Skin bacterial diversity of Panamanian frogs is associated with host susceptibility and presence of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Bai, J.Y.; Nam, Y.D.; Bae, J.W.; Lee, D.G.; Shin, S.C.; Ha, E.M.; Lee, W.J. Innate immune homeostasis by the homeobox gene caudal and commensal-gut mutualism in Drosophila. Science 2008, 319, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.-H.; Li, H.-J.; Ye, Y.-X.; Zhuo, J.-C.; Zhang, C.-X. Intersex Plays a Role in Microbial Homeostasis in the Brown Planthopper. Biology 2021, 10, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090875
Zhang H-H, Li H-J, Ye Y-X, Zhuo J-C, Zhang C-X. Intersex Plays a Role in Microbial Homeostasis in the Brown Planthopper. Biology. 2021; 10(9):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090875
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hou-Hong, Han-Jing Li, Yu-Xuan Ye, Ji-Chong Zhuo, and Chuan-Xi Zhang. 2021. "Intersex Plays a Role in Microbial Homeostasis in the Brown Planthopper" Biology 10, no. 9: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090875
APA StyleZhang, H.-H., Li, H.-J., Ye, Y.-X., Zhuo, J.-C., & Zhang, C.-X. (2021). Intersex Plays a Role in Microbial Homeostasis in the Brown Planthopper. Biology, 10(9), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090875






