Nuclear Syndecan-1 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Tumor Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
2.3. RNA Interference
2.4. Protein Extraction and Immunoblot Analysis
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time RT–PCR Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining and Quantitative Analysis
2.7. Invasion Assays
2.8. Gene Expression Analysis
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Loss of Nuclear SDC1 during TGF-β1-Induced EMT in A549 Cells
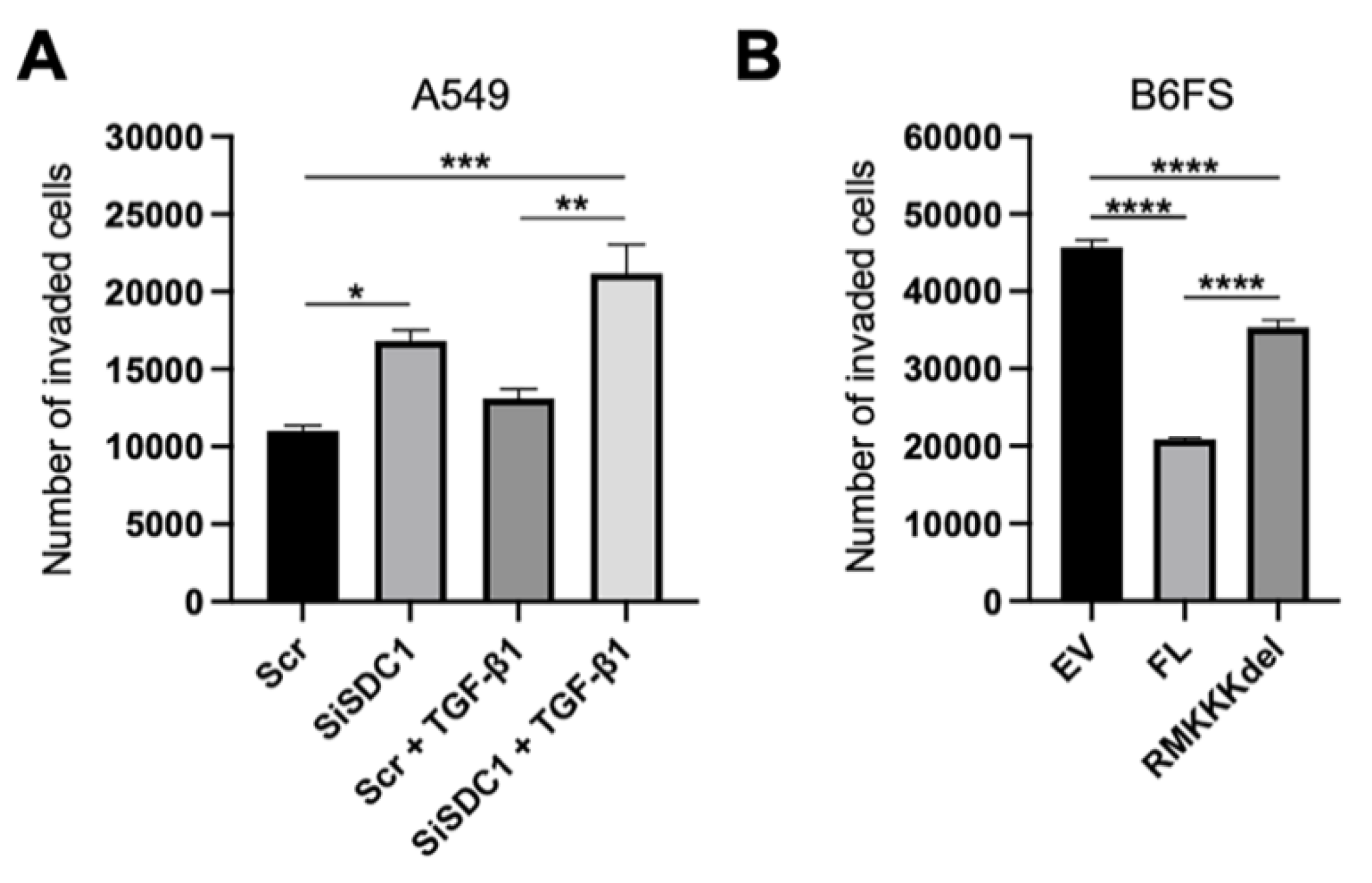
3.2. Loss of SDC1 Promotes EMT in A549 Cells
3.3. Nuclear SDC1 Reduces Mesenchymal Properties of B6FS Fibrosarcoma Cells
3.4. Nuclear SDC1 Inhibits the Invasive Properties of B6FS Fibrosarcoma Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markiewicz, A.; Topa, J.; Nagel, A.; Skokowski, J.; Seroczynska, B.; Stokowy, T.; Welnicka-Jaskiewicz, M.; Zaczek, A.J. Spectrum of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotypes in Circulating Tumour Cells from Early Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT and Cancer: More Than Meets the Eye. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. Emt: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and definitions for research on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, A.; Heldin, C.H. Mechanisms of TGFbeta-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuxe, J.; Vincent, T.; Garcia de Herreros, A. Transcriptional crosstalk between TGF-beta and stem cell pathways in tumor cell invasion: Role of EMT promoting Smad complexes. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, T.; Neve, E.P.; Johnson, J.R.; Kukalev, A.; Rojo, F.; Albanell, J.; Pietras, K.; Virtanen, I.; Philipson, L.; Leopold, P.L.; et al. A SNAIL1-SMAD3/4 transcriptional repressor complex promotes TGF-beta mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilchian, A.; Johansson, J.; Ghalali, A.; Asanin, S.T.; Santiago, A.; Rosencrantz, O.; Sollerbrant, K.; Vincent, C.T.; Sund, M.; Stenius, U.; et al. CXADR-Mediated Formation of an AKT Inhibitory Signalosome at Tight Junctions Controls Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, T.; Otvos, R.; Hjerpe, A.; Dobra, K. Syndecan-1 in Cancer: Implications for Cell Signaling, Differentiation, and Prognostication. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 796052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loussouarn, D.; Campion, L.; Sagan, C.; Frenel, J.S.; Dravet, F.; Classe, J.M.; Pioud-Martigny, R.; Berton-Rigaud, D.; Bourbouloux, E.; Mosnier, J.F.; et al. Prognostic impact of syndecan-1 expression in invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; McAlmon, K.R.; Davies, J.A.; Bernfield, M.; Hay, E.D. Simultaneous loss of expression of syndecan-1 and E-cadherin in the embryonic palate during epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1998, 42, 733–736. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M.; Saunders, S.; Nguyen, H.; Bernfield, M. Loss of cell surface syndecan-1 causes epithelia to transform into anchorage-independent mesenchyme-like cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 1995, 6, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppa, S.; Mali, M.; Miettinen, H.M.; Jalkanen, M. Syndecan expression regulates cell morphology and growth of mouse mammary epithelial tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, J.; Zhao, X.; Qi, T.; Zhang, T.; Kong, C. Syndecan-1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in human oral cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitselou, A.; Galani, V.; Skoufi, U.; Arvanitis, D.L.; Lampri, E.; Ioachim, E. Syndecan-1, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Markers (E-cadherin/beta-catenin) and Neoangiogenesis-related Proteins (PCAM-1 and Endoglin) in Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2016, 36, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farfan, N.; Ocarez, N.; Castellon, E.A.; Mejia, N.; de Herreros, A.G.; Contreras, H.R. The transcriptional factor ZEB1 represses Syndecan 1 expression in prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockstedt, U.; Dobra, K.; Nurminen, M.; Hjerpe, A. Immunoreactivity to cell surface syndecans in cytoplasm and nucleus: Tubulin-dependent rearrangements. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 274, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, T.; Mundt, F.; Heidari-Hamedani, G.; Zong, F.; Ferolla, E.; Alexeyenko, A.; Hjerpe, A.; Dobra, K. Novel genes and pathways modulated by syndecan-1: Implications for the proliferation and cell-cycle regulation of malignant mesothelioma cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, F.; Fthenou, E.; Wolmer, N.; Hollosi, P.; Kovalszky, I.; Szilak, L.; Mogler, C.; Nilsonne, G.; Tzanakakis, G.; Dobra, K. Syndecan-1 and FGF-2, but not FGF receptor-1, share a common transport route and co-localize with heparanase in the nuclei of mesenchymal tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobra, K.; Nurminen, M.; Hjerpe, A. Growth factors regulate the expression profile of their syndecan co-receptors and the differentiation of mesothelioma cells. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Sanderson, R.D. Heparanase regulates levels of syndecan-1 in the nucleus. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurzo, V.; Popovic, M.; Matoska, J.; Blasko, M.; Grofova, M.; Lizonova, A.; Steno, M. Human neoplastic cells in tissue culture: Two established cell lines derived from giant cell tumor and fibrosarcoma. Neoplasma 1976, 23, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zong, F.; Fthenou, E.; Castro, J.; Peterfia, B.; Kovalszky, I.; Szilak, L.; Tzanakakis, G.; Dobra, K. Effect of syndecan-1 overexpression on mesenchymal tumour cell proliferation with focus on different functional domains. Cell Prolif. 2010, 43, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamentsky, L.; Jones, T.R.; Fraser, A.; Bray, M.A.; Logan, D.J.; Madden, K.L.; Ljosa, V.; Rueden, C.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Carpenter, A.E. Improved structure, function and compatibility for CellProfiler: Modular high-throughput image analysis software. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, M.; Koinuma, D.; Ogami, T.; Umezawa, K.; Iwata, C.; Watabe, T.; Miyazono, K. TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells is enhanced by pro-inflammatory cytokines derived from RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. J. Biochem. 