Simple Summary
Hypericum revolutum (HR) is reported to produce vasodilating activity in phenylephrine-precontracted aortae, where the chloroform fraction is the most potent. Chemical investigation of this fraction yielded two new compounds, revolutin (1) and hyperevolutin C (2), along with three known metabolites, β-sitosterol (3), euxanthone (4), and 2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone (5). Isolated compounds 1, 2, 3, and 5 produce vasodilation activities that are dependent on endothelial nitric oxide release.
Abstract
Vasodilators are an important class in the management of hypertension and related cardiovascular disorders. In this regard, the chloroform fraction of Hypericum revolutum (HR) has been reported to produce vasodilating activity in phenylephrine-precontracted aortae. The current work aims to identify the active metabolites in the chloroform fraction of HR and illustrate the possible mechanism of action. The vasodilation activities were investigated using the isolated artery technique. NO vascular release was assessed by utilizing the NO-sensitive fluorescent probe DAF-FM. Free radical scavenging capacity was assessed utilizing DPPH. Chemical investigation of this fraction yielded two new compounds, revolutin (1) and hyperevolutin C (2), along with three known metabolites, β-sitosterol (3), euxanthone (4), and 2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone (5). Compounds 1, 2, 3, and 5 showed significant vasodilation activities that were blocked by either endothelial denudation or L-NAME (nitric oxide synthase inhibitor), pointing towards a role of endothelial nitric oxide in their activities. In confirmation of this role, compounds 1–3 showed a significant release of NO from isolated vessels, as indicated by DAF-FM. On the other hand, only compound 5 showed free radical scavenging activities, as indicated by DPPH. In conclusion, isolated compounds 1, 2, 3, and 5 produce vasodilation activities that are dependent on endothelial nitric oxide release.
1. Introduction
Elevated blood pressure is a serious disorder that underlies other cardiovascular diseases and is a direct complication of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Hypertension can be due to increased heart stimulation or, most likely, increased peripheral resistance and endothelial dysfunction [1]. Endothelial dysfunction has a crucial role in the progression of hypertension by affecting vascular relaxation and constriction. The endothelium-dependent vasodilatation regulatory system controls vascular function mainly through the release of nitric oxide (NO) [2,3]. Therefore, endothelial dysfunction can lead to a significant decrease in the bioavailability of nitric oxide, causing vasodilatation impairment in affected individuals [2].
Regular medicine has many drawbacks that encourage researchers to find safer compounds for hypertension [1]. Herbal drugs are popularly dispensed for treating various ailments owing to their efficiency and comparatively moderate cost and fewer side effects. Thus, the development of effective alternative treatments is rather important in order to protect against hypertension and its complications. A literature survey has shown that many plant extracts reveal antihypertensive activity [4]. Saudi Arabia is about two million square kilometers. It covers the majority of the Arabian Peninsula. The country is renowned for many natural regions with many biologically diverse medicinal plants [5].
Hypericum revolutum (Vahl) is native to southeast Africa and geographically available in the Arabian mountains, especially those located in the northern and southern parts of Saudi Arabia [6]. It has been used traditionally for treating various ailments such as tuberculosis, earache, depression, diarrhea, and rheumatism, as well as burns and skin wounds due to its wound-healing property [7,8,9,10]. H. revolutum has been shown to possess antioxidant, antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities. Hyperevolutins A and B were previously separated from the root bark and are closely related to hyperforin, previously isolated from H. perforatum [11]. Meanwhile, its leaves contain antifungal chromenyl ketones [12,13]. We have previously reported a significant vasodilating activity of the chloroform fraction of H. revolutum, produced in phenylephrine-precontracted aortae [14]. The aim of the current study is to separate and identify the biometabolites accountable for H. revolutum vasodilating potential. Moreover, a detailed mechanistic study of the separated compounds will be presented.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotation measurement was accomplished by a DIP-370-JASCO polarimeter. A UV–vis 1601 Shimadzu spectrophotometer was utilized for assessing UV spectra. Measuring NMR spectra was carried out using 850-INOVA BRUKER. Measuring the high-resolution mass was achieved by utilizing JEOL 102A-JMS-SX/SX and Orbitrap LTQ spectrometers. The chromatographic process was executed using RP-18 (reversed-phase) and SiO2 60 (silica gel) (0.04–0.063 mm). TLC (thin-layer chromatography) was accomplished utilizing SiO2 60 F254 TLC plates.
2.2. Plant Material
The aerial parts of H. revolutum were assembled in April 2019 from the Al-Baha governorate, KSA. No specific permission was required for the collection of this plant. Plant verification was ascertained by Dr. Emad Al-Sharif (Biology Dept., Faculty of Science and Arts, KAU). A specimen (Reg. No. HR-0438) has been deposited at the Natural Products and Alternative Medicine Department’s herbarium (Faculty of Pharmacy, *).
2.3. Plant Material Extraction
Dried powdered aerial parts (1 Kg) were extracted at room temperature with 5 L methanol (four times), utilizing Ultraturrax, until exhausted. The under-vacuum concentration of the total extract produced a brown residue (40 g). The residue was mixed with 200 ml of water, partitioned with 500 ml chloroform (4 times), and vaporized to furnish Fraction I (10 g).
