Comparative Chloroplast Genomes of Four Lycoris Species (Amaryllidaceae) Provides New Insight into Interspecific Relationship and Phylogeny
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Sample Collection, DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.2. Complete Cp Genome Assembly, Annotation and Structure Analysis
2.3. Interspecific Comparison of Chloroplast Genomes
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Features of the Cp Genomes of Lycoris
3.2. CpSSRs and Repeat Structures
3.3. Statistics of Codon Usage
3.4. Inverted Repeats Contraction, Expansion, and Interspecific Comparison
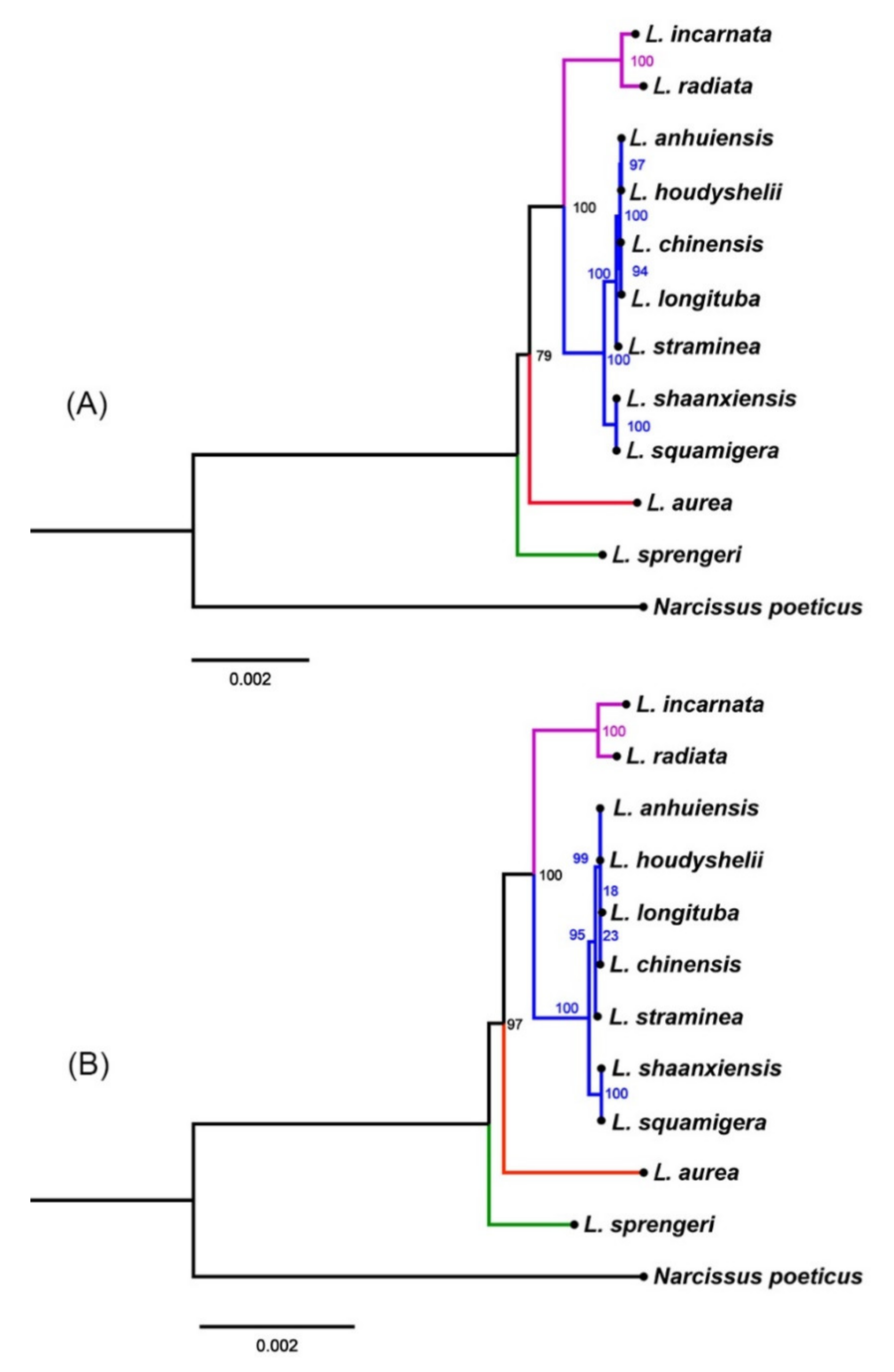
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meerow, A.; Snijman, D. Amaryllidaceae. Flowering Plants·Monocotyledons; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 83–110. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z. Amaryllidaceae and sceletium alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2003, 20, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahlíková, L.; Breiterová, K.; Opletal, L. Chemistry and biological activity of alkaloids from the genus Lycoris (Amaryllidaceae). Molecules 2020, 25, 4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae, K.H.; Ko, S.C. A taxonomic study of the genus Lycoris (Amaryllidaceae) based on morphological characters. Trop. Med. Int. Health 1995, 9, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, S. Variation and evolution in the karyotype of Lycoris, Amaryllidaceae. Cytologia 1986, 51, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, M.H.; Ou, L.J.; She, C.W. A new species of Lycoris (Amaryllidaceae) from Hunan, China. Novon 2013, 22, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Zheng, L.; Shao, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, K. A new natural allotriploid, Lycoris × hubeiensis hybr. nov. (Amaryllidaceae), identified by morphological, karyological and molecular data. Nord. J. Bot. 2018, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, P.C. Lycoris tsinlingensis (Amaryllidaceae), a new species from Shaanxi, China. