Influence of Three Probiotics Strains, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis BB-12 and Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on the Biochemical and Haematological Profiles and Body Weight of Healthy Rabbits
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Breeding Conditions and Experimental Design
- (i)
- Group 1: (C) (n = 10): control group, rabbits with none of the probiotics.
- (ii)
- Group 2: (BA) (n = 10); rabbits given 1 × 109 cfu/mL of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis BB-12 throughout the experiment following a previous protocol [18].
- (iii)
- Group 3: (LR) (n = 10); rabbits given 1 × 1010 cfu/mL Lactobacilllus rhamnosus GG throughout the experiment following a previous protocol [19].
- (iv)
- Group 4: (SB) (n = 10); rabbits given 3 × 109 cfu/mL of the yeast Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 throughout the experiment following a previous protocol [20].
2.2. Evaluation of the Blood Parameters
2.2.1. Haematological Parameters
2.2.2. Biochemical Parameters
2.3. Weight Measurement over Time and Growth Performance Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biochemical Parameters
3.1.1. Fasting Glucose Level
3.1.2. Lipids Parameters
3.1.3. Total Proteins and Albumin Contents
3.1.4. Urea, Creatinine, ALT and AST
3.1.5. Iron, Calcium, Phosphorus, Sodium and Potassium
3.2. Haematological Parameters
3.2.1. Red Blood Cells, Hemoglobin and Haematocrit
3.2.2. White Blood Cells, Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Neutrophils, Eosinophils and Basophils
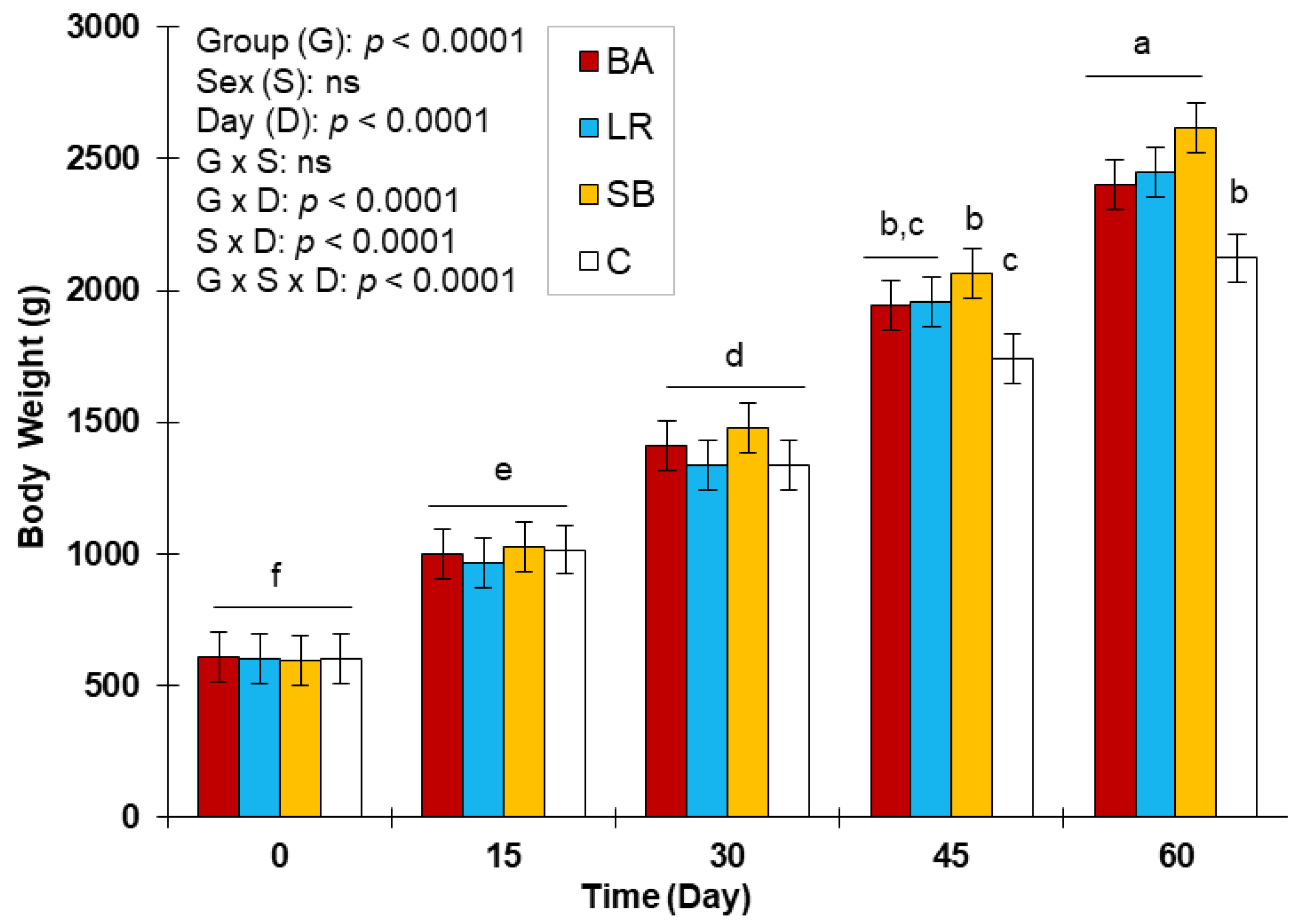
3.3. Evolution of Body Weight and Feed Conversation Ratio with the Three Probiotics Supplementation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. The role of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in animal nutrition. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, F.I.S.; El-Badawi, A.Y.; Abou-ward, G.A.; El-Naggar, S.; Hassan, A.A.; Basyoney, M.M.; Morad, A.A.A. Semen quality parameters of adult male nzw rabbits fed diets added with two different types of probiotics. Egypt. J. Nutr. Feed. 2018, 21, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhayoun, J. Abattage et Qualité de la Viande de Lapin In 5. Iournees de la Recherche Cunicole. 1990, p. 21. Available online: https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-02852269 (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Lebas, F.; Coudert, P.; Rouvier, R.; De Rochambeau, H. Le Lapin: Élevage et Pathologie; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Dalle Zotte, A. Rabbit farming for meat purposes. Anim. Front. 2014, 4, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, S.; Fortun-Lamothe, L.; Cauquil, L.; Gidenne, T. Piloter l’écosystème digestif du lapin: Pourquoi, quand et comment. In Proceedings of the Bolet G.14ème Journees de la Recherche Cunicole, Le Mans, France, 3 June 2011; pp. 33–48. [Google Scholar]
- Krieg, R.; Vahjen, W.; Awad, W.; Sysel, M.; Kroeger, S.; Zocher, E.; Hulan, H.W.; Arndt, G.; Zentek, J. Performance, digestive disorders and the intestinal microbiota in weaning rabbits are affected by an herbal feed additive. World Rabbit Sci. 2010, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortun-Lamothe, L.; Boullier, S. A review on the interactions between gut microflora and digestive mucosal immunity. Possible ways to improve the health of rabbits. Livest. Sci. 2007, 107, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, P.; Bernalier-Donadille, A. Les fonctions majeures du microbiote intestinal. Cah. Nutr. Diététique 2007, 42, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota-masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel-Gaillard, C. Le microbiote intestinal: Un compartiment biologique à explorer chez les animaux d’élevage. Bull. Acad. Vét. Fr. 2014, 167-2, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Boussair, L. Additifs Alimentaires en Nutrition Animale: Cas des Probiotiques et Prébiotiques. Bachelor’s Thesis, Université Mouloud Mammeri, Tizi Ouzou, Algeria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Butel, M.-J. Les probiotiques et leur place en médecine humaine. J. Des Anti Infect. 2014, 16, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacem, M.; Zerrouki, N.; Lebas, F.; Bolet, G. Strategy for developing rabbit meat production in Algeria: Creation and selection of a synthetic strain. In Proceedings of the 9th World Rabbit Congress, Verona, Italy, 10–13 June 2008; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaziz, A.; Dib, A.L.; Lakhdara, N.; Kadja, L.; Espigares, E.; Moreno, E.; Bouaziz, O.; Gagaoua, M. Study of Probiotic Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 and Lactobacillus plantarum 299v Strains on Biochemical and Morphometric Parameters of Rabbits after Obesity Induction. Biology 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, Z.; Langa, R.; Aiyegoro, O.; Okoh, A. Effects of probiotics on growth performance, blood parameters, and antibody stimulation in piglets. South. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 47, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Z.; Qin, Y.; Shen, Q.; Li, P. Anti-diabetic effects of Bifidobacterium animalis 01 through improving hepatic insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic rat model. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonová, M.; Marcináková, M.; Strompfová, V.; Cobanová, K.; Gancarcíková, S.; Vasilková, Z.; Lauková, A. Effect of probiotics Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and new isolate Enterococcus faecium EF2019 (CCM 7420) on growth, blood parameters, microbiota and coccidia oocysts excretion in rabbits. Int. J. Probiotics Prebiotics 2008, 3, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Briand, F.; Sulpice, T.; Giammarinaro, P.; Roux, X. Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 changes lipidemic profile and gut microbiota in a hamster hypercholesterolemic model. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Mutis, O.J.; Marrachelli, V.G.; Ruiz-Saurí, A.; Alberola, A.; Morales, J.M.; Such-Miquel, L.; Monleon, D.; Chorro, F.J.; Such, L.; Zarzoso, M. Development and characterization of an experimental model of diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rabbit. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaravadhi, S.C.; Mallam, M.; Manthani, G.P.; Komireddy, K.R. Effect of dietary supplementation of probiotics and enzymes on the haematology of rabbits reared under two housing systems. Vet. World 2012, 5, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erukainure, O.L.; Ebuehi, O.A.T.; Adeboyejo, F.O.; Aliyu, M.; Elemo, G.N. Hematological and biochemical changes in diabetic rats fed with fiber-enriched cake. J. Acute Med. 2013, 3, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammoun, M.; Picard, B.; Astruc, T.; Gagaoua, M.; Aubert, D.; Bonnet, M.; Blanquet, V.; Cassar-Malek, I. The invalidation of HspB1 gene in mouse alters the ultrastructural phenotype of muscles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158644. [Google Scholar]
- Kimse, M.; Soro, D.; Bleyere, M.N.; Yapi, J.N.; Fantodji, A. Apport d’un fourrage vert tropical, Centrosema pubescens, en complément au granulé: Effet sur les performances de croissance et sanitaire du lapin (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2013, 7, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezema, C.; Eze, D.C. Determination of the effect of probiotic (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) on growth performance and hematological parameters of rabbits. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 21, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, E.; Hyun, C.K. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG improves insulin sensitivity and reduces adiposity in high-fat diet-fed mice through enhancement of adiponectin production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Matamoros, S.; Geurts, L.; Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D. Saccharomyces boulardii administration changes gut microbiota and reduces hepatic steatosis, low-grade inflammation, and fat mass in obese and type 2 diabetic db/db mice. MBio 2014, 5, e01011-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Dey, D.K.; Vij, R.; Meena, S.; Kapila, R.; Kapila, S. Evaluation of anti-diabetic attributes of Lactobacillus rhamnosus MTCC: 5957, Lactobacillus rhamnosus MTCC: 5897 and Lactobacillus fermentum MTCC: 5898 in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farida, E.; Nuraida, L.; Giriwono, P.E.; Jenie, B.S.L. Lactobacillus rhamnosus Reduces Blood Glucose Level through Downregulation of Gluconeogenesis Gene Expression in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 2020, 6108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-Y.; Kim, B.; Hyun, C.-K. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG improves glucose tolerance through alleviating ER stress and suppressing macrophage activation in db/db mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 56, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.K.C.; Hosaka, T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kassu, A.; Dang, T.O.; Tran, H.B.; Pham, T.P.; Tran, Q.B.; Le, T.H.H.; Da Pham, X. Bifidobacterium species lower serum glucose, increase expressions of insulin signaling proteins, and improve adipokine profile in diabetic mice. Biomed. Res. 2015, 36, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonová, M.P.; Lauková, A.; Chrastinova, L.; Plachá, I.; Strompfová, V.; Cobanova, K.; Formelová, Z.; Chrenková, M. Combined administration of bacteriocin-producing, probiotic strain Enterococcus faecium CCM7420 with Eleutherococcus senticosus and their effect in rabbits. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 16, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, M.A.E.; Moselhy, S.S. Impact of probiotic-supplemented diet on the expression level of lactate dehydrogenase in the leukocytes of rabbits. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 30, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhu, H.; Gao, F.; Qian, Z.; Mao, W.; Yin, Y.; Tan, J.; Chen, D. Antidiabetic effects of selenium-enriched Bifidobacterium longum DD98 in type 2 diabetes model of mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6528–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, T.; Al-Gamal, M.; Hesham, A. Impact of Probiotic (Lactobacillus planterium) Supplementation on Productive and Physiological Performance of Growing Rabbits under Egyptian Conditions. Egypt. J. Rabbit Sci. 2019, 29, 125–148. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.L.; Martoni, C.J.; Parent, M.; Prakash, S. Cholesterol-lowering efficacy of a microencapsulated bile salt hydrolase-active Lactobacillus reuteri NCIMB 30242 yoghurt formulation in hypercholesterolaemic adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.; Friedrich, U.; Vogelsang, H.; Jahreis, G. Lactobacillus acidophilus 74-2 and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp lactis DGCC 420 modulate unspecific cellular immune response in healthy adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliland, S.; Nelson, C.; Maxwell, C. Assimilation of cholesterol by Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, M.; Nakano, M. The effect of a probiotic on faecal and liver lipid classes in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 1995, 73, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmawan, H.; Irfanuddin, I. Effect of age and sex on the association between lipid profile and obesity among telecomunication workers in Palembang. Med J. Indones. 2007, 16, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallini, D.C.U.; Bedani, R.; Bomdespacho, L.Q.; Vendramini, R.C.; Rossi, E.A. Effects of probiotic bacteria, isoflavones and simvastatin on lipid profile and atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits: A randomized double-blind study. Lipids Health Dis. 2009, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyat, M.S.; Al-Sagheer, A.A.; Abd El-Latif, K.M.; Khalil, B.A. Organic selenium, probiotics, and prebiotics effects on growth, blood biochemistry, and carcass traits of growing rabbits during summer and winter seasons. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonová, M.P.; Chrastinová, Ľ.; Lauková, A. Autochtonous Strain Enterococcus faecium EF2019 (CCM7420), Its Bacteriocin and Their Beneficial Effects in Broiler Rabbits—A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terciolo, C.; Dapoigny, M.; Andre, F. Beneficial effects of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on clinical disorders associated with intestinal barrier disruption. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhady, D.H.; El-Abasy, M.A. Effect of Prebiotic and Probiotic on Growth, Immuno-hematological responses and Biochemical Parameters of infected rabbits with Pasteurella multocida. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2015, 28, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abdel-Azeem, A.; Hassan, A.; Basyony, M.; Abu Hafsa, S.H. Rabbit growth, carcass characteristic, digestion, caecal fermentation, microflora, and some blood biochemical components affected by oral administration of anaerobic probiotic (ZAD®). Egypt. J. Nutr. Feed. 2018, 21, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, K.M. Age and sex effects on blood biochemical profile of local rabbits in Sudan. Wayamba J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 5, 548–553. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, N.; Bekyürek, T.; Cetin, E. Effects of sex, pregnancy and season on some haematological and biochemical blood values in angora rabbits. Scand. J. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2009, 36, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Olayemi, F.; Nottidge, H.O. Effect of age on the blood profiles of the New Zealand rabbit in Nigeria. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppe, L.; Mafra, D.; Fouque, D. Probiotics and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodgrass, P.; Lin, R.; Müller, W.; Aoki, T. Induction of urea cycle enzymes of rat liver by glucagon. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 2748–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatriste, P.V.M.; Arronte, R.U.; Espinosa, C.O.G.; Cuevas, M.d.l.Á.E. Effect of probiotics on human blood urea levels in patients with chronic renal failure. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 29, 582–590. [Google Scholar]
- Morizot, J. La Créatinine Plasmatique Comme Outil de Dépistage de la Dénutrition: Étude Préliminaire sur ses Intérêts Potentiels et Limites. Bachelor’s Thesis, Université Grenoble, Grenoble, France, 2014; 55p. [Google Scholar]