2.4. Separation of Major Metabolites
A 10 g chloroformic fraction was submitted to vacuum liquid chromatography (VLC) using silica gel (SiO2) (10 × 15 cm), utilizing an n-hexane/ethyl acetate (EtOAc) gradient. One hundred milliliter fractions were gathered and subjected to SiO2 TLC plates [solvent systems: n-hexane/EtOAc, 95:5 (S1) or 90:10 (S2)] and similar fractions were combined to furnish four main subfractions (I to IV). Subfraction I (50 mg, 13–15, 97:3; S3) included two main spots that yielded red color upon spraying with p-anisaldehyde:H2SO4 reagent, which was purified by SiO2 column chromatography (CC) using an S3-solvent system. The related fractions (20 mL each) were assembled on the basis of TLC (S1). The fractions (5–15, 20 mL each; 20–30, 20 mL each) each comprised one main spot that was additionally repurified on RP-18 CC (MeOH/water, 80:20) to provide 1 (4 mg) and 2 (20 mg). SiO2 CC of Subfraction II (50 mg, n-hexane/EtOAc 93:7; S4) yielded 3 (15 mg) and 4 (12 mg). Subfraction III (24–26, S2), having one main spot, was submitted to SiO2 CC (2 × 40 cm, S4) to furnish 5 (7 mg).
2.5. Biological Evaluation
2.5.1. Chemicals and Drugs
ACh (acetylcholine), PE (phenyl ephedrine), DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), and DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) were acquired from Sigma–Aldrich (Dorset, UK); DAF-FM (4-amino-5-methylamino-2’,7’-difluorofluorescein di-acetate) was acquired from Molecular Probes (New York, NY, USA). Deionized-Ultrapure H2O was utilized as solvent except for DPPH and natural metabolites, where DMSO (conc. not exceeding 0.1%) was utilized.
2.5.2. Animals
Seven-week-old male Wistar rats (180–200 g) were used (King Fahd Medical Research Center, KAU, KSA). The animals were housed with access to standard rodent pellets and purified water in clear polypropylene cages (4 rats each). Constant housing conditions were applied, including alternating 12 h light and dark, 22 ± 3 °C temperature, sufficient ventilation, and 50–60% relative humidity. The research ethics committee of King Abdulaziz University approved the study (approval number 126-1439). The study was carried out according to the Saudi Arabia Research Bioethics Guidelines and Regulations, which are in accordance with the Animals in Research: Reporting In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines for research involving animals [15]. The animals were executed by decapitation using a rodent guillotine administered by qualified personnel in the animal housing. The method is acceptable to induce a rapid loss of consciousness, according to the AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition (section M3.7) [16], and the descending thoracic aorta was precisely removed and washed from connective tissues and fats.
2.5.3. Evaluating the Chloroform Fraction and Isolated Metabolites’ Direct Relaxant Effect
Vasodilating capacities were assessed using the isolated artery method, as formerly reported [17,18]. Briefly, the aorta was removed, cleansed of any connective tissue and fats, and sliced into rings (3 mm). Each ring was hung in Krebs Henseleit buffer channels (4.8 mM KCl, 118 mM NaCl, 1.2 mM MgSO4, 1.2 mM KH2PO4, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 11.1 mM glucose, and 25 mM NaHCO3) at 37 °C, with continuous aeration with gas (5% CO2 and 95% O2). Every 30 min, the channel buffer solution was exchanged. Quantification of the aortic tension was accomplished using an isometric force transducer, and the results were presented through a PowerLab data interface module linked to a PC running Chart software v8 (ADI Instruments).
The aortic rings were set aside for 30 min for equilibration at a 1500 mg ± 50 resting tension. Initial aorta contraction and relaxation were then carried out by the addition of PE, followed by ACh (both at 10 μM). After the tension was reverted to the rest state, accumulative concentrations of 1–10 μg/mL and 1–10 μM for the chloroform fraction or the pure metabolites, respectively, were added to the organ bath precontracted (PE, 10 μM)-isolated aortae. Tension reduction was estimated as a measurement of vasodilating actions. In other sets of experiments for investigating the role of the endothelium in the vasodilating effect, it was mechanically made bare. Additionally, L-NAME (100 μM) was added in the organ bath 15 min before adding the isolated metabolites or chloroform fraction to explore the role of nitric oxide in the vasodilating influence on different sets of experiments.
2.5.4. Examining the Effect of Chloroform Fraction and Isolated Metabolites on Nitric Oxide (NO) Production
The separated aorta intracellular induction of NO production by the tested metabolites and the chloroform fraction was examined employing the DAF-FM fluorescence probe, as similarly outlined in our former work [19]. Similar to the earlier technique, the thoracic aorta was removed, the fats were washed off, and it was sliced into approximately 6 mm pieces. Every piece was put in a 96-well black plate separate well, maintained in dim light, having made a 2.5 µM DAF-FM/KHB mixture (37 °C) immediately before starting the procedure; 100 µL were accurately drawn and transported to the wells’ neighboring column; after that, ACh (10 µM) was included in one of the aortic segments, and the chloroform fraction (10 µg/mL) or separated metabolites (10 μM) was put in the other wells after 3 min. Again, after 3 min, 100 µL were taken from the wells with the aortae and transmitted to the nearby well columns. For the blank, a row without an aorta was retained for each ACh concentration, which was handled identically. The withdrawn volumes’ fluorescence intensity (and not the column including the aortae) was then assessed at λem = 515 nm and λex = 485 nm using a SpectraMax® M3 Monochromator plate reader.
2.5.5. Studying the ROS Scavenging Potential of the Isolated Metabolites and the Chloroform Fraction
ROS scavenging potential was assessed, as formerly stated in previous work from our laboratories [20]. In a 96-well clear plate, the pure metabolites (1–10 µM) or Fraction I (1–10 µg/mL) in MeOH was added to a DPPH (240 µM) solution in MeOH/tris (1:1 v/v). For the control (C), MeOH was utilized instead of the fraction or metabolites. DPPH was directly prepared before adding to the plate. The absorbance was estimated every minute at 520 nm for 10 min using a SpectraMax® M3-Monochromator plate reader.
