Phylogeography and Re-Evaluation of Evolutionary Rate of Powassan Virus Using Complete Genome Data
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic Data Sampling
2.2. Codon Saturation Measuring and Evolutionary Model Selection
2.3. Assessment of Temporal Structure of Heterochronous Sequences
2.4. Temporal Signal Dynamics
2.5. Phylogeographic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Codon Substitution Saturation and the Best-Fit Substitution Model
3.2. Molecular Clock Choosing
3.3. Comparing Prior and Posterior Distributions. Temporal Structure and Temporal Signal Dynamics
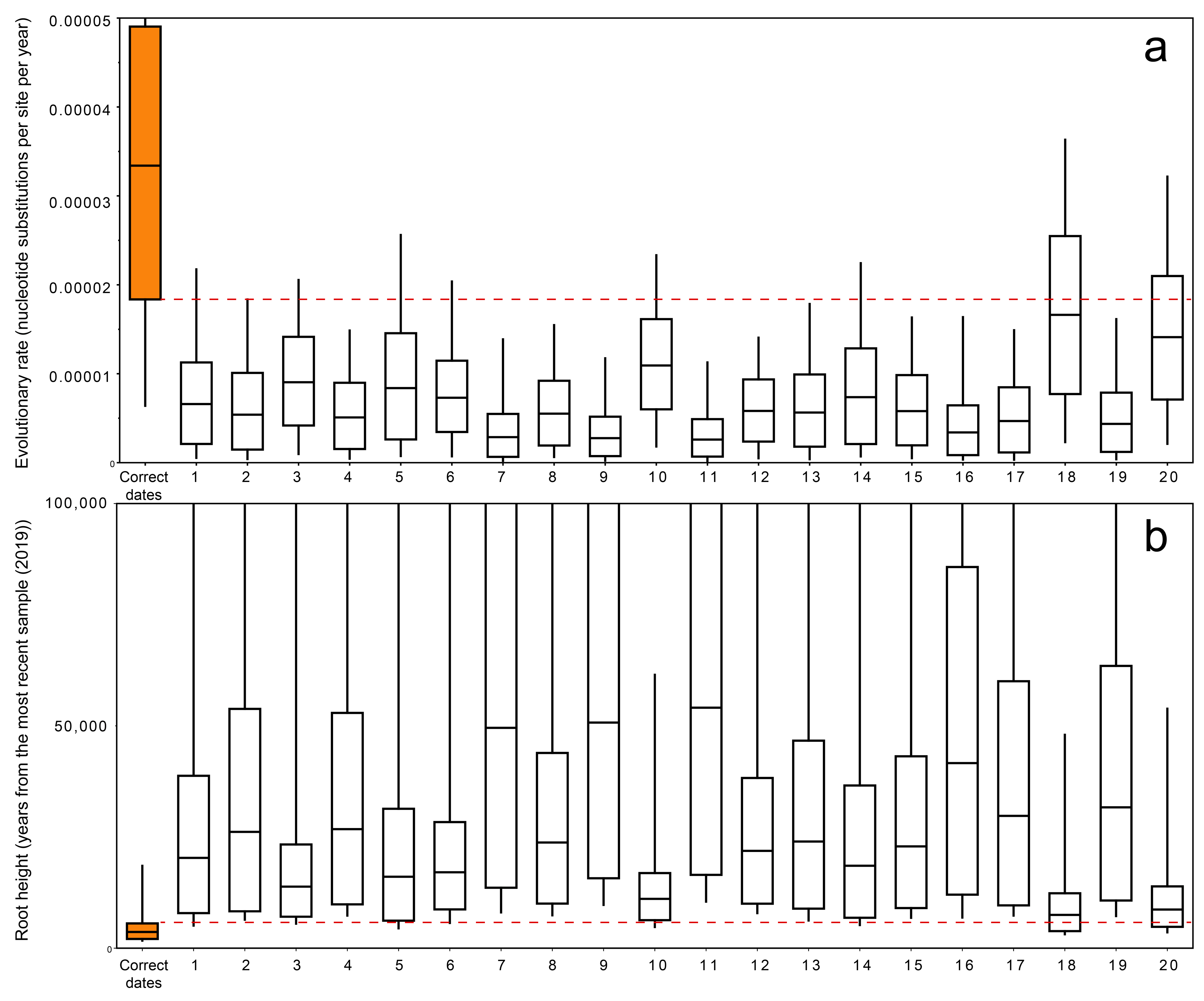
3.4. Permutation Test
3.5. Evolutionary Rate Estimates
3.6. Divergence Dating
3.7. Phylogeography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mc, L.D.; Donohue, W.L. Powassan virus: Isolation of virus from a fatal case of encephalitis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1959, 80, 708–711. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Hu, Z.; Deng, F.; Shen, S. Tick-Borne Viruses. Virol. Sin. 2018, 33, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuno, G.; Artsob, H.; Karabatsos, N.; Tsuchiya, K.R.; Chang, G.J. Genomic sequencing of deer tick virus and phylogeny of powassan-related viruses of North America. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 65, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebel, G.D. Update on Powassan virus: Emergence of a North American tick-borne flavivirus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.; Thorburn, H. Serum antibodies to louping-ill virus. Scott. Med. J. 1962, 7, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandl, C.W.; Holzmann, H.; Kunz, C.; Heinz, F.X. Complete genomic sequence of Powassan virus: Evaluation of genetic elements in tick-borne versus mosquito-borne flaviviruses. Virology 1993, 194, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesko, K.N.; Torres-Perez, F.; Hjelle, B.L.; Ebel, G.D. Molecular epidemiology of Powassan virus in North America. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2698–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbotina, E.L.; Loktev, V.B. Molecular evolution of the tick-borne encephalitis and Powassan viruses. Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duchene, S.; Lemey, P.; Stadler, T.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Duchene, D.A.; Dhanasekaran, V.; Baele, G. Bayesian Evaluation of Temporal Signal in Measurably Evolving Populations. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 3363–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, D.M.; Gould, E.A.; Forrester, N.L. Revisiting the clinal concept of evolution and dispersal for the tick-borne flaviviruses by using phylogenetic and biogeographic analyses. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8663–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonova, G.N.; Kondratov, I.G.; Ternovoi, V.A.; Romanova, E.V.; Protopopova, E.V.; Chausov, E.V.; Pavlenko, E.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Belikov, S.I.; Loktev, V.B. Characterization of Powassan viruses from Far Eastern Russia. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, N.F.; Rasmussen, D.; Stadler, T. MASCOT: Parameter and state inference under the marginal structured coalescent approximation. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3843–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchene, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kuhnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pickett, B.E.; Sadat, E.L.; Zhang, Y.; Noronha, J.M.; Squires, R.B.; Hunt, V.; Liu, M.; Kumar, S.; Zaremba, S.; Gu, Z.; et al. ViPR: An open bioinformatics database and analysis resource for virology research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D593–D598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE7: New and Improved Tools for Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Xie, Z.; Salemi, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. An index of substitution saturation and its application. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Bouckaert, R.R. Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis with BEAST; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, N.F.; Rasmussen, D.A.; Stadler, T. The Structured Coalescent and Its Approximations. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2970–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzcátegui, N.Y.; Sironen, T.; Golovljova, I.; Jääskeläinen, A.E.; Välimaa, H.; Lundkvist, Å.; Plyusnin, A.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Rate of evolution and molecular epidemiology of tick-borne encephalitis virus in Europe, including two isolations from the same focus 44 years apart. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelshin, R.V.; Sidorova, E.A.; Bondaryuk, A.N.; Trukhina, A.; Sherbakov, D.Y.; White III, R.A.; Andaev, E.I.; Balakhonov, S.V. “886-84-like” tick-borne encephalitis virus strains: Intraspecific status elucidated by comparative genomics. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.J.; Gilray, J.; Orton, R.J.; Baird, M.; Wilkie, G.; Filipe, A.D.S.; Johnson, N.; McInnes, C.J.; Kohl, A.; Biek, R. Population genomics of louping ill virus provide new insights into the evolution of tick-borne flaviviruses. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Oshitani, H. Origin of measles virus: Divergence from rinderpest virus between the 11th and 12th centuries. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, M.; Lu, T.; Li, C.; Lu, L. The evolutionary rates of HCV estimated with subtype 1a and 1b sequences over the ORF length and in different genomic regions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettersson, J.H.; Bohlin, J.; Dupont-Rouzeyrol, M.; Brynildsrud, O.B.; Alfsnes, K.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Gaunt, M.W.; Falconar, A.K.; de Lamballerie, X.; Eldholm, V.; et al. Re-visiting the evolution, dispersal and epidemiology of Zika virus in Asia. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worobey, M.; Watts, T.D.; McKay, R.A.; Suchard, M.A.; Granade, T.; Teuwen, D.E.; Koblin, B.A.; Heneine, W.; Lemey, P.; Jaffe, H.W. 1970s and ‘Patient 0’ HIV-1 genomes illuminate early HIV/AIDS history in North America. Nature 2016, 539, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boni, M.F.; Lemey, P.; Jiang, X.; Lam, T.T.; Perry, B.W.; Castoe, T.A.; Rambaut, A.; Robertson, D.L. Evolutionary origins of the SARS-CoV-2 sarbecovirus lineage responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Li, Y. Global evolutionary history and spatio-temporal dynamics of dengue virus type 2. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGuire, K.; Holmes, E.C.; Gao, G.F.; Reid, H.W.; Gould, E.A. Tracing the origins of louping ill virus by molecular phylogenetic analysis. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79 (Pt 5), 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.U.; Dyke, A.S.; Shakun, J.D.; Carlson, A.E.; Clark, J.; Wohlfarth, B.; Mitrovica, J.X.; Hostetler, S.W.; McCabe, A.M. The Last Glacial Maximum. Science 2009, 325, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, D.M. Aspects of the paleogeography of Beringia during the late Pleistocene. In Paleoecology of Beringia; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Meiri, M.; Lister, A.; Kosintsev, P.; Zazula, G.; Barnes, I. Population dynamics and range shifts of moose (Alces alces) during the Late Quaternary. J. Biogeogr. 2020, 47, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, E.; Kivisild, T.; Reidla, M.; Metspalu, M.; Smith, D.G.; Mulligan, C.J.; Bravi, C.M.; Rickards, O.; Martinez-Labarga, C.; Khusnutdinova, E.K.; et al. Beringian standstill and spread of Native American founders. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tedford, R.H.; Wang, X.; Taylor, B.E. Phylogenetic Systematics of the North American Fossil Caninae (Carnivora: Canidae). Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2009, 325, 1–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, R. Ticks and what You Can Do about Them; Wilderness Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013; p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.; Meehl, G.A.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; Waelbroeck, C.; Han, W.; Loutre, M.-F.; Lambeck, K.; Mitrovica, J.X.; Rosenbloom, N. Influence of Bering Strait flow and North Atlantic circulation on glacial sea-level changes. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R.; Hanincova, K.; Barker, I.K.; Bigras-Poulin, M.; Charron, D.F.; Heagy, A.; Francis, C.M.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Schwartz, I.; et al. Role of migratory birds in introduction and range expansion of Ixodes scapularis ticks and of Borrelia burgdorferi and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Canada. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burridge, C.P.; Craw, D.; Fletcher, D.; Waters, J.M. Geological dates and molecular rates: Fish DNA sheds light on time dependency. Mol. Biol Evol 2008, 25, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, S.Y.; Larson, G. Molecular clocks: When times are a-changin’. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, J.O.; Chu, D.K.; Peiris, J.S.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Poon, L.L. A case for the ancient origin of coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7039–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgomaster, K.E.; Foreman, B.M.; Aleshnick, M.A.; Larman, B.C.; Gordon, D.N.; Maciejewski, S.; Morabito, K.M.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Gaudinski, M.R.; Chen, G.L.; et al. Limited Flavivirus Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses Elicited by a Zika Virus Deoxyribonucleic Acid Vaccine Candidate in Humans. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemenesi, G.; Banyai, K. Tick-Borne Flaviviruses, with a Focus on Powassan Virus. Clin. Microbiol Rev. 2019, 32, e00106-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rathore, A.P.S.; St John, A.L. Cross-Reactive Immunity Among Flaviviruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
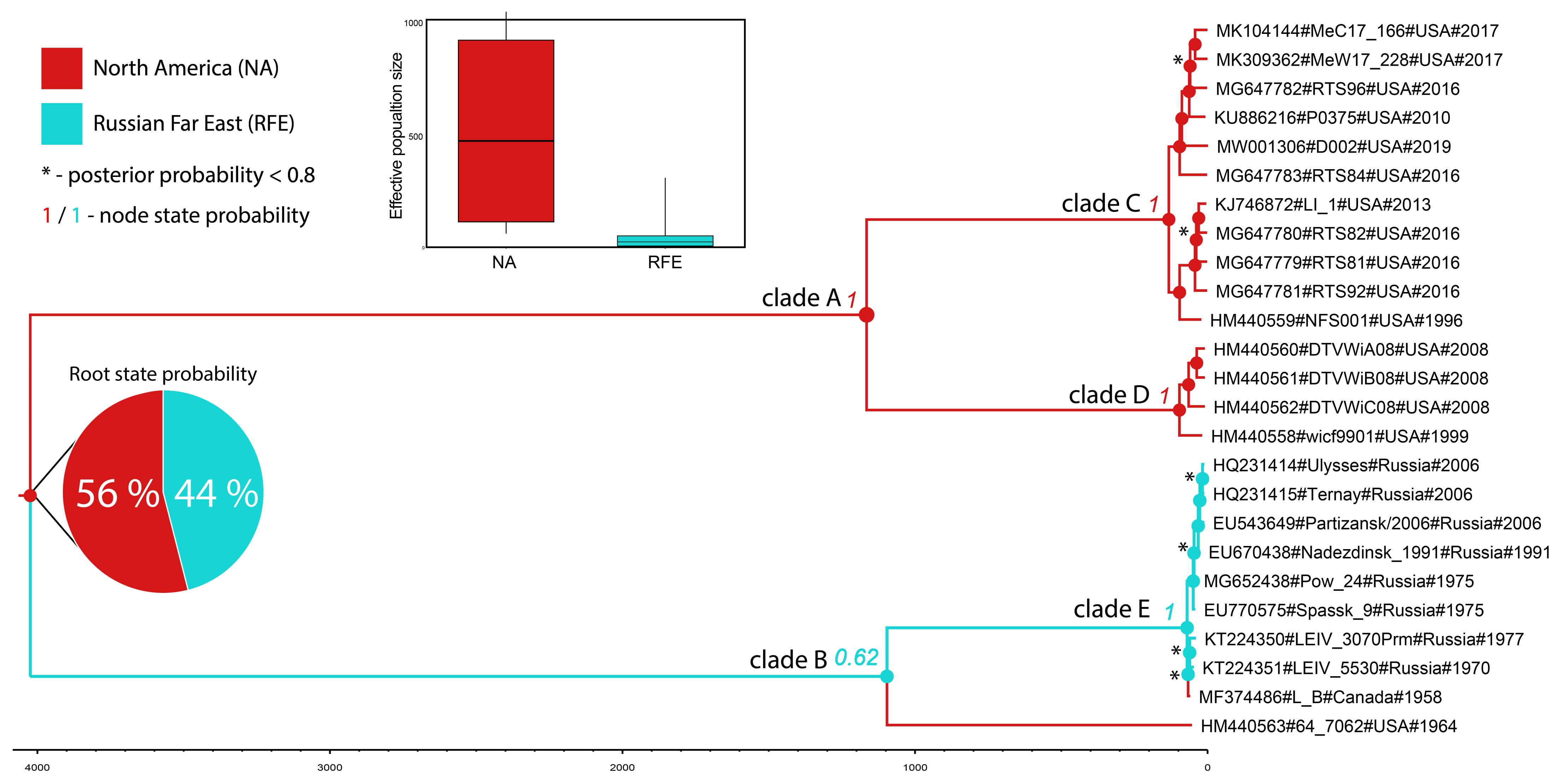

| GB_ID | Strain | Commentary | Country | Year | Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF374486 | L_B | Canada | 1958 | Human | |
| KT224351 | LEIV_5530 | Russia | 1970 | Ixodidae spp. | |
| EU770575 | Spassk_9 | Russia | 1975 | Dermacentor silvarum | |
| MG652438 | Pow_24 | Russia | 1975 | I. persulcatus | |
| KT224350 | LEIV_3070Prm | Russia | 1977 | Ixodidae spp. | |
