Metabolomics Profiling of Cystic Renal Disease towards Biomarker Discovery
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
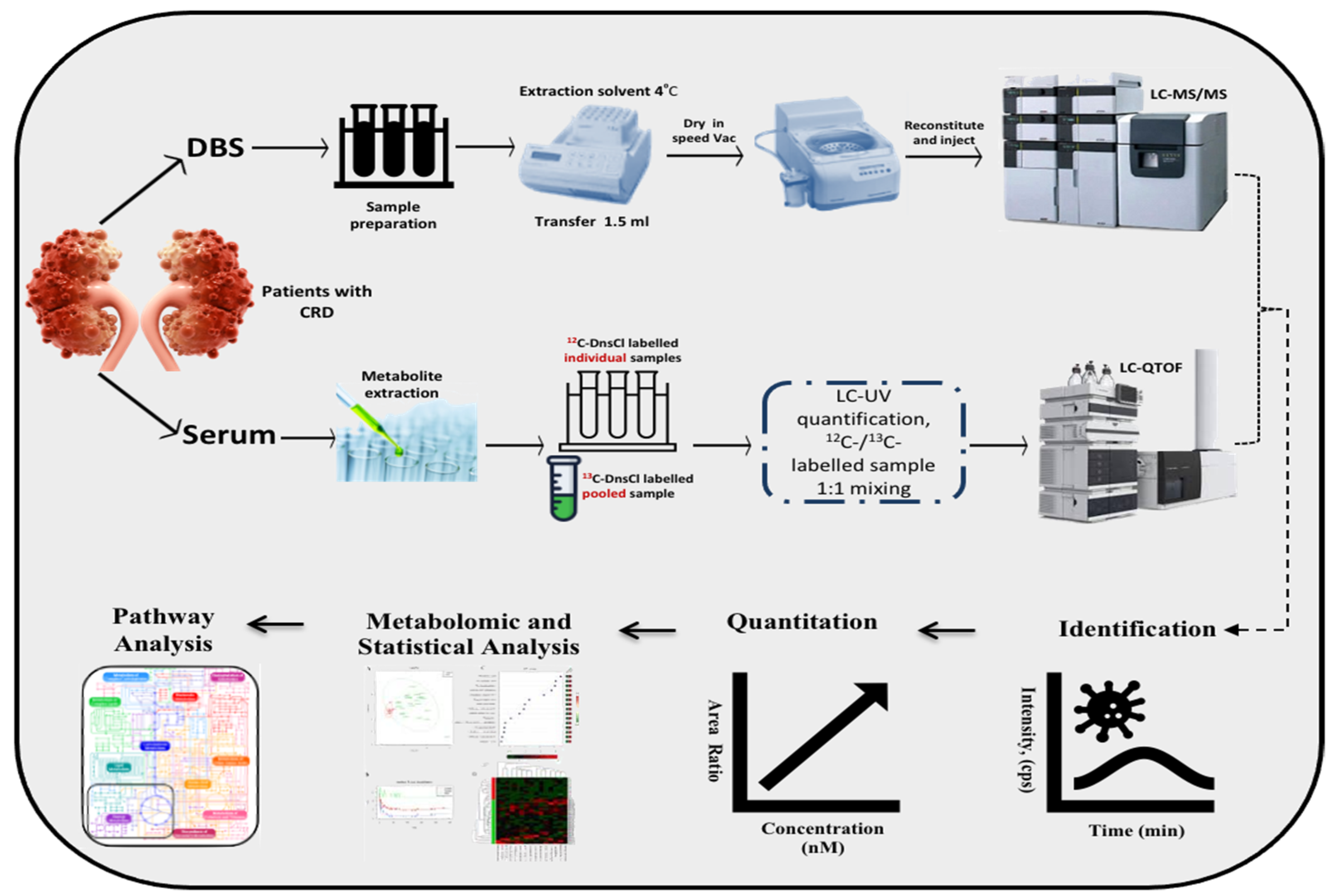
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Elements and Chemicals
2.2. Study Design, Patient Recruitment, and Sample Collection
2.3. Label-Free Metabolomics Profiling
2.4. CIL LC-MS Metabolomics Profiling on Serum for CRD Patients
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics, Clinical and Molecular Features in CRD Patients
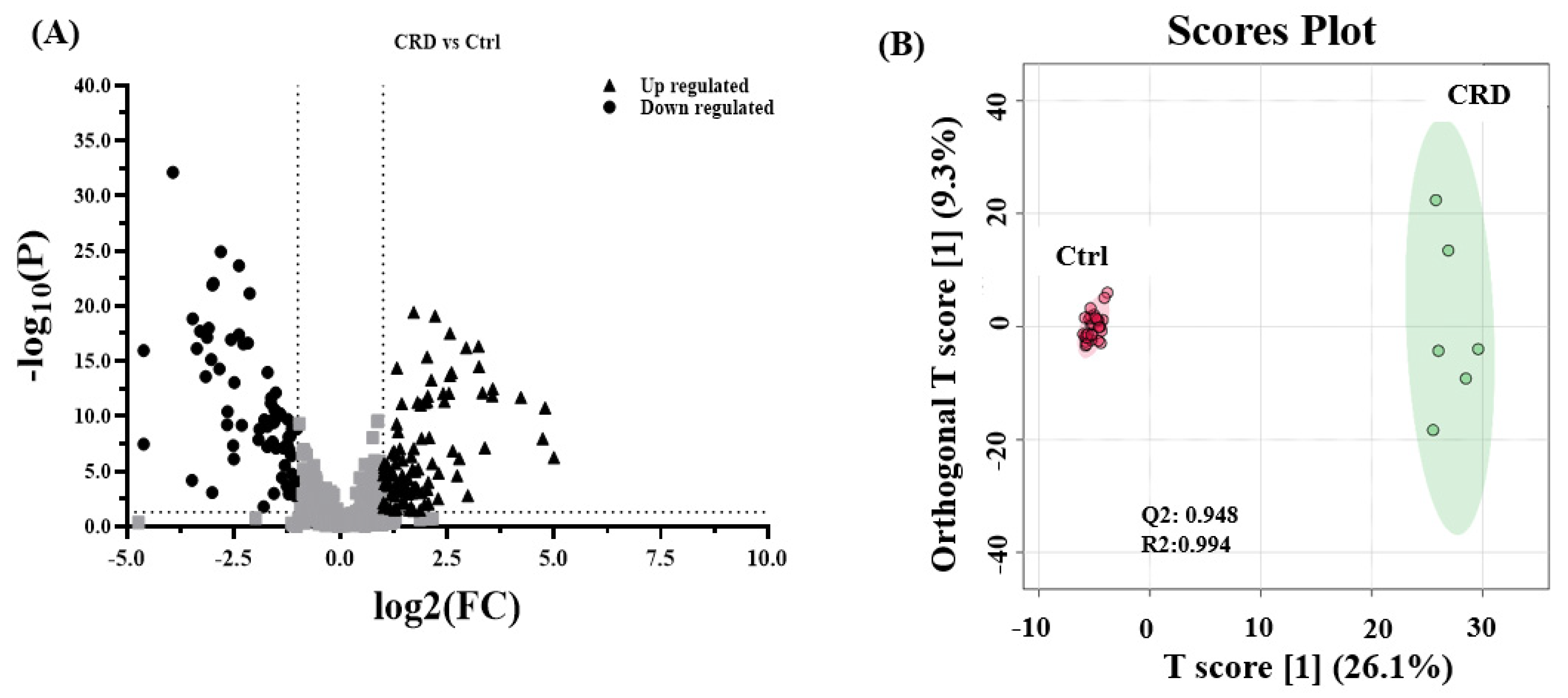
3.2. Metabolomics Pattern in DBS of CRD Patients
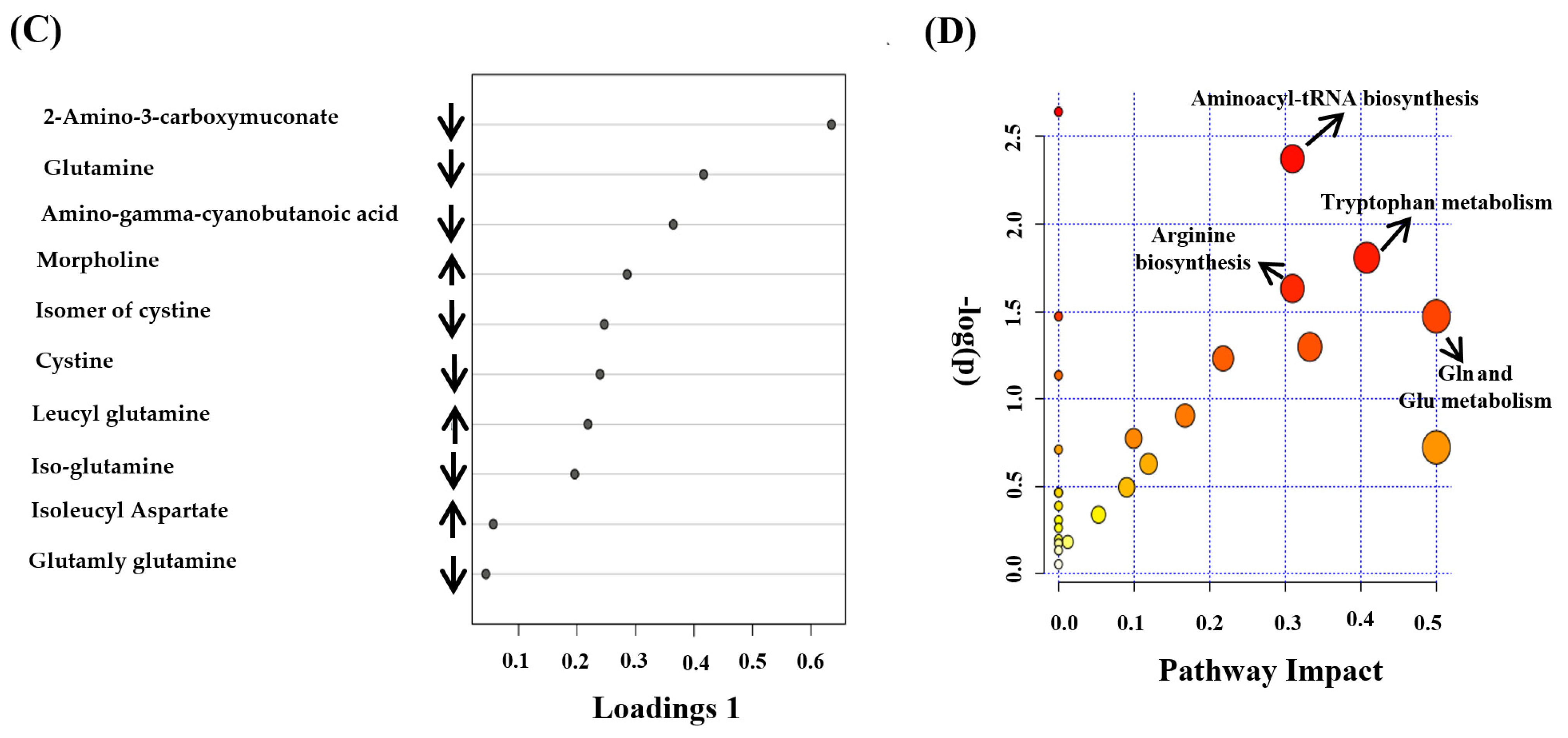
3.3. Metabolomics Pattern in Serum of CRD Patients
3.4. Biomarker Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sigmon, D.F.; Shikhman, R.; Nielson, J.L. Renal Cyst. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright© 2021; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hindman, N.M. Imaging of Cystic Renal Masses. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 55, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Snyder, M. Systems biology: Personalized medicine for the future? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.; Lopata, A.L.; Dasouki, M.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Metabolomics toward personalized medicine. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.; Gu, X.; Luo, X.; Al-Mousa, H.; Arnaout, R.; Al-Saud, B.; Lopata, A.L.; Li, L.; Dasouki, M.; Rahman, A.M.A. Metabolomics Distinguishes DOCK8 Deficiency from Atopic Dermatitis: Towards a Biomarker Discovery. Metabolites 2019, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.W.; Tung, K.Y.; Liang, P.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Kuo, N.W.; Lee, Y.L. Gene-gene and gene-environmental interactions of childhood asthma: A multifactor dimension reduction approach. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raamsdonk, L.M.; Teusink, B.; Broadhurst, D.; Zhang, N.; Hayes, A.; Walsh, M.C.; Berden, J.A.; Brindle, K.M.; Kell, D.B.; Rowland, J.J.; et al. A functional genomics strategy that uses metabolome data to reveal the phenotype of silent mutations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Susztak, K. Fat Burning Problem in Cystic Kidneys: An Emerging Common Mechanism of Chronic Kidney Disease. EBioMedicine 2016, 5, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Guo, K.; Li, L. Differential 12C-/13C-isotope dansylation labeling and fast liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for absolute and relative quantification of the metabolome. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3919–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Li, L. Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS for Human Blood Metabolome Analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1730, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.; Malkawi, A.; Albast, N.; Al Bougha, S.; Lopata, A.; Dasouki, M.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. A targeted metabolomics approach for clinical diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1025, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meola, M.; Samoni, S.; Petrucci, I. Clinical Scenarios in Chronic Kidney Disease: Cystic Renal Diseases. Contrib. Nephrol. 2016, 188, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, T.; Li, L. Counting missing values in a metabolite-intensity data set for measuring the analytical performance of a metabolomics platform. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, T.; Wu, Y.; Tang, C.; Lin, G.; Li, L. DnsID in MyCompoundID for rapid identification of dansylated amine- and phenol-containing metabolites in LC-MS-based metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9838–9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Zuniga, A.; Stanislaus, A.E.; Wu, Y.; Huan, T.; Zheng, J.; Shi, Y.; Wishart, D.S.; et al. MyCompoundID: Using an evidence-based metabolome library for metabolite identification. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Using MetaboAnalyst 3.0 for Comprehensive Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 55, 14.10.11–14.10.91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W652–W660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisceglia, M.; Galliani, C.A.; Senger, C.; Stallone, C.; Sessa, A. Renal cystic diseases: A review. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2006, 13, 26–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosniak, M.A. The current radiological approach to renal cysts. Radiology 1986, 158, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Aronov, P.; Zakharkin, S.O.; Anderson, D.; Perroud, B.; Thompson, I.M.; Weiss, R.H. Urine metabolomics analysis for kidney cancer detection and biomarker discovery. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2009, 8, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, W.; Abdel Jabar, M.; Masood, A.; Jacob, M.; Nizami, I.; Dasouki, M.