2.5.6. Statistical Analysis
Experimental values are depicted as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). For statistical analysis, one- or two-way ANOVA (analysis of variance) was applied, as designated in the figure legends, succeeded by Dunnett’s posthoc test utilizing GraphPad Instat software version 5. If p < 0.05, the differences were recognized as significant.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Isolated Compounds
Chemical examination of H. revolutum aerial parts’ CHCl3 fraction gave rise to the separation of two new constituents (1 and 2) and three known ones (3–5) (Figure 1 and Figures S1–S22, Tables S1–S3). Their structures were characterized using one- and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (1D and 2D NMR) and mass (MS) analyses, as well as a comparison with the literature. The known metabolites were euxanthone (1,7-dihydroxyxanthone) (4) [21], β-sitosterol (3) [22], and 2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone (5) [23].
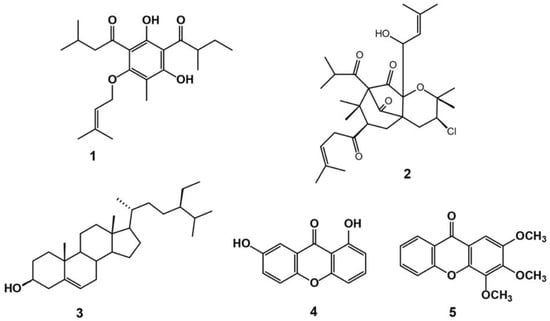
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of isolated compounds 1–5.
3.2. Compound 1
Compound 1 was separated as a yellow amorphous powder, having a C22H32O5 molecular formula, as assigned by HRESIMS (Figure S1), that possessed a pseudomolecular peak at m/z 377.2335 [M+H] +. The 13C and 1H NMR data illustrated that 1 had a phloroglucinol framework (Table 1, Figure 2, Figures S2 and S3) [24,25,26]. The phloroglucinol skeleton’s existence was endorsed from the noticed three oxygen-linked aromatic carbons, C-5 (δC 162.5), C-1 (δC 162.4), and C-3 (δC 149.9), and the three quaternary aromatic carbons, C-4 (δC 104.3), C-2 (δC 104.5), and C-6 (δC 104.8) [26,27,28], in 13C spectrum. The heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) (Figure S4) and 13C NMR featured 22 carbons: 3 methylenes, 7 methyls, 3 methines, and 9 quaternaries, including 2 carbonyls for ketone C-12 (δC 205.7) and C-17 (δC 210.3). The noticed signals for methylene (H-19, δH 1.41 and 1.84), a multiplet methine (H-18, δH 3.73), a secondary methyl (H-21, δH 1.16), and a primary methyl (H-20, δH 0.91), having HSQC correlations to the carbons at δC 26.9, 46.0, 16.7, and 12.0, respectively, represented a 2-methylbutyryl moiety [29]. The heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) correlations (Figure S5) of H-18 to C-19, C-17, C-21, and C-20, H-19 to C-18, C-17, C-21, and C-20, H-20 to C-19 and C-18, and H-21 to C-19, C-18, and C-17 connect this moiety to phloroglucinol at C-4. The 13C and 1H spectra disclosed signals for a 3-methylbutyryl moiety at δC 52.9 (C-13)/δH 2.94 (H-13), 25.3 (C-14)/1.65 (H-14), 22.8 (C-15, 16)/0.97 (H-15, 16), and δC 205.7 (C-12). This was ensured by the cross-peaks of H-16 and H-15/C-14 and C-13 and H-14 and H-13/C-16, and C-12, and C-15 in HMBC. In HMBC, the cross-peak of H-13 to C-2 set up the location of this chain at C-2 of the phloroglucinol skeleton (Figure 2). The 13C and 1H NMR data revealed signals for an oxymethylene [δC 65.3 (C-7)/δH 4.52 (H-7)], a tri-substituted olefinic bond [δC 119.2 (C-8)/δH 5.45 (H-8)], and two methyls [δC 18.3 (C-11)/δH 1.73 (H-11) and δC 25.8 (C-10)/δH 1.79 (H-10)], denoting the presence of a 3-methylbut-2-enoxy moiety in 1 that was ascertained by HMBC peaks [30,31]. Its connection to C-1 was affirmed by the cross peak of H-7 to C-1 in HMBC. Moreover, a signal for a methyl (δH 2.02, H-22), having an HSQC cross-peak to a carbon at δC 7.3 and HMBC cross-peaks to C-6, C-1, and C-5, characteristic for a C-6 aromatic methyl. Finally, 1 was assigned as phloroglucinol derivative and named revolutin.

Table 1.
NMR spectral data of compound 1 (CDCl3, 850 and 214 Hz).
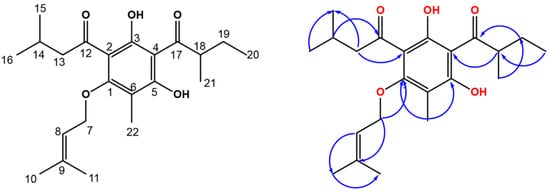
Figure 2.
Chemical structure of compound 1 and some HMBC correlations.
3.3. Compound 2
Compound 2 was a yellow amorphous solid, having two pseudo-molecular ion peaks at m/z 537.2821 (C30H4537ClO6, [M+H]+) and 535.2816 (C30H4535ClO6, [M+H]+) in a 1:3 ratio in HR-ESI-MS (Figure S6), suggesting that 2 has a chlorine atom [32]. This formula requires nine unsaturation degrees. The 1H spectrum revealed signals for four quaternary methyls [H-14 (δH 1.24), H-12 (δH 1.26), H-13 (δH 1.28), and H-11 (δH 1.38)], two γ,γ-dimethyl allyls, two secondary methyls [H-18 (δH 1.09) and H-17 (δH 1.10)], a methine (H-3), an oxymethine (H-19), and three methylenes (H-4, -5, and -25) (Table 2).

Table 2.
NMR spectral data of compound 2 (CDCl3, 850 and 214 Hz).