- Dore, J.; Ehrlich, D.; Monnet, V.; Le Chatelier, E.; de Paepe, M.; Thomas, M.; Gaillard, C.; Calenge, F.; Bernalier, A.; Feron, G. Microbiote, la révolution intestinale. Dossier de presse INRA; INRA: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe, M.; Önning, G.; Berggren, A.; Hulthén, L. Probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum 299v increases iron absorption from an iron-supplemented fruit drink: A double-isotope cross-over single-blind study in women of reproductive age. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Gawad, I.A.; Abou Elsamh, M.M.; Saleh, F.A.; Rayan, E.A. Bioavailability of Ca, P and Zn and bone mineralization in rats fed yoghurt and soy-yoghurt containing bifidobacteria. Eur. J. Nutr. Food Saf. 2014, 4, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N.; Moura, C.S.; Almada, C.N.; Felicio, T.L.; Esmerino, E.A.; Barros, M.E.; Amaya-Farfan, J.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Raices, R.R.S.; et al. Hypertension parameters are attenuated by the continuous consumption of probiotic Minas cheese. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Pomare, E.; Branch, W.; Naylor, C.; Macfarlane, G. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 1987, 28, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, Ö.; Pekkaya, S. Normal values of biochemical parameters in serum of New Zealand White Rabbits. Studies 2018, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.; Laird, C.; Kirshenbaum, J. Effect of strain, sex, and circadian rhythm on rabbit serum bilirubin and iron levels. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1974, 145, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, D.A. Nutritional pathology in rabbits: Current and future perspectives. Prepared and Presented for the Ontario Commercial Rab-bit Growers Association (OCRGA) Congress, 20 October 2001. Available online: https://www.caza-narg.ca/ref/ref200806-7.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Sheng, L.; Jena, P.K.; Liu, H.-X.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; French, S.W.; Krishnan, V.V.; Mills, D.A.; Wan, Y.-J.Y. Gender differences in bile acids and microbiota in relationship with gender dissimilarity in steatosis induced by diet and FXR inactivation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforidou, Z.; Mora Ortiz, M.; Poveda, C.; Abbas, M.; Walton, G.; Bailey, M.; Lewis, M.C. Sexual Dimorphism in Immune Development and in Response to Nutritional Intervention in Neonatal Piglets. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhur, A.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S. Iron status, immune capacity and resistance to infections. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1989, 94, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckermann-Ross, C. Hormonal Regulation and Calcium Metabolism in the Rabbit. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2008, 11, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alziadi, R.E.; Gatea, E.A. Evaluate the effectiveness of oral dosage with probiotic bacteria lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, lactobacillus planetarium and lactobacillus reuteri on some immune indicators in rabbits. J. Glob. Pharma Technol. 2018, 10, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, M.; Abdelsalam, M.; Al-Homidan, I.; Ebeid, T.; El-Zarei, M.; Abou-Emera, O. Effect of probiotic supplementation and genotype on growth performance, carcass traits, hematological parameters and immunity of growing rabbits under hot environmental conditions. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Mustari, A.; Salauddin, M.; Rahman, M. Effects of probiotics and enzymes on growth performance and haematobiochemical parameters in broilers. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2013, 11, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korčok, D.J.; Tršić-Milanović, N.A.; Ivanović, N.D.; Đorđević, B.I. Development of Probiotic Formulation for the Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariaty, Z.; Mahmoodi Shan, G.R.; Farajollahi, M.; Amerian, M.; Behnam Pour, N. The effects of probiotic supplement on hemoglobin in chronic renal failure patients under hemodialysis: A randomized clinical trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 22, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhalf, A.; Alhaj, M.; Al-Homidan, I. Influence of probiotic supplementation on blood parameters and growth performance in broiler chickens. Saudi J. Biol Sci 2010, 17, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suckow, M.A.; Stevens, K.A.; Wilson, R.P. The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Boussarie, D. Hématologie des rongeurs et lagomorphes de compagnie. Bull. Acad. Vét. Fr. 1999, 72, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayo-Ajasa, O.; Aina, A.; Sowande, O.; Egbeyale, L.; Ozoje, M.; Agaviezor, B.; Abel, F. Haematology and serum profile of rabbits due to generation interval, housing systems and sex. Niger. J. Anim. Prod. 2015, 42, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chineke, C.; Ologun, A.; Ikeobi, C. Haematological parameters in rabbit breeds and crosses in humid tropics. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 9, 2102–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barde, I.; Rauwel, B.; Marin-Florez, R.M.; Corsinotti, A.; Laurenti, E.; Verp, S.; Offner, S.; Marquis, J.; Kapopoulou, A.; Vanicek, J. A KRAB/KAP1-miRNA cascade regulates erythropoiesis through stage-specific control of mitophagy. Science 2013, 340, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, M. Effets des probiotiques sur le système immunitaire: Mécanismes d’action potentiels. Cah. Nutr. Diét. 2007, 42, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Gomez, M.; Lambour, J.; Piechaczyk, M.; Pelegrin, M. Neutrophils are essential for induction of vaccine-like effects by antiviral monoclonal antibody immunotherapies. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnet, S.; Kirin, S.; Kos, B.; Frece, J.; Šušković, J. Immunomodulatory effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG from low fat fresh cheese" BioAktiv LGG". Mljekarstvo Časopis Unaprjeđenje Proizv Prerade Mlijeka 2004, 54, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.; Ba, Z.; Lee, Y.; Peng, J.; Lin, J.; Fleming, J.A.; Furumoto, E.J.; Roberts, R.F.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Rogers, C.J. Consumption of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 in yogurt reduced expression of TLR-2 on peripheral blood-derived monocytes and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in young adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weger, B.D.; Gobet, C.; Yeung, J.; Martin, E.; Jimenez, S.; Betrisey, B.; Foata, F.; Berger, B.; Balvay, A.; Foussier, A. The mouse microbiome is required for sex-specific diurnal rhythms of gene expression and metabolism. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 362–382. e368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.G.; Vidyarthi, V.; Archana, K.; Zuyie, R. Probiotic supplementation in the diet of rabbits—A Review. Livest. Res. Int. 2016, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, E.; Călinoiu, L.F.; Mitrea, L.; Vodnar, D.C. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics: Implications and Beneficial Effects against Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thill, P.; Legrain, A.; Salle, V.; Smail, A.; Duhaut, P.; Schmidt, J. Valeur diagnostique du rapport neutrophiles/lymphocytes devant une fièvre et/ou un syndrome inflammatoire en médecine interne. Médecine Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidenne, T.; Garreau, H.; Drouilhet, L.; Aubert, C.; Maertens, L. Improving feed efficiency in rabbit production, a review on nutritional, technico-economical, genetic and environmental aspects. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 225, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, S.; Baselga, M.; Blas, E.; Cervera, C.; Gómez, E.A. Comparison of growth and feed efficiency among rabbit lines selected for different objectives. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1996, 45, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovera, F.; Lestingi, A.; Iannaccone, F.; Tateo, A.; Nizza, A. Use of dietary mannanoligosaccharides during rabbit fattening period: Effects on growth performance, feed nutrient digestibility, carcass traits, and meat quality. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 3858–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Wareth, A.A.A.; Elkhateeb, F.S.O.; Ismail, Z.S.H.; Ghazalah, A.A.; Lohakare, J. Combined effects of fenugreek seeds and probiotics on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, carcass criteria, and serum hormones in growing rabbits. Livest. Sci. 2021, 251, 104616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghandour, M.M.Y.; Tan, Z.L.; Abu Hafsa, S.H.; Adegbeye, M.J.; Greiner, R.; Ugbogu, E.A.; Cedillo Monroy, J.; Salem, A.Z.M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a probiotic feed additive to non and pseudo-ruminant feeding: A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayande, K.A.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Ateba, C.N. Probiotics in Animal Husbandry: Applicability and Associated Risk Factors. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassiony, S.S.; Al-Sagheer, A.A.; El-Kholy, M.S.; Elwakeel, E.A.; Helal, A.A.; Alagawany, M. Evaluation of Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 11181 and Clostridium butyricum probiotic supplements in post-weaning rabbits reared under thermal stress conditions. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotolo, L.; Gai, F.; Peiretti, P.G.; Ortoffi, M.; Zoccarato, I.; Gasco, L. Live yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii) supplementation in fattening rabbit diet: Effect on productive performance and meat quality. Livest. Sci. 2014, 162, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gippert, T.; Virag, G.; Nagy, I. Lacto-Sacc in rabbit nutrition. J. Appl. Rabbit Res. 1992, 15, 1101. [Google Scholar]