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 2020, 57, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.M.; Zhuge, Q.; Lou, L.H.; Zou, H.Y.; Huang, M.R.; Wang, M.X. Analysis of the inter-species relationships on Lycoris (Amaryllidaceae) by use of RAPD. Yi Chuan Xue Bao 2002, 29, 915–921. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Qiu, Y.; Li, E.; Wu, L.; Fu, C. Phylogenetic relationships and possible hybrid origin of Lycoris species (Amaryllidaceae) revealed by ITS sequences. Biochem. Genet. 2006, 44, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, L.; Fu, C. Interspecific relationships of Lycoris (Amaryllidaceae) inferred from inter-simple sequence repeat data. Sci. Hortic Amst. 2006, 110, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tong, Z.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Huang, C. Analysis of genetic diversity and relationships among genus Lycoris based on start codon targeted (SCoT) marker. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 57, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, I.; Wendel, J.F. Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 29, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Sun, Y.; Wei, L.; Lei, X.; Cameron, K.M.; Fu, C. Plastid DNA sequence data help to clarify phylogenetic relationships and reticulate evolution in Lycoris (Amaryllidaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 176, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, M.; Cronn, R.; Liston, A. Increasing phylogenetic resolution at low taxonomic levels using massively parallel sequencing of chloroplast genomes. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delseny, M.; Han, B.; Hsing, Y. High throughput DNA sequencing: The new sequencing revolution. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.; Lickey, E.B.; Schilling, E.E.; Small, R.L. Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: The tortoise and the hare III. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravi, V.; Khurana, J.; Tyagi, A.; Khurana, P. An update on chloroplast genomes. Plant Syst. Evol. 2008, 271, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.; Yu, M.; Chang, W. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.S.; Li, P.; Qiu, Y.X. The complete chloroplast genomes of three Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) species: Comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Lu, R.S.; Xu, W.Q.; Tetsuo, O.T.; Cai, M.Q.; Qiu, Y.X.; Cameron, K.M.; Fu, C.X. Comparative genomics and phylogenomics of East Asian tulips (Amana, Liliaceae). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahzadi, I.; Mehmood, F.; Ali, Z.; Ahmed, I.; Mirza, B. Chloroplast genome sequences of Artemisia maritima and Artemisia absinthium: Comparative analyses, mutational hotspots in genus Artemisia and phylogeny in family Asteraceae. Genomics 2020, 112, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T.; Mirza, B. Characterization of Withania somnifera chloroplast genome and its comparison with other selected species of Solanaceae. Genomics 2020, 112, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.W.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, S.J.; Park, H.S.; Shim, H.; Lee, T.J.; Kang, J.H.; Sung, S.H.; Yang, T.J. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Magic Lily (Lycoris squamigera). Mitochondrial DNA B 2018, 3, 1210–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, T.; Shu, X.; Wang, N.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, Z. Complete chloroplast genomes and comparative analyses of L. chinensis, L. anhuiensis, and L. aurea (Amaryllidaceae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: de novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, e18-e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Shu, X.