Kisspeptin, Neurokinin B, and Dynorphin Expression during Pubertal Development in Female Sheep
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. General Methods
2.2.1. Surgical Procedures
2.2.2. Blood and Tissue Collection
2.3. Determination of Age-Dependent mRNA and Protein Expression for Kisspeptin, NKB, and Dynorphin
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Assays
2.4.2. Immunocytochemical Assessment of Kisspeptin and NKB Cell Numbers
2.4.3. RNAscope in Situ Hybridization
2.4.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
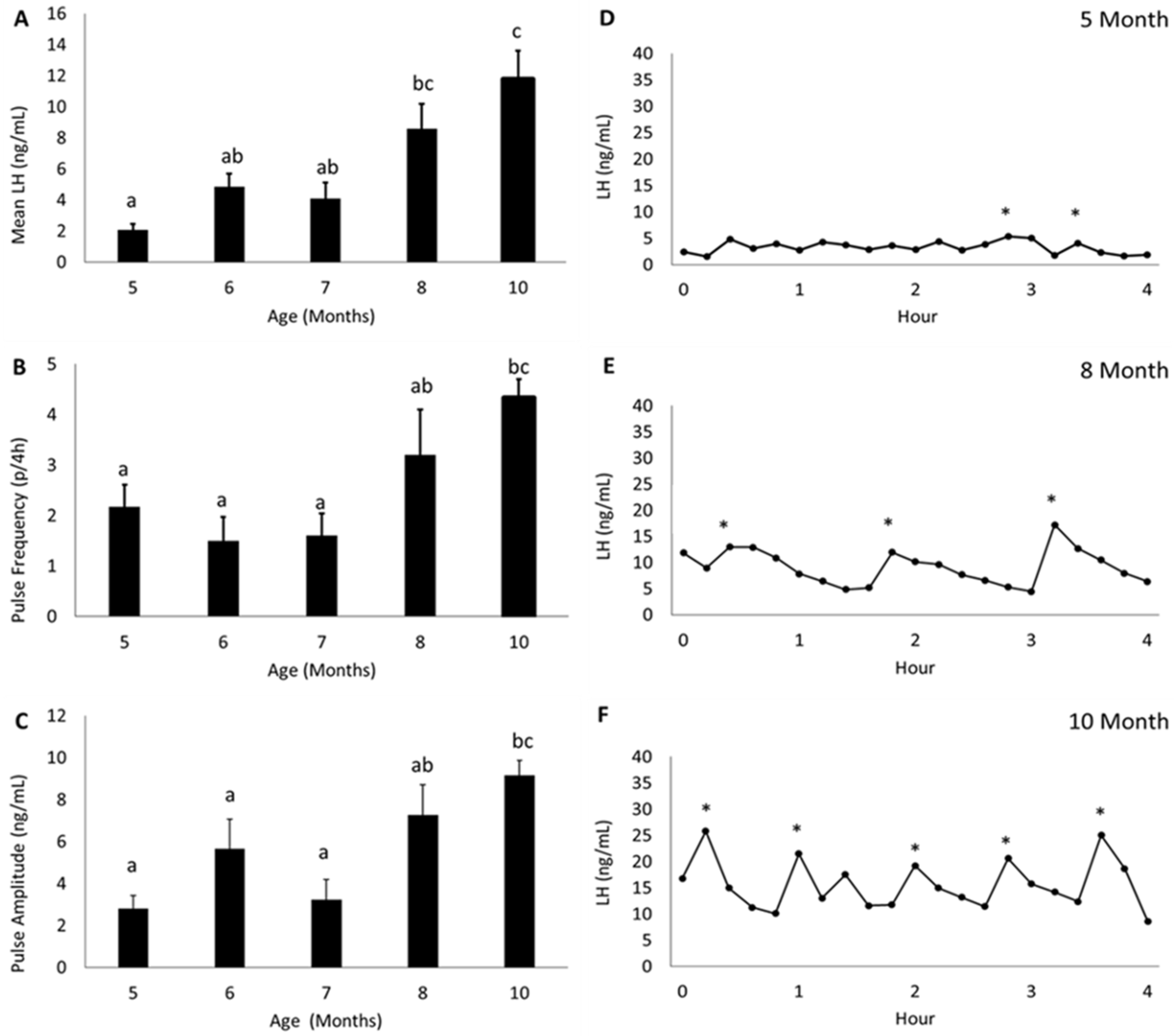
3.1. Changes in LH Secretion with Age
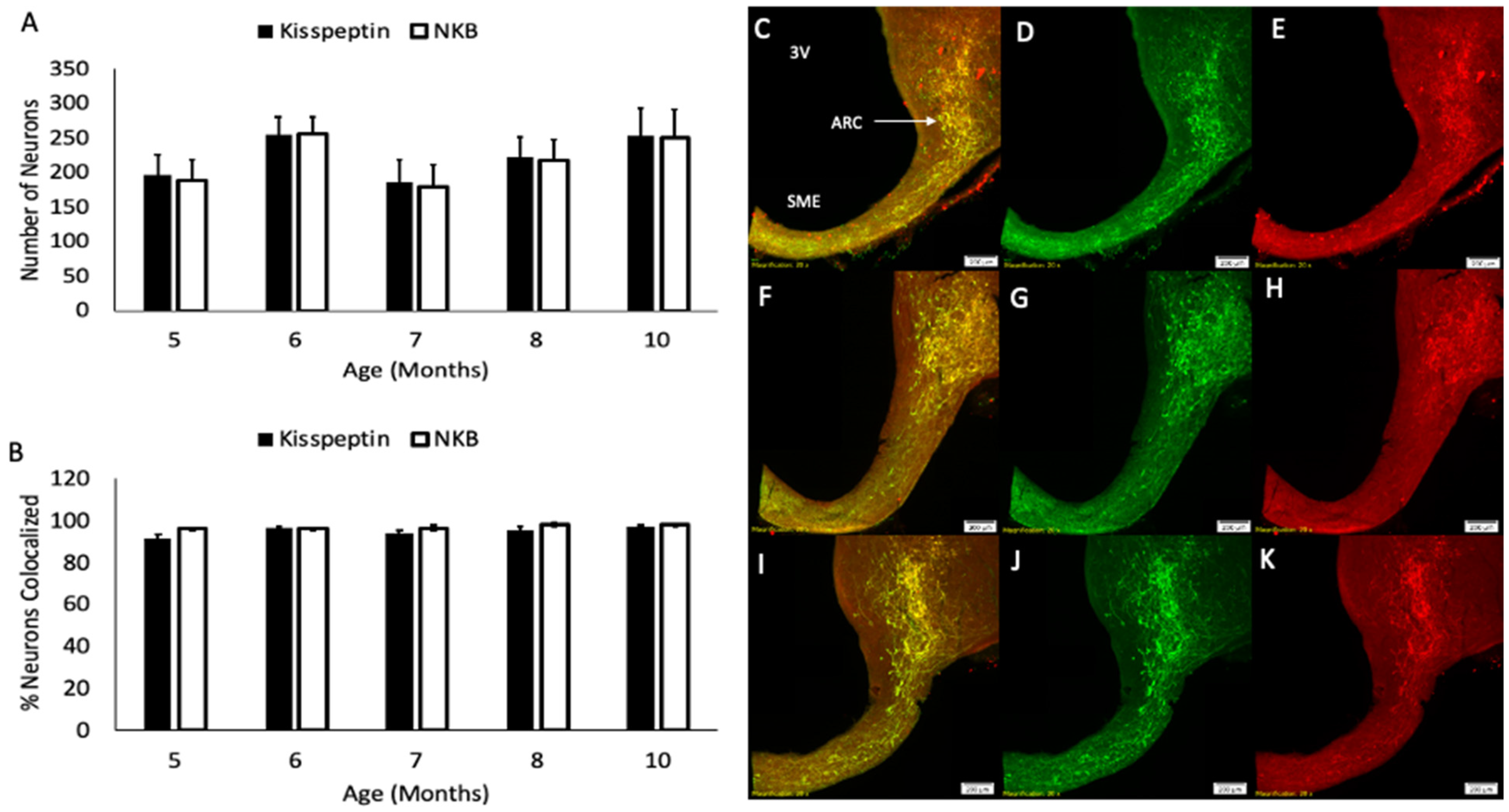
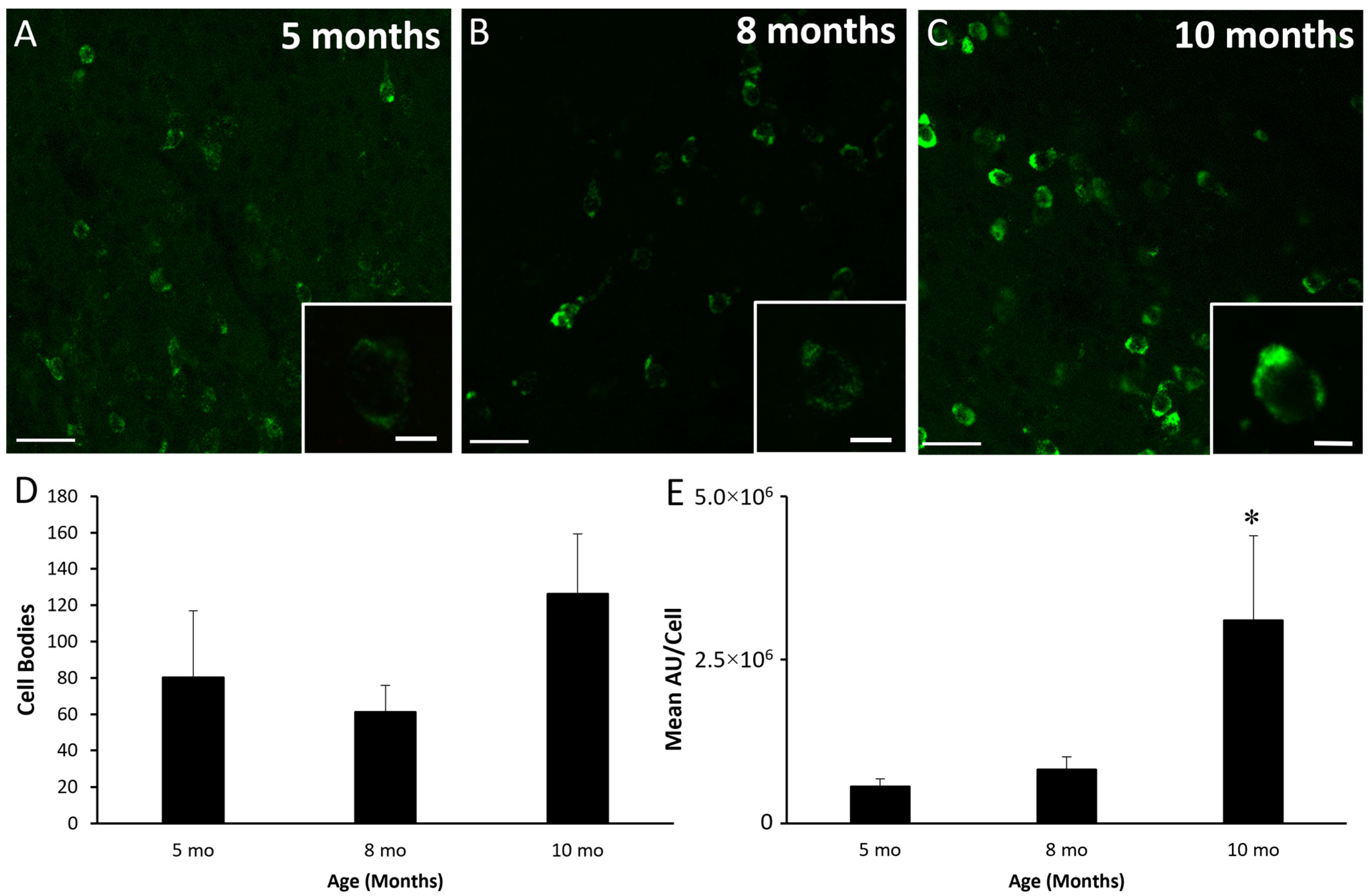
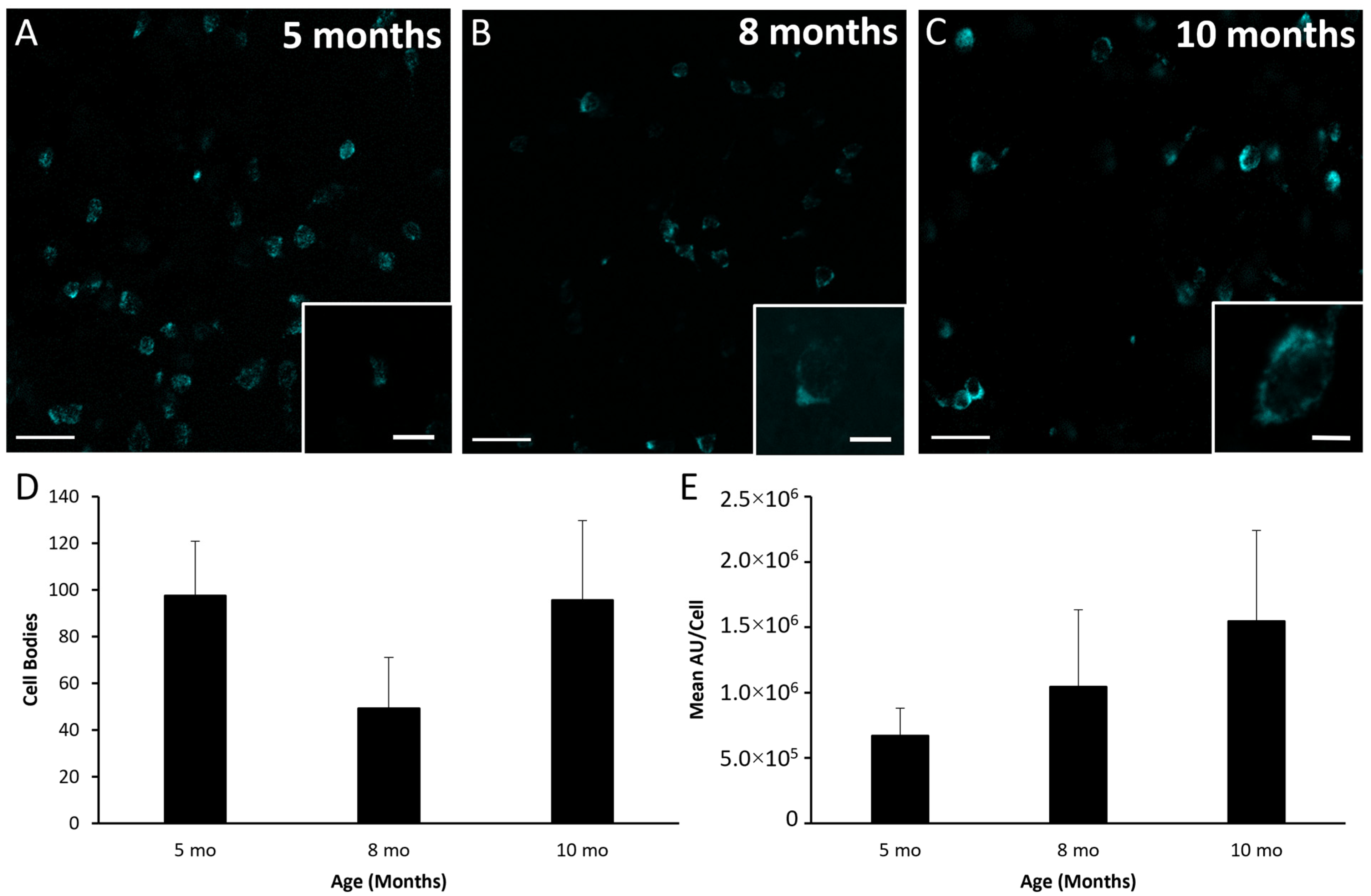
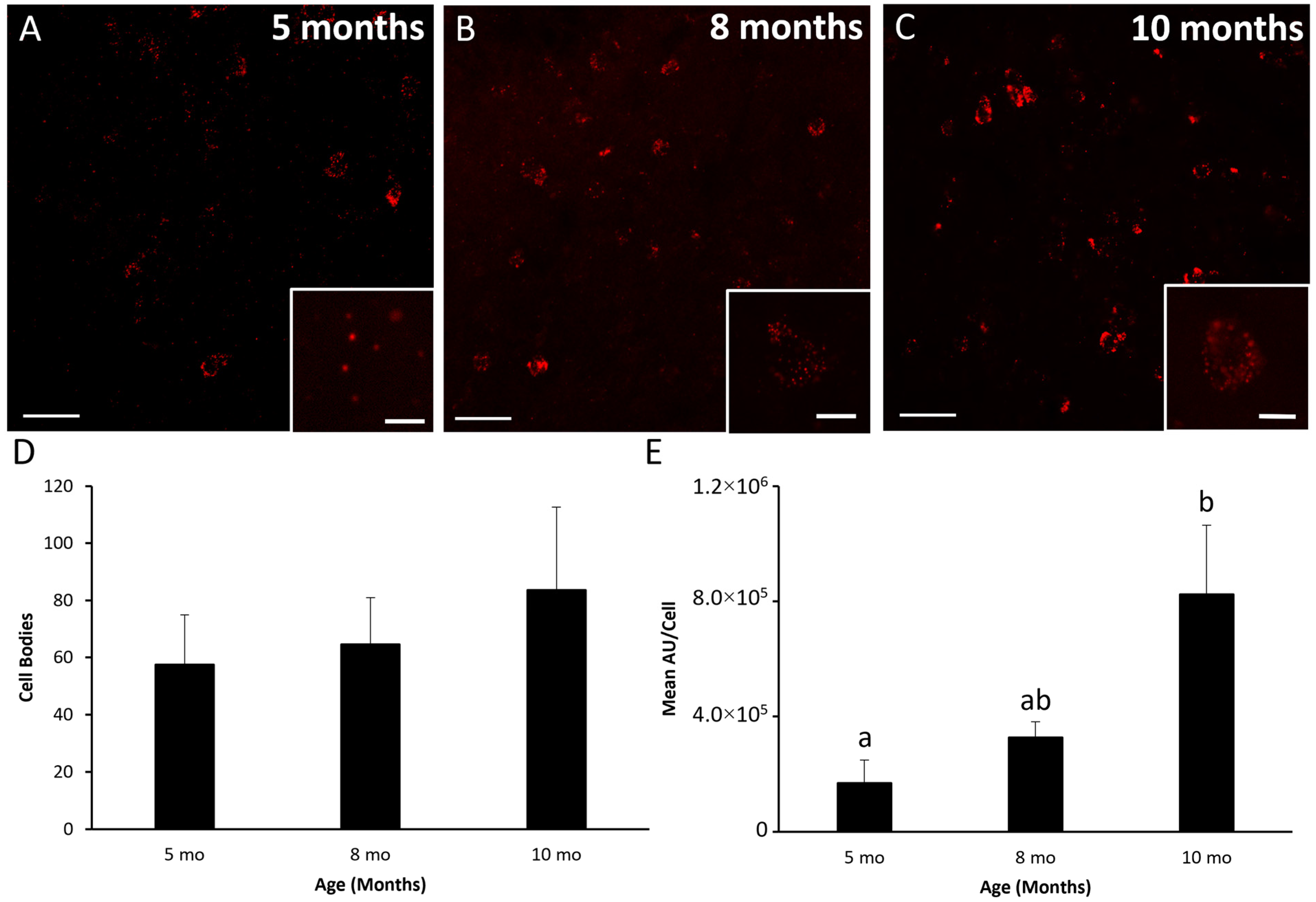
3.2. Kisspeptin, NKB, and Dynorphin Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendle, J.; Turkheimer, E.; Emery, R.E. Detrimental psychological outcomes associated with early pubertal timing in adolescent girls. Dev. Rev. 2007, 27, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, M.P.; Brooks-Gunn, J.; Fox, R.P.; Holderness, C.C.; Hyle, E.P.; Hamilton, W.G. Osteopenia in exercise-associated amenorrhea using ballet dancers as a model: A longitudinal study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3162–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, G.C.; Hibbert, M.E.; Carlin, J.; Shao, Q.; Rosier, M.; Caust, J.; Bowes, G. Menarche and the onset of depression and anxiety in Victoria, Australia. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1996, 50, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graber, J.A.; Lewinsohn, P.M.; Seeley, J.R.; Brooks-Gunn, J. Is psychopathology associated with the timing of pubertal development? J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1997, 36, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, F.R.; Elks, C.E.; Murray, A.; Ong, K.K.; Perry, J.R. Puberty timing associated with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and also diverse health outcomes in men and women: The UK Biobank study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, G.A.; Cushman, R. Effect of age at puberty/conception date on cow longevity. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2013, 29, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundiff, L.V.; Gregory, K.E.; Koch, R.M. Effects of heterosis on reproduction in Herford, Angus and Shorthorn cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 1974, 38, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafziger, S.R.; Tenley, S.C.; Summers, A.F.; Abedal-Majed, M.A.; Hart, M.; Bergman, J.W.; Kurz, S.G.; Davis, J.S.; Wood, J.R.; Cupp, A.S. Attainment and maintenance of pubertal cyclicity may predict reproductive longevity in beef heifers. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 104, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.; Hileman, S.M. Puberty in the sheep. In Knobil and Neill’s Physiology of Reproduction, 4th ed.; Plant, T., Zeleznik, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, D.L.; Ryan, K.D. Endocrine mechanisms governing transition into adulthood: A marked decrease in inhibitory feedback action of estradiol on tonic secretion of luteinizing hormone in the lamb during puberty. Endocrinology 1979, 105, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.V.; McCann, S.M. Comparison of the regulation of luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion in immature and adult rats. Endocrinology 1963, 72, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasawa, E.; Bridson, W.E.; Nass, T.E.; Noonan, J.J.; Dierschke, D.J. Developmental changes in the luteinizing hormone secretory pattern in peripubertal female rhesus monkeys: Comparisons between gonadally intact and ovariectomized animals. Endocrinology 1984, 115, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.E.; Gordon, T.P.; Collins, D.C. Ontogeny of luteinizing hormone secretion and first ovulation in seasonal breeding rhesus monkeys. Endocrinology 1986, 118, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivers, B.D.; Harlan, R.E.; Morrell, J.I.; Pfaff, D.W. Absence of oestradiol concentration in cell nuclei of LHRH-immunoreactive neurones. Nature 1983, 304, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, M.N.; Karsch, F.J. Do gonadotropin-releasing hormone, tyrosine hydroxylase-, and beta-endorphin-immunoreactive neurons contain estrogen receptors? A double-label immunocytochemical study in the Suffolk ewe. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couse, J.F.; Yates, M.M.; Walker, V.R.; Korach, K.S. Characterization of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis in estrogen receptor (ER) null mice reveals hypergonadism and endocrine sex reversal in females lacking ERalpha but not ERbeta. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 1039–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Coolen, L.M.; Padmanabhan, V.; Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.N. The kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) cell population of the arcuate nucleus: Sex differences and effects of prenatal testosterone in sheep. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.T.; Cunningham, M.J.; Rissman, E.F.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. Regulation of Kiss1 gene expression in the brain of the female mouse. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3686–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, I.; Lomet, D.; Cateau, M.; Delsol, G.; Tillet, Y.; Caraty, A. Kisspeptin immunoreactive cells of the ovine preoptic area and arcuate nucleus co-express estrogen receptor alpha. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 401, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkley, C.M.; Coolen, L.M.; Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.N. Evidence for Changes in Numbers of Synaptic Inputs onto KNDy and GnRH Neurones during the Preovulatory LH Surge in the Ewe. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 27, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminara, S.B.; Messager, S.; Chatzidaki, E.E.; Thresher, R.R.; Acierno, J.S.; Shagoury, J.K.; Bo-Abbas, Y.; Kuohung, W.; Schwinof, K.M.; Hendrick, A.G.; et al. The GPR54 gene as a regulator of puberty. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Roux, N.; Genin, E.; Carel, J.C.; Matsuda, F.; Chaussain, J.L.; Milgrom, E. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism due to loss of function of the KiSS1-derived peptide receptor GPR54. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10972–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funes, S.; Hedrick, J.A.; Vassileva, G.; Markowitz, L.; Abbondanzo, S.; Golovko, A.; Yang, S.; Monsma, F.J.; Gustafson, E.L. The KiSS-1 receptor GPR54 is essential for the development of the murine reproductive system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topaloglu, A.K.; Tello, J.A.; Kotan, L.D.; Ozbek, M.N.; Yilmaz, M.B.; Erdogan, S.; Gurbuz, F.; Temiz, F.; Millar, R.P.; Yuksel, B. Inactivating KISS1 mutation and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.K.; Gottsch, M.L.; Lee, K.J.; Popa, S.M.; Smith, J.T.; Jakawich, S.K.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A.; Herbison, A.E. Activation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons by kisspeptin as a neuroendocrine switch for the onset of puberty. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 11349–11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwig, M.S.; Fraley, G.S.; Smith, J.T.; Acohido, B.V.; Popa, S.M.; Cunningham, M.J.; Gottsch, M.L.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. Kisspeptin activation of gonadotropin releasing hormone neurons and regulation of KiSS-1 mRNA in the male rat. Neuroendocrinology 2004, 80, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillo, W.S.; Chaudhri, O.B.; Patterson, M.; Thompson, E.L.; Murphy, K.G.; Badman, M.K.; McGowan, B.M.; Amber, V.; Patel, S.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Kisspeptin-54 stimulates the hypothalamic-pituitary gonadal axis in human males. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 6609–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, T.M.; Ramaswamy, S.; Dipietro, M.J. Repetitive activation of hypothalamic G protein-coupled receptor 54 with intravenous pulses of kisspeptin in the juvenile monkey (Macaca mulatta) elicits a sustained train of gonadotropin-releasing hormone discharges. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.M.; Castellano, J.M.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Barreiro, M.L.; Roa, J.; Sanchez-Criado, J.E.; Aguilar, E.; Dieguez, C.; Pinilla, L.; Tena-Sempere, M. Developmental and hormonally regulated messenger ribonucleic acid expression of KiSS-1 and its putative receptor, GPR54, in rat hypothalamus and potent luteinizing hormone-releasing activity of KiSS-1 peptide. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4565–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottsch, M.L.; Cunningham, M.J.; Smith, J.T.; Popa, S.M.; Acohido, B.V.; Crowley, W.F.; Seminara, S.