| EU670438 | Nadezdinsk_1991 | Russia | 1991 | Human | |
| HQ231415 | Ternay | Russia | 2006 | Human | |
| EU543649 | Partizansk/2006 | Russia | 2006 | Human | |
| HQ231414 | Ulysses | Russia | 2006 | Human | |
| HM440563 | 64_7062 | USA | 1964 | Tick | |
| AF311056 | ctb30 | DTV subtype of POWV | USA | 1995 | -N/A- |
| HM440559 | NFS001 | USA | 1996 | I. scapularis | |
| HM440558 | wicf9901 | DTV subtype of POWV | USA | 1999 | I. scapularis |
| HM440561 | DTVWiB08 | DTV subtype of POWV | USA | 2008 | I. scapularis |
| HM440560 | DTVWiA08 | DTV subtype of POWV | USA | 2008 | I. scapularis |
| HM440562 | DTVWiC08 | DTV subtype of POWV | USA | 2008 | I. scapularis |
| KU886216 | P0375 | USA | 2010 | I. scapularis | |
| KJ746872 | LI_1 | USA | 2013 | I. scapularis | |
| MG647783 | RTS84 | USA | 2016 | I. scapularis | |
| MG647781 | RTS92 | USA | 2016 | I. scapularis | |
| MG647782 | RTS96 | USA | 2016 | I. scapularis | |
| MG647779 | RTS81 | USA | 2016 | I. scapularis | |
| MG647780 | RTS82 | USA | 2016 | I. scapularis | |
| MK309362 | MeW17_228 | USA | 2017 | I. scapularis | |
| MK104144 | MeC17_166 | USA | 2017 | I. scapularis | |
| MW001306 | D002 | USA | 2019 | Human |
| Model | Log marginal Likelihood | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PS Run 1 | PS Run 2 | PS Run 3 | |
| SChet 1 | −26,773.5 | −26,771.5 | −26,771.1 |
| SCiso | −26,808.8 | −26,808.5 | −26,807.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bondaryuk, A.N.; Peretolchina, T.E.; Romanova, E.V.; Yudinceva, A.V.; Andaev, E.I.; Bukin, Y.S. Phylogeography and Re-Evaluation of Evolutionary Rate of Powassan Virus Using Complete Genome Data. Biology 2021, 10, 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121282
Bondaryuk AN, Peretolchina TE, Romanova EV, Yudinceva AV, Andaev EI, Bukin YS. Phylogeography and Re-Evaluation of Evolutionary Rate of Powassan Virus Using Complete Genome Data. Biology. 2021; 10(12):1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121282
Chicago/Turabian StyleBondaryuk, Artem N., Tatiana E. Peretolchina, Elena V. Romanova, Anzhelika V. Yudinceva, Evgeny I. Andaev, and Yurij S. Bukin. 2021. "Phylogeography and Re-Evaluation of Evolutionary Rate of Powassan Virus Using Complete Genome Data" Biology 10, no. 12: 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121282
APA StyleBondaryuk, A. N., Peretolchina, T. E., Romanova, E. V., Yudinceva, A. V., Andaev, E. I., & Bukin, Y. S. (2021). Phylogeography and Re-Evaluation of Evolutionary Rate of Powassan Virus Using Complete Genome Data. Biology, 10(12), 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121282








