Culture-Independent Survey of Thermophilic Microbial Communities of the North Caucasus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Analysis of Water Physicochemical Parameters and Element Composition
2.3. DNA Isolation
2.4. High Throughput 16S Community Profiling
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Description and Physicochemical Parameters of Sampling Sites
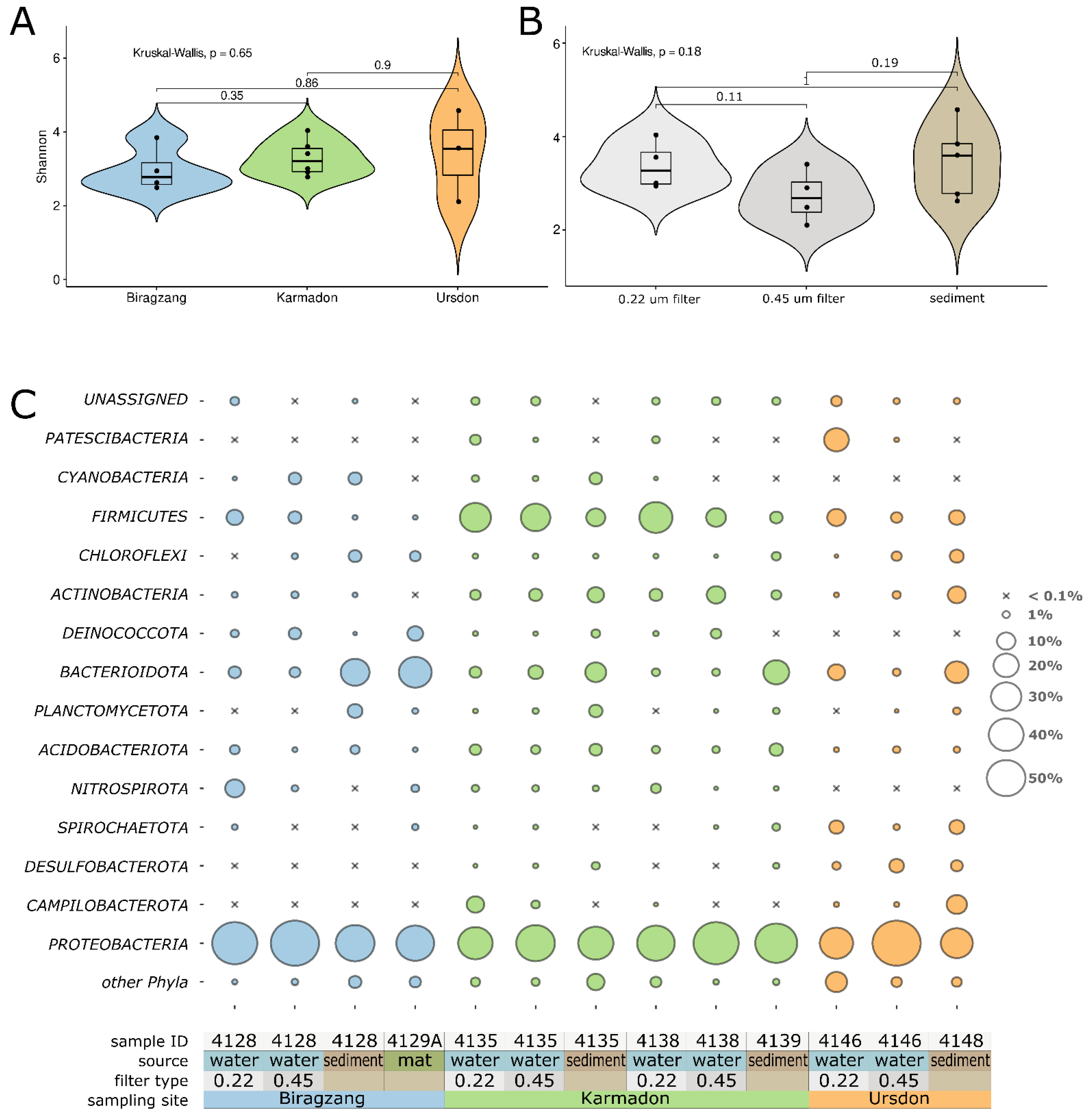
3.2. Analysis of Prokaryote Diversity Using 16S rRNA Profiling
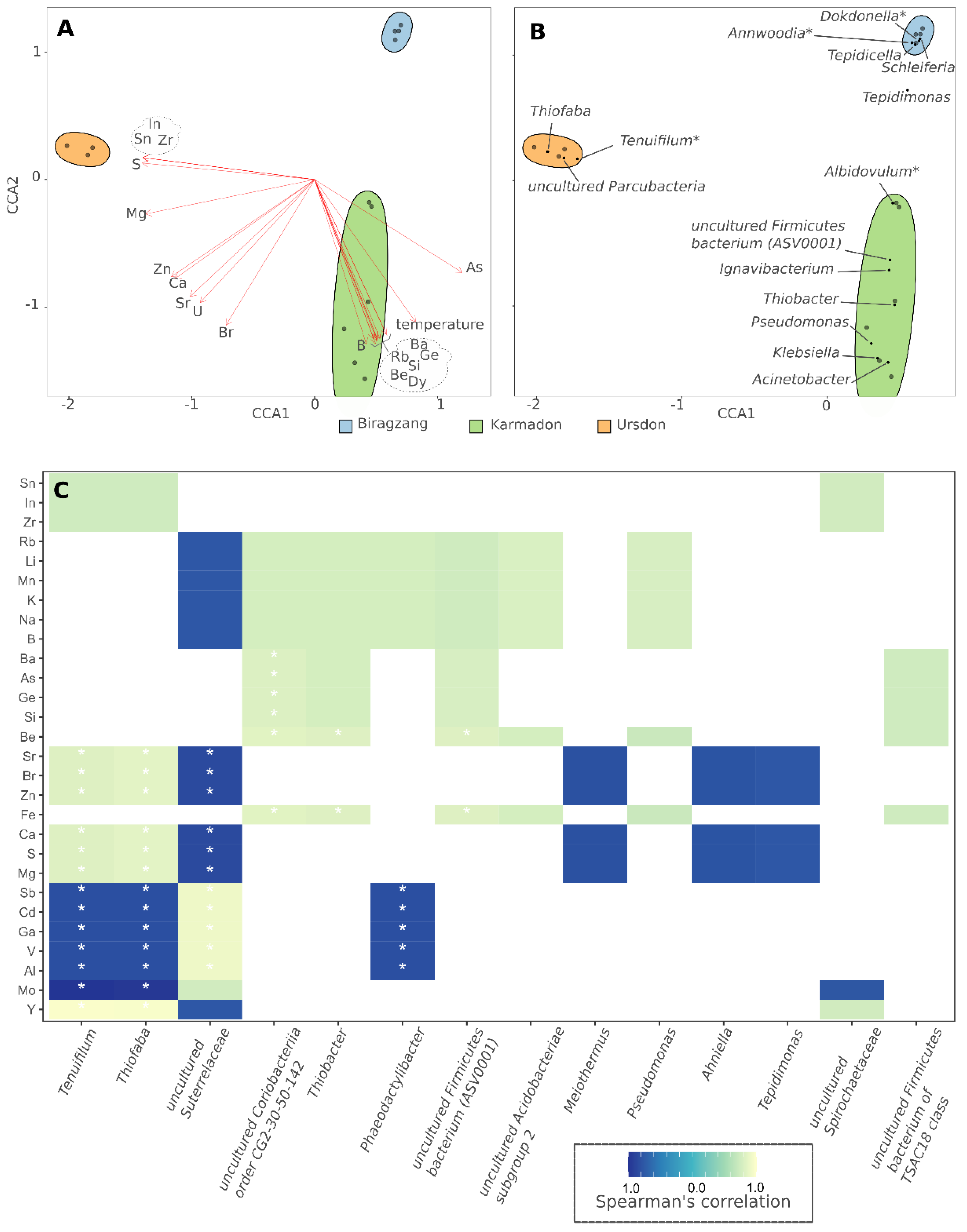
3.3. Analysis of Correlations between the Structure of the Microbial Community and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity and Taxonomic Composition of Microbial Communities
4.2. Correlation of Microbial Taxa with Elemental Composition of Water and Environmental Condition
4.3. Serial Filtering of Water Samples as a Strategy for Preliminary Insights on Ecological Niches and Better Resolution of Low Abundant Taxa
4.4. Detection of Deep and Possibly Endemic Lineages of Uncultivated Microorganisms
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Power, J.F.; Carere, C.R.; Lee, C.K.; Wakerley, G.L.J.; Evans, D.W.; Button, M.; White, D.; Climo, M.D.; Hinze, A.M.; Morgan, X.C.; et al. Microbial Biogeography of 925 Geothermal Springs in New Zealand. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.S.; Chan, K.-G.; Ee, R.; Hong, K.-W.; Urbieta, M.S.; Donati, E.R.; Shamsir, M.S.; Goh, K.M. Effects of Physiochemical Factors on Prokaryotic Biodiversity in Malaysian Circumneutral Hot Springs. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massello, F.L.; Chan, C.S.; Chan, K.