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, Z.L. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Lycoris radiata. Mitochondrial DNA B 2019, 4, 2886–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvonen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraku, S.; Zmasek, C.M.; Nishimura, O.; Katoh, K. aLeaves facilitates on-demand exploration of metazoan gene family trees on MAFFT sequence alignment server with enhanced interactivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozewicki, J.; Li, S.; Amada, K.M.; Standley, D.M.; Katoh, K. MAFFT-DASH: Integrated protein sequence and structural alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W5–W10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stéphane, G.; Jean-François, D.; Vincent, L.; Maria, A.; Wim, H.; Olivier, G. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.F.; Tan, J.B.; Yu, Y.; Gui, L.J.; Su, D.M.; Zhou, S.D.; He, X.J. Insights into phylogeny, age and evolution of Allium (Amaryllidaceae) based on the whole plastome sequences. Ann. Bot. Lond. 2020, 125, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, X.; Nie, L.; Sun, W.; Hu, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Zheng, X.; Song, J.; Yao, H. Comparison and phylogenetic analysis of chloroplast genomes of three medicinal and edible Amomum species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jurica, M.S.; Stoddard, B.L. Homing endonucleases: Structure, function and evolution. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 1304–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelchner, S.A. Group II introns as phylogenetic tools: Structure, function, and evolutionary constraints. Am. J. Bot 2002, 89, 1651–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambowitz, A.M.; Zimmerly, S. Mobile group II introns. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2004, 38, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hausner, G.; Olson, R.; Simon, D.; Johnson, I.; Sanders, E.R.; Karol, K.G.; McCourt, R.M.; Zimmerly, S. Origin and evolution of the chloroplast trnK (matK) intron: A model for evolution of group II intron RNA structures. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.; Peakall, R. Chloroplast simple sequence repeats (cpSSRs): Technical resources and recommendations for expanding cpSSR discovery and applications to a wide array of plant species. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelchner, S.A. The evolution of non-coding chloroplast DNA and its application in plant systematics. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2000, 87, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsch, T.; Quandt, D. Mutational dynamics and phylogenetic utility of noncoding chloroplast DNA. Plant Syst. Evol. 2009, 282, 169–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Xu, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.L.; Yin, X.R.; Li, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, K.S. Codon usage patterns in Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) based on RNA-Seq data. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, H.C.; Lin, I.P.; Chow, T.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Chen, W.H.; Cheng, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Liu, S.M.; Chang, C.C.; et al. The chloroplast genome of Phalaenopsis aphrodite (Orchidaceae): Comparative analysis of evolutionary rate with that of grasses and its phylogenetic implications. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.B.; Tang, M.; Li, H.T.; Zhang, Z.R.; Li, D.Z. Complete chloroplast genome of the genus Cymbidium: Lights into the species identification, phylogenetic implications and population genetic analyses. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Zhuang, W.; Shu, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Complete chloroplast genome of Lycoris sprengeri (Amaryllidaceae) and genetic comparison. Mitochondrial DNA B 2019, 4, 3577–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Tong, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, W.; Shu, X.; Wang, Z.L. Characterisation of the complete chloroplast genome of Lycoris longituba (Amaryllidaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2019, 4, 3782–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayor, C.; Brudno, M.; Schwartz, J.R.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Visualizing global DNA sequence alignments of arbitrary length. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 1046–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amar, M.H. ycf1-ndhF genes, the most promising plastid genomic barcode, sheds light on phylogeny at low taxonomic levels in Prunus persica. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Zhang, D.; Qin, H.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L.; Xia, Q.; Liu, K. Hybrid origin of Lycoris shaanxiensis revealed by karyotype survey. Cytologia 2018, 83, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Hsu, P.S. A study on karyotypes of the genus Lycoris. J. Syst. Evol. 1989, 27, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, T.A.; Hayashi, A.; Sasanuma, T.; Kurita, S. Genetic variations in the chloroplast genome and phylogenetic clustering of Lycoris species. Genes. Genet. Syst. 2006, 81, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liao, W.; Tong, Z. Analysis on rDNA-ITS sequence and research of intra-specific phylogeny of Lycoris albiflora. J. Plant. Resour. Environ. 2009, 18, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, M.; Ou, L.; She, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, D. rDNA internal transcribed spacer sequence analysis of Lycoris Hert. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 7361–7365. [Google Scholar]
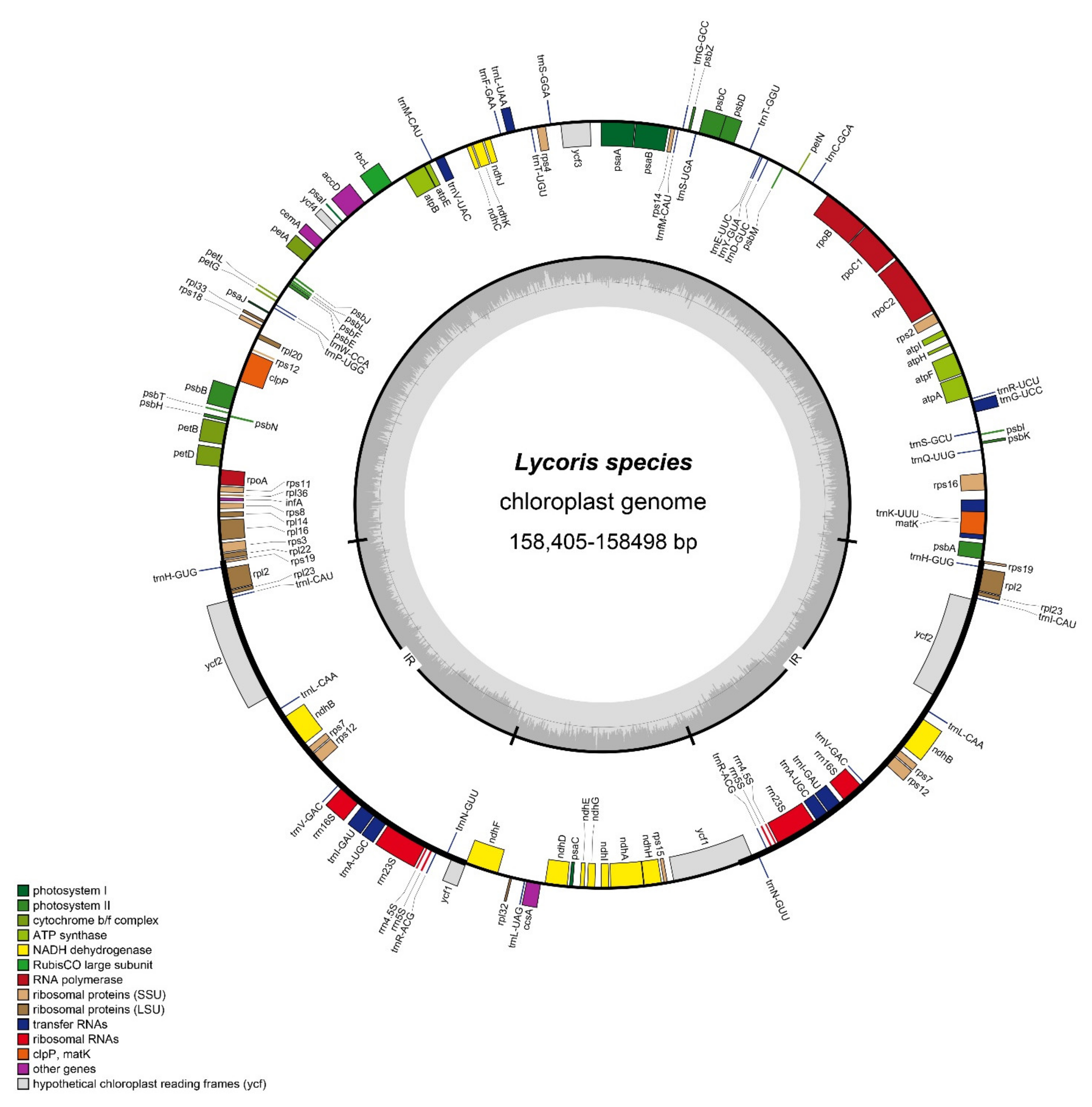

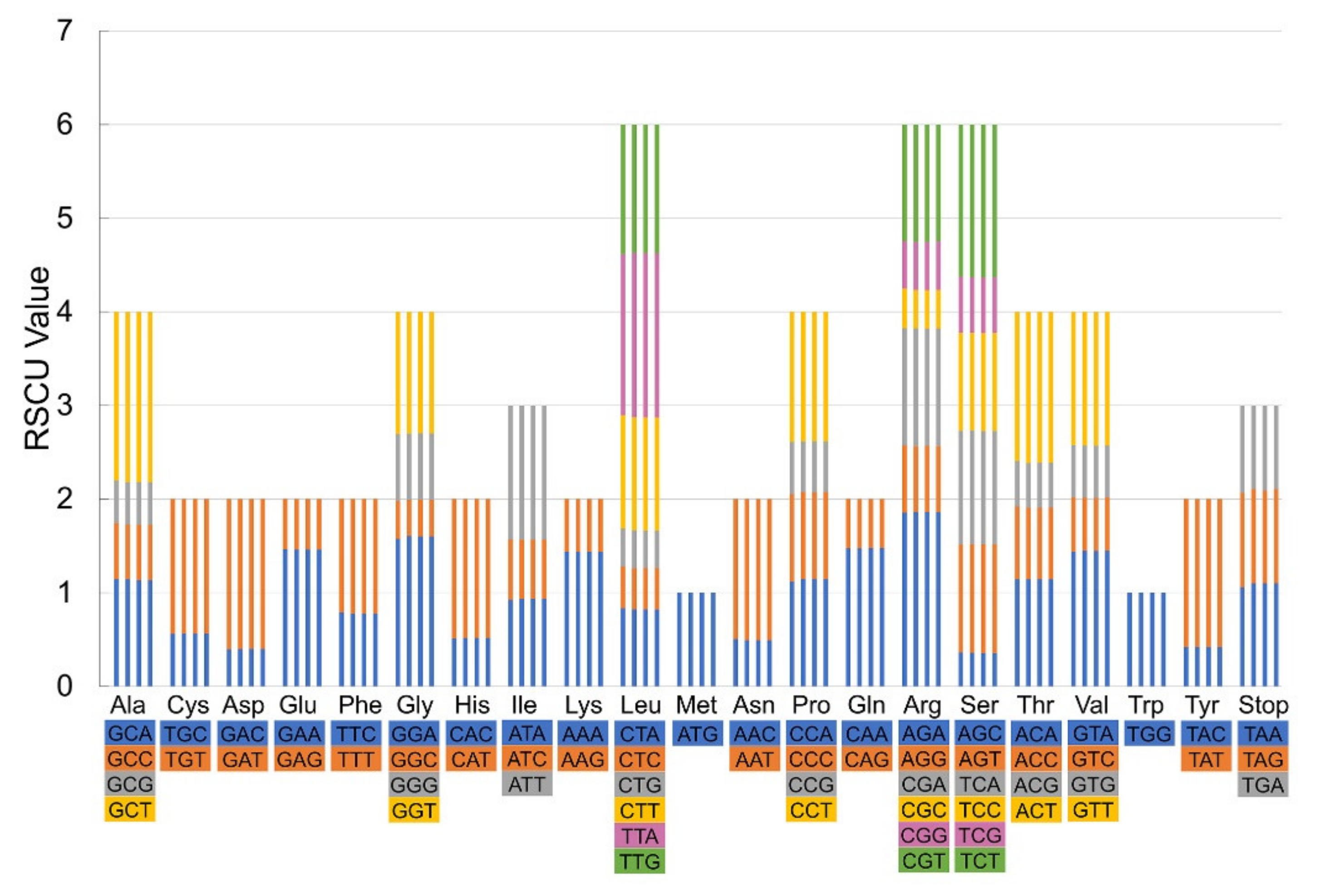