Its HSQC and 13C (Figures S8 and S9) spectra exhibited 3 methylenes, 10 methyls, 6 methines (from which there were one oxymethine and two olefinics), and 11 quaternaries comprising 4 carbonyls. 1H-1H correlated spectroscopy (COSY) of 2 (Figure S11) displayed cross-peaks of H-17/H-16 and H-18, H-19/H-20, H-3/H-4, and H-26/H-25 that confirmed the partial substructures demonstrated in bold lines (Figure 3a). The HMBC relations (Figure S10) of H-25 to C-27, C-24, and C-6 secured the connection of C-6 and C-26, C-24, and C-25 and affirmed the linking of the 1-oxo-4-methyl-pent-3-eneyl moiety at C-6 (Figure 3b). Further, the linkage of γ,γ-dimethyl allyl at C-25 was assured by the relations of H-26 to H-29 and H-28. Furthermore, the cross-peaks between H-5/C-7 and C-24 assured the linkage between C-5, C-6, and C-7. The cross-peaks of H-16/C-18, C-15 and C-17, H-14 and H-13/C-8 and C-6, and H-16/C-8, besides relation H-6/C-8, assured the connection between C-8/C-7 and C-7/C-6 and secured the location of the 1-oxo-2-methyl propyl moiety at C-8. The correlations of H-4/C-4a, C-9a, C-10, C-5, and C-2, and H-12 and H-11/C-2 in HMBC proved the 3,4-dihydropyran moiety and the connection between C-10 and C-4a. This evidence revealed the fusion of the pyran ring at C-4a and C-9a. The linkage of the γ,γ-dimethyl ally group to C-9a via a C-19 oxymethine was assured by the HMBC cross-peaks of H-20/C-23 and C-22, H-23, H-22, and H-19/C-21, and H-19/C-4a and C-9. The downfield shift of C-3/HC-3 established the existence of a chloride at C-3. Further, the nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) spectrum of 2 (Figure S12) displayed prominent cross-peaks between H-12/Hβ-4, H-3 and H-19/H-11, H-14/Hβ-5, and H-13/H-6, suggesting the existence of H-3, H-11, H-13, H-6, H-16, and H-19 on the same face of the molecule (Figure 3c). Therefore, the structure of 2 was elucidated as represented and named hyperevolutin C. The nomenclature of 2 was given based on its structural similarity to hyperevolutins A and B, which were previously separated from H. perforatum [11].
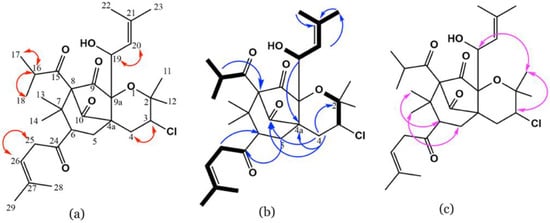
Figure 3.
Important COSY (a), HMBC (b), and NOESY (c) correlations of 2.
3.4. Chloroform Fraction Vasodilating Activity
The chloroform fraction exhibited reductions in tension and consequent concentration-dependent vasodilation of PE (10 μM)-precontracted separated aortae that approached statistical significance compared with time control (at conc. 3 and 10 µg/mL, both at p < 0.05). Removal of the endothelial layer (aorta denudation) prevented the chloroform fraction vasodilating effect, as obvious from the considerable prohibition (at conc. 1, 3, and 10 µg/mL, all at p < 0.05). Additionally, L-NAME (1 mM) blocked the vasodilating effect of the chloroform fraction, as manifest from the remarkable inhibition (at conc. 1, 3, and 10 µg/mL of the choroform fraction, all at p < 0.05) (Figure 4).
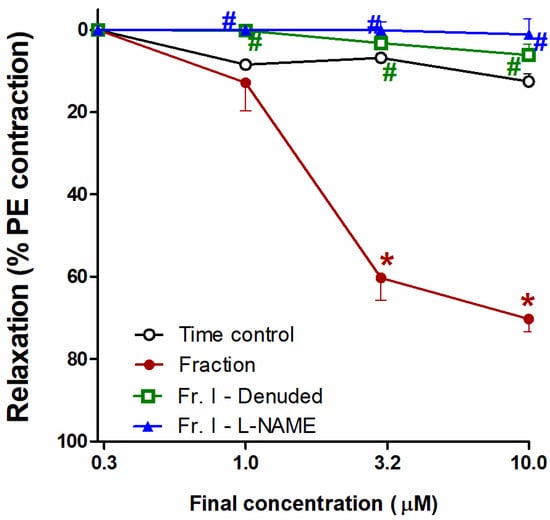
Figure 4.
Effect of the H. revolutum chloroform fraction on PE-precontracted separated intact or denuded aorta or aorta preincubated with a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (L-NAME) compared with time control. Results are introduced as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (n = 8). * Significantly varies from the corresponding time control values (p < 0.05); # Significantly varies from the corresponding chloroform fraction (p < 0.05) by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and the Newmans–Keuls posthoc test.
3.5. Vasodilating Activity of the Isolated Compounds
Figure 5A reveals that compound 1 caused the concentration-dependent vasodilation of PE (10 μM)–precontracted separated aortae, as apparent from the notable repression of vasodilation (at conc. 10 µM, p < 0.05), whilst L-NAME or endothelial denudation effectively hindered the vasodilation potential of compound 1, as indicated by the remarkable inhibition (both at conc. 3 and 10 µM, all at p < 0.05; Figure 5A). Likewise, compound 2 caused concentration-dependent vasodilation (at conc. 3 and 10 µM, both p < 0.05); however, L-NAME or endothelial denudation prevented the activity (both at conc. 3 and 10 µM, all at p < 0.05; Figure 5B).