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. A role for kisspeptins in the regulation of gonadotropin secretion in the mouse. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4073–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messager, S.; Chatzidaki, E.E.; Ma, D.; Hendrick, A.G.; Zahn, D.; Dixon, J.; Thresher, R.R.; Malinge, I.; Lomet, D.; Carlton, M.B.; et al. Kisspeptin directly stimulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone release via G protein-coupled receptor 54. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadokawa, H.; Matsui, M.; Hayashi, K.; Matsunaga, N.; Kawashima, C.; Shimizu, T.; Kida, K.; Miyamoto, A. Peripheral administration of kisspeptin-10 increases plasma concentrations of GH as well as LH in prepubertal Holstein heifers. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 196, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lents, C.A.; Heidorn, N.L.; Barb, C.R.; Ford, J.J. Central and peripheral administration of kisspeptin activates gonadotropin but not somatotropin secretion in prepubertal gilts. Reproduction 2008, 135, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guran, T.; Tolhurst, G.; Bereket, A.; Rocha, N.; Porter, K.; Turan, S.; Gribble, F.M.; Kotan, L.D.; Akcay, T.; Atay, Z.; et al. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism due to a novel missense mutation in the first extracellular loop of the neurokinin B receptor. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3633–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaloglu, A.K.; Reimann, F.; Guclu, M.; Yalin, A.S.; Kotan, L.D.; Porter, K.M.; Serin, A.; Mungan, N.O.; Cook, J.R.; Imamoglu, S.; et al. TAC3 and TACR3 mutations in familial hypogonadotropic hypogonadism reveal a key role for Neurokinin B in the central control of reproduction. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, T.T.; Crawley, Y.; Jones, H.; Luo, B.; Gilchrest, H.; Greenfeder, S.; Anthes, J.C.; Lira, S.; Wiekowski, M.; Cook, D.N.; et al. Tachykinin NK3-receptor deficiency does not inhibit pulmonary eosinophilia in allergic mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2004, 50, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Caligioni, C.S.; Chan, Y.M.; Seminara, S.B. Uncovering novel reproductive defects in neurokinin B receptor null mice: Closing the gap between mice and men. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1498–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pino, F.; Navarro, V.M.; Bentsen, A.H.; Garcia-Galiano, D.; Sanchez-Garrido, M.A.; Ciofi, P.; Steiner, R.A.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Pinilla, L.; Tena-Sempere, M. Neurokinin B and the control of the gonadotropic axis in the rat: Developmental changes, sexual dimorphism, and regulation by gonadal steroids. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4818–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstalden, M.; Coolen, L.M.; Hemmerle, A.M.; Billings, H.J.; Connors, J.M.; Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.N. Neurokinin 3 receptor immunoreactivity in the septal region, preoptic area and hypothalamus of the female sheep: Colocalisation in neurokinin B cells of the arcuate nucleus but not in gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neurones. J. Neuroendocr. 2010, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, C.C.; Briscoe, A.M.; Davis, S.M.; Valent, M.; Goodman, R.L.; Hileman, S.M. Evidence of a role for kisspeptin and neurokinin B in puberty of female sheep. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 2756–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, S.; Seminara, S.B.; Plant, T.M. Evidence from the agonadal juvenile male rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) for the view that the action of neurokinin B to trigger gonadotropin-releasing hormone release is upstream from the kisspeptin receptor. Neuroendocrinology 2011, 94, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.A.; Bedenbaugh, M.N.; McCosh, R.B.; Weems, P.W.; Meadows, L.J.; Wisman, B.; Coolen, L.M.; Goodman, R.L.; Hileman, S.M. Does Dynorphin Play a Role in the Onset of Puberty in Female Sheep? J. Neuroendocr. 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.M. New insights into the control of pulsatile GnRH release: The role of Kiss1/neurokinin B neurons. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.L.; Hileman, S.M.; Nestor, C.C.; Porter, K.L.; Connors, J.M.; Hardy, S.L.; Millar, R.P.; Cernea, M.; Coolen, L.M.; Lehman, M.N. Kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin act in the arcuate nucleus to control activity of the GnRH pulse generator in ewes. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4259–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, C.C.; Bedenbaugh, M.N.; Hileman, S.M.; Coolen, L.M.; Lehman, M.N.; Goodman, R.L. Regulation of GnRH pulsatility in ewes. Reproduction 2018, 156, R83–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, J.S.; Baez-Sandoval, G.M.; Spell, K.M.; Spencer, T.E.; Lents, C.A.; Williams, G.L.; Amstalden, M. Developmental changes in hypothalamic Kiss1 expression during activation of the pulsatile release of luteinising hormone in maturing ewe lambs. J. Neuroendocr. 2011, 23, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legan, S.J.; Karsch, F.J.; Foster, D.L. The endocrine control of seasonal reproductive function in the ewe: A marked change in response to the negative feedback action of estradiol on luteinizing hormone secretion. Endocrinology 1977, 101, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauger, R.L.; Karsch, F.J.; Foster, D.L. A new concept for control of the estrous cycle of the ewe based on the temporal relationships between luteinizing hormone, estradiol and progesterone in peripheral serum and evidence that progesterone inhibits tonic LH secretion. Endocrinology 1977, 101, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.N.; Smith, J.T.; Coolen, L.M.; de Oliveira, C.V.; Jafarzadehshirazi, M.R.; Pereira, A.; Iqbal, J.; Caraty, A.; Ciofi, P.; et al. Kisspeptin neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the ewe express both dynorphin A and neurokinin B. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5752–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foradori, C.D.; Amstalden, M.; Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.N. Colocalisation of dynorphin A and neurokinin B immunoreactivity in the arcuate nucleus and median eminence of the sheep. J. Neuroendocr. 2006, 18, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.L.; Karsch, F.J. Pulsatile secretion of luteinizing hormone: Differential suppression by ovarian steroids. Endocrinology 1980, 107, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase, K.; Uenoyama, Y.; Inoue, N.; Matsui, H.; Yamada, S.; Shimizu, M.; Homma, T.; Tomikawa, J.; Kanda, S.; Matsumoto, H.; et al. Possible role of oestrogen in pubertal increase of Kiss1/kisspeptin expression in discrete hypothalamic areas of female rats. J. Neuroendocr. 2009, 21, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi, K.; Iijima, N.; Ozawa, H. Developmental changes in the expression of kisspeptin mRNA in rat hypothalamus. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 43, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desroziers, E.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Duittoz, A.; Franceschini, I. Kisspeptin-immunoreactivity changes in a sex- and hypothalamic-region-specific manner across rat postnatal development. J. Neuroendocr. 2012, 24, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, J.C.; Wang, O.; Kakar, S.; Martinelli, E.; Carroll, R.S.; Kaiser, U.B. Reproductive hormone-dependent and -independent contributions to developmental changes in kisspeptin in GnRH-deficient hypogonadal mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, S.J.; Kauffman, A.S. Daily successive changes in reproductive gene expression and neuronal activation in the brains of pubertal female mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 401, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, M.; Mastronardi, C.; Seminara, S.B.; Crowley, W.F.; Ojeda, S.R.; Plant, T.M. Increased hypothalamic GPR54 signaling: A potential mechanism for initiation of puberty in primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, K.L.; Wegner, F.H.; Bloom, S.R.; Ghatei, M.A.; Terasawa, E. An increase in kisspeptin-54 release occurs with the pubertal increase in luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone-1 release in the stalk-median eminence of female rhesus monkeys in vivo. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 4151–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkley, C.M.; Porter, K.L.; Coolen, L.M.; Hileman, S.M.; Billings, H.J.; Drews, S.; Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.N. KNDy (kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin) neurons are activated during both pulsatile and surge secretion of LH in the ewe. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 5406–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rance, N.E.; Young, W.S. Hypertrophy and increased gene expression of neurons containing neurokinin-B and substance-P messenger ribonucleic acids in the hypothalami of postmenopausal women. Endocrinology 1991, 128, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, J.C.; Navarro, V.M.; Kwong, C.; Noel, S.D.; Martin, C.; Xu, S.; Clifton, D.K.; Carroll, R.S.; Steiner, R.A.; Kaiser, U.B. Increased neurokinin B (Tac2) expression in the mouse arcuate nucleus is an early marker of pubertal onset with differential sensitivity to sex steroid-negative feedback than Kiss1. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4883–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.M.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Sánchez-Garrido, M.A.; García-Galiano, D.; Hobbs, S.J.; Manfredi-Lozano, M.; León, S.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Castellano, J.M.; Clifton, D.K.; et al. Role of neurokinin B in the control of female puberty and its modulation by metabolic status. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taziaux, M.; Swaab, D.F.; Bakker, J. Sex differences in the neurokinin B system in the human infundibular nucleus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E2210–E2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Smith, J.T.; Henry, B.; Rao, A.; Pereira, A.; Clarke, I.J. Expression of genes for Kisspeptin (KISS1), Neurokinin B (TAC3), Prodynorphin (PDYN), and gonadotropin inhibitory hormone (RFRP) across natural puberty in ewes. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, T.; Uenoyama, Y.; Iwase, A.; Oishi, S.; Nakamura, S.; Minabe, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Deura, C.; Noguchi, T.; Fujii, N.; et al. Chronic peripheral administration of kappa-opioid receptor antagonist advances puberty onset associated with acceleration of pulsatile luteinizing hormone secretion in female rats. J. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 59, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foradori, C.D.; Coolen, L.M.; Fitzgerald, M.E.; Skinner, D.C.; Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.N. Colocalization of progesterone receptors in parvicellular dynorphin neurons of the ovine preoptic area and hypothalamus. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 4366–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foradori, C.D.; Goodman, R.L.; Adams, V.L.; Valent, M.; Lehman, M.N. Progesterone increases dynorphin A concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid and preprodynorphin messenger ribonucleic acid levels in a subset of dynorphin neurons in the sheep. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedenbaugh, M.N.; D’Oliveira, M.; Cardoso, R.C.; Hileman, S.M.; Williams, G.L.; Amstalden, M. Pubertal escape from estradiol negative feedback in ewe lambs is not accounted for by decreased ESR1 mRNA or protein in kisspeptin neurons. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.P.; Keen, K.L.; Seminara, S.B.; Terasawa, E. Role of kisspeptin and NKB in puberty in nonhuman primates: Sex differences. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2019, 37, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debus, N.; Breen, K.M.; Barrell, G.K.; Billings, H.J.; Brown, M.; Young, E.A.; Karsch, F.J. Does cortisol mediate endotoxin-induced inhibition of pulsatile luteinizing hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion? Endocrinology 2002, 143, 3748–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age | 5 months | 6 months | 7 months | 8 months | 10 months |
| Neuroendocrine State | Prepubertal | Prepubertal | Prepubertal | Peripubertal | Postpubertal |
| N | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| Photoperiod | 14.5L:9.5D | 13.5L:10.5D | 12L:12D | 11L:13D | 9.5L:14.5D |
| RNAscope Probe Information | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene Product | Probe ID | Catalog # | Accession Number | Target Region |
| Series 1 Probes | ||||
| Target Probe Channel 2: Dynorphin (PDYN) | Oa-PDYN-O1-C2 | 481421-C2 | NM_001280677.1 | 2–545 |
| Target Probe Channel 3: Kisspeptin (KISS1) | Oa-KISS1-C3 | 497471-C3 | NM_001306104.1 | 37–774 |
| Series 2 Probes | ||||
| Target Probe Channel 1: Neurokinin B (TAC3) | Oa-TAC3 | 481411 | AJ507210.1 | 2–311 |
| Positive Control Probes | ||||
| Positive Control Channel 1: Polymerase (RNA) II Subunit A | Oa-POLR2A | 516171 | XM_004013289.3 | 1197–2081 |
| Positive Control Channel 2: Cyclophilin B | Oa-PPIB | 457031-C2 | XM_004010536.2 | 4–913 |
| Positive Control Channel 3: Ubiquitin C | Oa-UBC-C3 | 516181-C3 | XM_012097675.2 | 56–1295 |
| Negative Control Probes | ||||
| 3-plex Negative Control Probe | 320871 | EF191515 | 414–862 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aerts, E.G.; Harlow, K.; Griesgraber, M.J.; Bowdridge, E.C.; Hardy, S.L.; Nestor, C.C.; Hileman, S.M. Kisspeptin, Neurokinin B, and Dynorphin Expression during Pubertal Development in Female Sheep. Biology 2021, 10, 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10100988
Aerts EG, Harlow K, Griesgraber MJ, Bowdridge EC, Hardy SL, Nestor CC, Hileman SM. Kisspeptin, Neurokinin B, and Dynorphin Expression during Pubertal Development in Female Sheep. Biology. 2021; 10(10):988. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10100988
Chicago/Turabian StyleAerts, Eliana G., KaLynn Harlow, Max J. Griesgraber, Elizabeth C. Bowdridge, Steven L. Hardy, Casey C Nestor, and Stanley M. Hileman. 2021. "Kisspeptin, Neurokinin B, and Dynorphin Expression during Pubertal Development in Female Sheep" Biology 10, no. 10: 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10100988
APA StyleAerts, E. G., Harlow, K., Griesgraber, M. J., Bowdridge, E. C., Hardy, S. L., Nestor, C. C., & Hileman, S. M. (2021). Kisspeptin, Neurokinin B, and Dynorphin Expression during Pubertal Development in Female Sheep. Biology, 10(10), 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10100988