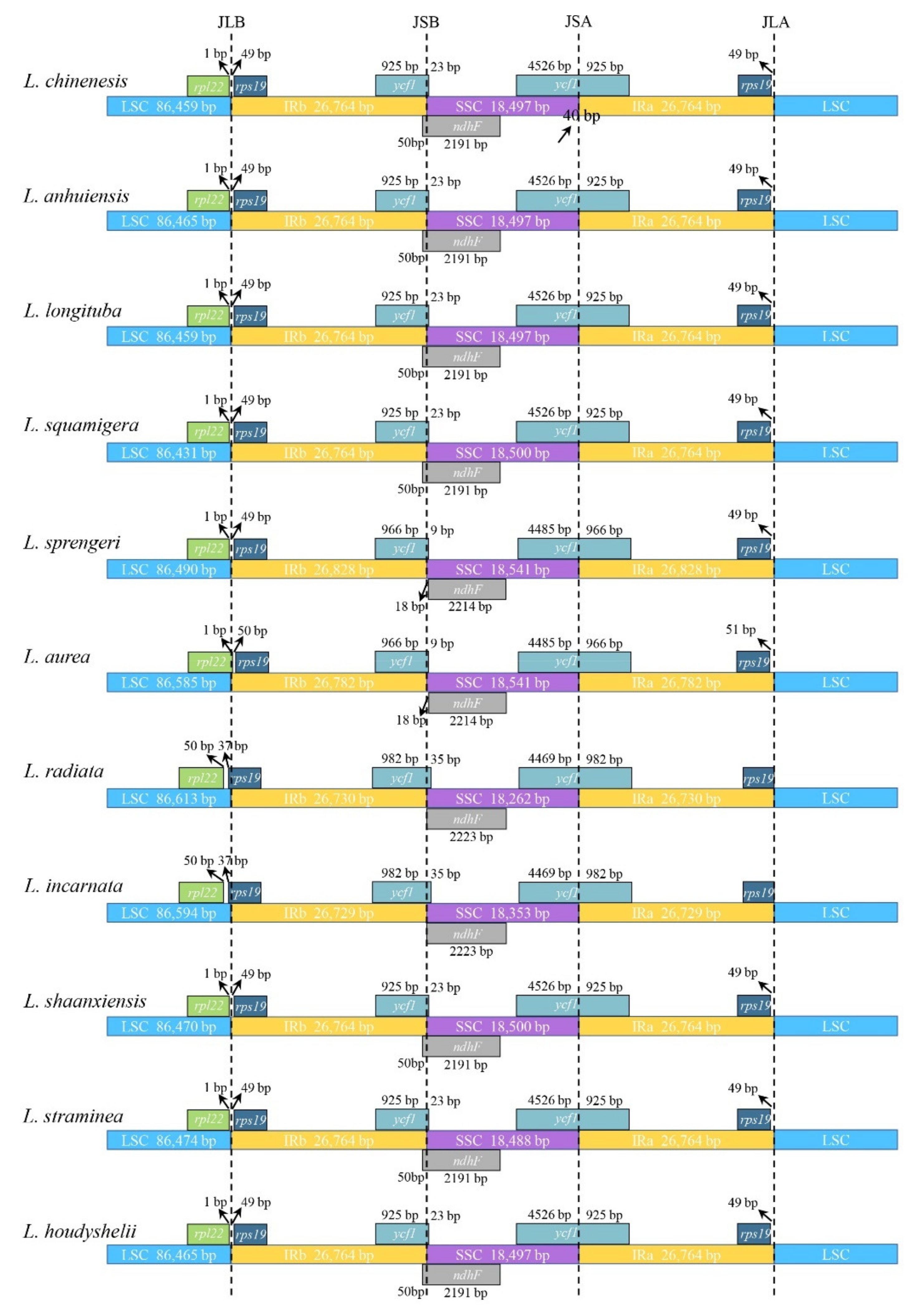
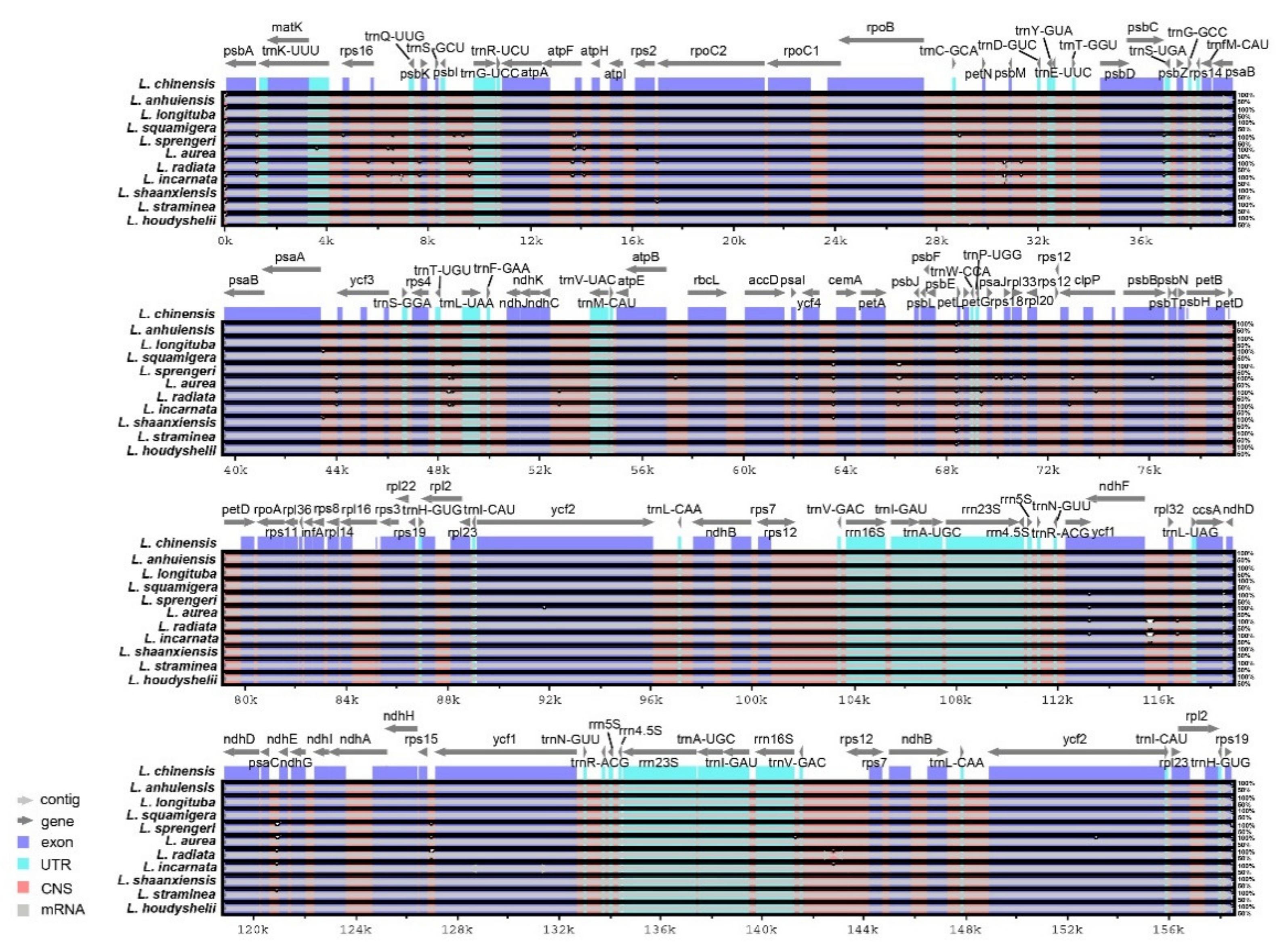
| Genome Features | L. incarnata | L. shaanxiensis | L. straminea | L. houdyshelii |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average organelle coverage | 7291× | 6761× | 5531× | 4581× |
| Genome size (bp) | 158,405 | 158,498 | 158,490 | 158,490 |
| LSC size (bp) | 86,593 | 86,469 | 86,473 | 86,464 |
| SSC size (bp) | 18,352 | 18,499 | 18,487 | 18,496 |
| IR size (bp) | 26,730 | 26,765 | 26,765 | 26,765 |
| GC content (%) | 37.8 | 37.8 | 37.8 | 37.8 |
| No. of genes | 113 | 113 | 113 | 113 |
| No. of PCGs | 79 | 79 | 79 | 79 |
| No. of tRNAs | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| No. of rRNAs | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Duplicated genes | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Category of Genes | Group of Genes | Name of Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Genes for photosynthesis | Subunits of photosystem I | psaB, psaA, psaI, psaJ, psaC, ycf4 |
| Subunits of photosystem II | psbA, psbK, psbI, psbM, psbD, psbC, psbZ, psbJ, psbL, psbF, psbE, psbB, psbT, psbN, psbH, ycf3 | |
| Subunits of NADH-dehydrogenase | ndhJ, ndhK, ndhC, ndhB a (×2), ndhF, ndhD, ndhE,ndhG, ndhI, ndhA a, ndhH | |
| Subunits of cytochrome b/f complex | petN, petA, petL, petG, petB a, petD a | |
| Subunits of ATP synthase | atpA, atpF a, atpH, atpI, atpE, atpB | |
| Subunit of rubisco | rbcL | |
| Self-replication | Large subunit of ribosome | rpl33, rpl20, rpl36, rpl14, rpl16 a, rpl22, rpl2 a (×2), rpl23 (×2), rpl32 |
| DNA dependent RNA polymerase | rpoC2, rpoC1 a, rpoB, rpoA | |
| Small subunit of ribosome | rps16 a, rps2, rps14, rps4, rps18, rps12 b (×2), rps11, rps8, rps3, rps19 (×2), rps7 (×2), rps15 | |
| Ribosomal RNAs | rrn16 (×2), rrn23 (×2), rrn4.5 (×2), rrn5 (×2) | |