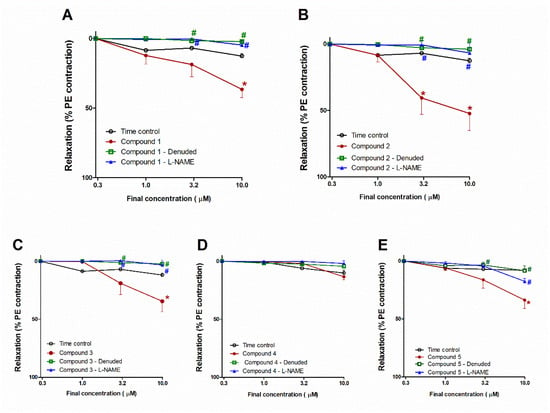
Figure 5.
Influence of compounds 1–5 on PE–precontracted separated intact or denuded aorta or aorta preincubated with a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (L-NAME) compared with time control (A–E). Results are introduced as mean ± SEM (n = 8). * Significantly varies from the corresponding time control values (p < 0.05). # Significantly varies from the corresponding values of compound 1 (p < 0.05) by two-way ANOVA and Newmans–Keuls posthoc test.
The compound 3 addition resulted in concentration-dependent vasodilation of PE (10 μM)–precontracted separated aortae (Figure 5C). At a concentration of 10 µM, the vasodilating effect of compound 3 attained a statistically significant level (p < 0.05) compared with time control. This effect was entirely blocked by L-NAME or endothelial denudation, as apparent from the notable prohibition (both at conc. 3 and 10 µM, all at p < 0.05; Figure 6A). Nevertheless, compound 4 did not possess any notable vasodilation of PE (10 μM)–precontracted separated aortae. Likewise, L-NAME or endothelial denudation had no significant influences (Figure 5D).
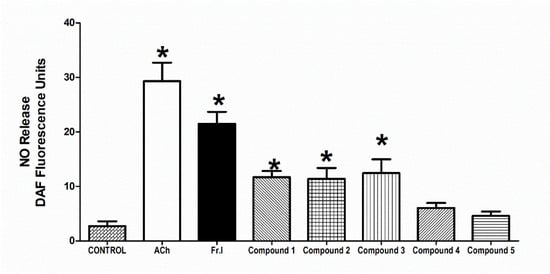
Figure 6.
Influence of H. revolutum, 10 µg/mL Fraction I, and compounds 1–5 (conc. 10 µM) on vascular NO production comparable to 10 µM Ach. * Significantly varies from the control value (p < 0.05) by one way-ANOVA and Newmans–Keuls posthoc test.
Figure 5E demonstrated that the compound 5 addition gave rise to a decline in tension and, consequently, concentration-dependent vasodilation of PE–precontracted separated aortae. This effect at 10 µM attained a statistically significant (p < 0.05) level. Moreover, this effect was inhibited by endothelial denudation (at conc. 10 µM) or L-NAME (at both conc.3 and 10 µM, all at p < 0.05; Figure 5E).
3.6. Effect on Vascular NO-Production
The addition of 10 µM Ach at 37 °C to the aortic rings caused a marked NO production (p < 0.05) in comparison to control that was quantified and detected using 2.5 µM DAF-FM reagent. The chloroform fraction addition (conc. 10 µg/mL) brought about a similar increase in NO production, as evident by a notable increase in the fluorescence of DAF-FM compared with the control values (p < 0.05). The isolated metabolites 1–3 provoked NO production that attained a statistically noteworthy level (all at p < 0.05) at a 10 µM concentration (Figure 6).
3.7. Free Radical Scavenging (FRS) Capacities
In the 10 min reaction results between 240 µM DPPH, the chloroform fraction, and compounds 1–5 (conc. 1, 3, and 10 µM), only 5 exhibited remarkable FRS activity. The other compounds, 1–4, did not have any significant FRS activities (data not shown). Figure 7 revealed that 5 (conc. 10 µM) possessed DPPH free radical scavenging activity that was translated into an antioxidant potential, which is clear from the noticeable variations from control, beginning from the 1st minute until the 10th minute (p < 0.05).
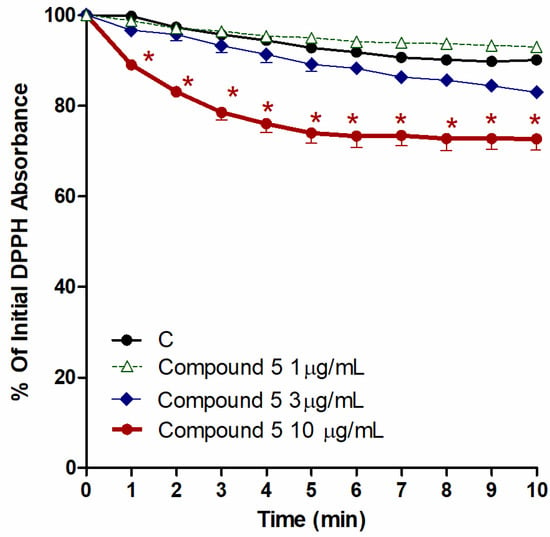
Figure 7.
Influence of the CHCl3 fraction and isolated metabolite 5 on the production of ROS, as inducted by 240 µM DPPH. Control (C) is a reaction mixture with DPPH only. Results are displayed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). * p < 0.05 when compared to each corresponding control.
4. Discussion
Natural products can exert vasodilation through either the endothelium (NO generation) or by acting on smooth muscle (Ca+ and K+ channels) [33]. The current work represents the first evaluation of the bioactive compounds from H. revolutum that are responsible for vasodilation activities; we also investigate the mechanism of action. A previous report from our laboratory [14] proved that the total methanol extract of H. revolutum gave rise to concentration-dependent vasodilation of phenylephrine–precontracted isolated aortae. The bio-guided fractions indicated that the chloroform fraction is accountable for the noticed total extract vasodilation potential. In this regard, similar vasodilating activities have been reported for other plant extracts; the methanol extract of Garcina mangostana as well as Mentha longifolia were reported to produce a direct vasorelaxant effect in phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction and in an experimental model of angina, respectively [34,35]. Moreover, different phytoconstituents are known for their vasodilation activity. Phenolic compounds are the most important class of vasodilators. For example, flavone can exert vasodilation by acting on the Ca+ channel and NO generation [33].