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Dried Blood Spot-Based Metabolomic Profiling in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2346–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Qiu, S.; Wang, X. Metabolomics insights into pathophysiological mechanisms of nephrology. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y. Metabolomics in chronic kidney disease. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2013, 422, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.H.; Kim, K. Metabolomics in the study of kidney diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 8, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalim, S.; Rhee, E.P. An overview of renal metabolomics. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbiss, H.; Maker, G.L.; Gummer, J.; Sharman, M.J.; Phillips, J.K.; Boyce, M.; Trengove, R.D. Development of a non-targeted metabolomics method to investigate urine in a rat model of polycystic kidney disease. Nephrology 2012, 17, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyohara, T.; Suzuki, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Yoshihara, D.; Takeuchi, Y.; Mishima, E.; Kikuchi, K.; Suzuki, C.; Tanemoto, M.; Ito, S.; et al. Metabolomic profiling of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease rat model. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2011, 15, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.L.; Ganti, S.; Bukanov, N.O.; Chapman, A.; Fiehn, O.; Osier, M.; Kim, K.; Weiss, R.H. A metabolomics approach using juvenile cystic mice to identify urinary biomarkers and altered pathways in polycystic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F909–F922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronwald, W.; Klein, M.S.; Zeltner, R.; Schulze, B.D.; Reinhold, S.W.; Deutschmann, M.; Immervoll, A.K.; Böger, C.A.; Banas, B.; Eckardt, K.U.; et al. Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, V.J.; Kim, J.; Rand, A.; Yang, C.; Sturdivant, S.; Hammock, B.; Bell, P.D.; Guay-Woodford, L.M.; Weiss, R.H. The cpk model of recessive PKD shows glutamine dependence associated with the production of the oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2015, 309, F492–F498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, I.; Chiaravalli, M.; Mannella, V.; Ulisse, V.; Quilici, G.; Pema, M.; Song, X.W.; Xu, H.; Mari, S.; Qian, F.; et al. Defective glucose metabolism in polycystic kidney disease identifies a new therapeutic strategy. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibba, M.; Soll, D. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 617–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, E.; Druml, W. Plasma amino acid imbalance: Dangerous in chronic diseases? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbiss, H.; Maker, G.L.; Trengove, R.D. Metabolomics Approaches for the Diagnosis and Understanding of Kidney Diseases. Metabolites 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, J.F.; Hwang, V.J.; Ishimaru, T.; Chmiel, K.J.; Zhou, J.X.; Shim, K.; Stewart, B.J.; Mahjoub, M.R.; Jen, K.Y.; Barupal, D.K.; et al. Arginine reprogramming in ADPKD results in arginine-dependent cystogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1855–F1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hruby, A.; Toledo, E.; Clish, C.B.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Hu, F.B. Metabolomics in Prediabetes and Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Kong, H.; Guan, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, G. A GC-based metabonomics investigation of type 2 diabetes by organic acids metabolic profile. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 850, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knott, M.E.; Manzi, M.; Zabalegui, N.; Salazar, M.O.; Puricelli, L.I.; Monge, M.E. Metabolic Footprinting of a Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma in Vitro Model for Human Kidney Cancer Detection. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3877–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger-Nukpezah, T.; Geynisman, D.M.; Nikonova, A.S.; Benzing, T.; Golemis, E.A. The hallmarks of cancer: Relevance to the pathogenesis of polycystic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Schutzer, W.E.; Lindsley, J.N.; Bagby, S.P.; Oyama, T.T.; Anderson, S.; Weiss, R.H. p21 is decreased in polycystic kidney disease and leads to increased epithelial cell cycle progression: Roscovitine augments p21 levels. BMC Nephrol. 2007, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, P.; Wei, S.; Xiong, F. Recent Advances of mTOR Inhibitors Use in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Is the Road Still Open? Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2962–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robey, M.T.; Ye, R.; Bok, J.W.; Clevenger, K.D.; Islam, M.N.; Chen, C.; Gupta, R.; Swyers, M.; Wu, E.; Gao, P.; et al. Identification of the First Diketomorpholine Biosynthetic Pathway Using FAC-MS Technology. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.C.; Yuwen, H.; Wang, K.; Bruno, P.M.; Bullock, K.; Deik, A.; Santaguida, S.; Trakala, M.; Pfau, S.J.; Zhong, N.; et al. Aneuploid Cell Survival Relies upon Sphingolipid Homeostasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5272–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Patient | Age (Yrs) | CRD Phenotype/Renal Disease | Other Comorbidities | eGFR (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRD-1 | 8 | Renal hypodysplasia/Facial dysmorphism | N/A | 46 |
| CRD-2 | 20 | Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease | ERSD on HD, autoimmune thrombocytopenia, congenital hepatic fibrosis | 10 |
| CRD-3 | 45 | Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease/Failed kidney transplant | DM, HTN, dyslipidemia, chronic HCV | 9 |
| CRD-4 | 22 | Cystic hypokalemic nephropathy/Apparent Mineralocorticoid excess | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia | 74 |
| CRD-5 | 78 | Bilateral cortical simple cysts/Diabetic kidney disease | DM, HTN, HNF1B mutation | 46 |
| CRD-6 | 51 | Bilateral cortical simple cysts/CKD | Valvular heart disease | 39 |
| CRD-7 | 59 | Bilateral cortical simple renal cysts/Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, CKD | DM, HTN, HNF-B mutation, proteinuria | 92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sriwi, D.; Alabdaljabar, M.S.; Jacob, M.; Mujamammi, A.H.; Gu, X.; Sabi, E.M.; Li, L.; Hussein, M.H.; Dasouki, M.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Metabolomics Profiling of Cystic Renal Disease towards Biomarker Discovery. Biology 2021, 10, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080770
Sriwi D, Alabdaljabar MS, Jacob M, Mujamammi AH, Gu X, Sabi EM, Li L, Hussein MH, Dasouki M, Abdel Rahman AM. Metabolomics Profiling of Cystic Renal Disease towards Biomarker Discovery. Biology. 2021; 10(8):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080770
Chicago/Turabian StyleSriwi, Dalia, Mohamad S. Alabdaljabar, Minnie Jacob, Ahmed H. Mujamammi, Xinyun Gu, Essa M. Sabi, Liang Li, Maged H. Hussein, Majed Dasouki, and Anas M. Abdel Rahman. 2021. "Metabolomics Profiling of Cystic Renal Disease towards Biomarker Discovery" Biology 10, no. 8: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080770
APA StyleSriwi, D., Alabdaljabar, M. S., Jacob, M., Mujamammi, A. H., Gu, X., Sabi, E. M., Li, L., Hussein, M. H., Dasouki, M., & Abdel Rahman, A. M. (2021). Metabolomics Profiling of Cystic Renal Disease towards Biomarker Discovery. Biology, 10(8), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080770