| Transfer RNAs | trnK-UUU a, trnQ-UUG, trnS-GCU, trnG-GCC a, trnR-UCU,trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnY-GUA, trnE-UUC, trnT-GGU,trnS-UGA, trnG-GCC, trnfM-CAU, trnS-GGA, trnT-UGU,trnL-UAA a, trnF-GAA, trnV-UAC a, trnM-CAU, trnW-CCA,trnP-UGG, trnH-GUG (×2), trnI-CAU (×2), trnL-CAA (×2),trnV-GAC (×2), trnI-GAU a (×2), trnA-UGC a (×2), trnR-ACG (×2)trnN-GUU (×2), trnL-UAG | |
| Other genes | Subunit of Acetyl-CoA-carboxylase | accD |
| c-type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA | |
| Envelop membrane protein | cemA | |
| Protease | clpP | |
| Translational initiation factor | infA | |
| Maturase | matK | |
| Component of TIC complex | ycf1 (x2) | |
| Unknown | Conserved open reading frames | ycf2 (x2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Wang, N.; Cheng, G.; Shu, X.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, W.; Lu, R.; Wang, Z. Comparative Chloroplast Genomes of Four Lycoris Species (Amaryllidaceae) Provides New Insight into Interspecific Relationship and Phylogeny. Biology 2021, 10, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080715
Zhang F, Wang N, Cheng G, Shu X, Wang T, Zhuang W, Lu R, Wang Z. Comparative Chloroplast Genomes of Four Lycoris Species (Amaryllidaceae) Provides New Insight into Interspecific Relationship and Phylogeny. Biology. 2021; 10(8):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080715
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fengjiao, Ning Wang, Guanghao Cheng, Xiaochun Shu, Tao Wang, Weibing Zhuang, Ruisen Lu, and Zhong Wang. 2021. "Comparative Chloroplast Genomes of Four Lycoris Species (Amaryllidaceae) Provides New Insight into Interspecific Relationship and Phylogeny" Biology 10, no. 8: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080715
APA StyleZhang, F., Wang, N., Cheng, G., Shu, X., Wang, T., Zhuang, W., Lu, R., & Wang, Z. (2021). Comparative Chloroplast Genomes of Four Lycoris Species (Amaryllidaceae) Provides New Insight into Interspecific Relationship and Phylogeny. Biology, 10(8), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080715