Chromatographic examination of the chloroform fraction gave rise to the separation of five active compounds that worked collaboratively but through different mechanisms to prompt NO-dependent vasodilatation. The isolated compounds were identified as revolutin (1) and hyperevolutin C (2), β-sitosterol (3), euxanthone (1, 7-dihydroxyxanthone, 4), and 2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone (5).
Compounds 1, 2, and 3 show significant vasodilation activities that were blocked by endothelial denudation (Figure 8). This points to the key role of the endothelium in mediating their vasodilating activities. In addition, L-NAME (NO synthase inhibitor) completely blocked the mentioned compounds’ activities, suggesting endothelial nitric oxide stimulation as a major mechanism of activity. It is well established that the endothelium has a crucial role in controlling arterial tone via the release of the key vasorelaxant molecule NO [36]. In order to confirm that endothelial NO stimulation is the main vasodilating mechanism of compounds 1, 2, and 3, the endothelial release of NO upon compound addition was measured by the NO-sensitive fluorescent probe, DAF-FM. The current study confirms the release of NO from the vascular endothelium upon the addition of compounds 1, 2, and 3.
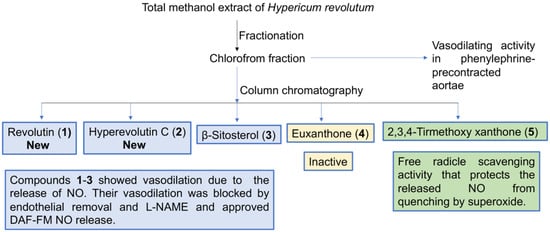
Figure 8.
Diagrammatic sketch summarizing the study design.
Revolutin (1) belongs to the phloroglucinol group of compounds, which are known for their ability to improve NO generation. Previous reports have reported its ability to increase NO levels, leading to a decrease in blood pressure in vivo [37]. Meanwhile, hyperevolutin C (2) is a novel terpenoid structure closely related to garcinielliptone G, which was previously isolated from Garcinia subelliptica [38] but not previously tested for its biological effects. β-Sitosterol (3) has previously exhibited hepatoprotective and cardioprotective effects in CdCl2-induced hypertensive rats [39]. Euxanthone (4) was previously investigated and showed a pronounced vasodilator effect through the release of endothelial factors such as NO and COX-derived factors. Additionally, it provoked the prohibition of a Ca+2-sensitive mechanism initiated by protein kinase C instead of repression of a contraction-dependent release of the intracellular Ca+ stores or prohibiting voltage-operated Ca+ channels [40].
Free radical scavenging (FRS) activity is another important way to preserve the released NO from quenching by superoxides and subsequent conversion into nitrites or nitrates. Only compound 5 among the tested metabolites 1–5 has substantial FRS capacities. We take into consideration that compound 5 showed moderate vasodilation that was endothelial-dependent and inhibited by L-NAME but was not associated with NO generation. These data suggest preserving NO bioavailability rather than stimulating NO generation as the major mechanism of action of compound 5. In the meantime, we cannot exclude the possibility that compound 5 may stimulate endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors or other vasodilators generated in the endothelium, such as prostacyclin. While compound 5 has not been previously investigated for its vasodilator effect, the xanthone group of compounds was reported to show vasorelaxant and antihypertensive activities [41]. While previous reports have shown the ability of flavonoids and benzophenone nuclei to enhance vasodilatation through NO production [35,42], our study is the first to introduce a similar effect for the phloroglucinol nucleus. Additionally, our study is the first to report the vasodilation activity of the xanthone nucleus through the inhibition of NO degradation. This finding is significant in terms of increased drug potency when NO production is intended. Interestingly, El-bassossy et al. [43] have reported a similar NO-protective mechanism by heme oxygenase-1. It is noteworthy to mention that the chloroform fraction of H. revolutum showed the highest potency relative to each isolated compound, which can be attributed to the synergistic effect of the bioactive compounds. The proposed pharmacological mechanism is illustrated in Figure 9.
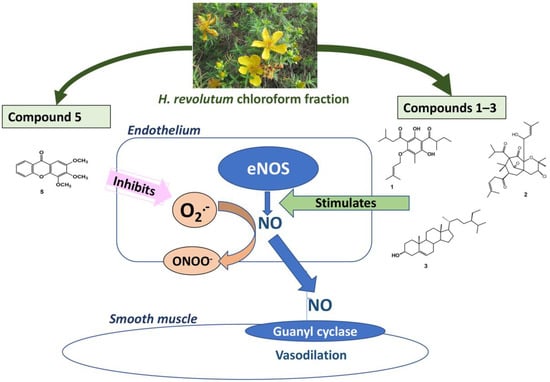
Figure 9.
Diagrammatic sketch summarizing the proposed pharmacological mechanism.
The main limitation of this study is exploring vasodilation only in the thoracic aortic model; other arteries such as cerebral and abdominal arteries were not investigated. Additionally, the study concentrates only on NO from the endothelium as the main mechanism; other mechanisms such as Ca and K channels need to be investigated. Additionally, vasodilator activity was proven only in vitro; therefore, in vivo studies on animals are required, in detail, to assess the toxicity of these compounds as well as their metabolites and their effects on blood vessels. Finally, planning to assess the activity of the isolated compounds in humans should be a final step after the detailed study of these compounds.