- Surdzhijska, S.; Ganev, G.; Stoilov, I.; Vladimirova, L.; Tankov, D. Effect of additive of probiotic Lactina to combined forages on productivity of rabbits. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 42, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Amber, K.; Yakout, H.; Hamed Rawya, S. Effect of feeding diets containing yucca extract or probiotic on growth, digestibility, nitrogen balance and caecal microbial activity of growing New Zealand white rabbits. In Proceedings of the 8th World Rabbit Congress, Puebla, Mexico, 7–10 September 2004; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Amat, C.; Planas, J.; Moreto, M. Kinetics of hexose uptake by the small and large intestine of the chicken. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1996, 271, R1085–R1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçin, S.; Onbasilar, E.; Onbasilar, I. Effect of sex on carcass and meat characteristics of New Zealand White rabbits aged 11 weeks. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 19, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trocino, A.; Xiccato, G.; Queaque, P.; Sartori, A. Effect of transport duration and sex on carcass and meat quality of growing rabbits. In Proceedings of the 2nd Rabbit Congress of the America, Habana, Cuba, 19–22 June 2002; pp. 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.-P.; Lee, K.-M.; Kang, J.-H.; Yun, S.-I.; Park, H.-O.; Moon, Y.; Kim, J.-Y. Effect of Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 on overweight and obese adults: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2013, 34, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Stratigou, T.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Tsigalou, C.; Dalamaga, M. Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, Postbiotics, and Obesity: Current Evidence, Controversies, and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups 3 | Parameters 2 | GLU (g/L) | TC (g/L) | HDL (g/L) | TG (g/L) | TP (g/L) | ALB (g/L) | UREA (g/L) | CREA (mg/L) | ALT (UI/L) | AST (UI/L) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | ||
| Days | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| C | 0 | 0.96 | 1.01 | 0.39 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 61.21 bc | 48.60 d | 34.06 b | 29.31 bc | 1.99 c | 2.27 b | 11.91 | 11.17 | 45.76 | 47.85 | 43.43 | 33.55 | |
| 15 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 62.15 bc | 47.74 d | 34.48 b | 27.04 bc | 2.31 b | 2.05 b | 12.52 | 11.59 | 42.52 | 48.55 | 46.98 | 31.54 | ||
| 30 | 1.04 | 1.09 | 0.55 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 64.22 bc | 43.68 d | 34.40 b | 24.50 c | 2.34 b | 1.98 c | 12.57 | 11.36 | 44.52 | 48.95 | 46.47 | 30.97 | ||
| 45 | 1.07 | 1.19 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 64.99 bc | 53.65 c | 33.64 bc | 28.00 bc | 2.31 b | 2.08 b | 13.02 | 11.62 | 45.00 | 46.63 | 46.06 | 30.07 | ||
| 60 | 1.13 | 1.08 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 64.57 bc | 54.65 c | 34.33 b | 27.77 bc | 2.22 b | 2.11 b | 13.26 | 11.88 | 44.52 | 47.96 | 45.40 | 31.31 | ||
| BA | 0 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 63.22 bc | 46.74 d | 35.44 b | 26.38 c | 2.02 b | 1.91 c | 12.03 | 10.91 | 46.59 | 42.06 | 38.93 | 36.24 | |
| 15 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 0.56 | 0.44 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 67.40 b | 49.38 d | 36.75 b | 32.02 bc | 2.17 b | 1.98 c | 12.05 | 10.98 | 47.30 | 48.21 | 40.90 | 34.93 | ||
| 30 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.56 | 0.46 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 90.01 a | 58.68 c | 48.82 a | 31.31 bc | 2.70 a | 2.36 b | 12.75 | 10.89 | 49.00 | 46.90 | 40.34 | 38.44 | ||
| 45 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 88.31 a | 57.57 c | 49.99 a | 29.46 bc | 2.60 ab | 2.41 ab | 13.05 | 11.33 | 49.00 | 46.90 | 39.96 | 38.31 | ||
| 60 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.59 | 0.52 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 88.51 a | 55.97 c | 48.16 a | 28.81 bc | 2.40 ab | 2.31 b | 13.39 | 11.75 | 49.34 | 46.18 | 40.80 | 38.36 | ||
| LR | 0 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.41 | 0.62 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 56.74 c | 54.07 c | 34.99 b | 29.91 bc | 2.43 ab | 1.85 c | 12.33 | 11.80 | 39.36 | 50.51 | 34.51 | 39.08 | |
| 15 | 0.96 | 1.07 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 66.47 b | 46.20 d | 35.85 b | 28.91 bc | 2.41 ab | 2.03 b | 12.32 | 11.77 | 42.57 | 48.70 | 36.33 | 39.75 | ||
| 30 | 1.05 | 0.86 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 66.01 b | 50.42 c | 36.06 b | 27.59 bc | 2.25 b | 2.11 b | 12.36 | 11.66 | 43.93 | 48.45 | 35.96 | 39.68 | ||
| 45 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 65.77 b | 51.24 c | 35.79 b | 29.16 bc | 2.25 b | 2.14 b | 12.44 | 12.37 | 43.93 | 48.45 | 36.40 | 40.96 | ||
| 60 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 68.41 b | 51.19 c | 34.81 b | 27.90 bc | 2.21 b | 2.12 b | 12.89 | 12.48 | 44.71 | 47.32 | 35.73 | 44.03 | ||
| SB | 0 | 1.05 | 0.95 | 0.37 | 0.57 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 53.40 c | 56.84 c | 31.70 bc | 29.11 bc | 2.13 b | 2.40 ab | 12.11 | 12.99 | 45.92 | 47.15 | 31.38 | 46.11 | |
| 15 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.50 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 55.42 c | 59.36 c | 33.80 bc | 33.10 bc | 2.29 b | 1.91 c | 12.30 | 12.16 | 43.73 | 47.70 | 35.85 | 44.94 | ||
| 30 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 94.59 a | 68.47 b | 49.14 a | 37.95 b | 2.90 a | 2.32 b | 12.35 | 12.31 | 44.34 | 43.36 | 36.58 | 44.78 | ||
| 45 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 92.88 a | 65.77 b | 48.41 a | 45.80 a | 2.83 a | 2.29 b | 12.77 | 12.27 | 44.34 | 43.35 | 37.54 | 45.74 | ||