-G.; Goh, K.M.; Donati, E.; Urbieta, M.S. Meta-Analysis of Microbial Communities in Hot Springs: Recurrent Taxa and Complex Shaping Factors beyond PH and Temperature. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, D.; Sompong, U.; Yim, L.C.; Barraclough, T.G.; Peerapornpisal, Y.; Pointing, S.B. The Effects of Temperature, PH and Sulphide on the Community Structure of Hyperthermophilic Streamers in Hot Springs of Northern Thailand: Hyperthermophilic Diversity and Abiotic Variables. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaneto, D.; Hortal, J. Microbial Biogeography: Is Everything Small Everywhere? In Microbial Ecological Theory: Current Perspectives; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2012; pp. 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.S.; Schaperdoth, I.; Macalady, J.L. Biogeography of Sulfur-Oxidizing Acidithiobacillus Populations in Extremely Acidic Cave Biofilms. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2879–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, F.; Selph, K. Thermophilic Bacterial Activity in a Deep-Sea Sediment from the Pacific Ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1997, 13, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Price, M.T.; Fullerton, H.; Moyer, C.L. Biogeography and Evolution of Thermococcus Isolates from Hydrothermal Vent Systems of the Pacific. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beblo, K.; Rabbow, E.; Rachel, R.; Huber, H.; Rettberg, P. Tolerance of Thermophilic and Hyperthermophilic Microorganisms to Desiccation. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podar, P.T.; Yang, Z.; Björnsdóttir, S.H.; Podar, M. Comparative Analysis of Microbial Diversity Across Temperature Gradients in Hot Springs From Yellowstone and Iceland. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaalishvili, V.B.; Nevskaya, N.I.; Nevskii, L.N.; Shempelev, A.G. Geophysical Fields above Volcanic Edifices in the North Caucasus. J. Volcanol. Seism. 2015, 9, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintsaev, M.S.; Machigova, F.; Khadasheva, Z.; Cherkasov, S.; Churikova, T. Mineral Resources of the Geothermal Sources of the North Caucasus. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2016, 11, 12973–12984. [Google Scholar]
- Khalilova, E.A.; Nuratinov, R.A.; Kotenko, S.C.; Islammagomedova, E.A. Hydrocarbon-Oxidizing Microorganisms of Hot Springs and Their Significance in the Assessment of the Biodiversity of Microbial Communities. Arid. Ecosyst. 2014, 4, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernousova, E.Y.; Akimov, V.N.; Gridneva, E.V.; Dubinina, V.A.; Grabovich, M.Y. Erratum to: “Biodiversity and Monitoring of Colorless Filamentous Bacteria in Sulfide Aquatic Systems of North Caucasus Region”. Microbiology 2010, 79, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chernousova, E.Y.; Akimov, V.N.; Gridneva, E.V.; Dubinina, G.A.; Grabovich, M.Y. Phylogenetic in Situ/Ex Situ Analysis of a Sulfur Mat Microbial Community from a Thermal Sulfide Spring in the North Caucasus. Microbiology 2008, 77, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetkova, T.; Podosokorskaya, O.; Elcheninov, A.; Kublanov, I. Diversity of Thermophilic Prokaryotes Inhabiting Russian Natural Hot Springs; 2022.