5. Conclusions
The phytochemical investigation of the chloroform fraction of H. revolutum yielded two new compounds that were identified as revolutin (1) and hyperevolutin C (2), together with three known metabolites (3–5). Compounds 1–3 and 5 showed significant vasodilation in isolated aortae. The observed vasodilation of compounds 1–3 seems to be mediated via NO generation, as blocked by endothelial removal and L-NAME, and approves DAF-FM NO release. Compound 5 vasodilation is thought to be mediated by its free radical scavenging activities that protect the released NO from quenching by superoxides. Due to the multifactorial nature of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, knowing the mechanisms of the vasodilation action of these compounds is a crucial element for developing and planning different therapeutic strategies. Concretely, the observed vasodilation ability of these metabolites may reveal their potential therapeutic use against high-blood-pressure-related cardiovascular diseases.
6. Patents
This work resulted in US Patent number 10,780,139, 2020.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology10060541/s1, Figure S1: HR-ESI, mass spectrometry spectrum of compound 1., Figure S2: 1H NMR spectrum of compound 1 (CDCl3, 850 Hz), Figure S3: 13C NMR spectrum of compound 1 (CDCl3, 214 Hz), Figure S4: HSQC spectrum of compound 1, Figure S5: HMBC spectrum of compound 1, Figure S6: HR-ESI, mass spectrometry spectrum of compound 2, Figure S7: 1H NMR spectrum of compound 2 (CDCl3, 850 Hz), Figure S8: 13C NMR spectrum of compound 2 (CDCl3, 214 Hz), Figure S9: HSQC spectrum of compound 2, Figure S10: HMBC spectrum of compound 2, Figure S11: COSY spectrum of compound 2, Figure S12: NOESY spectrum of compound 2, Figure S13: 1H NMR spectrum of compound 3 (CDCl3, 850 Hz), Figure S14: 13C NMR spectrum of compound 3 (CDCl3, 214 Hz), Figure S15: 1H NMR spectrum of compound 4 (euxanthone) (CDCl3, 850 Hz), Figure S16: 13C NMR spectrum of compound 4 (euxanthone) (CDCl3, 214 Hz), Figure S17: HSQC spectrum of compound 4 (euxanthone), Figure S18: HMBC spectrum of compound 4 (euxanthone), Figure S19: 1H NMR spectrum of compound 5 (2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone) (CDCl3, 850 Hz), Figure S20: 13C NMR spectrum of compound 5 (2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone) (CDCl3, 214 Hz), Figure S21: HSQC spectrum of compound 5 (2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone), Figure S22: HMBC spectrum of compound 5 (2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone), Table S1: NMR data of compound 3 (CDCl3, 850 and 214 Hz), Table S2: NMR data of compound 4 (euxanthone) (CDCl3, 850 and 214 Hz), Table S3: NMR data of compound 5 (2,3,4-tirmethoxy xanthone) (CDCl3, 850 and 214 Hz).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M.A.; methodology, H.M.A., N.Z.T., S.R.M.I., and H.M.E.-B.; validation, A.M.M.; resources, A.M.E.-H. and I.A.S.; data curation, H.M.E.-B.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M.A., S.R.M.I., and H.M.E.-B.; writing—review and editing, A.M.M.; supervision, H.M.A.; project administration, H.M.A.; funding acquisition, H.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by the Science and Technology Unit, King Abdulaziz University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (award number UE-41-115).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee at Faculty of Pharmacy, King Abdulaziz University (protocol code 126-1439) approved on 15 May 2018.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Science and Technology Unit, King Abdulaziz University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (award number UE-41-115).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction of the information included in the Institutional Review Board Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Bianchi, G.; Cusi, D.; Barlassina, C.; Pati, C.; Tripodi, M.; Niutta, E.; Vezzoli, G. Sodium balance and peripheral resistance in arterial hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1984, 6, S457–S464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddu, P.; Puddu, G.M.; Zaca, F.; Muscari, A. Endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Acta Cardiol. 2000, 55, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, E.M.; Wilkinson, F.L.; Parker, B.; Alexander, M.Y. Endothelial microparticles: Pathogenic or passive players in endothelial dysfunction in autoimmune rheumatic diseases? Vascul. Pharmacol. 2016, 86, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwuma, C.I.; Matsabisa, M.G.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Erukainure, O.L.; Chabalala, M.H.; Islam, M.S. Medicinal plants with concomitant anti-diabetic and anti-hypertensive effects as potential sources of dual acting therapies against diabetes and hypertension: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, H.A.; Ghazanfar, S.A. Conservation of medicinal plants on the Arabian Peninsula. J. Med. Plant Cons. 1991, 3, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Collenette, S. Wildflowers of Saudi Arabia; National Commission for Wildlife Conservation and Development (NCWCD): Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sher, H.; Alyemeni, M.N. Pharmaceutically important plants used in traditional system of Arab medicine for the treatment of livestock ailments in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 9153–9159. [Google Scholar]
- Miraldi, E.; Biagi, M.; Giachetti, D. Chemical constituents and effect of topical application of Oleum hyperici on skin sensitivity to simulated sun exposure. Nat. Prod. Comm. 2006, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuti, J.R.; Kukunda, C.B.; Waako, P.J. Medicinal plants used by traditional medicine practitioners in the treatment of tuberculosis and related ailments in Uganda. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yineger, H.; Kelbessa, E.; Bekele, T.; Lulekal, E. Plants used in traditional management of human ailments at Bale Mountains National Park, Southeastern Ethiopia. J. Med. Plants Res. 2013, 2, 132–153. [Google Scholar]