| 60 | 1.01 | 0.94 | 0.37 | 0.50 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 89.50 a | 67.21 b | 46.18 a | 35.46 b | 2.61 ab | 2.35 b | 13.57 | 12.89 | 44.84 | 42.67 | 38.01 | 45.82 | ||
| Effects 4,5 | Group (G) | *** | ** | ns | * | *** | *** | * | Ns | ns | Ns | |||||||||||
| Sex (S) | ns | ns | ns | ** | *** | *** | *** | ** | ns | Ns | ||||||||||||
| Day (D) | ns | ns | ns | ns | *** | ns | ** | Ns | ns | Ns | ||||||||||||
| G × S | ns | ** | ns | *** | ns | ns | ns | Ns | ns | *** | ||||||||||||
| G × D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | Ns | ns | Ns | ||||||||||||
| S × D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | Ns | ns | Ns | ||||||||||||
| G × S × D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | Ns | ns | Ns | ||||||||||||
| Groups 3 | Parameters 2 | Fe (mg/L) | Ca (mg/L) | P (mg/L) | Na (mmol/L) | K (mmol/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | ||
| Day | ||||||||||||
| C | 0 | 1.40 bc | 1.35 c | 60.50 c | 72.43 bc | 43.20 | 44.32 | 142.90 | 135.22 | 3.79 ab | 3.74 ab | |
| 15 | 1.48 abc | 1.36 c | 65.77 bc | 76.68 bc | 44.61 | 45.20 | 142.39 | 142.66 | 3.86 ab | 3.85 | ||
| 30 | 1.48 abc | 1.48 abc | 66.07 bc | 79.46 bc | 45.67 | 48.50 | 144.78 | 140.71 | 3.93 b | 3.46 ab | ||
| 45 | 1.51 abc | 1.71 abc | 68.54 bc | 80.42 bc | 48.52 | 44.99 | 144.62 | 140.48 | 3.87 ab | 3.91 ab | ||
| 60 | 1.45 abc | 1.67 abc | 69.47 bc | 81.06 bc | 49.20 | 45.93 | 144.36 | 141.35 | 3.88 ab | 3.80 ab | ||
| BA | 0 | 1.61 abc | 1.20 c | 73.36 bc | 56.80 c | 43.54 | 43.81 | 144.19 | 137.09 | 3.81 ab | 3.69 ab | |
| 15 | 1.60 abc | 1.45 c | 83.51 b | 59.09 c | 47.12 | 45.72 | 142.21 | 140.79 | 4.03 a | 3.94 ab | ||
| 30 | 1.76 abc | 1.59 abc | 91.22 a | 66.01 bc | 48.14 | 49.65 | 144.30 | 141.97 | 4.11 a | 3.99 ab | ||
| 45 | 1.81 abc | 1.56 abc | 90.93 a | 67.88 bc | 48.30 | 51.31 | 144.05 | 141.31 | 4.04 a | 3.89 ab | ||
| 60 | 1.79 abc | 1.56 abc | 91.88 a | 70.22 bc | 48.04 | 59.94 | 145.23 | 140.53 | 4.09 a | 3.92 ab | ||
| LR | 0 | 1.58 abc | 1.22 c | 70.36 bc | 63.05 c | 43.00 | 44.22 | 144.58 | 135.86 | 3.77 ab | 3.73 ab | |
| 15 | 1.92 abc | 1.48 abc | 78.88 bc | 71.53 bc | 42.98 | 47.50 | 143.77 | 133.27 | 3.89 ab | 3.91 ab | ||
| 30 | 2.17 a | 1.62 abc | 93.70 a | 83.02 b | 45.18 | 47.38 | 141.84 | 135.62 | 4.10 a | 3.79 ab | ||
| 45 | 2.18 a | 1.77 abc | 96.88 a | 88.00 b | 45.36 | 48.56 | 140.44 | 137.56 | 4.07 a | 3.82 ab | ||
| 60 | 2.13 a | 1.75 abc | 96.52 a | 91.85 a | 45.66 | 48.96 | 138.49 | 139.78 | 4.04 a | 3.81 ab | ||
| SB | 0 | 1.31 c | 1.44 c | 66.52 bc | 66.74 bc | 43.00 | 45.22 | 140.48 | 138.46 | 3.82 ab | 3.72 ab | |
| 15 | 1.46 abc | 1.58 | 72.50 bc | 72.30 bc | 46.06 | 44.74 | 135.69 | 134.61 | 3.87 ab | 3.92 ab | ||
| 30 | 1.73 abc | 1.75 abc | 81.60 bc | 84.83 b | 45.16 | 44.88 | 136.85 | 134.82 | 3.87 ab | 3.96 ab | ||
| 45 | 1.75 abc | 1.74 abc | 82.45 bc | 86.36 b | 46.06 | 47.50 | 137.14 | 133.71 | 3.92 ab | 3.88 ab | ||
| 60 | 1.71 abc | 1.80 abc | 82.22 bc | 87.34 b | 45.30 | 47.62 | 138.87 | 135.90 | 3.81 ab | 3.84 ab | ||
| Effects 4,5 | Group (G) | *** | *** | ns | ** | * | ||||||
| Sex(S) | ** | Ns | ns | ** | ** | |||||||
| Day (D) | *** | *** | ns | ns | ** | |||||||
| G × S | *** | *** | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| G × D | Ns | Ns | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| S × D | Ns | Ns | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| G × S × D | Ns | Ns | ns | ns | ns | |||||||
| Groups 3 | Parameters 2 | RBC (106/µL) | HGB (g/dL) | HCT (%) | WBC (103/µL) | LYMPHO≠ (103/µL) | MONO≠ (103/µL) | NEUT≠ (103/µL) | EO≠ (103/µL) | BASO≠ (103/µL) 6 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | ||
| Days | ||||||||||||||||||||
| C | 0 | 4.51 c | 4.91 bc | 10.56 bc | 10.67 bc | 33.06 | 31.94 | 6.12 d | 7.10 bc | 5.16 | 4.98 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 1.43 bc | 1.31 c | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
| 15 | 4.88 bc | 4.61 bc | 10.59 bc | 10.64 bc | 32.98 | 32.62 | 5.90 d | 7.79 ab | 5.05 | 5.03 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 1.50 bc | 1.26 c | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 30 | 4.79 bc | 4.47 c | 10.57 bc | 10.62 bc | 33.16 | 32.02 | 6.07 d | 7.26 b | 5.06 | 4.80 | 0.43 | 0.29 | 1.54 bc | 1.39 c | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 45 | 4.75 bc | 4.88 bc | 10.55 bc | 10.85 bc | 33.10 | 32.16 | 6.11 d | 7.47 ab | 4.84 | 4.63 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 1.52 bc | 1.91 bc | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 60 | 4.59 bc | 4.86 bc | 10.67 bc | 10.84 bc | 33.42 | 32.06 | 6.07 d | 7.41 ab | 4.73 | 4.77 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 1.64 bc | 1.91 bc | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| BA | 0 | 4.26 c | 5.11 b | 10.69 bc | 10.53 bc | 33.68 | 31.26 | 6.27 d | 7.27 b | 5.24 | 4.77 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 1.39 c | 1.35 c | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |
| 15 | 4.66 bc | 4.51 c | 10.80 bc | 10.50 c | 34.04 | 31.40 | 6.50 d | 7.65 ab | 5.49 | 4.62 | 0.32 | 0.47 | 1.58 bc | 1.52 bc | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 30 | 4.87 bc | 4.69 bc | 11.05 ab | 10.54 bc | 34.44 | 32.28 | 7.31 b | 7.39 bc | 5.02 | 4.78 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 2.94 b | 1.91 bc | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 45 | 4.85 bc | 5.37 bc | 10.72 bc | 10.90 ab | 34.64 | 32.18 | 7.25 b | 7.23 b | 5.05 | 4.78 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 2.26 b | 1.91 bc | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 60 | 4.85 bc | 5.37 bc | 10.93 ab | 11.06 ab | 34.66 | 32.22 | 6.90 c | 7.38 ab | 5.65 | 3.84 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 2.33 b | 1.81 bc | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| LR | 0 | 5.04 bc | 4.41 c | 10.12 c | 10.92 bc | 32.72 | 32.18 | 7.07 bc | 7.47 ab | 4.28 | 5.88 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 1.57 bc | 1.32 c | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 15 | 4.36 c | 4.96 bc | 10.14 c | 10.93 ab | 32.76 | 32.80 | 7.90 ab | 8.17 ab | 5.05 | 6.69 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 1.95 bc | 1.43 bc | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 30 | 4.73 bc | 6.54 a | 11.95 a | 11.96 a | 33.58 | 33.32 | 8.42 ab | 10.07 a | 6.04 | 6.07 | 0.50 | 0.46 | 3.22 a | 2.54 b | 0.03 | 0.3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 45 | 6.01 b | 6.35 b | 12.12 a | 12.29 a | 34.02 | 34.10 | 8.63 ab | 9.73 a | 5.46 | 5.76 | 0.45 | 0.87 | 3.48 a | 3.14 a | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 60 | 7.01 a | 7.00 a | 12.16 a | 12.24 a | 34.54 | 34.42 | 8.61 ab | 10.22 a | 5.07 | 5.83 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 3.38 a | 3.41 a | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| SB | 0 | 4.71 bc | 4.71 bc | 10.97 ab | 10.63 bc | 32.96 | 32.58 | 4.49 d | 7.09 bc | 5.02 | 4.97 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 1.37 c | 1.33 c | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 15 | 4.85 bc | 4.76 bc | 10.90 ab | 10.76 bc | 33.70 | 32.72 | 6.51 d | 7.38 ab | 4.28 | 6.03 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 1.56 bc | 1.39 c | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 30 | 5.02 b | 5.22 b | 10.95 ab | 10.91 ab | 34.54 | 32.94 | 7.53 ab | 8.13 ab | 4.64 | 6.21 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 2.01 b | 2.08 b | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 45 | 4.47 c | 5.62 b | 11.87 a | 11.22 ab | 33.58 | 33.58 | 7.62 ab | 8.10 ab | 4.62 | 6.13 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 2.13 b | 2.61 b | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| 60 | 5.47 b | 5.46 b | 11.83 a | 11.47 ab | 34.36 | 33.82 | 7.36 ab | 7.88 ab | 4.42 | 6.34 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 2.01 b | 2.14 b | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| Effects 4,5 | Group (G) | *** | *** | ns | *** | Ns | ns | *** | ns | ns | ||||||||||
| Sex(S) | * | Ns | ** | *** | Ns | ns | ** | ns | ns | |||||||||||
| Day (D) | *** | ** | ns | *** | Ns | ns | *** | ** | ns | |||||||||||
| G × S | ns | ** | ns | ns | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | |||||||||||
| G × D | ** | *** | ns | * | Ns | ns | *** | ns | ns | |||||||||||
| S × D | ns | Ns | ns | ns | Ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||
| G × S × D | ** | Ns | ns | ns | Ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadja, L.; Dib, A.L.; Lakhdara, N.; Bouaziz, A.; Espigares, E.; Gagaoua, M. Influence of Three Probiotics Strains, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis BB-12 and Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on the Biochemical and Haematological Profiles and Body Weight of Healthy Rabbits. Biology 2021, 10, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111194
Kadja L, Dib AL, Lakhdara N, Bouaziz A, Espigares E, Gagaoua M. Influence of Three Probiotics Strains, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis BB-12 and Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on the Biochemical and Haematological Profiles and Body Weight of Healthy Rabbits. Biology. 2021; 10(11):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111194
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadja, Louiza, Amira Leila Dib, Nedjoua Lakhdara, Assia Bouaziz, Elena Espigares, and Mohammed Gagaoua. 2021. "Influence of Three Probiotics Strains, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis BB-12 and Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on the Biochemical and Haematological Profiles and Body Weight of Healthy Rabbits" Biology 10, no. 11: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111194
APA StyleKadja, L., Dib, A. L., Lakhdara, N., Bouaziz, A., Espigares, E., & Gagaoua, M. (2021). Influence of Three Probiotics Strains, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis BB-12 and Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on the Biochemical and Haematological Profiles and Body Weight of Healthy Rabbits. Biology, 10(11), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111194