- Zaalishvili, V.B.; Melkov, D.A.; Burdzieva, O.G. Possibilities of Geothermal Energy Use on the North Caucasus (a View on a Problem from Azores Example). Ecol. Environ. Conserv. 2015, 21, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Beltrán, M.; Mueller, A.; Scofield, M.; Pachiadaki, M.G.; Taylor, C.; Tyshchenko, K.; Michiels, C.; Lam, P.; Ulloa, O.; Jürgens, K.; et al. Sampling and Processing Methods Impact Microbial Community Structure and Potential Activity in a Seasonally Anoxic Fjord: Saanich Inlet, British Columbia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Malfatti, F. Microbial Structuring of Marine Ecosystems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohl, D.; Gohl, D.M.; MacLean, A.; Hauge, A.; Becker, A.; Walek, D.; Beckman, K.B. An Optimized Protocol for High-Throughput Amplicon-Based Microbiome Profiling. Protoc. Exch. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugerth, L.W.; Wefer, H.A.; Lundin, S.; Jakobsson, H.E.; Lindberg, M.; Rodin, S.; Engstrand, L.; Andersson, A.F. DegePrime, a Program for Degenerate Primer Design for Broad-Taxonomic-Range PCR in Microbial Ecology Studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5116–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, A.Yu.; Tarnovetskii, I.Yu.; Podosokorskaya, O.A.; Toshchakov, S.V. Analysis of 16S RRNA Primer Systems for Profiling of Thermophilic Microbial Communities. Microbiology 2019, 88, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetkova, T.V.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Zayulina, K.S.; Elcheninov, A.G.; Zavarzina, D.G.; Lavrushin, V.Yu.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Kublanov, I.V. Hot in Cold: Microbial Life in the Hottest Springs in Permafrost. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, G.; Stenzel, U.; Maricic, T.; Wiebe, V.; Kelso, J. DeML: Robust Demultiplexing of Illumina Sequences Using a Likelihood-Based Approach. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 770–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, N.M.; Proctor, D.M.; Holmes, S.P.; Relman, D.A.; Callahan, B.J. Simple Statistical Identification and Removal of Contaminant Sequences in Marker-Gene and Metagenomics Data. Microbiome 2018, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Ordination Methods, Diversity Analysis and Other Functions for Community and Vegetation Ecologists. Available online: https://www.worldagroforestry.org/publication/vegan-community-ecology-package-ordination-methods-diversity-analysis-and-other (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, S.; Blake, T.; Salojarvi, J. Microbiome; Version 1.0.2; Bioconductor: 2017. Available online: https://bioconductor.statistik.tu-dortmund.de/packages/3.6/bioc/html/microbiome.html (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Hsieh, T.C.; Ma, K.H.; Chao, A. INEXT: An R Package for Rarefaction and Extrapolation of Species Diversity (H Ill Numbers). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhgamadze, A.K.; Gogichev, R.R.; Dzeranov, B.V. Hydrochemical Characteristics of the Biragzang Groundwater Area; 2019.
- Lavrushin, V.Y.; Kuleshov, V.N.; Kikvadze, O.E. Travertines of the Northern Caucasus. Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2006, 41, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzgoev, U.S. The Karmadon Resort; North Ossetian Book Publishing House: Ordzhonikidze, Russia, 1961; pp. 50–60. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Boden, R.; Hutt, L.P.; Rae, A.W. Reclassification of Thiobacillus Aquaesulis (Wood & Kelly, 1995) as Annwoodia Aquaesulis Gen. Nov., Comb. Nov., Transfer of Thiobacillus (Beijerinck, 1904) from the Hydrogenophilales to the Nitrosomonadales, Proposal of Hydrogenophilalia Class. Nov. within the ‘Proteobacteria’, and Four New Families within the Orders Nitrosomonadales and Rhodocyclales. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdigian, R.M.; Myerson, A.S. The Adsorption OfThiobacillus Ferrooxidans on Coal Surfaces. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1986, 28, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myerson, A.S.; Kline, P. The Adsorption OfThiobacillus Ferrooxidans on Solid Particles. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1983, 25, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Suzuki, K. Thiofaba Tepidiphila Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Obligately Chemolithoautotrophic, Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacterium of the Gammaproteobacteria Isolated from a Hot Spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Takahashi, N.; Hiraishi, A. Phylogenetic Characterization of a Polychlorinated-Dioxin- Dechlorinating Microbial Community by Use of Microcosm Studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4325–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeglin, L.H.; Wang, B.; Waythomas, C.; Rainey, F.; Talbot, S.L. Organic Matter Quantity and Source Affects Microbial Community Structure and Function Following Volcanic Eruption on Kasatochi Island, Alaska: Microbial Structure and Function after Volcanic Eruption. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, T.G.; Kostrikina, N.A.; Chernyh, N.A.; Tourova, T.P.; Kolganova, T.V.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. Carboxydocella Thermautotrophica Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Anaerobic, CO-Utilizing Thermophile from a Kamchatkan Hot Spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshchakov, S.V.; Lebedinsky, A.V.; Sokolova, T.G.; Zavarzina, D.G.; Korzhenkov, A.A.; Teplyuk, A.V.; Chistyakova, N.I.; Rusakov, V.S.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Kublanov, I.V.; et al. Genomic Insights Into Energy Metabolism of Carboxydocella Thermautotrophica Coupling Hydrogenogenic CO Oxidation With the Reduction of Fe(III) Minerals. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Koo, T.; Yulisa, A.; Hwang, S. Magnetite as an Enhancer in Methanogenic Degradation of Volatile Fatty Acids under Ammonia-Stressed Condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzhenkov, A.; Teplyuk, A.V.; Lebedinsky, A.V.; Khvashchevskaya, A.A.; Kopylova, Y.G.; Arakchaa, K.D.; Golyshin, P.; Lunev, E.; Golyshina, O.V.; Kublanov, I.V.; et al. Members of the Uncultured Taxon OP1 (“Acetothermia”) Predominate in the Microbial Community of an Alkaline Hot Spring at East-Tuvinian Upland. Microbiology 2018, 87, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, C.G.; Havig, J.R.; Hamilton, T.L. Hot Spring Microbial Community Composition, Morphology, and Carbon Fixation: Implications for Interpreting the Ancient Rock Record. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 5, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, K.J.; Teramoto, E.H.; Soriano, A.U.; Valoni, E.; Baessa, M.P.; Richnow, H.H.; Vogt, C.; Chang, H.K.; Oliveira, V.M. Taxonomic and Functional Diversity of the Microbiome in a Jet Fuel Contaminated Site as Revealed by Combined Application of in Situ Microcosms with Metagenomic Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méheust, R.; Castelle, C.J.; Matheus Carnevali, P.B.; Farag, I.F.; He, C.; Chen, L.-X.; Amano, Y.; Hug, L.A.; Banfield, J.F. Groundwater Elusimicrobia Are Metabolically Diverse Compared to Gut Microbiome Elusimicrobia and Some Have a Novel Nitrogenase Paralog. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2907–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlyakov, V.M.; Rototaeva, O.V.; Nosenko, G.A.; Chernov, R.A. Ten years after the Karmadon catastrophe, North Ossetia: On the causes of event and the glacier recovery processes. Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk. Seriya Geogr. 2015, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackett, L.P.; Dodge, A.G.; Ellis, L.B.M. Microbial Genomics and the Periodic Table. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, W.; Lloyd, J.; Guo, H.; Dai, W.; Nixon, S.; Bassil, N.M.; Ren, C.; Zhang, C.; Ke, T.; Polya, D. Linking microbial community composition to hydrogeochemistry in the western Hetao Basin: Potential importance of ammonium as an electron donor during arsenic mobilization. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podosokorskaya, O.A.; Kochetkova, T.V.; Novikov, A.A.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Elcheninov, A.G.; Kublanov, I.V. Tenuifilum thalassicum gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel moderate thermophilic anaerobic bacterium from a Kunashir Island shallow hot spring representing a new family Tenuifilaceae fam. nov. in the class Bacteroidia. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhasov, A.B.; Alkhasova, D.A. Up-to-Date State and Prospects for the Development of Geothermal Resources of the North Caucasus Region. Therm. Eng. 2014, 61, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershov, A.V.; Brunet, M.-F.; Nikishin, A.M.; Bolotov, S.N.; Nazarevich, B.P.; Korotaev, M.V. Northern Caucasus Basin: Thermal History and Synthesis of Subsidence Models. Sediment. Geol. 2003, 156, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto-Medina, A.; Shahsavari, E.; Cohen, M.; Mantri, N.; Ball, A.S. Analysis of the Microbiome (Bathing Biome) in Geothermal Waters from an Australian Balneotherapy Centre. Water 2020, 12, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, H.; Takai, K.; Inagaki, F.; Nealson, K.H.; Horikoshi, K. Thiobacter subterraneus gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligately chemolithoautotrophic, thermophilic, sulfur-oxidizing bacterium from a subsurface hot aquifer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- França, L.; Rainey, F.A.; Nobre, M.F.; da Costa, M.S. Tepidicella xavieri gen. nov., sp. nov., a betaproteobacterium isolated from a hot spring runoff. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Albuquerque, L.; Egas, C. Tepidimonas. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, Y.A.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Gavrilov, S.N.; Banks, D.; Gerasimchuk, A.L.; Podosokorskaya, O.A.; Merkel, A.Y.; Chernyh, N.A.; Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V.; et al. Stable and Variable Parts of Microbial Community in Siberian Deep Subsurface Thermal Aquifer System Revealed in a Long-Term Monitoring Study. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalwasińska, A.; Krawiec, A.; Deja-Sikora, E.; Gołębiewski, M.; Kosobucki, P.; Swiontek Brzezinska, M.; Walczak, M. Microbial Diversity in Deep-Subsurface Hot Brines of Northwest Poland: From Community Structure to Isolate Characteristics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, L.M.; Blake, R.E.; Greenwood, J.P.; Martini, A.M.; Rose, E.C. Microbial Diversity of Boron-Rich Volcanic Hot Springs of St. Lucia, Lesser Antilles. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 70, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, C.E.; Smirnova, A.V.; Graham, J.M.; Stott, M.B.; Khadka, R.; Moore, T.R.; Grasby, S.E.; Strack, M.; Dunfield, P.F. Distribution and Diversity of V Errucomicrobia Methanotrophs in Geothermal and Acidic Environments: Diversity of Verrucomicrobial Methanotrophs. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneron, A.; Cruaud, P.; Langlois, V.; Lovejoy, C.; Culley, A.I.; Vincent, W.F. Ultra-small and abundant: Candidate phyla radiation bacteria are potential catalysts of carbon transformation in a thermokarst lake ecosystem. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2020, 5, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, C.J.; Wrighton, K.C.; Thomas, B.C.; Hug, L.A.; Brown, C.T.; Wilkins, M.J.; Frischkorn, K.R.; Tringe, S.G.; Singh, A.; Markillie, L.M.; et al. Genomic expansion of domain archaea highlights roles for organisms from new phyla in anaerobic carbon cycling. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavourakis, C.D.; Andrei, A.-S.; Mehrshad, M.; Ghai, R.; Sorokin, D.Y.; Muyzer, G. A Metagenomics Roadmap to the Uncultured Genome Diversity in Hypersaline Soda Lake Sediments. Microbiome 2018, 6, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tian, L.; Chen, P.; Han, M.; Song, L.; Tong, X.; Sun, X.; Yang, F.; Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; et al. Over 50,000 Metagenomically Assembled Draft Genomes for the Human Oral Microbiome Reveal New Taxa. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, S1672022921001765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S. The Rates of Global Bacterial and Archaeal Dispersal. ISME J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papke, R.T.; Ramsing, N.B.; Bateson, M.M.; Ward, D.M. Geographical Isolation in Hot Spring Cyanobacteria: Geographical Isolation in Hot Spring Cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takacs-Vesbach, C.; Mitchell, K.; Jackson-Weaver, O.; Reysenbach, A.-L. Volcanic Calderas Delineate Biogeographic Provinces among Yellowstone Thermophiles. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killham, K.; Prosser, J.I. The prokaryotes. In Soil Microbiology, Ecology and Biochemistry, 3rd ed.; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 119–144. ISBN 0125468075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.; Tiago, I.; Pires, A.L.; Da Costa, M.S.; Veríssimo, A. Dokdonella fugitiva sp. nov., a Gammaproteobacterium isolated from potting soil. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 29, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Grimont, F. Klebsiella. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleroni, N.J. Pseudomonas. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, L.; Santos, J.; Travassos, P.; Nobre, M.F.; Rainey, F.A.; Wait, R.; Empadinhas, N.; Silva, M.T.; Da Costa, M.S. Albidovulum inexpectatum gen. nov., sp. nov., a Nonphotosynthetic and slightly thermophilic bacterium from a marine hot spring that is very closely related to members of the photosynthetic genus Rhodovulum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4266–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podosokorskaya, O.A.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Gavrilov, S.N.; Mardanov, A.V.; Merkel, A.Y.; Karnachuk, O.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Kublanov, I.V. Characterization of Melioribacter roseus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel facultatively anaerobic thermophilic cellulolytic bacterium from the class Ignavibacteria, and a proposal of a novel bacterial phylum Ignavibacteriae. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proença, D.N.; Whitman, W.B.; Varghese, N.; Shapiro, N.; Woyke, T.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Morais, P.V. Arboriscoccus pini gen. nov., sp. nov., an endophyte from a pine tree of the class Alphaproteobacteria, emended description of Geminicoccus roseus, and proposal of Geminicoccaceae fam. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, L.; Rainey, F.A.; Nobre, M.F.; da Costa, M.S. Schleiferia thermophila gen. nov., sp. nov., a slightly thermophilic bacterium of the phylum “bacteroidetes” and the proposal of schleiferiaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 2450–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Iino, T.; Ohkuma, M.; Kamagata, Y.; Amachi, S. Iodidimonas muriae gen. Nov., sp. nov., an aerobic iodide-oxidizing bacterium isolated from brine of a natural gas and iodine recovery facility, and proposals of Iodidimonadaceae fam. nov., Iodidimonadales ord. nov., Emcibacteraceae fam. nov. and Emcibact. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5016–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, L.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Barroso, C.; Froufe, H.J.C.; Lage, O.; Lobo-Da-Cunha, A.; Egas, C.; da Costa, M.S. Raineya orbicola gen. nov., sp. nov. a slightly thermophilic bacterium of the phylum bacteroidetes and the description of raineyaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lei, X.; Lai, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Zheng, W.; Tian, Y.; et al. Phaeodactylibacter xiamenensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Saprospiraceae isolated from the marine alga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 3496–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovre, K.; Henriksen, S.D. A new Moraxella species, Moraxella osloensis, and a revised description of Moraxella nonliquefaciens. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1967, 17, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodkina, G.B.; Baslerov, R.V.; Novikov, A.A.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Slobodkin, A.I. Thermodesulfitimonas autotrophica gen. Nov., sp. Nov., a thermophilic, obligate sulfite-reducing bacterium isolated from a terrestrial hot spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, H.-J. Micrococcus. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginova, L.G.; Egorova, L.A.; Golovacheva, R.S.; Seregina, L.M. Thermus ruber sp. nov., nom. rev. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1984, 34, 498–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, W.; Kroneck, P.M.H.; Pfennig, N. Comparative systematic study on “Spirillum” 5175, Campylobacter and Wolinella species—Description of “Spirillum” 5175 as Sulfurospirillum deleyianum gen. nov., spec. nov. Arch. Microbiol. 1992, 158, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, K.; Kojima, H.; Kato, Y.; Fukui, M. Dissulfurispira thermophila gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic chemolithoautotroph growing by sulfur disproportionation, and proposal of novel taxa in the phylum Nitrospirota to reclassify the genus Thermodesulfovibrio. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodkina, G.B.; Kolganova, T.V.; Kopitsyn, D.S.; Viryasov, M.B.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Slobodkin, A.I. Dissulfurirhabdus thermomarina gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic, autotrophic, sulfite-reducing and disproportionating deltaproteobacterium isolated from a shallow-sea hydrothermal vent. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2515–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieglmeier, M.; Klingl, A.; Alves, R.J.E.; Rittmann, S.K.M.R.; Melcher, M.; Leisch, N.; Schleper, C. Nitrososphaera viennensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic and mesophilic, ammonia-oxidizing archaeon from soil and a member of the archaeal phylum Thaumarchaeota. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 2738–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelschbach, J.S.; Mouttaki, H.; Pickl, C.; Heipieper, H.J.; Rache, R.; Lawson, P.A.; Meckenstock, R.U. Rectinema cohabitans gen. nov., sp. nov., a rod-shaped spirochaete isolated from an anaerobic naphthalene-degrading enrichment culture. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlschroeder, M.; Leschine, S.B.; Canale-Parola, E. Spirochaeta caldaria sp. nov., a thermophilic bacterium that enhances cellulose degradation by Clostridium thermocellum. Arch. Microbiol. 1994, 161, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Location | Latitude Longitude | Altitude | Depth of the Well | T, °C | pH | Eh | Enriched Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biragzang | 42.9957 N, 44.2290 E | 685 m | 2370 m | 48 | 8.8 | −20–0 | Sb, V, Al, Mo, Ga, Cd |