- Decosterd, L.A.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Chapuis, J.C.; Msonthi, J.D.; Sordat, B.; Hostettmann, K. New Hyperforin Derivatives from Hypericum revolutum Vahl with Growth-Inhibitory Activity Against a Human Colon Carcinoma Cell Line. Helv. Chim. Acta 1989, 72, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Décostered, L.A.; Hostettmann, K.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Msonthi, J.D. New antifungal chromenyl ketones and their pentacyclic dimers from Hypericum revolutum Vahl. Helv. Chim. Acta 1987, 70, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decosterd, L.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Msonthi, J.; Hostettmann, K. A new antifungal chromene and a related di-chromene from Hypericum revolutum. Planta Med. 1986, 52, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timraz, N.Z.; El-Bassossy, H.M.; Ibrahim, S.R.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Shehata, I.A.; Aljohani, O.S.; Abdallah, H.M. Vasodilating effect of Hypericum revolutum (Vahl) (Clusiaceae) methanol extract in rats. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 20, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Animal research: Reporting In Vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, W.; Anthony, R. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition; Retrieved on March 2020; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bassossy, H.M.; Elberry, A.A.; Ghareib, S.A. Geraniol improves the impaired vascular reactivity in diabetes and metabolic syndrome through calcium channel blocking effect. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassossy, H.M.; Abo-Warda, S.M.; Fahmy, A. Chrysin and luteolin attenuate diabetes-induced impairment in endothelial-dependent relaxation: Effect on lipid profile, AGEs and NO generation. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareib, S.A.; El-Bassossy, H.M.; Elberry, A.A.; Azhar, A.; Watson, M.L.; Banjar, Z.M. 6-Gingerol alleviates exaggerated vasoconstriction in diabetic rat aorta through direct vasodilation and nitric oxide generation. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 6019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tarkhan, M.M.; Balamsh, K.S.; El-Bassossy, H.M. Cinnamaldehyde protects from methylglyoxal-induced vascular damage: Effect on nitric oxide and advanced glycation end products. J. Food Biochem. 2019, e12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagem, T.J.; de Oliveira, F.F. Xanthones and other constituents of Vismia parviflora. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 1997, 8, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, L.L.; Moses, M.N. Isolation and characterisation of stigmasterol and β-sitosterol from Odontonema strictum (Acanthaceae). J. Innov. Pharm. 2015, 2, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, C.; Séraphin, D.; Oger, J.-M.; Litaudon, M.; Sévenet, T.; Richomme, P.; Bruneton, J. New xanthones from Calophyllum caledonicum. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, F.; Zdero, C. Neue phloroglucin-derivate aus Helichrysum natalitium und Helichrysum bellum. Phytochemistry 1979, 18, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.H.; Khoo, C.W.; Vittal, J.J.; Sim, K.Y. Phloroglucinol derivatives from Hypericum japonicum. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, M.Y.; Delgado, G. Polyprenols and acylphloroglucinols from Esenbeckia nesiotica. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, W.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Curry, J.; Stapleton, P.; Zloh, M.; Malkinson, J.P.; Gibbons, S. Antibacterial acylphloroglucinols from Hypericum olympicum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.; Jürgenliemk, G.; Schmidt, T.J.; Skaltsa, H.; Heilmann, J. Bi-, Tri-, and Polycyclic Acylphloroglucinols from Hypericum empetrifolium. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fobofou, S.A.; Franke, K.; Sanna, G.; Porzel, A.; Bullita, E.; La Colla, P.; Wessjohann, L.A. Isolation and anticancer, anthelminthic, and antiviral (HIV) activity of acylphloroglucinols, and regioselective synthesis of empetrifranzinans from Hypericum roeperianum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6327–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohlmann, F.; Suwita, A. Neue phloroglucin-derivate aus Leontonyx-arten sowie weitere verbindungen aus vertretern der tribus inuleae. Phytochemistry 1978, 17, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, F.; Suwita, A. Weitere phloroglucin-derivate aus Helichrysum-arten. Phytochemistry 1979, 18, 2046–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.; Mohamed, G.A.; Moharram, A.M.; Youssef, D.T. Aegyptolidines A and B: New pyrrolidine alkaloids from the fungus Aspergillus aegyptiacus. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Yan, H.-L.; Wang, L.-X.; Xu, J.-F.; Peng, C.; Ao, H.; Tan, Y.-Z. Review of Natural Resources With Vasodilation: Traditional Medicinal Plants, Natural Products, and Their Mechanism and Clinical Efficacy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, A.S.; El-Bassossy, H.M.; Abdallah, H.M. Mentha longifolia alleviates experimentally induced angina via decreasing cardiac load. J. Food Biochem. 2018, e12702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, H.M.; El-Bassossy, H.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Alshali, K.Z.; Banjar, Z.M. Phenolics from Garcinia mangostana alleviate exaggerated vasoconstriction in metabolic syndrome through direct vasodilatation and nitric oxide generation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.J.; Detterich, J.A.; Connes, P. Nitric oxide, vasodilation and the red blood cell. Biorheology 2014, 51, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashif, S.; Razdan, R.; Illuri, R. Potential of phloroglucinol to improve erectile dysfunction associated with streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 17, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.R.; Lin, C.N.; Tsao, L.T.; Wang, J.P. Terpenoids with a New Skeleton and Novel Triterpenoids with Anti-inflammatory Effects from Garcinia subelliptica. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 5520–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaiya, C.; Esan, A.; Alabi, T. Ameliorative effects of β-sitosterol on some biochemical indices of hypertension in wistar albino rats. Afr. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2014, 43, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Câmara, D.V.; Lemos, V.S.; Santos, M.H.; Nagem, T.J.; Côrtes, S.F. Mechanism of the vasodilator effect of Euxanthone in rat small mesenteric arteries. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-W.; Kang, J.-J.; Chen, J.; Teng, C.-M.; Lin, C.-N. Antihypertensive and vasorelaxing activities of synthetic xanthone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassossy, H.M.; Abo-Warda, S.M.; Fahmy, A. Chrysin and luteolin alleviate vascular complications associated with insulin resistance mainly through PPAR-gamma activation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassossy, H.M.; Hassan, N.; Zakaria, M.N. Heme oxygenase-1 alleviates vascular complications associated with metabolic syndrome: Effect on endothelial dependent relaxation and NO production. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 223, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