2012, 151, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, T.; Mundt, F.; Kumar-Singh, A.; Mobus, L.; Otvos, R.; Hjerpe, A.; Dobra, K. Molecular targets and signaling pathways regulated by nuclear translocation of syndecan-1. BMC Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, F.; Fthenou, E.; Mundt, F.; Szatmari, T.; Kovalszky, I.; Szilak, L.; Brodin, D.; Tzanakakis, G.; Hjerpe, A.; Dobra, K. Specific syndecan-1 domains regulate mesenchymal tumor cell adhesion, motility and migration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppa, S.; Vleminckx, K.; Van Roy, F.; Jalkanen, M. Syndecan-1 expression in mammary epithelial tumor cells is E-cadherin-dependent. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109 Pt 6, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfan, N.; Orellana-Serradell, O.; Herrera, D.; Chrzanowsky, D.; Cubillos, P.; Marin, G.; Antonio Garcia De Herreros, A.; Castellon, E.A.; Contreras, H.R. SNAIL expression correlates with the translocation of syndecan1 intracellular domain into the nucleus in prostate cancer cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar-Singh, A.; Shrinet, J.; Parniewska, M.M.; Fuxe, J.; Dobra, K.; Hjerpe, A. Mapping the Interactome of the Nuclear Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Syndecan-1 in Mesothelioma Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradella, D.; Naro, C.; Sette, C.; Ghigna, C. EMT and stemness: Flexible processes tuned by alternative splicing in development and cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, V.; Carson, B.B.; Feenstra, J.M.; Dass, R.A.; Sekyrova, P.; Hoshino, A.; Petersen, J.; Guo, Y.; Parks, M.M.; Kurylo, C.M.; et al. Ribosome biogenesis during cell cycle arrest fuels EMT in development and disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przygodzka, P.; Papiewska-Pajak, I.; Bogusz-Koziarska, H.; Sochacka, E.; Boncela, J.; Kowalska, M.A. Regulation of miRNAs by Snail during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in HT29 colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar-Singh, A.; Parniewska, M.M.; Giotopoulou, N.; Javadi, J.; Sun, W.; Szatmári, T.; Dobra, K.; Hjerpe, A.; Fuxe, J. Nuclear Syndecan-1 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Tumor Cells. Biology 2021, 10, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060521
Kumar-Singh A, Parniewska MM, Giotopoulou N, Javadi J, Sun W, Szatmári T, Dobra K, Hjerpe A, Fuxe J. Nuclear Syndecan-1 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Tumor Cells. Biology. 2021; 10(6):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060521
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar-Singh, Ashish, Malgorzata Maria Parniewska, Nikolina Giotopoulou, Joman Javadi, Wenwen Sun, Tünde Szatmári, Katalin Dobra, Anders Hjerpe, and Jonas Fuxe. 2021. "Nuclear Syndecan-1 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Tumor Cells" Biology 10, no. 6: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060521
APA StyleKumar-Singh, A., Parniewska, M. M., Giotopoulou, N., Javadi, J., Sun, W., Szatmári, T., Dobra, K., Hjerpe, A., & Fuxe, J. (2021). Nuclear Syndecan-1 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Tumor Cells. Biology, 10(6), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060521