| Karmadon | 42.7547 N, 44.4811 E | 2330 m | NA | 52–55 | 6.1 | −20–0 | K, Si, B, As, Fe, Li, Rb, Mn, Be, Ba |
| Ursdon | 43.0626 N, 44.0490 E | 643 m | 1530 m | 45–47 | 7.0 | −370–140 * | S, Mg, Ca Sn, Zr, In |
| Concentration of Major Elements, µg/L | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | V | |
| Biragzang | 2121.0 | 269,292.0 | 46.7 | 52.8 | 14,676.0 | 17,184.0 | 1458.0 | 904.0 | 0.7 |
| Karmadon #4135 | 62,696.0 | 1,975,454.0 | 44,306.0 | <LOD | 27,751.0 | 40,247.0 | 295,956.0 | 356,082.0 | <LOD |
| Karmadon #4138 | 72,680.3 | 2,126,284.0 | 47,948.0 | <LOD | 29,430.0 | 43,329.0 | 318,907.0 | 389,111.0 | <LOD |
| Ursdon | 7967.0 | 1,571,141.0 | 171,799.0 | <LOD | 14,327.0 | 867,285.0 | 62,203.0 | 651,088.0 | <LOD |
| LOD | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 16.0 | 74.0 | 110.0 | 0.2 |
| Mn | Fe | Zn | Ge | As | Br | Sr | Ba | Pb | |
| Biragzang | 0.4 | <LOD | 1.9 | 4.8 | 330.0 | 181.0 | 66.5 | 31.3 | <LOD |
| Karmadon #4135 | 761.0 | 3254.0 | 176.0 | 20.2 | 442.0 | 7120.0 | 10,243.0 | 345.0 | 0.6 |
| Karmadon #4138 | 784.0 | 3265.0 | 243.0 | 22.2 | 540.0 | 7805.0 | 11,102.0 | 364.0 | <LOD |
| Ursdon | 6.2 | <LOD | 398 | 3.3 | <LOD | 7942.0 | 15,624.0 | 4.9 | <LOD |
| LOD | 0.2 | 7.0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 8.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Concentration of Rare Elements, ng/L | |||||||||
| Li | Be | Rb | Y | Zr | Mo | Cd | In | Sn | |
| Biragzang | 41,785.0 | <LOD | 1937.0 | <LOD | <LOD | 15,677.0 | 53.2 | <LOD | <LOD |
| Karmadon #4135 | 11,831,981.0 | 2130.0 | 2,120,957.0 | 1079.0 | <LOD | 485.0 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Karmadon #4138 | 12,457,781.0 | 3033.7 | 2,235,407.0 | 905.0 | <LOD | 569.0 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Ursdon | 1,164,150.0 | <LOD | 68,102 | <LOD | 223.0 | <LOD | <LOD | 189.0 | 1025.0 |
| LOD | 80.0 | 6.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 30.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 29.0 |
| Sb | Cs | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | |
| Biragzang | 209.0 | 158.0 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Karmadon #4135 | <LOD | 2,049,997.0 | 160.0 | 171.0 | 22.3 | 156.0 | 26.4 | 21.5 | 39.8 |
| Karmadon #4138 | <LOD | 2,166,997.0 | 142.0 | 135.0 | 14.5 | 93.1 | 29.0 | <LOD | 41.3 |
| Ursdon | <LOD | 4405.0 | 116 | 38.2 | <LOD | 37.7 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| LOD | 10.0 | 6.0 | 33.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Dy | Ho | Er | Yb | W | Tl | Th | U | ||
| Biragzang | 41,785.0 | <LOD | 1937.0 | <LOD | <LOD | 15,677.0 | 53.2 | <LOD | |
| Karmadon #4135 | 11,831,981.0 | 2130.0 | 2,120,957.0 | 1079.0 | <LOD | 485.0 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Karmadon #4138 | 12,457,781.0 | 3033.7 | 2,235,407.0 | 905.0 | <LOD | 569.0 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Ursdon | 1,164,150.0 | <LOD | 68,102 | <LOD | 223.0 | <LOD | <LOD | 189.0 | |
| LOD | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 4.0 | 0.8 | 5.0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toshchakov, S.V.; Izotova, A.O.; Vinogradova, E.N.; Kachmazov, G.S.; Tuaeva, A.Y.; Abaev, V.T.; Evteeva, M.A.; Gunitseva, N.M.; Korzhenkov, A.A.; Elcheninov, A.G.; et al. Culture-Independent Survey of Thermophilic Microbial Communities of the North Caucasus. Biology 2021, 10, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121352
Toshchakov SV, Izotova AO, Vinogradova EN, Kachmazov GS, Tuaeva AY, Abaev VT, Evteeva MA, Gunitseva NM, Korzhenkov AA, Elcheninov AG, et al. Culture-Independent Survey of Thermophilic Microbial Communities of the North Caucasus. Biology. 2021; 10(12):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121352
Chicago/Turabian StyleToshchakov, Stepan V., Anna O. Izotova, Elizaveta N. Vinogradova, Gennady S. Kachmazov, Albina Y. Tuaeva, Vladimir T. Abaev, Martha A. Evteeva, Natalia M. Gunitseva, Aleksei A. Korzhenkov, Alexander G. Elcheninov, and et al. 2021. "Culture-Independent Survey of Thermophilic Microbial Communities of the North Caucasus" Biology 10, no. 12: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121352
APA StyleToshchakov, S. V., Izotova, A. O., Vinogradova, E. N., Kachmazov, G. S., Tuaeva, A. Y., Abaev, V. T., Evteeva, M. A., Gunitseva, N. M., Korzhenkov, A. A., Elcheninov, A. G., Patrushev, M. V., & Kublanov, I. V. (2021). Culture-Independent Survey of Thermophilic Microbial Communities of the North Caucasus. Biology, 10(12), 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121352







